Abstract
With rapid urbanization, retrieving information about residential complexes in a timely manner is essential for urban planning. To develop efficiency and accuracy of building extraction in residential complexes, a Segment Anything Model-based residential building instance segmentation method with an automated prompt generator was proposed combining LiDAR data and VHR remote sensing images in this study. Three key steps are included in this method: approximate footprint detection using LiDAR data, automatic prompt generation for the SAM, and residential building footprint extraction. By applying this method, residential building footprints were extracted in Pukou District, Nanjing, Jiangsu Province. Based on this, a comprehensive assessment model was constructed to systematically evaluate the spatial layout of urban complexes using six dimensions of assessment indicators. The results showed the following: (1) The proposed method was used to effectively extract residential building footprints. (2) The residential complexes in the study area were classified into four levels. The numbers of complexes classified as Excellent, Good, Average, and Poor were 10, 29, 16, and 1, respectively. Residential complexes of different levels exhibited varying spatial layouts and building distributions. The results provide a visual representation of the spatial distribution of residential complexes that belong to different levels within the study area, aiding in urban planning.
1. Introduction
With the continuous advancement of urbanization, cities have become the centers of economic development, offering increased employment opportunities, abundant social resources, and enhanced living conveniences, which attract a large influx of population into the cities. The demand for living space within cities is also constantly increasing. However, as urban land resources gradually become scarce and external expansion faces constraints, urban development has begun to transition from incremental expansion to optimizing existing resources. As the basic unit of urban composition, residential complexes are the main places where urban residents live and also the micro-carriers of urban development. Their design and development modes directly affect the development of the entire city [1]. As a basic component of residential complexes, buildings play an indispensable role in urban economic and social development [2]. Accurate and timely access to building information is crucial for comprehending urban dynamics [3], assessing urban growth [4], and devising strategies for sustainable urban development [5,6]. Zhao et al. presented an investigation on urban social function-based spatial structure analysis using building footprint data, which is essential for effective spatial planning and policy-making [7]. In addition to urban planning, accurate building footprint data were also important in natural disaster management and digital twin modeling development [8]. Remote sensing technology has gradually become an important approach to extracting information on urban buildings because of its real-time, efficient, and rapid data collection capabilities [9]. Using this technology, building information on a large scale, including the distribution, scale, and structural characteristics of buildings, can be swiftly obtained. This information provides important data support for understanding the spatial layout and developmental dynamics of urban residential complexes. Therefore, it is crucial to obtain accurate and objective information about buildings within residential complexes.
Traditional building extraction methods usually rely on manually labeled features and rules to identify buildings [10], which may not adequately characterize the complex structural and textural messages of a building, leading to a lack of accuracy in the extraction results. In recent years, deep learning [11] has been introduced into the remote sensing field as one of the most advanced and popular techniques, which is capable of learning feature representations from data with stronger data-driven capabilities and self-adaptability. It provides many effective ways to solve a series of problems. Mayank et al. [12]. proposed a Dilated-ResUnet deep learning architecture for extracting building information from moderate-resolution remote sensing images, and they enhanced the building extraction accuracy by increasing the processing details of building boundaries in their model. With the increasing availability of remote sensing imagery, the quality and spatial resolution of images have seen continuous improvements [13]. With the increasing abundance of remote sensing images, the quality and spatial resolution of the images have continuously improved [14]. Compared to moderate-resolution remote sensing images, Very High-Resolution (VHR) remote sensing images provide enriched feature information and texture semantics, making them the preferred data source for building extraction [15,16]. In addition, VHR images provide researchers with accurate spatial feature information [17], which contributes to the precise identification of objects and extraction of features [18]. However, when encountering complicated city environments with redundant interference information or varying building shapes, these methods cannot achieve satisfactory building extraction results [19]. In comparison with optical sensors, LiDAR technology is not affected by terrain factors. Additionally, due to features such as high accuracy, wide coverage, high density, less interference by the external environment, and strong initiative, LiDAR technology is widely used in millimeter-level accuracy mapping [20,21]. Su [22] used a deep learning approach to extract the corresponding features from LiDAR data and evaluated the effect of neighborhood size, intensity, RGB, and normal vectors on the detection of buildings. The LiDAR data provide elevation information of the terrain, and it is captured over an urban setting consisting of both the natural (trees and bare earth) and human-made features (buildings, cars, and roads). It is necessary to separate building segments from LiDAR data [23,24,25]. However, the lack of texture and boundary information in LiDAR data exposes the limitations of LiDAR-based building extraction methods, particularly in urban areas where the presence of tall trees and bridges near buildings further complicates the application of LiDAR data. At such junctures, integrating the LiDAR data with VHR images presents an effective approach for building extraction. This integration is expected to further improve the accuracy and efficiency of building extraction [26]. Presently, numerous scholars have developed a range of fusion techniques to integrate remote sensing imagery data and LiDAR data for building extraction [27]. A multitude of research findings [28,29] have demonstrated that the integration of VHR images with LiDAR data yields more significant effects in building extraction compared to using a single data source. LiDAR data provide precise elevation information, while high-resolution remote sensing imagery offers detailed visual information for identifying building features [30,31]. Nahhas et al. [32] combined LiDAR data with VHR images and utilized deep learning object-based detection methods, employing auto-encoders to enhance building recognition accuracy. Their results also reaffirmed that fusing LiDAR data with VHR images to recognize urban buildings results in more accurate extraction [33]. But the integration of data brings new problems to the extraction efficiency and accuracy. The models that are based on deep learning usually require high-quality datasets and a large number of labeled samples for training. In addition, these models tend to be problematic in terms of high consumption of computational resources and limited eventual generalization ability to adapt to new data and different conditions. It is also compelling to innovate and improve on the methodology. By continuously exploring novel techniques, the efficiency and accuracy of building extraction will be further increased.
In recent years, foundational models have instigated a revolution in the field of artificial intelligence. Training on vast amounts of data has endowed these models with impressive zero-shot generalization ability across various scenarios. Recently, the Segment Anything Model (SAM) [34] announced by Meta AI has garnered the attention of research scholars. A brief introduction to the SAM is provided in Section 3.1. Compared to deep learning models, the SAM has superior generalization ability. As a fundamental model that is trained on a dataset SA-1B containing over a billion masks, the SAM can process multiple prompts without training samples and maintains its efficiency and accuracy in different scenarios. As the first vision foundation model dedicated to image segmentation, the SAM shows potent zero-shot generalization ability and strong potential for applications in many downstream tasks due to its unique prompt engineering. However, the SAM also exhibits limitations when applied to remote sensing image segmentation [35,36]. The SAM is not a task-oriented model that facilitates end-to-end automatic segmentation, but rather a category-independent segmentation method. The SAM is a task-agnostic and class-agnostic segmentation method that cannot achieve end-to-end automated segmentation. Essentially, the SAM has not been optimized for specific semantic segmentation tasks [37]. In addition, the segmentation ability of the SAM will be affected by the complexity of remote sensing images and urban scenes. Urban buildings have different shapes, sizes, heights, and functions. And the building roofs, including flat roofs, sloping roofs, round roofs, and dormers, are also shown in different ways in remote sensing images. Under the instance segmentation for a specific scenario, appropriate prompts should be generated and inputted into the SAM to improve the accuracy of instance segmentation [38]. Based on the SAM model and appropriate prompts, urban building information can be extracted with greater accuracy. This information is essential for assessing the quality of residential complexes.
According to the compactness of the residential complexes, urban residential complexes in China are categorized into two forms: high-density residential complexes and low-density residential complexes. High-density residential complexes include three types: high-rise high-density, mid-rise high-density, and low-rise high-density. Similarly, low-density residential complexes also comprise high-rise low-density, mid-rise low-density, and low-rise low-density residential complexes. These different types of residential complexes have different space utilization characteristics, which are directly associated with the quality of the residential environment and the living experience of the residents [39,40]. Therefore, how to accurately assess and improve the spatial settings of urban residential complexes has become an important issue in urban planning and development [41]. Cities have generally undergone rapid urbanization and expansion within a brief period, and the environmental transformation of residential complexes has also been dramatic and accelerated [42]. With the advancement of modern society and material living standards, the demand for high-quality residential conditions in China has steadily increased [43]. The focus has turned from merely providing housing to a desire for better residential conditions. Urban development has transitioned from extensive development to refined evolution, and the quality of the residential complexes in urban residential complexes has attracted much attention. In order to meet the intense residential demand, it is particularly important to accurately assess and scientifically improve the spatial environment of residential complexes. Optimizing and improving the spatial layout of residential complexes can enhance quality of life and mitigate the adverse impacts of rapid urbanization, which contributes to urban sustainable development.
Different from the previous studies that emphasize the livability of urban cities from the perspective of streets and communities [44,45,46], this study focuses on the residential settings as defined by residential complexes. Integrating LiDAR data with VHR images, a SAM-based residential building instance segmentation method was proposed to extract buildings in urban residential complexes. In this method, an automated prompt generator was constructed to automatically generate prompts during the SAM segmentation process. Based on the extracted residential building footprints, a comprehensive evaluation model was constructed to objectively evaluate the spatial layout and settings of urban residential complexes. This study can be used to provide reference and scientific support for the study of urban development.
The main contributions of this paper are as follows:
- (1)
- According to the characteristics of LiDAR data and VHR remote sensing images, the automated prompt generator for the SAM-based residential building instance segmentation method is established.
- (2)
- Based on the residential building footprints extracted by the method, the comprehensive assessment model is constructed, which systematically evaluates the residential settings.
Descriptions of the study area and data sources are provided in Section 2. And the methods used in this paper are provided in Section 3. The distributions of residential building footprints extracted by our method and the assessment of the residential complexes are described in Section 4. And the significance and limitations of this study are discussed in Section 5. Finally, the main conclusions are drawn in Section 6. Abbreviations provides a compilation of acronyms in this paper. Appendix A provides a compilation of acronyms in this paper.
2. Study Area and Data
2.1. Study Area
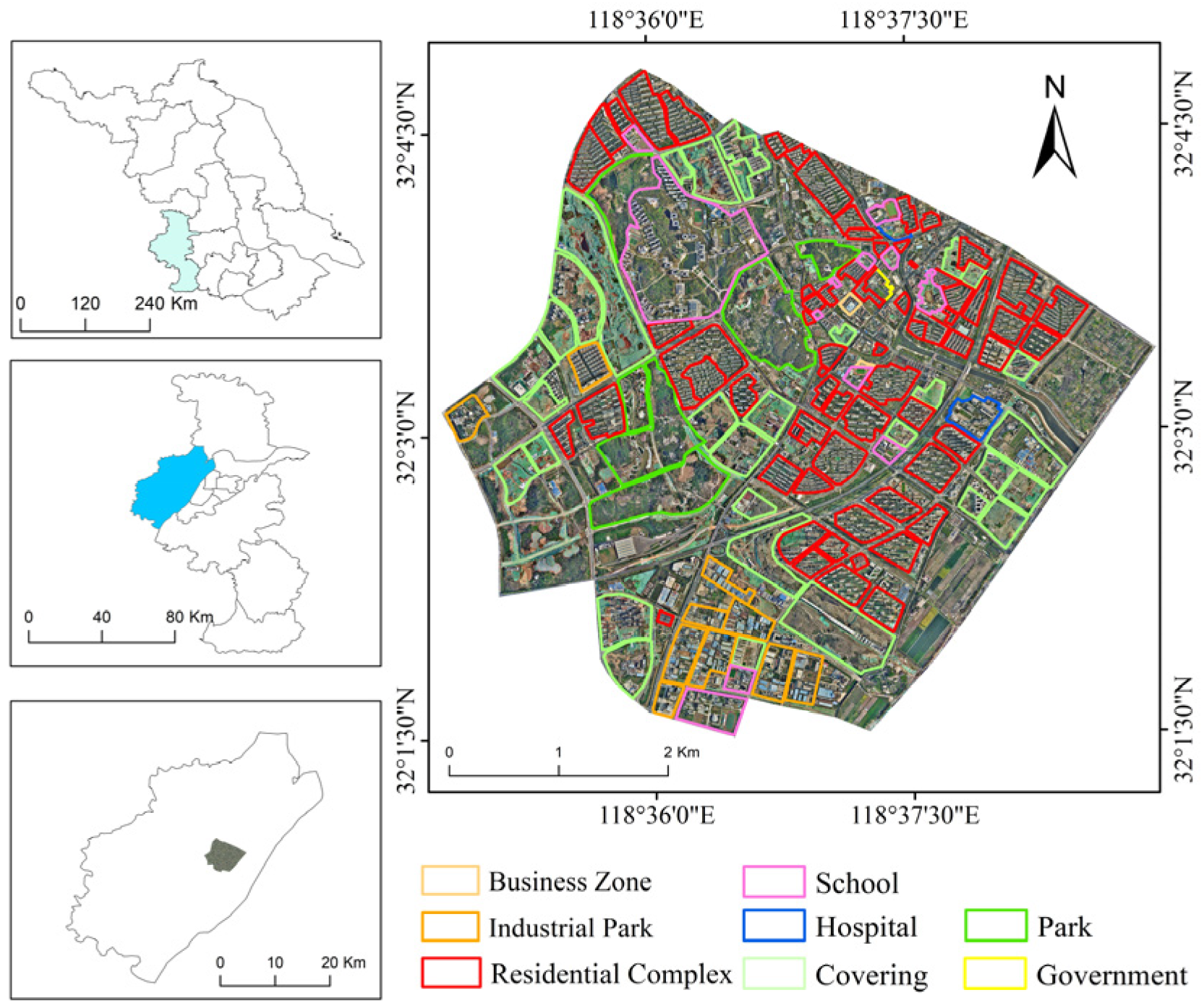
Located in the northwest of Nanjing, China, Pukou District serves as a pivotal hub for pharmaceuticals and advanced manufacturing industries. It also represents a core area for the development along the Yangtze River and cross-strait cooperation initiatives. Our study area lies in the central region of Pukou District, with an area of 23.56 km2. The area is located to the north of Laoshan National Forest Park and the south of the Yangtze River Basin. In addition, there is also a river called Chengnan River that branches off from the Yangtze River. The area mainly includes various functional zones such as commercial districts, industrial parks, industrial development zones, and residential complexes. The specific distribution is shown in Figure 1.
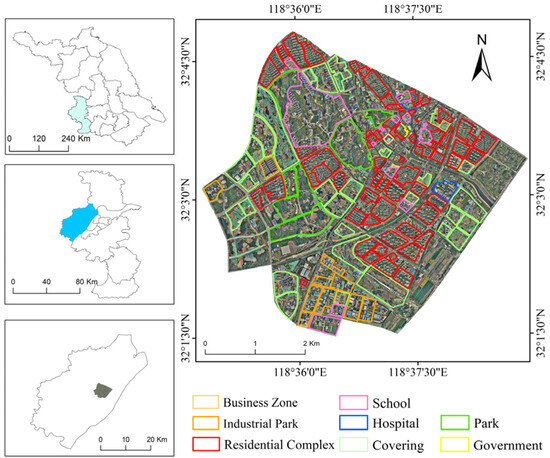
Figure 1.
The overview of the study area.
2.2. Data
The primary data used in this study include LiDAR data, VHR images, area of interest (AOI) data, and road networks. It is worth noting that the LiDAR data and VHR images were synchronously collected at the same height of 1200 m by integrating the Riegl laser scanner for LiDAR data and the Phase One camera for VHR images.
- LiDAR data: The LiDAR data were acquired in 2019 and collected using a Laser 3D Scanner equipped with Riegl 1560i laser systems. The attributes of the LiDAR data include X, Y, and Z coordinates and the intensity information. The range of reflection intensity values is from 0 to 65,535. And the density of point clouds is about 8.0 points/m2.
- VHR images: The very high-resolution orthophotos of the study area were multi-spectral images from 2019 with a spatial resolution of 0.15 m, including red, green, and blue bands.
- AOI data: The AOI data were obtained from the AMAP inside and each AOI with residential attributes was regarded as a basic unit for assessing the residential complex.
- Road networks: The road networks were obtained from the Open Street Map (OSM) website. The networks named “primary” and “secondary” roads were chosen to calculate the assessment indicators in the comprehensive assessment model.
3. Methodology
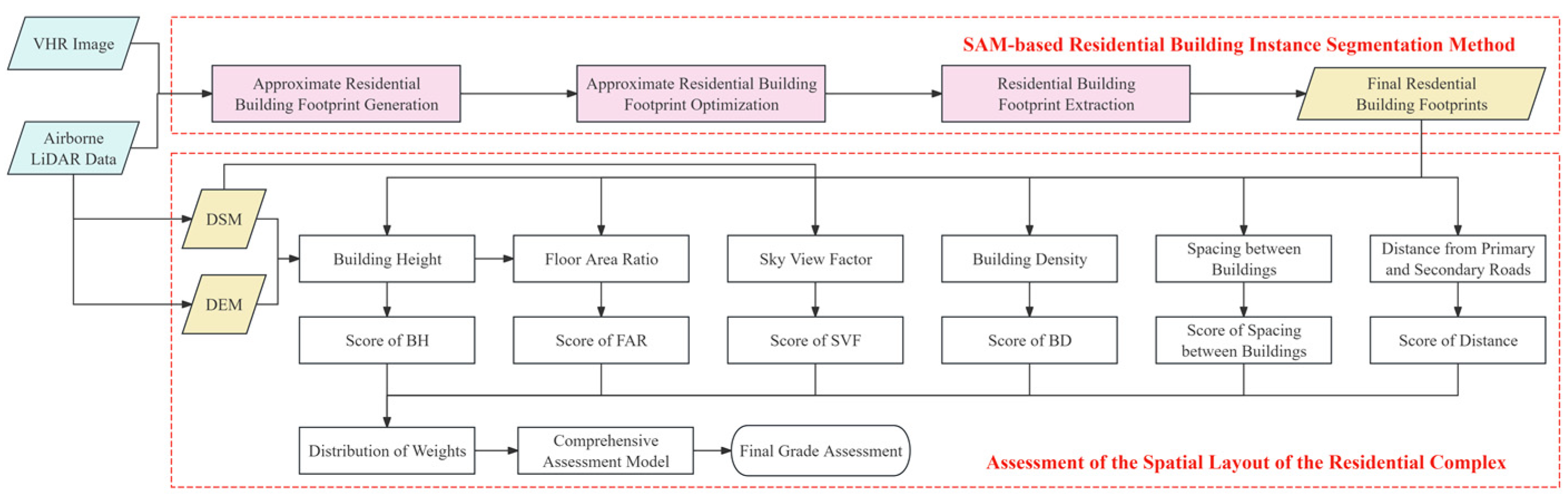
The methodology of this study is primarily divided into two parts. Firstly, a building instance segmentation method under the support of the SAM is proposed. Subsequently, a comprehensive assessment model for urban residential complexes is constructed to quantitatively assess the extracted residential buildings, thereby evaluating the spatial settings of each residential complex. This endeavor aims to provide decision support for urban planning and residential complex management (Figure 2).
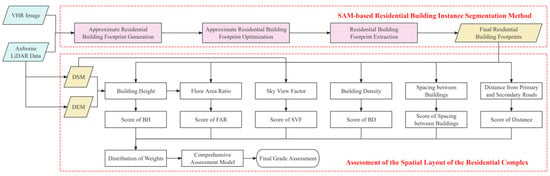
Figure 2.
The technical road map of this study.
3.1. Brief Introduction to the SAM
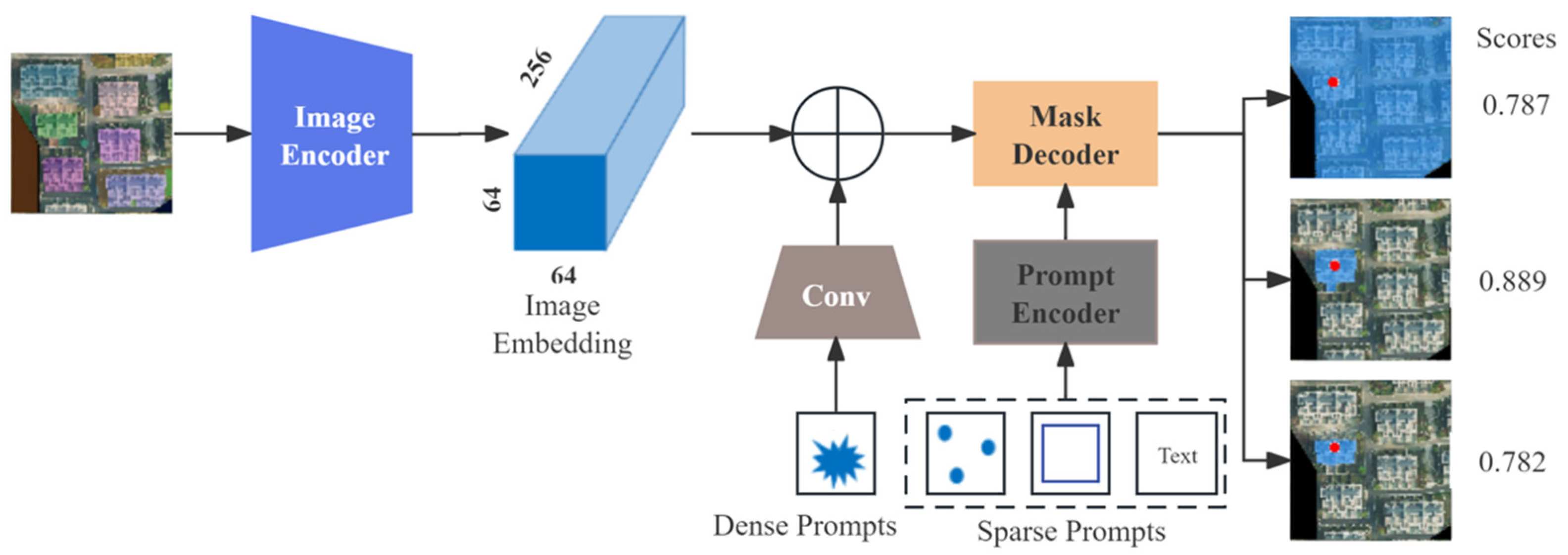
The SAM comprises an image encoder, a prompt encoder, and a lightweight mask decoder. The SAM operates within a heavyweight image encoder, which maps the image to a high-dimensional feature space, yielding a 256-dimensional image embedding. The SAM accepts various prompts, including sparse prompts such as points, boxes, and text, as well as dense prompts, also referred to as mask prompts. The primary task of the prompt encoder is to encode these prompts into feature embeddings. Within the mask decoder, the SAM offers two segmentation modes: interactive segmentation mode and automatic segmentation mode. In the interactive segmentation mode, segmentation results that capture the user’s interests can be generated by the SAM based on the prompts provided by the user. Meanwhile, in the automatic segmentation mode, the SAM generates a grid of point prompts on the image and segments the entire input image accordingly. The mask decoder updates all embeddings using two two-way-transformer blocks, performs up-sampling on image embeddings through deconvolution, and obtains foreground mask probabilities for each image position through two Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP) networks. This process effectively maps image embeddings, prompt embeddings, and an out token to masks. Finally, the SAM performs two up-sampling operations using bilinear interpolation before outputting the final result to acquire segmentation results of the same size as the input image. Additionally, to mitigate potential ambiguities arising from prompts, the SAM offers three different prediction results in the final output (Figure 3).
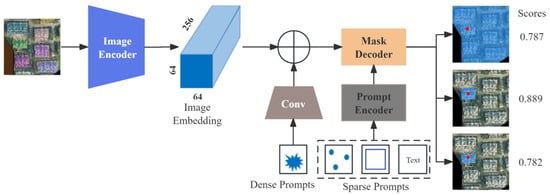
Figure 3.
The model structure of the SAM.
3.2. SAM-Based Residential Building Instance Segmentation Method
The accurate acquisition of building information within high-quality urban residential complexes is crucial for subsequent evaluations analyzing the spatial settings of the complex. In this study, an automated prompt generation instance segmentation method based on the foundational SAM combining airborne LiDAR data and aerial orthoimages was proposed to accurately obtain building footprints within residential complexes. The code is available at https://github.com/Wang-wei-lin/SAM_based_Building_Footprint_Extraction_for_Residential.git.
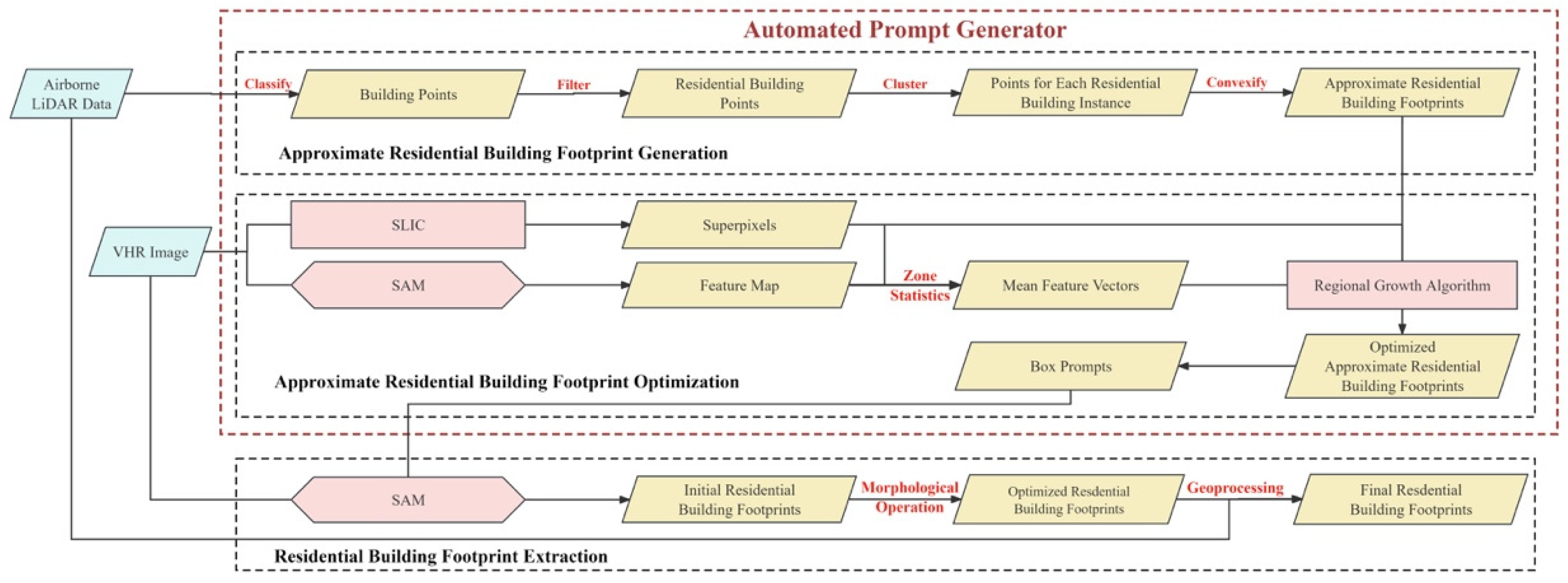
Semantic class information was incorporated into the method, intended for remote sensing images, whereby prompts suitable for buildings are generated through learning to serve as inputs to the SAM. Consequently, the SAM was empowered to produce semantically distinguishable segmentation results for remote sensing images. The method can automatically generate prompts tailored for instance segmentation of urban residential complex buildings, as illustrated in Figure 4. It comprised three components: approximate footprint generation, optimization, and extraction of residential building footprints. In the approximate footprint generation stage, a rough surface is generated for each residential building instance based on LiDAR data, indicating its precise spatial location and approximate footprint. In the optimization of approximate footprints of residential buildings, superpixels and deep visual features were utilized to refine the approximate footprints, resulting in more precise indications of the building footprints. Subsequently, the optimized footprints were employed to generate prompts. These prompts, along with VHR images, were fed into the SAM to obtain the initial segmentation results of residential buildings. Following this, a series of post-processing operations are performed on the initial segmentation results to derive the final building segmentation outcomes. The details of each part were presented in the subsequent sections. It is noteworthy that this method requires no model training on the user end.
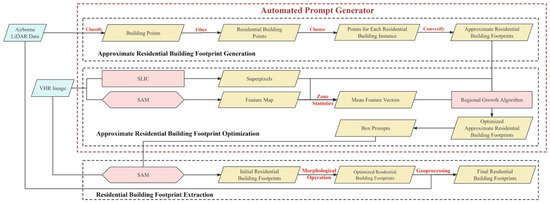
Figure 4.
The flowchart of the SAM-based residential building instance segmentation method.
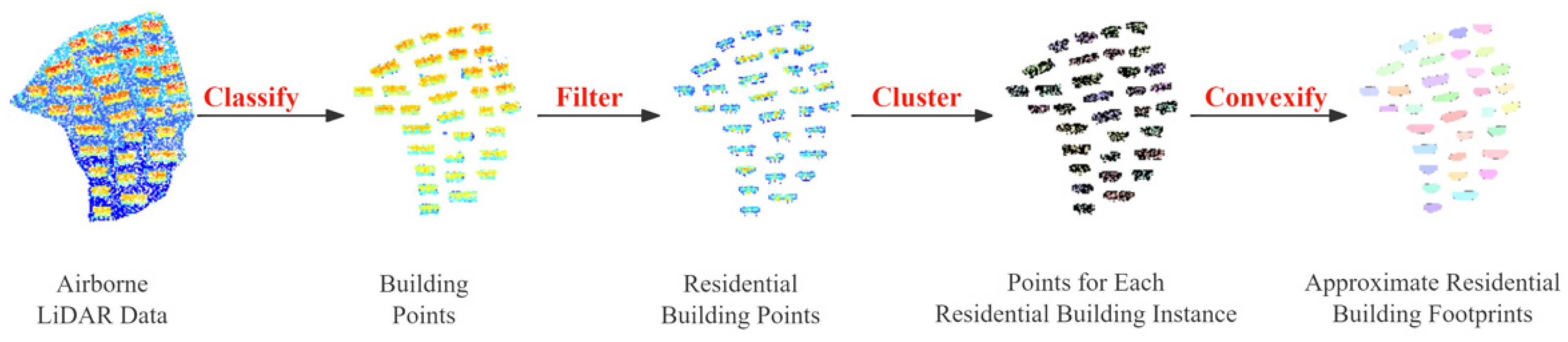
3.2.1. Approximate Footprint Detection Using LiDAR Data
LiDAR data are vast and diverse. Particularly in urban environments, LiDAR data may include various types such as trees, buildings, grasslands, and public facilities. Extracting the spatial location of each residential building from such complex point cloud data is crucial for obtaining building footprints. The primary process of this step is shown in Figure 5. First, the raw point cloud was classified to extract building points. A threshold (T) was set to filter the building point cloud, aiming to remove low-rise structures used for complex services, such as power rooms and security booths, thus isolating the point cloud data of residential buildings. Considering the height characteristics of buildings in the study area, the T was set to 10 m for point cloud filtering. Then, the point cloud data of residential buildings were vertically projected onto the 2D plane of VHR remote sensing images. The Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise (DBSCAN) method [47] was applied to cluster the point cloud projected onto the plane. Each cluster was considered a residential building instance. On this basis, the convex hull polygon of each cluster was computed as the residential building footprint for each instance.
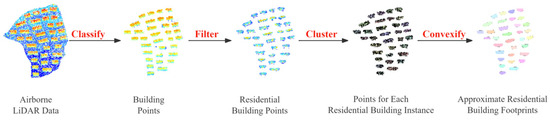
Figure 5.
The process of approximate footprint detection.
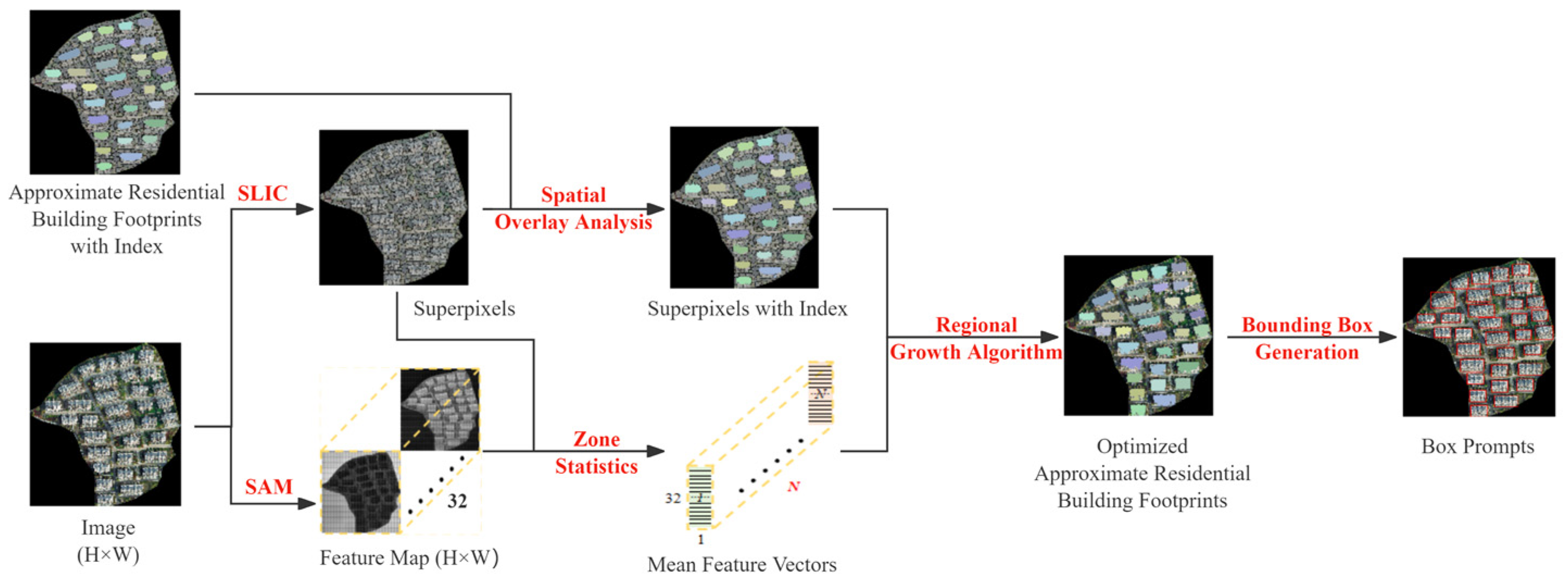
3.2.2. Automatic Prompt Generation for the SAM
Due to the matching accuracy of point clouds with images and the limitations of point cloud classification algorithms, there may be some errors between the approximate and actual building surfaces. This can affect the quality of the generated prompts and subsequently the segmentation results. Therefore, further optimization of the approximate surfaces is necessary. The box prompt generation process is shown in Figure 6. First, image embeddings were directly up-sampled using deconvolution. The two MLPs in the SAM model’s mask decoder were removed and bilinear interpolation was then applied twice to obtain a feature map with the same scale as the input image. Then, the Simple Linear Iterative Clustering (SLIC) method [48] was used to obtain image superpixels. Zone statistics were performed using the approximate footprint extracted in Section 3.2.1. Superpixels with more than 50% of their area intersecting with the approximate building surfaces were considered internal superpixels. Finally, all internal superpixels were spatially fused with the approximate building surfaces to obtain the optimized building surface data.
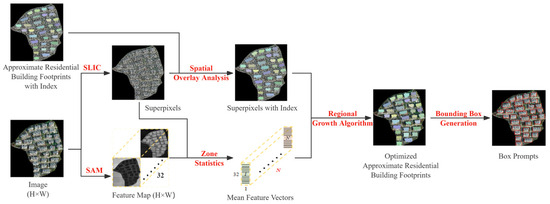
Figure 6.
The box prompt generation process.
In the process of optimizing the approximate building surfaces, two superpixel segmentation values (n_segment) were set when obtaining image superpixels: n1 = 1000 and n2 = 1500. This resulted in two different levels of refinement for the optimized building surfaces. Bounding boxes corresponding to n1 and n2 were generated from these results. The maximum and minimum values of the x and y coordinates of both bounding boxes were determined. The final bounding box coordinates were defined by the minimum and maximum values of x and y values from these extremes. This fused bounding box was used as the final input box prompts for the SAM.
3.2.3. Residential Building Footprint Extraction
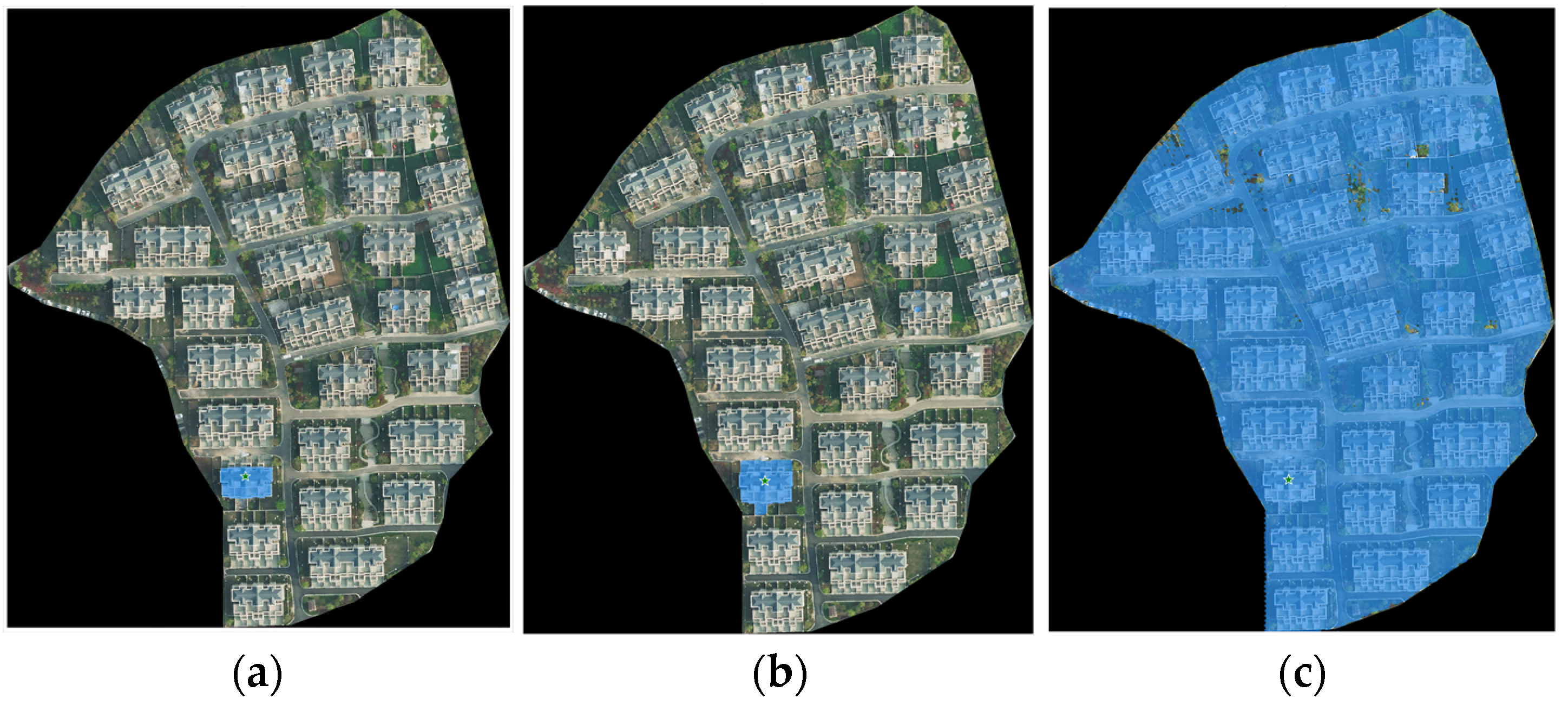
After constructing the prompts, the promptable SAM was used to segment building instances from an aerial orthophoto. First, the aerial photo was input into the SAM’s image encoder to obtain image embedding. Each building instance prompt was then input into the SAM’s prompt encoder to obtain prompt embedding. The image embedding and prompt embedding were combined in the SAM’s mask decoder to obtain the segmentation result for each prompt. Finally, all segmentation results were overlaid to produce the building instance segmentation for the aerial orthophoto, as shown in Figure 7. Among the three possible segmentation results output by the SAM, the result with the area closest to the approximate building surface area was chosen as the final segmentation output, rather than simply selecting the highest-scoring result.
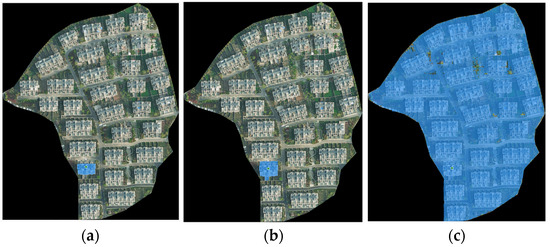
Figure 7.
Different segmentation results output by the SAM in one segmentation. (a) The result of segmentation (Mask 1) with a score of 0.782; (b) the result of segmentation (Mask 2) with a score of 0.889; and (c) the result of segmentation (Mask 3) with a score of 0.787.
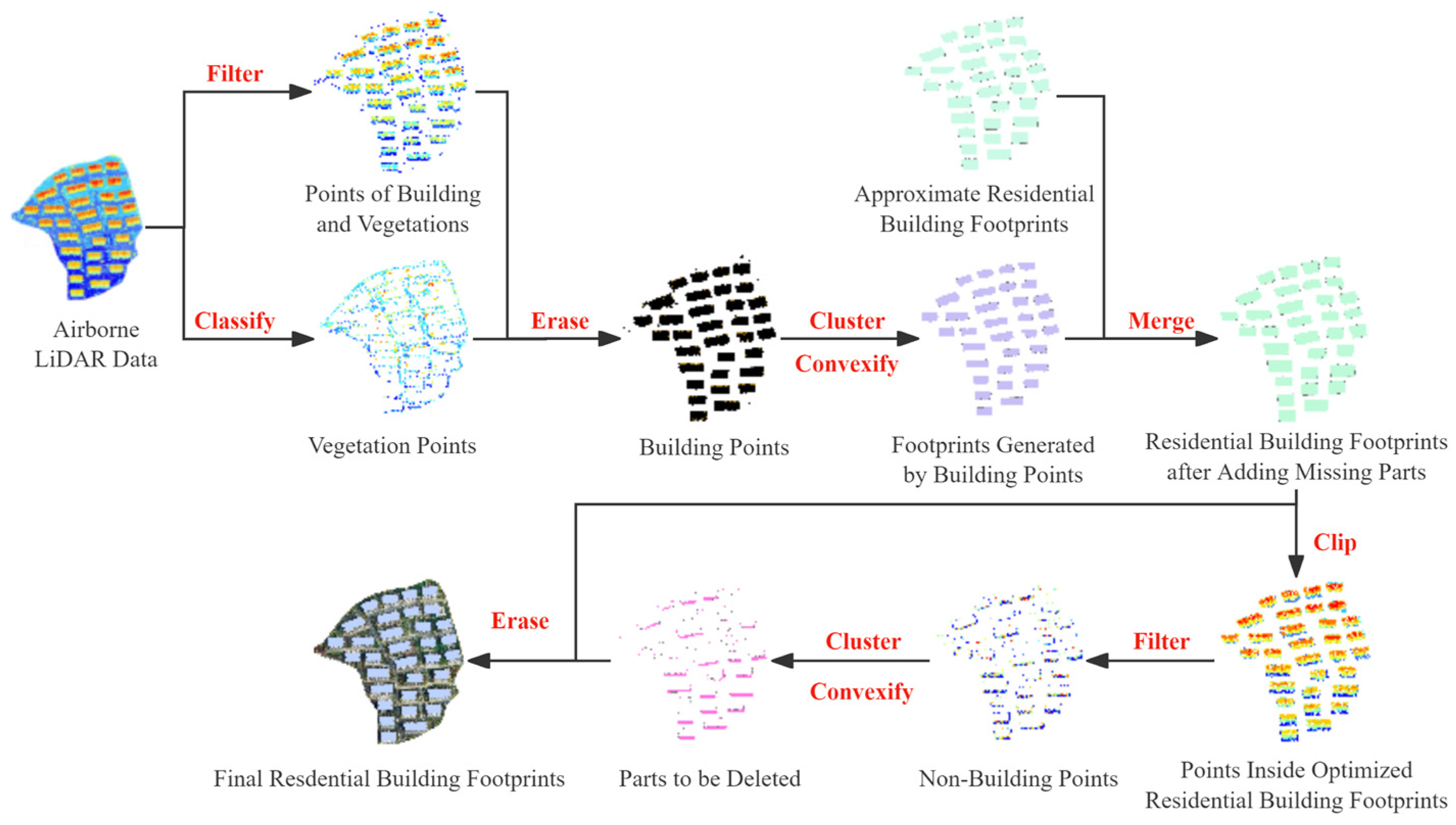
The segmentation results output by the SAM may contain small patches and internal holes. Morphological closing was used to eliminate internal holes within each building segment and filter out small patches, resulting in the final building instance segmentation. However, some errors remained: misidentification of non-building areas as buildings and omission of actual building parts. To further improve accuracy, point cloud data of the study area were used to refine the identification of residential building footprints. Point cloud filtering separated building points from non-building points. Concave hull polygons were then used to generate vectors for both building and non-building areas. The building vectors were merged with the optimized residential building footprints, while the non-building vectors were erased from them. This method effectively removed erroneous segments and filled in missing building parts, enhancing the accuracy and completeness of residential building footprint identification, resulting in the final residential building footprints. Finally, the oriented bounding box for each building was constructed based on the minimum bounding rectangle, serving as the final residential building extraction result, as shown in Figure 8.
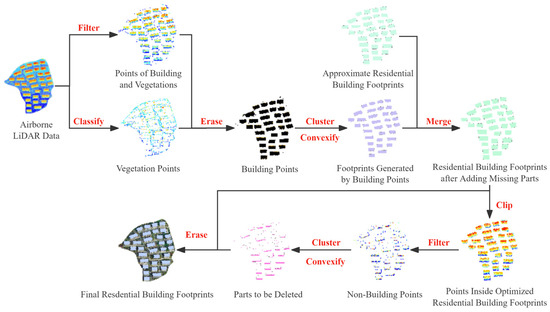
Figure 8.
The results of post-processing and oriented bounding box generation.
3.3. Assessment of Residential Complexes
The residential settings of urban complexes center on factors affecting the living conditions of residents within these areas. It is influenced by numerous factors, forming a complex system of interactions [49]. The layout of buildings within a residential complex is a key factor impacting the living quality of the area. Among the various indicators used to evaluate the urban residential settings. This study builds on previous research [50] and considers spatial openness and travel convenience within residential complexes. Six typical evaluation indicators were selected: building density [51], building height [52], floor area ratio [53], spacing between buildings, sky view factor [54,55], and distance to primary and secondary roads [56]. These indicators form a comprehensive evaluation system for the residential settings of urban complexes.
3.3.1. Selection and Calculation of Assessment Indicators
- Building Density (BD): The ratio of the total building footprint area to the land area within a residential complex. The calculation formula is shown in Equation (1):
- 2.
- Building Height (BH): The height of buildings within a complex directly impacts the internal landscape and visual comfort. The Digital Surface Model (DSM) includes height information of surface structures, bridges, and trees, while the Digital Elevation Model (DEM) represents the Earth’s surface topography without including building heights. The specific calculation formula of BH using DSM and DEM is shown in Equation (2):
- 3.
- Floor Area Ratio (FAR): This comprehensive indicator measures the quality of urban residential conditions and is a crucial technical parameter affecting developers’ economic interests. It reflects the comfort level of the residents. The FAR is calculated as the ratio of the total floor area of above-ground buildings to the land area. The total floor area is determined according to the “Calculation code for construction area of building” [57]. The number of floors of each building was calculated, and then the total floor area was obtained by combining the building footprint area. The specific calculation formulas are shown in Equations (3) and (4):
- 4.
- Spacing between buildings: This refers to the distance between the outer walls of two adjacent buildings within the same complex. This is one of the crucial factors for evaluating the residential complexes. Initially, the “Generate Near Table” tool in ArcMap10.2 spatial analysis tools was used to calculate the shortest distances between each building within the complex. Subsequently, the average of these distances was computed, using it as reference data to assess the score for building spacing in the residential complex.
- 5.
- Sky View Factor (SVF): The ratio of radiation received by a plane to the radiation emitted by the entire hemispheric environment. In simple terms, SVF reflects the proportion of sky visible to people in an urban area [58]. The SVF in this study was calculated using the SVF plugin in QGIS 3.16.3, with reference to https://github.com/UMEP-dev/UMEP-Docs/tree/master, accessed on 29 April 2024.
- 6.
- Distance from primary and secondary roads: The distance between residential complexes and primary or secondary roads to some extent reflects the convenience of transportation and daily life within the complexes. In this study, road network data around residential complexes were obtained from the Open Street Map official website. Primary and secondary roads were selected from this dataset. And then, the shortest distance from each building within the complex to the surrounding primary and secondary roads was calculated by using ArcMap10.2. The average of these distances was then used as reference data when assigning values to the assessment indicators.
3.3.2. Scoring Criteria for Assessment Indicators
- BD: Higher BD may lead to cramped internal spaces within a complex, affecting the comfort and quality of the residential environment. BD is negatively correlated with the spatial layout of residential complexes. This study refers to the maximum building density values for different residential building layouts in the “Standard for urban residential area planning and design” [59], categorizing building density according to the scoring criteria shown in Table 1.
 Table 1. BD scoring criteria.
Table 1. BD scoring criteria. - BH: Taller buildings may block the surrounding environment, leading to poorer lighting and ventilation conditions within the complex. They may also impact residents’ views and visual experiences. Building height is negatively correlated with the spatial environment. This study refers to the “Uniform standard for design of civil buildings” [60] regarding building height, categorizing building height according to the scoring criteria shown in Table 2.
 Table 2. BH scoring criteria.
Table 2. BH scoring criteria. - FAR: Higher FAR means constructing more buildings on limited land resources. Excessive FAR may lead to a sense of overcrowding within the complex, reducing the comfort and livability of the residential environment. Therefore, the FAR is also negatively correlated with spatial quality. The FAR is typically regulated by the government according to relevant provisions in the detailed control plans for various residential land uses under the current urban planning regulatory framework. Considering both domestic and international demand and the regulations of the “Standard for urban residential area planning and design” [59] for the FAR in residential complexes, as well as current trends and conditions, the scoring criteria for the FAR are defined as shown in Table 3.
 Table 3. FAR scoring criteria.
Table 3. FAR scoring criteria. - Spacing between buildings: This indicator directly affects ventilation, lighting, and landscape quality within a complex. Adequate spacing ensures clear spaces between buildings, providing good lighting and ventilation conditions, and allowing residents to enjoy the surrounding scenery. Spacing between buildings is positively correlated with the spatial layout of residential complexes. This study refers to the “Design code for residential buildings” [61] for building spacing guidelines. The grading criteria for building spacing are shown in Table 4.
 Table 4. Scoring criteria for the spacing between buildings.
Table 4. Scoring criteria for the spacing between buildings. - SVF: SVF is a dimensionless parameter, ranging from 0 to 1, with 0 indicating a completely obstructed sky and 1 indicating a completely open sky. SVF is positively correlated with spatial layout. Xu et al. [62] proposed an online method for rapidly estimating large-area SVF using SVI and obtained SVF for the Qinhuai District in Nanjing. The authors of [63] used LiDAR remote sensing to obtain high-resolution distributions of buildings and tree canopies at the urban scale and performed related SVF analysis, resulting in the SVF distribution for Incheon, South Korea. Based on research by domestic and international scholars, the grading criteria for SVF in this study are shown in Table 5.
 Table 5. SVF scoring criteria.
Table 5. SVF scoring criteria. - Distance from primary and secondary roads: This indicator evaluates the external spatial layout of residential complexes, considering transportation convenience. The closer a complex to primary and secondary roads, the more convenient travel becomes for residents. It is negatively correlated with spatial setting quality. The scoring criteria for this indicator are based on the complex life circle classification standards in the “Standard for urban residential area planning and design” [59], as shown in Table 6.
 Table 6. Scoring criteria for distance from primary and secondary roads.
Table 6. Scoring criteria for distance from primary and secondary roads.
3.3.3. Calculation of Weights for Assessment Indicators
The Analytic Hierarchy Process [64] was used to assign weights to the selected indicators. The weight distribution results for each evaluation indicator are shown in Table 7. These results passed the consistency test.

Table 7.
Weights of evaluation indicators.
3.3.4. Comprehensive Assessment Model
Based on the structure of the selected evaluation indicator system and the corresponding weight distribution, the urban residential settings quality index can be obtained through weighted comprehensive calculation [65]. By multiplying the scores of each indicator by their respective weights and summing them, the comprehensive evaluation model for urban residential settings quality is derived as follows:
where W represents the total score, Wi represents the scores of each indicator, Pi represents the weights of each indicator, and k is the number of the evaluation indicators.
Based on the results of the comprehensive evaluation model of urban residential complexes, further classification of the comprehensive score is conducted to determine the quality level of urban residential conditions. Referring to various grading methods of comprehensive indices at home and abroad [66], Ma et al. evaluated the quality of public space using a multi-criteria framework [67]. Le et al. [68] built a system of indicators divided into 4 levels (good, fair, pass, and fail) to measure the social housing quality in Vietnam. And Zhu et al. [69] defined five intervals of score to classify the residential communities into highly dissatisfactory, dissatisfactory, average, relatively satisfactory, and highly satisfactory ranges in Beijing. Combined with the overview of domestic urban residential complexes, and considering the characteristics of the residential areas in our study area, a classification standard was designed as shown in Table 8, along with corresponding grading comments, to perform a comprehensive evaluation of the quality of urban residential spatial layout. This standard categorizes residential complexes into four levels: Excellent, Good, Average, and Poor.

Table 8.
Assessment levels for residential complexes.
4. Results
In this section, firstly, the results of the residential building footprints extracted from the SAM-based residential building instance segmentation method are shown for each residential complex in the study area. And then, the results for each of the assessment indicators are presented. Finally, the calculation results of the comprehensive assessment model and the concluding assessment results are provided.
4.1. Results of Building Extraction
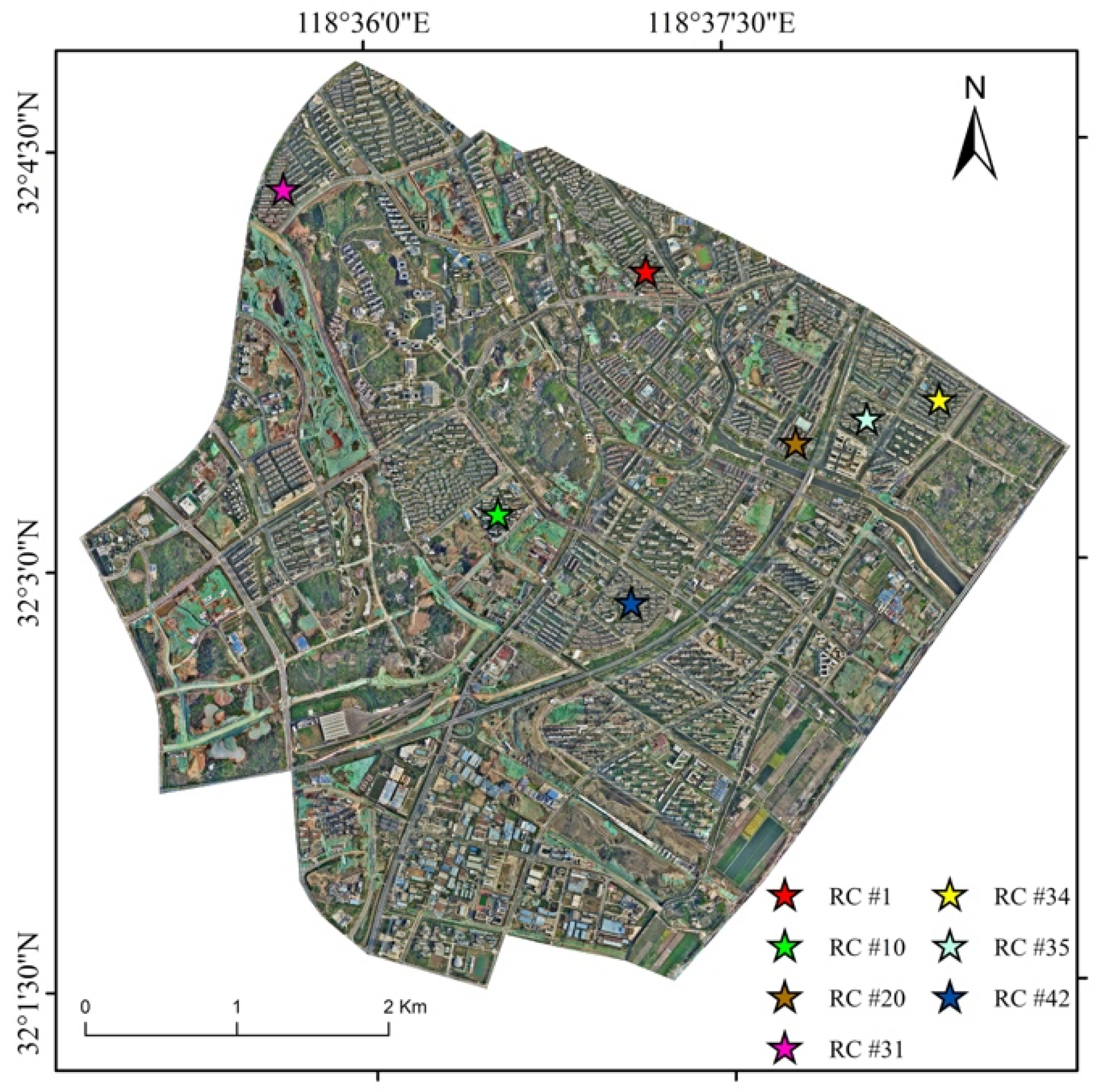
Building footprints within urban residential complexes in the study area were extracted by using the SAM-based residential building instance segmentation method based on LiDAR data and VHR images. As shown in Figure 9, the specific locations of seven residential complexes within the study area are illustrated. These complexes are labeled RC #1, RC #10, RC #20, RC #31, RC #34, RC #35, and RC #42.
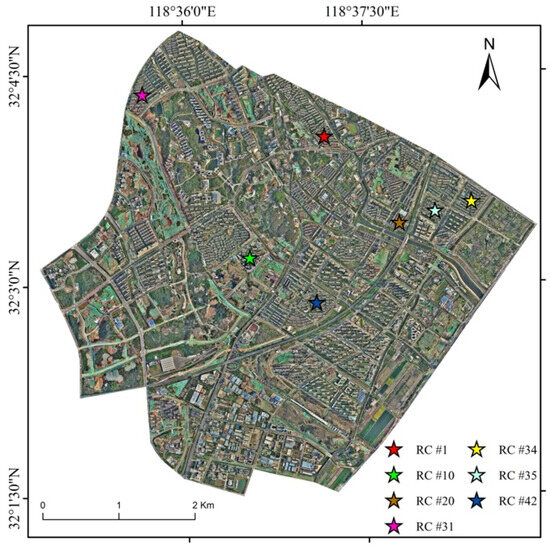
Figure 9.
The specific locations of the seven residential complexes in the study area.
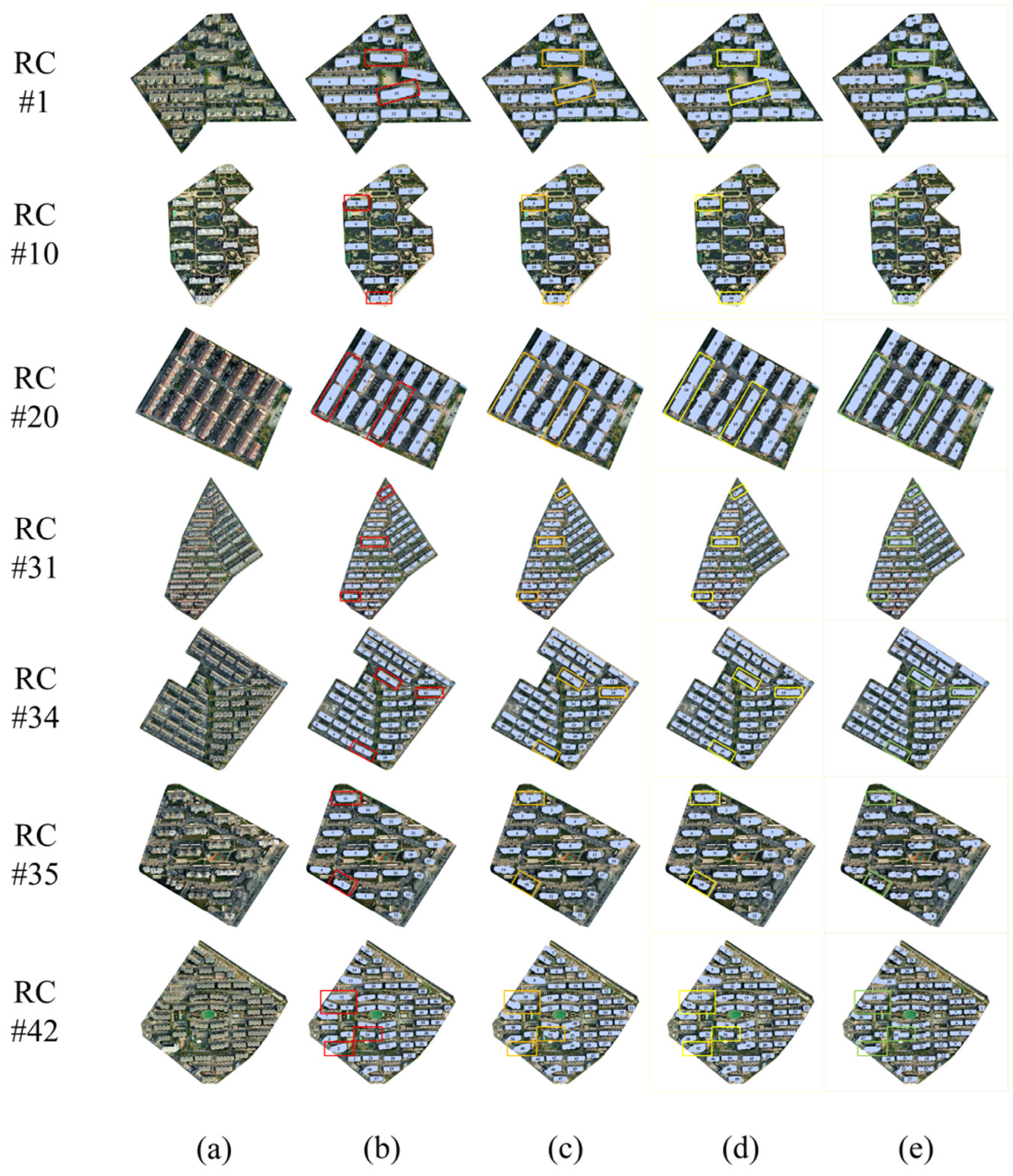
Further details of the experimental process are illustrated with seven residential complexes in the study area (Figure 10). The first column shows the original VHR images and the second column displays the approximate residential building footprints of each residential complex. The optimized approximate residential building footprints with n1_segment = 1000 and n2_segment = 1500 are in the third and fourth columns, respectively. And the final residential building footprints for each residential complex are presented in the last column.
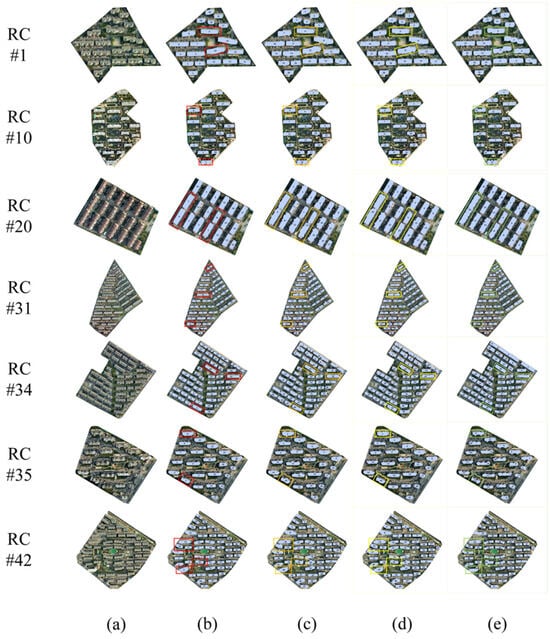
Figure 10.
Residential building footprint extraction results. (a) VHR images of the residential complexes; (b) approximate residential building footprints of each residential complex; (c) optimized approximate residential building footprints with n1_segment = 1000; (d) optimized approximate residential building footprints with n2_segment = 1500; and (e) final residential building footprints for each residential complexes. The localized detection results of (b–e) are marked with red, orange, yellow, and green boxes respectively.
The extracted building footprints were refined over the process of the experiment and became more consistent with the actual building footprints. As shown in Figure 10, a number of situations arose during the experiment: Firstly, the initial approximate residential building footprints avoided misclassification but exhibited indistinct boundaries and instances of omission (RC #11 and RC #42 in the second column). Secondly, due to lighting conditions, residential complexes with sloped roofs appeared in varying shades in the images, which may have resulted in the incomplete approximation of residential building footprints (RC #41 in the second column). Therefore, the optimization of the approximate residential building footprints was necessary. However, the effects of optimization varied with different superpixel parameter settings in the optimization process. These effects manifested as under-supplementation (RC #23 in the third column, n1_segment = 1000) or over-supplementation (RC #37 in the fourth column, n2_segment = 1500). Integrating two optimization results to generate bounding box prompts for the SAM, the final residential building footprints were extracted. In conclusion, comparing the final results with the actual building footprints on the VHR remote sensing imagery, the extracted residential building footprints were reliable. This result proved the feasibility of combining LiDAR data and VHR images in residential building footprint extraction.
4.2. Results of the Assessment of the Residential Complexes
Based on the final residential building footprints, the values of the six assessment indicators were calculated separately for each residential complex in the study area; the results are shown in Table 9. According to the data, approximately 66% of the residential complexes have a building density belong to 20~40%. These complexes provide adequate public space without appearing overcrowded. In contrast, 25% of the complexes are less than 20%, and these complexes have more favorable spatial openness. Secondly, building height significantly impacts residential settings in various ways. Appropriate building height contributes to the spatial openness of residential complexes. However, excessive height or inappropriate distribution may lead to issues such as sunlight obstruction and poor ventilation within the complex. Most residential complexes in the study area exhibit moderately scaled building heights. Notably, it has been observed that there is a residential complex with a building height exceeding 100 m. This type of heightened building structure may decrease the spatial openness and the livability of residential settings.

Table 9.
Values of the assessment indicators for the whole residential complexes in the study area.
Thirdly, the value of the FAR is very important to spatial compactness. An appropriate FAR can balance the building density and enhance the livability of the residential complex. In our study area, about 84% of the residential complexes have FAR values that fall into the range of 2 to 4, which is a suitable range of FAR for urban residential complexes. Fourthly, the value of SVF represents the ratio of the visible sky of a specific point. With greater openness, a higher SVF enhances the thermal comfort and livability of a residential complexes. The SVF values for all residential complexes in our study area are above 0.6, with approximately 43% falling within the range of 0.6 to 0.8, while the remainder belong to the rate of 0.8 to 1.
Fifthly, the spacing between buildings can significantly impact daylighting and ventilation within residential complexes. In our study area, nine residential complexes have inter-building distances of less than 6 m. Further analysis of VHR remote sensing images reveals that these complexes are marked by an excessively dense distribution of buildings, leading to a conspicuous lack of public spaces within the complexes. Finally, the distance from primary and secondary roads significantly impacts the convenience of travel for residents within residential complexes, including transportation accessibility, travel time, and travel options. A total of 79% of residential complexes within the study area are situated less than 300 m from primary and secondary roads. This proximity suggests that a significant majority of the residential complexes are well positioned to benefit from convenient access to public transportation and main traffic routes, thereby enhancing the overall mobility and commuting efficiency of their residents
To achieve a systematic and intuitive assessment of each residential complex, the indicator values are assigned new scores based on the rating criteria for each indicator. Subsequently, as shown in Table 10, the final scores (W) calculated by the comprehensive assessment model are used for assessing the residential complexes.

Table 10.
Values of the final scores (W) for all of the residential complexes in the study area.
According to the comprehensive assessment model, the total scores for seven example complexes detailed in Section 4.1, including RC #1, RC #10, RC #20, RC #31, RC #34, RC #35, and RC #42, are as follows: 74.10, 87.11, 73.17, 83.12, 72.98, 87.31, and 80.79. RC #31 and RC #42 fall into Level II with a favorable residential setting. On the contrary, RC #1, RC #20, and RC #34 are classified as Level III, indicating relatively moderate residential settings. Furthermore, RC #10 and RC #35 belong to Level I with scores of 87.11 and 87.31. These two complexes possess superior residential conditions. Further analysis combined with remote sensing images reveals the characteristics of those high-quality residential complexes: appropriate building distribution, sufficient public space, wide spacing between buildings, and moderate building heights, which together create a desirable and livable residential setting. After objectively assessing all the residential complexes in our study area with the comprehensive assessment model, the assessment results of residential complexes within the study area are shown in Figure 10.
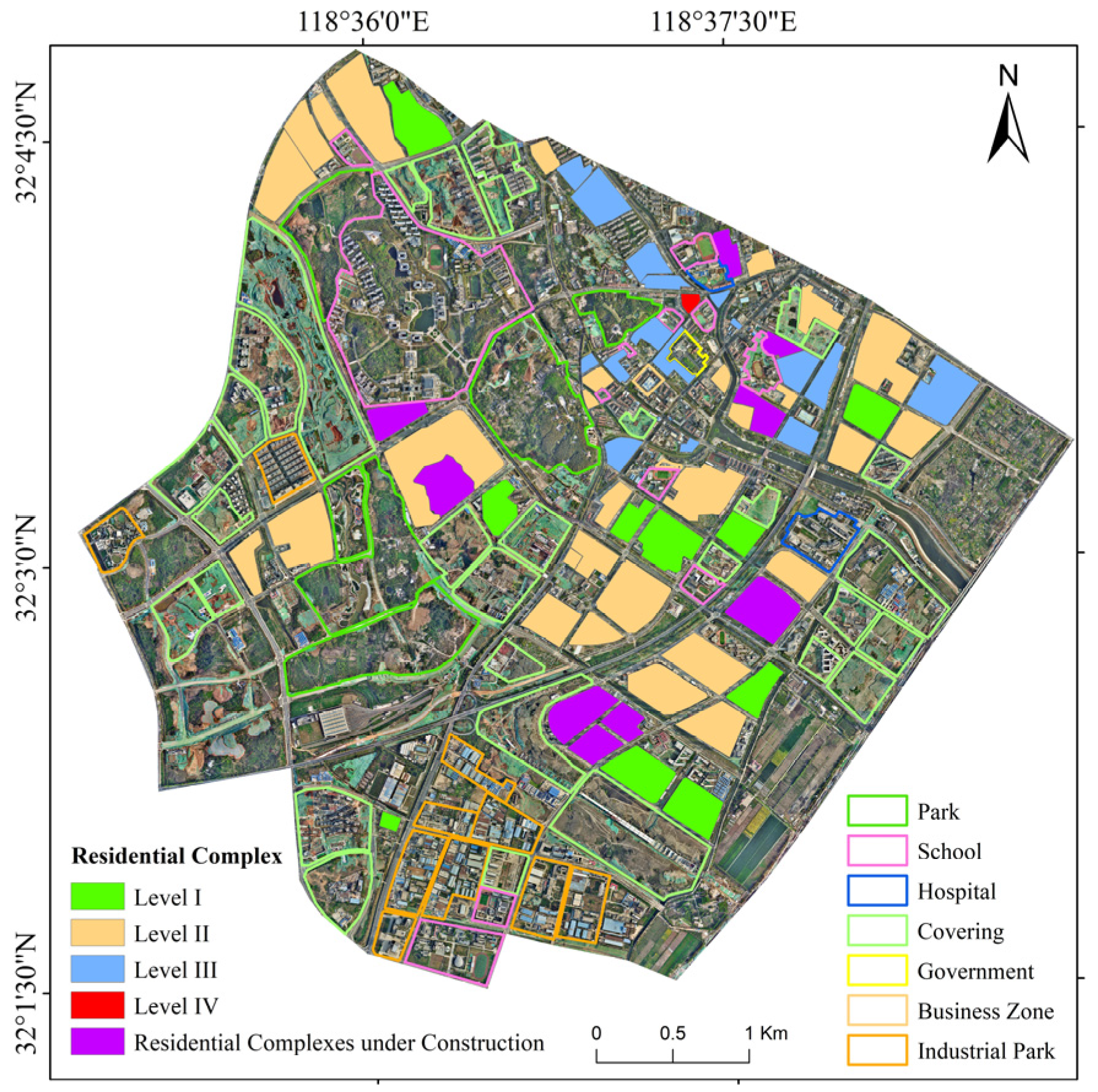
The residential complexes assessment results map (Figure 11) illustrates the classification of residential complexes based on the comprehensive assessment model. Each residential complex is color-coded according to its grade, with Level I indicating superior residential settings and layout, Level II representing moderate conditions, Level III reflecting residential conditions with room for improvement, and Level IV indicating residential conditions with significant challenges. In our study area, there were 10 residential complexes that belonged to Level I, while the number of residential complexes classified as Level II reached 29. In addition, there were 16 residential complexes classified as Level III due to narrow spacing between buildings, high building density, and FAR. It is worth noting that there is a residential complex classified as Level IV, which presents a reverse case in spatial layout. Within this complex, the value of building density has reached 50.5%, which means that almost half of the space in the complex was occupied by residential buildings. And the spacing between buildings was excessively narrow, with an average value of only 3.95 m. The spatial compactness of this complex is so dense that it may cause spatial confinement and oppression.
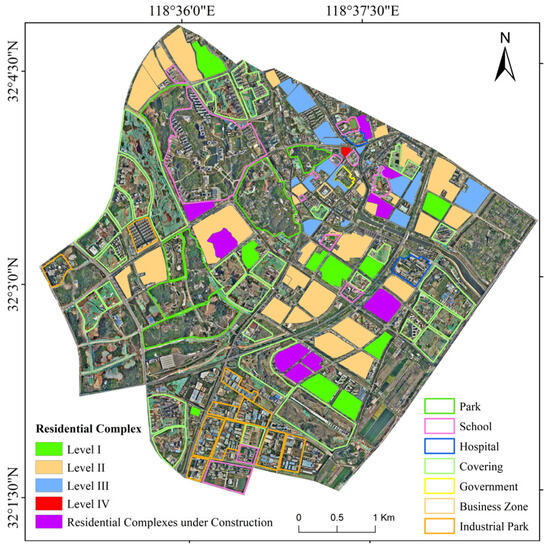
Figure 11.
The assessment results map of residential complexes within the study area.
From residential complexes categorized as Level I to Level IV, there are evident gradations in our study area. These level disparities reflect the quality and features of the spatial layout and reveal differences in socioeconomic conditions and development levels among different regions. The results provided a visual representation of the spatial distribution of residential complexes that belong to different levels within the study area, aiding in urban planning.
5. Discussion
5.1. The Effect of Different Prompts for the SAM
The SAM has certain limitations in remote sensing image object segmentation, and the quality of segmentation results heavily depends on the type, location, and quantity of prompts. The utilization of different prompt construction methods in the SAM can yield varied segmentation effects. To enhance the instance segmentation capability of the base model for remote sensing images, this study compared five prompt construction methods: bounding box, grid point sampling, centroids, global random sampling, and equidistant random sampling.
- Bounding box: A bounding box is a simple rectangular frame that tightly encloses one or more objects in an image. In this study, based on clustered point cloud data, a bounding box was constructed for each class of point clouds as prompts, according to the X and Y coordinate values of each class of point clouds.
- Grid point sampling: A series of points is uniformly generated within each approximate vector surface of residential buildings as prompts in this study.
- Centroid: In this study, centroids are selected as prompts based on the approximate vector surfaces of residential buildings.
- Global Random Sampling: In this study, 10 points are randomly selected within each approximate vector surface of residential buildings, and the centroid within each vector surface is chosen as the prompt.
- Equidistant Random Sampling: In this study, points are uniformly and irregularly selected within the approximate vector surfaces of residential buildings as prompts.
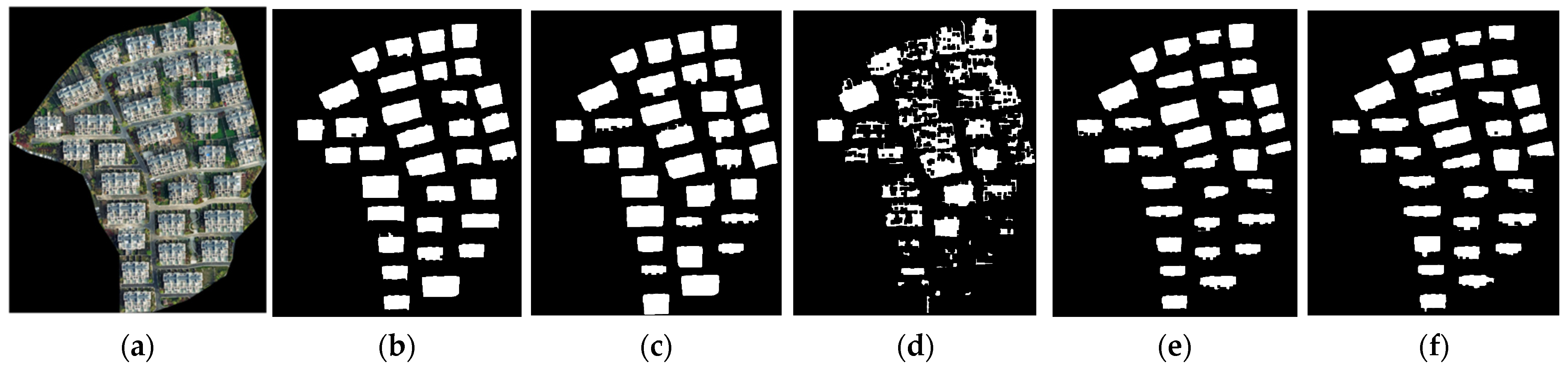
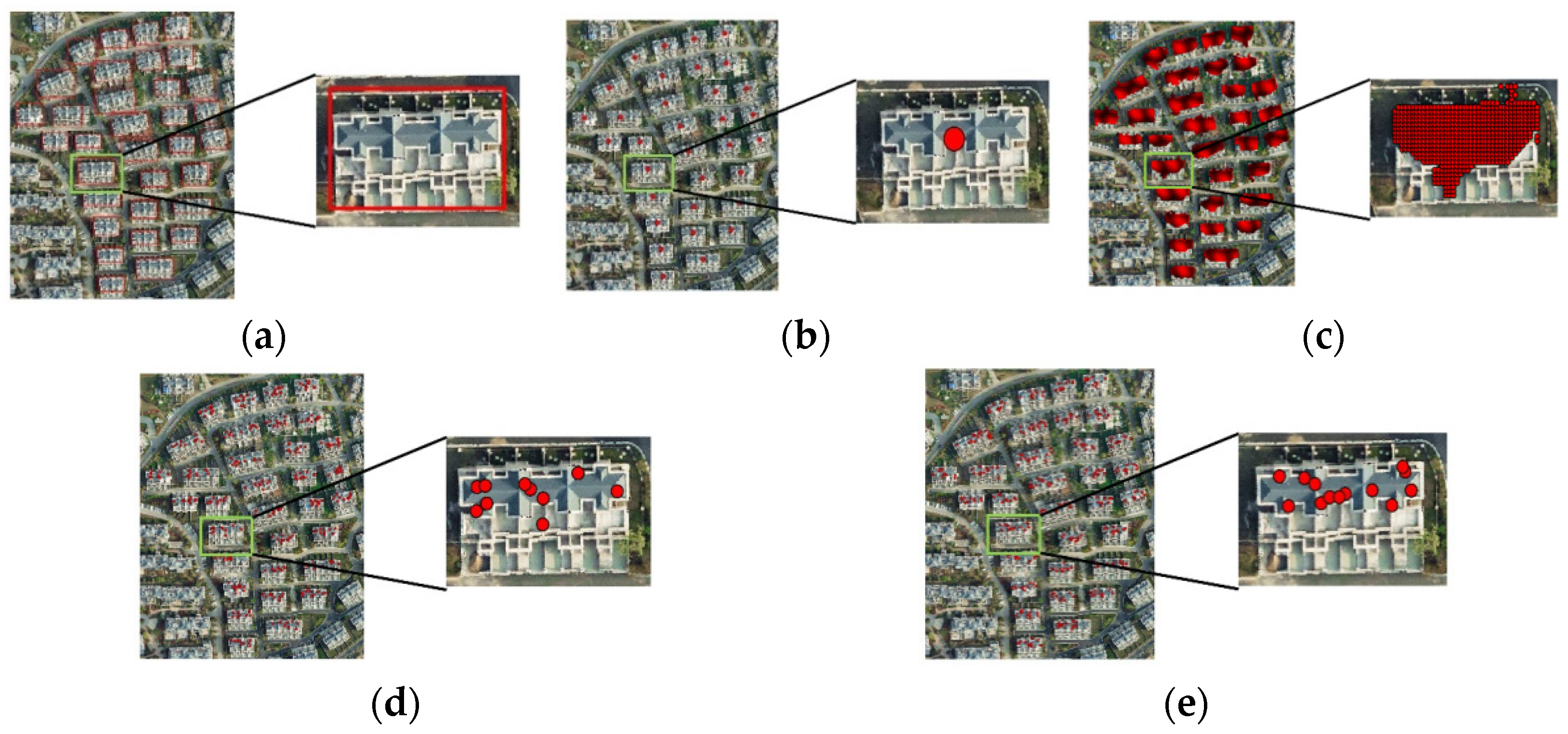
Using five different prompts (Figure 12) as input data for the SAM, residential buildings were segmented in the same area of VHR satellite images, resulting in the segmentation shown in Figure 13. A comparison revealed that constructing prompts with bounding boxes yielded better segmentation results using the SAM. Therefore, bounding boxes were utilized to construct the box prompts in this study.
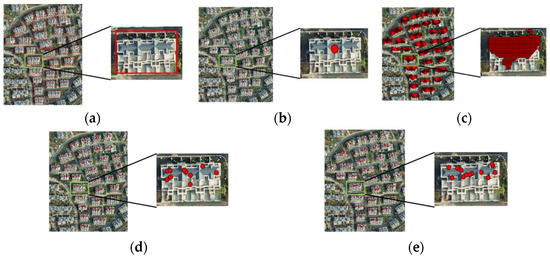
Figure 12.
Five different prompts in red overlaid on the VHR image: (a) bounding box; (b) centroid; (c) grid point sampling; (d) global random sampling; and (e) equidistant random sampling. In (a–e), the right sub-image is a zoomed-in view of the boxed area with a green border in the left sub-image.

Figure 13.
Segmentation results for building instances using different prompts: (a) VHR images; (b) the results of bounding box prompts; (c) the results of centroid prompts; (d) the results of grid point sampling prompts; (e) the results of global random sampling prompts; and (f) the results of equidistant random sampling prompts.
5.2. Study Significance and Uncertainties
To enhance the efficiency and accuracy of building extraction in residential complexes, an automated prompt generator for SAM-based residential building instance segmentation methods was established combining LiDAR data and VHR remote sensing images in this study. Additionally, based on the extracted building results, an assessment model for the spatial layout of residential complexes was proposed. This model systematically evaluates the residential settings of urban complexes using six dimensions of assessment indicators. The evaluation results can assist government agencies in understanding the quality of residential spatial layouts in different complexes and provide data references for urban planning. On the one hand, by assessing the quality of residential spatial layouts, planners can determine appropriate zoning designations that align with community needs and development goals, on the other hand, understanding the spatial distribution and layout of residential complexes helps in planning infrastructure such as roads, utilities, and public amenities to serve the population.
However, some limitations remain in this study. First, when extracting buildings, this study considered all buildings extracted within residential complexes as residential buildings. However, it did not consider whether buildings higher than 10 m within urban residential complexes were used for residential purposes, potentially including buildings used for commercial or other purposes. Secondly, in the year of 2019, some residential buildings in the study area were still under construction, and although some were completed, the community infrastructure was still being developed. When assessing urban residential complexes, the analysis focused only on aspects like spatial openness of buildings and convenience of travel within the complexes, without considering other indicators such as green space ratio and the level of public facility completeness. In future assessments of residential spatial layout, it will be necessary to consider the impact of multiple factors. Additionally, due to the discontinuity in the initial LiDAR data and ongoing construction in certain residential complexes, the extraction results of building footprints in some residential complexes were unsatisfactory. Therefore, these types of residential complexes were not considered during the assessment of the residential settings within the residential complexes.
6. Conclusions
With the acceleration of urbanization, the scale and number of residential complexes continue to grow. Evaluating and managing these complexes effectively has become a critical issue in urban planning and governance. Under this circumstance, it becomes especially critical to accurately obtain information about the buildings within these residential complexes. However, limited by efficiency and accuracy, obtaining building information using traditional methods of building extraction is challenging. In this paper, the SAM-based residential building instance segmentation method with an automated prompt generator was proposed to detect residential building footprints from LiDAR data and VHR remote sensing images. First, the spatial positions of each residential building were extracted from complex point cloud data to generate approximate building footprints. Then, these footprints were refined using VHR imagery to create bounding box prompts. Finally, the SAM model was used to extract residential building footprints by combining the images and bounding box prompts. Additionally, based on the extracted building footprints, a comprehensive assessment model for the spatial layout of residential complexes was proposed. This model categorizes residential complexes into different levels based on various criteria, including building density, building height, floor area ratio, sky view factor, spacing between buildings, and distance from primary and secondary roads. This method and model were applied to Pukou District, Nanjing, Jiangsu Province, China, in 2019. The following conclusions were drawn from this study:
- (1)
- The SAM-based residential building instance segmentation method was used to effectively extract residential building footprints. Comparing the final results with the actual building footprints on the VHR remote sensing imagery, it was proven that the extracted residential building footprints were reliable. The method demonstrated the feasibility of combining LiDAR data and VHR imagery in the SAM for extracting residential building footprints.
- (2)
- The residential layout of the complexes was classified into four levels. Significant differences in quality were observed among these levels. The numbers of residential complexes classified as level I (Excellent), II (Good), III (Average), and IV (Poor) were 10, 29, 16, and 1, respectively. Residential complexes with better residential settings had evenly distributed buildings, reasonable spacing between buildings, and high levels of greenery and open spaces. In contrast, residential complexes with poorer residential conditions mostly consisted of multi-story buildings. Although the building heights were moderate, the buildings were crowded with narrow spacing, and the complexes lacked greenery and public spaces, resulting in a cramped and oppressive spatial layout.
The results of this study indicate that the SAM-based residential building instance segmentation method effectively extracts building footprints. The proposed urban residential assessment model evaluates residential complexes quickly and effectively. These findings are effective and expandable for rapidly assessing residential complexes. It also provides detailed and useful information on residential complexes for sustainable urban planning.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.J. and S.L.; methodology, Y.J. and W.W. (Weiguo Wu); software, Y.J., G.W. and Y.Z.; validation, Y.Z., W.W. (Weilin Wang) and H.Y.; formal analysis, W.W. (Weilin Wang), Z.T. and H.Y.; investigation, G.W., W.W. (Weilin Wang) and H.Y.; resources, Y.J., Y.Z. and Z.T.; data curation, W.W. (Weilin Wang) and Z.T.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.J. and G.W.; writing—review and editing, W.W. (Weiguo Wu) and S.L.; visualization, Y.Z. and H.Y.; supervision, W.W. (Weiguo Wu) and S.L.; project administration, Y.J. and W.W. (Weiguo Wu). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2022YFB4501604).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We appreciate all reviewers who provided constructive comments on this paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
The summary table of abbreviations.
Table A1.
The summary table of abbreviations.
| Abbreviation | Full Name | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| LiDAR | Light Detection and Ranging | A technology that uses laser light to measure distances to the Earth’s surface or other objects. |
| VHR | Very High Resolution | Refers to satellite or aerial imagery with extremely fine spatial detail. |
| SAM | Segment Anything Model | A model or algorithm used for object segmentation tasks in images or data. |
| AOI | Area of Interest | A specific geographic area defined and used for analysis or processing in geographic information systems (GISs). |
| AMAP inside | AMAP inside | Refers to professional services provided by AutoNavi’s open platform. |
| OSM | Open Street Map | An open-source geographic information project that provides free map data and services. |
| MLP | Multi-Layer Perceptron | A type of artificial neural network commonly used for classification and regression tasks in machine learning. |
| DBSCAN | Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise | A clustering algorithm that identifies clusters based on density in spatial data that is capable of handling noise and outliers. |
| SLIC | Simple Linear Iterative Clustering | An algorithm used for image segmentation that partitions an image into cohesive regions or superpixels. |
| DSM | Digital Surface Model | A model representing the Earth’s surface, including natural and human-made objects such as buildings and trees. |
| DEM | Digital Elevation Model | A 3D representation of terrain elevation data, typically used in geographic and spatial analysis. |
| nDSM | normalized Digital Surface Model | A Digital Surface Model adjusted to normalize elevations relative to a Digital Elevation Model (DEM), is often used for specific analysis purposes. |
| BD | Building Density | The ratio of the area of buildings within a specific area of land. |
| BH | Building Height | The vertical distance from the ground level to the highest point of a building. |
| FAR | Floor Area Ratio | The ratio of the total floor area of above-ground buildings to the land area. |
| SVF | Sky View Factor | The ratio of the visible area of the sky as seen from a specific point on the ground. |
References
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, R.; Wu, Y.; Chu, G.; Wu, X. The Influence of Built-Environment Factors on Connectivity of Road Networks in Residential Areas: A Study Based on 204 Samples in Nanjing, China. Buildings 2023, 13, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, R.C.; Galo, M.; Carrilho, A.C.; Pessoa, G.G.; de Oliveira, R.A.R. Automatic Building Change Detection Using Multi-Temporal Airborne Lidar Data. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Latin American GRSS & ISPRS Remote Sensing Conference (LAGIRS), Santiago, Chile, 22–26 March 2020; pp. 54–59. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, Z.; Cheng, T.; Fu, H.; Li, D.; Huang, X. Emerging Issues in Mapping Urban Impervious Surfaces Using High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellmann, T.; Lausch, A.; Andersson, E.; Knapp, S.; Cortinovis, C.; Jache, J.; Scheuer, S.; Kremer, P.; Mascarenhas, A.; Kraemer, R.; et al. Remote Sensing in Urban Planning: Contributions towards Ecologically Sound Policies? Landsc. Urban Plan. 2020, 204, 103921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Najjar, H.A.H.; Kalantar, B.; Pradhan, B.; Saeidi, V.; Halin, A.A.; Ueda, N.; Mansor, S. Land Cover Classification from Fused DSM and UAV Images Using Convolutional Neural Networks. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malbhage, P.; Khoje, S. Building and Tree Detection by Fusing LiDar and Aerial Images for Urban Development Planning. In Proceedings of the 2017 Ninth International Conference on Advanced Computing (ICoAC), Chennai, India, 14–16 December 2017; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Zheng, X.; Fan, H.; Sun, M. Urban Spatial Structure Analysis: Quantitative Identification of Urban Social Functions Using Building Footprints. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 15, 507–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Zlatanova, S.; Aleksandrov, M.; Diakite, A.A.; Pettit, C. Integration of 3D objects and terrain for 3D modelling supporting the digital twin. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2019, IV-4-W8, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Xing, C.; Cai, L. Building Image Feature Extraction Using Data Mining Technology. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, e8006437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Wang, B.; Wang, Z.; Li, H.; Li, H.; Fu, K. Research Progress on Few-Shot Learning for Remote Sensing Image Interpretation. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 2387–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Shao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, X. Deep Learning in Different Remote Sensing Image Categories and Applications: Status and Prospects. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2022, 43, 1800–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, M.; Chaurasia, K.; Kumar Mishra, V. Dilated-ResUnet: A Novel Deep Learning Architecture for Building Extraction from Medium Resolution Multi-Spectral Satellite Imagery. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 184, 115530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z. A Theoretical Review of Vegetation Extraction Methods Based on UAV. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 546, 032019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Xiong, X.; Cao, L.; Yu, D.; Yang, G.; Yang, L. Pixel-Level Prediction for Ocean Remote Sensing Image Features Fusion Based on Global and Local Semantic Relations. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 11644–11654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghandour, A.J.; Jezzini, A.A. Autonomous Building Detection Using Edge Properties and Image Color Invariants. Buildings 2018, 8, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yu, M.; Chen, X.; Zhou, F.; Ren, J.; Xu, H.; Xu, S. Combining Deep Fully Convolutional Network and Graph Convolutional Neural Network for the Extraction of Buildings from Aerial Images. Buildings 2022, 12, 2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Huang, J.; Wang, M.; Tao, S.; Yang, R.; Zhang, X. Semantic Feature-Constrained Multitask Siamese Network for Building Change Detection in High-Spatial-Resolution Remote Sensing Imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2022, 189, 78–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Zhang, T.; Yu, D.; Ji, S.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, J. From Lines to Polygons: Polygonal Building Contour Extraction from High-Resolution Remote Sensing Imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2024, 209, 213–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes Reyes, M.; Xie, Y.; Yuan, X.; d’Angelo, P.; Kurz, F.; Cerra, D.; Tian, J. A 2D/3D Multimodal Data Simulation Approach with Applications on Urban Semantic Segmentation, Building Extraction and Change Detection. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2023, 205, 74–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Gong, J.; Hu, X. Community-Scale Multi-Level Post-Hurricane Damage Assessment of Residential Buildings Using Multi-Temporal Airborne LiDAR Data. Autom. Constr. 2019, 98, 30–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Gong, J. Automated Residential Building Detection from Airborne LiDAR Data with Deep Neural Networks. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2018, 36, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Nakano, K.; Wakabayashi, K. Building detection from aerial lidar point cloud using deep learning. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2022, XLIII-B2-2022, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, Z.; Li, Z.; Cheng, P.; Ziggah, Y.Y.; Fan, J. Building Extraction from Airborne LiDAR Data Based on Multi-Constraints Graph Segmentation. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zheng, G.; Chi, X.; Yang, L.; Geng, Q.; Li, J.; Qiao, Y. Mapping Fine-Scale Building Heights in Urban Agglomeration with Spaceborne Lidar. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 285, 113392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramiya, A.M.; Nidamanuri, R.R.; Krishnan, R. Segmentation Based Building Detection Approach from LiDAR Point Cloud. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2017, 20, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullo, S.L.; Zarro, C.; Wojtowicz, K.; Meoli, G.; Focareta, M. LiDAR-Based System and Optical VHR Data for Building Detection and Mapping. Sensors 2020, 20, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Zhang, L.; Cui, X.; Ai, H.; Xu, B. Extraction of Buildings from Multiple-View Aerial Images Using a Feature-Level-Fusion Strategy. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemian, N.; Wang, J.; Reza Najafi, M. Building Detection Using a Dense Attention Network from LiDAR and Image Data. Geomatica 2021, 75, 209–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Du, P.; Lin, C.; Wang, X.; Li, E.; Xue, Z.; Bai, X. A Hybrid Attention-Aware Fusion Network (HAFNet) for Building Extraction from High-Resolution Imagery and LiDAR Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wu, H.; An, R.; Xu, H.; He, Q.; Xu, J. An Improved Building Boundary Extraction Algorithm Based on Fusion of Optical Imagery and LIDAR Data. Optik 2013, 124, 5357–5362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Han, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, S. Semantic Segmentation for Remote Sensing Based on RGB Images and Lidar Data Using Model-Agnostic Meta-Learning and Partical Swarm Optimization. IFAC-PapersOnline 2020, 53, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahhas, F.H.; Shafri, H.Z.M.; Sameen, M.I.; Pradhan, B.; Mansor, S. Deep Learning Approach for Building Detection Using LiDAR–Orthophoto Fusion. J. Sens. 2018, 2018, e7212307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Gorte, B.; Lindenbergh, R.; Widyaningrum, E. 3D building change detection between current VHR images and past lidar data. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2018, XLII–2, 1229–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirillov, A.; Mintun, E.; Ravi, N.; Mao, H.; Rolland, C.; Gustafson, L.; Xiao, T.; Whitehead, S.; Berg, A.C.; Lo, W.-Y.; et al. Segment Anything. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 3992–4003. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, L.; Zhu, K.; Peng, D.; Tang, H.; Yang, K.; Bruzzone, L. Adapting Segment Anything Model for Change Detection in VHR Remote Sensing Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Zhu, L.; Ding, C.; Cao, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, Z.; Sun, L.; Zang, Y.; Mao, P. SAM-Adapter: Adapting Segment Anything in Underperformed Scenes. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCVW), Paris, France, 2–6 October 2023; pp. 3359–3367. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Ma, K.; Kapse, S.; Saltz, J.; Vakalopoulou, M.; Prasanna, P.; Samaras, D. SAM-Path: A Segment Anything Model for Semantic Segmentation in Digital Pathology. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2023 Workshops, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–12 October 2023; Celebi, M.E., Salekin, M.S., Kim, H., Albarqouni, S., Barata, C., Halpern, A., Tschandl, P., Combalia, M., Liu, Y., Zamzmi, G., et al., Eds.; Springer Nature Switzerland: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 161–170. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wang, D.; Yuan, C.; Li, H.; Hu, J. Enhancing Agricultural Image Segmentation with an Agricultural Segment Anything Model Adapter. Sensors 2023, 23, 7884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wei, Y.; Omrani, H.; Pijanowski, B.; Doucette, J.; Li, K.; Wu, Y. Analysis on Residential Density Dynamics in USA-a Case Study in Southeast Wisconsin. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 52, 101866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.; Zhang, T.; Dewancker, B.J.; He, J.; Liu, S. Exploring the Unit Spatial Layout Preference for Urban Multi-Unit Residential Buildings: A Survey in Beijing, China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, C.; Meng, J.; Ju, L.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, W. Assessing Community-Level Livability Using Combined Remote Sensing and Internet-Based Big Geospatial Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 4026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Jia, L.; Zhang, F.; Wang, R.; Liu, X.; Zou, L.; Tang, X. Do New Urbanization Policies Promote Sustainable Urbanization? Evidence from China’s Urban Agglomerations. Land 2024, 13, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Shi, W.; Zhang, S. Progress of Research on Urban Growth Boundary and Its Implications in Chinese Studies Based on Bibliometric Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 16644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.-H.; Yuan, Q.; Cai, H. Unravelling Urban Governance Challenges: Objective Assessment and Expert Insights on Livability in Longgang District, Shenzhen. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 155, 110989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Liu, Y. Livability Assessment of 101,630 Communities in China’s Major Cities: A Remote Sensing Perspective. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2022, 65, 1073–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onnom, W.; Tripathi, N.; Nitivattananon, V.; Ninsawat, S. Development of a Liveable City Index (LCI) Using Multi Criteria Geospatial Modelling for Medium Class Cities in Developing Countries. Sustainability 2018, 10, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ester, M.; Kriegel, H.-P.; Xu, X. A Density-Based Algorithm for Discovering Clusters in Large Spatial Databases with Noise. KDD 1996, 96, 226–231. [Google Scholar]
- Achanta, R.; Shaji, A.; Smith, K.; Lucchi, A.; Fua, P.; Süsstrunk, S. SLIC Superpixels Compared to State-of-the-Art Superpixel Methods. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2012, 34, 2274–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guellab, S.; Benkhelifa, I. Enhancing Parking Online Reservation with a Recommendation System Based on User Preferences: A Hybrid Approach. In Proceedings of the 2023 20th ACS/IEEE International Conference on Computer Systems and Applications (AICCSA), Giza, Egypt, 4–7 December 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lapidus, A.; Topchiy, D.; Kuzmina, T.; Shesterikova, Y.; Bidov, T. An Integrated Quality Index of High-Rise Residential Buildings for All Lifecycle Stages of a Construction Facility. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, I.Y.S.; Liu, A.M.M. Effects of Neighborhood Building Density, Height, Greenspace, and Cleanliness on Indoor Environment and Health of Building Occupants. Build. Environ. 2018, 145, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Zhou, W.; Yan, J.; Qian, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, W. The Higher, the Cooler? Effects of Building Height on Land Surface Temperatures in Residential Areas of Beijing. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2019, 110, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, H.; Yan, T. Quality Assessment for Human Settlement of Urban Community Based on Remote Sensing Technology. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Spatial Data Mining and Geographical Knowledge Services, Fuzhou, China, 29 June–1 July 2011; pp. 417–420. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Liu, R.; Cheng, Q.; Chen, Y.; Cao, S.; Du, M.; Li, K. Evaluating the Impact of Sky View Factor and Building Shadow Ratio on Air Temperature in Different Residential and Commercial Building Scenarios: A Case Study of Beijing, China. Urban Clim. 2023, 49, 101509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, D.-K.; Brown, R.D.; Kim, S.; Kim, J.-H.; Sung, S. The Effect of Extremely Low Sky View Factor on Land Surface Temperatures in Urban Residential Areas. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 80, 103799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Lei, K.; Tong, H.; Li, B.; Wang, W.; Hou, Q. Land Use Characteristics of Xi’an Residential Blocks Based on Pedestrian Traffic System. Alex. Eng. J. 2021, 60, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T50353-2013; Calculation Code for Construction Area of Building. China Planning Press: Beijing, China, 2013.
- Oduncu, E.; Yüksel, S.E. Analyzing the Correlation of Sky-View Factor and Shadow Regions in Hyperspectral Data. In Proceedings of the 2016 24th Signal Processing and Communication Application Conference (SIU), Zonguldak, Turkey, 16–19 May 2016; pp. 1989–1992. [Google Scholar]
- GB50180-2018; Standard for Urban Residential Area Planning and Design. China Architecture and Building Press: Beijing, China, 2018.
- GB50352_2019; Uniform Standard for Design of Civil Buildings. China Architecture and Building Press: Beijing, China, 2019.
- GB 50096—1999; Design Code for Residential Buildings. China Architecture and Building Press: Beijing, China, 2003.
- Xu, H.; Lu, H.; Liu, S. Online Street View-Based Approach for Sky View Factor Estimation: A Case Study of Nanjing, China. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.M. A Study on Urban-Scale Building, Tree Canopy Footprint Identification and Sky View Factor Analysis with Airborne LiDAR Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, I.F.C.; Ferreira, F.A.F.; Meidutė-Kavaliauskienė, I.; Govindan, K.; Fang, W.; Falcão, P.F. An Evaluation Thermometer for Assessing City Sustainability and Livability. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 47, 101449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, U.; Ahmad, S.R.; Mohey-ud-din, G.; Butt, H.J.; Ashraf, U. An Integrated Approach for Developing an Urban Livability Composite Index—A Cities’ Ranking Road Map to Achieve Urban Sustainability. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valcárcel-Aguiar, B.; Murias, P.; Rodríguez-González, D. Sustainable Urban Liveability: A Practical Proposal Based on a Composite Indicator. Sustainability 2019, 11, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mela, A.; Vryzidis, I.; Varelidis, G.; Tsotsolas, N. Urban Space Quality Evaluation Using Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis-Based Framework. In Multicriteria Decision Aid and Resource Management: Recent Research, Methods and Applications; Spyridakos, A., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 59–84. ISBN 978-3-031-34892-1. [Google Scholar]
- Le, L.H.; Ta, A.D.; Dang, H.Q. Building up a System of Indicators to Measure Social Housing Quality in Vietnam. Procedia Eng. 2016, 142, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Jin, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H. Construction of Residential Quality Assessment System Using Factor Analysis Method Based on Residents’ Satisfaction Survey: Case Study of Beijing, China. J. Asian Archit. Build. Eng. 2023, 22, 3253–3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).