Abstract
This paper investigates ionospheric response characteristics from multiple perspectives based on globally distributed GNSS data and products, ionosonde data, FORMOSAT-7/COSMIC-2 occultation data, and Swarm satellite observations caused by the total solar eclipse of 8 April 2024 across North and Central America. The results show that both GNSS-derived TEC products have detected the ionospheric TEC degradation triggered by the total solar eclipse, with the maximum degradation exceeding 10 TECU. The TEC data from nine GNSS stations in the path of the maximum eclipse reveal that the intensity of ionospheric TEC degradation is related to the spatial location, with the maximum degradation value of the ionospheric TEC being about 14~23 min behind the moment of the maximum eclipse. Additionally, a negative anomaly of foF2 with a maximum of more than 2.7 MHz is detected by ionosonde. In the eclipse region, NmF2 and hmF2 show trends of decrease and increase, with percentages of variation of 40~70% and 4~16%, respectively. The Ne profile of the Swarm-A satellite is significantly lower than the reference value during the eclipse period, with the maximum negative anomaly value reaching 11.2 × 105 el/cm3, and it failed to show the equatorial ionization anomaly.
1. Introduction
A solar eclipse is a phenomenon that occurs when the Moon moves between the Earth and the Sun, completely or partially blocking the Sun. This astronomical event can only occur during a new moon, and an eclipse is visible to observers when the Moon’s shadow falls on the Earth. Due to the tilt of the Moon’s orbit relative to the Earth’s orbit, solar eclipses do not occur during every new moon. In fact, solar eclipses are relatively rare at any given location, with an average of only one eclipse observed at the same location every 1.5 years. Each particular eclipse event serves as a unique natural experiment, providing a valuable opportunity to explore the atmospheric effects in Earth’s space during eclipses.
It is well known that solar radiation is the primary factor affecting the Earth’s space atmosphere, especially for the ionosphere, which contains a large number of free electrons and ions. Consequently, the ionosphere also exhibits a variety of different cycle characteristics such as diurnal variations, quasi-27-day variations, semiannual variations, annual variations, and 11-year cycle variations under the modulation of the solar activity cycle [1]. Solar eclipse events, which are similar to diurnal variations (rapid sunset and sunrise phenomena), provide an excellent opportunity to study ionospheric response mechanisms and complex dynamical processes. During solar eclipses, the obscuration caused by the Moon’s shadow leads to a rapid decrease in solar radiation, thereby weakening the photo-chemical and thermodynamic reactions in the ionosphere and reducing the electron density [2].
In recent decades, significant progress has been made in the study of the eclipse–ionosphere effect. In terms of data sources, observations and simulations are carried out in parallel. Since information about solar eclipse events can be obtained in advance, there is ample time to simulate them numerically. For example, simulated prediction of eclipse–ionosphere effects was carried out for the 11 August 1999 solar eclipse event [3,4,5]. Huba and Drob [6] quantitatively predicted the impacts of the 21 August 2017 solar eclipse on the ionosphere and plasma layer based on the SAMI3 model (SAMI3 is also a model of the ionosphere). The simulation results of TIEGCM (thermosphere ionosphere electrodynamics general circulation model) showed that the solar eclipse event triggered large-scale traveling atmospheric disturbances [7]. Martínez-Ledesma et al. [8] and Bravo et al. [9] evaluated the ionospheric response to the 14 December 2020 total solar eclipse using the SUPIM (the Sheffield University plasmasphere ionosphere model) predictions.
Unlike numerical simulations, direct observations using various instruments can visualize the ionospheric response to the eclipse, such as by observing the Faraday rotation measurement of the polarization of lunar radio waves [10], ionosonde measurements for vertical sounding [11,12,13,14,15,16,17], very low frequency (VLF) signal measurements [18,19,20,21,22,23], Doppler measurements [24,25], in situ measurements with rockets and satellites [26,27,28], incoherent scattering radar measurements [29,30,31,32], and ionosphere total electron content (TEC) from GNSS inversions [33,34,35,36,37,38]. Based on the above direct measurements, data assimilation and ionospheric tomography have also become significant technical approaches [32,39,40,41,42,43].
The variations in the ionosphere caused by solar eclipses mainly include a decrease in electron density, a change in the rate of chemical reactions, decreases in the temperatures of electrons and ions, a disturbance in ionosphere–plasma coupling, the emergence of dynamical processes, the generation of ionospheric perturbations and other effects [38]. In terms of mechanism exploration, the physical effects of the ionosphere caused by the solar eclipse are very complex, and all the above changes show diverse variations at different altitudes and latitudes and longitudes. For example, photo-chemical processes below the F2 layer and transport processes above the F2 layer produce different variations in ionospheric electron density during an eclipse [41]. In Chen et al. [13], the downward plasma flux has been adopted to explain the night-time ionospheric density variations triggered by the solar eclipse event across Asia on 15 January 2010. Chen et al. [44] showed that wind perturbations of tidal winds and a decrease in photo-chemical processes during the solar eclipse of 21 August 2017 resulted in a decrease in fbEs, and the enhanced electron density gradient in the E layer may be attributed to the gravity wave rupture in the mesosphere/hypotherm. Zhang et al. [45] proposed the eclipse-induced plasma pressure gradient reduction mechanism to explain the phenomenon of TEC changes in the conjugate hemisphere during a solar eclipse.
In addition to the exploration of physical mechanisms, practical applications related to the impact of the eclipse–ionosphere effect should also be in focus. For example, ionospheric correction information is applied to GNSS navigation and positioning, and sudden ionospheric variations during solar eclipses may lead to the degradation of navigation and positioning performance for GNSS single-frequency users [22,23]. However, the ionospheric response due to each eclipse event varies dramatically. Therefore, investigating the eclipse–ionosphere effect remains an urgent geophysical task. Observations of each new eclipse provide new understanding of eclipse-induced ionospheric changes and their intrinsic mechanisms, while being able to provide new information on ionospheric corrections for GNSS navigation and positioning applications under the influence of the eclipse–ionosphere effect.
The scope of the total solar eclipse event on 8 April 2024 across North and Central America and the eclipse path through both low latitudes and mid-latitudes provide new opportunities to investigate eclipse–ionosphere effects in different regions. Therefore, this paper comprehensively analyzes the characteristics of ionospheric variations during the eclipse based on globally distributed GNSS data and products, ionosonde data, FORMOSAT-7/COSMIC-2 occultation data, and Swarm satellite observation data, and it gives preliminary observation results for the eclipse–ionosphere effect.
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Data Sources
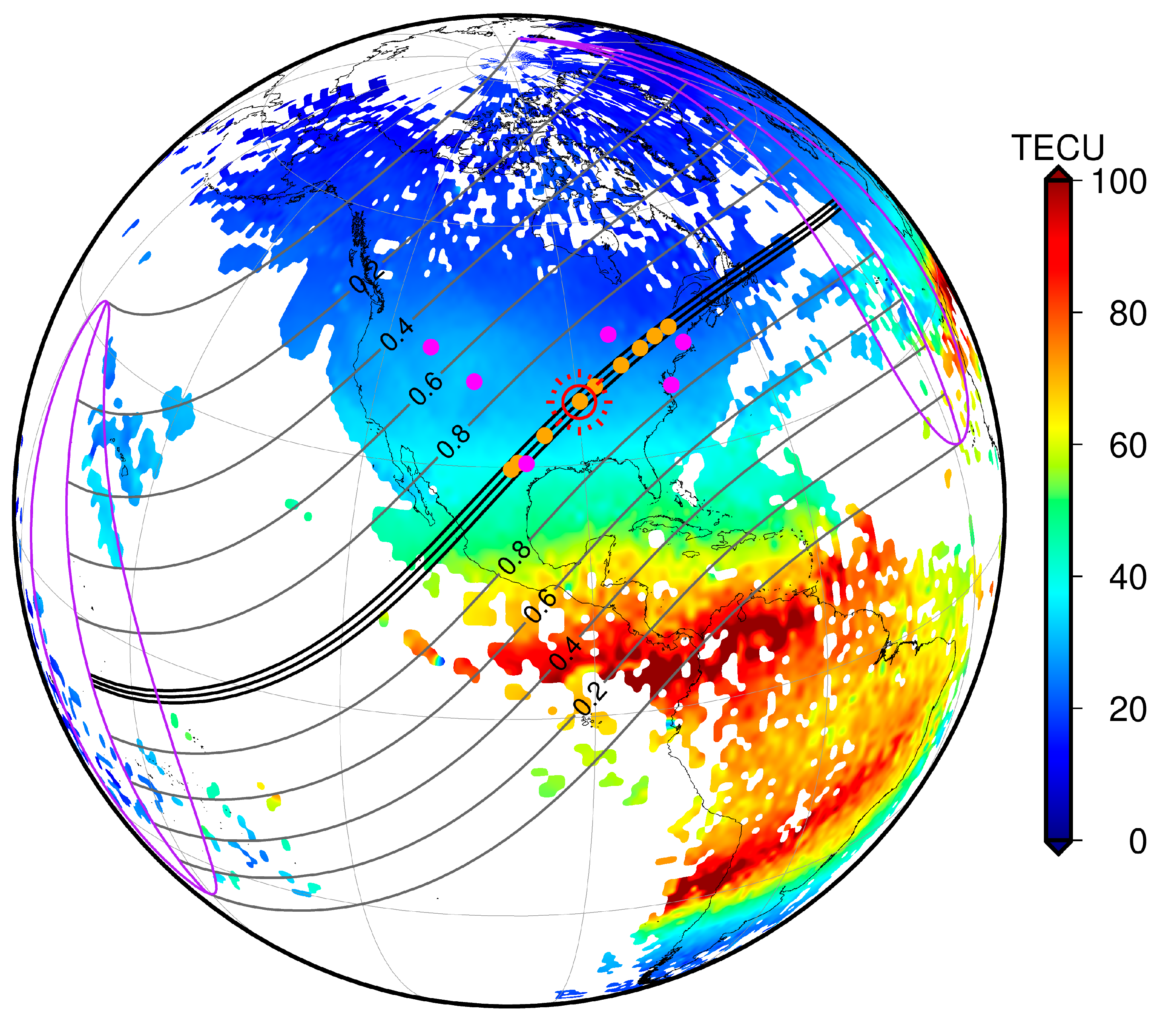
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) Haystack Observatory automatically processes raw observational data from about 6000 GNSS receivers around the world every day and generates a global ionospheric TEC product with a spatial resolution of 1° × 1° (geographic latitude × geographic longitude) every 5 min [46], and the product data are stored in the Madrigal database. Figure 1 shows the MIT TEC distribution for 8 April 2024 at 19:00 UT, and the orange dots represent the nine GNSS stations selected for this paper that are located in the path of the maximum eclipse. In addition to the MIT TEC product, the Center for Orbit Determination in Europe’s (CODE) global ionospheric map (GIM) product was used to study large-scale ionospheric variations during solar eclipses. Since the establishment of the ionospheric working group at IGS in 1998, GIM has provided strong data support for global ionospheric research and applications. Among them, the GIM product provided by the CODE of the University of Bern is of high accuracy and is widely used. The product is calculated from a spherical harmonic function of 15 orders, with a spatial resolution of 2.5° × 5° (geographic latitude × geographic longitude).
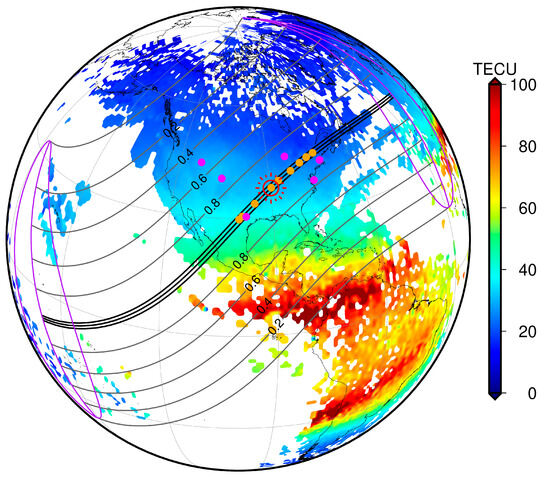
Figure 1.
Distribution of ionospheric TEC at 19:00 UT on 8 April 2024 and the eclipse region; orange dots indicate the nine selected GNSS stations, and magenta dots indicate the locations of ionosondes. The black line region of represents the path of the maximum magnitude of the eclipse, and the gray lines mark the region where the partial eclipse is experienced, with the magnitude of partiality.
As the most widely used instrument for ground-based detection of the ionosphere, the ionosonde measured the correspondence between the acquired frequency and the elevation of the echo (ionospheric frequency-height diagram) and then used POLAN and other methods to invert to obtain the characteristic parameters of the ionosphere, for example, the O-wave critical frequency in the F2 layer (foF2), the height at which the maximum value of the electron density is located in the ionosphere in the F2 layer (hmF2), and highest available frequency for oblique propagation at a distance of D kilometers apart (MUF(D)). The six ionosonde data used in this study were obtained from the Global Ionospheric Radio Observatory (GIRO) (see the magenta dots in Figure 1). GIRO provides ionosonde soundings from more than a hundred ionosonde stations around the globe and also provides near-real-time access to ionospheric plasma measurements from 42 stations, which facilitates the study of ionospheric response to space weather events [47].
The FORMOSAT-7/COSMIC-2 (F7/C2) radio occultation mission satellite, jointly developed by the United States and Taiwan, China. The mission carries the advanced Tri-GNSS Radio Occultation System (TGRS) instrument, which receives GPS and GLONASS signals and has the capability to receive Galileo and BDS signals, as well as provides about 5000 occultation events per day, including TEC data arcs and electron density vertical profiles. These contribute to a better understanding of the structure and electrodynamics of the equatorial and low-latitude ionosphere [48,49]. The NmF2 and hmF2 data used in this paper are from ionPrf, a secondary product of F7/C2.
Swarm is the first constellation mission of the European Space Agency (ESA) for Earth environmental observations, whose main scientific objectives are to study the geomagnetic field, the currents in the magnetosphere and ionosphere, and the effects of the solar wind on the dynamics of the upper atmosphere. The Swarm mission consists of three satellites: Swarm-A and Swarm-C with an initial flight altitude of approximately 460 km and Swarm-B with an initial flight altitude of approximately 530 km [50]. The Langmuir probe on board the Swarm satellite can be used to probe the ionospheric plasma coefficients, allowing for direct observations of the ionosphere. The data used in this study were the extended Swarm EFI Langmuir probe data, which contain ionospheric electron density information derived from the faceplate current at 16 Hz [51].
2.2. Methods and Statistical Indicators
In this paper, carrier-to-code leveling (CCL) was utilized to obtain the ionospheric TEC of a GNSS station [52]. Since the delays produced by the ionosphere on the pseudorange and phase observations are equal in size and opposite in sign, the ionospheric TEC can be obtained by averaging the sum of the pseudorange and phase ionospheres in a consecutive arc segment in order to determine the information of the pseudorange differential code bias and phase ambiguity parameter, which is given in the following formulas:
where r and s denote receiver and satellite, respectively; i and j denote signals at different frequencies ( and ); denotes a combination of pseudorange observations; denotes a combination of carrier-phase observations; <•> denotes the average value of a continuous arc segment; and denotes a combination of integer ambiguity. and are the differential code biases of receivers and satellites, respectively.
CODE GIM and single-station GNSS TEC data were processed using the sliding interquartile range method [53]. Compared with the traditional method, this method can calculate the background value more accurately and then calculate the upper and lower limits of the ionospheric TEC based on the background value to detect the presence of outliers. First, a suitable sliding time window was chosen (the window chosen in this paper was 7 days), and the TEC values under the window were arranged from smallest to largest and divided into four equal parts. Taking 20 days of data as an example, the data were arranged from smallest to largest as follows: . The tie line is denoted as , , and in turn, and the quartile values are denoted as . The upper bound of TEC anomaly is denoted as , and the lower bound is denoted as .
The spherical harmonic function model is a commonly used function model in ionospheric TEC modeling [54], and it has the following mathematical expression:
where is NmF2 or hmF2, is the latitude of the ionospheric piercing point, is the longitude of the ionospheric piercing point, N is the maximum order of expansion of the spherical harmonic function, is the normalized Legendre function of order n of degree m, and and are the unknown coefficients of the spherical harmonic function.
A spherical harmonic function model with an eighth-order was applied to model the NmF2 and hmF2 data of F7/C2. After modeling NmF2 and hmF2 using the spherical harmonic function, the root mean square (RMS) was used to evaluate the model accuracy. Also, based on the model to the difference values of NmF2 and hmF2 (dNmF2 and dhmF2) and their percentage variations (PVs) were determined as follows:
3. Results
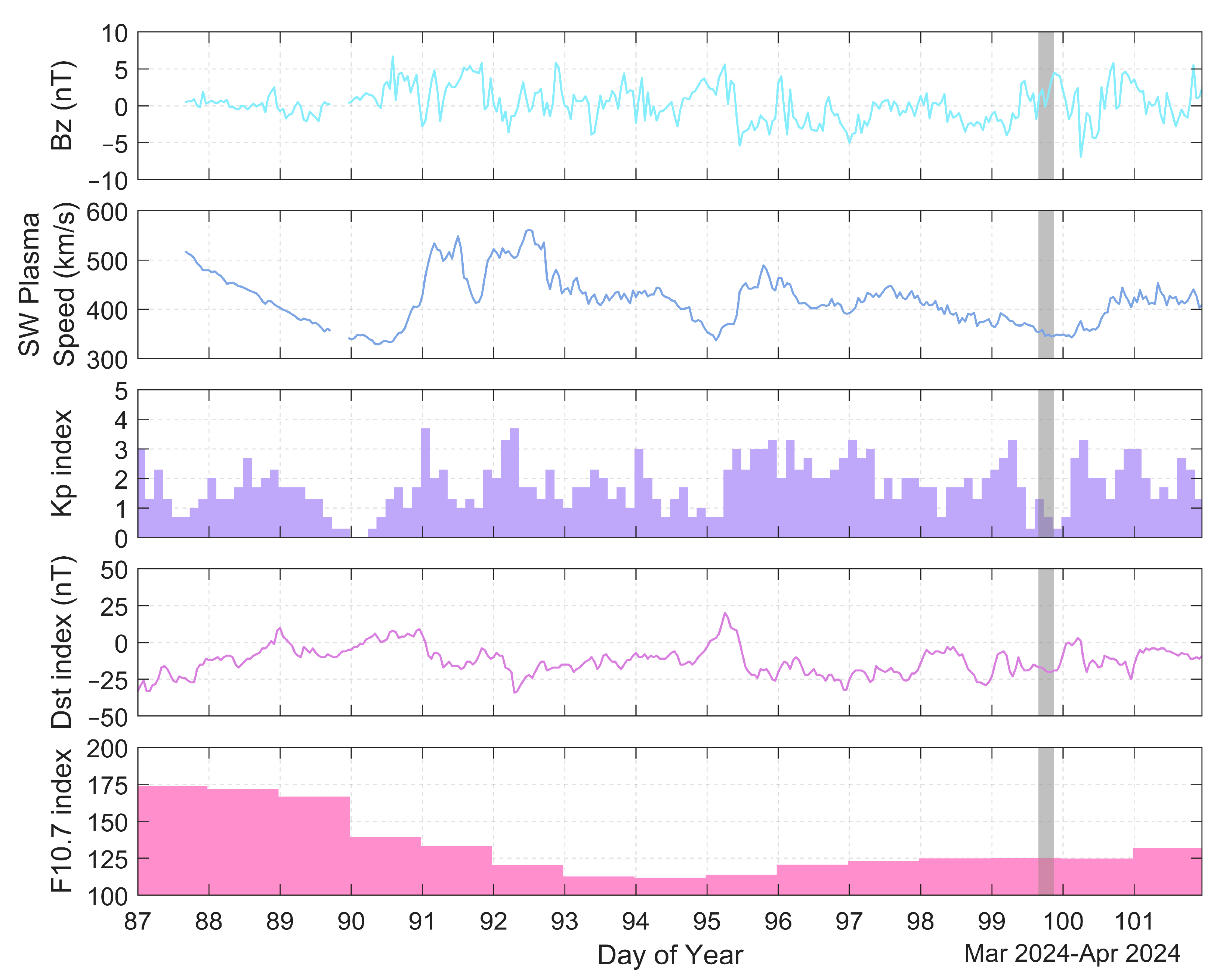
The MIT TEC product has a resolution of 5 min. After testing, we found that the 5 min TEC map covers a limited area, and in order to more comprehensively show how the ionosphere is affected by the solar eclipse, we resampled the 5 min TEC map, taking into account the rate of variation in local time, and generated a TEC map with a resolution of 15 min, as shown in Figure 1. It is well known that space weather events (e.g., geomagnetic storms) affect the ionosphere, which, in turn, generates ionospheric disturbances. Therefore, the corresponding space weather conditions need to be analyzed before conducting this study in order to exclude the interference of other events causing ionospheric perturbations. The variations in solar activity and geomagnetic activity parameters from 27 March to 10 April 2024 are given in Figure 2. As can be seen from Figure 2, the Bz component of the interplanetary magnetic field (IMF) is in the range of −5 nT to 5 nT, indicating a weak north–south variation in the IMF. The solar wind plasma speed has no obvious sudden increase in this time period, and the solar radiation flux of 10.7 cm (F10.7) has no sharp ups and downs fluctuations as well. The maximum value of the Kp index, which characterizes the intensity of geomagnetic activity, is within 4, and the minimum value of the Dst index is around −25 nT, so the geomagnetic activity is relatively calm. Therefore, the ionospheric data for this period used in the subsequent experiments are considered to be the reference values in the quiet state.
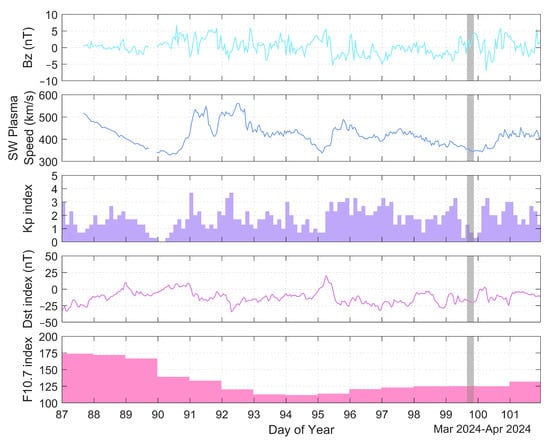
Figure 2.
Variation in solar and geomagnetic activity parameters from 27 March to 10 April 2024, with gray shading denoting the eclipse time period.
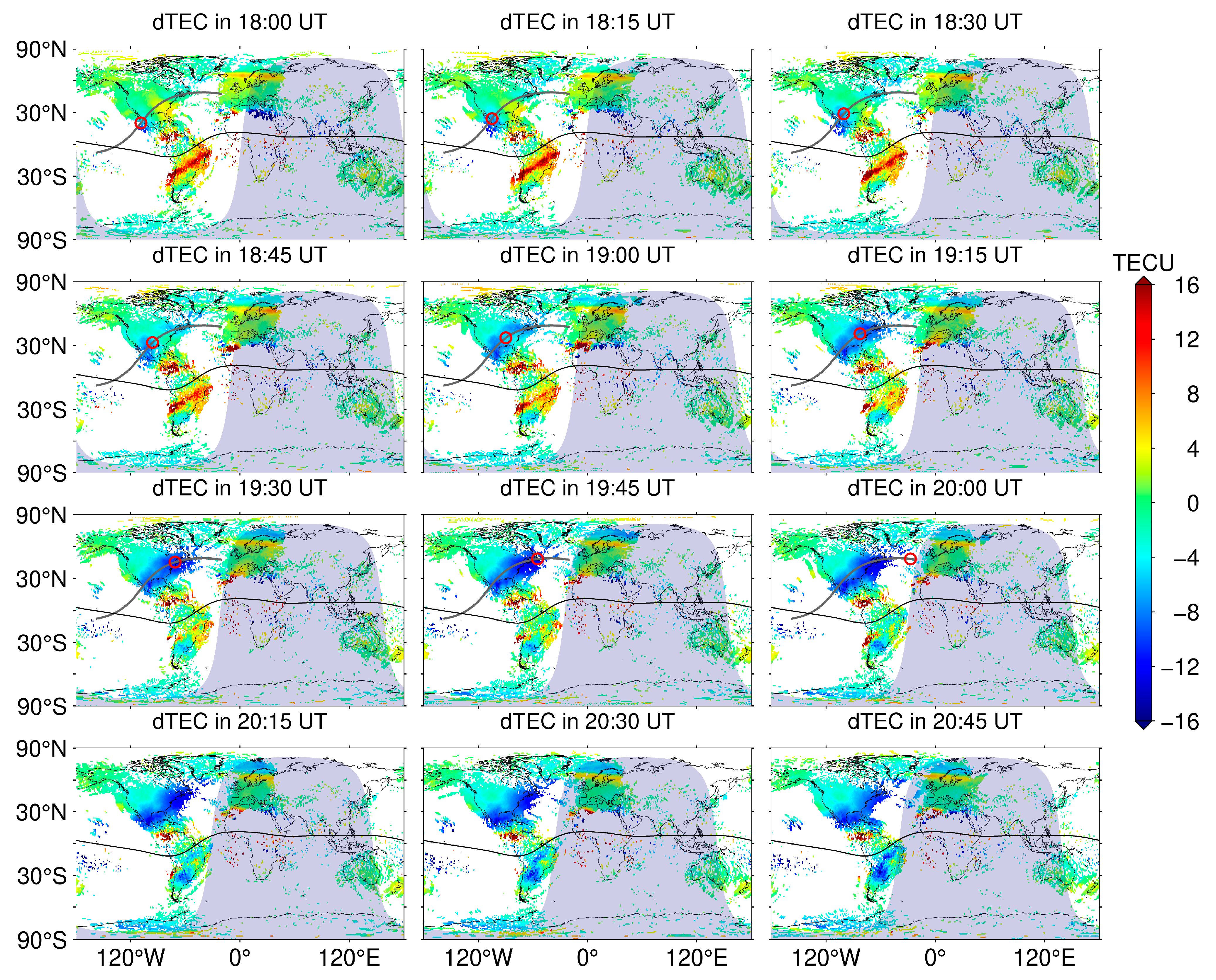
To focus on the attenuation of the ionospheric TEC during the solar eclipse, we obtained the average value of each moment of the two days based on the TEC maps of 7 April and 9 April, which were used as the background value in the quiet state and then used as the background value to arrive at the residual ionospheric TEC (dTEC) on April 8, as shown in Figure 3. It can be seen in Figure 3 that at 18:00 UT, the Sun’s position is near the west coast of North America, at which time the ionospheric TEC was observed to start showing a decreasing trend, with an attenuation value of about 10 TECU. With the variation in the Sun’s position, the spatial trend of the ionospheric TEC attenuation gradually spread eastward, and the positive dTEC is gradually replaced by a negative value. By 18:45 UT, the spatial extent of the ionospheric TEC attenuation extends to the central part of North America, and at the same time, it can be found that the weakening of the ionospheric TEC also begins to occur along the east coast of North America, with a reduction value near 5 TECU. At 19:00 UT, the range of ionospheric TEC attenuation is distributed near the line of maximum solar eclipse, and the minimum dTEC value is less than −10 TECU. After 15 min, the range of TEC attenuation further expands toward the region far away from the line of maximum solar eclipse, and the average attenuated TEC value is about 8 TECU. During the period from 19:30 UT to 20:00 UT, when the Sun’s position is gradually moving away from North America, the range of negative dTEC values is still gradually expanding and the maximum attenuation value increases to close to 15 TECU. The dTEC distribution from 20:15 UT to 20:45 UT also clearly shows that the attenuation of the ionospheric TEC is lagging behind the moment of the solar eclipse.
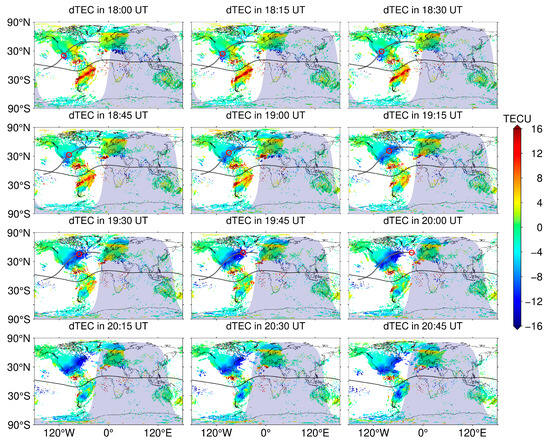
Figure 3.
Variation in the residuals of the global ionospheric TEC from 18:00 UT to 20:45 UT on 8 April 2024, with the path of the maximum solar eclipse indicated by the dark gray line, the position of the Sun indicated by the red circle, and the magnetic equator indicated by the solid black line.
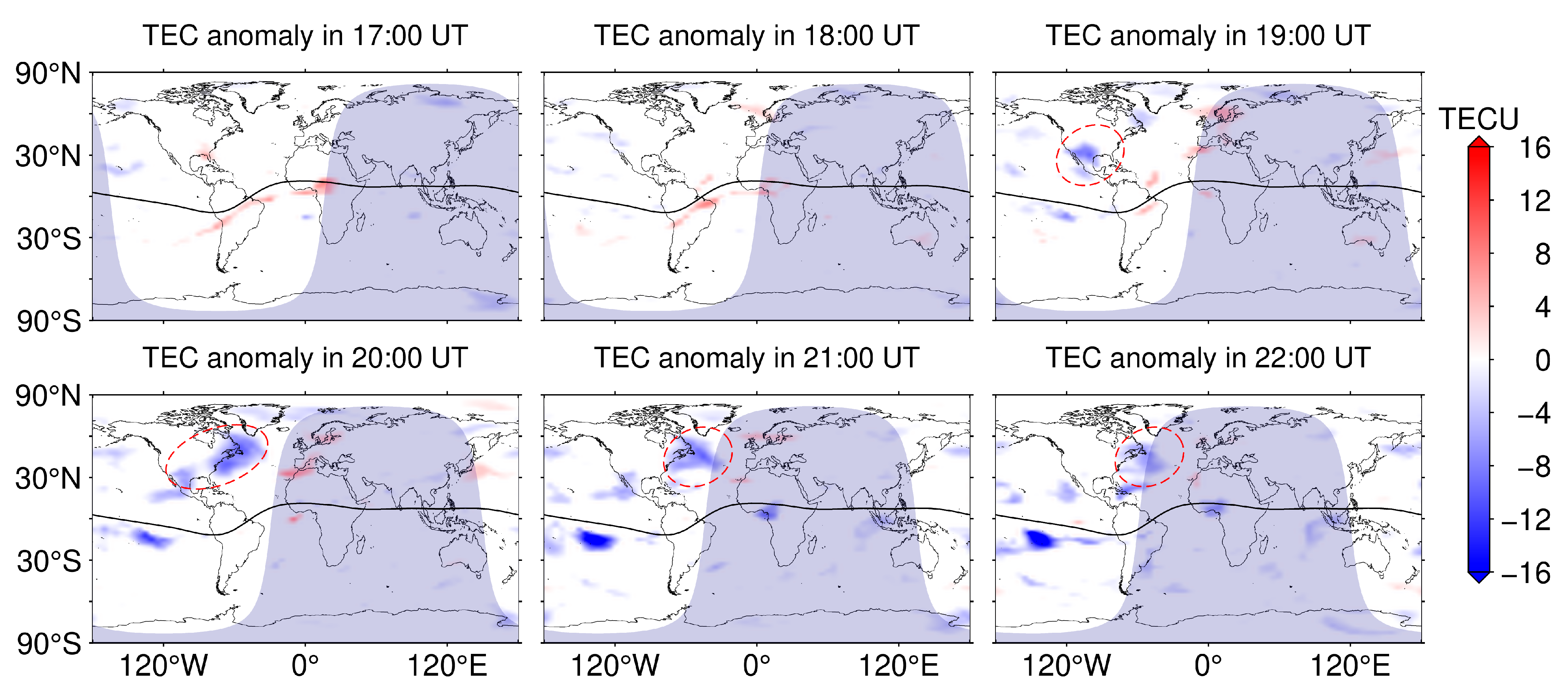
Then, we processed the GIM data for 8 April using the sliding interquartile range method based on the CODE GIM data products for the 12 days prior to the day of the solar eclipse to obtain the distribution of global ionospheric TEC anomaly variations, as shown in Figure 4. In Figure 4, it can be clearly seen that no anomalies appear in the North American region when there is no solar eclipse in the region, and at 19:00 UT, negative anomalies appear in most of the North American region (red dashed circle), with the maximum negative anomaly being close to 10 TECU. The range of the ionospheric TEC anomalies is gradually enlarged at 20:00 UT, and in particular, the range of the negative anomalies is larger near the east coast of North America, with the average negative anomaly value being about 8 TECU. The range of negative ionospheric TEC anomalies remains near the east coast of North America near sunset (i.e., 21:00 UT and 22:00 UT), but the range and negative anomalies gradually decrease. In contrast to the MIT TEC product, even though CODE used only a few hundred stations around the world to generate the GIM product, it still shows similar variations in the distribution of global ionospheric TEC anomalies as the residual TEC variations in MIT, which can be used to monitor the trend of ionospheric decay during the solar eclipse. It is worth noting that the GIM product has some limitations for ionospheric perturbation variations over a short period of time because of its temporal resolution of 1 h.
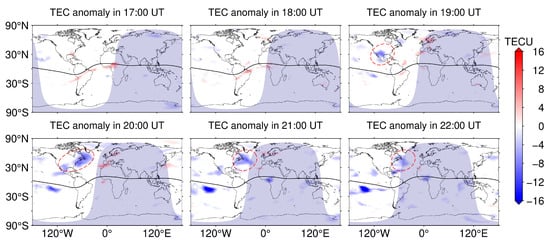
Figure 4.
Distribution of global ionospheric TEC anomaly variation for CODE from 17:00 UT to 22:00 UT on 8 April 2024, with the solid black line indicating the magnetic equator.
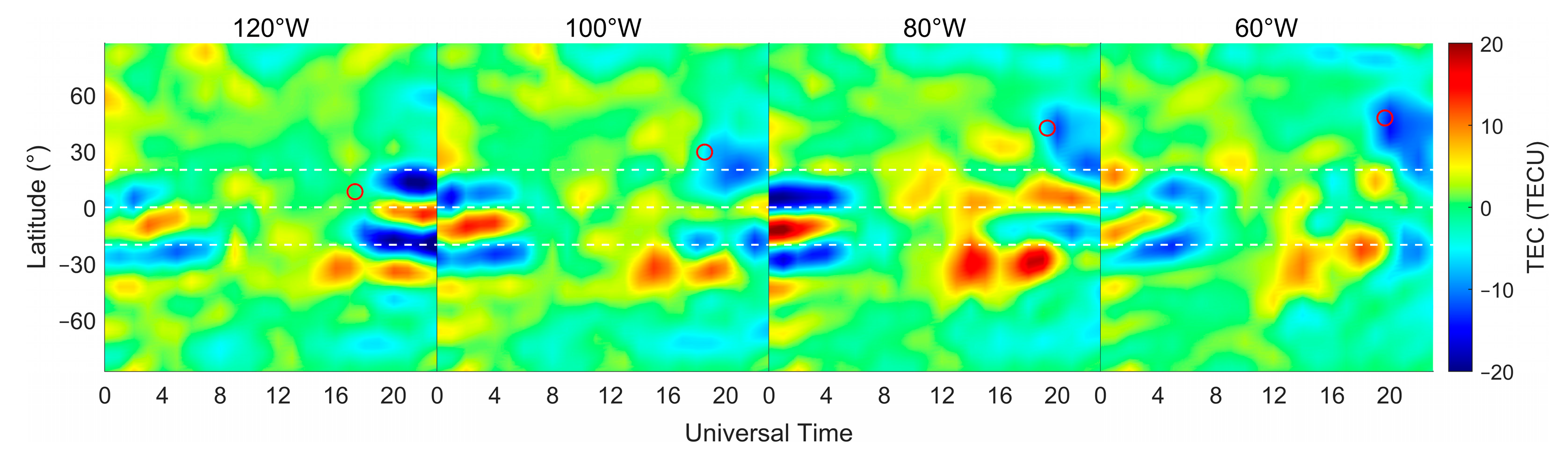
Ionospheric TEC is more closely related to local time and latitude, so it is of great significance to explore the variation in ionospheric TEC in different longitude sectors (different latitudes). The latitude–time variation in CODE GIM in different longitude sectors on 8 April is given in Figure 5, and its data processing method is consistent with that of Figure 3. In Figure 5, it can be seen that in the 120°W sector, there is no obvious ionospheric TEC loss in the solar eclipse path, but there is a TEC loss of more than 20 TECU in the equatorial anomalous peak region during the time period from 17:00 UT to 24:00 UT, and this phenomenon is also reflected in Figure 4. The phenomenon of ionospheric TEC depletion due to the solar eclipse is observed in the 100°W, 80°W and 60°W sectors and clearly shows a lag phenomenon, which is consistent with the variation in MIT TEC. Among them, the 100°W sector shows the region of ionospheric TEC weakening near 20°N, with a loss value of about 12 TECU, and the 60°W sector observes the widest coverage of ionospheric TEC loss, with a loss value close to that of the 100°W sector. In addition, since there are no GNSS stations (or fewer GNSS stations) within the eclipse path in the ocean region, neither the MIT TEC maps nor the CODE TEC maps adequately represent the ionospheric variations within the ocean region.
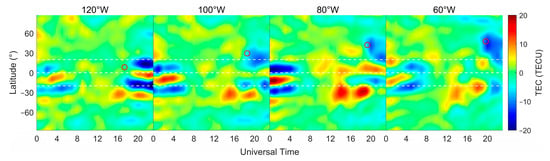
Figure 5.
Latitude–time variation in global ionospheric TEC for CODE in different longitude sectors on 8 April 2024, with the white dashed lines indicating 20°N, 0°, and 20°S from top to bottom and the red circle representing the position of the Sun.
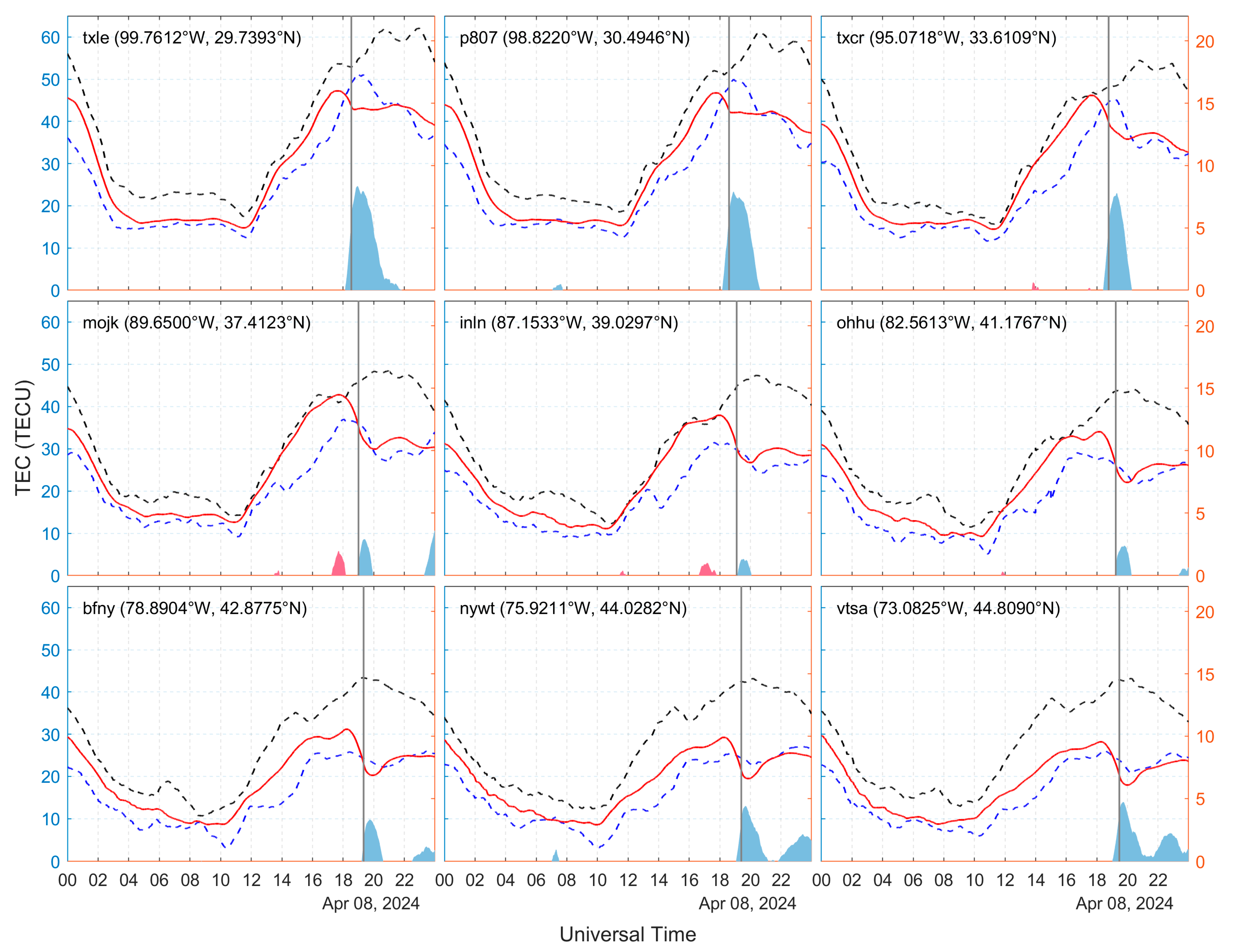
The ionospheric TEC maps provide large-scale data support for detecting ionospheric disturbances under solar eclipse events. However, based on the fact that a single GNSS station can study the influence of ionospheric disturbance on a small range of temporal and spatial effects in detail, we selected nine GNSS stations in the path of the maximum solar eclipse to analyze the eclipse–ionosphere effects over the stations using the sliding interquartile range method. Figure 6 shows the trend of TEC variation over the 9 GNSS stations on 8 April and the upper and lower boundaries calculated by the sliding interquartile range method. In Figure 6, it can be seen that all nine GNSS stations showed the phenomenon of post-eclipse ionospheric TEC depletion, among which the ionospheric TEC of stations txle, p807, and txcr decayed more significantly, exceeding 7 TECU. Smaller negative ionospheric anomalies were detected at stations mojk, inln, and ohhu, and it is noteworthy that stations mojk and inln detected positive anomalies ranging from 0.8 to 1.8 TECU prior to the occurrence of ionospheric TEC depletion, and none of the other stations showed similar phenomena. The negative TEC anomalies of 3 to 5 TECU were detected at the bfny, nywt, and vtsa stations, in addition to the negative anomalies close to 2 TECU again at the three stations after the ionospheric loss directly caused by the eclipse. The time between the moment of maximum solar eclipse and the moment of TEC decay to the maximum value at the nine GNSS stations ranged from 14 to 23 min, and the time from the moment of maximum TEC loss to the return to a quiet state was about 1 h.
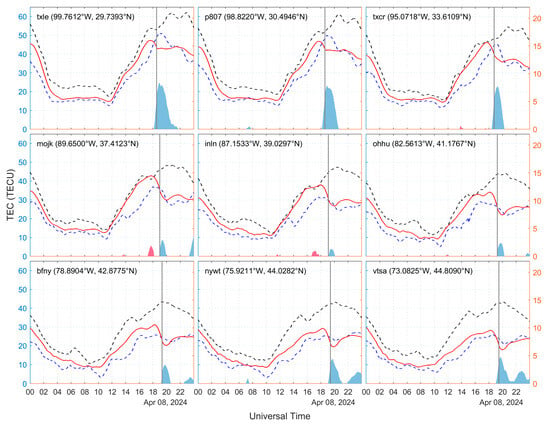
Figure 6.
Variations in TEC at GNSS stations on 8 April 2024 (red line): black dashed and blue dotted lines indicate the upper and lower bounds of the sliding interquartile range method calculations, respectively; red and blue bars indicate positive and negative anomalies of the TEC, respectively (indicated by the right vertical axis); and the gray vertical line indicates the moment of maximum solar eclipse.
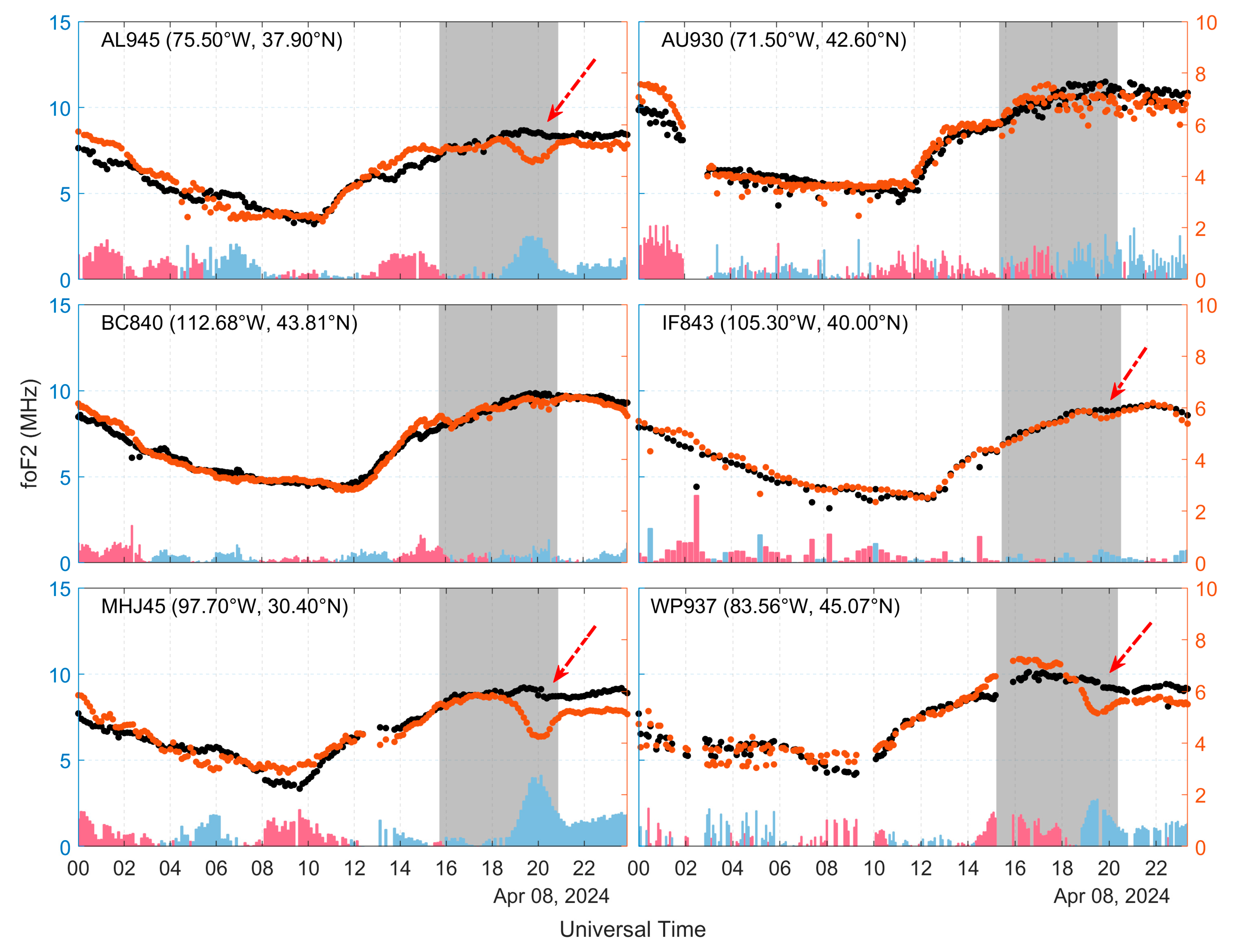
We then selected data from six ionosondes located in the United States to study the variation in foF2. Since GIRO uses a program to automatically calibrate the parameters of the ionosonde, some calibration errors can occur. Therefore, we manually corrected the results of the six ionosondes on the ionogram, as shown in Figure 7. We can see in Figure 7 that AL945, IF843, MHJ45, and WP937 ionosondes all detected the phenomenon of reduced foF2 associated with the solar eclipse (see the position of the red arrows), with negative anomalies around 1.6 MHz at station AL945, 0.4 MHz at station IF843, and 1.8 MHz at station WP937, as well as the largest negative foF2 anomaly at station MHJ45, which is more than 2.7 MHz. Ionospheric disturbances at the other two ionosonde stations were not significant.
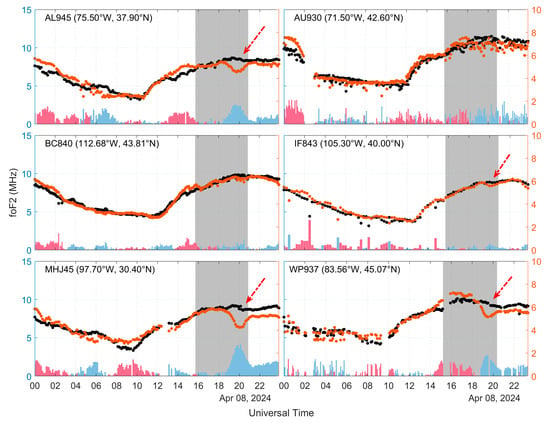
Figure 7.
Variation in foF2 at the ionosonde station on 8 April 2024 (orange dots): black dots indicate the mean value of the day before and after; red and blue bars indicate positive and negative anomalies of foF2, respectively (indicated by the vertical axis on the right); and grey shading indicates the time of the solar eclipse.
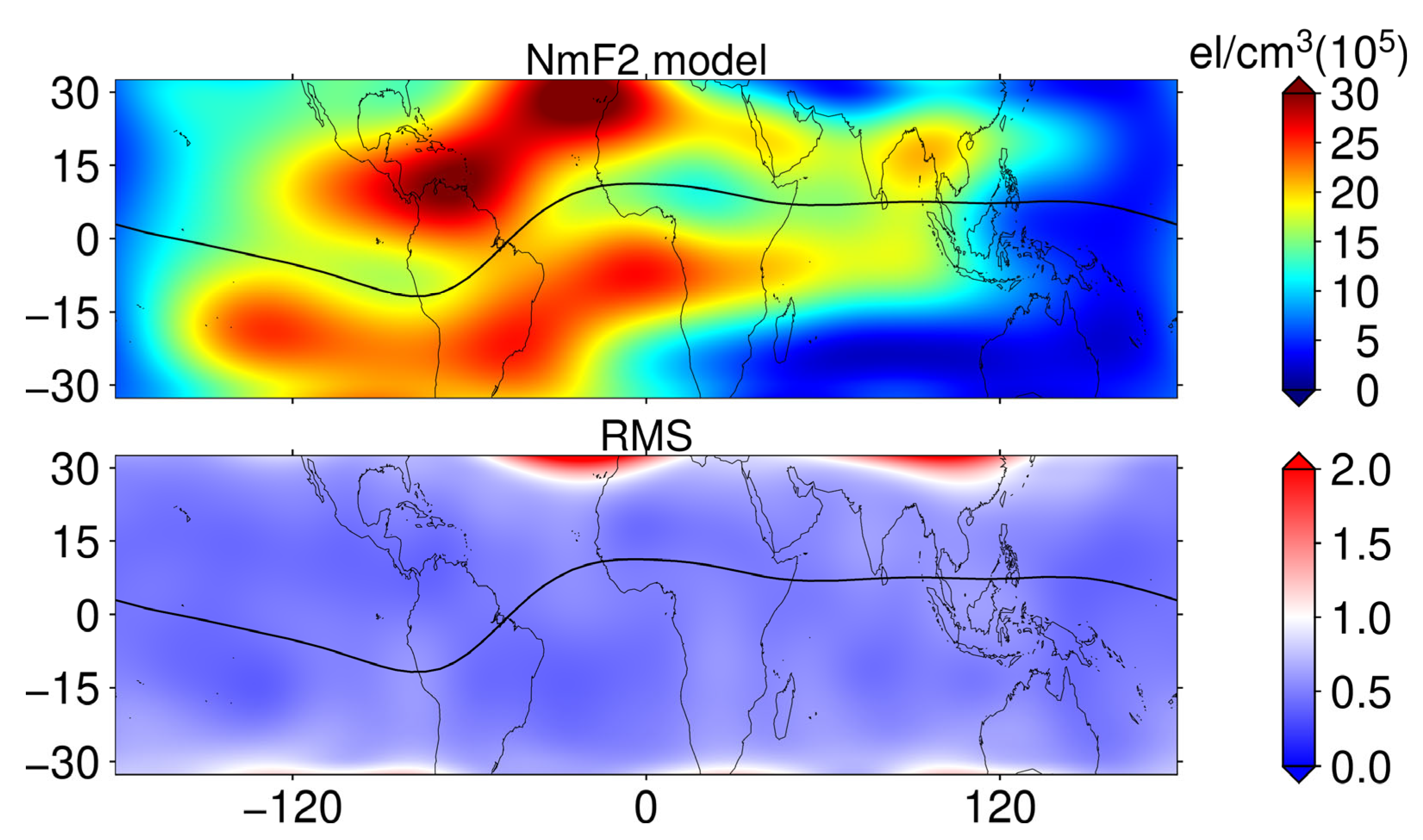
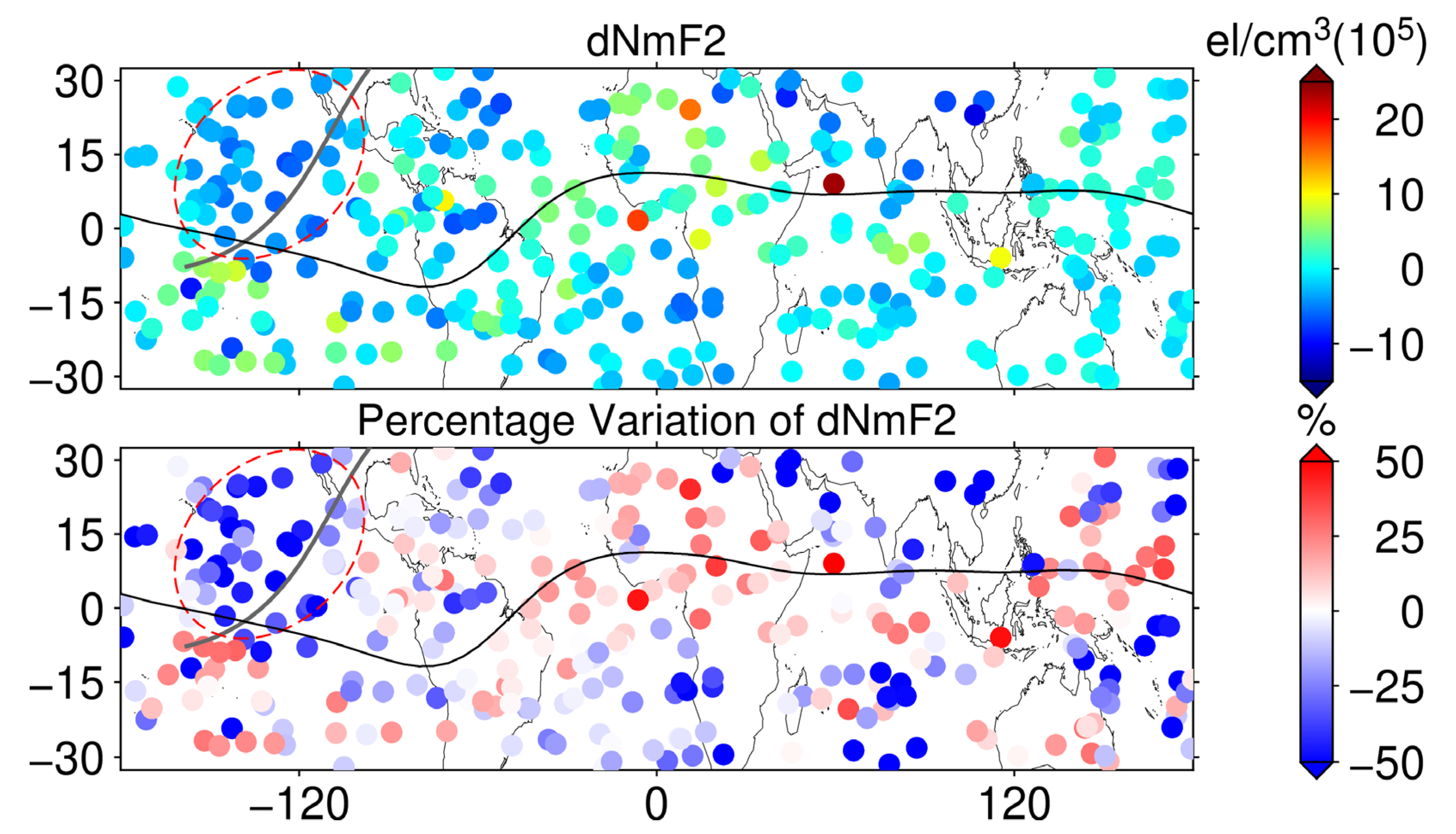
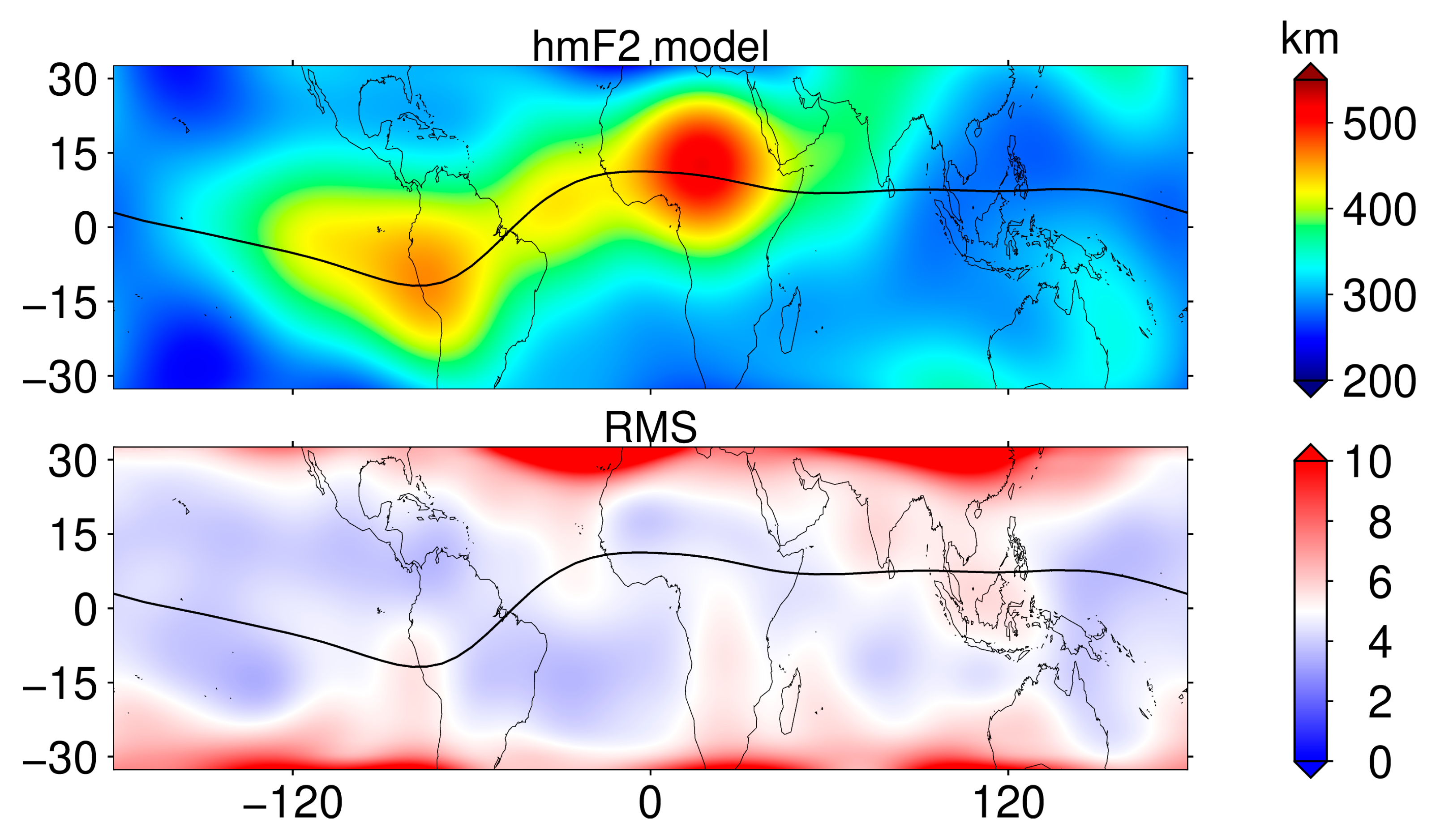
The ionospheric TEC maps of MIT and CODE fail to capture the eclipse-induced ionospheric effects in the ocean region, which is compensated by space-based GNSS observations. We established NmF2 and hmF2 models based on the F7/C2 occultation data between 17:00 UT and 19:00 UT from 27 March to 7 April, combined with the eighth-order spherical harmonic function model, respectively. Since the occultation data only cover the low and middle latitude range, the latitude range of the modeled region is from 32.5°N to 32.5°S with a resolution of longitude 5° × latitude 2.5°. The NmF2 model and its modeled RMS are shown in Figure 8. From the NmF2 model, the modeling results are basically consistent with the variation rule of the ionosphere, showing obvious equatorial ionization anomaly (EIA), and the modeling RMS is lower than 0.5 × 105 el/cm3 in most regions, which is highly reliable. The NmF2 model is used as the background value under space weather and geomagnetic quietness, and dNmF2 and its PV are obtained based on the occultation NmF2 data in the same time period on 8 April, as shown in Figure 9. It can be seen in Figure 9 that the values of dNmF2 in the red dashed ellipse are significantly smaller than those in other regions, and the ionospheric NmF2 loss is between 4 × 105 el/cm3 and 7 × 105 el/cm3. Combined with the PV, the percentage variation in ionospheric NmF2 in this region is between 40% and 70%. Based on the above results, the ionospheric depletion effect induced by the eclipse path in the ocean region can be significantly detected.
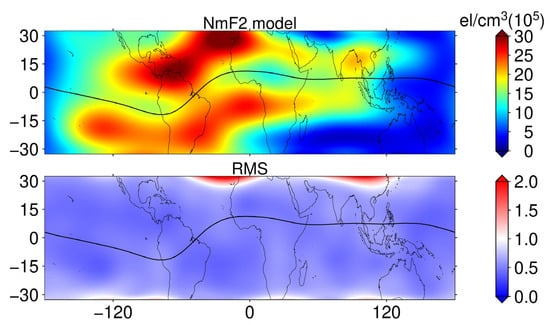
Figure 8.
Regional distribution of the NmF2 model (top) and its RMS error (bottom) established with F7/C2 NmF2 data and the eighth-order spherical harmonic function.
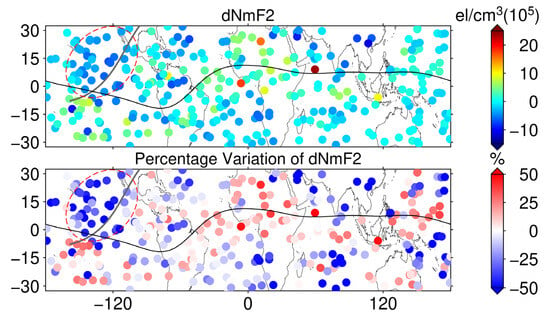
Figure 9.
The difference between the F7/C2 occultation point NmF2 and the model (top) and its PV (bottom) from 17:00 UT to 19:00 UT on 8 April 2024, with the path of the maximum solar eclipse indicated by the dark gray line and the magnetic equator indicated by the black line.
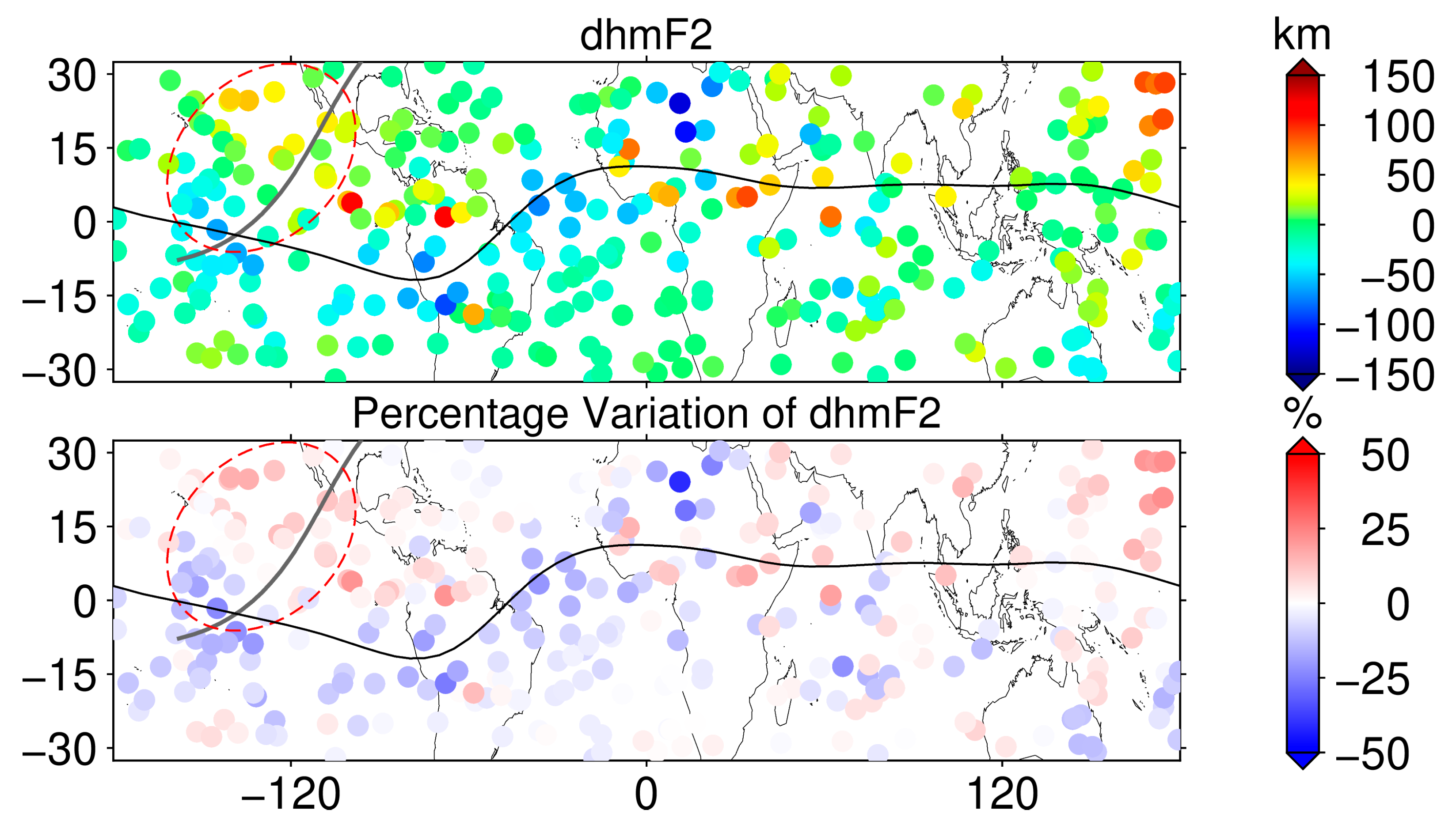
An approach consistent with the NmF2 model was used to model hmF2 and detect anomalous variations in hmF2, as shown in Figure 10 and Figure 11. The modeling RMS of hmF2 is below 6 km in most of the region. The variation in dhmF2 in the solar eclipse region is the opposite of that of the foF2, showing an increasing trend, with an increase ranging from about 4 to 55 km, and the PV of the ionospheric hmF2 in the region ranges from between 4% and 16%. This also indicates that the ionospheric effect caused by the solar eclipse not only reduces NmF2 but also has an impact on the hmF2.
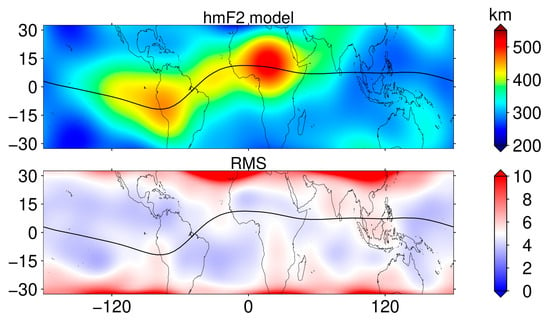
Figure 10.
Regional distribution of the hmF2 model (top) and its RMS error (bottom) established with F7/C2 hmF2 data and the eighth-order spherical harmonic function.
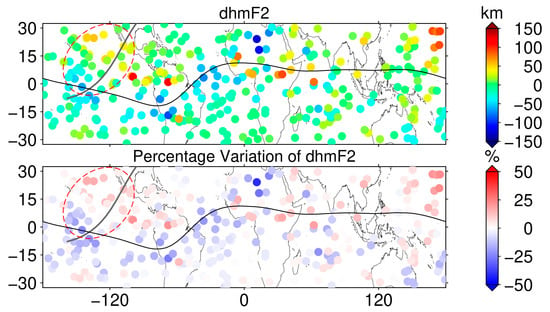
Figure 11.
The difference between the F7/C2 occultation point hmF2 and the model (top) and its PV (bottom) from 17:00 UT to 19:00 UT on 8 April 2024, with the path of the maximum solar eclipse indicated by the dark gray line and the magnetic equator indicated by the black line.
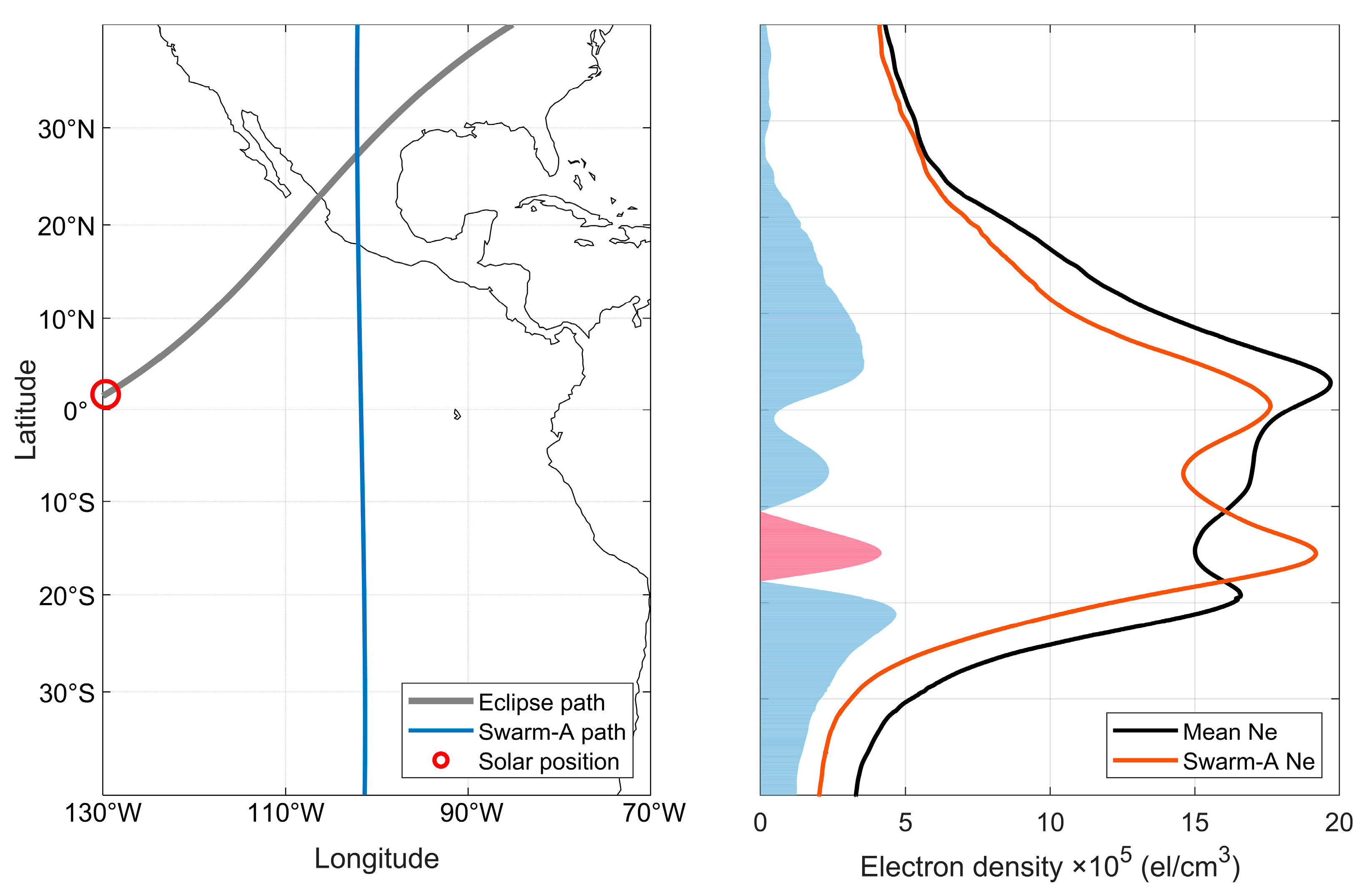
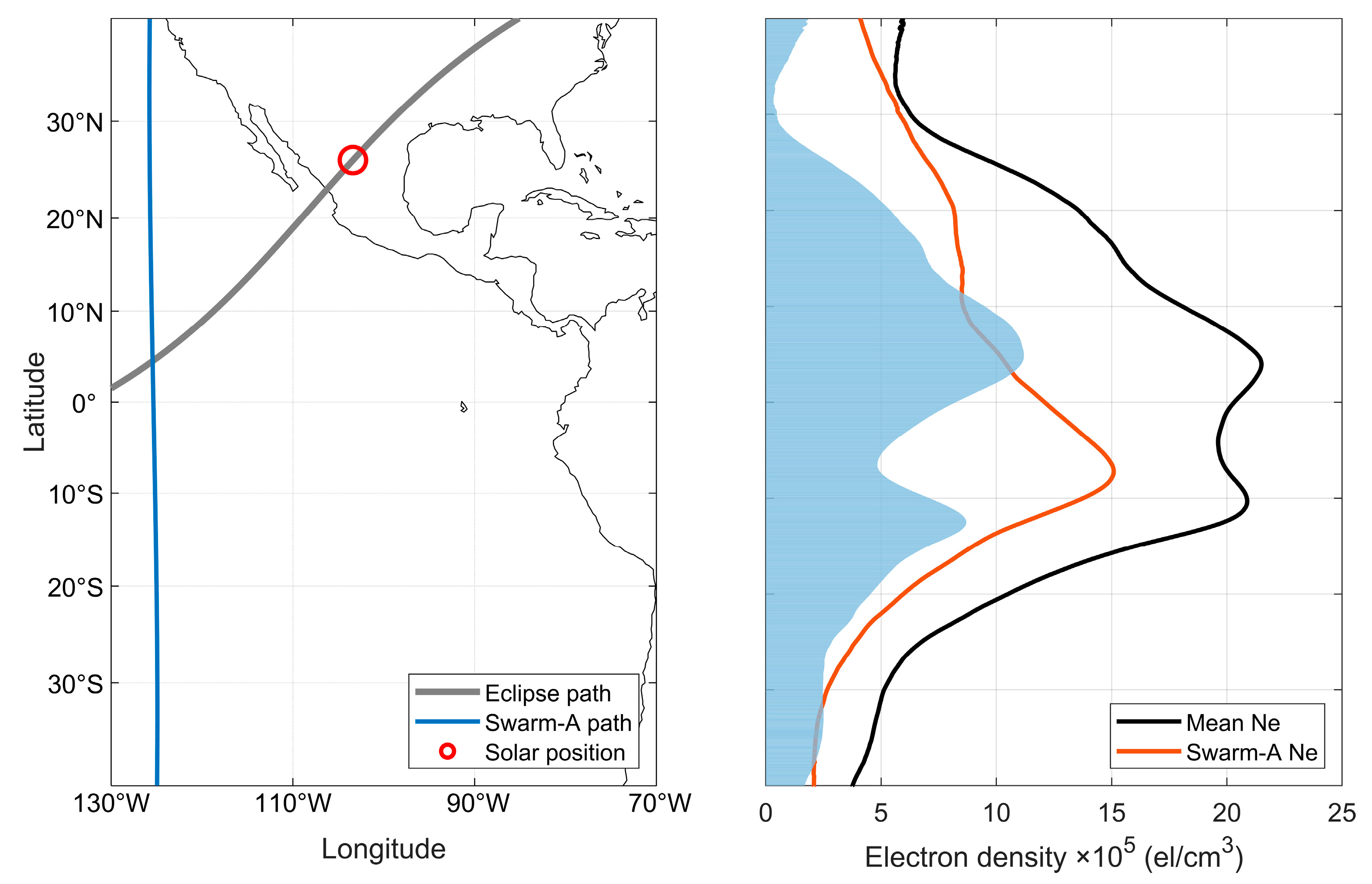
The ionospheric Ne variation for Swarm satellite is also involved in this paper. Since Swarm satellite is a polar-orbiting satellite, its trajectory can be approximated as a straight line at low and middle latitudes, i.e., the direction of the longitude line, so it can directly detect the variation in the ionospheric latitude on the sector of the same longitude to make up for the insufficient observation of CODE data in the oceanic region. The variations in the satellite trajectory of Swarm-A (flying at ~450 km) and its Ne measurements using the Langmuir probe at 17:00 UT and 18:20 UT on April 8 are given in Figure 12 and Figure 13, respectively. In this case, the average value calculated from the Ne values of the satellite’s approximate trajectory on April 7 and April 9 is used as the reference background value for 8 April. In Figure 12, it can be seen that the profile of the Ne of Swarm-A along the latitude shows a significant equatorial anomaly, and since the position of the Sun is before the satellite track at this time, Figure 12 can also be regarded as the value of the state of the ionosphere before the solar eclipse. The satellite track given in Figure 13 is after the solar eclipse and can be taken as the ionospheric state affected by the solar eclipse. It is obvious in Figure 13 (right) that the Ne profile is significantly lower than the reference value, with a maximum negative anomaly of 11.2 × 105 el/cm3, and fails to show the EIA, the EIA double-wave peak disappears, and the equatorial trough is similarly affected with a negative anomaly of 4.8 × 105 el/cm3.
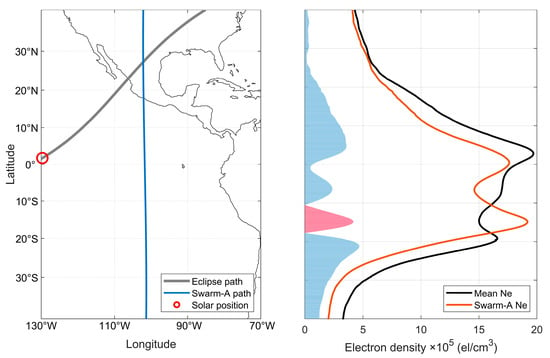
Figure 12.
Satellite trajectory of Swarm-A (left) and its Ne variation (right) at 17:00 UT on 8 April 2024, with the orange line indicating Swarm-A measurements, the black line indicating the average of the approximate trajectories for the day before and after, and the red and blue bars indicating positive and negative anomalies of Ne, respectively.
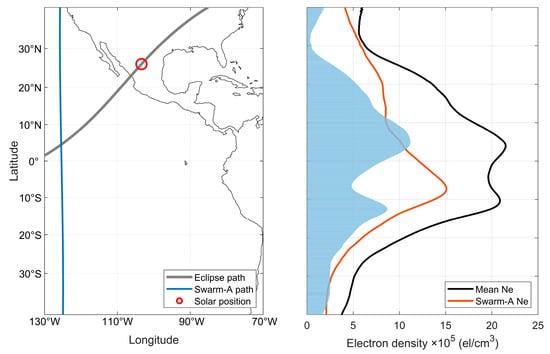
Figure 13.
Satellite trajectory of Swarm-A (left) and its Ne variation (right) at 18:20 UT on 8 April 2024, with the orange line indicating Swarm-A measurements, the black line indicating the average of the approximate trajectories for the day before and after, and the red and blue bars indicating positive and negative anomalies of Ne, respectively.
4. Discussion
The eclipse-induced anomalies in ionospheric electron density and TEC are roughly divided into two periods, i.e., during and after the solar eclipse. At the beginning of the solar eclipse, the reduction in EUV radiation led to a decrease in photo-chemical and thermodynamic reactions and, consequently, to a gradual decrease in the plasma density of the ionosphere. At the same time, the lunar shadow leads to a contraction of the neutral atmosphere and a decrease in atmospheric temperature, which alters the neutral components such as O/N2 [14,55], and the neutral winds converge toward the center of the eclipse, where the temperature is lower, and modulate the E × B drift process [56]. During the eclipse, the downward diffusion of plasma from the plasmasphere will slow down the decrease in plasma in the F2 region of the ionosphere. After the lunar shadow, ionospheric plasma will increase due to the recovery of the solar ionization rate. Based on the TEC products of MIT and CODE, we observed the eclipse-induced depletion phenomenon of ionospheric TEC, as shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4, which is consistent with the variation pattern of the ionosphere during the eclipse. In addition, we have also explored the different behaviors of the eclipse–ionosphere effect in different latitude and longitude regions, where the attenuation of the ionospheric TEC lags behind the moment of the eclipse.
The end of this solar eclipse event in the U.S. sector was roughly before sunset, and in addition to showing the ionospheric TEC loss during the eclipse, Figure 6 shows that the bfny, nywt, and vtsa stations once again had negative anomalies close to 2 TECU after 23:00 UT (18:00 local time). Taking into account the fact that the anomaly appeared after 23:00 UT (18:00 local time), after the end of the eclipse, the solar radiation increased, promoting the photo-chemical process and a slow increase in electron density. However, the solar radiation did not return to the normal level at this time near sunset, and the sunset again led to a decrease in solar radiation, which inhibited the photo-chemical processes and slowly decreased the electron density, thus leading to the second negative TEC anomaly.
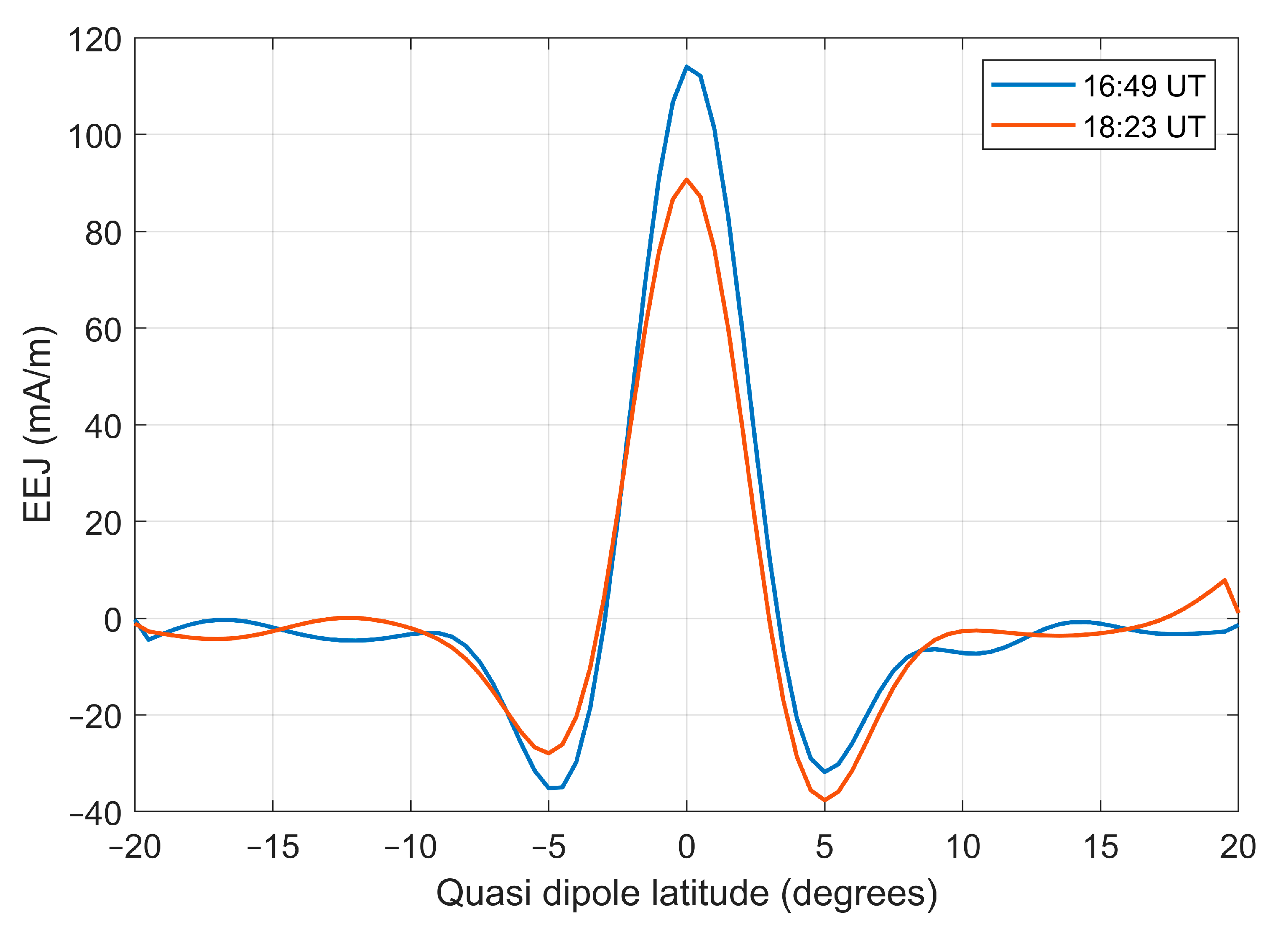
The response of the low-latitude ionosphere to solar eclipses is mainly affected by the geyser effect and equatorial ionization anomalies. Low-pressure systems induced by solar eclipses can trigger localized generators that significantly weaken the equatorial electrojet (EEJ) as it approaches the magnetic equator, leading to a decrease in electron density at the equator and in the EIA region [57]. In this paper, the Ne measured by Swarm-A satellite in Figure 13 shows significant attenuation in the equatorial anomaly region, especially at the EIA double-peak location, where the EIA northern peak is more attenuated than the southern peak because the path of the maximum eclipse is north of the equator. The EEJs obtained from Swarm-A measurements are given in Figure 14, with the blue line showing the measurements at 16:49 UT on 8 April 2024, corresponding to the results of Figure 12, and the orange line showing the measurements at 18:23 UT on 8 April 2024, corresponding to the results of Figure 13. It can be found that the peak EEJ of the orange line is significantly smaller than that of the blue line, indicating that the intensity of the EEJ decreases significantly after the eclipse. Combining the results of Figure 12 and Figure 13 further illustrates that the eclipse-triggered local dynamo attenuates the EEJ, which, in turn, affects the equatorial anomaly double wave peak.
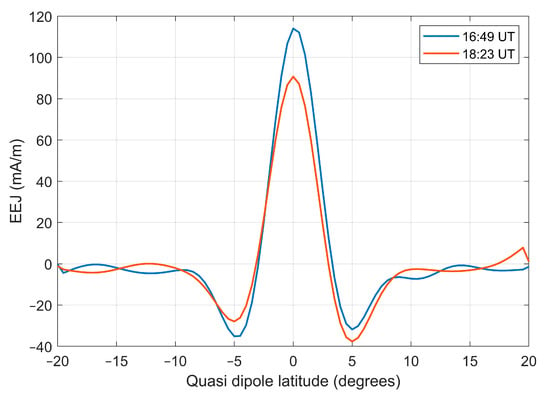
Figure 14.
Height-integrated east current profile in quasi-dipole latitude (EEJ) measured using Swarm-A.
5. Conclusions
In this paper, we comprehensively investigate the ionospheric response characteristics due to the 8 April 2024 total solar eclipse across North and Central America based on multi-instrument observational data. The main results are summarized below:
Both GNSS-derived MIT and CODE TEC products have detected total solar eclipse-induced ionospheric TEC losses, with maximum losses exceeding 10 TECU. The TEC data from nine GNSS stations in the path largest eclipses show that the intensity of eclipse-induced ionospheric TEC losses is spatially dependent, with the moment of maximum loss lagging behind the moment of the largest eclipse by about 14 to 23 min, and the ionosonde has detected negative foF2 anomalies with a maximum of more than 2.7 MHz.
The combination of F7/C2 ionospheric NmF2 and hmF2 modeling results reveals that the NmF2 in the eclipse region shows an attenuation trend, with the PV of differential NmF2 ranging from 40% to 70%, and the hmF2 is slightly increasing, with the PV of differential hmF2 ranging from 4% to 16%. The Ne profile of Swarm-A satellite is significantly lower than the reference value at the eclipse time, with a maximum negative anomaly value of 11.2 × 105 el/cm3, and fails to show EIA phenomenon.
In this paper, we give an example of the variation in the eclipse–ionosphere effect and the influence mechanism. It should be noted that the ionospheric response triggered by each eclipse event is different. Therefore, we will statistically analyze the ionospheric response of the existing solar eclipse events in future studies and increase the work conducted on the physical mechanism, as well as investigate the impact of the eclipse–ionosphere effect on GNSS navigation and positioning.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing, H.Z., T.Z., X.Z., Y.Y., Y.W. and Y.M.; methodology, T.Z. and Y.Y.; validation, H.Z., Y.W., X.Z. and T.Z.; data curation, H.Z., Y.W. and Y.M.; formal analysis, H.Z., T.Z., X.Z. and Y.Y.; funding acquisition, H.Z., Y.W., and Y.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Science and Technology Project of the China Southern Power Grid, the Yunnan Power Grid Company Ltd. (grant number YNKJXM20220033).
Data Availability Statement
The MIT products are stored in the Madrigal database (http://cedar.openmadrigal.org/openmadrigal, accessed on 29 May 2024). CODE products are available from the IGS (https://cddis.nasa.gov/archive/gnss/data/, registration required, accessed on 29 May 2024), and the GNSS observations are available from the NOAA’s National Geodetic Survey (https://geodesy.noaa.gov/corsdata/rinex/, accessed on 29 May 2024). The solar geomagnetic parameters are available from the GSFC/SPDF OMNIWeb (https://omniweb.gsfc.nasa.gov/form/dx4.html, accessed on 29 May 2024). The ionosonde data are available from the USAF NEXION Digisonde network (http://spase.info/SMWG/Observatory/GIRO, accessed on 29 May 2024). The FORMOSAT-7/COSMIC-2 occultation data are available from CDAAC (https://data.cosmic.ucar.edu/gnss-ro/cosmic2/, accessed on 29 May 2024). and Swarm data are available from ESA (https://swarm-diss.eo.esa.int/, accessed on 29 May 2024).
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the use of MATrix LABoratory (MATLAB R2022b) software and Generic Mapping Tools. We would also like to thank the anonymous reviewers for their helpful suggestions.
Conflicts of Interest
Hui Zhang, Yifan Wang, and Yutang Ma were employed by the Yunnan Power Grid Company Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
References
- Feng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Han, B.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, T.; Huang, R. Analysis of ionospheric TEC response to solar and geomagnetic activities at different solar activity stages. Adv. Space Res. 2023, 71, 2225–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, C.J.; Lockwood, M.; Bell, S.A.; Smith, J.A.; Clarke, E.M. Ionospheric measurements of relative coronal brightness during the total solar eclipses of 11 August 1999 and 9 July 1945. Ann. Geophys. 2000, 18, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimenko, V.V.; Bessarab, F.S.; Korenkov, Y.N. Numerical simulation of effects of the 11 August 1999 solar eclipse in the outer ionosphere. Cosm. Res. 2007, 45, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, H.; Liu, L.; Yue, X.; Wan, W. The midlatitude F2 layer during solar eclipses: Observations and modeling. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2008, 113, A08309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller-Wodarg, I.C.F.; Aylward, A.D.; Lockwood, M. Effects of a mid-latitude solar eclipse on the thermosphere and ionosphere—A modelling study. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1998, 25, 3787–3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huba, J.D.; Drob, D. SAMI3 prediction of the impact of the 21 August 2017 total solar eclipse on the ionosphere/plasmasphere system. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 5928–5935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, T.; Lei, J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, B.; Burns, A.; Le, H.; Wu, Q.; Ruan, H.; Dou, X.; Wan, W. Global Responses of the Coupled Thermosphere and Ionosphere System to the August 2017 Great American Solar Eclipse. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2018, 123, 7040–7050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Ledesma, M.; Bravo, M.; Urra, B.; Souza, J.; Foppiano, A. Prediction of the Ionospheric Response to the 14 December 2020 Total Solar Eclipse Using SUPIM-INPE. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2020, 125, e2020JA028625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, M.A.; Molina, M.G.; Martínez-Ledesma, M.; de Haro Barbás, B.; Urra, B.; Elías, A.; Souza, J.; Villalobos, C.; Namour, J.H.; Ovalle, E.; et al. Ionospheric response modeling under eclipse conditions: Evaluation of 14 December 2020, total solar eclipse prediction over the South American sector. Front. Astron. Space Sci. 2022, 9, 1021910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klobuchar, J.A.; Whitney, H.E. Ionospheric electron content measurements during a solar eclipse. J. Geophys. Res. 1965, 70, 1254–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farges, T.; Jodogne, J.C.; Bamford, R.; Le Roux, Y.; Gauthier, F.; Vila, P.M.; Altadill, D.; Sole, J.G.; Miro, G. Disturbances of the western European ionosphere during the total solar eclipse of 11 August 1999 measured by a wide ionosonde and radar network. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2001, 63, 915–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakowski, N.; Stankov, S.M.; Wilken, V.; Borries, C.; Altadill, D.; Chum, J.; Buresova, D.; Boska, J.; Sauli, P.; Hruska, F.; et al. Ionospheric behavior over Europe during the solar eclipse of 3 October 2005. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2008, 70, 836–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Qi, H.; Ning, B.; Zhao, Z.; Yao, M.; Deng, Z.; Li, T.; Huang, S.; Feng, W.; Wu, J.; et al. Nighttime ionospheric enhancements induced by the occurrence of an evening solar eclipse. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2013, 118, 6588–6596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinisch, B.W.; Dandenault, P.B.; Galkin, I.A.; Hamel, R.; Richards, P.G. Investigation of the Electron Density Variation during the 21 August 2017 Solar Eclipse. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 1253–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezzopane, M.; Pietrella, M.; Pignalberi, A.; Tozzi, R. 20 March 2015 solar eclipse influence on sporadic E layer. Adv. Space Res. 2015, 56, 2064–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harjosuwito, J.; Husin, A.; Dear, V.; Muhamad, J.; Faturahman, A.; Bahar, A.; Erlansyah; Syetiawan, A.; Pradipta, R. Ionosonde and GPS total electron content observations during the 26 December 2019 annular solar eclipse over Indonesia. Ann. Geophys. 2023, 41, 147–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emelyanov, L.Y.; Bogomaz, O.V.; Chernogor, L.F.; Domnin, I.F. Response of the mid-latitude ionosphere to the solar eclipse on 25 October 2022: Results of F2–layer vertical sounding. Adv. Space Res. 2024, 73, 2338–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogrinčič, R.; Lara, A.; Borgazzi, A.; Raulin, J.P. Effects of the Great American Solar Eclipse on the lower ionosphere observed with VLF waves. Adv. Space Res. 2020, 65, 2148–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes Da Costa, A.; Paes Leme, N.M.; Rizzo Piazza, L. Lower ionosphere effect observed during the 30 June 1992 total solar eclipse. J. Atmos. Terr. Phys. 1995, 57, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Maji, S.K.; Chakrabarti, S.K. First ever VLF monitoring of the lunar occultation of a solar flare during the 2010 annular solar eclipse and its effects on the D-region electron density profile. Planet. Space Sci. 2012, 73, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guha, A.; De, B.K.; Choudhury, A.; Roy, R. Spectral character of VLF sferics propagating inside the Earth-ionosphere waveguide during two recent solar eclipses. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesham, K.; Singh, R.; Maurya, A.K.; Dube, A.; Kumar, S.; Phanikumar, D.V. The 22 July 2009 Total Solar Eclipse: Modeling D Region Ionosphere Using Narrowband VLF Observations. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2019, 124, 616–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoque, M.M.; Wenzel, D.; Jakowski, N.; Gerzen, T.; Berdermann, J.; Wilken, V.; Kriegel, M.; Sato, H.; Borries, C.; Minkwitz, D. Ionospheric response over Europe during the solar eclipse of March 20, 2015. J. Space Weather Space Clim. 2016, 6, A36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zhao, Z.; Yang, G.; Zhou, C.; Yao, M.; Li, T.; Huang, S.; Li, N. Enhancement and HF Doppler observations of sporadic-E during the solar eclipse of 22 July 2009. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2010, 115, A09325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernogor, L.F. Effects of solar eclipses in the ionosphere: Results of Doppler sounding: 1. Experimental data. Geomagn. Aeron. 2012, 52, 768–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manju, G.; Sridharan, R.; Ravindran, S.; Madhav Haridas, M.K.; Pant, T.K.; Sreelatha, P.; Mohan Kumar, S.V. Rocket borne in-situ Electron density and Neutral Wind measurements in the equatorial ionosphere—Results from the January 2010 annular solar eclipse campaign from India. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2012, 86, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hairston, M.R.; Mrak, S.; Coley, W.R.; Burrell, A.; Holt, B.; Perdue, M.; Depew, M.; Power, R. Topside Ionospheric Electron Temperature Observations of the 21 August 2017 Eclipse by DMSP Spacecraft. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 7242–7247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdés-Abreu, J.C.; Díaz, M.; Bravo, M.; Stable-Sánchez, Y. IonosphericTotal Electron Content Changes during the 15 February 2018 and 30 April 2022 Solar Eclipses over South America and Antarctica. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacPherson, B.; González, S.A.; Sulzer, M.P.; Bailey, G.J.; Djuth, F.; Rodriguez, P. Measurements of the topside ionosphere over Arecibo during the total solar eclipse of February 26, 1998. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2000, 105, 23055–23067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncharenko, L.P.; Erickson, P.J.; Zhang, S.-R.; Galkin, I.; Coster, A.J.; Jonah, O.F. Ionospheric Response to the Solar Eclipse of 21 August 2017 in Millstone Hill (42N) Observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 4601–4609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domnin, I.F.; Yemel’yanov, L.Y.; Kotov, D.V.; Lyashenko, M.V.; Chernogor, L.F. Solar eclipse of August 1, 2008, above Kharkov: 1. Results of incoherent scatter observations. Geomagn. Aeron. 2013, 53, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aa, E.; Zhang, S.-R.; Erickson, P.J.; Wang, W.; Coster, A.J. 3-D Ionospheric Electron Density Variations during the 2017 Great American Solar Eclipse: A Revisit. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afraimovich, E.L.; Palamartchouk, K.S.; Perevalova, N.P.; Chernukhov, V.V.; Lukhnev, A.V.; Zalutsky, V.T. Ionospheric effects of the solar eclipse of March 9, 1997, as deduced from GPS data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1998, 25, 465–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, L.W.; Ephishov, I.I.; Shagimuratov, I.I.; Ivanov, V.P.; Lagovsky, A.F. The response of the ionospheric total electron content to the solar eclipse on August 11, 1999. Adv. Space Res. 2003, 31, 989–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Wan, W.; Ning, B.; Liu, L.; Le, H.; Xu, G.; Wang, M.; Li, G.; Chen, Y.; Ren, Z.; et al. GPS TEC response to the 22 July 2009 total solar eclipse in East Asia. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2010, 115, A07308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherniak, I.; Zakharenkova, I. Ionospheric Total Electron Content Response to the Great American Solar Eclipse of 21 August 2017. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 1199–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şentürk, E.; Arqim Adil, M.; Saqib, M. Ionospheric total electron content response to annular solar eclipse on June 21, 2020. Adv. Space Res. 2021, 67, 1937–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernogor, L.F.; Mylovanov, Y.B.; Zhdanko, Y.H. Response of total electron content to the 25 October 2022 partial solar eclipse from high to low latitudes in the Euro-Asian region. Adv. Space Res. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, C.; Dang, T.; Yao, Y.; Kong, J.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, X. Three-Dimensional Ionospheric Evolution and Asymmetry of the Electron Density Depletion Generated by the 21 June 2020 Annular Solar Eclipse. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2023, 128, e2023JA031725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aa, E.; Coster, A.J.; Zhang, S.-R.; Vierinen, J.; Erickson, P.J.; Goncharenko, L.P.; Rideout, W. 2-D Total Electron Content and 3-D Ionospheric Electron Density Variations during the 14 October 2023 Annular Solar Eclipse. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2024, 129, e2024JA032447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Heki, K.; Wu, L. Three-Dimensional and Trans-Hemispheric Changes in Ionospheric Electron Density Caused by the Great Solar Eclipse in North America on 21 August 2017. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 10933–10940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Lin, C.C.H.; Lee, C.J.; Liu, J.Y.; Saito, A. Ionospheric responses on the 21 August 2017 solar eclipse by using three-dimensional GNSS tomography. Earth Planets Space 2022, 74, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-Y.; Liu, J.-Y.; Lin, C.C.; Chou, M.-Y. The Ionospheric Three-Dimensional Electron Density Variations Induced by the 21 August 2017 Total Solar Eclipse by Using Global Ionospheric Specification. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Wang, J.; Reinisch, B.W.; Li, Y.; Gong, W. Disturbances in Sporadic-E during the Great Solar Eclipse of August 21, 2017. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2021, 126, e2020JA028986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.-R.; Erickson, P.J.; Vierinen, J.; Aa, E.; Rideout, W.; Coster, A.J.; Goncharenko, L.P. Conjugate Ionospheric Perturbation During the 2017 Solar Eclipse. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2021, 126, e2020JA028531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rideout, W.; Coster, A. Automated GPS processing for global total electron content data. GPS Solut. 2006, 10, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinisch, B.W.; Galkin, I.A. Global Ionospheric Radio Observatory (GIRO). Earth Planets Space 2011, 63, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heelis, R.A.; Stoneback, R.A.; Perdue, M.D.; Depew, M.D.; Morgan, W.A.; Mankey, M.W.; Lippincott, C.R.; Harmon, L.L.; Holt, B.J. Ion Velocity Measurements for the Ionospheric Connections Explorer. Space Sci. Rev. 2017, 212, 615–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreiner, W.S.; Weiss, J.P.; Anthes, R.A.; Braun, J.; Chu, V.; Fong, J.; Hunt, D.; Kuo, Y.H.; Meehan, T.; Serafino, W.; et al. COSMIC-2 Radio Occultation Constellation: First Results. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2019GL086841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friis-Christensen, E.; Lühr, H.; Knudsen, D.; Haagmans, R. Swarm—An Earth Observation Mission investigating Geospace. Adv. Space Res. 2008, 41, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomidze, L.; Knudsen, D.J.; Burchill, J.; Kouznetsov, A.; Buchert, S.C. Calibration and Validation of Swarm Plasma Densities and Electron Temperatures Using Ground-Based Radars and Satellite Radio Occultation Measurements. Radio Sci. 2018, 53, 15–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y. Study on Theories and Methods of Correcting Ionospheric Delay and Monitoring Ionosphere Based on GPS. Ph.D. Thesis, Institute of Geodesy and Geophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Wuhan, China, 2002. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Feng, J.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Meng, D. Analysis of Ionospheric Anomalies before the Tonga Volcanic Eruption on 15 January 2022. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Wang, N.; Li, Z.; Huo, X. The BeiDou global broadcast ionospheric delay correction model (BDGIM) and its preliminary performance evaluation results. NAVIGATION 2019, 66, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Ridley, A.J.; Goncharenko, L.; Chen, G. GITM-Data Comparisons of the Depletion and Enhancement during the 2017 Solar Eclipse. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 3319–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, H.; Liu, L.; Ren, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, H. Effects of the 21 June 2020 Solar Eclipse on Conjugate Hemispheres: A Modeling Study. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2020, 125, e2020JA028344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, R.K.; St.-Maurice, J.P.; Ambili, K.M.; Sunda, S.; Pathan, B.M. The impact of the 15 January 2010, annular solar eclipse on the equatorial and low latitude ionospheric densities. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).