Abstract
Spectral confusion among land cover classes is quite common, let alone in a complex and heterogenous system like the semi-arid Mediterranean environment; thus, employing new developments in remote sensing, such as multispectral imagery (MSI) captured by unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and airborne light detection and ranging (LiDAR) techniques, with deep learning (DL) algorithms for land cover classification can help to address this problem. Therefore, we propose an image-based land cover classification methodology based on fusing multispectral and airborne LiDAR data by adopting CNN-based semantic segmentation in a semi-arid Mediterranean area of northeastern Aegean, Greece. The methodology consists of three stages: (i) data pre-processing, (ii) semantic segmentation, and (iii) accuracy assessment. The multispectral bands were stacked with the calculated Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) and the LiDAR-based attributes height, intensity, and number of returns converted into two-dimensional (2D) images. Then, a hyper-parameter analysis was performed to investigate the impact on the classification accuracy and training time of the U-Net architecture by varying the input tile size and the patch size for prediction, including the learning rate and algorithm optimizer. Finally, comparative experiments were conducted by altering the input data type to test our hypothesis, and the CNN model performance was analyzed by using accuracy assessment metrics and visually comparing the segmentation maps. The findings of this investigation showed that fusing multispectral and LiDAR data improves the classification accuracy of the U-Net, as it yielded the highest overall accuracy of 79.34% and a kappa coefficient of 0.6966, compared to using multispectral (OA: 76.03%; K: 0.6538) or LiDAR (OA: 37.79%; K: 0.0840) data separately. Although some confusion still exists among the seven land cover classes observed, the U-Net delivered a detailed and quite accurate segmentation map.
1. Introduction
Semi-arid Mediterranean environments are characterized by the complexity and heterogeneity of their land cover types [1], with significant spatial variation in their vegetation dynamics due to the distribution of water and sediments [2], making them challenging for remote sensing-based classification tasks [3]. The literature on remote sensing image classification of these landscapes has highlighted several reasons that lead to difficulties in image interpretation, such as the great temporal variability in the spectral properties of large-scale land covers causing high spectral intra-class variability and low inter-class separability, the assortment of spatial frequency of the landscape resulting in habitat fragmentation, and the high reflectance similarity of land cover features complicating spectral segregation [3,4]. Furthermore, challenges stem from the diverse vegetation coverages, the imbalances in multi-object class distribution, and the “Hughes phenomenon” due to the high dimensionality of spectral information [5,6,7].
Despite the challenging task of classifying semi-arid ecosystems through remote sensing techniques, precise and high-resolution land cover mapping of these regions is essential for effectively monitoring, recording, and managing their natural resources [1,8]. Other than management tasks, the identification, delineation, and mapping of land cover [9] can assist in analyzing the status and the dynamics of a region’s terrestrial surface, developing conservation plans, evaluating land degradation (e.g., desertification and deforestation), explaining patterns in species abundance and distributions, providing insight into economic stability, etc. [10,11,12,13,14,15]. Therefore, systematically generating land cover maps is imperative for planning and implementing actions to prevent the depletion of natural resources, in addition to keeping track of environmental changes [16].
The role of remote sensing (RS) for land cover classification tasks has been described through a large volume of published studies [14,15,17,18]. During its phase of rapid growth in the recent past, remote sensing acquisition technology resulted in a significant increase in the number and availability of datasets, captured through passive or active sensors [e.g., multispectral (MS), hyperspectral (HS), light detection and ranging (LiDAR), and synthetic aperture radar (SAR) sensors], which created the opportunity for combining multi-modal datasets to enhance the effectiveness of processing methods for a wide range of applications [5,19,20,21,22,23]. Utilizing different and additional information, i.e., spectral properties and spatial features, in a coupled and joint manner has exhibited the potential to improve the interpretation performance on very-high-resolution (VHR) images and the discrimination performance of land cover types [5,12,19,20,21,24]. Thus, multispectral LiDAR point clouds, which contain both spectral and spatial information, have garnered more and more interest in various fields applying remote sensing [25].
The rapid growth of computational approaches and hardware resulted in the development of innovative methods in image classification. Deep learning (DL) algorithms, which autonomously learn features and their hierarchical representations from bottom-up, have become extremely popular in the geoscience and RS communities [26] because of their significant success at many image analysis tasks, including land cover classification [27], surpassing conventional supervised machine learning (ML) models, such as support vector machine (SVM), random forest (RF), decision trees (DT), k-nearest neighbor (KNN), etc., in terms of adaptability and flexibility due to their high independence on manual descriptors [15].
Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) constitute a type of DL algorithm that has come again under the spotlight in the past ten years due to their characteristic of processing data arranged in a grid pattern, such as signals, images, videos, etc. [28]. Of course, this makes them promising candidates to tackle the challenges of processing RS datasets (e.g., multi-band images) [27]. CNNs are capable of learning spectral and spatial information from images by automatically extracting mid- and high-level abstract features from an input image [29]. As noted by Zhu et al. [30], CNN-learned feature representations, derived from its nonlinear feature extraction ability [7], are highly efficient in many computer vision tasks, such as image recognition, object detection, and semantic segmentation.
To date, several studies have investigated semantic segmentation, i.e., the task of assigning a semantic annotation to each pixel in an image [30], in both remote sensing and computer vision [31]. The significant progress in the semantic segmentation of RS images is owed to deep CNNs (DCNNs) and especially to fully connected networks (FCNs) [32], while most recent attention has focused on multi-modal data fusion to enhance the performance and the robustness of semantic segmentation [33].
Considering the preceding statements and motivated by the promising results of applying fusion strategies for semantic segmentation and the particularities of a semi-arid Mediterranean environment, we investigated the potential of fusing multispectral and LiDAR data for land cover classification in this type of ecosystem by adopting a CNN-based semantic segmentation approach. It was hypothesized that the fused input data would be associated with an increase in the performance of the network by delivering better accuracy in the discrimination of the classes compared to utilizing a single dataset. To validate our hypothesis, we used the acclaimed U-Net architecture according to the results derived from the hyper-parameter analysis, and then, a comparative analysis was performed by training the model with different datasets and evaluating the results. To summarize, the main contributions of this work are as follows:
- Due to limited studies existing for semi-arid Mediterranean environment land cover classification, our study gives insight into how the fusion of multispectral and LiDAR data positively impacts the performance of a deep learning framework.
- The data used in this study were captured by different sensors, i.e., a multispectral imaging system and a 3D LiDAR point cloud system, and not by a single multispectral airborne LiDAR sensor.
- The CNN model was optimized based on the nature of the classification task for more accurate results.
2. Related Work
Much of the literature since the mid-2000s emphasizes that the synergism of multispectral imagery and LiDAR data can improve land cover mapping due to the different types of information that both deliver [34,35]. Several authors have considered the effects of the joint use of aerial multispectral data and LiDAR-derived height features to improve classification accuracy [18,36,37,38]. Other studies exploited different LiDAR point cloud-derived attributes, such as elevation [39], intensity [40], multiple returns [41], and texture [42], by converting them into two-dimensional (2D) images, so as to test their effectiveness in land cover classification via machine learning approaches (e.g., rule-based classification, maximum likelihood, decision tree, etc.), while publications that concentrate on combining the LiDAR intensity feature with aerial multispectral or satellite imagery adopt the application of the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) [38,43].
Traditionally, two processing strategies have existed for the land cover classification task using multispectral LiDAR data: (i) the image-based strategy, where the three-dimensional (3D) multispectral LiDAR data are converted into feature images according to their geometrical and spectral attributes, and (ii) the point cloud-based strategy, where the 3D LiDAR point clouds are operated directly [14,25]. According to Matikainen et al. [44], the former strategy tends to be more compatible with vast sceneries, while Shi et al. [45] have pointed out that its data processing is simpler than that of the latter strategy; nevertheless, the conversion of the data into raster format results in the degradation of both spatial and spectral information. On the contrary, the point cloud-based strategy preserves the geometrical characteristics of the land covers, which leads to more accurate results [14,45].
A combination of features derived from aerial LiDAR (multi-echo and full-waveform) and multispectral data was used by Guo et al. [46] to analyze which were most pertinent for the classification of dense urban scenes, and the findings demonstrated the relevance of the joint use of airborne LiDAR and multispectral data for urban scene classification. Similarly, Fernandez-Diaz et al. [47] examined the performance of the Optech Titan Multispectral LiDAR System on various topics, such as land cover classification, canopy characterization, and bathymetric mapping. Concerning the first topic, the authors worked with different combinations of intensity and elevation information to assess the quality of the classification and how it improves as more spectral information is made available. On the other hand, Wichmann et al. [48] conducted a 3D LiDAR point-based analysis of the spectral signatures of seven different land cover classes through point cloud merging and intensity grouping by using a nearest neighbor approach, and the results showed that the multispectral LiDAR data—acquired by Optech Titan airborne laser scanning—have the potential for separating classes and that their quality was deemed suitable for conventional terrain mapping. Using the same airborne multispectral LiDAR system for data acquisition, Ekhtari et al. [49] explored the possibility of directly classifying the 3D point clouds into ten different land cover classes by treating single-return and multi-return LiDAR points individually. The single-return points were classified using SVMs based on three-channel intensities and heights, while the multi-return points were categorized using rule-based classification based on their heights and neighboring points. In addition, Morsy et al. [50] attempted to evaluate two different classification scenarios on multispectral LiDAR data, namely an image-based classification and a point-based classification. In the first scenario, the LiDAR intensity and height attributes were converted into images, and after band stacking, the derived three-intensity images were combined with a digital surface model (DSM) and classified with a maximum likelihood classifier. In the second scenario, the 3D LiDAR points in the three channels were combined; three intensity values were assigned to each single LiDAR point, where ground filtering was applied to the LiDAR dataset for separating it into ground and non-ground points; and different NDVIs were computed. The classification accuracies exceeded 85% in both scenarios, and this study concluded that the intensity attribute on one hand and the NDVI on the other provided better results. Finally, Hell et al. [51] applied the PointCNN and 3DmFV-Net architectures to a fused LiDAR and multispectral dataset for a tree species classification approach, showing that the fusion of LiDAR and multispectral data is extremely useful. Although the results of these works appear promising, a closer look at them reveals that the classification schemes were employed mostly in urban environments or tree forests, where low vegetation is not dominant, like in a semi-arid Mediterranean environment.
The studies presented thus far have dealt with multispectral LiDAR data classification tasks using machine learning approaches. Such approaches, however, have failed to exploit the high-level features of multispectral LiDAR data. Hence, more recent attention has focused on the implementation of deep learning architectures, which can extract high-level characteristics directly from the data for accurate land cover classification [29]. For example, Yu et al. [52] developed a hybrid capsule network consisting of an encoder and a decoder, where a set of feature images, derived from the rasterization of elevation, number of returns, and spectral intensities of multispectral LiDAR data, was applied to the network for extracting high-level local and global features for accurate land cover classification. In the same vein, an Efficient Self-Attention Capsule Network (ESA-CapsNet) was proposed in [14] for land cover classification. Five types of rasterized feature images, generated from multispectral LiDAR data, were taken in the ESA-CapsNet—a capsule encoder–decoder architecture—to extract features and yield pixel-wise land cover predictions. For better encoding, a two-branch capsule-based efficient self-attention (ESA) module was designed and embedded into the network for recalibrating the channel and spatial features. In contrast, the authors in [53] suggested a deep learning-based method for classifying airborne LiDAR point clouds in point-wise order. First, a selection of LiDAR point cloud attributes, i.e., height, intensity, and roughness, was made to generate multi-scale contextual images for each point in the data using interpolation. Then, a multi-scale convolutional neural network (MCNN) was designed to automatically learn deep features from the images. A combination of the deep features learnt from different scales was used to classify each point into eight different ground object categories using a softmax regression classifier. The authors in [54] proposed a new DL architecture, called SE-PointNet++, for the point-wise classification of multispectral LiDAR point clouds by integrating a Squeeze-and-Excitation block to emphasize important features and suppress unimportant channels for prediction. The classification performance of the proposed framework emerged from the quantitative evaluations, and the comparative experiments with five deep learning models indicated that the SE-PointNet++ was effective in point cloud classification tasks.
Although extensive research has been undertaken on land cover classification tasks, with (mostly) hyperspectral/(rarely) multispectral data, LiDAR data, or a combination of them making up deep learning approaches, only a few studies have examined the optimal hyper-parameters of CNN models and the problem of the computational cost needed during the learning stage [55]. For instance, the trade-off between the land cover classification accuracy and computational efficiency of a CNN framework was investigated in [29]. To obtain high classification accuracies, they conducted an exploratory study on the hyper-parameters of a light CNN model, which consisted of seven stacked, fundamental layers for reducing the computational complexity in the multispectral LiDAR land cover classification task.
One of the most widely used architectures of CNN models for multi-band image classification tasks is the U-Net [56,57]. For example, in [58], the authors examined the potential of fusing Sentinel-1 radar imagery and Sentinel-2 optical imagery to generate promising land cover/land use (LULC) products of a tropical montane forest in the Philippines, Asia. A variety of ML classifiers was also used and compared with the U-Net architecture. The latter performed best in multi-class classification, accurately classifying LULC into six classes, with an overall accuracy over 88%, but it was proven less robust in binary classification, where the ML classifiers stood out. In addition to its application in multispectral or hyperspectral images, U-Net has also been used with LiDAR data. Ma et al. in [59] applied U-net for individual tree crown delineation in a canopy height model derived from LiDAR data. In line with our methodology, the authors in [60] utilized the U-Net model on various combinations of RGB/LiDAR fused data to segment pavement cracks. Their findings indicate that while the noise from point clouds may lead to decreased accuracy, in the majority of examined cases, there was a marginal improvement in precision, recall, and F-measure.
Few recent studies have explored the capability of using multi-modal data with machine learning or deep learning approaches for obtaining better classification results in semi-arid environments. As an illustration, Ali and Johnson [61] addressed the issue of the high similarity of several land cover classes in semi-arid regions by using medium-resolution remote sensing imagery with a fixed deep learning framework. The CNN model was trained on Sentinel-2 data from a semi-arid area in Pakistan, Asia, for fine-tuning its hyper-parameters, and the transferability of the optimized CNN model was tested in two additional sites of the country. The performance of the CNN models using different band composites (i.e., four bands and ten bands) of the imagery was evaluated, and the results showed that the four-band CNN model, utilizing bands with 10 m resolution, achieved higher overall accuracy compared to the ten-band CNN model. The researchers in [62] investigated the effect of combining Sentinel-1 SAR, Sentinel-2 MSI, LiDAR, and derived data like indices and texture for land cover classification in a semi-arid Mediterranean area in Spain, Europe, using machine learning algorithms, and the results demonstrated the value of an integrated multi-sensor approach for classifying landscapes with complex, fragmented compositions. Moreover, in [63], the authors designed an improved U-Net architecture, called LResU-Net, which consisted of residual convolution units (RCUs) and loop convolution units (LCUs) to extract features from UAV imagery to classify land covers in a mixed forest–grassland ecosystem in a semi-arid area of Mongolia, Asia. Compared to other semantic segmentation models, i.e., U-Net, ResU-Net, and LU-Net, the proposed CNN model achieved the highest classification accuracy (93.7%) and kappa coefficient (0.86), and the analysis also suggested that RCUs and LCUs help improve the model’s performance by enhancing feature extraction and reducing training time.
Further, Sankey et al. [64] postulated that the fusion of hyperspectral and LiDAR data acquired by an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) will perform better than either data type alone for classifying vegetation at the species level in an arid and semi-arid region of Arizona, USA. Indeed, the classification accuracy of the fused data (OA: 84–89%) improved by over 30% compared to the hyperspectral data alone (OA: 72–76%) from leveraging the differences in height, canopy structure, and spectroscopy. Similarly, Norton et al. [65] dealt with the discrimination problem of woody vegetation in a semi-arid region of Arizona, USA, containing various tree and shrubs species, by combining canopy height models (CHMs), derived from multi-temporal airborne LiDAR, and vegetation indices (VIs), generated from hyperspectral data and a machine learning classification scheme. A five-tree-species classification task was performed by a random forest classifier, achieving an overall accuracy of 95.28%, while validation showed that fusing spectral and structural data improved species delineation over using spectral data alone.
As discussed above, little research has focused on adopting deep learning approaches for land cover mapping in semi-arid regions, and to the best of our knowledge, there is no detailed study fusing multispectral and LiDAR data for CNN-based semantic segmentation in semi-arid Mediterranean environments. Given that the Mediterranean Basin is regarded as a prominent hotspot for climate change [66] and that new semi-arid areas will surface while the existing ones will further occupy the region in the upcoming years [67], accurate and updated land cover mapping is essential for monitoring these changes [68]. In this work, we report the investigation of the effectiveness of fused data, which deliver both spectral and spatial information, paired with the U-Net framework for land cover mapping of a semi-arid area of northeastern Aegean, Greece.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Study Area
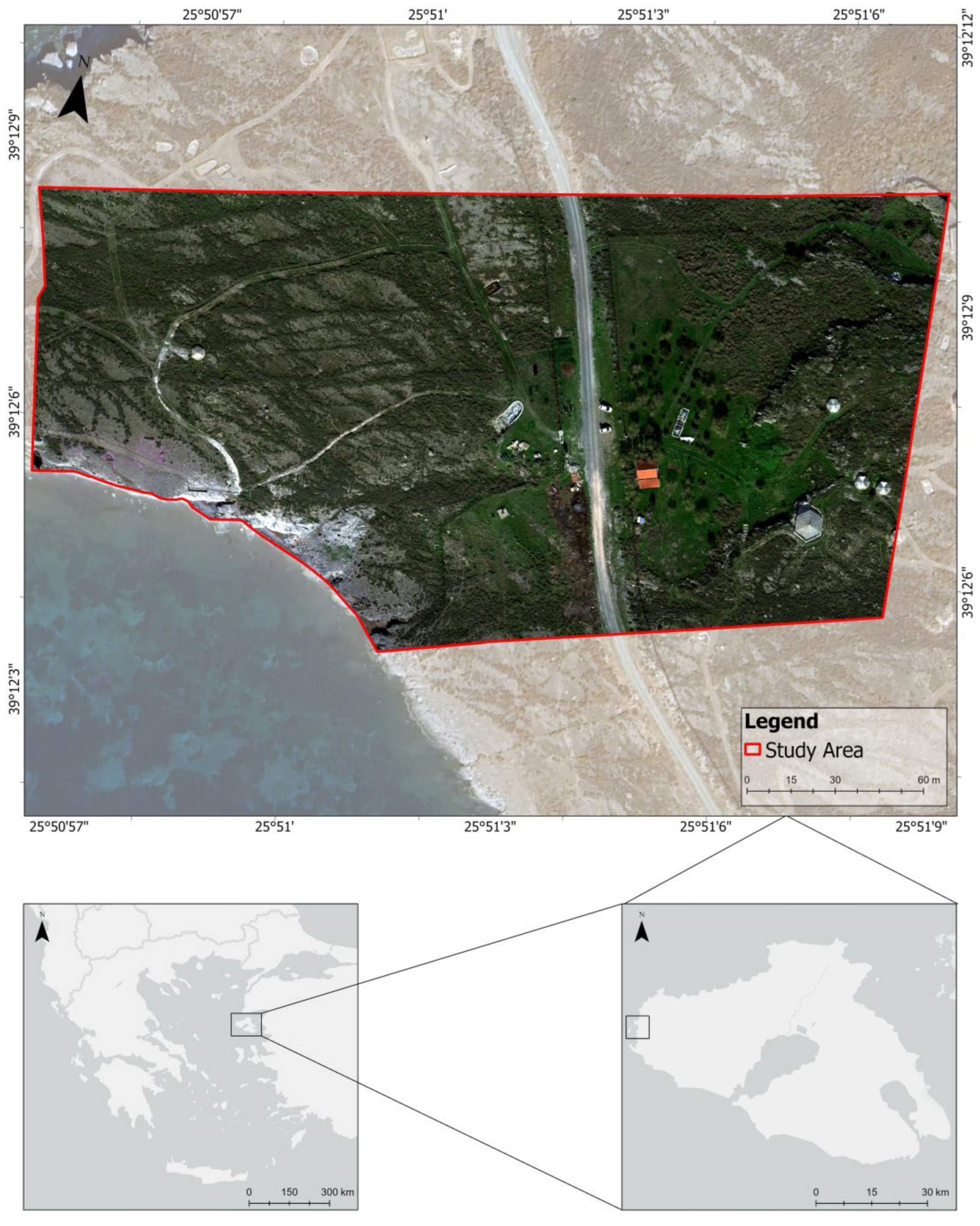
The study area is a semi-arid Mediterranean habitat dominated by phrygana vegetation, which includes Plaka Park, one of the four parks composing the Lesvos Petrified Forest, which has been declared a Protected Natural Monument [69]. Plaka Park is situated in the vicinity of Sigri (N 39.204497, E 25.853222), in the western part of Lesvos island, in the northeastern Aegean Sea, Greece (Figure 1), and it covers an area of about 89,500 m2, with an elevation ranging from 0 m to 39.8 m above mean sea level. The park is characterized by plant fossils, mainly root nodes, root systems, and lower trunk parts. The study site covers an area of 40,080 m2, and its size was determined based on the maximum altitudes up to the flight level. The reasons for selecting this study site were as follows: (a) This region is home to a unique geological heritage of great relevance, which needs a strong management and conservation plan for facilitating its protection. The area is a typical semi-arid environment dominated by grassland and phrygana vegetation; trees; barren land; and a number of artificial targets such as buildings, kiosks, fossil trunks, walking trails, etc. (b) We intended to use only one battery in each flight mission; thus, we acquired data from the maximum area that a single battery can cover from the airborne LiDAR system.
Figure 1.
Map of the study area: Plaka Park on Lesvos island, northeastern Aegean, Greece.
3.2. Data Acquisition and Description
Two datasets, a multispectral dataset and a LiDAR dataset, were acquired through unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) missions in February 2022 for the purpose of conducting our experiments. The multispectral imagery (MSI) was acquired by a four-propeller DJI P4 Multispectral UAV Real Time Kinematic positioning (RTK) (DJI, Shenzhen, China), which integrates six 1/2.9′′ complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) sensors covering five wavebands: (i) blue (B), 450 nm ± 16 nm; (ii) green (G), 560 nm ± 16 nm; (iii) red (R), 650 nm ± 16 nm; (iv) red edge (RE), 730 nm ± 16 nm; and (v) near-infrared (NIR), 840 nm ± 26 nm. Each sensor has a resolution of 2.08 MP and an ISO range of 200 to 800, while the focal length is 5.74 mm (35 mm format equivalent: 40 mm). An aerial multispectral imagery acquisition flight was conducted over the study area on 17 February 2022, between 09:00 and 09:30 UTC. A portion of the study area was captured through 183 images in a grid pattern of six parallel flight lines from 57.4 m above the ground, with 75% front overlap and 60% side overlap, yielding a ground sampling distance (GSD) of 3.5 cm/pixel.
The LiDAR data were captured by the Zenmuse L1 (DJI, Shenzhen, China) scanning sensor that was mounted on an airborne DJI Matrice 300 Real Time Kinematic positioning (RTK) (DJI, Shenzhen, China), which contains one active laser wavelength of 905 nm. The airborne LiDAR survey was undertaken on 17 February 2022, between 09:30 and 10:00 UTC, at an average altitude of 120 m above sea level, resulting in the collection of 65,705,332 high-accuracy points for the entire study area, with an average point density of 483 points/m2. The dataset consists of points from 70% side overlapping flight-lines. The aerial acquired data were imported to DJI Terra V3.6.6 software for post-processing. After reconstruction processing, a 3D point cloud was generated, and all the points were stored in LAS format.
Both datasets were aligned based on the real-time kinematic positioning protocol that utilizes existing Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) technology to provide accuracy within centimeters for geospatial location.
3.3. Methodology
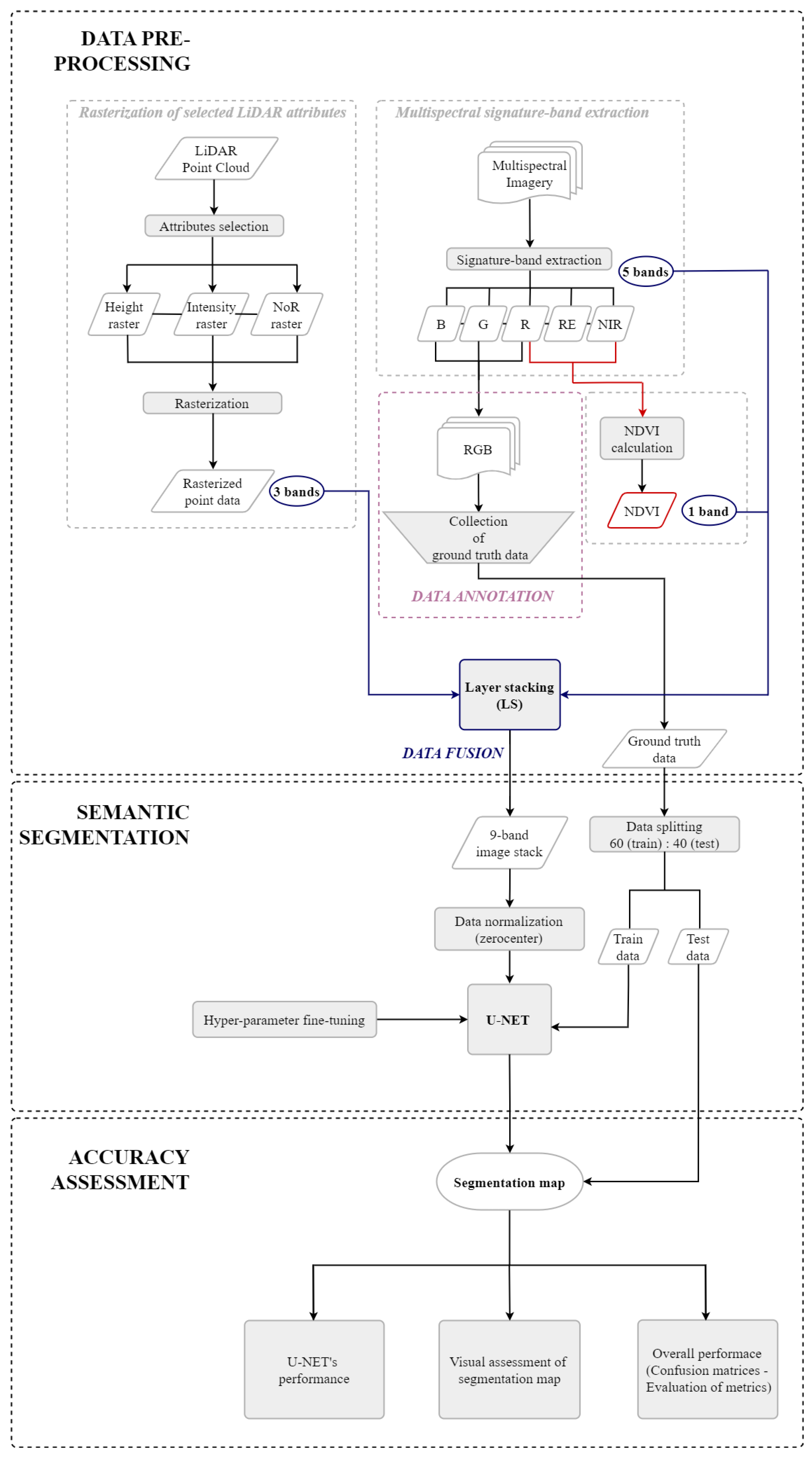
The methodology employed here to evaluate whether fusing multispectral and LiDAR data can improve the overall accuracy of the proposed network for semantic segmentation in semi-arid environments is outlined in Figure 2. In summary, the land cover classification via CNN-based semantic segmentation consists of three main steps: (i) data pre-processing, (ii) semantic segmentation, and (iii) accuracy assessment.
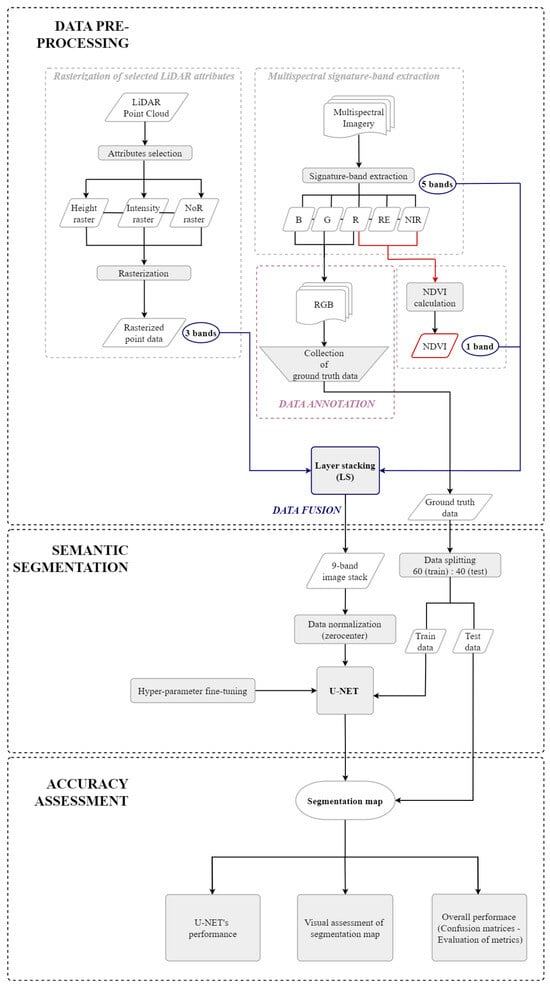
Figure 2.
Methodology workflow.
3.3.1. Data Pre-Processing
The proposed network architecture requires a multi-band input, which was generated through two-step data pre-processing: (i) data fusion and (ii) data annotation. Before fusing the two datasets, different pre-processing steps needed to be followed, by virtue of the diverging set of properties of each dataset. On one side, the five bands of the unified multispectral imagery were extracted in ArcGIS Pro V3.3.0 software, and accordingly, the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) [70] was calculated. On the other side, the three-dimensional (3D) point cloud was rasterized into a two-dimensional (2D) grid with a standard interpolation method using selected LiDAR attributes.
A drone-mounted integrated spectral sunlight sensor captured the solar irradiance, enhancing the precision and consistency of data collection throughout various times of the day. When integrated with post-processed data, this information proves instrumental in attaining highly accurate NDVI results. The multispectral orthomosaic, generated through the photogrammetric processing of images captured by the UAV, was then employed to compute the widely recognized multispectral and visible-band vegetation index NDVI. The NDVI is a common vegetation index of several remote sensing products, which has been widely used in RS studies of semi-arid environments [71,72,73]. By considering NDVI as a standalone band, it becomes easier to correlate the spectral information with ground truth data. This is particularly valuable in validation processes and the calibration of remote sensing data with real-world conditions. Moreover, the index facilitates the differentiation between heterogeneous areas. Consequently, due to the heterogeneity of the study area, the dominant classes can be easily distinguished and separated during the segmentation process [74].
The LiDAR data provide, by default, information about the position (x, y), height (z), multiple returns, reflected intensity, texture, and waveform-derived feature spaces from the object hit by the laser pulse [75]. Previous research works that concentrated on land cover classification tasks by utilizing LiDAR data more frequently adopted a combination of attributes approach [47,49,50,53]. Inspired by this strategy and bearing in mind our study area, which consists of various land cover types, we chose to use the height, intensity, and number of returns attributes. The selection was performed based on the following:
- The height attribute is related to geometry; thus, it contributes to the estimation of the ground objects’ geometric characteristics [53].
- The intensity attribute is a spectrum, and it provides separability among the material characteristics of the ground objects [75].
- The number of returns attribute is related to elevation, and it manages to detect the ground objects at different height levels (e.g., tree crown and trunk) within the laser footprint of an emitted pulse [75].
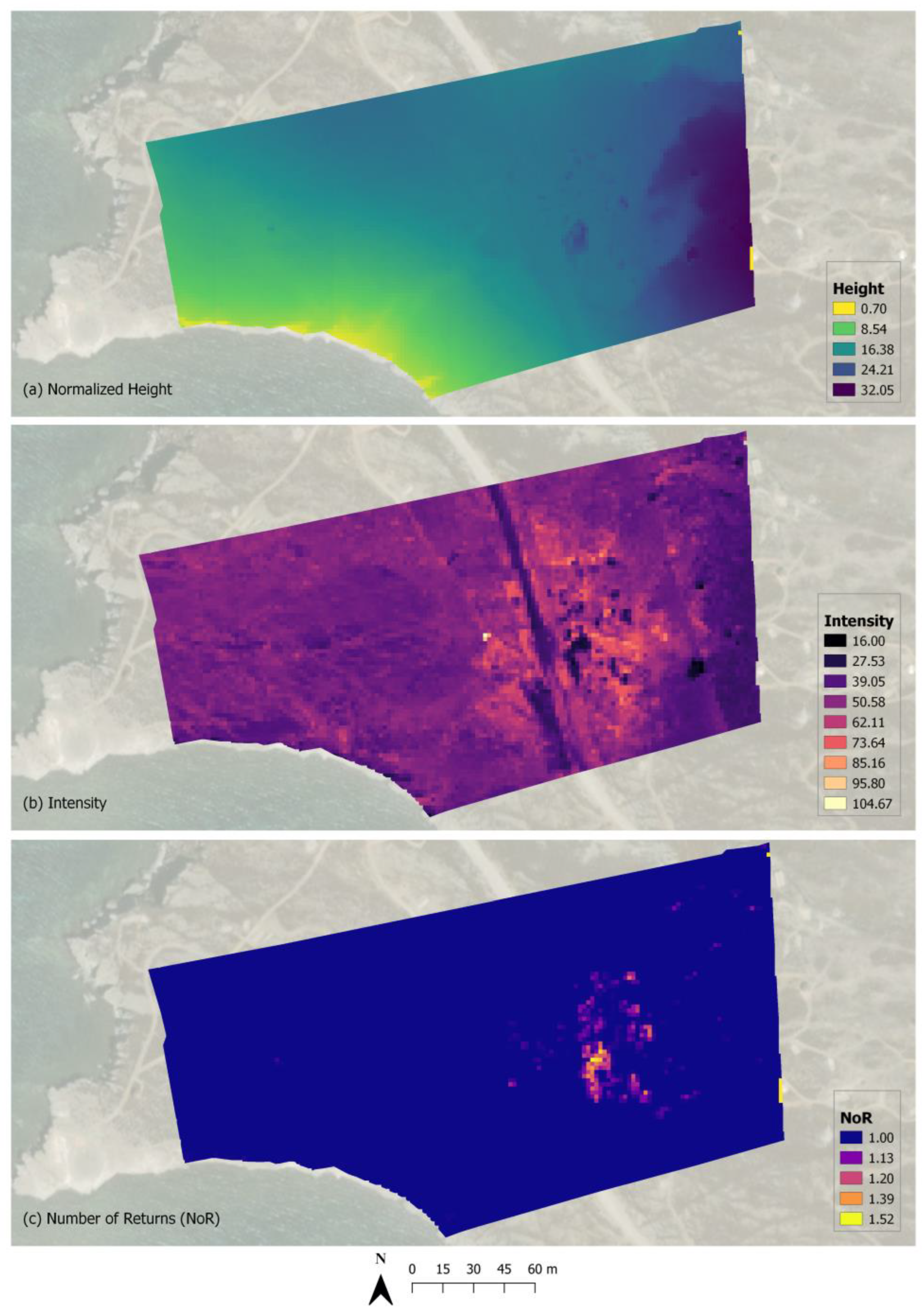
Figure 3 presents the rasterization of the three LiDAR attributes that we selected. For each of them, the information is concentrated around high vegetation, the built-up environment, and other objects. More specifically, the height attribute mainly provides information about the built-up environment of the area; some other objects, e.g., kiosks; and phrygana vegetation, while intensity effectively reflects the differences in vegetation, the built-up environment, and some other objects. The number of returns (NoR) attribute expresses the structural parameters of the targets i.e., the density of the surfaces. A NoR value of 1.00 represents dense surfaces, while other values correspond to less dense structures, i.e., vegetation, given that each pixel reflects the average NoR of all points that fall inside that pixel. After attribute selection, the airborne LiDAR point cloud was processed by CloudCompare V2.11.3 software [76], where it was converted into a raster grid dataset. Before rasterization, the height attribute was normalized by subtracting the coastal height of the area.
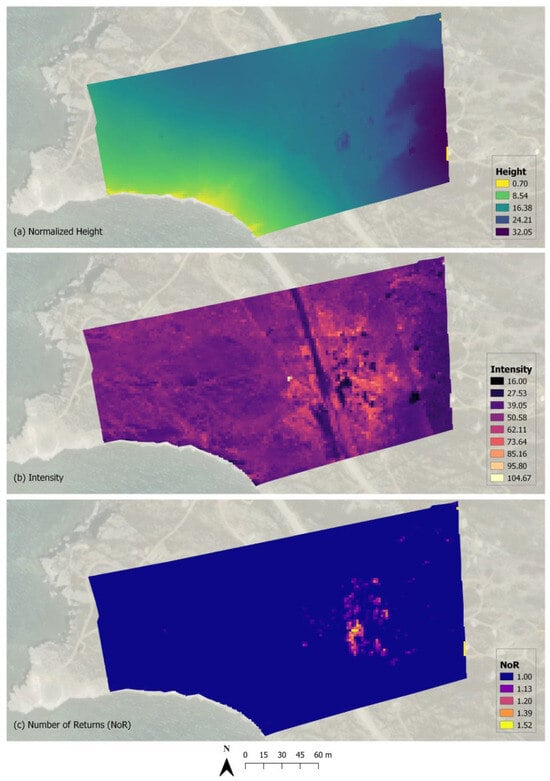
Figure 3.
Visualization of the three rasterized LiDAR attributes.
To generate a single multi-band image with rich spectral and spatial information, we combined the multispectral imagery and the rasterized LiDAR data through a layer-stacking (LS) process by ensuring uniformity across all bands in terms of coordinate system, spatial extent, spatial resolution, and map projection. This resulted in a seamless integration and accurate representation of the spatial data. At the end, a nine-band raster was created, including the blue, green, red, red edge, and near-infrared wavebands; NDVI; height; intensity; and number of returns, and used as an input image layer to U-Net.
The normalization of the dataset was performed by using a zero-centering technique. The process was completed automatically in a MATLAB 2022b environment while creating the U-Net layers. Zero-center normalization typically means that each pixel value is subtracted from the average value of the pixel’s subsample. Thus, the dataset is zero-centered, i.e., the average of the pixels is equal to zero.
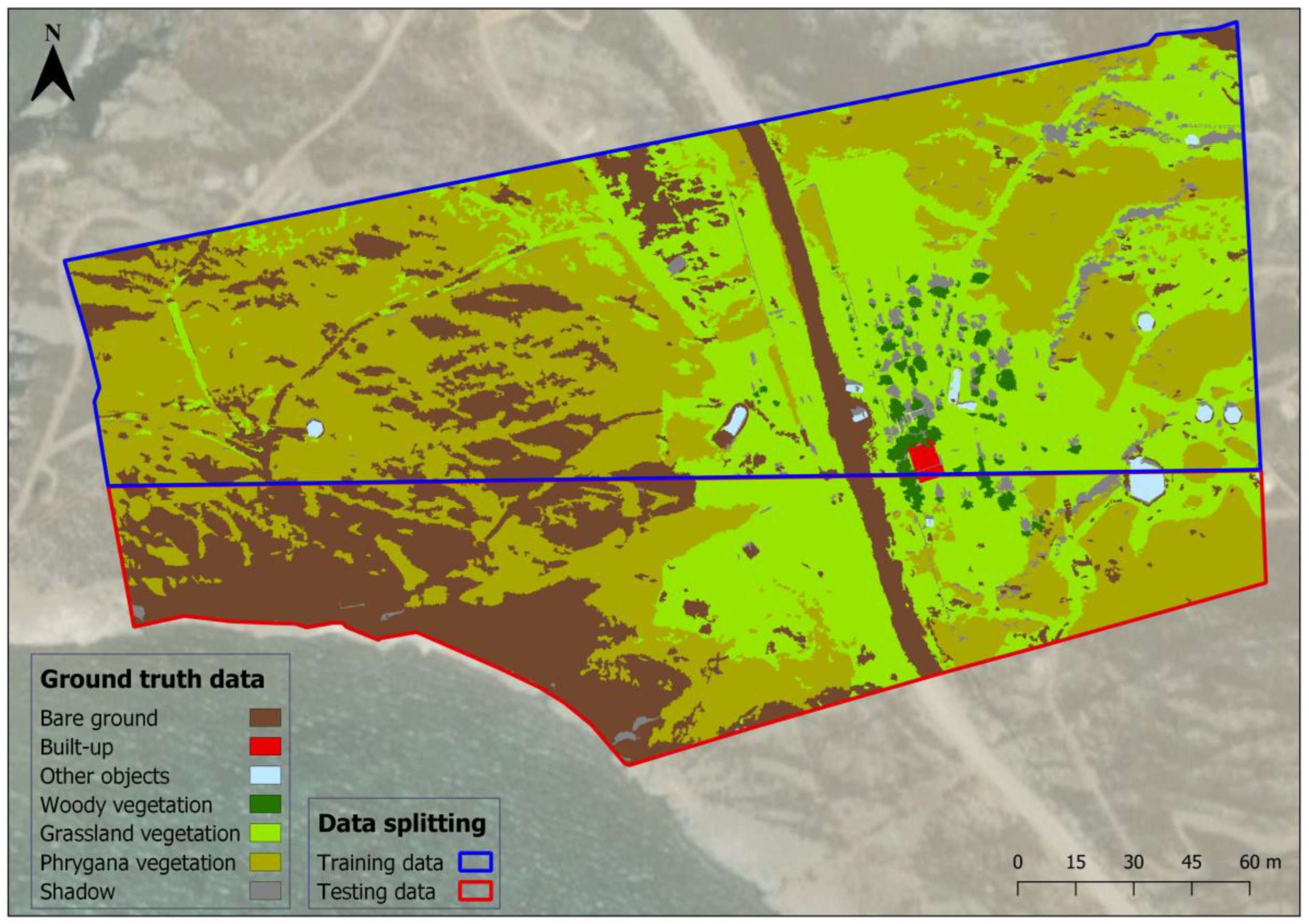
To train a network for predicting land cover classes for each pixel in testing data, labeling the pixels in the training data is required as a ground truth [77]. In the data annotation process, the study area was labelled manually into several classes to obtain the training dataset for our proposed architecture. The process of classification into the following seven classes was completed through photo-interpretation of the images and field sampling.
Seven classes, namely (i) “bare ground”, (ii) “built-up”, (iii) “other objects”, (iv) “woody vegetation”, (v) “grassland vegetation”, (vi) “phrygana vegetation”, and (vii) “shadow”, were generated. Apart from bare land, the class “bare ground” also contains unmade roads, rocky land, as well as the rocks/stones of the study area. Metal surfaces, plaster cast, fossilized trunks, plastic surfaces, and fabric covers are under the class “other objects”. The “grassland vegetation” class encompasses burnt areas too. This union of various classes was made due to the low number of pixels of some targets.
A common method that is used to guarantee good generalization of the model and to evaluate its performance is data splitting [78]. In the most simplified strategy of data separation, a portion of the dataset is held for training the model, while the other that was set aside is used for evaluating the model’s accuracy [79]. A two-part splitting procedure was performed on the dataset before going ahead with the hyper-parameter analysis of the network. One part of the main dataset was used to train the CNN-model, while the other one was used to evaluate the accuracy of the network. The training–test ratio was chosen to be 60:40, meaning 60% would be used as a training set and 40% as a test set. The separation was implemented on the dataset horizontally, from the upper left corner to 10% above the middle of the image. To wit, 60% of the image corresponds to a dimension of 3296 × 8847, as the whole image has 5492 rows and 8847 columns, and the remaining 40% of the image corresponds to a dimension of 2196 × 8847. No validation set was left out of the dataset due to the small size of the study area and the concentration of some classes in a specific location of the area.
Table 1 presents the number of pixels per class and dataset that were ultimately generated, while Figure 4 illustrates the RGB representation and land cover true class annotation of the study area. As can be seen from the table below, both datasets include all the land cover classes; however, some classes have a quite smaller number of pixels in the test set than in the training set, and vice versa.

Table 1.
Number of pixels per class and dataset.
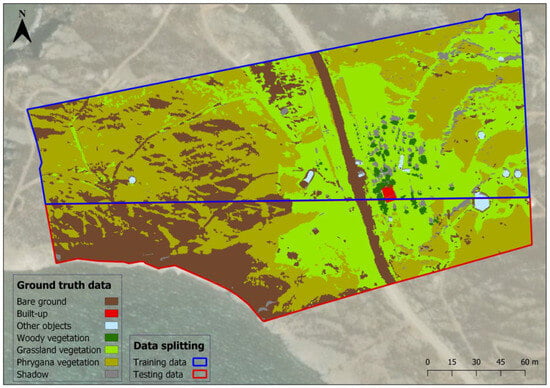
Figure 4.
Training data, test data, and ground truth data.
3.3.2. Semantic Segmentation
For the multispectral and LiDAR data semantic segmentation task, we used U-Net, a fully convolutional architecture developed by Ronneberger et al. [80]. U-Net constitutes an extension of the fully connected network (FCN) architecture [81] proposed in [82]; therefore, it skips the connections—a mechanism firstly introduced in Residual Networks (ResNet) [83] that has been shown to aid in the reconstruction of the spatial resolution at the network output, making this architecture appropriate for semantic segmentation [81,84]. An asset of the U-Net architecture is its precise localization [80], which offers the concatenation of high-resolution feature maps from the downsampling step with the output from the upsampling step, which is used as a skip connection [85].
The U-shape architecture, that lends the name to the network, is based on an encoder–decoder scheme [85], and it is formed by two symmetric paths joined with long-range connections [86]: the contracting path (left-hand side), where the typical convolutional process is performed, and the expansive path (right-hand side), where the up-convolution process is applied [80]. That is, the left-hand side plays the role of the encoder by extracting the image features via downsampling, while the right-hand side acts like a decoder by constructing the segmentation map from the downsampled features via upsampling, to attain effectively semantic segmentation tasks [85,87]. U-Net architecture has 58 layers in total: the input layer, 23 convolutional layers of 11 3 × 3 convolution layers at each path, a final 1 × 1 convolution layer, 22 ReLU layers, 4 max pooling layers, 2 dropout layers, 4 concatenation layers, 1 Softmax layer combined with the cross-entropy loss function for performing the classification task, and the output layer (128 × 128 × 7).
Inspired by Krizhevsky et al. [88] and Chen et al. [89], we tackled the challenge of the imbalance between the high-dimensionality of the input data and the limited available training samples for the classification task by using L2 regularization (Ridge Regression) and dropout during the training process. The U-Net architecture has two dropout layers built-in after the ReLU layers for preventing overfitting in class data modeling. We have also employed L2Regularization by setting the factor l2reg to 0.0001 in the training options to ensure that the model stays versatile and operates reliably over an unseen dataset. Thus, the models’ performance was evaluated on an unknown dataset, namely the test set, and the results showed that the models have probably not been overfitted.
3.3.3. Accuracy Assessment—Evaluation Metrics
Evaluating the accuracy of the derived segmentation map is a key component of an image segmentation analysis protocol [90]. Thus, a variety of supervised and unsupervised methods have been proposed for classification accuracy assessment over the years [91]. Among the supervised methods, which aim to measure the similarity or discrepancy between the predicted output and the annotated segmentation [90], the confusion matrix is the prevailing method that is used in traditional remote sensing (RS) studies [92]. This cross-tabulation of the predicted results against the ground truth (reference data) serves as the foundation for calculating summary metrics, such as the overall accuracy (OA); Cohen’s kappa, known as kappa coefficient of agreement; and the statistics per class of producer’s accuracy (PA) and user’s accuracy (UA) [93]. Other common evaluation metrics used for performance measuring in computer vision are the Intersection-over-Union (IoU), known as the Jaccard Index [94], and the Boundary F1 score (BF) [95].
Notwithstanding, the assessment of semantic segmentation can be a tough task because the measurement of the classification accuracy together with the localization correctness is required [94]; there are three principal advantages over the calculation of the accuracy metrics in deep learning (DL) studies, specifically (i) providing the benchmarking and comparison of methods; (ii) understanding the model’s performance, i.e., its strengths and shortcomings; and (iii) shedding light on the real-world application of the proposed methodology [93].
Therefore, this study employs the following metrics for evaluating the performance of the CNN-based model and the classification accuracy:
where TP, TN, FP, and FN denote the true positive, true negative, false positive, and false negative counts, respectively. In Equation (2), p0 and pe mean the probability of agreement and probability of random agreement, correspondingly. In Equation (8), and stand for precision and recall, respectively. In Equations (9) and (10), is the contour map for the predicted segmentation map for class c, is the boundary map of the ground truth segmentation map for class c, is the Euclidean distance, and is the distance error tolerance.
The overall accuracy (OA) is a simple summary measure of the percentage of correctly allocated cases [92], and it is computed by dividing the total number of correctly classified pixels by the total number of reference pixels [93], namely the sum of elements along the major diagonal of the confusion matrix [96]. On the other hand, Cohen’s kappa coefficient (K) is a more robust measure than overall accuracy, and it is used frequently to deal with the chance agreement issue [92]. This metric is a measure of classification success compared to random chance, and its values lie in the range of [−1, 1]. Interpreting its values, −1 hints that the agreement is worse than random, 0 means that there is a random or no agreement, while +1 presents complete agreement [94].
Besides overall accuracy, the confusion matrix may be used to obtain estimates on an individual class accuracy [97]. Producer’s accuracy (PA) and user’s accuracy (UA) are two standpoints related to omission and commission errors, respectively, and they are used for measuring per class accuracies [92]. PA represents how well reference pixels of the ground cover type are classified, while UA corresponds to the probability that a pixel classified into a given category represents that category on the ground [96]. The calculation of these is based on the division of the number of correctly classified pixels in each class by either the total number of pixels in the corresponding column, PA, or the corresponding row, UA.
In the context of semantic segmentation, Intersection-over-Union (IoU) is a metric used for measuring the number of pixels that are similar between the predicted region and the ground truth region, divided by the total number of pixels across both regions [98], and it belongs to region-based accuracies [95]. In particular, the IoU score is the ratio of the intersection of two regions to their area of union [93]; thus, it takes into consideration both the false positive and the false negative values for each class [95].
Moreover, the boundary F1 score (BF) pertains to boundary-based metrics, which focus on how to assess the distortion of the boundary due to segmentation from that of the ground truth [99]. BF is defined as the harmonic mean (F1-measure) of both classification’s precision and recall values with a distance error tolerance to decide whether a point of the predicted boundary has a match on the ground truth boundary or not [95]. It should be stressed that Equation (8) represents the F1 score as class-dependent because it has been computed for one value per class between the corresponding segmentation maps. Hence, to obtain the BF (per image F1 score), the average of the scores over all classes present either in the ground truth or in the predicted segmentation must be calculated [95].
Lastly, to test if the difference in the classification performances of the models is significant, a statistical comparison of the three models was conducted using McNemar’s test [100], which is commonly used for comparing classifier performances [101]. The models were compared in pairs, and the McNemar’s value was given by the following:
where is the number of samples misclassified only by model A and is the number of samples misclassified only by model B. The null hypothesis states that the error rate of both classification methods is equal. McNemar’s test relies on a Chi-squared test with one degree of freedom. The critical Chi-squared value, with a 95% confidence interval and a 5% level of significance, is 3.841. If the calculated McNemar’s value exceeds 3.841 for each pair, then the null hypothesis is rejected, indicating significant differences between the two classification methods.
4. Experimental Results and Analysis
4.1. Hyper-Parameter and Training Setting Analysis
Data augmentation is a method that aids in preventing a model from overfitting and makes it perform better on future testing samples [102]. This method differs from other solutions based on its regularization, such as dropout, batch normalization, transfer learning, etc. [103], since the overfitting problem can be traced back to its origins, namely the training dataset [102]. Various augmentation techniques can be applied on a dataset, while leaving the annotated labels unaffected [104], which are based on affine, geometric, and color transformations, such as flipping, rotation, cropping, resizing, reflecting, the color space, translation, noise injection, etc. [102]. To improve the CNN model’s overall accuracy, we explored an artificial enhancement of the dataset’s size by using a few data augmentation techniques during training. Three techniques were chosen to generate modified versions of the dataset: (i) random horizontal and vertical reflection, (ii) random rotation between −10 and 10 degrees, and (iii) random resize at scales of 0.8 and 1.2. Although the benefits of this method have been demonstrated in several studies [102,105], the OA of the CNN model was not improved; on the contrary, it dropped from 79.3% to 74.1%. Consequently, we decided to not apply augmentation to the dataset.
A key hyper-parameter during the configuration of a neural network is the learning rate [106], which determines the size of the step taken in the direction of the negative gradient [107]. The learning rate controls the speed at which the CNN model learns [29]. Specifically, it regulates the magnitude of the network’s weight updates at every iteration to minimize the network’s loss function [108]. To make sure that the CNN model is learning properly, an appropriate learning rate must be chosen, as a low learning rate may cause sluggish convergence, while a high learning rate allows the model to learn faster but may result in undesirable divergent behavior in the loss function [106,108]. In this work, the initial learning rate was set to 0.05, and it was gradually reduced by a factor of 10 for every 5000 iterations. This value yielded an overall accuracy of 71.8%. To increase the accuracy of the network, we also tried a lower initial learning rate, viz. 0.0005, in tandem with a rise in the number of epochs from 30 to 50. However, the OA dropped to 59%; thus, we reset the learning rate to the initial value.
One of the essential components of deep learning is optimization, which solves the curse of dimensionality and assists a model in being trained more effectively during backpropagation, when the weights are adjusted to reduce loss errors [109]. Learning can be implemented in a variety of ways using different optimization algorithm types, such as the stochastic gradient descent (SGD), which is considered by far the most common way to optimize a neural network; the Nesterov Momentum; the Adagrad; the Adadelta; the RMSProp; the ADAM; etc. [110]. The optimization algorithm that was chosen for conducting our experiments was the SGD with a momentum of 0.9, a method with moderate oscillations that aids in accelerating SGD in the appropriate direction. ADAM and RMSProp were also tested; however, they delivered poor results. The SGD with momentum returned an OA of 71.8%, while ADAM and RMSProp yielded an OA of 13.6%. Therefore, the comparative analysis was performed with the SGD algorithm.
One of the most crucial parameters is the input image size, as it affects the efficiency of the network [111], as well as the training time [112]. In the domain of remote sensing, where data are often stored in the form of very large images, training CNNs with those images is challenging due to graphics processing unit (GPU) limitations in the computer hardware. Thus, researchers use either the downsampling method or the tiling method to overcome these limitations [113]. In this study, we adopted a tiling approach—during both model training and prediction—to investigate its influence on the predictive performance of the model. To determine the optimal input tile size, we conducted three experiments by varying the input tile size from 64 × 64 to 256 × 256, while the input image’s source resolution of 5492 × 8847 was preserved. The land cover classification results in terms of overall accuracy (OA), Cohen’s kappa, and training time are set out in Table 2. What stands out in this table is that the highest values of both OA and K were achieved by selecting a random crop with a 128 × 128 × 9 input tile size. From the Table 2, we can also see that increasing the size of the input tile led to an expansion of the training time, which was anticipated as the models train slower on large input data.

Table 2.
A comparison of input image sizes and patch sizes in classification accuracies and time complexity.
Another important factor when building DL models is the selection of the right patch size for achieving favorable results [114]. Due to the higher richness of contextual information captured in a large patch size, the classification accuracy as well as the image segmentation are remarkably better than those from a small patch size [115]. In the case of fully convolutional networks, due to their architecture, the patch (tile) size for training can differ in patch size for performing inference [113]. However, for U-NET, it must be ensured that the patch size is a multiple of 16/32 (input patch size/prediction patch size). To compute the effective patch size for prediction, we varied its dimension from 256 × 256 to 1024 × 1024. Although it has been demonstrated that the segmentation performance has been improved significantly when using larger patch sizes, the best scores of OA and K were recorded for a medium patch size, as can be seen from Table 2, while the model performance was depleted when the patch size increased to 1024 × 1024. Thus, the comparative analysis was conducted based on a 512 × 512 prediction patch size.
4.2. Comparative Analysis
The optimal values of the hyper-parameters, namely input tile size = 128 × 128 and patch size = 512 × 512 for the prediction, which were determined through trials, were applied to the model to explore whether it achieves a satisfactory classification accuracy or not. To evaluate the synergism in multispectral imagery and LiDAR data for land cover classification via CNN-based semantic segmentation, we conducted two more experiments utilizing either only multispectral or LiDAR data for the land cover classification task. Finally, we compared the predictive performances of the model while using each dataset. Three different imagery inputs, i.e., fused multispectral and LiDAR data, multispectral data only, and LiDAR data only were applied in our experiments alongside the labels and the mask. Each dataset was divided into two parts, where 60% was used as the training dataset and the remaining 40% was used as the test dataset. The proposed CNN model used the SGD with a momentum 0.9 optimizer with an initial learning rate of 0.05 and cross-entropy loss. The number of the epochs was set to 30, and the model ran using a minibatch size of 16. All of the experiments were implemented on a configured computer with an 11th Gen Intel(R) Core (TM) i9-11900F CPU @ 2.50GHz 2.50 GHz processor, a 16 GB RAM, and a NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1600 SUPER GPU. In addition, all of the models were implemented with MATLAB 2022b.
In order to investigate whether the fusion of multispectral and LiDAR data for land cover classification is associated with an increase in the predictive performance of the CNN model, we carried out three experiments by training the model with different inputs. In experiment No. 1 (EX1 model), U-Net was trained with fused multispectral and LiDAR data and the input tile size was 128 × 128 × 9. Experiment No. 2 (EX2 model) used only multispectral data and the input tile size was 128 × 128 × 6, while experiment No. 3 (EX3 model) used only LiDAR data and the size of the input tile was 128 × 128 × 3. In the following subsections, we evaluate the performance of the proposed CNN model architecture, and we conduct an accuracy assessment via objective evaluation metrics, besides a visual evaluation of the segmentation maps.
The first step in the experimental analysis is the investigation of the learning capabilities of the U-Net architecture on the land cover classification task. The EX1 model had an accuracy of 88.68% and a loss of 0.2107, while the EX2 model had an accuracy of 85.05% and a loss of 0.2050. The results of both experiments indicate that the CNN model is inclined to achieve high accuracy on the land cover classification task. On the other hand, the EX3 model showed poor results with an accuracy of 43.81%, while the loss was 0.5939.
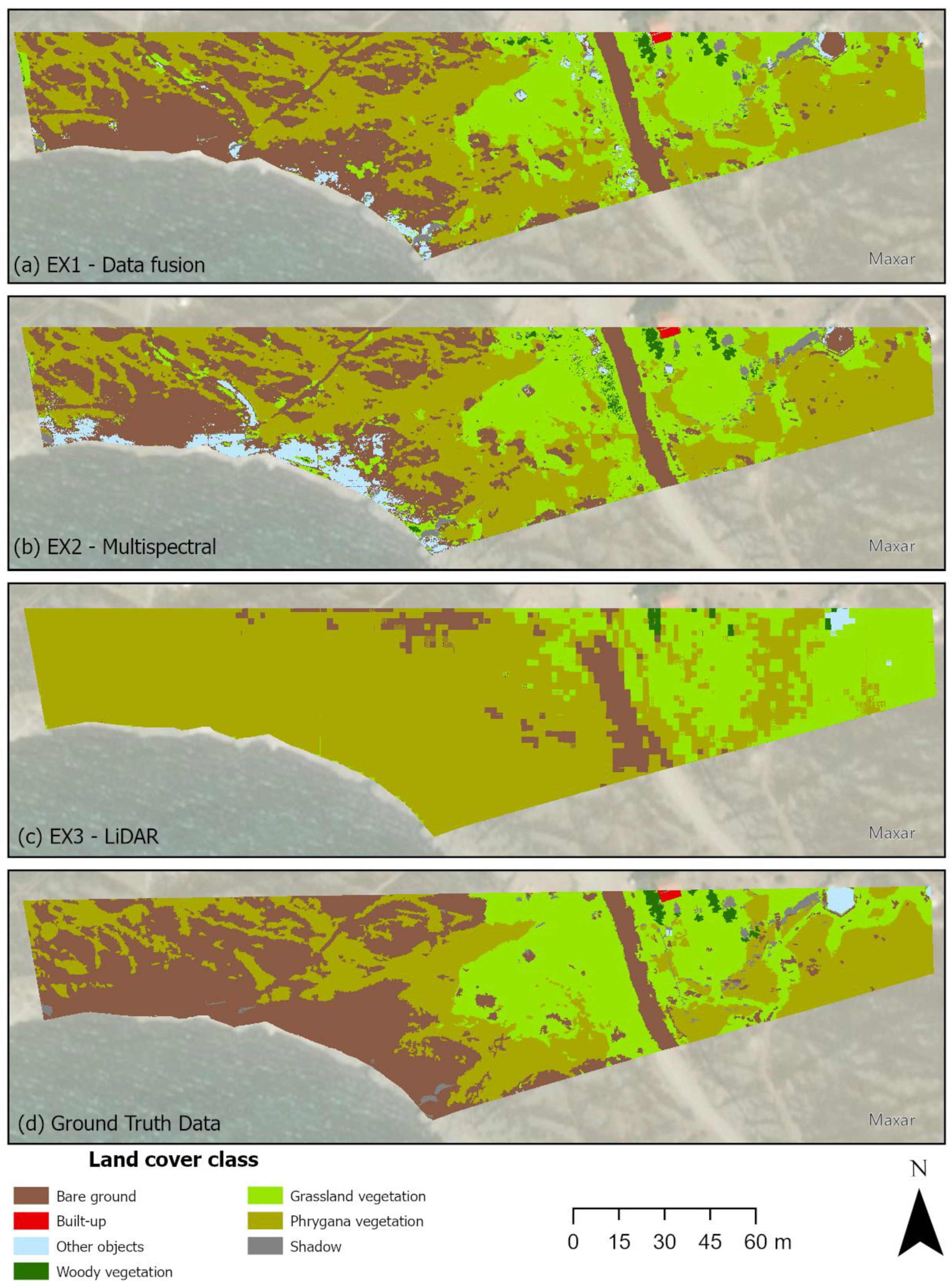
A visual assessment of segmentation maps is relatively subjective as it leans on human visual judgement [116]; however, it allows us to gain important insights into the segmentation output [90]. Figure 5 provides the semantic segmentation results obtained by all three experiments compared to true values. As shown in Figure 5a, the CNN model that was trained with the fused data delivered significantly better discrimination accuracy of most of the classes. Yet, there is a confusion between the classes “other objects” and “bare ground”.
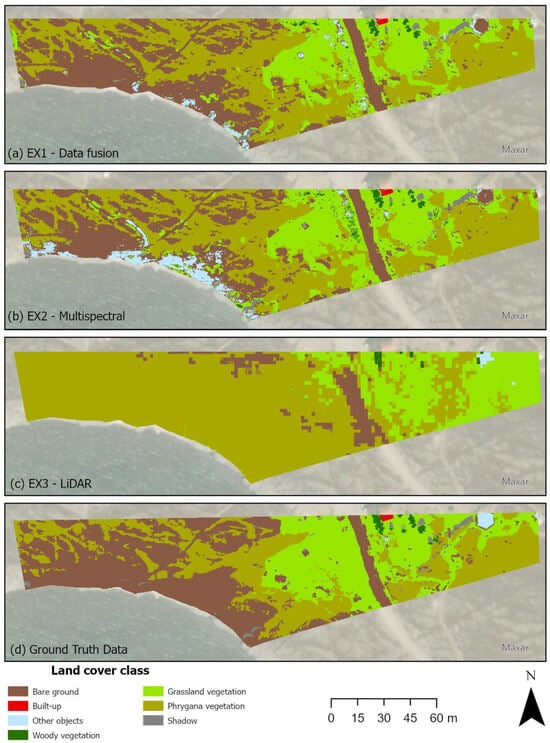
Figure 5.
Semantic segmentation results obtained by (a) EX1, (b) EX2, (c) EX3, and (d) the ground truth data.
Similar mistakes, but on a larger scale, are obvious in Figure 5b. The model in which only multispectral data were applied falsely classified the south part of the study area as “other object”, while bare land is dominant there. This result indicates that only multispectral imagery is not enough for classifying such a heterogeneous region. Inspecting Figure 5c, it is apparent that utilizing only LiDAR information for classification tasks is barely sufficient for providing acceptable results. The model perplexes “bare ground” class with “phrygana vegetation” class in the southwest part of the study area, and, at the same time, “phrygana vegetation” class with “grassland vegetation” class in the southeast part of the study area. Interestingly, the kiosk, which belongs to the “other object” class, has been classified correctly, while the other two models failed to distinguish that object. Nevertheless, the quality of the segmentation map derived from the EX3 model is significantly lower than that of the other two segmentation maps, (a) and (b).
4.3. Accuracy Assesment
The CNN model applied in the task of land cover classification was evaluated by using a series of objective evaluation metrics, including overall accuracy (OA), producer’s accuracy (PA) and user’s accuracy (UA), mean Intersection-over-Union score (mIoU), mean boundary F1 score (mBF), and Cohen’s kappa coefficient (K) in the test dataset. The experimental results obtained from the comparative experiments are summarized in Table 3. It is evident from this table that the highest overall accuracy (79.34%), as well as the highest scores of mIoU (55.64%) and mBF-score (69.86%) were acquired by applying the fused data to the model. Similarly, the highest value of Cohen’s kappa (0.6966) was obtained by the EX1 model, indicating that the strength of agreement can be regarded as substantial. The results achieved from the model trained with only multispectral data followed very closely (OA: 76.03%, mIoU: 52.70%, mBF: 62.21%, K: 0.6538). On the contrary, the overall accuracy of the model that used only the LiDAR dataset was poor, as it only achieved 37.79%, while the Cohen’s kappa value (0.084) implies that there is a slight strength of agreement. However, the training time of the EX3 model was shorter compared to those of the other two experiments.

Table 3.
A comparison of the land cover classification accuracies, scores, and training time complexity with different datasets.
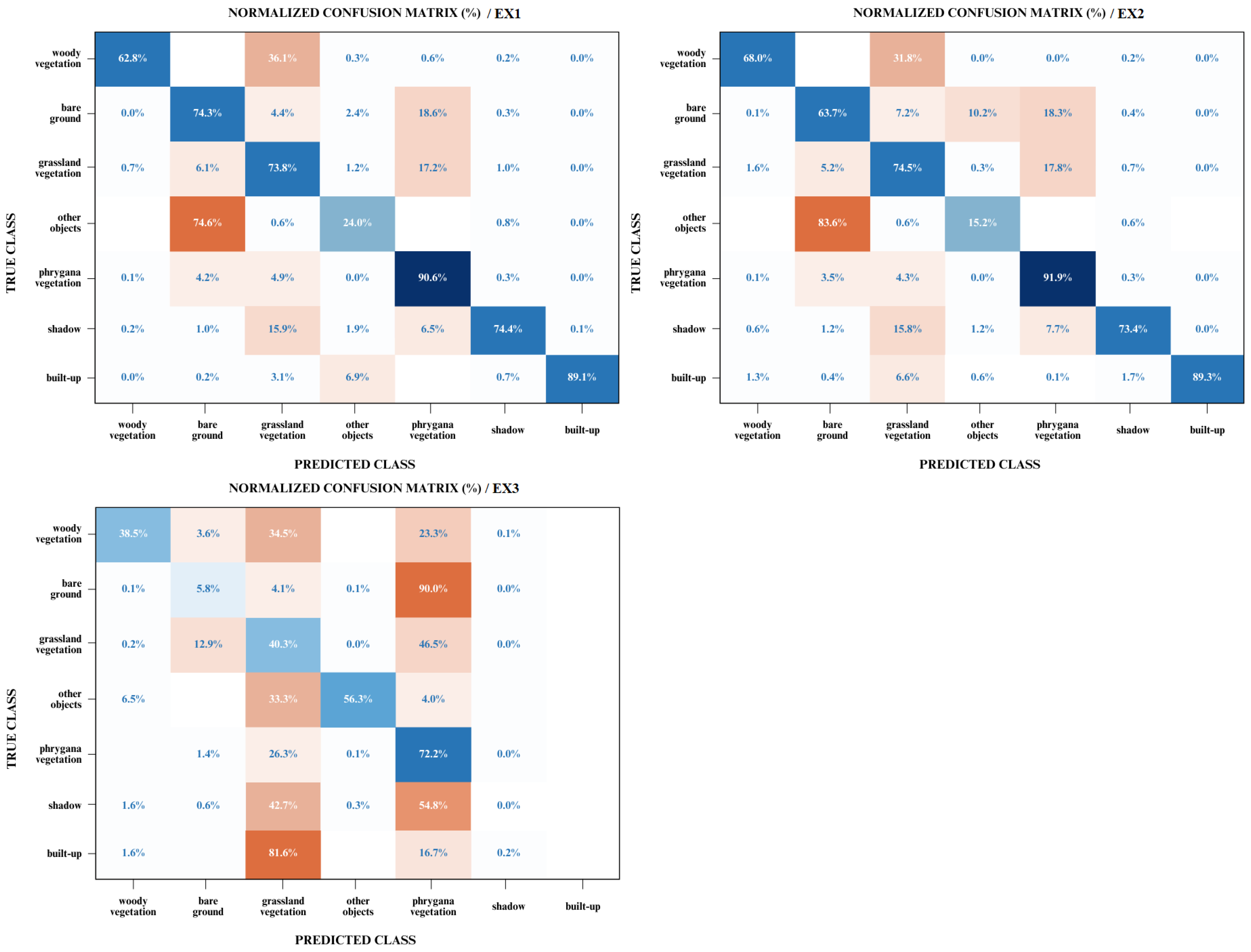
Besides the overall metrics, per class performance was assessed by computing confusion matrices for the test area. Table 4 provides the producer’s accuracy (UA), the user’s accuracy (UA), the Intersection-over-Union (IoU), and the mean boundary F1 score (mBF-score) for each experiment, while the calculated confusion matrices are shown in Figure 6.

Table 4.
Per class performances of the models for each experiment.
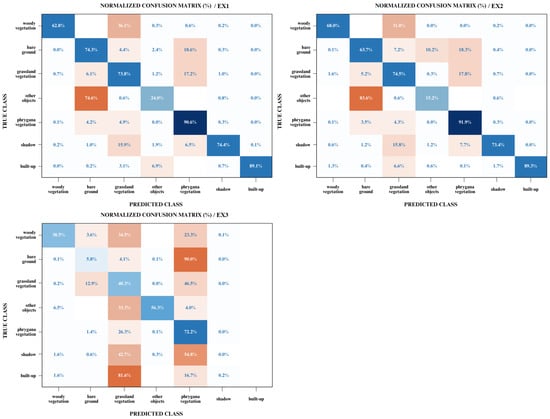
Figure 6.
Confusion matrices for the three experimental datasets. Dark blue colour denotes high correctly classified cases while dark orange colour implies high falsely classified cases.
Table 4 demonstrates that the U-Net network exhibited superior discriminating performance when utilizing fused multispectral and LiDAR data (EX1) or solely multispectral data (EX2). However, the model’s performance using only LiDAR data (EX3) was deemed unsatisfactory for most classes. The results obtained from the EX1 and EX2 models indicate that the “built-up” class had the best results (>87%) as far as user’s and producer’s accuracy (UA and PA) is concerned, while the main misclassified class was “other objects”. Producer’s and user’s accuracies revealed that “other objects” did not exceed 25%, ranking as the most unreliable class, as many pixels were misclassified as “bare ground”. Moreover, the “woody vegetation” class was classified quite well by the model, which was trained with fused data (PA: 63%–UA: 69%), while the classification performance of the model trained with multispectral imagery only was inadequate because even though 68% of the reference trees were correctly identified as “woody vegetation”, only 48% of the trees identified as “woody vegetation” in the classification were trees. A similar attitude was exhibited by both the EX1 and EX2 models for the “phrygana vegetation” class, which had low user’s accuracy (74%) but a high producer’s accuracy (>90%), which indicates that this vegetation type is overclassified, with many false positives.
The standout finding from Table 4 is the classification of the “other objects” class, which exhibited moderate performance, ranging from 56% to 85% in terms of both producer’s accuracy (PA) and user’s accuracy (UA) when solely utilizing LiDAR data. Conversely, the other two models displayed the weakest discrimination performance in this specific class. However, the model misclassified the “bare ground” and “shadow” classes with the “phrygana vegetation” class, as well as the “built-up” class with the “grassland vegetation” class. Thus, utilizing only LiDAR data for land cover mapping appeared to be insufficient. By comparing the mean boundary F1 score (mBF) per class, it is apparent from Table 5 that the EX1 model yielded higher scores in three classes (“bare ground”, “woody vegetation”, and “grassland vegetation”), while its lowest score was observed for a single class (ΔmBF-score: 0.52; “other object”). On the other hand, the EX2 achieved higher scores in three other classes (“built-up”, “phrygana vegetation”, and “shadow”) and quite similar scores for the “bare ground” and “grassland vegetation” classes to the ones from EX1, but there is a deviation for the “woody vegetation” class (ΔmBF-score: 0.38), and its lowest score was marked for the “other object” class (ΔmBF-score: 0.63). In comparison with the EX1 and EX2 models, the EX3 model had its highest score in a single class (ΔmBF-score:0; “other objects”), followed by another one (ΔmBF-score: 0.05; “woody vegetation”), whereas its lowest scores were noticed in the “built-up” class (ΔmBF-score: NaN), followed by the “shadow” class (ΔmBF-score: 0.58).

Table 5.
mBF-score and the difference from the highest score (ΔmBF-score) for each class obtained from each experiment.
A further analysis by computing McNemar’s test statistic showed that the differences in accuracy between the EX1 and EX2, EX1 and EX3, and EX2 and EX3 models are statistically significant (Table 6). All of the test values are greater than 3.841 (critical Chi-squared value with 1 degree of freedom) at the 95% confidence interval at the 0.05 level.

Table 6.
McNemar’s test Chi-squared values for pair comparison of the classification performance of the models.
Taken together, these results suggest that there is a significant positive correlation between the number of input information layers and the predictive performance of the model. Therefore, fusing multispectral and LiDAR data leads to more accurate land cover mapping of this semi-arid Mediterranean environment.
5. Discussion
5.1. Importance of Fusing Multispectral and LiDAR Data for Land Cover Classification
Semi-arid ecosystems are occupied by small and widely scattered vegetation patches, making it challenging to identify them through satellite remote sensing [64]. In this study, we combined multispectral and LiDAR data for the land cover classification of a semi-arid Mediterranean site using an optimized deep learning algorithm. The findings indicate that the fusion of multispectral and airborne LiDAR data improves the overall accuracy of the CNN model compared to the utilization of other data type alone, i.e., multispectral imagery or LiDAR data.
Herein, we classified the fused dataset into seven classes, i.e., woody vegetation, bare ground, grassland vegetation, other objects, phrygana vegetation, shadow, and built-up environment, by taking up a CNN-based semantic segmentation approach. First, we merged five bands of multispectral imagery (B, G, R, RE, and NIR), an image-derived vegetation index (NDVI), and three rasterized LiDAR point cloud attributes (height, intensity, and number of returns). Then, the U-Net architecture was optimized based on the values of the hyper-parameters obtained from an exploratory study, and the results were quite satisfactory, with an OA of 79.34% and a kappa coefficient of 0.6966. Prior studies have noted the importance of data fusion for land cover mapping [34,35,38] and its impact on the classification accuracy. In addition, a strong relationship between parameter selection and the predictive performance of deep learning architectures [53], as well as the fine-tuning of the hyper-parameters and the overall performance of CNN models for classification tasks [29,61] have been reported in the recent literature. Consistent with previous studies adopting an image-based strategy in terms of the input data format, this research found that the image stack generated from the fusion of multispectral and LiDAR data, in tandem with analysis of the hyper-parameters of the CNN model, can improve classification accuracy.
Further, this study demonstrated that the joint use of spatial and spectral features is effective in yielding the highest classification accuracy; nevertheless, employing multispectral data only produced results that were nearly as accurate. This indicates that the classification capability of the model trained with combined data was primarily obtained by multispectral imagery. This finding reflects that of Solórzano et al. [56], who also found that the classification accuracy of a U-Net architecture trained with fused multispectral and SAR data was higher than of other architectures trained with either multispectral imagery or SAR data only; however, the CNN model including only multispectral image input gave almost the same results. This is also in accordance with the observation in [34], where the spectral features were noted to be the most significant information for image classification.
The results obtained from the comparative analysis (Table 4) show that among the seven classes, the “grassland vegetation” class benefited the most in the case of using fused data (84%) regarding user’s accuracy, while the mBF-score was satisfactory (75%). This finding denotes that the selected attributes of the LiDAR point cloud enhanced the classification accuracy, and the one with the most significance was probably the intensity attribute (see Figure 3). Apart from intensity attribute, the NDVI probably also played an important role in the discrimination of this class. The NDVI is extensively acknowledged as a proxy for vegetation greenness [72], and it contributes to the classification of all vegetation types. These results reflect those of da Silveira et al. [73], who also found that the most important attributes for the classification of Caatinga physiognomies in a semi-arid region of northeast Brazil was the vegetation indexes, including the NDVI.
The “bare ground” and “phrygana vegetation” classes exhibited similar user’s accuracy results, 89% and 73%, respectively; however, the “bare ground” class is characterized by a slightly higher mBF-score (90%) obtained from EX1 compared to the one from EX2 (87%), and vice versa for the “phrygana vegetation” class (92% for EX2 vs. 91% for EX1). Of course, these results came as no surprise due to the dominance of these land cover types in the study area. The CNN model had enough training data to learn to distinguish these three classes (see Table 1); nevertheless, both models confused the “bare ground” class with the “other object” class, probably due to the similar reflectivity of the artificial objects and the rocky area, a “mask” problem observed by [4].
With regard to the “woody vegetation” class, the employment of fused data or the LiDAR data alone to the model produced the same results in terms of user’s accuracy (69%); however, the mean boundary F1 score obtained by EX1 indicates the superiority of fusing the data (75% for EX1 vs. 70% for EX3). This finding supports the idea of combining spectral and structural information, i.e., features derived from height information, as it leverages the variation in plant height and the NDVI and provides better accuracy [64,65,73]. Nonetheless, these classification results are probably associated with the number of returns attribute too (see Figure 3), which delivers elevation information. The capability of a LiDAR pulse to penetrate the tree crown and acquire information about the geometry and texture of woody vegetation has been proven valuable for classifying vegetation.
In addition, the EX2 model correctly identified the “built-up” class, yielding 89% for PA and 91% for UA, and the IoU value (82%) was the highest achieved among the three experiments, indicating the best alignment between predicted and actual areas; still, the mBF-score did not exceed 70%. Along the same lines, the results obtained from EX1 were quite the same, although it was expected that the height information from the LiDAR data would contribute positively to the accuracy (see Figure 3). Conversely, nothing but disappointing were the results achieved by the EX3 model, which did not manage to identify the “built-up” class in the slightest. Surprisingly, the model that only used LiDAR data outperformed the other two regarding the “other object” class, as it yielded an up 71% mBF-score, while the corresponding results that were produced by the models of EX1 (19%) and EX2 (8%) reflect the difficulty that they had with this class. It is hard to explain why the models presented such a performance on these two classes, even though they both contain human-made objects. With regard to the accuracy obtained by the EX3 model, the absence of multispectral data was proven unfavorable for the “build-up” class, and it seems like the structural information derived from LiDAR point cloud was not taken into consideration in the model. On the other hand, the results obtained from EX1 and EX2 for the “other objects” class might be related to the inclusion of heterogeneous ground objects with different reflectiveness, causing this incorrect discrimination from the models. Additionally, the mBF-scores of 76% (EX2) and 74% (EX1) indicate a satisfactory performance of the models for the “shadow” class, but the results obtained with respect to the producer’s and user’s accuracies show that mistakes were made. Undoubtedly, these errors are minor compared to the ones appearing in EX3, where the model produced poor results (PA: 0%; UA: 28%).
5.2. CNN-Based Sematic Segmentation Approach and Hyper-Parameter Analysis
The U-Net network was adopted as the deep learning architecture for this study due to the promising results obtained from previous studies dealing with multi-class land cover classification tasks [56,57,58]. To achieve better results, most of the studies reviewed here either improved the network’s architecture [57,63] or conducted hyper-parameter optimization [117,118]. In this study, the original U-Net architecture with small alterations in terms of the input tile size and patch size for prediction was used, and we explored the impact of different hyper-parameters values (i.e., learning rate and optimizer) on the overall accuracy of the model and the training complexity. After an exploration of the optimal values of the hyper-parameters, we proceeded with a comparative analysis of the models by differentiating the input data type.
The input tile size controls the quantity of feature information used as input for the CNN model [29]. The trend of the higher the input tile size, the better the classification performance of the model was not found in this study. The overall accuracy of the model gradually improved as the input tile size increased from 64 × 64 to 128 × 128, but it started to decrease when the size was altered to 1024 × 1024 (Table 2). The most favorable results were yielded when the model was trained with a 128 × 128 input tile size, as it produced the best overall accuracy of 79.34%. This finding supports the work of other studies in this area linking the classification accuracy with the input data size [29,117]. For instance, Pan et al. [29] noticed that a small input data size corresponds to inadequate feature representation of land covers, entailing a lower classification accuracy. Conversely, a large input data size contains abundant and possibly superfluous feature information, which ultimately results in a depleted classification accuracy. Thus, they used a medium input size for their classification problem. Similarly, Lee et al. [117] compared different input image sizes (64 × 64; 128 × 128; and 256 × 256) and found that the optimal one for their land cover classification task using RapidEye satellite data was the smallest one. However, having a 5 m spatial resolution is equivalent to an approximately 300 m width, and it was proven to be more efficient in capturing the characteristics of individual objects in the training images compared to the one with the largest input image size.
Additionally, the optimum patch size for prediction was investigated to improve the accuracy of the land cover predictions. In a related way to the input tile size, the overall accuracy of the model was progressively increased when the patch size changed from 256 × 256 to 512 × 512, but when it varied from 512 × 512 to 1024 × 024, the overall accuracy decreased. The observed decrease in overall accuracy after doubling the patch size could be attributed to not changing the architecture design of the network, as Hamwood et al. [115] suggested. In their analysis, they examined the impact of the patch size and the network architecture design on CNN performance, and they highlighted that the increase in the patch size should be accompanied by changes in the architecture design of the network. Kavzoglou and Yilmaz [114] have also highlighted that the impact of patch size on classification accuracy varies depending on the model’s different characteristics and the data type. Therefore, the findings of the current study do not support the previous research reviewed here as they use different types of data and DL algorithms, e.g., hyperspectral data and 2D/3D CNN models.
In terms of time complexity, the experimental results showed that the model with the smallest input tile size and patch size for prediction achieved quite good accuracies (OA: 76.27%; K: 0.6525) and costed less time (23′ and 21′′) than the other two models. In an opposite way, the training time dramatically increased (506′ and 6′′) when the model was fed the largest input tile size and patch size for prediction, although it yielded quite similar accuracies (OA: 76.45%; K: 0.6605) to the first model. The medium sizes for the input tile and patch for prediction were proven to be the optimal ones because they managed to trade off the classification accuracies (OA: 79.34%; K: 0.6966) and the training time consumption (82’). These results reflect those of Pan et al. [29], who also found that the optimal input size was a medium one, when taking training time into account.
In accordance with the present results, previous studies have demonstrated that the CNN model’s performance is significantly influenced by the learning rate, which impacts the training time and the optimization algorithm selected [29,118]. Testing different learning rates and optimization algorithms, we found that a learning rate of 0.05 was the optimal one as it yielded 71.8%, while reducing it to 0.0005 caused slower learning and, as result, a lower accuracy (59%) after 30 epochs of training. The SGD with a momentum of 0.9 was ranked at the top among the three optimizers we tried, namely SGD and ADAM (71.8%; SGD, 13.6%; ADAM, 13.6%; RMSProp). The results of this investigation are opposite to those produced by the optimized U-Net of Clark et al. [118], which was employed for land cover classification using multispectral aerial imagery. Their network achieved an average kappa score of 0.77 with the RMSProp optimizer, while taking 2.7 h to train, and the optimal value of the learning rate was 0.01. This inconsistency may be due to the type of data (only multispectral data), the input tile size (512 × 512), and slower learning rate (0.01) that were selected for their study.
5.3. Comparison with Similar Studies
Compared with similar studies, the focus of our research is to investigate whether the fusion of multispectral and LiDAR point cloud data improves the accuracy of CNN-based semantic segmentation and to develop an image-based land cover classification methodology for semi-arid Mediterranean environments. The two-dimensional (2D) image-based processing method is commonly used for large-scale land cover mapping [44], although a classification task based on multispectral LiDAR data requires a significant amount of time and labor [45]. In reviewing the literature, the fusion of multispectral and LiDAR data in conjunction with an image-based processing strategy was found effective in enhancing the classification accuracy (OA of around 90% or even higher) using either machine learning or deep learning algorithms [14,29,47,50,52]. On the other hand, the U-Net architecture has achieved significant land cover classification results when it was optimized or its design was modified, reaching an overall accuracy of even higher than 80% [57,58,117,118]. Further, the land cover mapping of semi-arid environments using either single datasets [61,65] or combined ones [56,64,65] and CNN models has obtained quite satisfactory results, ranging from >75% to >95% in overall accuracy.
Although the results reported in our land cover classification are lower (OA: 79.34%; K: 0.6966) compared to those of other studies, this can be attributed largely to the data used, which were captured by different sensors; the hyper-parameters of U-Net selected to be fine-tuned; and of course, the complexity of the classification system. Most researchers investigating the fusion of multispectral and LiDAR data for image-based land cover classification tasks have utilized data acquired by a single sensor, specifically the Optech Titan Multispectral LiDAR System [47,50,52], and therefore, the difference in accuracies observed may be derived from this. In this study, the multispectral imagery was acquired by a high-precision UAV, while the 3D LiDAR point cloud was obtained by a scanning sensor capable of capturing the details of complex structures and providing precise photogrammetric models. Feeding our CNN model alternative types of data inputs, like fused hyperspectral and LiDAR data or data captured by different sensors, could be of interest when conducting future land cover classification tasks in the study area. Moreover, the components of U-Net architecture used here were the same as those in the original, and the alterations implemented were only related to the input tile size and the patch size for prediction, while a short investigation took place in learning rate and optimization algorithm. The findings of other works indicated that further hyper-parameter exploration, like in the studies in [29,117,118], as well as modifications to the network’s structure (for example, see [57]) might be needed for obtaining more accurate classification results. To develop a full picture of fusing multispectral and LiDAR data for land cover classification, additional CNN models will need to be investigated.
To obtain a better comparison of our study with the recent literature, we also need to consider the classification system, since more complex systems, like semi-arid environments, have their own particularities. Simpler classification systems, such as forest/non-forest systems are probably easier to classify [56]; however, plant species discrimination is a tough task [64,65]. Nevertheless, different areas of the planet, although they have similar conditions, e.g., semi-arid climate, are inhabited by different species of plants and animals. Therefore, the factor of geographical location and the number of land cover types in similar studies should be also considered. In [61], the study area consisted of intricate patterns of LULC with similar spectral and spatial features, such as barren land, settlements, vegetation, water bodies, and fallow land. Their proposed CNN model achieved a higher than 92% overall accuracy by using medium-resolution remote sensing imagery. The performance of the LResU-Net in [63] was tested in a semi-arid area of Mongolia, Asia, which is composed of forests, grassland vegetation, and cultivated land and was suitable for providing a variety of land covers, such as natural grasslands, trees, roads, rivers, buildings, etc. The model achieved an overall accuracy of 93.7% and a kappa coefficient of 0.86, and the UAV imagery used for training the model was proven sufficient for this region. Obviously, the vegetation and topography of the semi-arid landscapes in Pakistan, Asia [61]; Mongolia, Asia [63]; or Arizona, USA [64], are dissimilar to the Mediterranean semi-arid ecosystem in Greece investigated in this study. Yet, the synergistic use of Sentinel-1 SAR, Sentinel-2 multispectral imagery, LiDAR, and derived data like indices and texture for land cover classification in a semi-arid Mediterranean area in Spain, Europe, using machine learning algorithms, which proposed by [62], resulted in an overall accuracy of 91%, a significantly higher accuracy than the one yielded from our approach, but they used features from three different sources.
Bearing in mind that previous works used different types of data and deep learning approaches, along with the different study sites tested, we conclude that the comparison is of no practical significance. Still, there is abundant room for further exploration of the efficacy of our methodology in a wider range of scenarios to address the practical requirements of land cover classification in semi-arid Mediterranean environments.
6. Conclusions
The purpose of the current study was to explore the influence of fusing multispectral and LiDAR data on the predictive performance of the CNN model used for the semantic segmentation task, and specifically, the land cover mapping of a semi-arid Mediterranean region. It was anticipated that increasing the number of input information layers and selecting the optimal values of some hyper-parameters of the deep learning network would improve the overall accuracy of the model. By combining five multispectral bands, NDVI, and three rasterized LiDAR attributes, we generated a nine-band image stack that was fed into a U-Net model, whose optimal values of input tile size, patch size for prediction, learning rate, and optimization algorithm were derived from an exploratory study on these hyper-parameters. The comparative experiments that were carried out by differentiating the number of input information layers of the image (9: fused data, 6: multispectral data only, and 3: LiDAR data only) and the assessment via objective metrics that followed showed that our hypothesis was correct. The model that was trained with fused data surpassed the performance of the other two models, which used either multispectral or LiDAR data only, in terms of discrimination capability by yielding an overall accuracy of 79.34% and a kappa coefficient of 0.6966. The experimental results of this study demonstrated that fusing multispectral and LiDAR data enhanced the classification accuracy in semi-arid Mediterranean environments. By using an input tile size and a prediction patch size with medium dimensions, i.e., 128 × 128 and 512 × 512, respectively, and conducting a hyper-parameter analysis, we obtained improvements in OA, K, and training time.
The multispectral imagery being collected at a 3.5 × 3.5 cm/pixel resolution at a 57.4 m altitude and the shadows present in the images obscuring information, in tandem with the small amount of training samples, are limitations of our study: the network misjudged some classes and achieved a quite low accuracy compared to relevant studies. Still, the low accuracy of the U-Net could be addressed by either improving its architecture or employing another CNN model in the future.
Due to the singularity of the study area, these results are particularly valuable because they can be utilized by the management body—the Natural History of the Lesvos Petrified Forest—to strengthen its conservation and management plan. Therefore, several aspects need to be explored in future research: (i) the fusion of multispectral and LiDAR with different processing strategies, e.g., the point cloud-based strategy using the direct classification of point clouds for a classification accuracy improvement; (ii) taking into account the seasonal variation in land cover types; (iii) a further exploration of the hyper-parameters (e.g., loss function, kernel size, etc.) and network’s architecture, aiming to boost the classification accuracy; and (iv) a test of transferability of our CNN model to similar environments.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.V. and A.C.; methodology, C.V. and A.C.; software, A.C., M.C. and C.V.; formal analysis, A.C., M.C. and C.V.; resources, C.V. and N.S.; data curation, A.C. and M.C.; writing—original draft preparation, A.C.; writing—review and editing, A.C., C.V., M.C. and N.S.; funding acquisition, N.S. and C.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the research e-Infrastructure “Interregional Digital Transformation for Culture and Tourism in Aegean Archipelagos” {Code Number MIS 5047046}, which is implemented within the framework of the “Regional Excellence” Action of the Operational Program “Competitiveness, Entrepreneurship, and Innovation”. The action was co-funded by the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF) and the Greek State [Partnership Agreement 2014–2020].
Data Availability Statement
The data are available on request. The data are not publicly available due to legal reasons.
Acknowledgments
We greatly thank our colleagues in the Geo-Informatics and Cartography Laboratory for their support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Alrababah, M.A.; Alhamad, M.N. Land Use/Cover Classification of Arid and Semi-Arid Mediterranean Landscapes Using Landsat ETM. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 2703–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pueyo, Y.; Alados, C.L. Effects of Fragmentation, Abiotic Factors and Land Use on Vegetation Recovery in a Semi-Arid Mediterranean Area. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2007, 8, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berberoglu, S.; Lloyd, C.D.; Atkinson, P.M.; Curran, P.J. The Integration of Spectral and Textural Information Using Neural Networks for Land Cover Mapping in the Mediterranean. Comput. Geosci. 2000, 26, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berberoglu, S.; Curran, P.J.; Lloyd, C.D.; Atkinson, P.M. Texture Classification of Mediterranean Land Cover. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2007, 9, 322–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Du, S. Learning Multiscale and Deep Representations for Classifying Remotely Sensed Imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 113, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wambugu, N.; Chen, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Wei, M.; Aminu Bello, S.; Marcato Junior, J.; Li, J. A Hybrid Deep Convolutional Neural Network for Accurate Land Cover Classification. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 103, 102515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, D.; Shi, B.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, J.; Yao, R.; Xue, Y. Multi-Source Collaborative Enhanced for Remote Sensing Images Semantic Segmentation. Neurocomputing 2022, 493, 76–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langley, S.K.; Cheshire, H.M.; Humes, K.S. A Comparison of Single Date and Multitemporal Satellite Image Classifications in a Semi-Arid Grassland. J. Arid Environ. 2001, 49, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobi, E.P.; Umamaheswari, R.; Stella, C.; Thangaradjou, T. Land Use and Land Cover Assessment along Pondicherry and Its Surroundings Using Indian Remote Sensing Satellite and GIS. J. Sci. Res. 2009, 4, 54–58. [Google Scholar]
- Hüttich, C.; Herold, M.; Wegmann, M.; Cord, A.; Strohbach, B.; Schmullius, C.; Dech, S. Assessing Effects of Temporal Compositing and Varying Observation Periods for Large-Area Land-Cover Mapping in Semi-Arid Ecosystems: Implications for Global Monitoring. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2445–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, C.; White, J.C.; Wulder, M.A. Optical Remotely Sensed Time Series Data for Land Cover Classification: A Review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 116, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Du, B.; Zhang, L.; Cerra, D.; Pato, M.; Carmona, E.; Prasad, S.; Yokoya, N.; Hansch, R.; Le Saux, B. Advanced Multi-Sensor Optical Remote Sensing for Urban Land Use and Land Cover Classification: Outcome of the 2018 Ieee Grss Data Fusion Contest. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 1709–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, Y.; Tong, Y.; Feng, W.; Dauphin, G.; Huang, W.; Xing, M. A Novel Image Fusion Method of Multi-Spectral and Sar Images for Land Cover Classification. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Liu, C.; Guan, H.; Wang, L.; Gao, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J. Land Cover Classification of Multispectral LiDAR Data with an Efficient Self-Attention Capsule Network. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 6501505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zheng, S.; Duan, C.; Wang, L.; Zhang, C. Land Cover Classification from Remote Sensing Images Based on Multi-Scale Fully Convolutional Network. Geo-Spat. Inf. Sci. 2022, 25, 278–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzepkenlis, A.; Marthoglou, K.; Grammalidis, N. Efficient Deep Semantic Segmentation for Land Cover Classification Using Sentinel Imagery. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yüksel, A.; Akay, A.E.; Gundogan, R. Using ASTER Imagery in Land Use/Cover Classification of Eastern Mediterranean Landscapes According to CORINE Land Cover Project. Sensors 2008, 8, 1237–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, Y.; Quackenbush, L.J.; Im, J. Synergistic Use of QuickBird Multispectral Imagery and LIDAR Data for Object-Based Forest Species Classification. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 1141–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalla Mura, M.; Prasad, S.; Pacifici, F.; Gamba, P.; Chanussot, J.; Benediktsson, J.A. Challenges and Opportunities of Multimodality and Data Fusion in Remote Sensing. Proc. IEEE 2015, 103, 1585–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghamisi, P.; Rasti, B.; Yokoya, N.; Wang, Q.; Hofle, B.; Bruzzone, L.; Bovolo, F.; Chi, M.; Anders, K.; Gloaguen, R.; et al. Multisource and Multitemporal Data Fusion in Remote Sensing: A Comprehensive Review of the State of the Art. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2019, 7, 6–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Chen, Z.; Peng, D.; Benediktsson, J.A.; Liu, B.; Zou, L.; Li, J.; Plaza, A. Remotely Sensed Big Data: Evolution in Model Development for Information Extraction [Point of View]. Proc. IEEE 2019, 107, 2294–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitton, D.; Laurens, E.; Hongkarnjanakul, N.; Schwob, C.; Mezeix, L. Land Cover Classification through Convolutional Neur-Al Network Model Assembly: A Case Study of a Local Rural Area in Thailand. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2022, 26, 100740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, R.; Li, Z.; Ghamisi, P.; Hong, D.; Xia, G.; Liu, Q. Classification of Hyperspectral and LiDAR Data Using Coupled CNNs. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 4939–4950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghassemian, H. A Review of Remote Sensing Image Fusion Methods. Inf. Fusion 2016, 32, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Guan, H.; Li, D.; Yu, Y.; Wang, H.; Gao, K.; Marcato Junior, J.; Li, J. Airborne Multispectral LiDAR Point Cloud Classification with a Feature Reasoning-Based Graph Convolution Network. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 105, 102634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Du, B. Deep Learning for Remote Sensing Data: A Technical Tutorial on the State of the Art. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2016, 4, 22–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ye, Y.; Yin, G.; Johnson, B.A. Deep Learning in Remote Sensing Applications: A Meta-Analysis and Review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 152, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Hinton, G.; Bengio, Y. Deep Learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Guan, H.; Chen, Y.; Yu, Y.; Nunes Gonçalves, W.; Marcato Junior, J.; Li, J. Land-Cover Classification of Multispectral LiDAR Data Using CNN with Optimized Hyper-Parameters. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 166, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.X.; Tuia, D.; Mou, L.; Xia, G.S.; Zhang, L.; Xu, F.; Fraundorfer, F. Deep Learning in Remote Sensing: A Comprehensive Review and List of Resources. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2017, 5, 8–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemker, R.; Salvaggio, C.; Kanan, C. Algorithms for Semantic Segmentation of Multispectral Remote Sensing Imagery Using Deep Learning. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 145, 60–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotaridis, I.; Lazaridou, M. Remote Sensing Image Segmentation Advances: A Meta-Analysis. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 173, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Y.; Wu, Y.; Yang, X.; Liu, F.; Liao, Y. Review the State-of-the-Art Technologies of Semantic Segmentation Based on Deep Learning. Neurocomputing 2022, 493, 626–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Weng, Q. A Survey of Image Classification Methods and Techniques for Improving Classification Performance. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 823–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturari, M.; Frontoni, E.; Pierdicca, R.; Mancini, A.; Malinverni, E.S.; Tassetti, A.N.; Zingaretti, P. Integrating Elevation Data and Multispectral High-Resolution Images for an Improved Hybrid Land Use/Land Cover Mapping. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 50, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bork, E.W.; Su, J.G. Integrating LIDAR Data and Multispectral Imagery for Enhanced Classification of Rangeland Vegetation: A Meta Analysis. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 111, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmgren, J.; Persson, Å.; Söderman, U. Species Identification of Individual Trees by Combining High Resolution LiDAR Data with Multi-Spectral Images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 1537–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartfield, K.A.; Landau, K.I.; van Leeuwen, W.J.D. Fusion of High Resolution Aerial Multispectral and Lidar Data: Land Cover in the Context of Urban Mosquito Habitat. Remote Sens. 2011, 3, 2364–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonarakis, A.S.; Richards, K.S.; Brasington, J. Object-Based Land Cover Classification Using Airborne LiDAR. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 2988–2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, R.; Webster, T.L. Object-Oriented Land Cover Classification of Lidar-Derived Surfaces. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 32, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charaniya, A.P.; Manduchi, R.; Lodha, S.K. Supervised Parametric Classification of Aerial LiDAR Data. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Washington, DC, USA, 27 June –2 July 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, L.; Gong, W. Information Fusion of Aerial Images and LIDAR Data in Urban Areas: Vector-Stacking, Re-Classification and Post-Processing Approaches. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Alcón, S.; Coll, L.; De Cáceres, M.; Guitart, L.; Cabré, M.; Just, A.; González-Olabarría, J.R. Combining Aerial LiDAR and Multispectral Imagery to Assess Postfire Regeneration Types in a Mediterranean Forest. Can. J. For. Res. 2015, 45, 856–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matikainen, L.; Karila, K.; Hyyppä, J.; Litkey, P.; Puttonen, E.; Ahokas, E. Object-Based Analysis of Multispectral Airborne Laser Scanner Data for Land Cover Classification and Map Updating. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 128, 298–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Bi, S.; Gong, W.; Chen, B.; Chen, B.; Tang, X.; Qu, F.; Song, S. Land Cover Classification with Multispectral LiDAR Based on Multi-Scale Spatial and Spectral Feature Selection. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Chehata, N.; Mallet, C.; Boukir, S. Relevance of Airborne Lidar and Multispectral Image Data for Urban Scene Classification Using Random Forests. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2011, 66, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Diaz, J.C.; Carter, W.E.; Glennie, C.; Shrestha, R.L.; Pan, Z.; Ekhtari, N.; Singhania, A.; Hauser, D.; Sartori, M. Capability Assessment and Performance Metrics for the Titan Multispectral Mapping Lidar. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wichmann, V.; Bremer, M.; Lindenberger, J.; Rutzinger, M.; Georges, C.; Petrini-Monteferri, F. Evaluating the Potential of Multispectral Airborne Lidar for Topographic Mapping and Land Cover Classification. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2015, 2, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekhtari, N.; Glennie, C.; Fernandez-Diaz, J.C. Classification of Airborne Multispectral Lidar Point Clouds for Land Cover Mapping. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 2068–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsy, S.; Shaker, A.; El-Rabbany, A. Multispectral Lidar Data for Land Cover Classification of Urban Areas. Sensors 2017, 17, 958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hell, M.; Brandmeier, M.; Briechle, S.; Krzystek, P. Classification of Tree Species and Standing Dead Trees with Lidar Point Clouds Using Two Deep Neural Networks: PointCNN and 3DmFV-Net. PFG-J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Geoinf. Sci. 2022, 90, 103–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Guan, H.; Li, D.; Gu, T.; Wang, L.; Ma, L.; Li, J. A Hybrid Capsule Network for Land Cover Classification Using Multispectral LiDAR Data. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 17, 1263–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Pang, M.; Wang, J. Classifying Airborne LiDAR Point Clouds via Deep Features Learned by a Multi-Scale Convolutional Neural Network. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2018, 32, 960–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Z.; Guan, H.; Zhao, P.; Li, D.; Yu, Y.; Zang, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, J. Multispectral Lidar Point Cloud Classification Using Se-Pointnet++. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaseminik, F.; Aghamohammadi, H.; Azadbakht, M. Land Cover Mapping of Urban Environments Using Multispectral LiDAR Data under Data Imbalance. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2021, 21, 100449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solórzano, J.V.; Mas, J.F.; Gao, Y.; Gallardo-Cruz, J.A. Land Use Land Cover Classification with U-Net: Advantages of Combining Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 Imagery. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Roslan, S.N.A.B.; Wang, C.; Quan, L. Research on Land Cover Classification of Multi-Source Remote Sensing Data Based on Improved U-Net Network. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 16275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altarez, R.D.D.; Apan, A.; Maraseni, T. Deep Learning U-Net Classification of Sentinel-1 and 2 Fusions Effectively Demarcates Tropical Montane Forest’s Deforestation. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2023, 29, 100887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Im, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhen, Z. A Deep-Learning-Based Tree Species Classification for Natural Secondary Forests Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Hyperspectral Images and LiDAR. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 159, 111608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elamin, A.; El-Rabbany, A. UAV-Based Image and LiDAR Fusion for Pavement Crack Segmentation. Sensors 2023, 23, 9315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, K.; Johnson, B.A. Land-Use and Land-Cover Classification in Semi-Arid Areas from Medium-Resolution Remote-Sensing Imagery: A Deep Learning Approach. Sensors 2022, 22, 8750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdivieso-Ros, C.; Alonso-Sarria, F.; Gomariz-Castillo, F. Effect of the Synergetic Use of Sentinel-1, Sentinel-2, LiDAR and Derived Data in Land Cover Classification of a Semiarid Mediterranean Area Using Machine Learning Algorithms. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, B.Y.J.; Sun, J.; Dong, S.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Xu, J.; Chu, W.; Dong, Y.; et al. Land Cover Classification in a Mixed Forest-Grassland Ecosystem Using LResU-Net and UAV Imagery. J. For. Res. 2022, 33, 923–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankey, T.T.; McVay, J.; Swetnam, T.L.; McClaran, M.P.; Heilman, P.; Nichols, M. UAV Hyperspectral and Lidar Data and Their Fusion for Arid and Semi-Arid Land Vegetation Monitoring. Remote Sens. Ecol. Conserv. 2018, 4, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, C.L.; Hartfield, K.; Collins, C.D.H.; van Leeuwen, W.J.D.; Metz, L.J. Multi-Temporal LiDAR and Hyperspectral Data Fusion for Classification of Semi-Arid Woody Cover Species. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diffenbaugh, N.S.; Giorgi, F. Climate Change Hotspots in the CMIP5 Global Climate Model Ensemble. Clim. Chang. 2012, 114, 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douvis, K.; Kapsomenakis, J.; Solomos, S.; Poupkou, A.; Stavraka, T.; Nastos, P.; Zerefos, C. Change in Aridity Index in the Mediterranean Region under Different Emission Scenarios. Environ. Sci. Proc. 2023, 26, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szantoi, Z.; Geller, G.N.; Tsendbazar, N.E.; See, L.; Griffiths, P.; Fritz, S.; Gong, P.; Herold, M.; Mora, B.; Obregón, A. Addressing the Need for Improved Land Cover Map Products for Policy Support. Environ. Sci. Policy 2020, 112, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zouros, N.; Velitzelos, E.; Valiakos, I.; Labaki, O. The Plaka Petrified Forest Park in Western Lesvos—Greece. Bull. Geol. Soc. Greece 2007, 40, 1880–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, C.J. Red and Photographic Infrared Linear Combinations for Monitoring Vegetation. Remote Sens. Environ. 1979, 8, 127–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, H.A.; Huete, A.R.; Baethgen, W.E. A 20-Year Study of NDVI Variability over the Northeast Region of Brazil. J. Arid Environ. 2006, 67, 288–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erasmi, S.; Schucknecht, A.; Barbosa, M.P.; Matschullat, J. Vegetation Greenness in Northeastern Brazil and Its Relation to ENSO Warm Events. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 3041–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silveira, H.L.F.; Galvão, L.S.; Sanches, I.D.A.; de Sá, I.B.; Taura, T.A. Use of MSI/Sentinel-2 and Airborne LiDAR Data for Mapping Vegetation and Studying the Relationships with Soil Attributes in the Brazilian Semi-Arid Region. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 73, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowravaram, S.; Tian, P.; Flanagan, H.; Goyer, J.; Chao, H. UAS-Based Multispectral Remote Sensing and NDVI Calculation for Post Disaster Assessment. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Unmanned Aircraft Systems, ICUAS 2018, Dallas, TX, USA, 12–15 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, W.Y.; Shaker, A.; El-Ashmawy, N. Urban Land Cover Classification Using Airborne LiDAR Data: A Review. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 158, 295–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girardeau-Montaut, D. CloudCompare: 3D Point Cloud and Mesh Processing Software. 2015. Available online: http://www.cloudcompare.org (accessed on 10 February 2024).
- Jagannathan, J.; Divya, C. Deep Learning for the Prediction and Classification of Land Use and Land Cover Changes Using Deep Convolutional Neural Network. Ecol. Inform. 2021, 65, 101412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, V.R. Optimal Ratio for Data Splitting. Stat. Anal. Data Min. 2022, 15, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, V.R.; Vakayil, A. SPlit: An Optimal Method for Data Splitting. Technometrics 2022, 64, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI), Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Volume 9351. [Google Scholar]
- Punn, N.S.; Agarwal, S. Modality Specific U-Net Variants for Biomedical Image Segmentation: A Survey. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2022, 55, 5845–5889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully Convolutional Networks for Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Drozdzal, M.; Vorontsov, E.; Chartrand, G.; Kadoury, S.; Pal, C. The Importance of Skip Connections in Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the Deep Learning and Data Labeling for Medical Applications, Athens, Greece, 21 October 2016; Volume 10008 LNCS. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Cheng, J.; Quan, Q.; Wu, F.X.; Wang, Y.P.; Wang, J. A Survey on U-Shaped Networks in Medical Image Segmentations. Neurocomputing 2020, 409, 244–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zioulis, N.; Albanis, G.; Drakoulis, P.; Alvarez, F.; Zarpalas, D.; Daras, P. Hybrid Skip: A Biologically Inspired Skip Connection for the UNet Architecture. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 53928–53939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibtehaz, N.; Rahman, M.S. MultiResUNet: Rethinking the U-Net Architecture for Multimodal Biomedical Image Segmentation. Neural Netw. 2020, 121, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Commun. ACM 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Jiang, H.; Li, C.; Jia, X.; Ghamisi, P. Deep Feature Extraction and Classification of Hyperspectral Images Based on Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 6232–6251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, H.; Foody, G.M.; Boyd, D.S. Supervised Methods of Image Segmentation Accuracy Assessment in Land Cover Mapping. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 205, 338–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.J. A Survey on Evaluation Methods for Image Segmentation. Pattern Recognit. 1996, 29, 1335–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foody, G.M. Status of Land Cover Classification Accuracy Assessment. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 80, 185–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, A.E.; Warner, T.A.; Guillén, L.A. Accuracy Assessment in Convolutional Neural Network-Based Deep Learning Remote Sensing Studies—Part 1: Literature Review. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, D.; Soto-Rey, I.; Kramer, F. Towards a Guideline for Evaluation Metrics in Medical Image Segmentation. BMC Res. Notes 2022, 15, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csurka, G.; Larlus, D.; Perronnin, F. What Is a Good Evaluation Measure for Semantic Segmentation? In Proceedings of the BMVC 2013—British Machine Vision Conference, Bristol, UK, 9–13 September 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Vasilakos, C.; Kavroudakis, D.; Georganta, A. Machine Learning Classification Ensemble of Multitemporal Sentinel-2 Images: The Case of a Mixed Mediterranean Ecosystem. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foody, G.M.; Boyd, D.S.; Sanchez-Hernandez, C. Mapping a Specific Class with an Ensemble of Classifiers. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 1733–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.; Wang, Y. Optimizing Intersection-over-Union in Deep Neural Networks for Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the Advances in Visual Computing, ISVC 2016, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 12–14 December 2016; Volume 10072 LNCS. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, R.; Ngan, K.N.; Li, S. Jaccard Index Compensation for Object Segmentation Evaluation. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, ICIP 2014, Paris, France, 27–30 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, A.L. Note on the “Correction for Continuity” in Testing the Significance of the Difference between Correlated Proportions. Psychometrika 1948, 13, 185–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavzoglu, T. Object-Oriented Random Forest for High Resolution Land Cover Mapping Using Quickbird-2 Imagery. In Handbook of Neural Computation; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; ISBN 9780128113196. [Google Scholar]
- Shorten, C.; Khoshgoftaar, T.M. A Survey on Image Data Augmentation for Deep Learning. J. Big Data 2019, 6, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemley, J.; Bazrafkan, S.; Corcoran, P. Smart Augmentation Learning an Optimal Data Augmentation Strategy. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 5858–5869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatfield, K.; Simonyan, K.; Vedaldi, A.; Zisserman, A. Return of the Devil in the Details: Delving Deep into Convolutional Nets. In Proceedings of the BMVC 2014—British Machine Vision Conference, Nottingham, UK, 1–5 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Mikołajczyk, A.; Grochowski, M. Data Augmentation for Improving Deep Learning in Image Classification Problem. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Interdisciplinary PhD Workshop, IIPhDW 2018, Swinoujscie, Poland, 9–12 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, L.N. Cyclical Learning Rates for Training Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, WACV 2017, Santa Rosa, CA, USA, 24–31 March 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zeiler, M.D. ADADELTA: An Adaptive Learning Rate Method. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1212.5701 (accessed on 10 February 2024).
- Wu, Y.; Liu, L.; Bae, J.; Chow, K.H.; Iyengar, A.; Pu, C.; Wei, W.; Yu, L.; Zhang, Q. Demystifying Learning Rate Policies for High Accuracy Training of Deep Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Big Data, Big Data 2019, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 9–12 December 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Dogo, E.M.; Afolabi, O.J.; Nwulu, N.I.; Twala, B.; Aigbavboa, C.O. A Comparative Analysis of Gradient Descent-Based Optimization Algorithms on Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computational Techniques, Electronics and Mechanical Systems, CTEMS 2018, Belgaum, India, 21–22 December 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zaheer, R.; Shaziya, H. A Study of the Optimization Algorithms in Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Inventive Systems and Control, ICISC 2019, Coimbatore, India, 10–11 January 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Richter, M.L.; Byttner, W.; Krumnack, U.; Wiedenroth, A.; Schallner, L.; Shenk, J. (Input) Size Matters for CNN Classifiers. In Proceedings of the Artificial Neural Networks and Machine Learning—ICANN 2021; Bratislava, Slovakia, 14–17 September 2021; Volume 12892 LNCS. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q.V. EfficientNet: Rethinking Model Scaling for Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Machine Learning, ICML 2019, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Reina, G.A.; Panchumarthy, R.; Thakur, S.P.; Bastidas, A.; Bakas, S. Systematic Evaluation of Image Tiling Adverse Effects on Deep Learning Semantic Segmentation. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavzoglu, T.; Yilmaz, E.O. Analysis of Patch and Sample Size Effects for 2D-3D CNN Models Using Multiplatform Dataset: Hyperspectral Image Classification of ROSIS and Jilin-1 GP01 Imagery. Turk. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2022, 30, 2124–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamwood, J.; Alonso-Caneiro, D.; Read, S.A.; Vincent, S.J.; Collins, M.J. Effect of Patch Size and Network Architecture on a Convolutional Neural Network Approach for Automatic Segmentation of OCT Retinal Layers. Biomed. Opt. Express 2018, 9, 3049–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Zhu, H. Visual Quality Evaluation for Semantic Segmentation: Subjective Assessment Database and Objective Assessment Measure. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 28, 5785–5796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Sim, W.; Park, J.; Lee, J. Evaluation of Hyperparameter Combinations of the U-Net Model for Land Cover Classification. Forests 2022, 13, 1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, A.; Phinn, S.; Scarth, P. Optimised U-Net for Land Use–Land Cover Classification Using Aerial Photography. PFG-J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Geoinf. Sci. 2023, 91, 125–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).