Spatiotemporal Evolution and Factors Influencing Regional Ecological Land in a Multidimensional Perspective: A Case Study of the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Region
Abstract
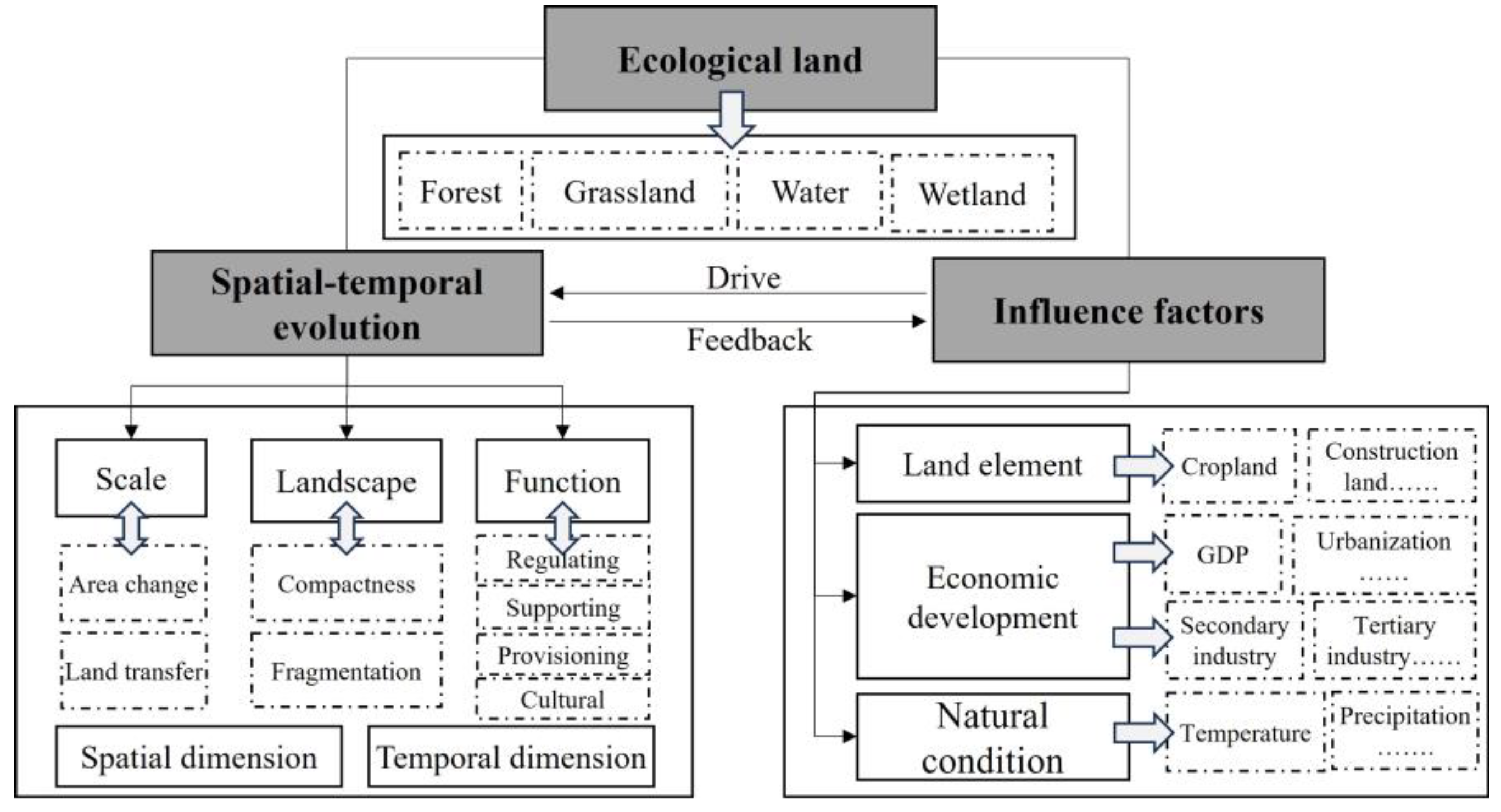
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Connotation Analysis of EL
2.2. Study on the Spatiotemporal Evolution and Driving Factors of EL
3. Study Area, Methods, and Materials
3.1. Study Area
3.2. Study Methods
3.2.1. Gravity Center Shift Model
3.2.2. Calculation of Landscape Morphology Indicators
3.2.3. Equivalent Factor Method
3.2.4. Two-Way Fixed-Effects Model
3.3. Study Materials
4. Results
4.1. Multidimensional Spatiotemporal Evolution of EL in BTH Region
4.1.1. Area Dimension
4.1.2. Landscape Dimension
4.1.3. Function Dimension
4.2. Analysis of Factors Influencing the Multidimensional Evolution of EL
4.3. Heterogeneity Analysis of Factors Influencing EL Evolution
5. Discussion
5.1. Multidimensional Effects of Cultivated Land and Construction Land on the EL
5.2. The Differentiation Characteristics of Influencing Factors under Different Conditions
5.3. Policy Suggestions for EL Protection and Management in BTH Region
5.4. Limitations and Prospects
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, Z.; Peng, J.; Liu, Y.; Qiu, S.; Zhang, H.; Dong, J. Exploring the Combined Impact of Ecosystem Services and Urbanization on SDGs Realization. Appl. Geogr. 2023, 153, 102907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.L.R.; Jones, S.K.; Johnson, J.A.; Brauman, K.A.; Chaplin-Kramer, R.; Fremier, A.; Girvetz, E.; Gordon, L.J.; Kappel, C.V.; Mandle, L.; et al. Distilling the Role of Ecosystem Services in the Sustainable Development Goals. Ecosyst. Serv. 2018, 29, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Fang, C.; Zhang, Q. Coupling Coordinated Development between Social Economy and Ecological Environment in Chinese Provincial Capital Cities-Assessment and Policy Implications. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 229, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Xu, W.; Fu, R.; Wang, H. Study of ecological land in China: Conception, classification, and spatial-temporal pattern. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2015, 35, 4931–4943. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Yan, J.; Xia, F. Trade-Offs under Pressure? Development of Urban Green Space under Economic Growth and Governance. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 427, 139261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Zhao, M.; Guo, X.; Pan, Y.; Liu, Y. Spatial-Temporal Dynamics and Associated Driving Forces of Urban Ecological Land: A Case Study in Shenzhen City, China. Habitat Int. 2017, 60, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Kong, W.; Yan, J.; Xia, F. Trapped in Dilemma: Inverted N-Shaped EKC Evidence of Economic Growth and Ecological Land in a Spatial Spillover Perspective. Appl. Geogr. 2023, 161, 103145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Fu, M.; Zhao, X.; Wang, J.; Jiang, P. Ecological Effects of Land-Use Change on Two Sides of the Hu Huanyong Line in China. Land Use Policy 2022, 113, 105895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, C.; Yao, X.; Yun, W.; Ma, J.; Gao, L.; Li, P. Scenario Simulation of the Tradeoff between Ecological Land and Farmland in Black Soil Region of Northeast China. Land Use Policy 2022, 114, 105991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y. Classification evaluation and spatial-temporal analysis of “production-living-ecological” spaces in China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 72, 1290–1304. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.; Su, M.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Chang, X.; Zhang, P. Spatial–Temporal Evolution and Prediction of Habitat Quality in Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Region Based on Land Use Change. Land 2023, 12, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, H.; Li, J. The Integration of Urban Streetscapes Provides the Possibility to Fully Quantify the Ecological Landscape of Urban Green Spaces: A Case Study of Xi’an City. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 133, 108388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xiao, B.; Jiao, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X. Modeling the Response of Ecological Service Value to Land Use Change through Deep Learning Simulation in Lanzhou, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 796, 148981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhuang, D. A Highly Integrated, Expansible, and Comprehensive Analytical Framework for Urban Ecological Land: A Case Study in Guangzhou, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 268, 122360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, P.; Zhang, L.; Tian, Y.; Li, X. Spatio-Temporal Changes in Ecosystem Service Value and Its Coordinated Development with Economy: A Case Study in Hainan Province, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Bao, W.; Liu, Y. Coupling Coordination Analysis of Rural Production-Living-Ecological Space in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 106512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, W.; Yang, Y.; Zou, L. How to Reconcile Land Use Conflicts in Mega Urban Agglomeration? A Scenario-Based Study in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 296, 113168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Pei, X.; Zhu, W.; Jiao, J. Understanding the Intricate Tradeoffs among Ecosystem Services in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration across Spatiotemporal Features. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 898, 165453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Li, S.; Liu, L.; Liang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Wu, S. Uncovering the Relationships between Ecosystem Services and Social-Ecological Drivers at Different Spatial Scales in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 290, 125193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernstson, H. The Social Production of Ecosystem Services: A Framework for Studying Environmental Justice and Ecological Complexity in Urbanized Landscapes. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2013, 109, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prato, T. Modeling Ecological Impacts of Landscape Change. Environ. Model. Softw. 2005, 20, 1359–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puppim De Oliveira, J.A.; Bellezoni, R.A.; Shih, W.; Bayulken, B. Innovations in Urban Green and Blue Infrastructure: Tackling Local and Global Challenges in Cities. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 362, 132355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Druckman, A.; Gallagher, J.; Gatersleben, B.; Allison, S.; Eisenman, T.S.; Hoang, U.; Hama, S.; Tiwari, A.; Sharma, A.; et al. The Nexus between Air Pollution, Green Infrastructure and Human Health. Environ. Int. 2019, 133, 105181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demuzere, M.; Orru, K.; Heidrich, O.; Olazabal, E.; Geneletti, D.; Orru, H.; Bhave, A.G.; Mittal, N.; Feliu, E.; Faehnle, M. Mitigating and Adapting to Climate Change: Multi-Functional and Multi-Scale Assessment of Green Urban Infrastructure. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 146, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolch, J.R.; Byrne, J.; Newell, J.P. Urban Green Space, Public Health, and Environmental Justice: The Challenge of Making Cities ‘Just Green Enough’. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 125, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zuo, L.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Yi, L.; Liu, F.; Xu, J. Spatial Differentiation of Land Use and Landscape Pattern Changes in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Area. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, O.; Soto, E.; Rojas, C.; López, J.J. Assessment of the Flood Mitigation Ecosystem Service in a Coastal Wetland and Potential Impact of Future Urban Development in Chile. Habitat Int. 2022, 123, 102554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Sun, C.; Wang, X.; Tian, P.; Chen, L.; Zhang, H.; Yang, X.; He, G. Thirty-Year Changes of the Coastlines, Wetlands, and Ecosystem Services in the Asia Major Deltas. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 326, 116675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, K.; Fuchs, R.; Rounsevell, M.; Herold, M. Global Land Use Changes Are Four Times Greater than Previously Estimated. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vliet, J. Direct and Indirect Loss of Natural Area from Urban Expansion. Nat. Sustain. 2019, 2, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Fu, J.; Xie, X.; Ding, F.; Jiang, D. Spatiotemporal Evolution of Urban-Agricultural-Ecological Space in China and Its Driving Mechanism. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 371, 133684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R.; Wang, F.; Wang, K.; Xu, S. Quantifying Influences of Anthropogenic-Natural Factors on Ecological Land Evolution in Mega-Urban Agglomeration: A Case Study of Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 283, 125304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Li, Z.; Gao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Z.; Song, Z.; Qin, P.; Tian, X. Identification and Assessment of the Factors Driving Vegetation Degradation/Regeneration in Drylands Using Synthetic High Spatiotemporal Remote Sensing Data—A Case Study in Zhenglanqi, Inner Mongolia, China. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 107, 105614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Barrera, F.; Manson, R.H.; Landgrave, R. Identifying Deforestation Attractors and Patterns of Fragmentation for Seasonally Dry Tropical Forest in Central Veracruz, Mexico. Land Use Policy 2014, 41, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, D.; Dong, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, W.; Liu, K.; Li, L. Analysis of the environmental Kuznets curve for forest fragmentation: The case of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region in China. For. Policy Econ. 2023, 151, 102970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J. China Faces up to “terrible” State of Its Ecosystems. Nature 2011, 471, 19–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puskás, N.; Abunnasr, Y.; Naalbandian, S. Assessing Deeper Levels of Participation in Nature-Based Solutions in Urban Landscapes—A Literature Review of Real-World Cases. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2021, 210, 104065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassauer, J.I.; Raskin, J. Urban Vacancy and Land Use Legacies: A Frontier for Urban Ecological Research, Design, and Planning. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 125, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Shan, N.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, F.; Liu, W.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, Q. Separating the Effects of Climate Change and Human Activity on Water Use Efficiency over the Beijing-Tianjin Sand Source Region of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 690, 584–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, D.; Wang, Z.; Wu, B.; Zeng, Y.; Luo, L.; Zhang, B. Land Degradation and Restoration in the Arid and Semiarid Zones of China: Quantified Evidence and Implications from Satellites. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 3841–3851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Lü, Y.; Fu, B.; Comber, A.; Li, T.; Hu, J. Driving Factors of Land Change in China’s Loess Plateau: Quantification Using Geographically Weighted Regression and Management Implications. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Jia, B.Q.; Liu, W.R.; Zhang, Q.M. Spatial pattern of ecological land stability analysis and influencing factor in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 9927–9944. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, H. Analysis of Regionally Ecological Land Use and Its Influencing Factors Based on a Logistic Regression Model in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region, China. Resour. Sci. 2011, 33, 2063–2070. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Niedertscheider, M.; Erb, K. Land System Change in Italy from 1884 to 2007: Analysing the North–South Divergence on the Basis of an Integrated Indicator Framework. Land Use Policy 2014, 39, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.H.; Dargusch, P.; Moss, P.; Aziz, A.A. Land-Use Change and Socio-Ecological Drivers of Wetland Conversion in Ha Tien Plain, Mekong Delta, Vietnam. Land Use Policy 2017, 64, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, M.A.; Auch, R.F.; Karstensen, K.A.; Sayler, K.L.; Taylor, J.L.; Loveland, T.R. Land Change Variability and Human–Environment Dynamics in the United States Great Plains. Land Use Policy 2012, 29, 710–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Zhang, Z. Dynamics of Territorial Spatial Pattern and Landscape Impact under Different Economic Gradients: A Case Study of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei (BTH) Region, China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Yang, Y.; Xia, F.; Sun, W.; Li, X.; Xie, Y. Exploring the Influences of Different Processes of Habitat Fragmentation on Ecosystem Services. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2022, 227, 104544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, W.; Feng, Q.; Zhu, M.; Yang, L.; Zhang, J.; Yin, X. The Role of Land Use Change in Affecting Ecosystem Services and the Ecological Security Pattern of the Hexi Regions, Northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 855, 158940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, G.; Zhang, C.; Zhen, L.; Zhang, L. Dynamic Changes in the Value of China’s Ecosystem Services. Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 26, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Z.; Feng, X. Urban Green Space Pattern in Core Cities of the Greater Bay Area Based on Morphological Spatial Pattern Analysis. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S. High-Spatial-Resolution Monthly Temperatures Dataset over China during 1901–2017. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2019, 11, 1931–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, Y.; van Vliet, J. Spatiotemporal Patterns and Drivers of the Urban Air Pollution Island Effect for 2273 Cities in China. Environ. Int. 2024, 184, 108455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Fan, H.; Sun, L.; Liu, W.; Wang, C.; Wu, Z.; Lv, T. Identifying Regional Eco-Environment Quality and Its Influencing Factors: A Case Study of an Ecological Civilization Pilot Zone in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 435, 140308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astell-Burt, T.; Hartig, T.; Putra, I.G.N.E.; Walsan, R.; Dendup, T.; Feng, X. Green Space and Loneliness: A Systematic Review with Theoretical and Methodological Guidance for Future Research. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 847, 157521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Sun, C.; Ye, J.; Gan, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, Y. Spatio-Temporal Heterogeneity of Ecological Quality in Hangzhou Greater Bay Area (HGBA) of China and Response to Land Use and Cover Change. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Dimension | Variable | Description | Mean | SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EL | Scale | Per capita | 0.160 | 0.306 |
| Fragmentation | - | 0.507 | 0.130 | |
| Compactness | - | 0.602 | 0.225 | |
| Value | Taking the logarithm | 0.273 | 0.503 | |
| Land element | Cropland | Per capita | 0.170 | 0.140 |
| Cons. land | Per capita | 0.027 | 0.033 | |
| Unused land | Per capita | 0.001 | 0.005 | |
| Economic development | Urb | The share of urban household population in the total population | 0.239 | 0.251 |
| GDP | Taking the logarithm | 0.319 | 0.150 | |
| Road | The ratio of road length to land area | 0.802 | 0.750 | |
| Ind2 | The share of the secondary industry output value in the GDP | 0.408 | 0.167 | |
| Ind3 | The share of the tertiary industry output value in the GDP | 0.319 | 0.150 | |
| Resource endowment | Temp | Annual average | 11.79 | 2.502 |
| Pre | Annual average | 42.44 | 8.629 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area | Compactness | Fragmentation | Function | |
| Cropland | −0.4719 *** | −0.6532 | 0.1351 | −0.1734 *** |
| (0.1124) | (2.4765) | (0.2712) | (0.0343) | |
| Cons. land | −0.4048 ** | −5.0941 *** | −1.4182 * | −0.0087 *** |
| (0.1334) | (1.1663) | (0.5886) | (0.0000) | |
| Unused land | −0.3315 | −56.6845 | 0.0355 | 2.1534 |
| (0.6551) | (50.9617) | (1.0126) | (4.1005) | |
| Urb | −0.0176 * | −0.2016 | 0.0225 ** | −0.7579 *** |
| (0.0087) | (0.0092) | (0.0086) | (0.0249) | |
| GDP | −0.0004 *** | −0.0000 | 0.0019 *** | −1.0089 *** |
| (0.000) | (0.0000) | (0.0000) | (0.0897) | |
| Road | −0.0129 *** | −0.0085 * | 0.0186 ** | −0.0736 * |
| (0.0028) | (0.0033) | (0.0065) | (0.0294) | |
| Ind2 | −0.0023 *** | −0.0322 | 0.0115 ** | −0.0716 ** |
| (0.0002) | (0.0312) | (0.0040) | (0.0232) | |
| Ind3 | 0.0015 | 0.1786 *** | 0.0027 | 0.0394 |
| (0.0032) | (0.0480) | (0.0047) | (0.0262) | |
| Rain | 0.0004 * | 0.1443 ** | 0.0001 | 0.0536 *** |
| (0.0002) | (0.0467) | (0.0002) | (0.0012) | |
| Temp | 0.0154 * | 0.3089 *** | 0.0198 | 0.1289 *** |
| (0.0075) | (0.0846) | (0.0101) | (0.0340) | |
| Cons. Land 2 | 1.5206 * | |||
| (0.6706) | ||||
| Cons | 0.0389 *** | −7.8652 *** | 0.3371 ** | −4.8906 *** |
| (0.006) | (1.0060) | (0.1082) | (0.3709) | |
| N | 780 | 780 | 780 | 780 |
| Fixed year | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Fixed unit | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| adj. R-sq | 0.322 | 0.711 | 0.294 | 0.880 |
| Low Economic Development | Medium Economic Development | High Economic Development | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) | (10) | (11) | (12) | (13) | (14) | (15) | (16) | |
| Area | Compactness | Fragmentation | Function | Area | Compactness | Fragmentation | Function | Area | Compactness | Fragmentation | Function | |
| Cropland | −1.4535 *** | −0.0591 *** | 2.5899 ** | −2.5134 ** | −0.4384 *** | −3.8818 *** | −3.5932 | −0.1306 *** | −0.3493 * | 3.2253 | 2.8327 | 2.0867 |
| (0.2570) | 0.0012 | (0.8026) | (0.9555) | (0.0767) | 0.6884 | (2.0605) | (0.0166) | (0.1247) | 1.8380 | (1.7859) | (2.5045) | |
| Cons. land | 0.0046 | 1.7787 | 1.3069 | −10.4215 *** | −0.002 *** | −1.4701 | −0.5169 *** | −5.5221 | −0.9957 * | −0.2024 ** | 0.5896 *** | −0.0088 *** |
| (0.2638) | 4.4664 | (3.1101) | (1.5855) | (0.0000) | 6.7356 | (0.0118) | (3.5773) | (0.4261) | 0.0897 | (0.0014) | (0.0002) | |
| Unused land | 0.2208 | −35.4498 | −2.5782 | 3.7371 | −0.2252 | −18.8260 | 2.9876 | 23.3347 *** | −0.5819 | 0.6095 | 44.2853 ** | 29.3294 |
| (0.7825) | 14.9817 | (3.0005) | (4.9365) | (0.6993) | 10.5066 | (9.9109) | (3.7763) | (1.2504) | 14.4821 | (14.6434) | (19.5217) | |
| Urb | −0.0137 | 0.1068 | 0.0284 | −0.6515 * | −0.0070 | 0.1814 | 0.0199 *** | 0.2632 * | −0.0241 ** | 0.5209 * | 0.1899 *** | −0.0763 ** |
| (0.0106) | 0.1327 | (0.0725) | (0.2403) | (0.0146) | 0.1370 | (0.0009) | (0.0997) | (0.0088) | 0.2211 | (0.0415) | (0.0264) | |
| GDP | −0.0102 | 0.6092 *** | −0.0359 | −0.0110 | 0.0069 | 0.3906 ** | −0.0298 | −0.0982 | −0.0169 *** | −0.0161 ** | 0.0509 *** | −0.0427 *** |
| (0.0087) | 0.1079 | (0.0395) | (0.0681) | (0.0105) | 0.1330 | (0.0245) | (0.0984) | (0.0047) | 0.0055 | (0.0121) | (0.0118) | |
| Road | 0.0026 | 0.3161 *** | −0.0041 | −0.0252 | 0.0075 | 0.3949 *** | 0.0168 ** | −0.1256 | −0.0163 *** | 0.0954 | −0.1102 * | −0.0990 * |
| (0.0028) | 0.0857 | (0.0108) | (0.0384) | (0.0071) | 0.0926 | (0.0070) | (0.0668) | (0.0043) | 0.0480 | (0.0442) | (0.0379) | |
| Ind2 | 0.0047 | −0.2412 | 0.0202 | −0.1680 *** | −0.0171 | −0.2202 * | 0.0172 | −0.1476 * | −0.0003 *** | 0.0049 | −0.0023 | −0.1680 *** |
| (0.0042) | 0.0670 | (0.0219) | (0.0343) | (0.0089) | 0.1018 | (0.0167) | (0.0561) | (0.0000) | 0.0098 | (0.0045) | (0.0343) | |
| Ind3 | −0.0013 | −0.1156 | 0.0268 | −0.0657 | 0.0102 | 0.0214 | −0.0105 | 0.0120 | −0.0012 | −0.0282 | −0.0430 | −0.0789 |
| (0.0051) | 0.0801 | (0.0213) | (0.0379) | (0.0077) | 0.0855 | (0.0241) | (0.0668) | (0.0058) | 0.0652 | (0.0231) | (0.0819) | |
| Rain | −0.0002 | −0.0086 * | 0.0003 | 0.0549 *** | 0.0005 * | −0.0047 | 0.0002 | 0.0477 *** | −0.0003 | 0.0027 *** | −0.0017 | 0.0459 *** |
| (0.0002) | 0.0040 | (0.0008) | (0.0019) | (0.0002) | 0.0042 | (0.0006) | (0.0022) | (0.0002) | (0.0000) | (0.0010) | (0.0034) | |
| Temp | 0.0124 | 0.2792 * | −0.1008 * | 0.0973 * | 0.0124 | 0.2762 | −0.0240 | −0.2007 * | 0.0014 | −0.0503 | 0.0233 | 0.3844 *** |
| (0.0083) | 0.1167 | (0.0445) | (0.0448) | (0.0075) | 0.1019 | (0.0150) | (0.0750) | (0.0068) | 0.0575 | (0.0225) | (0.0906) | |
| Cons. Land 2 | −26.0189 | −26.3652 | −1.3430 *** | |||||||||
| (30.6395) | (30.8494) | (0.1920) | ||||||||||
| Cons | 0.1473 | −3.4924 * | −2.3948 *** | −3.9268 *** | −0.1658 | −5.7718 *** | −0.0955 | −6.2898 *** | 0.2721 * | −5.6648 ** | −1.1127 | −9.5436 *** |
| (0.1047) | 1.4749 | (0.5829) | (0.8695) | (0.1402) | 1.5261 | (0.4452) | (0.8744) | (0.1211) | 1.9660 | (0.6382) | (1.9242) | |
| adj. R-sq | 0.338 | 0.804 | 0.140 | 0.896 | 0.786 | 0.863 | 0.122 | 0.854 | 0.509 | 0.929 | 0.488 | 0.885 |
| Fixed year | YES | |||||||||||
| Fixed unit | YES | |||||||||||
| N | 525 | 174 | 81 | |||||||||
| Low-Altitude | High-Altitude | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (17) | (18) | (19) | (20) | (21) | (22) | (23) | (24) | |
| Area | Compactness | Fragmentation | Function | Area | Compactness | Fragmentation | Function | |
| Cropland | −0.0156 *** | 1.4066 | −0.5890 | −1.0563 *** | 0.8863 | 2.5504 | 0.3562 | −0.5127 *** |
| (0.0002) | (2.6341) | (1.2557) | (0.1859) | (0.4938) | (3.6982) | (0.2931) | (0.1868) | |
| Cons. land | −0.3172 *** | 3.5124 | −3.7170 ** | −1.2399 *** | 0.4476 | −12.0038 | 0.4398 | −9.4389 ** |
| (0.0807) | (3.2614) | (1.2980) | (0.2489) | (0.6401) | (19.0514) | (1.3714) | (2.7280) | |
| Unused land | −0.2460 | 43.1133 | −0.8522 | 12.5788 ** | −0.9187 | −1.2×102 *** | 1.2979 | 2.8277 |
| (0.2187) | (29.8244) | (9.7041) | (4.2944) | (1.1391) | (31.6184) | (1.3535) | (3.4913) | |
| Urb | −0.0014 *** | −0.3188 *** | −0.0743 ** | −0.3145 *** | −0.0410 * | 0.2560 | 0.0451 * | −0.2010 * |
| (0.002) | (0.0508) | (0.0256) | (0.0351) | (0.0170) | (0.2254) | (0.0167) | (0.0829) | |
| GDP | −0.0062 ** | 0.0529 | 0.0688 ** | −0.1833 *** | −0.0002 *** | 0.7791 ** | −0.0165 | −0.7591 *** |
| (0.0023) | (0.0475) | (0.0254) | (0.0509) | (0.0000) | (0.2223) | (0.0096) | (0.1596) | |
| Road | 0.0022 | 0.1411 ** | 0.0362 *** | −0.0711 ** | −0.0432 ** | 0.0230 | 0.0157 *** | −0.2822 ** |
| (0.0011) | (0.0452) | (0.0023) | (0.0245) | (0.0130) | (0.2494) | (0.0014) | (0.0961) | |
| Ind2 | 0.0006 | 0.0223 | 0.0203 | −0.0920 *** | −0.0011 *** | −0.3728 | 0.0142 *** | −0.1635 ** |
| (0.0007) | (0.0289) | (0.0037) | (0.0244) | (0.0002) | (0.1915) | (0.0003) | (0.0582) | |
| Ind3 | 0.0021 | 0.0040 | 0.0381 | 0.0184 | 0.0091 | −0.1414 | −0.0019 | 0.0427 |
| (0.0018) | (0.0330) | (0.0208) | (0.0283) | (0.0089) | (0.1373) | (0.0056) | (0.0525) | |
| Rain | 0.0002 * | −0.0057 *** | −0.0006 | 0.0516 *** | 0.0004 *** | −0.0106 | 0.0002 | 0.0535 *** |
| (0.0001) | (0.0013) | (0.0006) | (0.0016) | (0.0000) | (0.0081) | (0.0005) | (0.0026) | |
| Temp | 0.0023 | 0.0932 * | −0.0915 ** | 0.1021 ** | −0.0025 | 0.3103 | −0.0025 | 0.3466 *** |
| (0.0024) | (0.0437) | (0.0293) | (0.0370) | (0.0159) | (0.3383) | (0.0164) | (0.0588) | |
| Cons. Land 2 | 4.2019 * | −10.8676 | ||||||
| (1.6467) | (18.6808) | |||||||
| Cons | 0.0022 | −6.2862 *** | −1.6699 *** | −4.6560 *** | 0.5016 | −2.1101 | −0.7591 *** | −3.6287 *** |
| (0.0376) | (0.8303) | (0.4143) | (0.5841) | (0.2583) | (3.0427) | (0.1321) | (0.7303) | |
| adj. R-sq | 0.311 | 0.911 | 0.105 | 0.893 | 0.643 | 0.676 | 0.249 | 0.871 |
| Fixed year | YES | |||||||
| Fixed unit | YES | |||||||
| N | 590 | 190 | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Xu, Z.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Z. Spatiotemporal Evolution and Factors Influencing Regional Ecological Land in a Multidimensional Perspective: A Case Study of the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Region. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1714. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16101714
Wang X, Xu Z, Huang J, Zhang Z. Spatiotemporal Evolution and Factors Influencing Regional Ecological Land in a Multidimensional Perspective: A Case Study of the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Region. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(10):1714. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16101714
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xingbang, Ze Xu, Jing Huang, and Zhengfeng Zhang. 2024. "Spatiotemporal Evolution and Factors Influencing Regional Ecological Land in a Multidimensional Perspective: A Case Study of the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Region" Remote Sensing 16, no. 10: 1714. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16101714
APA StyleWang, X., Xu, Z., Huang, J., & Zhang, Z. (2024). Spatiotemporal Evolution and Factors Influencing Regional Ecological Land in a Multidimensional Perspective: A Case Study of the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Region. Remote Sensing, 16(10), 1714. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16101714








