A Goaf-Locating Method Based on the D-InSAR Technique and Stratified Okada Dislocation Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
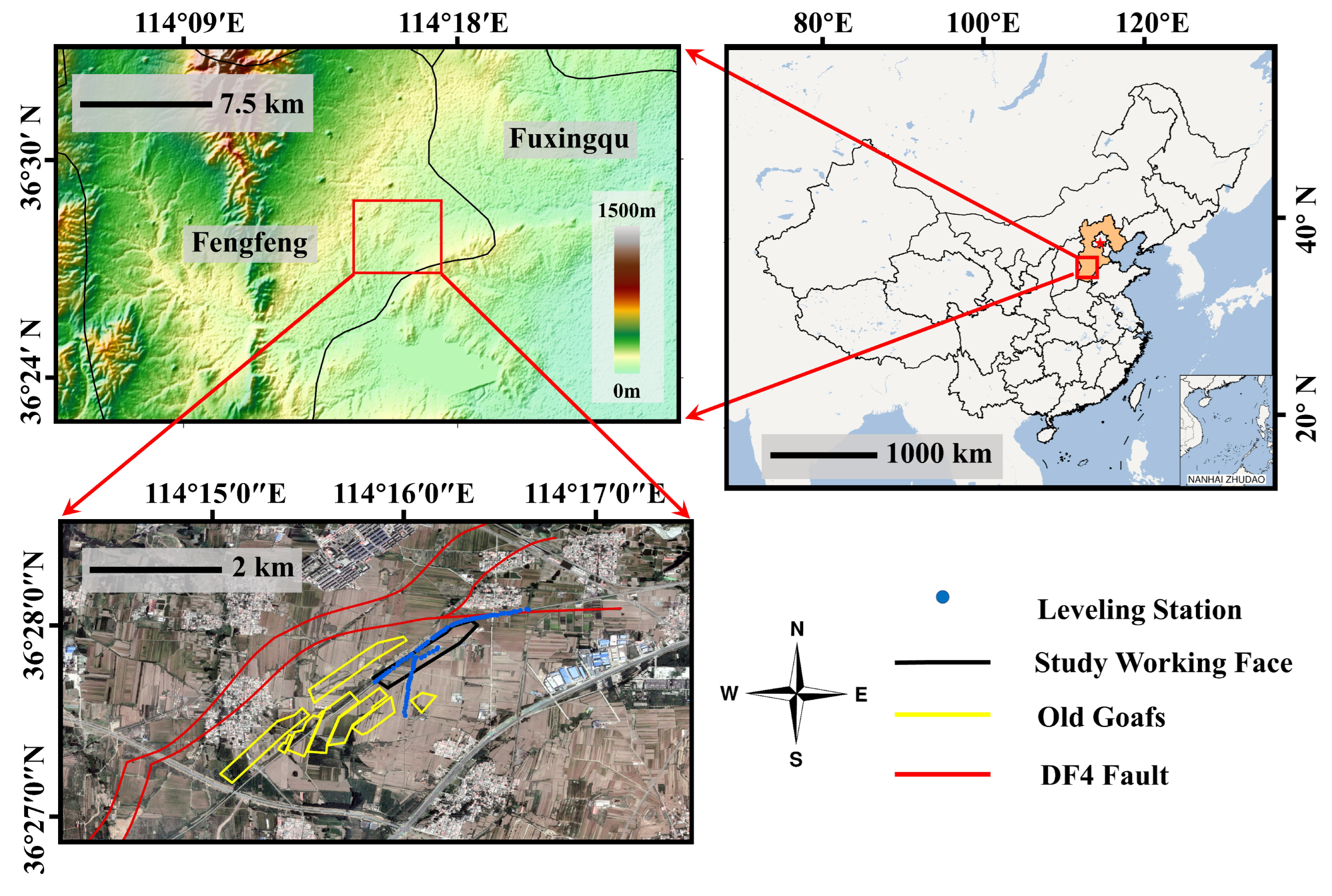
2. Study Area and Datasets
3. Methods
- Acquire times-series line-of-sight (LOS) deformation utilizing the D-InSAR technique;
- Determine the S-ODM parameters based on basic geological investigations;
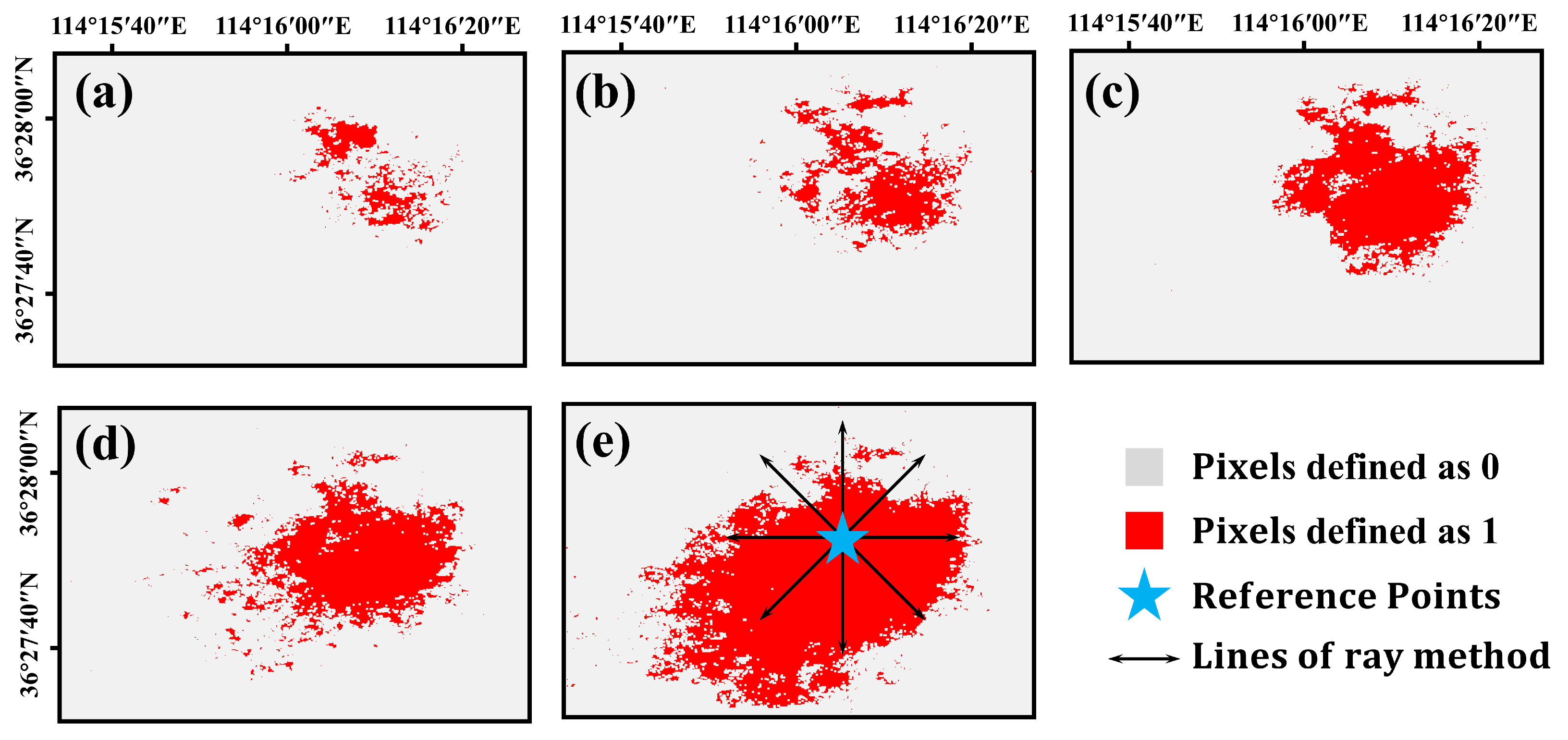
- Apply the ray method to estimate the goaf azimuth with the textures and trends of the InSAR-derived deformation;
- Use GA-PSO to estimate the goaf parameters. The process will stop when either the best fitness value is less than the threshold or the iteration number reaches a preset maximum value.
3.1. Differential InSAR
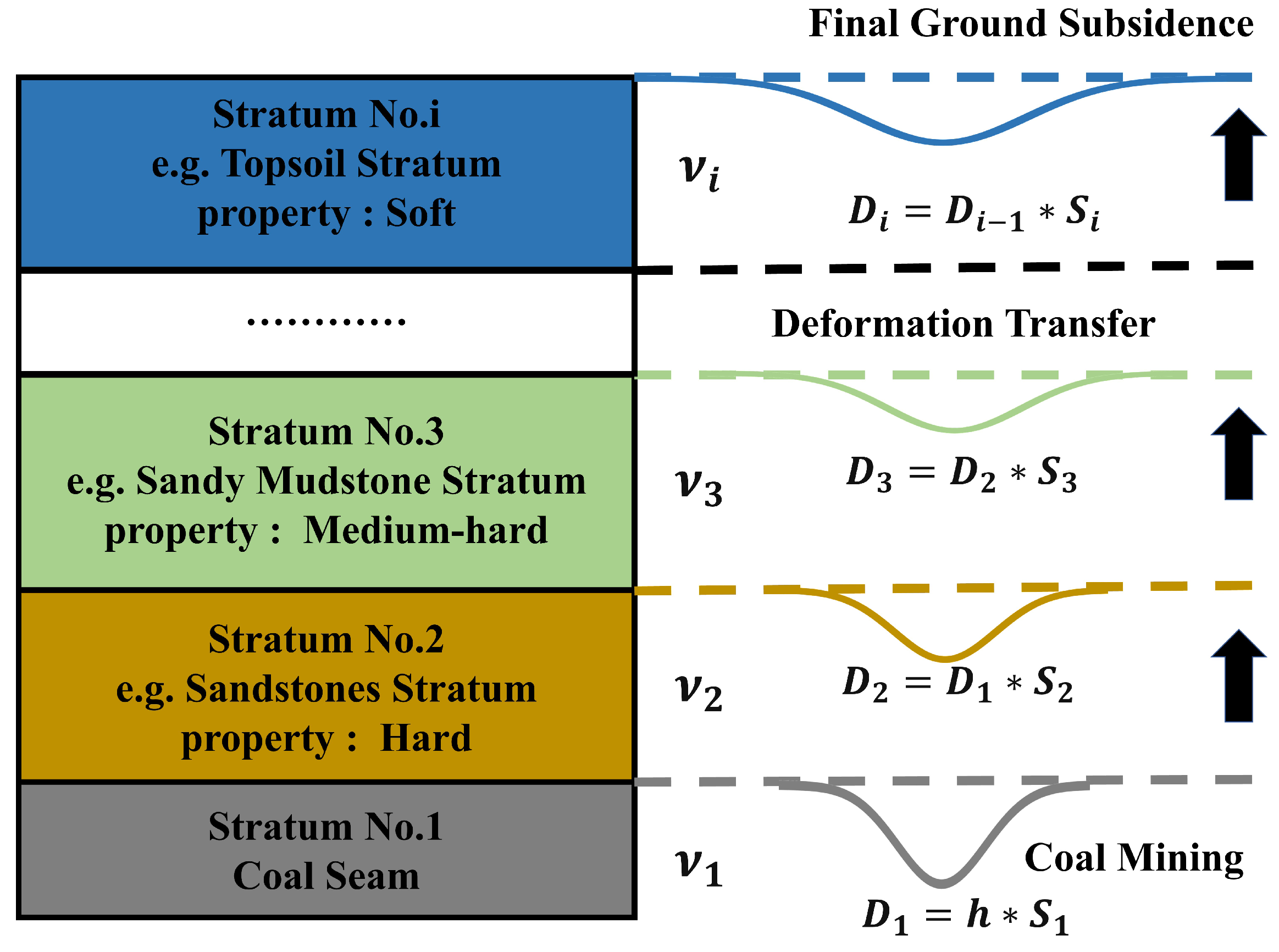
3.2. Stratified Okada Dislocation Model
3.3. Underground Goaf Locating
3.3.1. Mining Azimuth Estimation
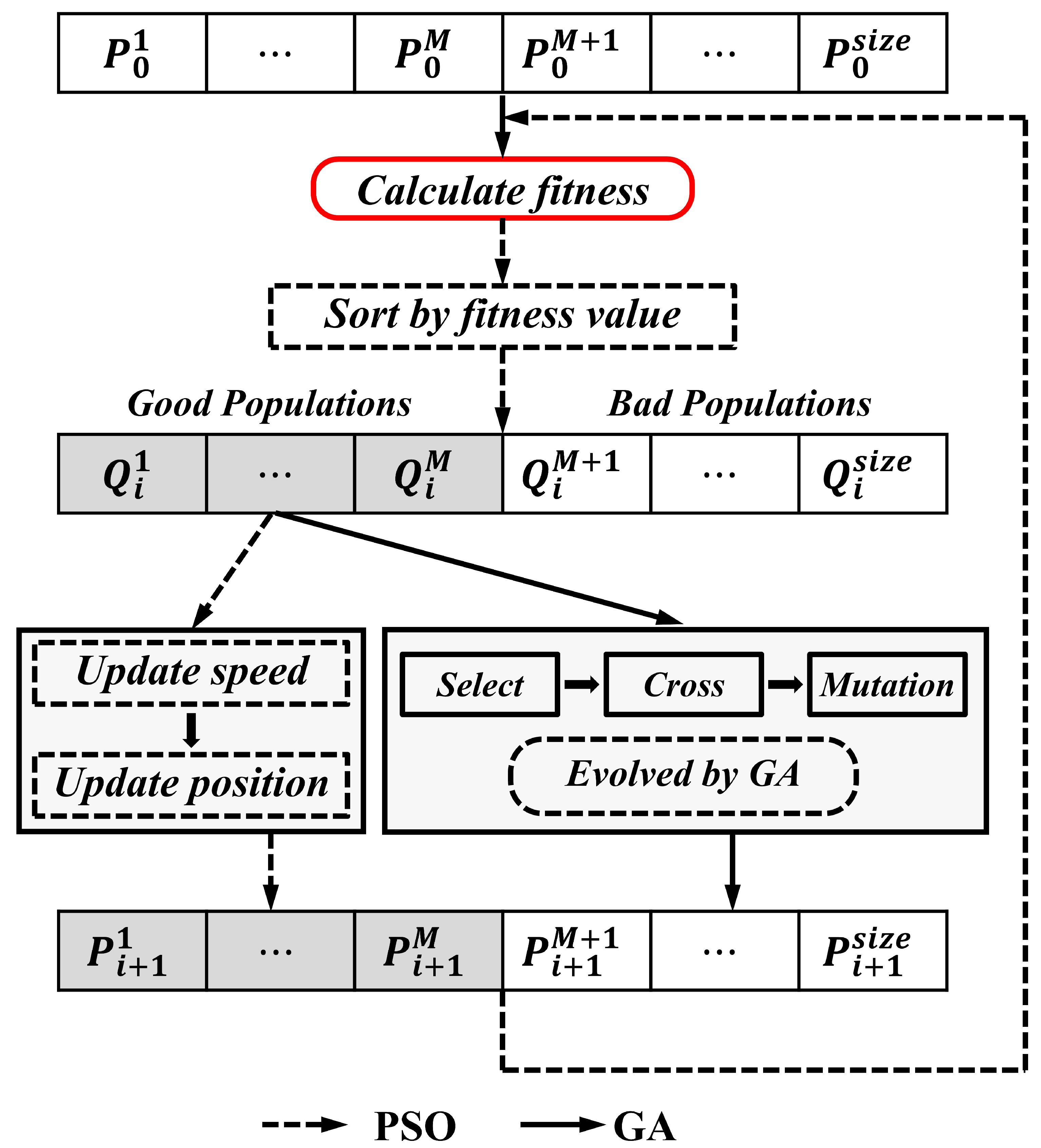
3.3.2. Estimation of Goaf Parameters
4. Results
4.1. Simulation Results
4.2. Real Data Results
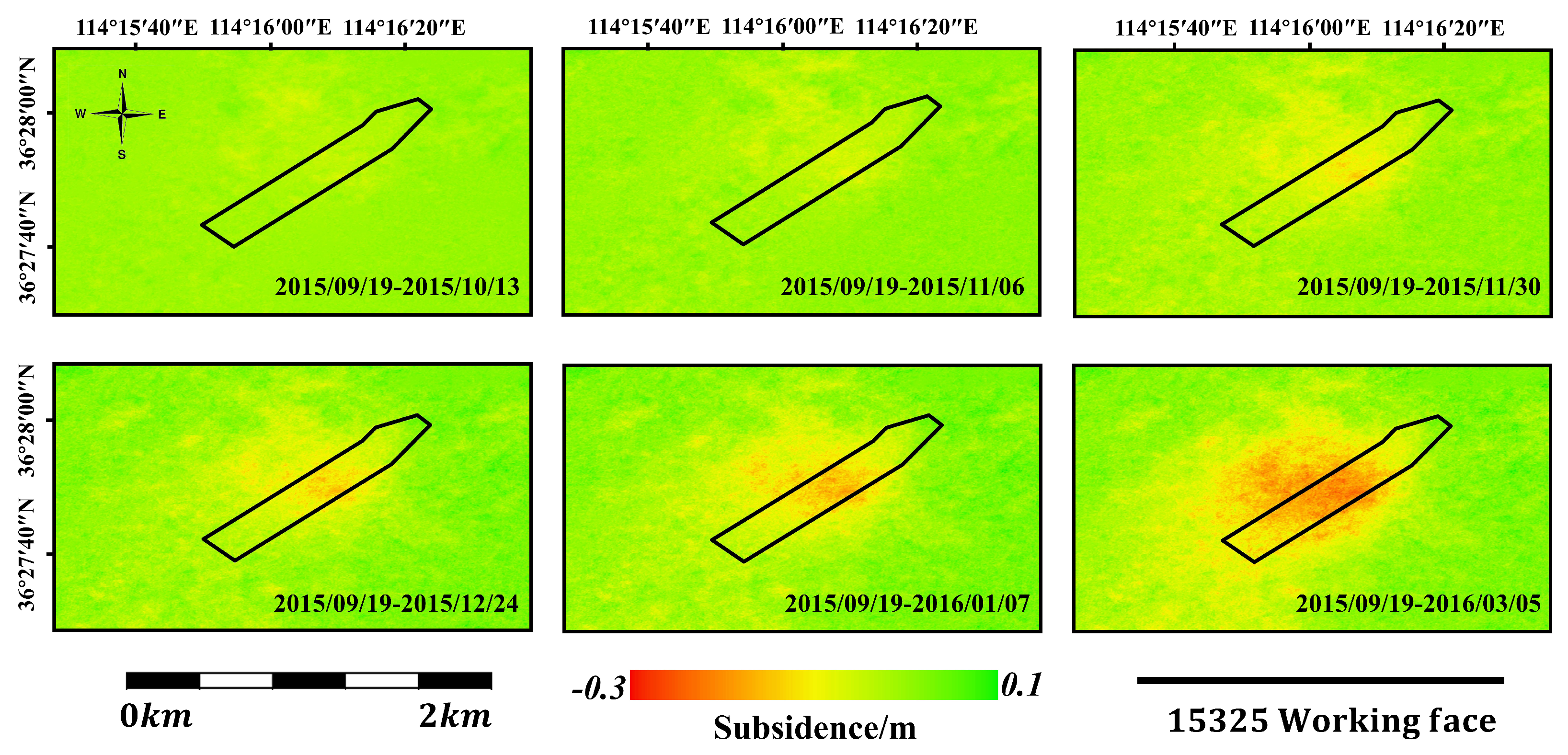
4.2.1. Deformation Results
4.2.2. Goaf Azimuth Estimate
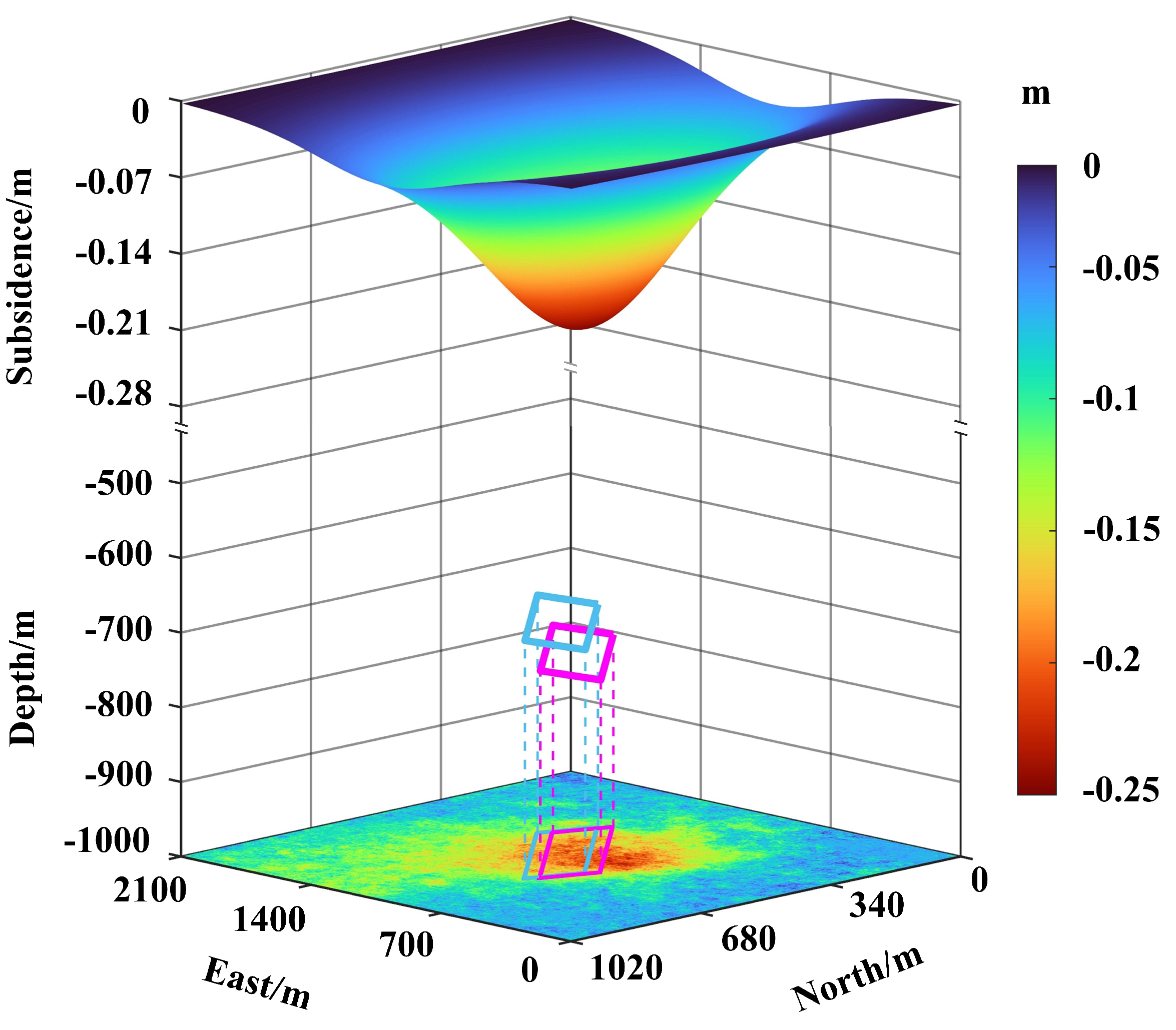
4.2.3. Underground Goaf Locating
5. Discussion
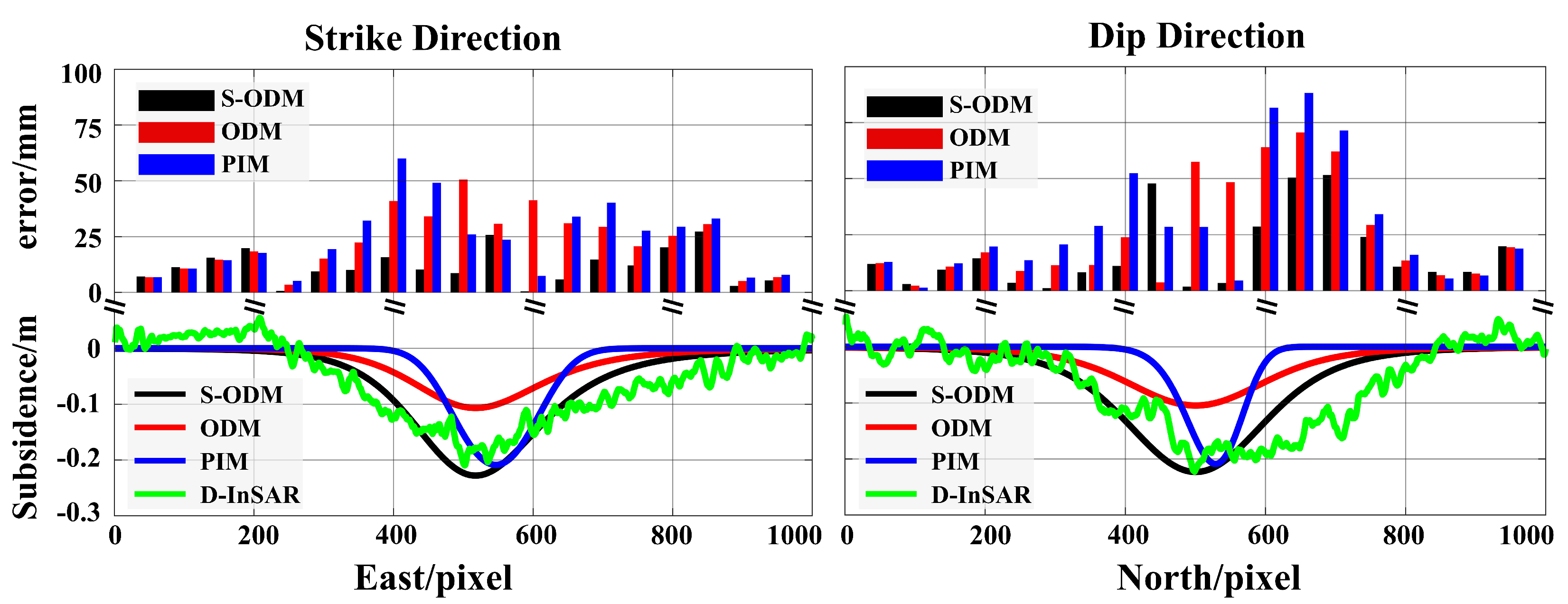
5.1. Comparison with Existing Methods
5.2. Errors Introduced by GA-PSO
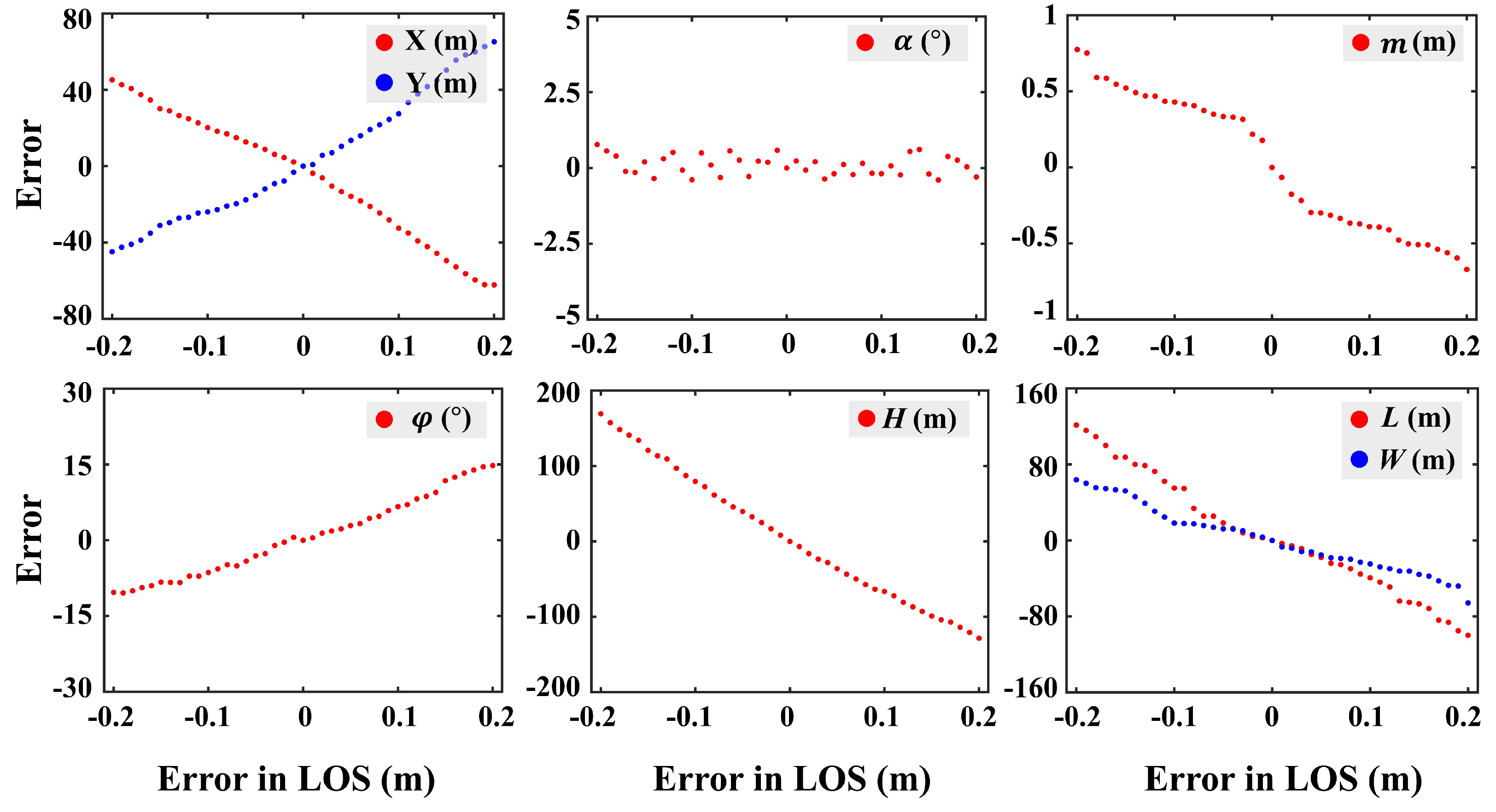
5.3. Influence of Ground Deformation Monitoring Errors
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mao, J.; Tong, H. Coal resources, production, and use in China. Coal Handb. 2023, 2, 431–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.D.; Cheng, D.; Deng, K.Z.; Chen, B.Q.; Zhu, C.G. Subsidence monitoring using D-InSAR and probability integral prediction modelling in deep mining areas. Emp. Surv. Rev. 2015, 47, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, L. Use of SAR/InSAR in mining deformation monitoring, parameter inversion, and forward predictions: A review. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2020, 8, 71–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhang, H.; Fan, H.; Zheng, C.; Liu, J. Position inversion of goafs in deep coal seams based on DS-InSAR data and the probability integral methods. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maus, V.; Werner, T.T. Impacts for half of the world’s mining areas are undocumented. Nature 2024, 625, 26–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhen, F.; Huang, X.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Z. Factors influencing the development potential of urban underground space: Structural equation model approach. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2013, 38, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Huang, X.; Zou, J. Research on multi-frequency ultrasonic scanning detecting technology of cavity in the test borehole. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2021, 80, 1249–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahorec, P.; Pašteka, R.; Papčo, J.; Putiška, R.; Mojzeš, A.; Kušnirák, D.; Plakinger, M. Mapping hazardous cavities over collapsed coal mines: Case study experiences using the microgravity method. Near Surf. Geophys. 2021, 19, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Su, B.; Malekian, R.; Xing, X. Detection of water-filled mining goaf using mining transient electromagnetic method. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2019, 16, 2977–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, F.; Wang, T.; Zhang, L.; Hao, M.; Yan, S.; Dang, L.; Peng, B. Accuracy assessment and scale effect investigation of UAV thermography for underground coal fire surface temperature monitoring. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 102, 102426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, F.; Yan, S.; Zhang, H.; Lang, F.; Hao, M.; Cao, F.; Peng, B.; Dang, L.; et al. Spatiotemporal Correlation Characteristics between Thermal Infrared Remote Sensing Obtained Surface Thermal Anomalies and Reconstructed 4D Temperature Fields of Underground Coal Fires. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, F.; Feng, H.; Liu, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, N.; Yuan, G.; Wang, D. A spatio-temporal temperature-based thresholding algorithm for underground coal fire detection with satellite thermal infrared and radar remote sensing. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 110, 102805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Li, Z.; Hu, J. Research Progress and Methods of InSAR for Deformation Monitoring. Acta Geod. Et Cartogr. Sin. 2017, 46, 1717–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Liao, M.; Liu, X.; Xu, W.; Fang, N. Source geometry and causes of the 2019 Ms6. 0 Changning earthquake in Sichuan, China based on InSAR. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anantrasirichai, N.; Biggs, J.; Albino, F.; Bull, D. A deep learning approach to detecting volcano deformation from satellite imagery using synthetic datasets. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 230, 111179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Liu, G.; Jia, H.; Zhang, B.; Wu, R.; Fu, Y.; Xiang, W.; Mao, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, R. A new algorithm for landslide dynamic monitoring with high temporal resolution by Kalman filter integration of multiplatform time-series InSAR processing. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 110, 102812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, F.; Wang, T.; Zhang, K.; Fan, H.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, L.; Yan, S.; Diao, X.; et al. Monitoring and Analysis of the Collapse at Xinjing Open-Pit Mine, Inner Mongolia, China, Using Multi-Source Remote Sensing. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Yan, S.; Shao, Y.; Zhou, H.; Li, Y. Ground subsidence characteristics associated with urbanization in East China analyzed with a Sentinel-1A-based InSAR time series approach. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2019, 78, 4003–4015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Huo, W.; Zhao, F.; Hu, Z.; Wang, T.; Song, R.; Liu, J.; Zhang, L.; Fernández, J.; et al. Ground Deformation Monitoring over Xinjiang Coal Fire Area by an Adaptive ERA5-Corrected Stacking-InSAR Method. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yuan, G.; Wang, T.; Liu, J.; Zhao, F.; Feng, H.; Dang, L.; Peng, K.; Zhang, L. Research on Multi-source Remote Sensing Detection of Concealed Fire Sources in Coalfields. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2022, 47, 1651–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Ge, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, L. An underground-mining detection system based on DInSAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 51, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, M.; Zhou, D.; Xia, Y. Goaf locating based on InSAR and probability integration method. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhu, J.; Yi, H.; Feng, G.; Hu, J.; Wu, L.; Preusse, A.; Wang, Y.; Papst, M. Locating and defining underground goaf caused by coal mining from space-borne SAR interferometry. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 135, 112–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhao, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, N.; Zhou, D.; Diao, X.; Zhao, X. An Algorithm for Locating Subcritical Underground Goaf Based on InSAR Technique and Improved Probability Integral Model. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, C.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Kang, J.; Guo, C.; He, R. Time series interferometric synthetic aperture radar-based modeling and analysis of complex land subsidence caused by multi-seam coal mining on the Liaohe Plain, China. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2022, 16, 024512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wu, K.; He, Q.; He, Y.; Gu, Y.; Wu, S. A novel method of monitoring surface subsidence law based on probability integral model combined with active and passive remote sensing data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, Y.; Furuta, R. Slow slip event displacement on 2018 offshore Boso Peninsula detected by Sentinel-1 InSAR time-series analysis with numerical weather model assistance. Geophys. J. Int. 2024, 237, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepe, A.; Lanari, R. On the extension of the minimum cost flow algorithm for phase unwrapping of multitemporal differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 2374–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosetto, M.; Monserrat, O.; Cuevas-González, M.; Devanthéry, N.; Crippa, B. Persistent scatterer interferometry: A review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 115, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Deng, K.; Fan, H.; Du, S. Monitoring and analysis of surface deformation in mining area based on InSAR and GRACE. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspri, A.; Beretta, E.; Mazzucato, A.L.; De Hoop, M.V. Analysis of a model of elastic dislocations in geophysics. Arch. Ration. Mech. Anal. 2020, 236, 71–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, Y. Surface deformation due to shear and tensile faults in a half-space. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 1985, 75, 1135–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikhalishahi, M.; Ebrahimipour, V.; Shiri, H.; Zaman, H.; Jeihoonian, M. A hybrid GA–PSO approach for reliability optimization in redundancy allocation problem. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2013, 68, 317–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gercek, H. Poisson’s ratio values for rocks. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2007, 44, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Interferogram Pair | Spatial Baseline | Time Baseline |
|---|---|---|
| 20150919–20151013 | 101.8260 m | 24 d |
| 20151013–20151106 | 47.2675 m | 24 d |
| 20151106–20151130 | 3.1222 m | 24 d |
| 20151130–20151224 | −30.4078 m | 24 d |
| 20151224–20160117 | −43.6049 m | 24 d |
| 20160117–20160305 | −37.7825 m | 48 d |
| Parameter | Simulated Value | Estimated Value | Absolute Error | Relative Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| X(m) | 1000 | 1007.26 | 7.26 | - |
| Y(m) | 1000 | 995.38 | 4.62 | - |
| L(m) | 600 | 627.72 | 27.72 | 4.62% |
| W(m) | 100 | 90.36 | 9.64 | 9.64% |
| H(m) | 500 | 519.51 | 19.51 | 3.9% |
| 30 | 26.87 | 3.13 | - | |
| 45 | 45.77 | 0.77 | - | |
| m(m) | 5 | 4.65 | 0.35 | 7% |
| Parameter | Real Value | Estimated Value | Absolute Error | Relative Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| X(m) | 1057 | 1078.66 | 21.66 | - |
| Y(m) | 565 | 550.38 | 14.62 | - |
| L(m) | 493 | 522.21 | 19.21 | 5.92% |
| W(m) | 142 | 161.86 | 19.86 | 13.98% |
| H(m) | 740 | 701.6 | 38.4 | 5.19% |
| 13 | 10.98 | 2.02 | - | |
| 236 | 234 | 2 | - | |
| m(m) | 4.5 | 4.70 | 0.20 | 4.4% |
| Parameter | True Value | S-ODM | PIM | ODM | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estimated Value | Absolute Error | Estimated Value | Absolute Error | Estimated Value | Absolute Error | ||
| X(m) | 1057 | 1078.66 | 21.66 | 1089.31 | 32.31 | 1134.14 | 74.14 |
| Y(m) | 565 | 550.38 | 14.62 | 545.15 | 19.85 | 512.64 | 52.36 |
| L(m) | 493 | 522.21 | 19.21 | 510.62 | 17.62 | 465.14 | 27.86 |
| W(m) | 142 | 161.86 | 19.86 | 167.14 | 25.14 | 183.87 | 41.87 |
| H(m) | 740 | 701.6 | 38.4 | 687.83 | 52.17 | 680.15 | 59.85 |
| 13 | 10.98 | 2.02 | 10.08 | 2.92 | 10.12 | 2.88 | |
| 236 | 234 | 2.0 | 241 | 5.0 | 221 | 15 | |
| m(m) | 4.5 | 4.7 | 0.2 | 4.64 | 0.14 | 4.86 | 0.36 |
| Parameter | Simulated Value | Estimated Value | Absolute Error | Relative Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| X(m) | 2000 | 2007.26 | 7.26 | - |
| Y(m) | 2000 | 1995.38 | 4.62 | - |
| L(m) | 500 | 517.72 | 17.72 | 3.54% |
| W(m) | 100 | 91.36 | 8.64 | 8.64% |
| H(m) | 500 | 519.51 | 19.51 | 3.9% |
| 15 | 15.87 | 3.87 | - | |
| 45 | 45.77 | 0.77 | - | |
| m(m) | 5 | 4.65 | 0.35 | 7% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, K.; Wang, Y.; Du, S.; Zhao, F.; Wang, T.; Zhang, N.; Zhou, D.; Diao, X. A Goaf-Locating Method Based on the D-InSAR Technique and Stratified Okada Dislocation Model. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2741. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16152741
Zhang K, Wang Y, Du S, Zhao F, Wang T, Zhang N, Zhou D, Diao X. A Goaf-Locating Method Based on the D-InSAR Technique and Stratified Okada Dislocation Model. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(15):2741. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16152741
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Kewei, Yunjia Wang, Sen Du, Feng Zhao, Teng Wang, Nianbin Zhang, Dawei Zhou, and Xinpeng Diao. 2024. "A Goaf-Locating Method Based on the D-InSAR Technique and Stratified Okada Dislocation Model" Remote Sensing 16, no. 15: 2741. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16152741
APA StyleZhang, K., Wang, Y., Du, S., Zhao, F., Wang, T., Zhang, N., Zhou, D., & Diao, X. (2024). A Goaf-Locating Method Based on the D-InSAR Technique and Stratified Okada Dislocation Model. Remote Sensing, 16(15), 2741. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16152741








