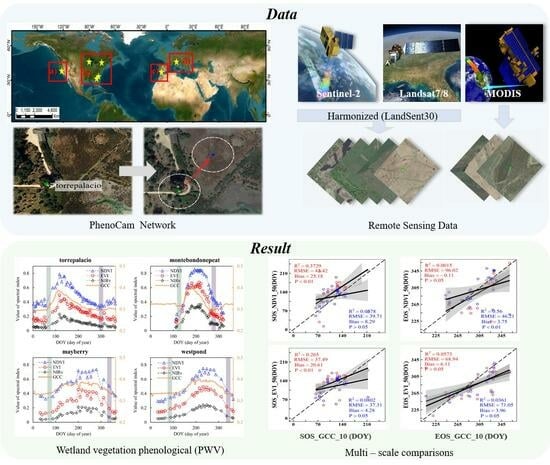
Mapping Phenology of Complicated Wetland Landscapes through Harmonizing Landsat and Sentinel-2 Imagery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
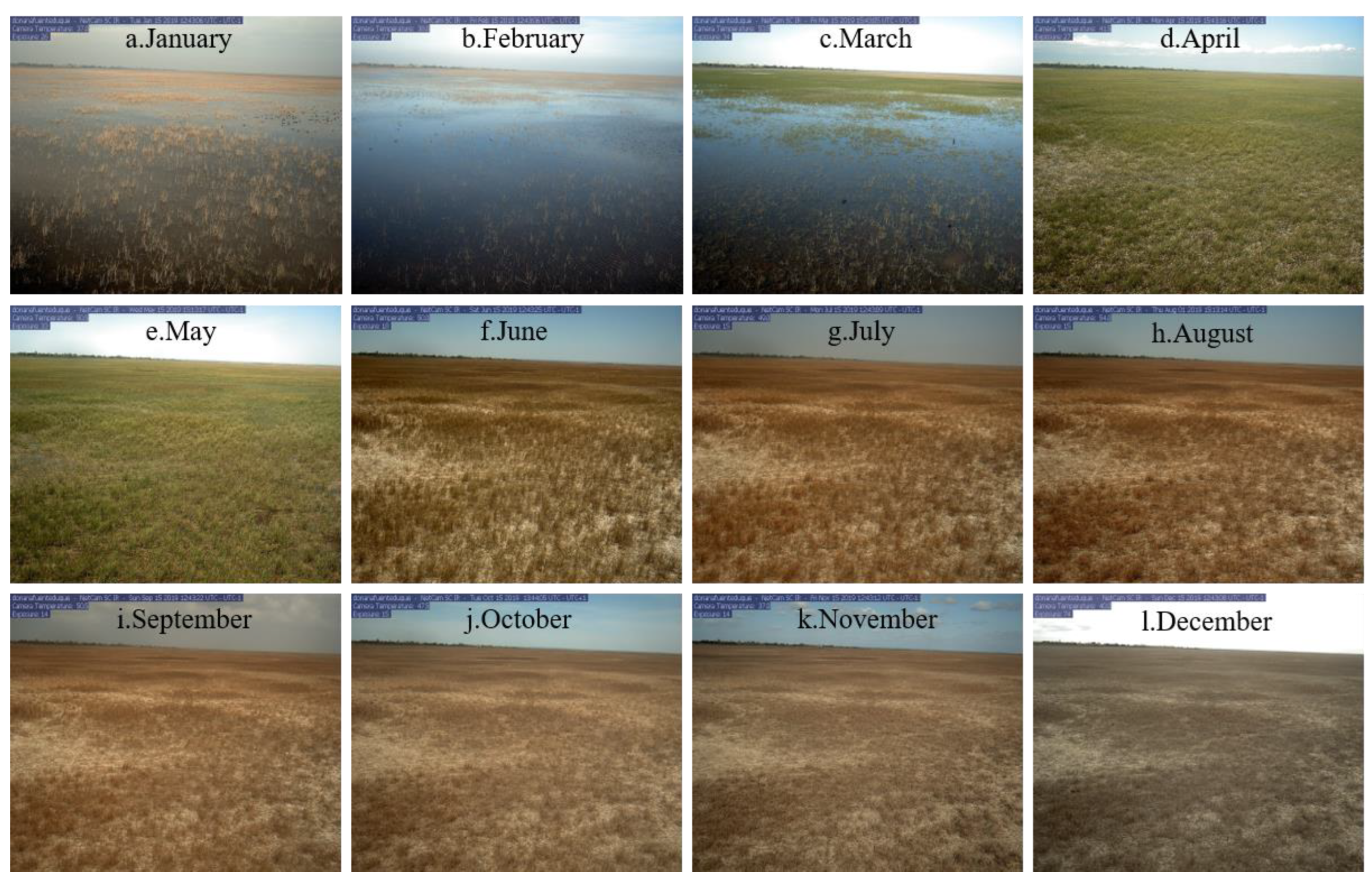
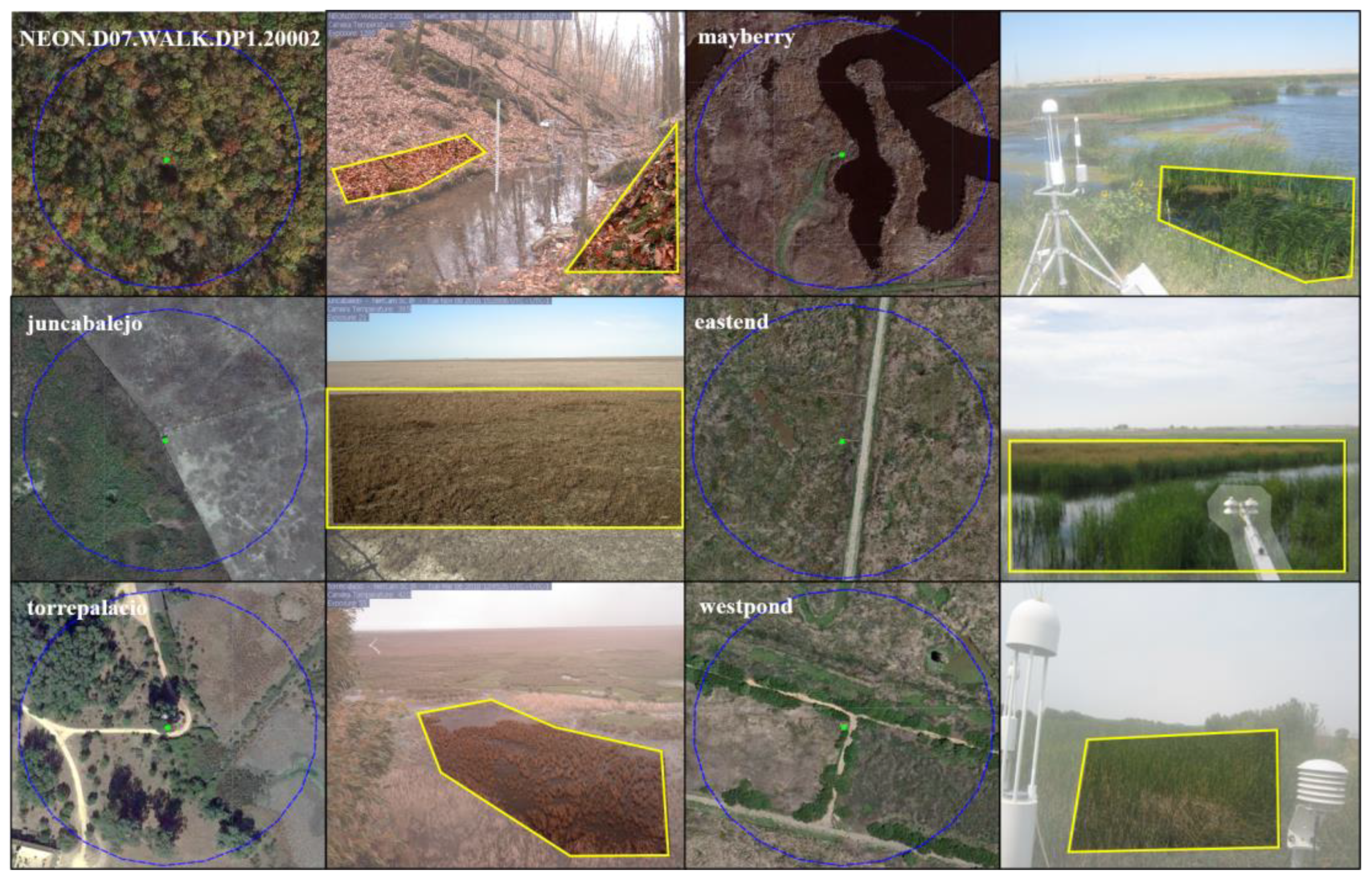
2.2.1. Near-Surface Remote Sensing Data—PhenoCam Dataset
2.2.2. Landsat-7/8 and Sentinel-2A/B Data
2.2.3. MODIS Data
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Screening and Correction of PhenoCam Sites
2.3.2. Landsat-7/8 and Sentinel-2 Data Fusion
2.3.3. Wetland Vegetation Phenological Metrics Estimation
2.3.4. Comparisons between Satellite- and PhenoCam-Based Phenology
3. Results
3.1. Comparisons of before and after Consistency of Site Correction Positions
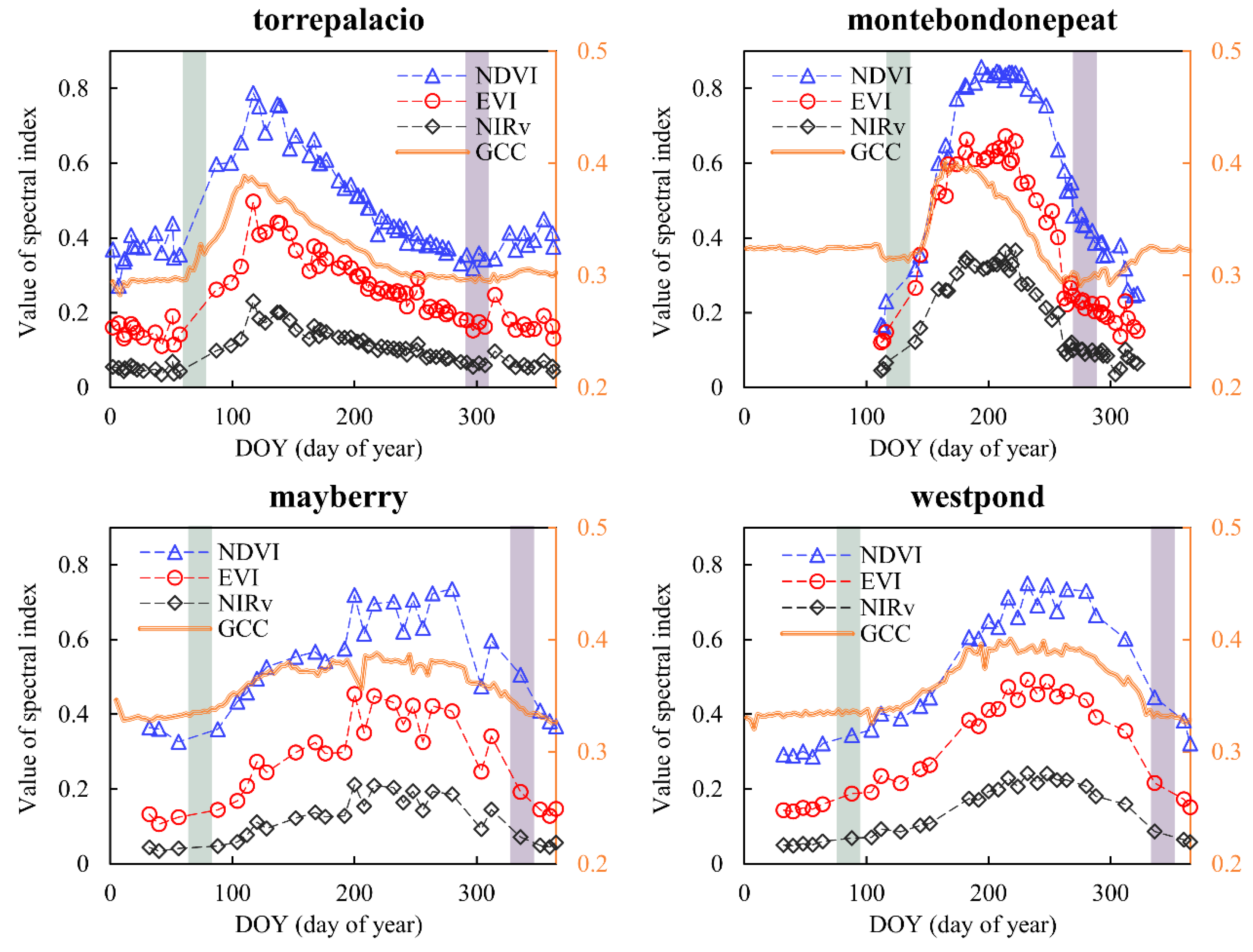
3.2. Wetland Vegetation Phenological Metrics Based on Landsat7/8 and Sentinel-2 Fusion
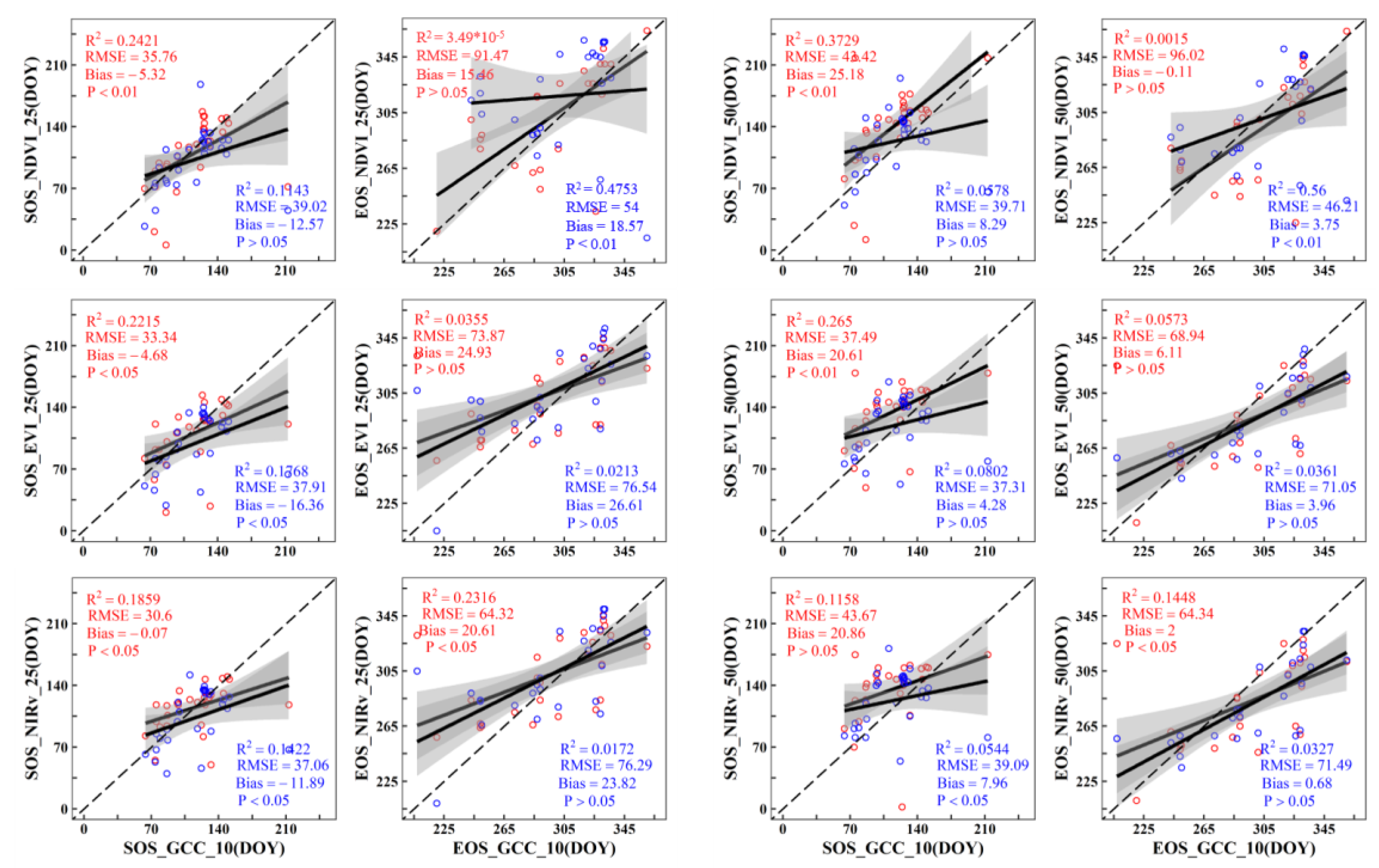
3.3. Agreement between Different Remote Sensing Data and PhenoCam Phenology
3.4. Determination of Buffer and Threshold for LandSent30 Extract Phenology
4. Discussion
4.1. Performance of MODIS and LandSent30 in Wetland Phenology
4.2. Uncertainty in the PhenoCam Network
4.3. Implications and Future Work
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morisette, J.T.; Richardson, A.D.; Knapp, A.K.; Fisher, J.I.; Graham, E.A.; Abatzoglou, J.; Wilson, B.E.; Breshears, D.D.; Henebry, G.M.; Hanes, J.M.; et al. Tracking the rhythm of the seasons in the face of global change: Phenological research in the 21st century. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2009, 7, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnell, N.W.; Lloyd-Hughes, B. The global-scale impacts of climate change on water resources and flooding under new climate and socio-economic scenarios. Clim. Change 2014, 122, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.J.; Niu, Z.G.; Chen, Y.F. Global Wetland Datasets: A Review. Wetlands 2017, 37, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bureau, R.C. Wetlands Values and Functions; Ramsar Convention Bureau: Gland, Switzerland, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Dronova, I.; Gong, P.; Wang, L. Object-based analysis and change detection of major wetland cover types and their classification uncertainty during the low water period at Poyang Lake, China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 3220–3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.J.; Jiang, M.; Lu, X.G.; Liu, X.T.; Liu, B.; Zhang, J.Q.; Wang, X.W.; Tong, S.Z.; Lei, G.C.; Wang, S.Z.; et al. Aboveground biomass and its spatial distribution pattern of herbaceous marsh vegetation in China. Sci. China-Earth Sci. 2021, 64, 1115–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halabisky, M.; Moskal, L.M.; Gillespie, A.; Hannam, M. Reconstructing semi-arid wetland surface water dynamics through spectral mixture analysis of a time series of Landsat satellite images (1984–2011). Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 177, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russi, D.; Brink, P.T.; Badura, T.; Farmer, A.; Badura, T.; Coates, D.; Förster, J.; Kumar, R.; Davidson, N. The Economics of Ecosystems and Biodiversity for Water and Wetlands. IEEP Lond. Bruss. 2013, 78, 118. [Google Scholar]
- Bridgham, S.D.; Cadillo-Quiroz, H.; Keller, J.K.; Zhuang, Q.L. Methane emissions from wetlands: Biogeochemical, microbial, and modeling perspectives from local to global scales. Glob. Change Biol. 2013, 19, 1325–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, J.; Xiao, X. Green-up dates in the Tibetan Plateau have continuously advanced from 1982 to 2011. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 4309–4314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, X.; Hao, Y.; Cui, X.; Chen, H.; Huang, S.; Du, Y.; Li, W.; Kardol, P.; Xiao, X.; Cui, L. Variability and Changes in Climate, Phenology, and Gross Primary Production of an Alpine Wetland Ecosystem. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helfter, C.; Gondwe, M.; Murray-Hudson, M.; Makati, A.; Lunt, M.F.; Palmer, P.I.; Skiba, U. Phenology is the dominant control of methane emissions in a tropical non-forested wetland. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touzi, R.; IEEE. Wetland characterization using polarimetric RADARSAT-2 capability. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Denver, CO, USA, 31 July–4 August 2006; pp. 1639–1642. [Google Scholar]
- Houlahan, J.E.; Keddy, P.A.; Makkay, K.; Findlay, C.S. The effects of adjacent land use on wetland species richness and community composition. Wetlands 2006, 26, 79–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, J.P. Wetland loss and biodiversity conservation. Conserv. Biol. 2000, 14, 314–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, T.H.; Menzel, A. Observed changes in seasons: An overview. Int. J. Climatol. 2002, 22, 1715–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hufkens, K.; Melaas, E.K.; Mann, M.L.; Foster, T.; Ceballos, F.; Robles, M.; Kramer, B. Monitoring crop phenology using a smartphone based near-surface remote sensing approach. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 265, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyednasrollah, B.; Young, A.M.; Hufkens, K.; Milliman, T.; Friedl, M.A.; Frolking, S.; Richardson, A.D. Tracking vegetation phenology across diverse biomes using Version 2.0 of the PhenoCam Dataset. Sci. Data 2019, 6, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.L.; Wardlow, B.D.; Xiang, D.X.; Hu, S.; Li, D.R. A review of vegetation phenological metrics extraction using time-series, multispectral satellite data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 237, 111511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, A.D.; Hufkens, K.; Milliman, T.; Frolking, S. Intercomparison of phenological transition dates derived from the PhenoCam Dataset V1.0 and MODIS satellite remote sensing. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, A.D.; Klosterman, S.; Toomey, M. Near-Surface Sensor-Derived Phenology. In Phenology: An Integrative Environmental Science; Springer Netherlands: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Garrity, S.R.; Bohrer, G.; Maurer, K.D.; Mueller, K.L.; Vogel, C.S.; Curtis, P.S. A comparison of multiple phenology data sources for estimating seasonal transitions in deciduous forest carbon exchange. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2011, 151, 1741–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huemmrich, K.F.; Black, T.A.; Jarvis, P.G.; McCaughey, J.H.; Hall, F.G. High temporal resolution NDVI phenology from micrometeorological radiation sensors. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1999, 104, 27935–27944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soudani, K.; Hmimina, G.; Delpierre, N.; Pontailler, J.Y.; Aubinet, M.; Bonal, D.; Caquet, B.; de Grandcourt, A.; Burban, B.; Flechard, C.; et al. Ground-based Network of NDVI measurements for tracking temporal dynamics of canopy structure and vegetation phenology in different biomes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 123, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahl, D.E.; Gower, S.T.; Burrows, S.N.; Shabanov, N.V.; Myneni, R.B.; Knyazikhin, Y. Monitoring spring canopy phenology of a deciduous broadleaf forest using MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 104, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xiao, X.; Braswell, B.; Linder, E.; Ollinger, S.; Smith, M.-L.; Jenkins, J.P.; Baret, F.; Richardson, A.D.; Moore, B.; et al. Characterization of seasonal variation of forest canopy in a temperate deciduous broadleaf forest, using daily MODIS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 105, 189–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Q.C.; Broich, M.; Zhu, P.; Gong, P. Modeling grassland spring onset across the Western United States using climate variables and MODIS-derived phenology metrics. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 161, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, T.F.; Martz, L.; Zhao, L.; Guo, X.L. Investigating the impact of the temporal resolution of MODIS data on measured phenology in the prairie grasslands. Giscience Remote Sens. 2020, 57, 395–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Xiao, X.; Biradar, C.M.; Dong, J.; Qin, Y.; Menarguez, M.A.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, C.; Wang, J.; et al. Spatiotemporal patterns of paddy rice croplands in China and India from 2000 to 2015. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 579, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastor-Guzman, J.; Dash, J.; Atkinson, P.M. Remote sensing of mangrove forest phenology and its environmental drivers. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 205, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hmimina, G.; Dufrene, E.; Pontailler, J.Y.; Delpierre, N.; Aubinet, M.; Caquet, B.; de Grandcourt, A.; Burban, B.; Flechard, C.; Granier, A.; et al. Evaluation of the potential of MODIS satellite data to predict vegetation phenology in different biomes: An investigation using ground-based NDVI measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 132, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khare, S.; Deslauriers, A.; Morin, H.; Latifi, H.; Rossi, S. Comparing Time-Lapse PhenoCams with Satellite Observations across the Boreal Forest of Quebec, Canada. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearney, M.S.; Stutzer, D.; Turpie, K.; Stevenson, J.C. The Effects of Tidal Inundation on the Reflectance Characteristics of Coastal Marsh Vegetation. J. Coast. Res. 2009, 25, 1177–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, K.B.; O’Connell, J.L.; Di Tommaso, S.; Kelly, M. Evaluation of sensor types and environmental controls on mapping biomass of coastal marsh emergent vegetation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 149, 166–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, G.J.; Dronova, I.; Oikawa, P.Y.; Knox, S.H.; Windham-Myers, L.; Shahan, J.; Stuart-Haentjens, E. The Potential of Satellite Remote Sensing Time Series to Uncover Wetland Phenology under Unique Challenges of Tidal Setting. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melaas, E.K.; Friedl, M.A.; Zhu, Z. Detecting interannual variation in deciduous broadleaf forest phenology using Landsat TM/ETM plus data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 132, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolton, D.K.; Gray, J.M.; Melaas, E.K.; Moon, M.; Eklundh, L.; Friedl, M.A. Continental-scale land surface phenology from harmonized Landsat 8 and Sentinel-2 imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 240, 111685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hill, M.J.; Zhang, X.Y.; Wang, Z.S.; Richardson, A.D.; Hufkens, K.; Filippa, G.; Baldocchi, D.D.; Ma, S.Y.; Verfaillie, J.; et al. Using data from Landsat, MODIS, VIIRS and PhenoCams to monitor the phenology of California oak/grass savanna and open grassland across spatial scales. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2017, 237, 311–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.W.; Xiao, X.M.; Kou, W.L.; Qin, Y.W.; Zhang, G.L.; Li, L.; Jin, C.; Zhou, Y.T.; Wang, J.; Biradar, C.; et al. Tracking the dynamics of paddy rice planting area in 1986-2010 through time series Landsat images and phenology-based algorithms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 160, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xiao, X.; Zou, Z.; Hou, L.; Qin, Y.; Dong, J.; Doughty, R.B.; Chen, B.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; et al. Mapping coastal wetlands of China using time series Landsat images in 2018 and Google Earth Engine. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 163, 312–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, L.; Xia, H.M.; Yang, J.; Niu, W.H.; Wang, R.M.; Song, H.Q.; Guo, Y.; Qin, Y.C. Mapping cropping intensity in Huaihe basin using phenology algorithm, all Sentinel-2 and Landsat images in Google Earth Engine. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 102, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Xiao, X.; Qin, Y.; Wang, J.; Xu, X.; Hu, Y.; Qiao, Z. Mapping cropping intensity in China using time series Landsat and Sentinel-2 images and Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 239, 111624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, J.J.; Wang, Y.Q.; Zhang, H.Y.; Zhang, Z.X.; Guo, X.Y. Comparison of land surface phenology in the Northern Hemisphere based on AVHRR GIMMS3g and MODIS datasets. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 169, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Meng, L.; Asrar, G.R.; Lu, C.; Wu, Q. A dataset of 30 m annual vegetation phenology indicators (1985-2015) in urban areas of the conterminous United States. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2019, 11, 881–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andresen, C.G.; Tweedie, C.E.; Lougheed, V.L. Climate and nutrient effects on Arctic wetland plant phenology observed from phenocams. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 205, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, M.; Ozdogan, M.; Richardson, A.D.; Radeloff, V.C. Phenology from Landsat when data is scarce: Using MODIS and Dynamic Time-Warping to combine multi-year Landsat imagery to derive annual phenology curves. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2017, 54, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, M.; Zhang, X.Y.; Henebry, G.M.; Liu, L.L.; Gray, J.M.; Melaas, E.K.; Friedl, M.A. Long-term continuity in land surface phenology measurements: A comparative assessment of the MODIS land cover dynamics and VIIRS land surface phenology products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 226, 74–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Y.X.; Teng, S.W.; Liu, C.; Dash, J.; Morris, H.; Pastor-Guzman, J. Assessing the Accuracy of Forest Phenological Extraction from Sentinel-1 C-Band Backscatter Measurements in Deciduous and Coniferous Forests. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Tao, S.Q.; Qi, J.G.; Ding, M.J.; Guan, Q.H.; Wu, B.F.; Zhang, M.; Nabil, M.; Tian, F.Y.; et al. A new framework to map fine resolution cropping intensity across the globe: Algorithm, validation, and implication. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 251, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, A.D.; Hufkens, K.; Milliman, T.; Aubrecht, D.M.; Chen, M.; Gray, J.M.; Johnston, M.R.; Keenan, T.F.; Klosterman, S.T.; Kosmala, M.; et al. Tracking vegetation phenology across diverse North American biomes using PhenoCam imagery. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keenan, T.F.; Richardson, A.D. The timing of autumn senescence is affected by the timing of spring phenology: Implications for predictive models. Glob. Change Biol. 2015, 21, 2634–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klosterman, S.T.; Hufkens, K.; Gray, J.M.; Melaas, E.; Sonnentag, O.; Lavine, I.; Mitchell, L.; Norman, R.; Friedl, M.A.; Richardson, A.D. Evaluating remote sensing of deciduous forest phenology at multiple spatial scales using PhenoCam imagery. Biogeosciences 2014, 11, 4305–4320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyednasrollah, B.; Young, A.M.; Hufkens, K.; Milliman, T.; Friedl, M.A.; Frolking, S.; Richardson, A.D.; Abraha, M.; Allen, D.W.; Apple, M.; et al. PhenoCam Dataset v2.0: Vegetation Phenology from Digital Camera Imagery, 2000–2018; ORNL DAAC: Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, A.D.; Braswell, B.H.; Hollinger, D.Y.; Jenkins, J.P.; Ollinger, S.V. Near-surface remote sensing of spatial and temporal variation in canopy phenology. Ecol. Appl. 2009, 19, 1417–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonnentag, O.; Hufkens, K.; Teshera-Sterne, C.; Young, A.M.; Friedl, M.; Braswell, B.H.; Milliman, T.; O’Keefe, J.; Richardson, A.D. Digital repeat photography for phenological research in forest ecosystems. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2012, 152, 159–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, A.M.; Friedl, M.A.; Seyednasrollah, B.; Beamesderfer, E.; Carrillo, C.M.; Li, X.L.; Moon, M.; Arain, M.A.; Baldocchi, D.D.; Blanken, P.D.; et al. Seasonality in aerodynamic resistance across a range of North American ecosystems. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2021, 310, 108613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.P.; Wulder, M.A.; Loveland, T.R.; Woodcock, C.E.; Allen, R.G.; Anderson, M.C.; Helder, D.; Irons, J.R.; Johnson, D.M.; Kennedy, R.; et al. Landsat-8: Science and product vision for terrestrial global change research. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 145, 154–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mas, J.F.; de Araujo, R.S. Assessing Landsat Images Availability and Its Effects on Phenological Metrics. Forests 2021, 12, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irons, J.R.; Dwyer, J.L.; Barsi, J.A. The next Landsat satellite: The Landsat Data Continuity Mission. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 122, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drusch, M.; Del Bello, U.; Carlier, S.; Colin, O.; Fernandez, V.; Gascon, F.; Hoersch, B.; Isola, C.; Laberinti, P.; Martimort, P.; et al. Sentinel-2: ESA’s Optical High-Resolution Mission for GMES Operational Services. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frantz, D. FORCE—Landsat + Sentinel-2 Analysis Ready Data and Beyond. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaaf, C.B.; Liu, J.C.; Gao, F.; Strahler, A.H. Aqua and Terra MODIS Albedo and Reflectance Anisotropy Products; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 11, pp. 549–561. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Liu, L.L.; Liu, Y.; Jayavelu, S.; Wang, J.M.; Moon, M.; Henebry, G.M.; Friedl, M.A.; Schaaf, C.B. Generation and evaluation of the VIIRS land surface phenology product. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 216, 212–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.K.; Roy, D.P.; Yan, L.; Li, Z.; Huang, H.; Vermote, E.; Skakun, S.; Roger, J.-C. Characterization of Sentinel-2A and Landsat-8 top of atmosphere, surface, and nadir BRDF adjusted reflectance and NDVI differences. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 215, 482–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Dong, J.; Xiao, X.; Dai, J.; Wu, C.; Xia, J.; Zhao, G.; Zhao, M.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Divergent shifts in peak photosynthesis timing of temperate and alpine grasslands in China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 233, 111395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Jonsson, P.; Tamura, M.; Gu, Z.H.; Matsushita, B.; Eklundh, L. A simple method for reconstructing a high-quality NDVI time-series data set based on the Savitzky-Golay filter. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 91, 332–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Xiao, X.; Menarguez, M.A.; Zhang, G.; Qin, Y.; Thau, D.; Biradar, C.; Moore, B., III. Mapping paddy rice planting area in northeastern Asia with Landsat 8 images, phenology-based algorithm and Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 185, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.X.; Wang, C.Z.; Yu, Q.Y.; Smith, E. Spatiotemporal assessment of potential drivers of salt marsh dieback in the North Inlet-Winyah Bay estuary, South Carolina (1990-2019). J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 313, 114907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connell, J.L.; Alber, M.; Pennings, S.C. Microspatial Differences in Soil Temperature Cause Phenology Change on Par with Long-Term Climate Warming in Salt Marshes. Ecosystems 2020, 23, 498–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; He, T.; Song, D.X.; Wang, C.Q. Land Surface Phenology Retrieval through Spectral and Angular Harmonization of Landsat-8, Sentinel-2 and Gaofen-1 Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xiao, X.; Qiu, S.; Xu, X.; Wang, X.; Chang, Q.; Wu, J.; Li, B. Quantifying latitudinal variation in land surface phenology of Spartina alterniflora saltmarshes across coastal wetlands in China by Landsat 7/8 and Sentinel-2 images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 269, 112810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melaas, E.K.; Sulla-Menashe, D.; Gray, J.M.; Black, T.A.; Morin, T.H.; Richardson, A.D.; Friedl, M.A. Multisite analysis of land surface phenology in North American temperate and boreal deciduous forests from Landsat. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 186, 452–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jong, R.; Verbesselt, J.; Zeileis, A.; Schaepman, M.E. Shifts in Global Vegetation Activity Trends. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 1117–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulder, M.A.; White, J.C.; Loveland, T.R.; Woodcock, C.E.; Belward, A.S.; Cohen, W.B.; Fosnight, E.A.; Shaw, J.; Masek, J.G.; Roy, D.P. The global Landsat archive: Status, consolidation, and direction. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 185, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, J.L.; Alber, M. A smart classifier for extracting environmental data from digital image time-series: Applications for PhenoCam data in a tidal salt marsh. Environ. Model. Softw. 2016, 84, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cescatti, A.; Marcolla, B.; Vannan, S.K.S.; Pan, J.Y.; Roman, M.O.; Yang, X.Y.; Ciais, P.; Cook, R.B.; Law, B.E.; Matteucci, G.; et al. Intercomparison of MODIS albedo retrievals and in situ measurements across the global FLUXNET network. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 121, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, L.Y.; Zhao, T.T.; Chen, X.D.; Lin, S.R.; Wang, J.Q.; Mi, J.; Liu, W.D. GWL_FCS30: A global 30 m wetland map with a fine classificationsystem using multi-sourced and time-series remote sensing imagery in 2020. Earth Syst. Sci. Data. 2023, 15, 265–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
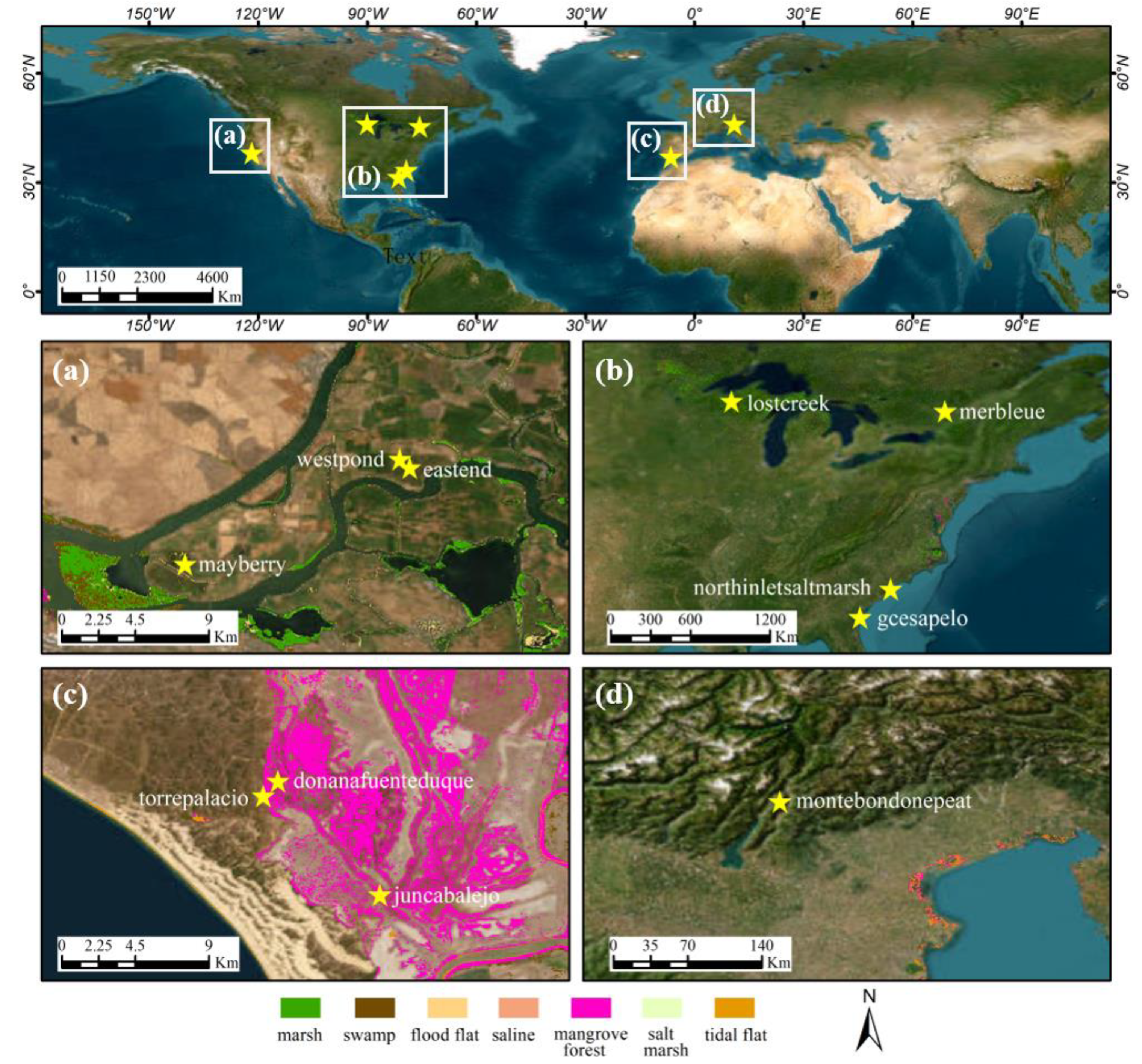




| Site | Latitude (°) | Longitude (°) | Altitude (m) | Start Date | End Date | Level 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| donanafuenteduque | 36.99855 | −6.43460 | 1 | 1 January 2018 | 31 December 2018 | I |
| eastend | 38.10273 | −121.64132 | −5 | 1 January 2015 | 31 December 2017 | I |
| gcesapelo | 31.44404 | −81.28353 | 0 | 1 January 2015 | 31 December 2018 | I |
| juncabalejo | 36.93619 | −6.37845 | 1 | 1 January 2018 | 31 December 2018 | I |
| lostcreek | 46.08270 | −89.97920 | 480 | 1 January 2017 | 31 December 2017 | I |
| mayberry | 38.04977 | −121.76507 | −5 | 1 January 2018 | 31 December 2018 | II |
| merbleue | 45.40940 | −75.51870 | 69 | 1 January 2013 | 31 December 2018 | I |
| montebondonepeat | 46.01770 | 11.04090 | 1563 | 1 January 2015 | 1 January 2018 | I |
| northinletsaltmarsh | 33.34550 | −79.19570 | 1 | 1 January 2018 | 31 December 2018 | I |
| torrepalacio | 36.99050 | −6.44260 | 3 | 1 January 2018 | 31 December 2018 | I |
| westpond | 38.10742 | −121.64687 | −5 | 1 January 2013 | 31 December 2018 | II |
| Wetland Sites | Correction Direction | lat_Correction 1 | lon_Correction 1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| donanafuenteduque | - | 36.99855 | −6.43460 |
| eastend | west | 38.10276 | −121.64203 |
| gcesapelo | - | 31.44404 | −81.28353 |
| juncabalejo | east | 36.93624 | −6.37631 |
| lostcreek | - | 46.08270 | −89.97920 |
| mayberry | west | 38.04984 | −121.76531 |
| merbleue | - | 45.40940 | −75.51870 |
| montebondonepeat | - | 46.01770 | 11.04090 |
| northinletsaltmarsh | - | 33.34550 | −79.19570 |
| torrepalacio | north | 36.99132 | −6.44178 |
| westpond | west | 38.10734 | −121.64739 |
| Bands | Landsat-7 | Bands | Sentinel-2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blue | Land8 1 = 0.0003 + 0.8474 × Land7 1 | Blue | Land8 1 = 0.0003 + 0.9570 × Sent2 1 |
| Red | Land8 1 = 0.0061 + 0.9047 × Land7 1 | Red | Land8 1 = 0.0041 + 0.9533 × Sent2 1 |
| NIR | Land8 1 = 0.0412 + 0.8462 × Land7 1 | NIR (Band8A) | Land8 1 = 0.0077 + 0.9644 × Sent2 1 |
| SWIR | Land8 1 = 0.0254 + 0.8937 × Land7 1 | SWIR | Land8 1 = 0.0034 + 0.9522 × Sent2 1 |
| Remote Sensing Index | Statistic | SOS | EOS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Before|After | Before|After | ||
| NDVI | R2 RMSE | 0.47|0.64 37.28|25.27 | 0.15|0.18 53.47|53.48 |
| EVI | R2 RMSE | 0.34|0.45 33.53|23.63 | 0.29|0.23 36.94|39.25 |
| NIRv | R2 RMSE | 0.37|0.49 29.84|22.9 | 0.26|0.24 37.09|37.94 |
| Remote Sensing Index | Statistic | SOS | EOS |
|---|---|---|---|
| LandSent30|MODIS | LandSent30|MODIS | ||
| NDVI | R2 RMSE Bias | 0.35|0.04 46.92|39.85 28.50|8.64 | 0.14|0.41 57.80|37.07 −9.68|−2.11 |
| EVI | R2 RMSE Bias | 0.24|0.06 35.12|37.35 18.54|4.36 | 0.12|0.30 46.02|39.09 −4.11|−8.21 |
| NIRv | R2 RMSE Bias | 0.27|0.04 36.78|39.11 24.46|8.00 | 0.13|0.31 45.80|40.01 −7.71|−11.68 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, C.; Yang, J.; Zhao, G.; Dai, J.; Zhu, M.; Dong, J.; Liu, R.; Zhang, G. Mapping Phenology of Complicated Wetland Landscapes through Harmonizing Landsat and Sentinel-2 Imagery. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2413. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15092413
Fan C, Yang J, Zhao G, Dai J, Zhu M, Dong J, Liu R, Zhang G. Mapping Phenology of Complicated Wetland Landscapes through Harmonizing Landsat and Sentinel-2 Imagery. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(9):2413. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15092413
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Chang, Jilin Yang, Guosong Zhao, Junhu Dai, Mengyao Zhu, Jinwei Dong, Ruoqi Liu, and Geli Zhang. 2023. "Mapping Phenology of Complicated Wetland Landscapes through Harmonizing Landsat and Sentinel-2 Imagery" Remote Sensing 15, no. 9: 2413. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15092413
APA StyleFan, C., Yang, J., Zhao, G., Dai, J., Zhu, M., Dong, J., Liu, R., & Zhang, G. (2023). Mapping Phenology of Complicated Wetland Landscapes through Harmonizing Landsat and Sentinel-2 Imagery. Remote Sensing, 15(9), 2413. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15092413