Abstract
Detecting oriented small objects is a critical task in remote sensing, but the development of high-performance deep learning-based detectors is hindered by the need for large-scale and well-annotated datasets. The high cost of creating these datasets, due to the dense and numerous distribution of small objects, significantly limits the application and development of such detectors. To address this problem, we propose a single-point-based annotation approach (SPA) based on the graph cut method. In this framework, user annotations act as the origin of positive sample points, and a similarity matrix, computed from feature maps extracted by deep learning networks, facilitates an intuitive and efficient annotation process for building graph elements. Utilizing the Maximum Flow algorithm, SPA derives positive sample regions from these points and generates oriented bounding boxes (OBBOXs). Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of SPA, with at least a 50% improvement in annotation efficiency. Furthermore, the intersection-over-union (IoU) metric of our OBBOX is 3.6% higher than existing methods such as the “Segment Anything Model”. When applied in training, the model annotated with SPA shows a 4.7% higher mean average precision (mAP) compared to models using traditional annotation methods. These results confirm the technical advantages and practical impact of SPA in advancing small object detection in remote sensing.
1. Introduction
With the advancement in the resolution of remote sensing imagery, the effective detection and recognition of small objects have emerged as pivotal areas of research [1]. These small objects, the sizes of which fall below pixels, play a crucial role in diverse applications such as maritime safety, traffic monitoring, and urban planning [2,3]. Among machine learning methods, deep learning-based methods have witnessed promising performance in oriented small object detection [4], with enormous delicate annotated samples for weight optimization.
Different from general scenes, images in remote sensing are often taken in bird-eye perspective, demanding consideration of object orientation. The conventional horizontal bounding box approach may overlap more background region around small objects, causing erroneous detection. This motivates the adoption of an oriented bounding box (OBBOX) generated from the segmentation results of SAM (Segment Anything Model), denoted as . However, OBBOX annotations requires more precision in terms of angle and positioning, resulting in considerable challenges in terms of annotation effort, time, and cost [5,6,7]. As a result, the annotation cost of an OBBOX may be far higher than HBBOX [8]. Moreover, identifying small objects may encounter several obstacles including the low-quality visible features, low signal-to-noise ratios, and insufficient contrast between the targets and their backgrounds [9]. Additionally, identifying small objects in remote sensing imagery faces obstacles such as low-quality visible features, low signal-to-noise ratios, and insufficient contrast between targets and their backgrounds. These challenges make it imperative to explore accurate, automated, and semi-automated annotation methods for oriented small objects. Consequently, it is imperative to explore methodologies for their accurate, automated, and semi-automated annotation methods of oriented small objects, to enhance the utility of remote sensing data.
To alleviate the annotation burden of oriented small objects, we propose an innovative single-point-based annotation methodology, termed SPA. SPA relies on a single-point annotation to indicate object locations. As seen in Figure 1, the position of the point is not specified, which is more flexible and could reduce the manual work significantly. Then, the scale and the orientation angle of an object are determined via the proposed graph-based segmentation method [10,11,12], and which integrate the knowledge from both high-dimensional semantic features and hand-crafted local features, enabling precise identification and annotation of small objects in remote sensing images.

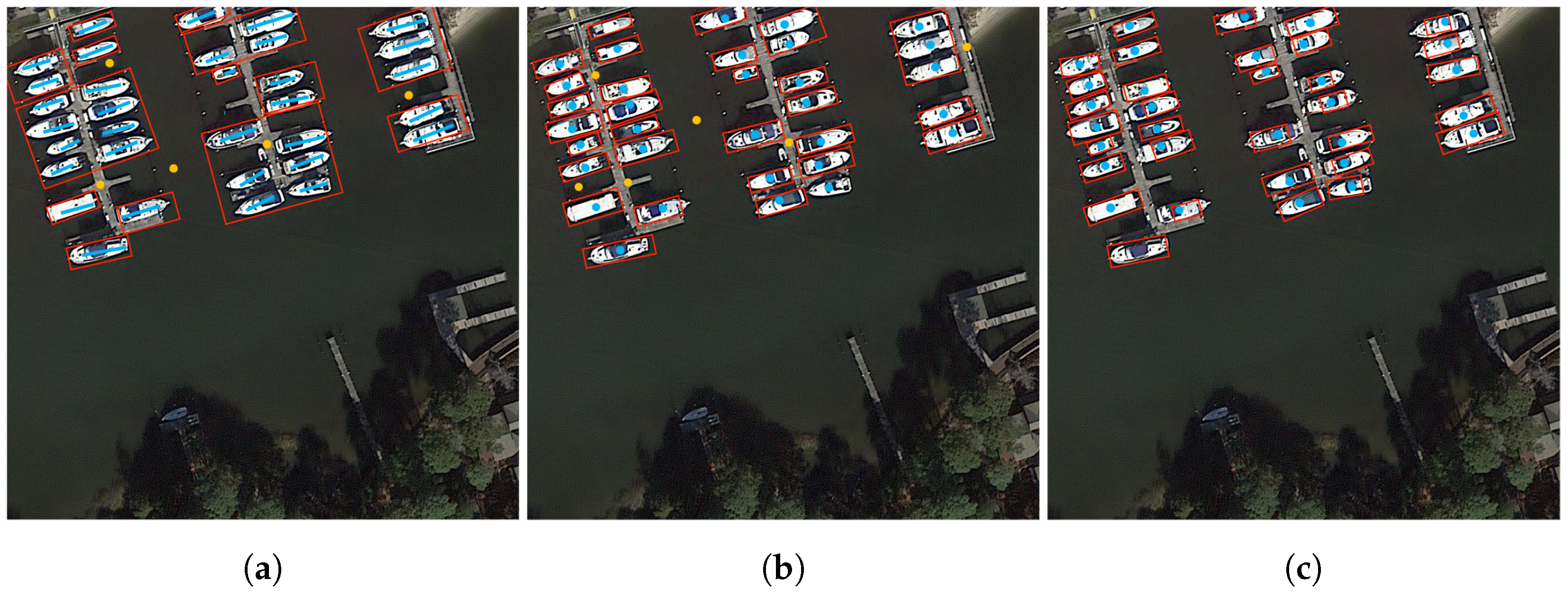
Figure 1.
Example of existing labeling methods. (a) The graph cut-based method, (b) SAM, and (c) the proposed SPA. Blue and orange dots indicate the positive and negative annotations, respectively. Red boxes indicate the generated bounding boxes. Notably, the proposed SPA approach requires only a single point as annotation, eliminating the need for additional negative annotations in the background region.
The primary innovations introduced in this study encompass:
- A small-scale graph building method: Building a graph with pixels as the nodes is computational and unreliable because of the large image scale and complex background information. Motivated by this, we propose a small-scale graph building method, where the edges and nodes are obtained from a feature map, extracted from a pretrained deep learning model. This technique affords a more precise characterization of the similarities and differences across various regions of the image, thus providing an enriched dataset for subsequent selection of the object area. The built graph will be applied to the max flow method for effectively predicting the object mask;
- An edge-guided mask refined module: The high-dimensional semantic features are robust to the background interference. However, local details are neglected by the convolution operation, causing the inaccurate prediction around the boundary region. Thus, we leverage the low-level features to refine those ambiguous pixels. More concretely, the boundaries are refined using edge detection [13,14] techniques. These enhancements not only bolster the precision of the annotations but also refine the annotation frame’s shape and positioning to mirror the actual target’s contours more accurately.
In summary, the main new ideas offered in this paper include the development of a small-scale graph building method and an edge-guided mask refined module. These innovations collectively enhance the precision and robustness of the annotation process for small and medium-sized targets in remote sensing images, addressing key challenges in the field.
The integration of deep learning feature analysis with edge detection significantly reduces the manual labor associated with annotations while simultaneously elevating the accuracy of the annotations, thereby optimizing both efficiency and efficacy in the object detection process.
2. Related Work
This section reviews previous research in three critical areas: semi-automatic annotation techniques, image segmentation algorithms, and feature extraction architectures, all of which hold significant relevance to the present experiments.
2.1. Semi-Automatic Annotation
In the realm of semi-automatic annotation [15,16,17], existing methodologies have demonstrated promising results across a range of applications. These techniques aim to reduce the manual effort, i.e., box annotation [18], line annotation [19,20], point annotation [21], and pixel annotation [22] required for annotation by leveraging a combination of human expertise and automated processes. Among these, SimpleClick [23] streamlines the annotation process by minimizing the number of clicks needed for precise object delineation, whereas FocalClick [24] focuses on refining annotations through a focus-driven approach that targets ambiguous or complex image regions. RITM [25] enhances the interaction between users and the annotation process by interpreting natural language references in conjunction with image cues. SAM [26] employs machine learning algorithms to predict object boundaries, allowing for rapid adjustments and refinements by the annotator. However, their efficacy in the field of remote sensing remains limited. The unique challenges presented by remote sensing data [27], including high variability and complex spatial relationships, necessitate the development of more tailored semi-automatic annotation approaches that can effectively handle these intricacies.
2.2. Image Segmentation
Regarding image segmentation, several algorithms have stood out for their ability to delineate distinct objects or regions within an image. Traditional methods, such as graph cut [28,29] and region growing algorithms [30,31], are particularly noteworthy. The graph cut approach models the segmentation problem as a graph partitioning task, where the goal is to divide a graph into disjoint sets while minimizing the cost of the cut. This method is effective in providing globally optimal solutions and has been successfully applied in various contexts. However, its performance can be limited by the computational complexity, especially when dealing with high-resolution remote sensing images. Additionally, the quality of the segmentation heavily depends on the accuracy of the initial seed points and the cost function used, which might not always align well with the diverse characteristics of remote sensing data. Region growing algorithms, on the other hand, start with a seed point and iteratively add neighboring pixels to the region based on predefined criteria, such as color or intensity similarity. These algorithms are simple and effective for segmenting homogeneous regions. However, they often struggle with images that have significant noise or varying intensities, common in remote sensing applications. The need for manual selection of seed points and the sensitivity to initial conditions can also result in inconsistent segmentation results. While these traditional methods have been extensively applied due to their simplicity and effectiveness, they have notable limitations when applied to the complex and varied nature of remote sensing images. Therefore, there is a need for the development of tailored segmentation approaches that leverage the strengths of traditional methods while addressing their shortcomings to meet the specific demands of remote sensing.
2.3. Oriented Object Detection
Rotating target detection is essential in applications such as remote sensing imagery, medical imagery, and UAV imagery [32], where targets can appear at arbitrary angles. Early methods for rotating target detection relied on feature engineering and classical computer vision techniques like the Hough transform and template matching. However, these methods had limited effectiveness in dealing with complex backgrounds and variably shaped targets. With the advent of deep learning, CNNs [18] have become widely used for rotated target detection, achieving rotational invariance by designing rotated bounding boxes or oriented anchors. Popular detection frameworks like Faster R-CNN [18], YOLO [33], and SSD have been adapted to incorporate rotation angle prediction, enhancing their detection performance. Despite these advancements, several limitations persist when dealing with the specific challenges of remote sensing imagery. They often struggle with the small size and high density of objects typical in remote sensing images. For instance, Faster R-CNN, while effective in general object detection, can find it challenging to accurately detect small, densely packed objects due to its reliance on region proposal networks that may not be finely tuned for such tasks. YOLO and SSD, known for their real-time detection capabilities, can similarly face difficulties in maintaining high accuracy for small objects because their grid-based prediction approach may miss or inaccurately predict small targets, especially when these targets are highly rotated or occluded. While these deep learning-based methods have shown improved performance on datasets such as DOTA, HRSC2016, and UCAS-AOD, they still face significant challenges. Handling highly rotated targets, complex backgrounds, and target occlusion remains a critical issue. These limitations underscore the need for further research and the development of more robust and specialized approaches tailored to the unique demands of remote sensing imagery, where small and highly rotated objects are common.
2.4. Feature Extraction
Feature extraction is a crucial step in numerous computer vision and image analysis tasks, and a large number of network structures for feature extraction have emerged after the introduction of deep learning [34]. VGG [35], with its sequential architecture of convolutional layers followed by pooling layers, has been instrumental in the advancement of deep learning in image recognition. Its simplicity and depth are its main strengths, enabling the extraction of rich feature hierarchies. GoogLeNet [36], or Inception, introduced an innovative inception module, allowing the network to choose from multiple scales of convolutional filters within the same layer. This architecture significantly increases the depth and width of the network while maintaining computational efficiency. Alongside ResNet [37], which addresses the vanishing gradient problem [38,39] encountered in deep neural networks by introducing residual learning blocks, these architectures have collectively pushed the boundaries of feature extraction. ResNet, in particular, enables the training of substantially deeper networks, advancing the performance of feature extraction techniques. This has facilitated more accurate and robust image analysis across a wide array of applications [40], including those in remote sensing. The ability of ResNet to learn highly discriminative features makes it a cornerstone in the development of more sophisticated images. However, applying the extracted features to image tasks still presents certain challenges.
3. The Proposed Method
In this section, we detail the proposed single-point annotation (SPA) method. The process includes several critical stages: feature extraction, similarity matrix computation, small-scale graph construction, graph partitioning, edge correction, and the generation of labeled bounding boxes. Each stage is meticulously crafted to enhance the accuracy and efficiency of the labeling process, offering a thorough framework for small target labeling tasks.
3.1. Overview of the Methodology
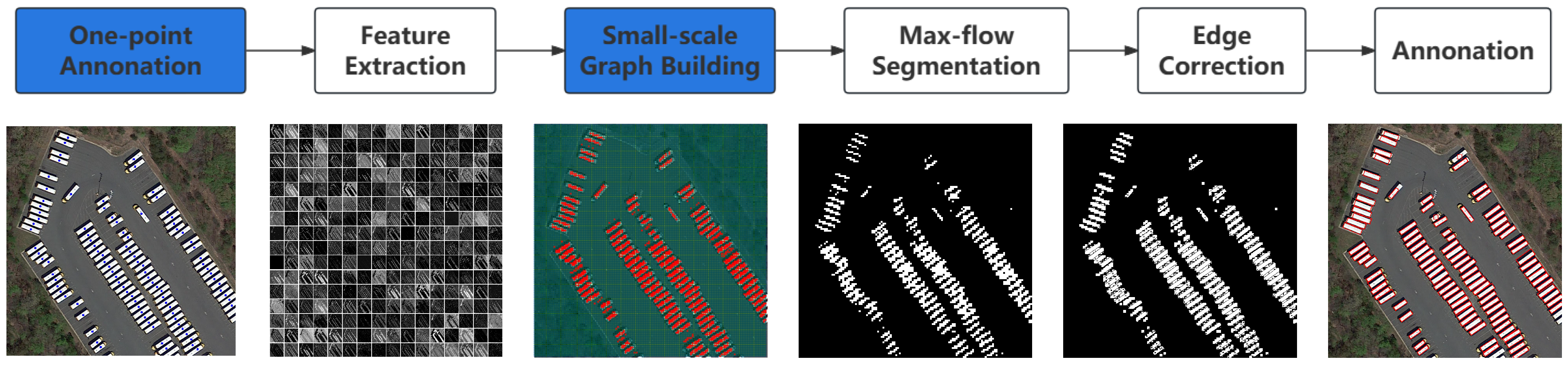
As depicted in Figure 2, our algorithm is specifically engineered to generate bounding box annotations for small objects within remote sensing images with high efficiency. In contrast to the costly manual labeling process, our method utilizes a cost-effective single-point labeling technique. The segmentation process operates unsupervised, effectively completing the annotation without requiring any training steps.
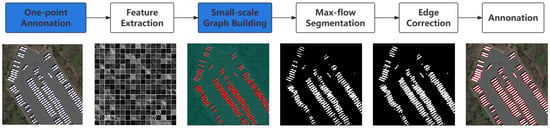
Figure 2.
The workflow of our proposed methodology incorporates two novel modules, prominently highlighted in blue, designed to enhance the efficiency of the annotation process. Initially, our approach simplifies the annotation task by utilizing a versatile single-point selection method, thereby circumventing the constraints imposed by rigid placement rules. Following this, we introduce an innovative method for calculating a similarity matrix, significantly boosting computational efficiency. This technique expeditiously computes the cosine distance between pixels in the feature map, facilitating the identification of positive sample regions crucial for graph-based segmentation. Consequently, this enables the precise determination of bounding boxes using sophisticated graph segmentation methods.
To mitigate the impact of low-dimensional features such as color on the positive sample region, the algorithm initiates by inputting the image into a deep neural network, specifically ResNet101. It then computes a similarity matrix on the extracted feature maps to identify the positive sample regions at the feature map scale. These regions are subsequently mapped back to the original image size using interpolation techniques. Notably, unlike traditional four-point labeling methods, our approach requires only a single click to label an object. This user-friendly solution demands less precision in labeling, as discussed in Section 3.2.
Remote sensing images are influenced by the complex geographical environment, varying light conditions, and occlusions. Low-dimension features like color and edges often prove insufficient for accurate remote sensing image object annotation. Given that the scale of remote sensing images usually exceeds 1000 pixels, computing positive sample points at the pixel level becomes computationally prohibitive. To address this, we reduce the number of nodes through feature extraction, obtaining positive sample regions at the size of the Layer_2 feature map, as outlined in Section 3.3.
Despite these advancements in reducing computational demands, processing nodes in extensive scenes remains a significant challenge. We propose a method of computing the similarity matrix based on matrix multiplication for the Layer_2 feature map, interpreting its channels as feature vectors for each pixel point. This approach calculates the similarity between every pair of pixels at the feature map scale through matrix multiplication, significantly reducing the time consumption compared to traditional region growing algorithms. After obtaining the positive sample points at the feature graph size, we perform graph construction and graph cutting at that scale. Working with a graph containing nodes significantly reduces the time required for these operations compared to a graph with the original nodes, as outlined in Section 3.4.
The feature graph is then mapped to the original graph size through interpolation. However, due to the use of nearest neighbor interpolation and the high density of targets in remote sensing images, the boundaries of the positive sample points shrink at the original graph size. To address this issue, edge detection is employed to refine and correct the boundaries, as demonstrated in Section 3.5. This approach ensures more accurate and clearly defined boundaries for the positive sample regions.The SPA algorithm is presented in Algorithm 1.
| Algorithm 1: The proposed SPA paradigm in Python style |
 |
3.2. One-Point Annotation
In the realm of remote sensing image annotation, traditional approaches such as multi-point localization and bounding box drawing often struggle to meet the rapid processing demands of extensive image datasets due to their inherent complexity and time-consuming nature. Addressing this challenge, our study introduces an innovative single-point annotation method designed to significantly enhance annotation efficiency by minimizing user interactions.
The fundamental concept behind the single-point annotation method is straightforward. The user is required to perform a solitary click at the salient central point of the target object. This single interaction point subsequently serves as the foundation for the algorithm to generate a precise bounding box. This method notably simplifies the annotation process compared to traditional techniques, substantially reducing operational complexity and markedly decreasing the likelihood of human errors during the annotation process.
3.3. Feature Extraction
Target annotation utilizing low-level information, such as color and edges from raw images, confronts numerous obstacles due to the intricate geographical landscapes, variable lighting conditions, and frequent occlusions characteristic of remote sensing imagery. Furthermore, considering the typical scale of remotely sensed images often exceeds 1000 pixels, conducting extensive analysis and processing directly at the pixel level would incur prohibitive computational costs. To navigate these challenges effectively, advanced feature representations are efficiently extracted using deep learning models, particularly through pretrained convolutional neural networks like ResNet101. These models adeptly capture a spectrum of information from basic textures and shapes to complex objects and scene-level details through successive layers of nonlinear transformations.
Our research particularly concentrates on the output from the Layer_2 layer of the ResNet101 model, chosen for its critical attributes in feature extraction:
- Maintenance of spatial resolution: Post its initial convolution and pooling operations, the Layer_2 layer preserves substantial spatial resolution, enabling the model to retain image details while extracting potent feature information;
- Integration of complex features: This layer marks the beginning of amalgamating more sophisticated visual data, significantly aiding in the identification of specific targets against complex backgrounds.
Remote sensing images undergo a preliminary normalization process and are resized to a consistent dimension of pixels. Subsequently, these images are fed into the ResNet101 model. Through forward propagation, the data reach the Layer_2 layer, where the output feature map provides a distinct feature vector for each pixel point. These vectors encapsulate the essential visual information extracted from the image, offering invaluable insights for further analytical tasks.
3.4. Small-Scale Graph Building
While constructing the graph at the original graph size undoubtedly involves significant computation, we can obtain nodes and edges from the extracted feature graph and build the graph at the feature graph size when high-dimensional features are available. We use the similarity matrix computation to identify nodes and edges from the feature graph, enabling us to construct the graph at that level.
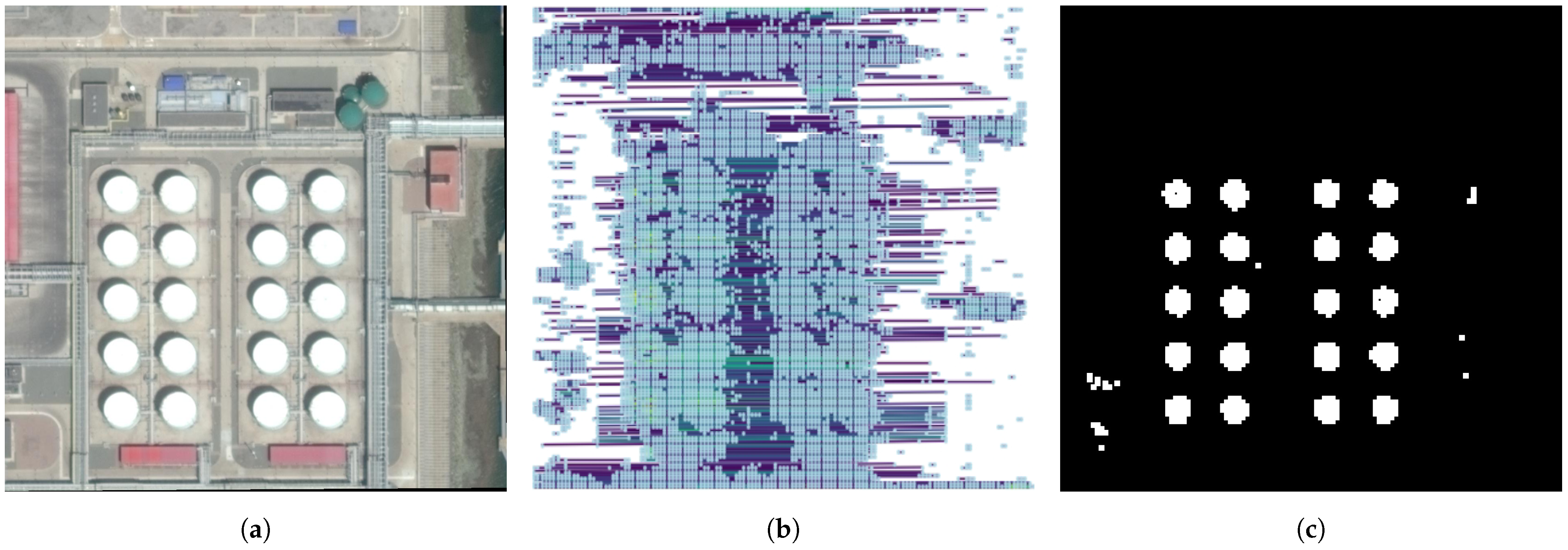
To enhance the processing of the obtained feature map and facilitate effective target detection and segmentation in remote sensing imagery, we introduce the computation of a similarity matrix. This matrix serves as a crucial data structure, conceptualized as a connected graph, represented in Figure 3, where each edge quantifies the cosine similarity [41] between the pixel feature vectors of the image [42]. Such a formulation lays the groundwork for graph-based segmentation techniques.
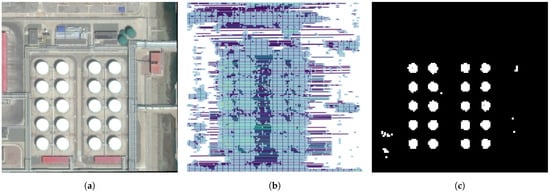
Figure 3.
Visualization of the similarity matrix and resulting mask. (a) is the picture to be annotated. In (b), the similarity matrix at the feature map scale is visualized, where varying colors represent different degrees of similarity between nodes, highlighting the varying relationships within the data. As shown in (b), the mask derived from the similarity matrix is shown, effectively segmenting the areas of interest based on the computed similarities. This illustrates the practical application of the similarity matrix in identifying and isolating target regions within the image. And we can see the mask in (c).
Normalization is employed on the feature vectors extracted from the remote sensing images to prepare them for similarity calculations:
where f is the feature vector at a pixel location on the feature map before normalization and is the feature vector after normalization, this conversion helps in the calculation of cosine similarity. This step is imperative as it standardizes the feature vectors, ensuring they adhere to a uniform norm. By doing so, it enhances the precision of the similarity measurements, providing a reliable basis for subsequent analytical operations. This normalization process not only aligns the data but also significantly bolsters the accuracy and effectiveness of the similarity matrix in capturing and reflecting the intrinsic similarities across the image features.
Following the normalization process, the feature map is transformed into matrix form, where each row corresponds to the feature vector of an individual pixel. This transformation is achieved by reshaping the feature map tensor, flattening the features from each channel into a one-dimensional array. This arrangement facilitates straightforward computation of pairwise interactions between features.
Subsequently, the similarity matrix is computed. Each element of this matrix quantifies the cosine similarity between feature vectors i and j. The cosine similarity is derived from the dot product of the feature vectors, normalized by their magnitudes. This measure effectively captures the directional alignment between any two feature vectors, providing a robust basis for identifying similar features across the image.
The computation of cosine similarity is mathematically represented as follows:
where and are feature vectors of a pixel point on the feature map. This formula ensures that the similarity scores range from —1 to 1, where a score of 1 denotes perfect alignment, 0 denotes orthogonality, and —1 indicates diametric opposition. This scaling is crucial for accurately assessing the alignment of feature vectors, facilitating a nuanced comparison. Such precise measurement of cosine similarity provides a robust framework for analyzing spatial relationships and patterns across varied landscapes.
Using the feature matrix, we begin with user-provided single-point annotations as the starting point. By comparing similarities, we extract positive sample points at the feature graph scale () and construct a graph at this scale. This reduced graph size significantly lowers the computational complexity compared to working at the original scale (). Each node represents a pixel on the feature graph, and the edge weights are determined by the similarity and adjacency between pixels. The weight magnitude reflects the connectivity and correlation between nodes, giving higher weights to pixels with similar values.
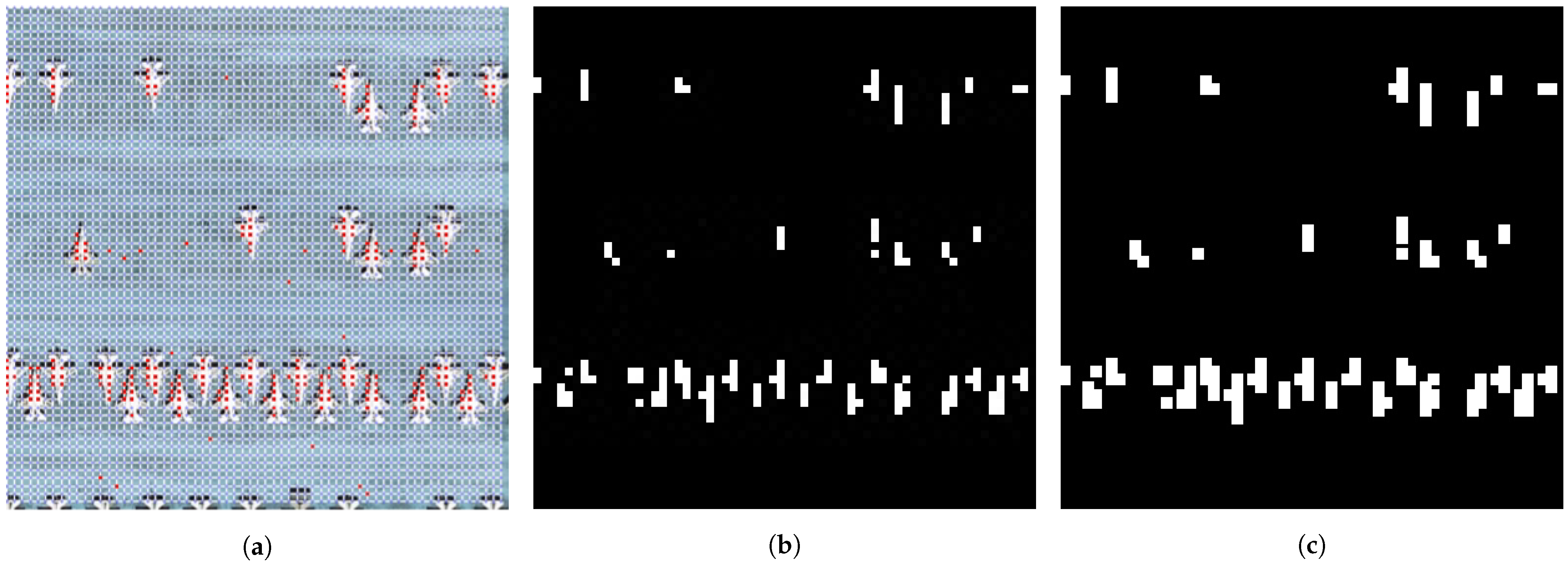
After constructing the graph like Figure 4, we apply the graph cut algorithm, which leverages the maximum flow [43] theory to divide the graph into foreground and background regions. Each node is assigned to the appropriate region, and the algorithm optimizes the segmentation by maximizing the edge weights between the two regions, thus minimizing variability within each internal node group. This approach ensures precise target segmentation, ultimately yielding an accurate positive sample region at the feature graph size.
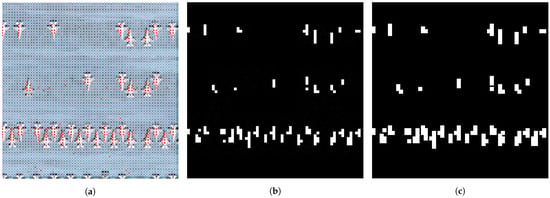
Figure 4.
Graph constructed using graph cut. (a) shows positive sample regions highlighted in red, while all other nodes represent negative sample points. (b) shows the mask obtained by graph cut using the positive sample points at the feature map size; (c) is the mask mapped to the original map size.
3.5. Edge Correction
After identifying the positive sample region within the feature map dimensions, we interpolate it to the original map size. However, nearest neighbor interpolation, combined with the high density of targets in remotely sensed images, often causes the positive sample boundaries to shrink when mapped to the original size. To address this issue, we refine these boundaries using edge detection.
In particular, we employ the Canny operator [44] to accurately identify target boundaries at higher resolutions, thus preventing blurring or misalignment caused by interpolation [45]. The initial step involves applying the Canny edge detector to the original image to identify prominent edges. Once the edges are detected, they are refined using morphological closing [46,47] with a kernel, which closes small gaps and ensures the edges are continuous. The refined edge image is then inverted to create a mask.
The positive sample regions, now scaled to the original map size, are combined with the results of the inverted edge mask to ensure accurate and distinct boundaries in the final image, as shown in Figure 5. This approach corrects and optimizes the positive sample boundaries, providing a more accurate representation of the targets. By incorporating edge detection into the process, we improve the localization of the positive samples, offering clearer separation between the targets and the surrounding environment, which is crucial for subsequent analysis and classification tasks.
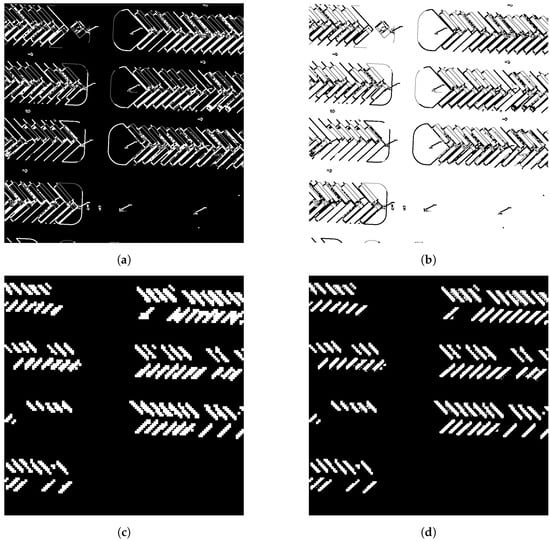
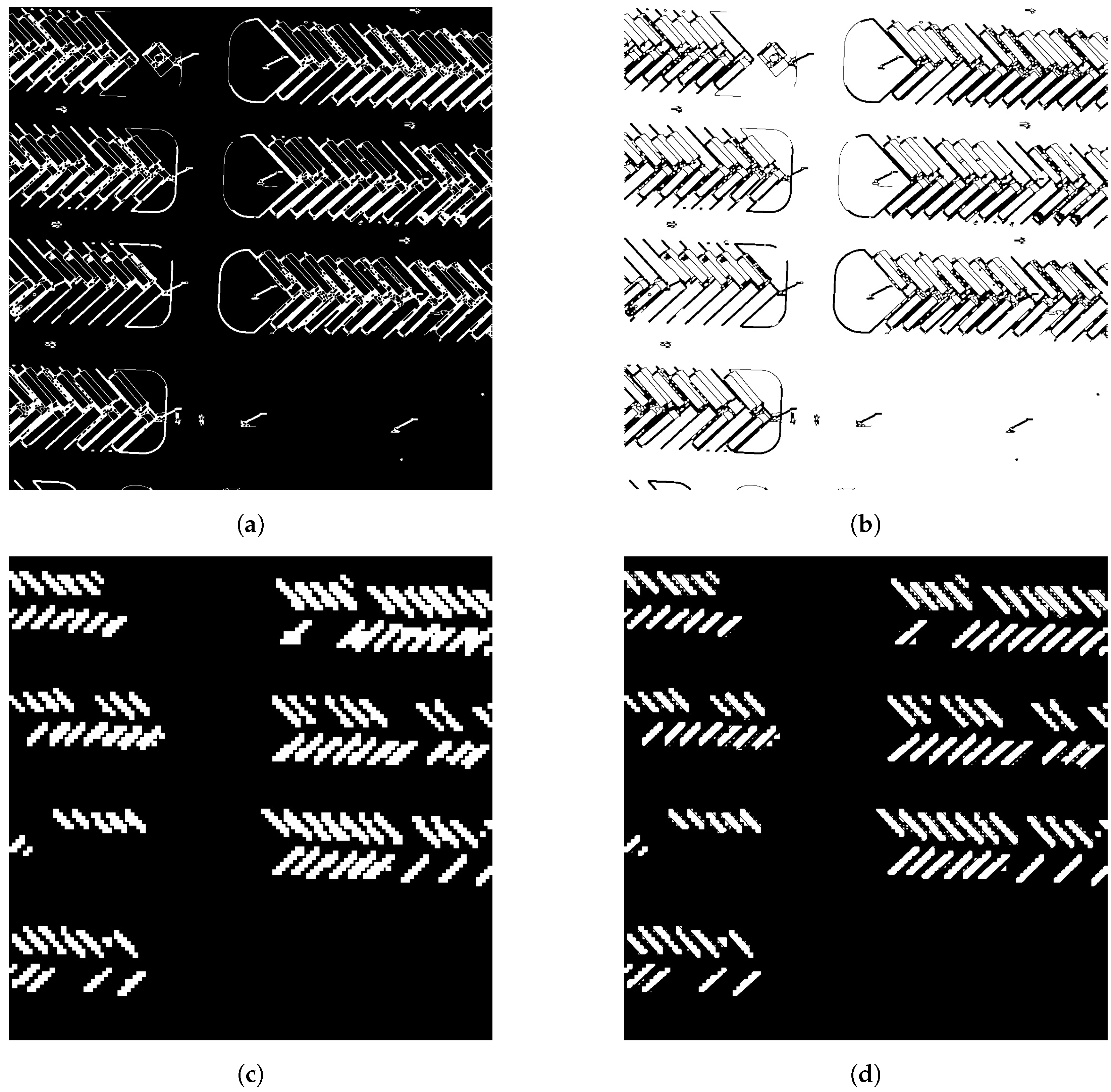
Figure 5.
Positive sample region refinement using edge detection. (a) Extracted edge features show the detected boundaries around the targets, highlighting the essential edges within the region of interest. (b) The inverted mask, based on these detected edge features, isolates the relevant target areas by creating a negative image that can effectively differentiate target regions from the background. (c) The positive sample region without edge detection displays a less accurate boundary, often resulting in blurred or misaligned target edges due to interpolation. (d) The positive sample region incorporating edge detection demonstrates refined and accurate boundaries, significantly improving the localization of positive samples.
4. Experimental Results
4.1. Datasets
DOTA-v1.5: DOTA-v1.5 [48] represents a significant enhancement of the widely used DOTA-v1.0 [48] aerial imagery target detection dataset. This updated dataset retains the image collection from DOTA-v1.0 but extends annotations to include extremely small instances (less than 10 pixels), thereby augmenting the model’s capabilities in detecting small-sized targets. Additionally, DOTA-v1.5 introduces a novel category, “Container Crane”, expanding the dataset to encompass 16 common categories of aerial imagery targets. This version comprises 2806 images and 403,318 instances, maintaining the original dataset’s structure with the training, validation, and test sets proportioned at 1/2, 1/6, and 1/3, respectively. These meticulous annotations and the broadening of categories furnish a valuable asset for research into the automated parsing and detection of targets in aerial imagery.
The experimental procedure initiates by segmenting the DOTA-v1.5 dataset into 1024 × 1024 pixel blocks. This segmentation facilitates a reduction in computational complexity and enhances the efficiency of the target detection algorithms, making it a critical preparatory step in handling high-resolution aerial images effectively.
4.2. Evaluation Metrics
IoU (Intersection over Union): Intersection over Union is a pivotal metric in object detection that quantifies the overlap between predicted and actual bounding boxes. It is calculated by dividing the area of intersection between the predicted and the actual box by the area of their union. IoU values span from 0, indicating no overlap, to 1, indicating perfect congruence. Typically, an IoU threshold of 0.5 is employed, whereby predictions with IoU ≥ 0.5 are deemed accurate.
mAP (Mean Average Precision): mAP is a crucial metric for assessing the comprehensive performance of object detection models, particularly in scenarios involving multiple categories. It involves computing the Average Precision (AP) for each category and then averaging these values across all categories. Here, it is essential to note that an IoU threshold (typically set at 0.5) is considered, and a detection is considered correct only when the predicted bounding box’s IoU value with the actual bounding box exceeds this threshold [48,49]. The AP for each category is derived from the area under the precision–recall (PR) curve across varying recall levels. Averaging the AP values of all the categories yields the mAP value, providing a comprehensive assessment that reflects the detection’s precision based on IoU and the confidence ranking of each detected object.
Time: Time gauges the efficiency of object detection models, encapsulating the duration required to complete a prediction. This metric accounts for the cumulative time across all processing stages, including image manipulation, feature extraction, and bounding box prediction.
4.3. Ablation Study
In this paper, we conducted a series of ablation experiments to rigorously assess the significance and function of each component within the model algorithm presented in Figure 6. Our focus was on evaluating the impact of edge detection and feature extraction layers on model performance, as detailed in Table 1. By toggling edge detection functionality, we were able to observe changes in model behavior across different layers. For instance, with edge detection enabled, Layer_2 achieved an IoU of 63.98% compared to 50.39% when disabled. Similar trends were evident in other layers, such as Layer_3 and Layer_4, reinforcing the critical role of edge detection in maintaining high performance.
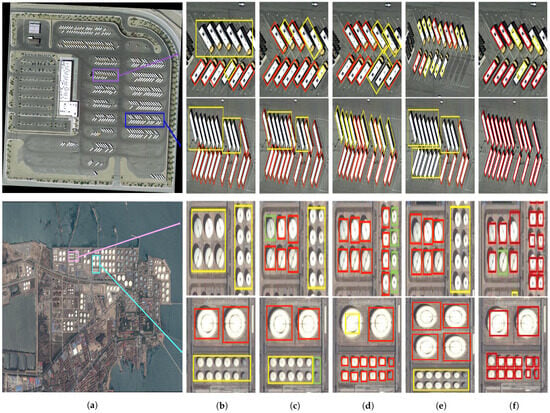
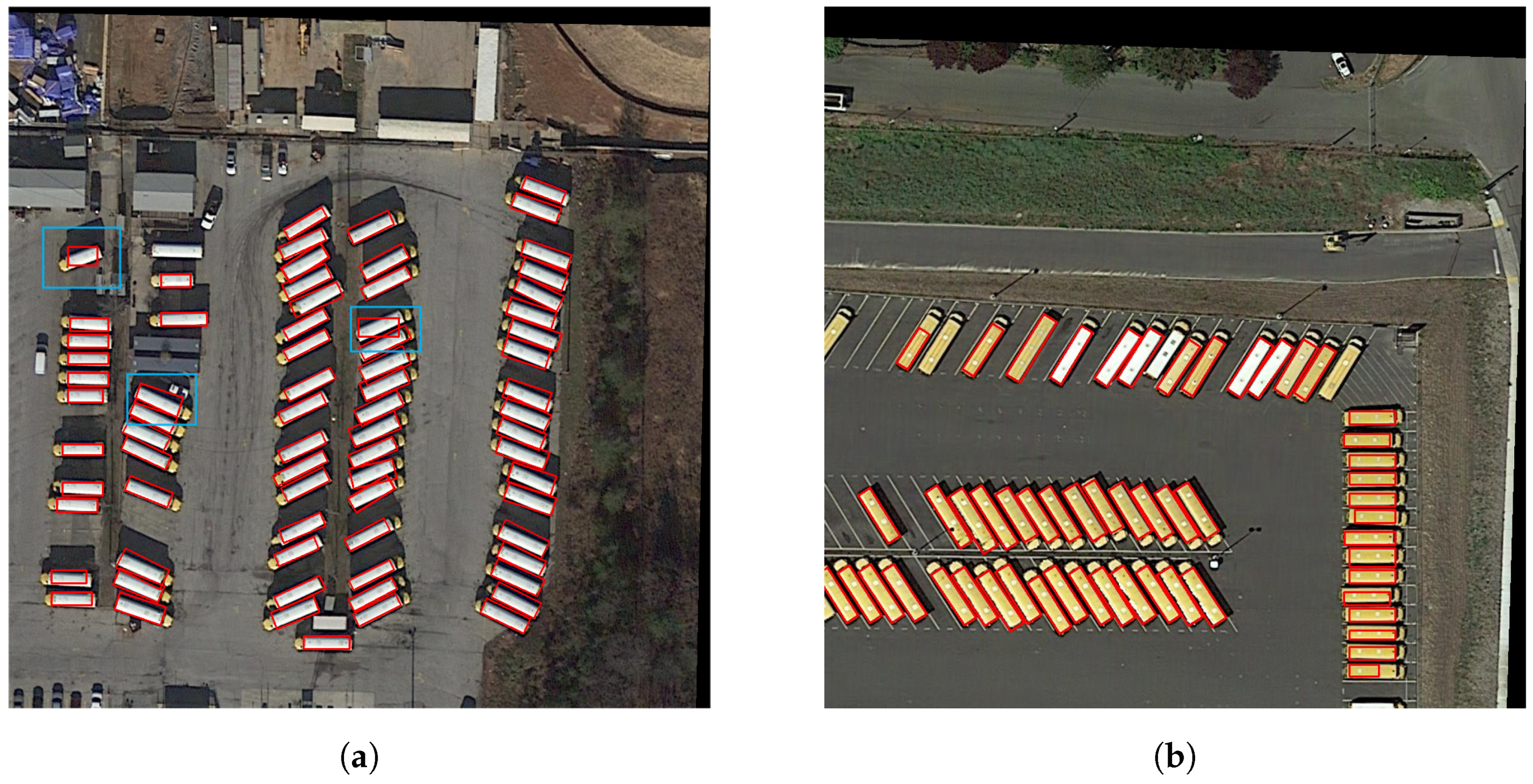
Figure 6.
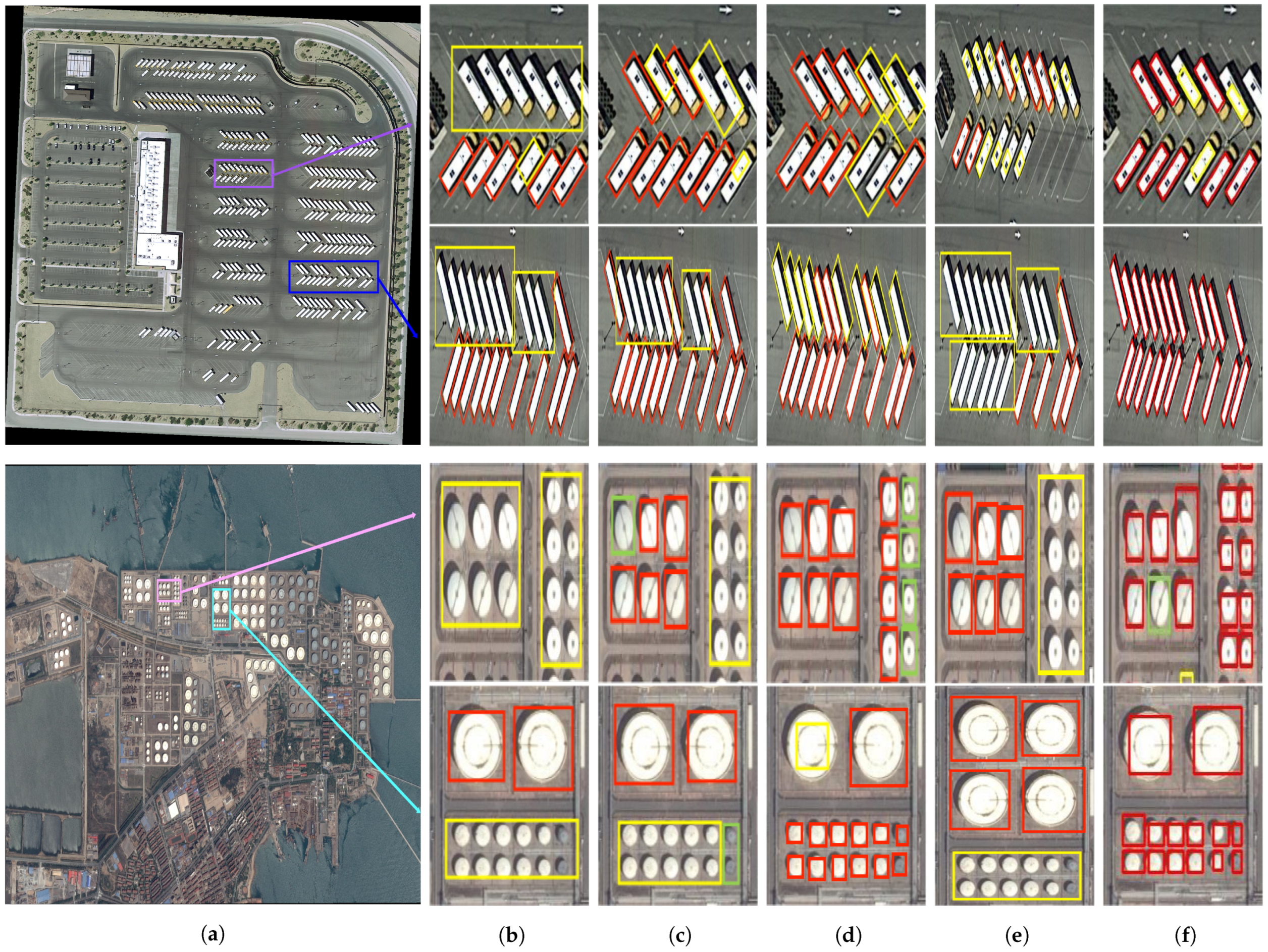
Visualization of (a) origin picture to be annotated, (b) the vanilla graph cut, (c) lazy snapping, (d) SAM, (e) PNL, and (f) SPA results, respectively. The original positions of the annotated regions are marked in orange, blue, pink, and light blue, respectively. Boxes for erroneous annotations are highlighted in yellow, while true positive examples (IoU > 0.75) annotations are labeled in red, and missed objects are labeled with green boxes. Occlusion and blurring are the two main challenges in annotating small objects. Graph cut and lazy snapping may not be able to annotate dense small objects, which may combine multiple objects into a single OBBOX. SAM annotation is more accurate, but interference from object blurring and shading leads to large annotation boxes. PNL using a radius of 1 for labeling points does not work well in our application scenario. In contrast, the proposed algorithm is more robust with respect to occlusion and blurring and can generate more accurate boxes.

Table 1.
Impact of edge detection and feature extraction layers on model performance.
Moreover, by varying feature extraction layers, we observed distinct differences in model behavior based on changes in feature size and similarity matrix dimensions. This provided a comprehensive understanding of the relative importance of each layer. These systematic evaluations highlight the significance of each component, guiding future optimization efforts to enhance the model’s accuracy and robustness.
4.3.1. Feature Extraction
To explore the influence of varying depths of feature extraction on model performance, we conducted a series of experiments examining three distinct layers—layer2, layer3, and layer4—within a uniform evaluation framework. These layers were selected to probe the disparities in feature representations between shallower and deeper network levels. The findings, as detailed in Table 1, underscore that the selection of the feature extraction layer markedly impacts model performance. This performance can be enhanced by strategically choosing the optimal layer for feature extraction. Among the layers tested, Layer_2 yielded the most effective results. Although the feature matrix for Layer_2 is more substantial, the extraction time remains competitively slow—only marginally higher by less than one second compared to the other layers—and it achieves an Intersection over Union (IoU) that is approximately 20% greater than that of its counterparts. This demonstrates a balanced trade-off between computational efficiency and performance efficacy, highlighting the practical advantages of selecting Layer_2 for robust feature extraction.
4.3.2. Edge Detection
In scenarios demanding high-precision edge detection, implementing edge detection techniques proves to be a highly effective strategy. For our experiments, we employed the Canny edge detection algorithm to delineate the jagged regions of the mask. As documented in Table 1, the integration of edge detection significantly enhances the Intersection-over-Union (IoU) metrics of the models. Specifically, models equipped with edge detection demonstrated an approximate 10% increase in average IoU, underscoring the technology’s capability to enhance the model’s accuracy in identifying and pinpointing object boundaries within images. Regarding the time overhead, the introduction of edge detection incurred a marginal increase in processing time—about 0.1 s on average. Given the notable improvement in IoU, this minor increment in processing duration is justified and considered a reasonable trade-off for the gained accuracy.
4.4. Time Consumption
SPA comprises five primary components: edge detection, feature extraction, similarity matrix computation, graph construction, and graph segmentation followed by bounding box generation. Due to the extensive time required for point labeling on a large set of images, we employ a streamlined method that minimizes human intervention to simulate the manual labeling process. Utilizing the DOTA-v1.5 dataset, which provides annotations in the format , this paper calculates the center point of the annotation box to facilitate an automated and efficient labeling framework:
To simulate real-world labeling errors and enhance the robustness of the model to noise, we introduce a random offset to the centroids of the bounding boxes. This offset represents the random noise typically encountered during the manual labeling process. Specifically, after calculating the centroid of each bounding box, we apply a random translation within the 8-connected neighborhood. This simulation reflects the minor inaccuracies that can occur during manual labeling, resulting in new coordinates for each centroid:
To evaluate the efficiency of our method, we measured the runtime for each component after applying the random offsets to the centroids of the bounding boxes, as obtained from the annotations. The results are detailed in Table 2.

Table 2.
Execution times of different components of the proposed method.
As indicated in the table, the computation of the similarity matrix is the most time-consuming component, constituting the majority of the overall processing time. This phase is critical within the context of our image segmentation algorithm. During this stage, the algorithm meticulously evaluates and quantifies the similarity between each pair of pixels across the entire image. The remainder of the processing time is predominantly dedicated to tasks such as image reading and preprocessing.
4.5. Comparison of Annotation Cost in Practice
The proposed SPA method works to reduce the cost of manual annotation, and that benefit is demonstrated in the following experiments.
We extracted 20 images from the DOTA-v1.5, ensuring that they included samples from all categories. The number of objects per image was approximately equal to the average number of objects in the entire DOTA-v1.5. To ensure the professionalism of the experiment, we invited five volunteers with annotation-related experience to participate.
In the manual annotation, the five participants used the labelme tool to annotate 20 images with rotated boxes. The annotation time for each participant was recorded for comparative analysis. Initially, the subjects manually labeled single points using the labelme tool and then input the labeled data into the algorithm to generate the corresponding directional annotations. The time required for the algorithm to run was also recorded. The total time cost of the SPA method was calculated by adding the manual labeling time and the time for automatically generating OBBOX annotations. To minimize errors due to unforeseen incidents, the experiment was repeated twice.
Single-point annotation significantly reduces the time required for the annotation process. Our study demonstrates that SPA achieves a time improvement of approximately 70% compared to the traditional four-point annotation method. As shown in Table 3, PNL, which utilizes single-point annotation, also demonstrates certain advantages in terms of annotation cost. Single-point annotation proves to be an effective method for reducing annotation cost. The proposed SPA leverages this approach and achieves remarkable results. By capitalizing on the efficiency of single-point annotation, SPA not only reduces the time required for the annotation process but also enhances overall productivity, making it a highly effective solution in the field of data annotation.This substantial efficiency gain is evident in Table 3, where it is clear that the time required for SPA is markedly shorter than that of both the SAM and PNL methods. These findings underscore the effectiveness of SPA in streamlining the annotation process, providing a compelling advantage over conventional techniques.

Table 3.
Annotation cost(s) of 5 annotators on the DOTA-v1.5 dataset. The symbol “↑” indicates the ratio of cost saving compared with existing four-point annotation work.
4.6. Evaluation of Annotation Effectiveness
To evaluate the annotation effectiveness of SPA in practical scenarios, we conducted a comprehensive analysis by comparing IoUs between the predictive annotations generated by our algorithm and GT (Ground Truth). We selected 65 representative images for our evaluation. These images were employed to create single-point annotations, which were subsequently input into our algorithm for further image segmentation and annotation processes. This method allows us to gauge the accuracy and consistency of our annotations.
Subsequently, we benchmark our method against traditional interactive segmentation techniques, especially the improved graph cut and lazy snapping method. In addition, we introduce the latest interactive segmentation method called SAM and latest point annotation method PNL [50] to demonstrate the competitiveness of our methods. To tailor these techniques for the segmentation of small objects within remote sensing imagery, we have implemented necessary adjustments and optimizations.
- In addition to positive annotations, techniques such as graph cut and lazy snapping necessitate negative annotations to effectively distinguish between target and non-target regions. Therefore, areas designated as negative are maintained throughout the segmentation process until all positive instances have been accurately identified. This dual-annotation strategy ensures a comprehensive and precise segmentation, facilitating the distinction between areas of interest and the surrounding background.
- Each object is marked with a single-point annotation, and the corresponding object region is automatically segmented using SAM. As highlighted in the RSPrompter [51] study, additional bounding box annotations are essential for remote sensing applications. However, in this context, SAM is employed primarily as an annotation tool rather than a traditional segmentation model. Therefore, no fine-tuning of the model is undertaken, emphasizing its role in simplifying the annotation process without the need for extensive model adjustments.
From the data presented, as shown in Table 3, the IoU of our proposed method achieves 64.0%, surpassing the performance of traditional segmentation approaches. Specifically, our method exceeds the graph cut method by approximately 21.9%, lazy snapping [52] by about 8.2%, SAM [26] by 3.6%, and PNL [50] by 14.2%. In the realm of object detection, an IoU greater than 50% is considered a positive sample, indicating that the annotations generated by our method are sufficiently accurate to be used as training labels for object detectors. This comparative analysis demonstrates the effectiveness of our approach, highlighting its superior accuracy in generating annotations when compared to established techniques.Our method extracts high-dimensional features through a deep learning network, making the annotation information more accurate and stable. Additionally, it employs edge correction to adjust the mask, thereby improving its coverage accuracy.
The graph cut method utilizes low-dimensional information to construct the graph structure required for segmentation. However, this approach may struggle to accurately capture the edge details of small objects, potentially leading to inaccuracies, particularly in cases of densely distributed small objects. As demonstrated in the second column of Figure 6, graph cut tends to amalgamate multiple objects into a single bounding box. To mitigate this issue, enhancements have been proposed for the graph cut method, incorporating edge detection to refine the segmentation mask post-graph cutting. This enhancement aids in better delineation of edges among densely placed objects, resulting in more precise segmentation outcomes.
In real-world labeling scenarios, the lazy snapping method demands extensive interactive labeling. This involves not only the placement of a large number of positive sample seeds but also a significant number of negative sample seeds. Given the complex background often associated with small objects in remote sensing images, the quality of these negative sample seeds critically impacts the segmentation results. This intricate process requires considerable manual fine-tuning, thereby significantly increasing the workload for operators.
While SAMs achieve top-tier results in general imaging applications, their efficacy diminishes when applied to annotating small objects in remote sensing contexts. The small size and limited visual details of such objects often result in subpar segmentation outcomes, as illustrated in the fourth column of Figure 6. This highlights the challenges SAMs encounter in effectively addressing the unique demands of remote sensing scenarios.
PNL segments objects via the point neighborhood learning framework, which applies the neighborhood information to enhance the expressive power of the model. After evaluating with numerous point radii, we adopt the radius of point as 1, to enable the PNL capturing the features of the remote sensing small objects. The experimental results shown in Table 3 indicate PNL is suboptimal, with the IoU of only 49.8%. We deduce that the interference from the background is more severe than that in the medical applications. Thus, the surrounding features around point annotations cannot always help with segmentation. In comparison, the proposed SPA discriminates foreground regions using deep learning models, which could effectively alleviate the background interference.
4.7. Effect on Training Object Detectors
To further validate the effectiveness of the proposed method in generating annotations, we utilize the annotations generated by graph cut, SAM, and our method to compare the results with the original manually labeled GT for training the directed object detection method. During the testing period, the original GT is applied to compute the mAP. in this paper, Rotate RetinaNet is used as the directed object detection network. To ensure the fairness of the experiment, the networks use the same parameter settings. The rotation angle is in “OC” format, and the backbone network is ResNet 50. The network is trained for 12 epochs with a batch size of 2. The initial learning rate is 0.0025. SGD is used as the optimizer with a momentum of 0.9 and a weight decay of 0.0001. Table 4 shows the models trained by the four annotation methods’ mAP results on DOTA-v1.5.

Table 4.
Comparison of IoUs for different methods.
The experimental results in Table 5 demonstrate that our proposed annotation method consistently enhances the RetinaNet model’s performance on the DOTA-v1.5 dataset compared to other annotation strategies. In particular, our method significantly boosts the average mAP (57.1%) across all categories when compared with graph cut (44.6%), lazy snapping (47.52%), SAM (52.4%), and PNL(47.3%). However, there remains a substantial gap of over 10% relative to GT (67.45%). This discrepancy arises due to the loss of accuracy in feature extraction and mapping back to the original image for dense and small targets. This issue can potentially be mitigated by scaling up the image size. Future work should focus on refining the annotation process to better handle challenging scenarios, such as objects with low contrast, occlusion, and intricate shapes.

Table 5.
The mAP (%) comparison of the RetinaNet trained using different annotations. “GT” is the “ground truth annotation” supplied by the dataset publisher.
5. Discussion
Our research addresses a critical gap in the field of remote sensing: the efficient and effective detection of oriented small objects. The primary challenge lies in the dense distribution and high number of such objects within remote sensing images, which makes the creation of large-scale annotated datasets both time-consuming and costly. The fundamental hypothesis of our study is that a single-point-based annotation approach (SPA) can significantly reduce the annotation workload while maintaining, or even improving, the accuracy of object detection. Accurate and efficient detection of oriented small objects has a wide range of applications, from environmental monitoring to military surveillance. By addressing the limitations associated with traditional annotation methods, our research contributes to the development of more practical and scalable solutions in remote sensing.
The high cost of creating large-scale annotated datasets has been a significant bottleneck in the field. Our SPA framework, which leverages graph cut methods and deep learning, offers a more intuitive and efficient annotation process. This approach not only reduces the time and cost associated with manual annotation but also enhances the quality of the annotations, as evidenced by the improved intersection over union (IoU) and mean average percentage (mAP). By demonstrating a 50% improvement in annotation efficiency and a 4.7% higher mAP compared to traditional methods, our study provides compelling evidence of the technical and practical advantages of SPA. These improvements suggest that SPA can facilitate the development of more robust and accurate models for detecting oriented small objects in remote sensing images, thereby pushing the boundaries of what is currently achievable in the field.
However, there are still some limitations to our method. One notable issue is the misalignment between the rotation direction of the labeling box and the rotation direction of the object being labeled as shown in Figure 7. This misalignment can result in a slight tilt angle, which affects the accuracy of the labeling. Additionally, when annotating larger objects, such as cars, the front end of the vehicle is often excluded from the labeling box like in Figure 7. This can lead to incomplete annotations and reduce the overall precision of the object detection.

Figure 7.
Two examples of problematic labeling effects are shown. In (a), the labeling frame is tilted, with the encroachment highlighted in blue. In (b), the front end of the large vehicle is not labeled correctly.
To mitigate these issues, further refinements to the SPA framework are necessary. Incorporating more sophisticated alignment algorithms and enhancing the robustness of the labeling process can help address the tilt angle discrepancy. Furthermore, developing techniques to ensure complete coverage of larger objects within the labeling box is essential for improving annotation accuracy. Despite these shortcomings, our method demonstrates significant potential. Developing techniques to ensure complete coverage of larger objects within the labeling box is essential for improving annotation accuracy. This could involve implementing advanced segmentation methods that dynamically adjust the size and shape of the labeling box based on the object’s dimensions. Leveraging deep learning approaches to predict the optimal bounding box configurations for various object sizes can also be a viable solution. Moreover, exploring multi-scale annotation strategies can provide a more granular and comprehensive representation of larger objects. By annotating objects at multiple scales, we can capture finer details that might be missed with a single-scale approach, thereby enhancing the overall quality of the annotations.
Despite these shortcomings, our method demonstrates significant potential. It has shown promising results in improving the accuracy and robustness of image analysis tasks. Continued research and development in these areas will be crucial for overcoming the identified limitations and unlocking the full potential of our approach.
6. Conclusions
To address the challenges of high costs and low annotation accuracy for small and medium-sized targets in remote sensing, this paper introduces a low-cost method based on single-point annotation (SPA). SPA is an efficient approach for labeling small targets in remote sensing images, employing single-point labeling to generate a directed bounding box without the need for pretraining or fine-tuning. The algorithm begins with feature extraction from the image, then computes a similarity matrix and identifies positive sample points based on single-point annotations combined with the similarity matrix. It constructs a graph based on the feature map size and uses the maximum flow method to segment the graph and obtain the positive sample region. This region is then mapped to the original image size, and edge correction is applied to yield the final binary mask. Each target region is ultimately transformed into a directed rectangular box.
A series of experiments demonstrated the effectiveness of SPA. Our method achieves a 3.6% higher IoU compared to SAM and a 14.2% higher IoU compared to PNL. In terms of mAP, our method outperforms SAM by 4.7% and PNL by 9.8%. and the results verified that the proposed algorithm is a viable semi-automatic labeling method for small objects in remote sensing images.
Despite the promising results, certain limitations remain:
- Positive sample point selection: The selection of positive sample points in combination with the similarity matrix can significantly influence the labeling outcome due to the impact of threshold selection, potentially leading to false positive sample points. A more refined strategy for selecting positive sample points, such as incorporating positional relationships, could improve the quality of the labeling frames;
- Tilt angle discrepancy: There is a misalignment between the rotation direction of the labeling box and the rotation direction of the object being labeled, which can result in a slight tilt angle affecting the accuracy of the labeling;
- Incomplete coverage of larger objects: When annotating larger objects, such as cars, the front end of the vehicle is often excluded from the labeling box, leading to incomplete annotations and reducing the overall precision of the object detection.
- Annotation time cost: The time required for the annotation process remains between 5–7 s per annotation, with some fluctuation depending on the number of objects to be labeled in the image. This time cost can be a significant factor in large-scale projects.
To overcome these limitations and enhance the SPA framework, future research could focus on the following areas:
- Refined positive sample point selection: Developing more sophisticated methods for positive sample point selection that incorporate additional contextual information and positional relationships;
- Improved alignment algorithms: Incorporating advanced alignment algorithms to address the tilt angle discrepancy and ensure more accurate bounding box orientations;
- Reducing time cost: Implementing methods to optimize the annotation process, such as adaptive automation techniques, machine learning models for pre-labeling, to help reduce the annotation time;
- Multi-scale annotation strategies: Exploring multi-scale annotation strategies to capture finer details and provide a more comprehensive representation of objects.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.Z. and Z.F.; methodology, W.Z.; software, W.Z.; validation, Z.F., J.C. and Z.J.; data curation, W.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, W.Z.; writing—review and editing, Z.F., J.C. and Z.J.; supervision, project administration, and funding acquisition, Z.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 62202385, in part by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities under Grant G2021KY05103, and in part by the Basic Research Programs of Taicang under Grant TC2022JC21.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
This paper uses the DOTA. Data sources: https://captain-whu.github.io/DOTA/dataset.html (accessed on 18 May 2024).
Conflicts of Interest
Author Jun Cao was employed by the company Nanjing RuiYue Technology Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Wang, X.; Wang, A.; Yi, J.; Song, Y.; Chehri, A. Small Object Detection Based on Deep Learning for Remote Sensing: A Comprehensive Review. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Yin, Y.; Jing, Q.; Shao, Z. A High-Precision Detection Model of Small Objects in Maritime UAV Perspective Based on Improved YOLOv5. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Hu, Y.; Ji, H.; Zhang, M.; Yu, Q. A Deep Learning Method for Ship Detection and Traffic Monitoring in an Offshore Wind Farm Area. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wang, Z.; Li, Z.; Su, A.; Teng, X.; Liu, M.; Yu, Q. Oriented object detection in optical remote sensing images using deep learning: A survey. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.10473. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Li, X.; Fang, Y. Few-Shot Object Detection on Remote Sensing Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 60, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Xie, X.; Chen, W.; Feng, X.; Yao, X.; Han, J. Self-Guided Proposal Generation for Weakly Supervised Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, G.; Da, F.; Yan, J. H2RBox-v2: Incorporating Symmetry for Boosting Horizontal Box Supervised Oriented Object Detection. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.04403. [Google Scholar]
- Mullen, J.F.; Tanner, F.R.; Sallee, P.A. Comparing the Effects of Annotation Type on Machine Learning Detection Performance. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–17 June 2019; pp. 855–861. [Google Scholar]
- Mirzaei, B.; Nezamabadi-pour, H.; Raoof, A.; Derakhshani, R. Small Object Detection and Tracking: A Comprehensive Review. Sensors 2023, 23, 6887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.D.; Chen, D. Segmentation for Object-Based Image Analysis (OBIA): A review of algorithms and challenges from remote sensing perspective. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 150, 115–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Yang, Y.; Xia, Y.; Chen, Y.T.; Parekh, Z.; Pham, H.; Le, Q.V.; Sung, Y.H.; Li, Z.; Duerig, T. Scaling Up Visual and Vision-Language Representation Learning With Noisy Text Supervision. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2102.05918. [Google Scholar]
- Ramesh, A.; Pavlov, M.; Goh, G.; Gray, S.; Voss, C.; Radford, A.; Chen, M.; Sutskever, I. Zero-Shot Text-to-Image Generation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2102.12092. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, R.; Lei, T.; Chen, Q.; Wang, Z.; Du, X.; Zhao, W.; Nandi, A.K. Survey of Image Edge Detection. Front. Signal Process. 2022, 2, 826967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BenHajyoussef, A.; Saidani, A. Recent Advances on Image Edge Detection. In Digital Image Processing—Latest Advances and Applications; Cuevas, D.F.J., Mazzeo, D.P.L., Bruno, D.A., Eds.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Tosi, D.; Morasca, S. Supporting the semi-automatic semantic annotation of web services: A systematic literature review. Inf. Softw. Technol. 2015, 61, 16–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Liang, Y.; Shang, R.; Jiao, L. CFDRM: Coarse-to-Fine Dynamic Refinement Model for Weakly Supervised Moving Vehicle Detection in Satellite Videos. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Jiao, L. SDANet: Semantic-Embedded Density Adaptive Network for Moving Vehicle Detection in Satellite Videos. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2023, 32, 1788–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Li, S.; Liu, P. A review of lane detection methods based on deep learning. Pattern Recognit. 2021, 111, 107623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oğuz, E.; Küçükmanisa, A.; Duvar, R.; Urhan, O. A deep learning based fast lane detection approach. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2022, 155, 111722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhard, M.; Schubert, M. Robust object detection in remote sensing imagery with noisy and sparse geo-annotations. In Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Advances in Geographic Information Systems, Seattle, WA, USA, 1–4 November 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, T.; Wang, R.; Wan, Y.; Du, X.; Meng, H.; Nandi, A.K. Medical Image Segmentation Using Deep Learning: A Survey. arXiv 2020, arXiv:abs/2009.13120. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Xu, Z.; Bertasius, G.; Niethammer, M. SimpleClick: Interactive Image Segmentation with Simple Vision Transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, France, 1–6 October 2022; pp. 22233–22243. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, M.; Qi, D.; Zhao, H. FocalClick: Towards Practical Interactive Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 1290–1299. [Google Scholar]
- Sofiiuk, K.; Petrov, I.A.; Konushin, A. Reviving Iterative Training with Mask Guidance for Interactive Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Bordeaux, France, 16–19 October 2021; pp. 3141–3145. [Google Scholar]
- Kirillov, A.; Mintun, E.; Ravi, N.; Mao, H.; Rolland, C.; Gustafson, L.; Xiao, T.; Whitehead, S.; Berg, A.C.; Lo, W.Y.; et al. Segment Anything. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 3992–4003. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Han, W.; Huang, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Li, J. Trustworthy remote sensing interpretation: Concepts, technologies, and applications. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2024, 209, 150–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boykov, Y.; Jolly, M.P. Interactive graph cuts for optimal boundary & region segmentation of objects in N-D images. In Proceedings of the Eighth IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. ICCV 2001, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 7–14 July 2001; Volume 1, pp. 105–112. [Google Scholar]
- Garvin, M.K.; Wu, X. Graph Algorithmic Techniques for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Advanced Computational Approaches to Biomedical Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, R.; Bischof, L. Seeded region growing. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1994, 16, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremeau, A.; Colantoni, P. Regions adjacency graph applied to color image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2000, 9, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Ding, J.; Li, J.; Xia, G. Align Deep Features for Oriented Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 60, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, Y.; Liu, W.; Feng, L.; Gao, W. Improved YOLO Network for Free-Angle Remote Sensing Target Detection. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovska, B.; Zdravevski, E.; Lameski, P.; Corizzo, R.; Štajduhar, I.; Lerga, J. Deep Learning for Feature Extraction in Remote Sensing: A Case-Study of Aerial Scene Classification. Sensors 2020, 20, 3906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.E.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2014; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2015; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Bengio, Y.; Simard, P.; Frasconi, P. Learning long-term dependencies with gradient descent is difficult. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1994, 5, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Zhang, H. Convergence Analysis of Deep Residual Networks. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.06571. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuo, Z.; Zhou, Z. Remote Sensing Image Retrieval with Gabor-CA-ResNet and Split-Based Deep Feature Transform Network. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steck, H.; Ekanadham, C.; Kallus, N. Is Cosine-Similarity of Embeddings Really About Similarity? arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.05440. [Google Scholar]
- Yasser, M.; Hussain, K.F.; Ali, S.A. Comparative Analysis of Similarity Methods in High-Dimensional Vectors: A Review. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence Science and Applications in Industry and Society (CAISAIS), Galala, Egypt, 3–5 September 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Boykov, Y.; Kolmogorov, V. An experimental comparison of min-cut/max- flow algorithms for energy minimization in vision. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2004, 26, 1124–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canny, J. A Computational Approach to Edge Detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1986, PAMI-8, 679–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thevenaz, P.; Blu, T.; Unser, M. Interpolation revisited [medical images application]. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2000, 19, 739–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haralick, R.M.; Sternberg, S.R.; Zhuang, X. Image Analysis Using Mathematical Morphology. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1987, PAMI-9, 532–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, L. Morphological area openings and closings for grey-scale images. In Proceedings of the Shape in Picture: Mathematical Description of Shape in Grey-Level Images; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1994; pp. 197–208. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, G.S.; Bai, X.; Ding, J.; Zhu, Z.; Belongie, S.J.; Luo, J.; Datcu, M.; Pelillo, M.; Zhang, L. DOTA: A Large-Scale Dataset for Object Detection in Aerial Images. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2017; pp. 3974–3983. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, G.; Yuan, X.; Yao, X.; Yan, K.; Zeng, Q.; Han, J. Towards Large-Scale Small Object Detection: Survey and Benchmarks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 45, 13467–13488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, P.; Liu, W.; Gao, C.; Wen, Y.; He, R.; Li, P.; Zhang, J.; Meng, D. A Point-Neighborhood Learning Framework for Nasal Endoscope Image Segmentation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.20044. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.; Liu, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, H.; Li, W.; Zou, Z.; Shi, Z.X. RSPrompter: Learning to Prompt for Remote Sensing Instance Segmentation Based on Visual Foundation Model. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 62, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sun, J.; Tang, C.K.; Shum, H. Lazy snapping. In ACM SIGGRAPH 2004 Papers; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).