A Bayesian Framework to Quantify Uncertainty in Aerosol Optical Model Selection Applied to TROPOMI Measurements
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. TROPOMI/S5P Observations
2.2. AERONET
2.3. Aerosol Model Properties and Creation of the Look-Up Tables
2.3.1. Aerosol Types
2.3.2. Radiative Transfer Simulation for FORWARD Model
2.4. Methodology Description
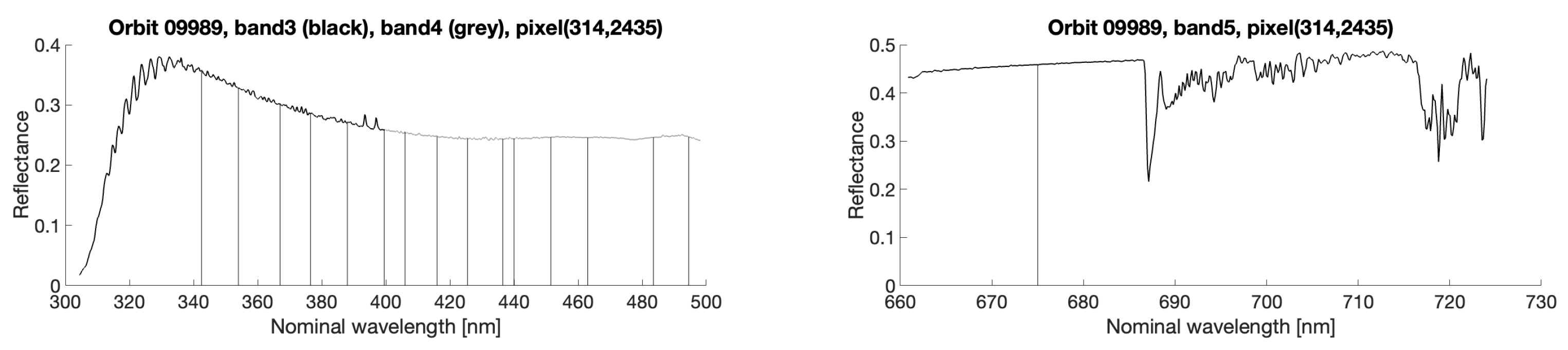
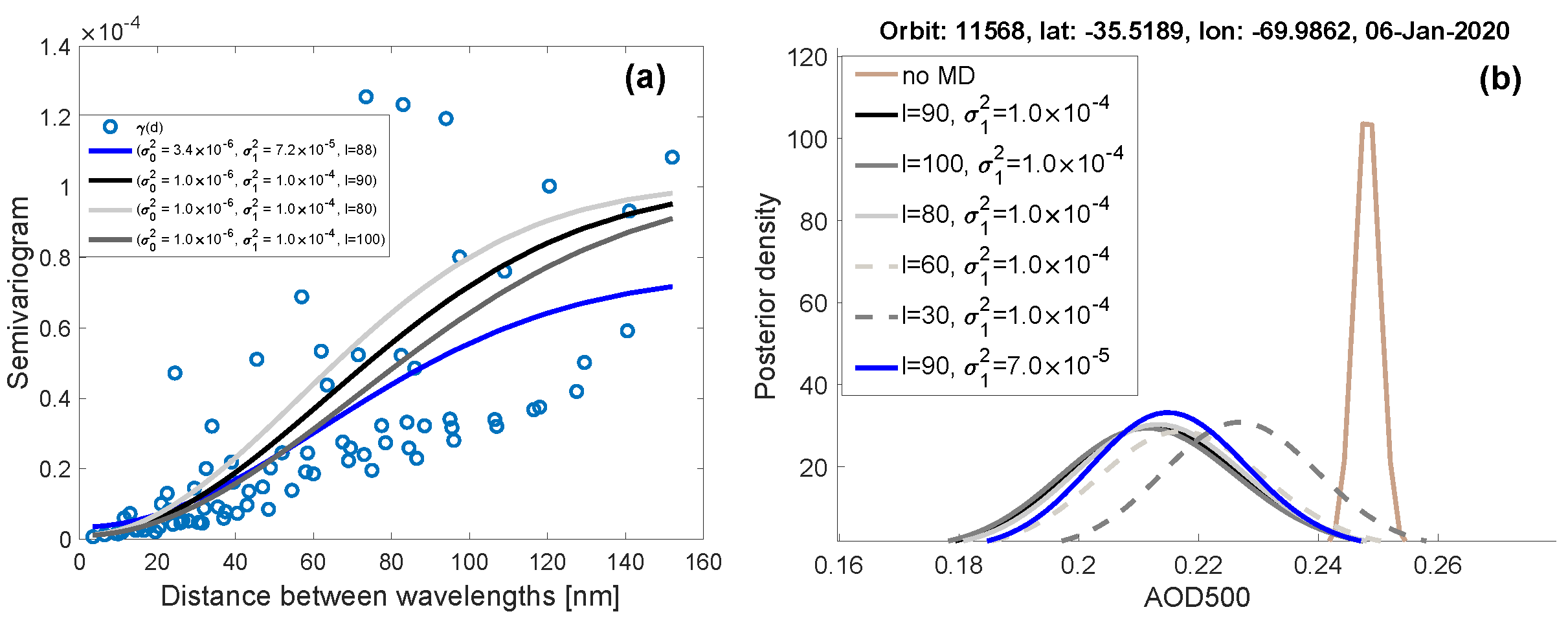
2.5. Model Discrepancy Estimation
2.6. Bayesian Approach for Retrieving AOD
2.7. Aerosol Model Selection
2.8. Bayesian Model Averaging
2.9. Goodness of Fit
3. Results
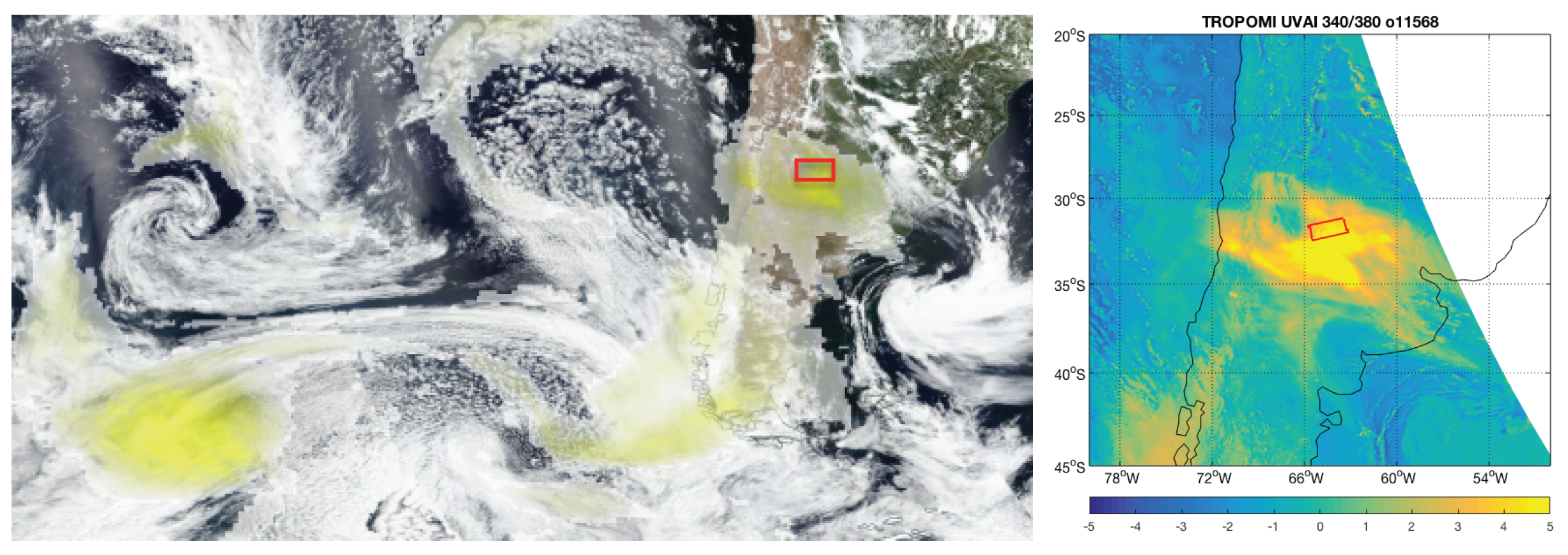
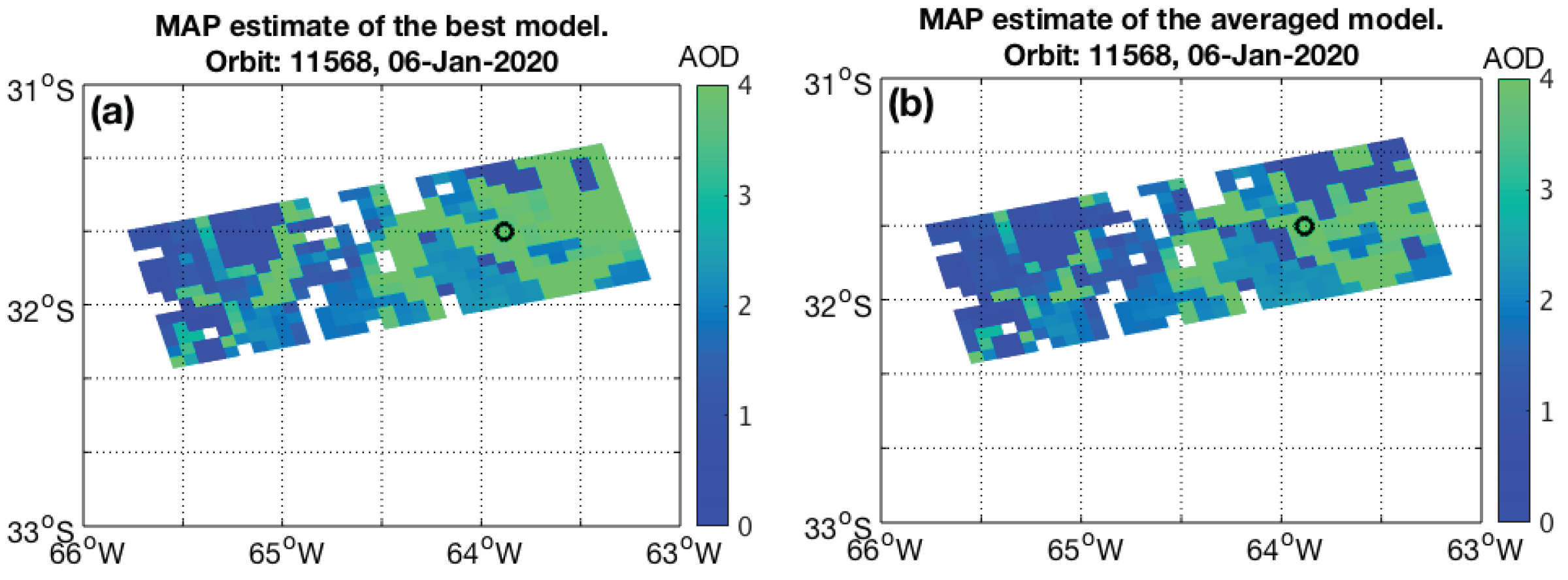
3.1. Case South America: Transported Smoke from Australian Bush Fires in January 2020
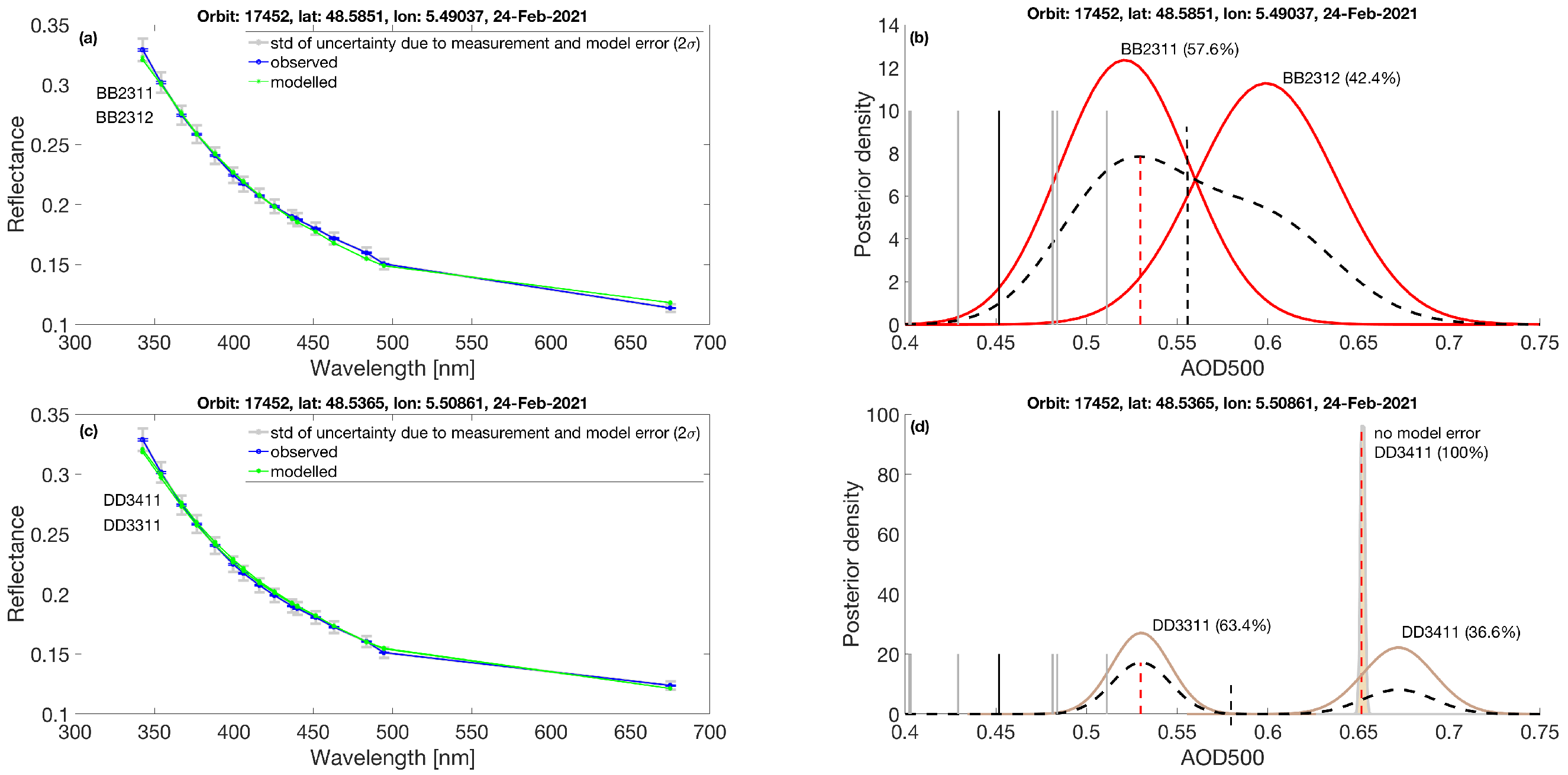
3.2. Desert Dust Cases
4. Discussion
- Testing the retrieval method with aerosol optical models with different aerosol microphysical, optical and shape characteristics;
- Experimenting with how the method can detect and classify different aerosol situations and atmospheric ageing (such as aerosols near the source or transported aerosols);
- Studying the effect of different surface reflection assumptions on model selection and the resulting AOD.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Description of Aerosol Properties and LUTs
| Type | Model ID | References |
|---|---|---|
| WA | 1111, 1112, 1113 | [17,35,36] |
| WA | 1211, 1212, 1213 | [17,35,36] |
| WA | 1311, 1312, 1313 | [17,35,36] |
| BB | 21 × 1, 21 × 2, 21 × 3 | [17,35,36] |
| BB | 22 × 1, 22 × 2, 22 × 3 | [17,35,36] |
| BB | 23 × 1, 23 × 2, 23 × 3 | [17,35,36] |
| DD | 31 × 1, 31 × 2 | [17,35,36] |
| DD | 32 × 2, 32 × 2 | [17,35,36] |
| DD | 33 × 1, 33 × 2 | [37] (particle shape: spherical) |
| DD | 34 × 1, 34 × 2 | [37] (particle shape: prolate spheroid) |
| DD | 35 × 1, 35 × 2 | [38,39] |

References
- Povey, A.C.; Grainger, R.G. Known and unknown unknowns: Uncertainty estimation in satellite remote sensing. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 8, 4699–4718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayer, A.M.; Govaerts, Y.; Kolmonen, P.; Lipponen, A.; Luffarelli, M.; Mielonen, T.; Patadia, F.; Popp, T.; Povey, A.C.; Stebel, K.; et al. A review and framework for the evaluation of pixel-level uncertainty estimates in satellite aerosol remote sensing. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 373–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipponen, A.; Kolehmainen, V.; Kolmonen, P.; Kukkurainen, A.; Mielonen, T.; Sabater, N.; Sogacheva, L.; Virtanen, T.H.; Arola, A. Model-enforced post-process correction of satellite aerosol retrievals. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2021, 14, 2981–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veefkind, J.P.; Aben, I.; McMullan, K.; Förster, H.; de Vries, J.; Otter, G.; Claas, J.; Eskes, H.J.; de Haan, J.F.; Kleipool, Q.; et al. TROPOMI on the ESA Sentinel-5 Precursor: A GMES mission for global observations of the atmospheric composition for climate, air quality and ozone layer applications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein Zweers, D.C. TROPOMI ATBD of the UV Aerosol Index; S5P-KNMI-L2-0008-RP; Royal Netherlands Meteorological Institute: De Bilt, The Netherlands, 2018; Issue 1.1; p. 30. [Google Scholar]
- Kooreman, M.L.; Stammes, P.; Trees, V.; Sneep, M.; Tilstra, L.G.; de Graaf, M.; Stein Zweers, D.C.; Wang, P.; Tuinder, O.N.E.; Veefkind, J.P. Effects of clouds on the UV Absorbing Aerosol Index from TROPOMI. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 6407–6426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Veefkind, P.; Nanda, S.; van Velthoven, P.; Levelt, P. The role of aerosol layer height in quantifying aerosol absorption from ultraviolet satellite observations. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 6319–6340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, O.; Jethva, H.; Ahn, C.; Jaross, G.; Loyola, D.G. TROPOMI aerosol products: Evaluation and observations of synoptic-scale carbonaceous aerosol plumes during 2018–2020. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 6789–6806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, L.; Xu, J.; Efremenko, D.S.; Loyola, D.G.; Doicu, A. Optimization of Aerosol Model Selection for TROPOMI/S5P. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Määttä, A.; Laine, M.; Tamminen, J.; Veefkind, J.P. Quantification of uncertainty in aerosol optical thickness retrieval arising from aerosol microphysical model and other sources, applied to Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI) measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 1185–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, B.; Kylling, A. Technical note: The libRadtran software package for radiative transfer calculations—Description and examples of use. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2005, 5, 1855–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emde, C.; Buras-Schnell, R.; Kylling, A.; Mayer, B.; Gasteiger, J.; Hamann, U.; Kylling, J.; Richter, B.; Pause, C.; Dowling, T.; et al. The libRadtran software package for radiative transfer calculations (version 2.0.1). Geosci. Model Dev. 2016, 9, 1647–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKay, D.J.C. Bayesian interpolation. Neural Comput. 1992, 4, 415–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiegelhalter, D.J.; Best, N.G.; Carlin, B.P.; van der Linde, A. Bayesian measures of model complexity and fit. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 2002, 64, 583–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, M.C.; O’Hagan, A. Bayesian Calibration of Computer Models. J. R. Stat. Soc. B 2001, 63, 425–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brynjarsdóttir, J.; O’Hagan, A. Learning about physical parameters: The importance of model discrepancy. Inverse Probl. 2014, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veihelmann, B.; Levelt, P.F.; Stammes, P.; Veefkind, J.P. Simulation study of the aerosol information content in OMI spectral reflectance measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 3115–3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leloux, J.; Rozemeijer, N.; van Swol, R.; Vonk, F. Input/Output Data Specification for the TROPOMI L01b Data Processor; S5P-KNMI-L01B-0012-SD, CI-6510-IODS; Royal Netherlands Meteorological Institute: De Bilt, The Netherlands, 2022; Issue 11.0.0; p. 116. [Google Scholar]
- Apituley, A.; Pedergnana, M.; Sneep, M.; Veefkind, J.P.; Loyola, D.; Stein Zweers, D. Sentinel-5 Precursor/TROPOMI Level 2 Product User Manual UV Aerosol Index; S5P-KNMI-L2-0026-MA, CI-7570-PUM; Royal Netherlands Meteorological Institute: De Bilt, The Netherlands, 2018; Issue 1.0.0; p. 116. [Google Scholar]
- Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I.; Tanré, D.; Buis, J.P.; Setzer, A.; Vermote, E.; Reagan, J.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Nakajima, T.; et al. AERONET—A federated instrument network and data archive for aerosol characterization. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 66, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, D.M.; Sinyuk, A.; Sorokin, M.G.; Schafer, J.S.; Smirnov, A.; Slutsker, I.; Eck, T.F.; Holben, B.N.; Lewis, J.R.; Campbell, J.R.; et al. Advancements in the Aerosol Robotic Network (AERONET) Version 3 database – automated near-real-time quality control algorithm with improved cloud screening for Sun photometer aerosol optical depth (AOD) measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 169–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.K.; Tesche, M.; Noh, Y.; Müller, D. Aerosol-type classification based on AERONET version 3 inversion products. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 3789–3803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovik, O.; King, M.D. A flexible inversion algorithm for retrieval of aerosol optical properties from sun and sky radiance measurements. J. Geophys. Res. 2000, 105, 20673–20696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasteiger, J.; Wiegner, M. MOPSMAP v1.0: A versatile tool for the modeling of aerosol optical properties. Geosci. Model Dev. 2018, 11, 2739–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelman, A.; Carlin, J.B.; Stern, H.S.; Dunson, D.B.; Vehtari, A.; Rubin, D.B. Bayesian Data Analysis, 3rd ed.; Chapman & Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Chandrasekhar, S. Radiative Transfer; Dover Publ.: New York, NY, USA, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen, C.E.; Williams, C.K.I. Gaussian Processes for Machine Learning; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee, S.; Carlin, B.P.; Gelfand, A.E. Hierarchical Modeling and Analysis for Spatial Data; Chapman and Hall/CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- O’Neill, N.T.; Ignatov, A.; Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F. The lognormal distribution as a reference for reporting aerosol optical depth statistics; Empirical tests using multi-year, multi-site AERONET sunphotometer data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2000, 27, 3333–3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeting, J.A.; Madigan, D.; Raftery, A.E.; Volinsky, C.T. Bayesian Model averaging: A Tutorial. Statist. Sci. 1999, 14, 382–417. [Google Scholar]
- Jethva, H.; Torres, O. Satellite-based evidence of wavelength-dependent aerosol absorption in biomass burning smoke inferred from Ozone Monitoring Instrument. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 10541–10551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, R.; Toledano, C.; Román, R.; Mateos, D.; Asmi, E.; Rodríguez, E.; Lau, I.C.; Ferrara, J.; D’elia, R.; Antuña-Sánchez, J.C.; et al. Characterization of Stratospheric Smoke Particles over the Antarctica by Remote Sensing Instruments. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovik, O.; Sinyuk, A.; Lapyonok, T.; Holben, B.N.; Mishchenko, M.; Yang, P.; Eck, T.F.; Volten, H.; Munõz, O.; Veihelmann, B.; et al. Application of spheroid models to account for aerosol particle nonsphericity in remote sensing of desert dust. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, D11208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merikallio, S.; Lindqvist, H.; Nousiainen, T.; Kahnert, M. Modelling light scattering by mineral dust using spheroids: Assessment of applicability. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 5347–5363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, O.; Tanskanen, A.; Veihelmann, B.; Ahn, A.; Braak, R.; Bhartia, P.K.; Veefkind, P.; Levelt, P. Aerosols and Surface UV Products from Ozone Monitoring Instrument Observations: An Overview. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, D24S47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curier, R.L.; Veefkind, J.P.; Braak, R.; Veihelmann, B.; Torres, O.; de Leeuw, G. Retrieval of aerosol optical properties from OMI radiances using a multiwavelength algorithm: Application to western Europe. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, D17S90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, R.; Ajtai, T.; Kandler, K.; Lieke, K.; Linke, C.; Müller, T.; Schnaiter, M.; Vragel, M. Complex refractive indices of Saharan dust samples at visible and near UV wavelengths: A laboratory study. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 2491–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; O’Donnell, D.; Kazil, J.; Stier, P.; Kinne, S.; Lohmann, U.; Ferrachat, S.; Croft, B.; Quaas, J.; Wan, H.; et al. The global aerosol-climate model ECHAM-HAM, version 2: Sensitivity to improvements in process representations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 8911–8949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Räisänen, P.; Haapanala, P.; Chung, C.E.; Kahnert, M.; Makkonen, R.; Tonttila, J.; Nousiainen, T. Impact of dust particle non-sphericity on climate simulations. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 139, 2222–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindqvist, H.; Jokinen, O.; Kandler, K.; Scheuvens, D.; Nousiainen, T. Single scattering by realistic, inhomogeneous mineral dust particles with stereogrammetric shapes. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
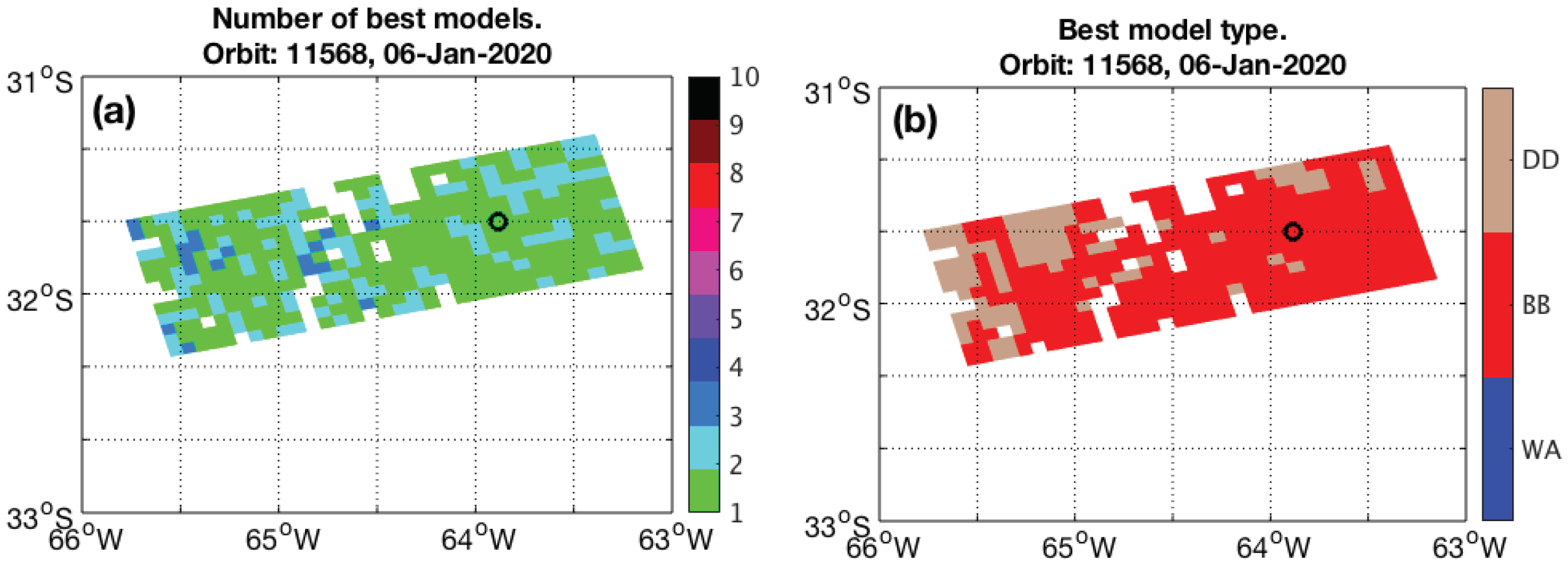
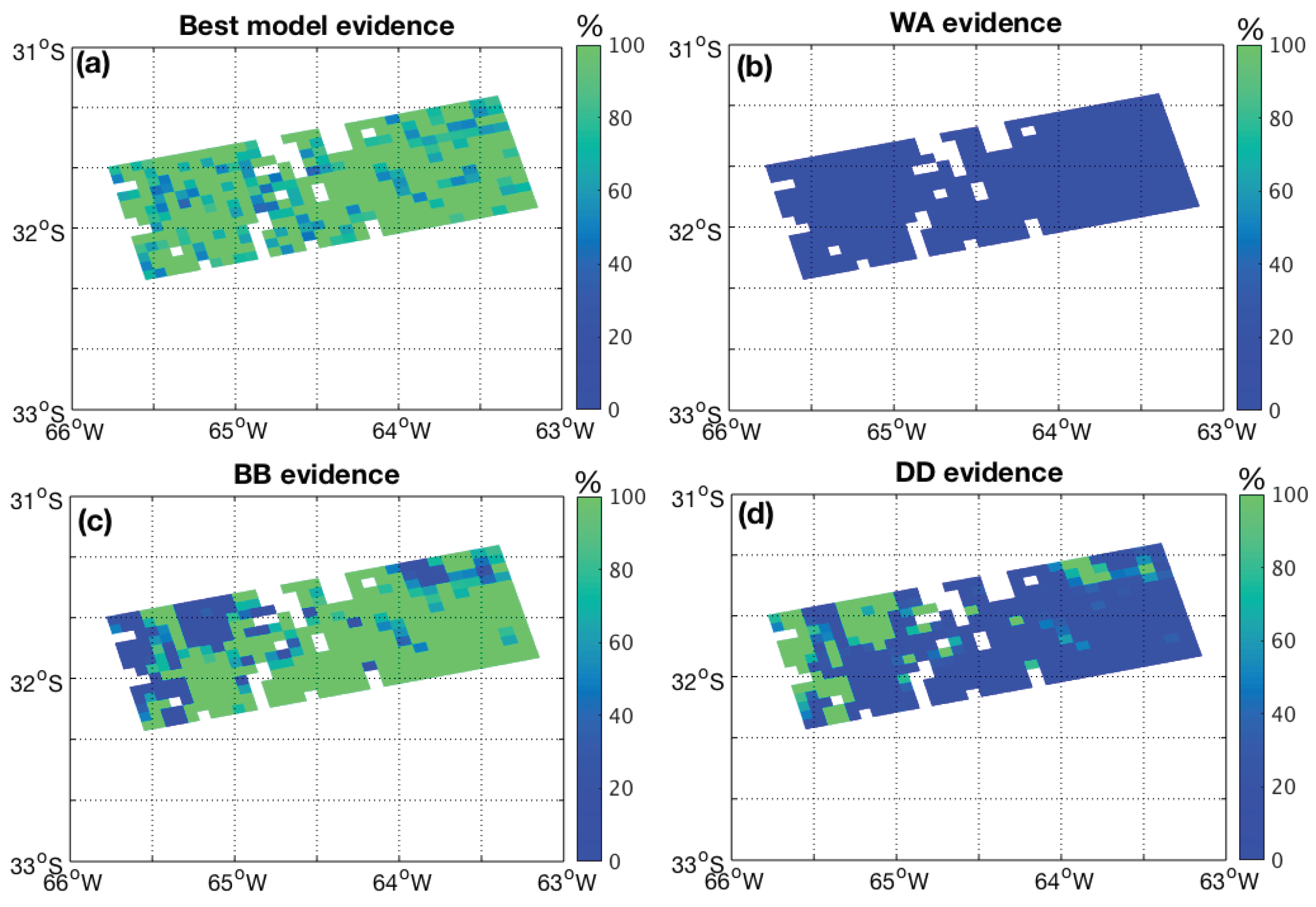
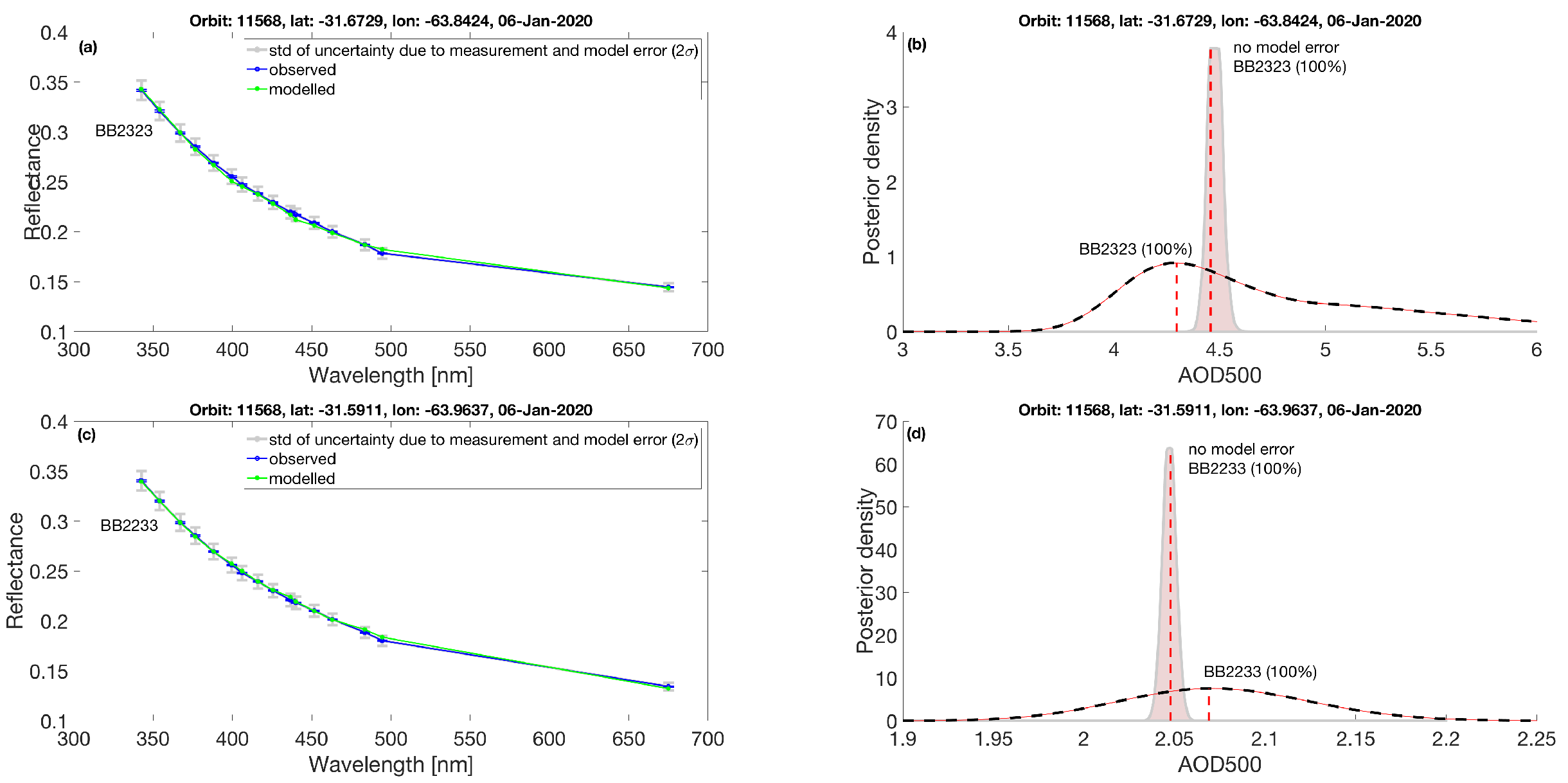

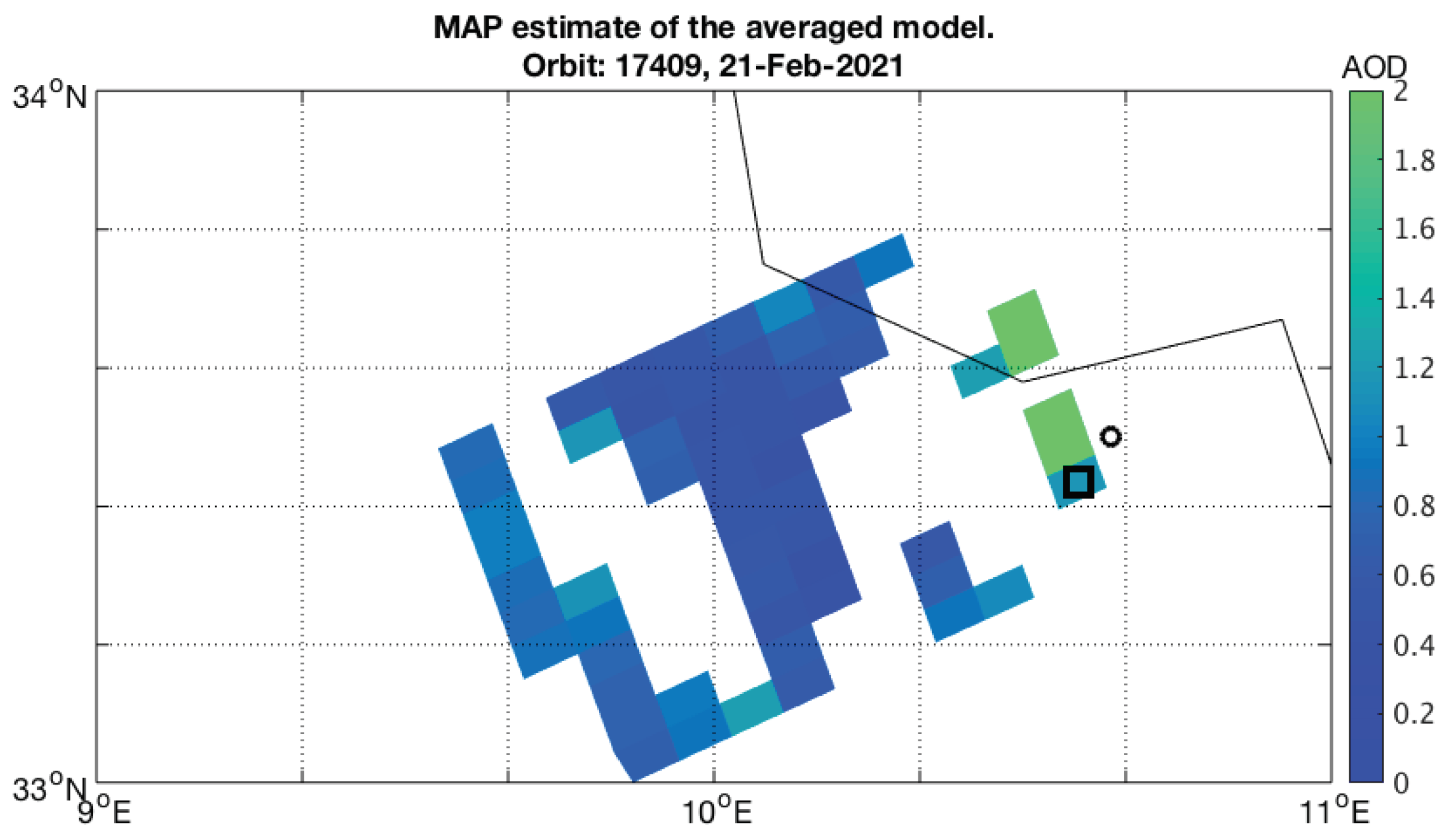

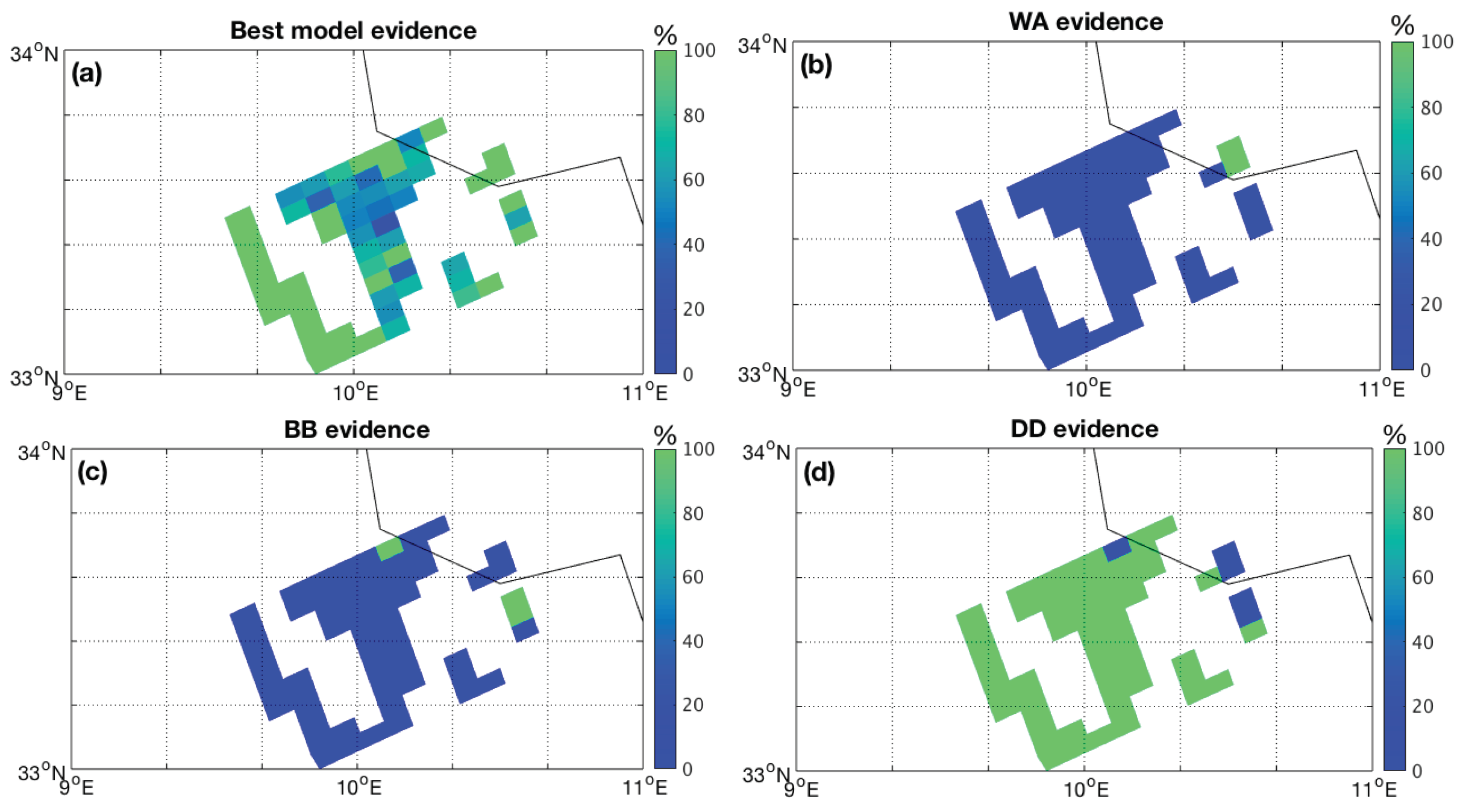
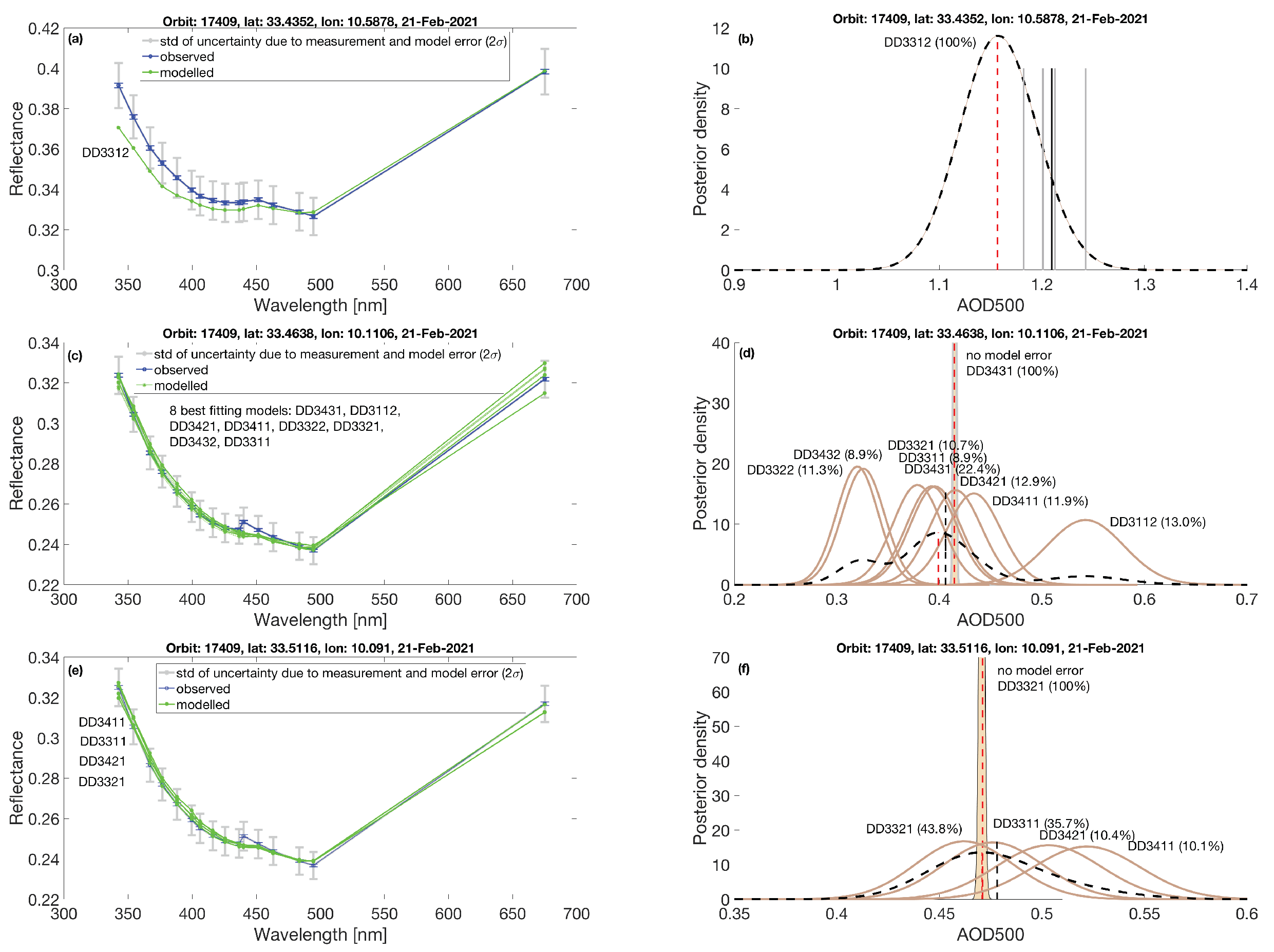
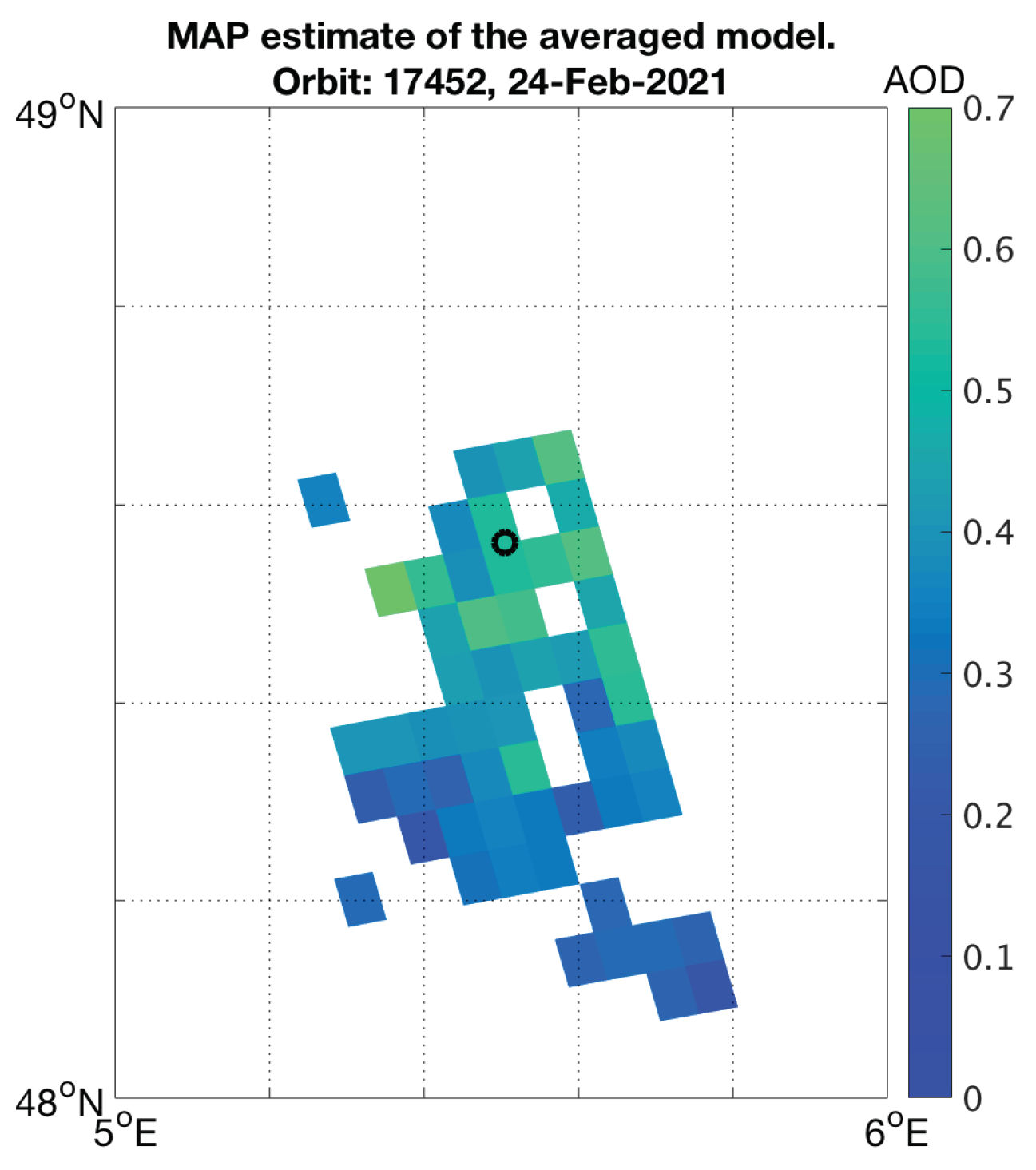
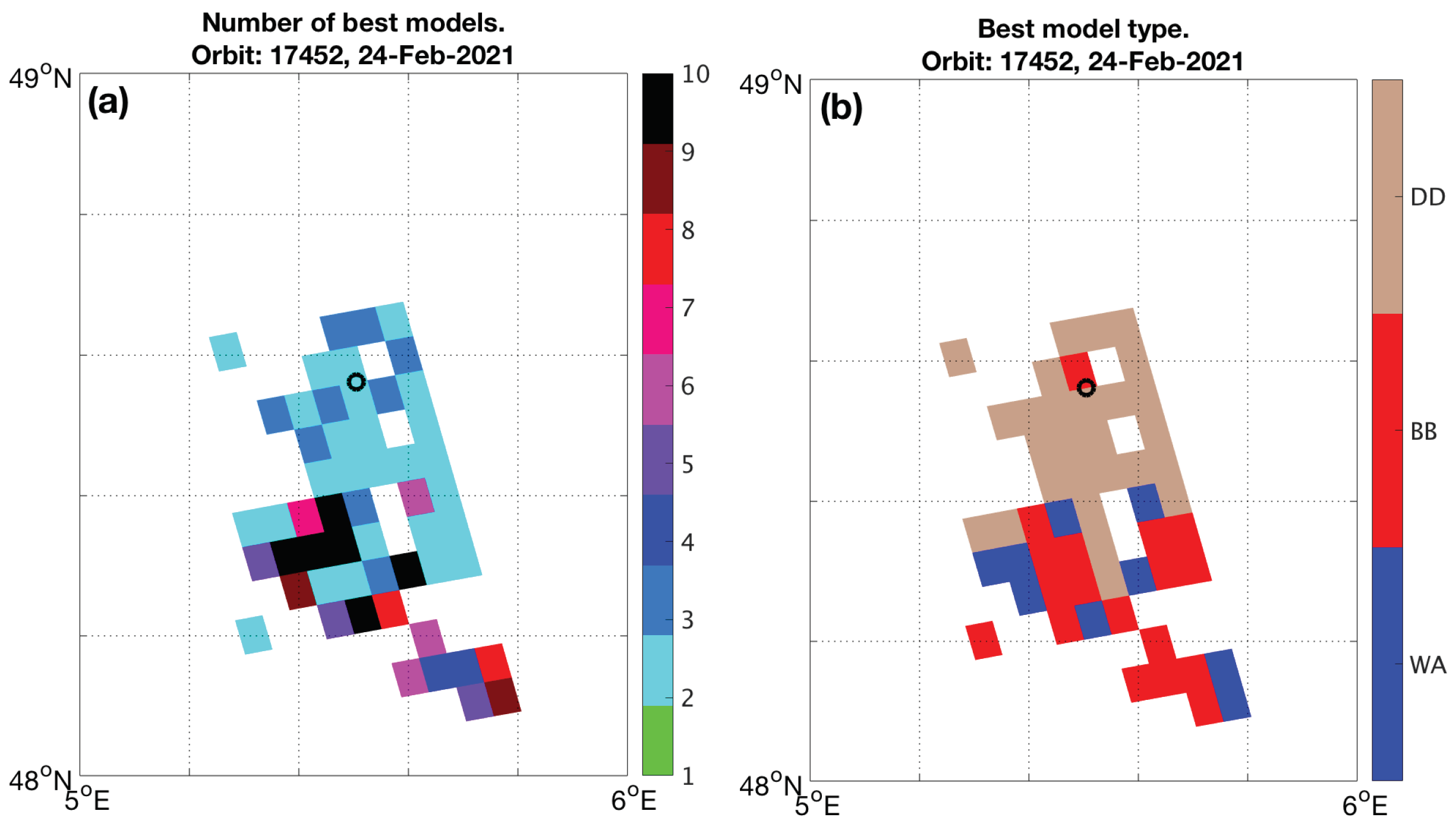
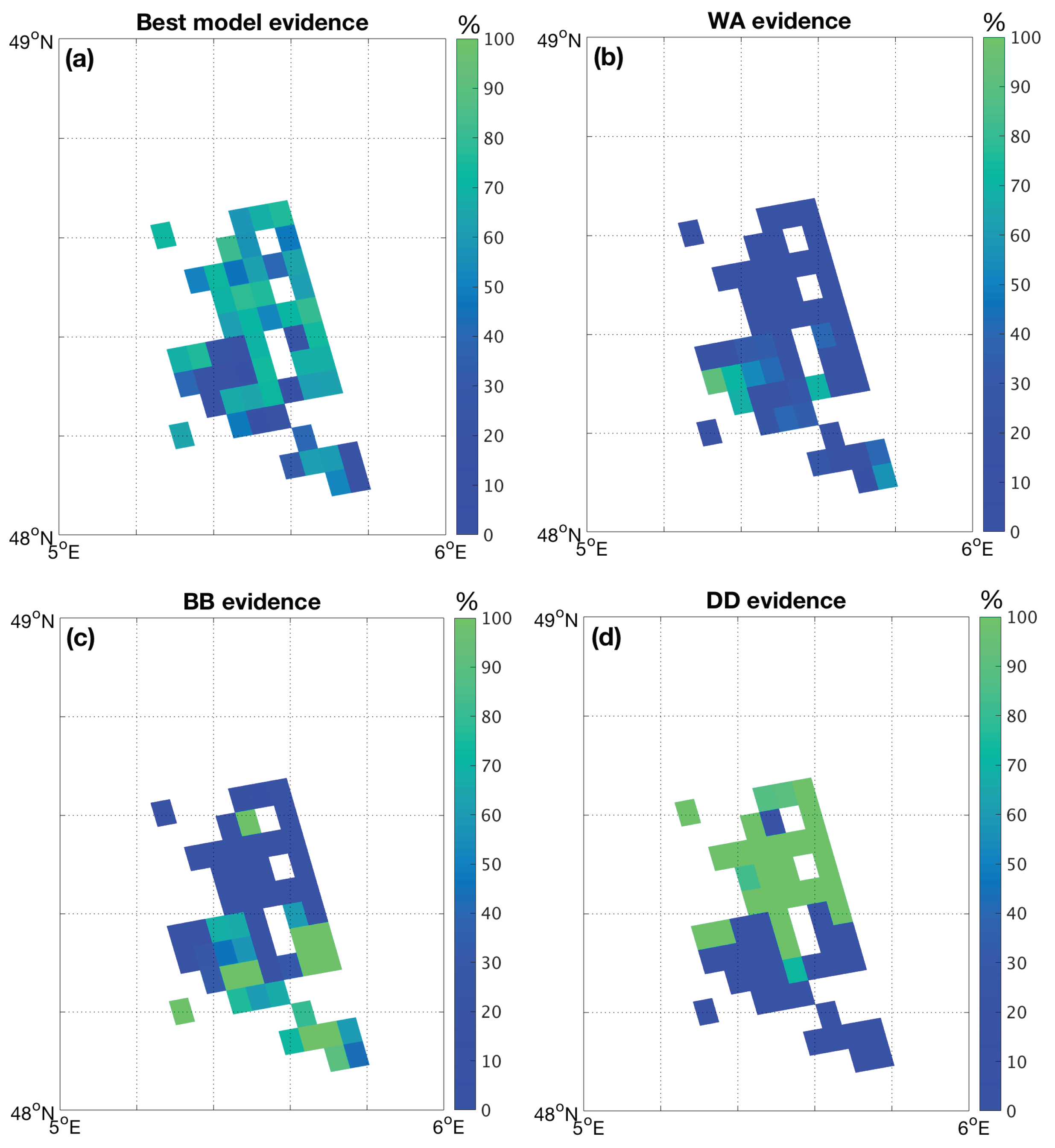

| Date | Site Name | (Lat, Lon) | AOD (500) | Orbit | Pixel Index | AOD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AERONET | AERONET | AERONET | S5P | S5P | S5P | |
| 6 January 2020 | Pilar_Cordoba | (31.7° S, 63.9° W) | 0.719 | 11,568 | (394,1834) | 4.29 |
| 21 February 2021 | Medenine_IRA | (33.5° N, 10.6° E) | 1.209 1 | 17,409 | (60,2977) 2 | 1.16 |
| 24 February 2021 | Bure_OPE | (48.6° N, 5.5° E) | 0.452 | 17,452 | (274,3205) | 0.53 |
| (274,3204) | 0.53 |
| Variable Name | Symbol | Dimensions | Dependencies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Atmospheric path reflectance | (19, 9, 8, 8, 19, 2) | () | |
| Spherical albedo | s | (19, 9, 2) | () |
| Transmittance | T | (19, 9, 8, 8, 2) | () |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kauppi, A.; Kukkurainen, A.; Lipponen, A.; Laine, M.; Arola, A.; Lindqvist, H.; Tamminen, J. A Bayesian Framework to Quantify Uncertainty in Aerosol Optical Model Selection Applied to TROPOMI Measurements. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1945. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16111945
Kauppi A, Kukkurainen A, Lipponen A, Laine M, Arola A, Lindqvist H, Tamminen J. A Bayesian Framework to Quantify Uncertainty in Aerosol Optical Model Selection Applied to TROPOMI Measurements. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(11):1945. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16111945
Chicago/Turabian StyleKauppi, Anu, Antti Kukkurainen, Antti Lipponen, Marko Laine, Antti Arola, Hannakaisa Lindqvist, and Johanna Tamminen. 2024. "A Bayesian Framework to Quantify Uncertainty in Aerosol Optical Model Selection Applied to TROPOMI Measurements" Remote Sensing 16, no. 11: 1945. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16111945
APA StyleKauppi, A., Kukkurainen, A., Lipponen, A., Laine, M., Arola, A., Lindqvist, H., & Tamminen, J. (2024). A Bayesian Framework to Quantify Uncertainty in Aerosol Optical Model Selection Applied to TROPOMI Measurements. Remote Sensing, 16(11), 1945. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16111945





