Study on the Variations in Water Storage in Lake Qinghai Based on Multi-Source Satellite Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
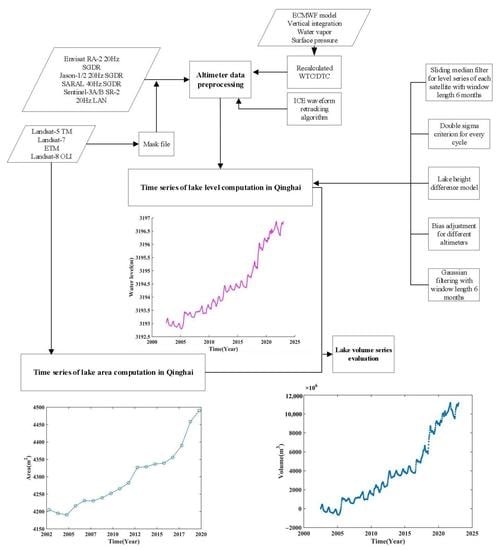
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Hydrological Gauge Data
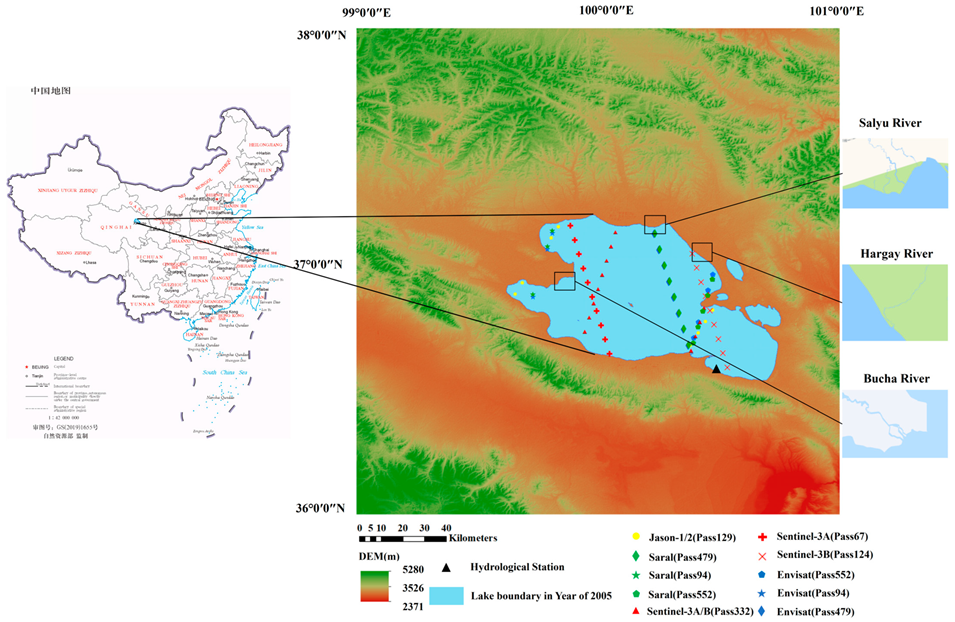
2.1.2. Altimetry Satellite Data
2.1.3. Landsat Data
2.1.4. European Center for Mesoscale Weather Forecasting Data
2.1.5. Lake Level Data from Other Databases
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. The Study of Water Variation Based on Multi-Mission Altimeter Data
- Creating a mask file
- 2.
- Calculation of lake’s water level
- 3.
- Atmospheric path delay correction
- 4.
- Waveform re-tracking
- 5.
- Abnormal value elimination and averaged lake water level calculation
- 6.
- Lake orthometric height difference model and position reduction
- 7.
- Deviation adjustment
- 8.
- Gaussian filtering
2.2.2. The Study of Lake Area Capture Based on Landsat Data
- Landsat image data preprocessing
- 2.
- Extraction of lake surface area
2.2.3. Water Level–Area Relationship Fitting
2.2.4. Water Storage Estimation Based on Water Level and Area Series
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Time Series of Lake Water Level in LQ
3.2. Analysis of Water Level Variation in LQ
3.3. Lake Surface Area Extraction and Fitting
3.4. Analysis of LQ Area Variation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qiu, J. China: The third pole. Nature 2008, 454, 393–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yao, T.D.; Thompson, L.G.; Mosbrugger, V.; Zhang, F.; Ma, Y.M.; Luo, T.X.; Xu, B.Q.; Yang, X.X.; Joswiak, D.R.; Wang, W.C. Third Pole Environment (TPE). Environ. Dev. 2012, 3, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.Y.; Mu, D.P.; Liu, X.; Yan, H.M.; Sun, Z.C.; Guo, B. Water storage changes over the Tibetan Plateau revealed by GRACE mission. Acta Geophys. 2016, 64, 463–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Wang, S.; Yu, S.; Yang, D.; Zhang, L. Climate warming and growth of high-elevation inland lakes on the Tibetan Plateau. Glob. Planet. Chang 2009, 67, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Ye, Q.; Sheng, Y.; Gong, T. Combined ICESat and CryoSat-2 Altimetry for accessing water level dynamics of Tibetan lakes over 2003–2014. Water 2015, 7, 4685–4700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lei, Y.; Yang, K.; Wang, B.; Sheng, Y.; Bird, B.W.; Zhang, G.; Tian, L. Response of inland lake dynamics over the Tibetan plateau to climate change. Clim. Chang. 2014, 125, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Huang, B.; Ke, L.; Richards, K.S. Seasonal and abrupt changes in the water level of closed lakes on the Tibetan plateau and implications for climate impacts. J. Hydrol. 2014, 514, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Wu, H.; Qin, J.; Lin, C.; Tang, W.; Chen, Y. Recent climate changes over the Tibetan plateau and their impacts on energy and water cycle: A review. Glob. Planet Chang. 2014, 112, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, G.H.; Deng, W.; Li, A.N.; Zhang, T.B. Response of lakes to climate change in Xainza Basin Tibetan Plateau using multi-mission satellite data from 1976 to 2008. J. Mt. Sci. 2015, 12, 604–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.H.; Yang, G.S.; Duan, H.T.; Jiang, J.H.; Wang, S.M.; Feng, X.Z.; Li, A.N.; Kong, F.X.; Xue, B.; Wu, J.L.; et al. China’s lakes at present: Number, area and spatial distribution. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2011, 54, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.H.; Shi, Y.F. Impact of climate change on the water regime of Lake Qinghai—I. Analysis of the past 30 years. Sci. Sin. 1992, 22, 537–542. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, L.Y.; Duan, X.F.; Kong, F.J.; Zhang, F.; Zheng, Y.F.; Li, Z.; Mei, Y.; Zhao, Y.W.; Hu, S.J. Influences of climate change on area variation of Lake Qinghai on Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau since 1980s. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Phan, V.H.; Lindenbergh, R.; Menenti, M. ICESat derived elevation changes of Tibetan lakes between 2003 and 2009. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2012, 17, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.Q.; Xie, H.J.; Kang, S.C.; Yi, D.H.; Ackley, S.F. Monitoring lake level changes on the Tibetan Plateau using ICESat altimetry data (2003–2009). Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1733–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinherenbrink, M.; Lindenbergh, R.C.; Ditmar, P.G. Monitoring of lake level changes on the Tibetan Plateau and Tian Shan by re-tracking Cryosat SARIn waveform. J. Hydrol. 2015, 521, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.G.; Nielsen, K.; Andersen, O.B.; Bauer-Gottwein, P. Monitoring recent lake level variations on the Tibetan Plateau using CryoSat-2 SARIn mode data. J. Hydrol. 2017, 544, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, C.Q.; Huang, B.; Ke, L.H. Modeling and analysis of lake water storage changes on the Tibetan Plateau using multi-mission satellite data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 135, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutz, B.E.; Zwally, H.J.; Shuman, C.A.; Hancock, D.; Dimarzio, J.P. Overview of the ICESat mission. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L21S01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hwang, C.; Cheng, Y.; Yang, W.; Zhang, G.; Huang, Y.; Shen, W.; Pan, Y. Lake level changes in the Tibetan Plateau from Cryosat-2, SARAL, ICESat, and Jason-2 altimeters. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. 2019, 30, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, C.; Ye, Q.; Cheng, X. Shifts in water-level variation of Namco in the central Tibetan Plateau from ICESat and Cryosat-2 altimetry and station observations. Sci. Chin. 2015, 60, 1287–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Gong, P.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Cheng, X.; Niu, Z.; Luo, Z.; Huang, H.; Sun, F.; Li, X. Water-level changes in China’s large lakes determined from ICESat/GLAS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 132, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Xie, H.; Yao, T.; Kang, S. Water balance estimates of ten greatest lakes in China using ICESat and Landsat data. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2013, 58, 3815–3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, W.P.; Zhu, Y.H.; Li, J.C.; Yao, Y.S. Water Level Variation of Lake Qinghai from Altimeteric Data. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2008, 33, 64–67. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kleinherenbrink, M.; Ditmar, P.G.; Lindenbergh, R.C. Re-tracking Cryosat data in the SARIn mode and robust lake level extraction. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 152, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liao, J.J.; Sheng, G.Z.; Zhang, X.L. Monitoring the water level changes in Lake Qinghai with satellite altimetry data. Natl. Remote Sens. Bull. 2017, 21, 633–644. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sun, M.; Guo, J.; Yuan, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, H.; Li, C. Detecting Lake Level Change From 1992 to 2019 of Zhari Namco in Tibet Using Altimetry Data of TOPEX/Poseidon and Jason-1/2/3 Missions. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 9, 640553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Wu, Y.H.; Liu, Y.J.; Guo, L.N. Water storage variation of the Lake Qinghai in recent decades based on satellite observation. Prog. Geogr. 2018, 37, 823–832. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Du, J.N.; Li, Q.J.; Liu, X.S.; Wen, D.P. Hydrological Characteristics of Lake Qinghai, 1956–2017. J. Hydroecol. 2020, 41, 27–33. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hao, M.Y.; Luo, Z. A Dataset of Lake Qinghai Water Body Periphery During 1987–2017. Science Data Bank, 14 October 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.Y.; Sun, J.L.; Chang, X.T.; Guo, S.Y.; Liu, X. Correlation analysis of NINO3.4 SST and inland lake level variations monitored with satellite altimetry: Case studies of lakes Hongze, Khanka, La-ang, Ulungur, Issyk-kul and Baikal. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. 2011, 22, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Guo, J.Y.; Sun, Y.; Yuan, J.J.; Chang, X.T.; Zhang, H.R. Inversion of global sea level change and its component contributions by combining time-varying gravity data and altimeter data. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2022, 51, 1768–1778. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, H.M.; Song, Y.G. Shrinkage history of Lake Qinghai and causes during the last 52 years. Int. Symp. Water Resour. Environ. Prot. 2011, 1, 446–449. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Z.D.; You, C.F.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Y.W. Hydrological and solute budgets of Lake Qinghai, the largest lake on the Tibetan Plateau. Quat. Int. 2010, 218, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, B.Q.; Shi, Y.F. The hydrological characteristics and the cause of the declining of water level in Lake Qinghai. Acta Geogr. Sin. 1992, 47, 267–273. [Google Scholar]
- Schwatke, C.; Dettmering, D.; Bosch, W.; Seitz, F. DAHITI an innovative approach for estimating water level time series over inland waters using multi-mission satellite altimetry. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 4345–4364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, G. Lake Volume Changes on the Tibetan Plateau during 1976–2020 (>1 km2) v2.0; National Tibetan Plateau/Third Pole Environment Data Center: Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Bolch, T.; Chen, W.; Crétaux, J.F. Comprehensive estimation of lake volume changes on the Tibetan Plateau during 1976–2019 and basin-wide glacier contribution. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 772, 14546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crétaux, J.F.; Calmant, S.; Romanovski, V.; Shabunin, A.; Lyard, F.; Bergé-Nguyen, M.; Cazenave, A.; Hernandez, F.; Perosanz, F. An absolute calibration site for radar altimeters in the continental domain: Lake Issykkul in Central Asia. J. Geod. 2009, 83, 723–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Yang, L.; Liu, X.; Hwang, C.; Yang, H. On temporal-spatial distribution of backscatter coefficients over China determined by TOPEX/Poseidon mission. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2012, 55, 2068–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Hao, L.; Chen, X. Evaluation of ERA-interim monthly temperature data over the Tibetan Plateau. J. Mount. Sci. 2014, 11, 1154–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chu, Y.; Huang, Z.; Hwang, C.; Chao, N. Robust, long-term lake level change from multiple satellite altimeters in Tibet: Observing the rapid rise of ngangzi co over a New Wetland. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, R.; Gao, J.X.; Zhu, P. The Impact of Different Mapping Function Models and Meteorological Parameter Calculation Methods on the Calculation Results of Single-Frequency Precise Point Positioning with Increased Tropospheric Gr. Math. Probl. Eng. 2020, 2020, 9730129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, B.; Pacione, R.; Sciarretta, C.; Bianco, G. Computation of zenith total delay correction fields using ground-based GNSS. In International Association of Geodesy Symposia; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 142, pp. 131–137. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, C.; Peng, M.F.; Ning, J.S.; Luo, J.; Sui, C.H. Lake level variations in China from TOPEX/Poseidon altimetry: Data quality assessment and links to precipitation and ENSO. Geophys. J. Int. 2005, 161, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wingham, D.J.; Rapley, C.G.; Griffiths, H. New techniques in satellite altimeter tracking systems. In Proceedings of IGARss’ 86 Symposium; ESA Publications Division: Zurich, Switzerland, 1986; pp. 1339–1344. [Google Scholar]
- Bamber, J.L. Ice sheet altimeter processing scheme. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1994, 15, 925–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stammer, D.; Cazenave, A. Satellite Altimetry over Oceans and Land Surfaces; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Frappart, F.; Calmant, S.; Cauhope, M.; Seyler, F.; Cazenave, A. Preliminary results of ENVISAT RA-2-derived water levels validation over the Amazon basin. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 100, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okeowo, M.; Lee, H.; Hossain, F.; Getirana, A. Automated generation of lakes and reservoirs water elevation changes from satellite radar altimetry. IEEE J. Select Topics. Appl. Earth Observat. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 3465–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Shum, C.K.; Tseng, K.H.; Guo, J.Y.; Kuo, C.Y. Present-Day Lake Level Variation from Envisat Altimetry over the Northeastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau: Links with Precipitation and Temperature. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. 2011, 22, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vu, P.L.; Frappart, F.; Darrozes, J.; Marieu, V.; Blarel, F.; Ramillien, G.; Bonnefond, P.; Birol, F. Multi-satellite altimeter validation along the French Atlantic coast in the southern bay of Biscay from ERS-2 to SARAL. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abileah, R.; Vignudelli, S.; Scozzari, A. A completely remote sensing approach to monitoring reservoirs’ water volume. IWTC 2011, 1, 63–77. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q. Research on Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Lake Qinghai Water Body Variation Based on Remote Sensing Data; China University of Geosciences: Wuhan, China, 2021. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Wu, Y.; Lei, L.; Guo, L. Remote Estimation of Water Storage Variation of Lakes in Tibetan Plateau Over the Past 20 Years. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2018—2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Valencia, Spain, 22–27 July 2018; pp. 8412–8415. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.F. The Development and Application of the Monitoring Method of Lake Ice Based on MODIS Images, A Case of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau; Northwest Normal University: Lanzhou, China, 2018. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Long, D.; Huang, Q.; Zhao, F. Lake Ice Thickness in the Northern Hemisphere (1992–2019, 2071–2099); National Tibetan Plateau/Third Pole Environment Data Center: Beijing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Duan, S.Q.; Jin, Y.M. Analysis of features and causes of Qinghai Lake during the period of 1956–2011. Yellow River 2014, 36, 87–89. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Z.D.; Zhang, F.; Wang, H.L.; Bai, A.J.; Qiu, X.N. The reason of rising water level in Lake Qinghai since 2005. J. Earth Environ. 2013, 4, 1355–1362. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Shi, X.; Shen, H.; Dai, S.; Xiao, J. Cause of Water level fluctuation in Qinghai Lake from 1960 to 2009 and its future trend forecasting. J. Nat. Resour. 2011, 26, 1566–1574. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.H.; Li, S.C.; An, D.; Li, D.L.; Su, Z. A study of the change of Qinghai Lake evaporation. Clim. Environ. Res. 2010, 15, 787–796. [Google Scholar]
















| Sensor | Time | Cloud Cover (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Landsat-5 TM | 11 October 2002 | 12.93, 10.25 |
| 12 September 2003 | 13.54, 13.39 | |
| 20 September 2006 | --, -- | |
| 28 September 2009 | 0.41, 1.3 | |
| Landsat-7 ETM | 8 October 2004 | 0.06, 18.17 |
| 9 September 2005 | 0.81, -- | |
| 15 September 2007 | 3.05, 33.19 | |
| 4 November 2008 | 0.59, 49.35 | |
| 7 September 2010 | 0.81, 26.23 | |
| 28 October 2011 | 9.43, 2.45 | |
| Landsat 8 OLI | 9 October 2013 | 0.12 |
| 13 November 2014 | 1.55 | |
| 15 October 2015 | 1.35 | |
| 17 October 2016 | 1.44 | |
| 4 October 2017 | 3.93 | |
| 21 September 2018 | 1.67 | |
| 11 November 2019 | 2.8 |
| Env/Jas1 | Jas1/SARAL | SARAL/Jas2 | SARAL/S3A | SARAL/S3B | S3A/S3B | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Middle | 34/0.4457 | 3/0.0744 | 50/−1.1519 | 79/0.0105 | 71/0.4266 | 72/0.5577 |
| East | 34/0.4532 | 3/0.0532 | 50/−1.1347 | 79/0.0250 | 73/0.4552 | 72/0.5569 |
| West | 34/0.4418 | 3/0.0855 | 50/−1.1608 | 79/0.0030 | 71/0.4191 | 72/0.5582 |
| North | 34/0.4463 | 3/0.0727 | 50/−1.1505 | 79/0.0117 | 71/0.4278 | 72/0.5577 |
| South | 34/0.4499 | 3/0.0908 | 50/−1.1651 | 79/−6.5 × 10−4 | 71/0.4156 | 72/0.5584 |
| Maximum time interval (days) | 10 | 10 | 10 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Products | Max | Min | Mean | STD | RMS | Distance (km) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| East in situ gauge (639 points) | 0.2356 | −0.1772 | −0.0057 | 0.0696 | 0.0698 | 16.763 |
| West in situ gauge | 0.3219 | −0.0918 | 0.0778 | 0.0673 | 0.1028 | 66.137 |
| North in situ gauge | 0.2849 | −0.1256 | 0.0447 | 0.0678 | 0.0811 | 59.024 |
| South in situ gauge | 0.3372 | −0.0778 | 0.0915 | 0.0673 | 0.1136 | 40.268 |
| Middle in situ gauge | 0.2898 | −0.1211 | 0.0491 | 0.0677 | 0.0835 | 37.38 |
| Mean value 1 in situ gauge | 0.2925 | −0.1187 | 0.0515 | 0.0676 | 0.0849 | |
| DAHITI data—east (145 points) | 0.4154 | −0.3347 | 0.0258 | 0.1242 | 0.1264 | |
| DAHITI data—west | 0.3186 | −0.3170 | −0.0541 | 0.1178 | 0.1292 | |
| DAHITI data—south | 0.3027 | −0.3330 | −0.0680 | 0.1176 | 0.1356 | |
| DAHITI data—north | 0.3569 | −0.3868 | −0.0229 | 0.1216 | 0.1233 | |
| DAHITI data—north | 0.3569 | −0.3868 | −0.0229 | 0.1216 | 0.1233 | |
| DAHITI data—middle | 0.3518 | −0.3918 | −0.0273 | 0.1215 | 0.1241 | |
| DAHITI data—mean value 1 | 0.3491 | −0.3526 | −0.0293 | 0.1201 | 0.1232 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Chen, S.; Luo, J.; Sun, M.; Sun, J.; Yuan, J.; Guo, J. Study on the Variations in Water Storage in Lake Qinghai Based on Multi-Source Satellite Data. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1746. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15071746
Wang J, Wang J, Chen S, Luo J, Sun M, Sun J, Yuan J, Guo J. Study on the Variations in Water Storage in Lake Qinghai Based on Multi-Source Satellite Data. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(7):1746. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15071746
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jianbo, Jinyang Wang, Shunde Chen, Jianbo Luo, Mingzhi Sun, Jialong Sun, Jiajia Yuan, and Jinyun Guo. 2023. "Study on the Variations in Water Storage in Lake Qinghai Based on Multi-Source Satellite Data" Remote Sensing 15, no. 7: 1746. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15071746
APA StyleWang, J., Wang, J., Chen, S., Luo, J., Sun, M., Sun, J., Yuan, J., & Guo, J. (2023). Study on the Variations in Water Storage in Lake Qinghai Based on Multi-Source Satellite Data. Remote Sensing, 15(7), 1746. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15071746