MFO-Fusion: A Multi-Frame Residual-Based Factor Graph Optimization for GNSS/INS/LiDAR Fusion in Challenging GNSS Environments
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- A factor graph-optimized odometry framework based on GNSS, IMU, and LiDAR is proposed, which tightly integrates GNSS pseudorange measurement, IMU attitude measurement, and LiDAR point cloud measurement for precise and stable positioning in complex scenes;
- (2)
- A fusion strategy based on two-stage optimization was proposed, and a multi-frame residual factor was introduced for outlier detection and the calibration of positioning errors, achieving robust and globally consistent state estimation;
- (3)
- The proposed method has been extensively experimentally validated in both public urban challenge scenarios and complex on-site scenarios, demonstrating its effectiveness.
2. Related Work
2.1. Dual-Sensor Integrated Localization
2.2. Multi-Sensor Integrated Localization
3. Materials and Methods
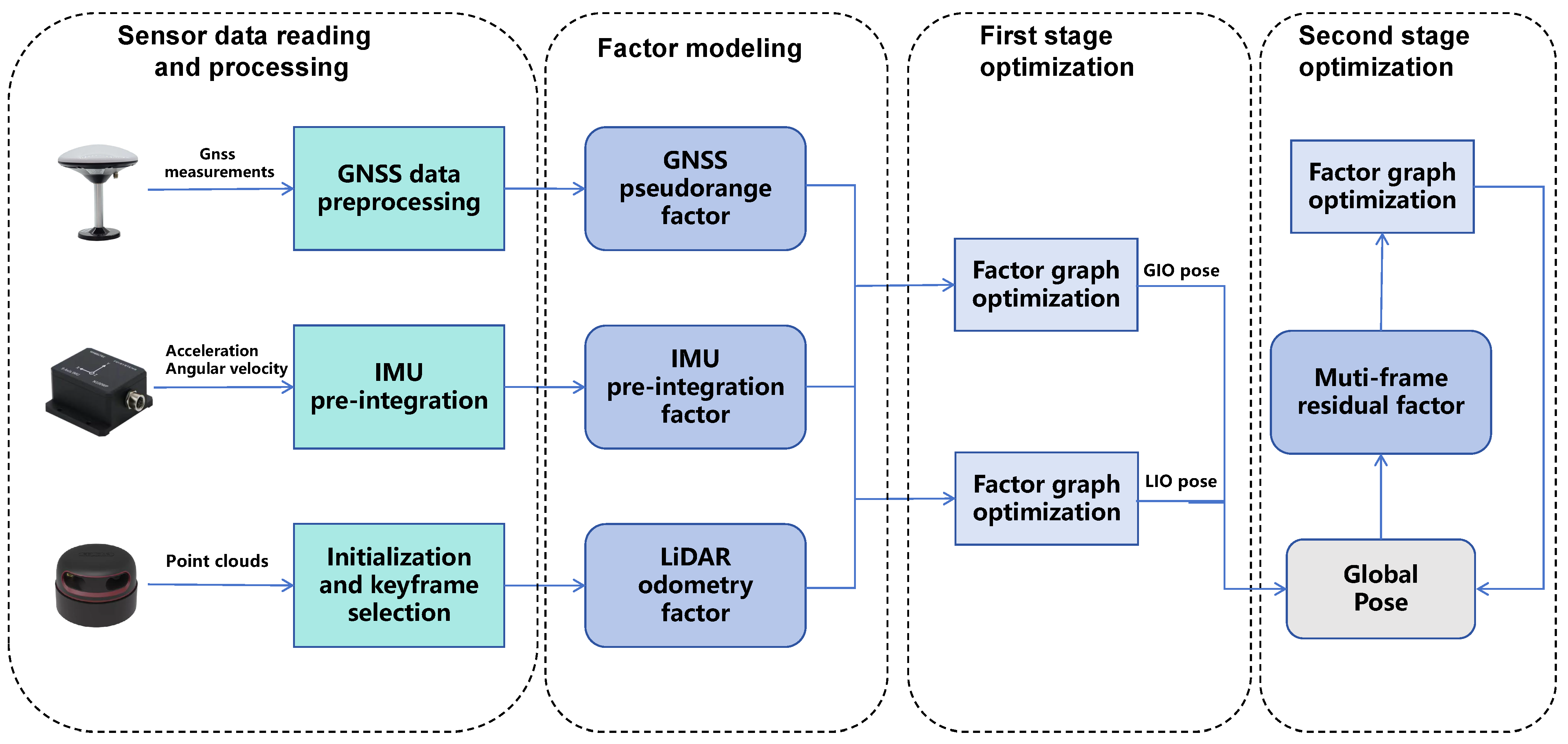
3.1. System Overview
3.2. GPS-Inertial Odometry
3.2.1. GNSS Pseudorange Factor
3.2.2. IMU Pre-Integration Factor
3.3. LiDAR-Inertial Odometry
3.4. Multi-Frame Residual Factor
3.5. Secondary Optimization
| Algorithm 1 Multi-Frame Residual Factor Optimization |
|
4. Results
4.1. Experimental Platform Equipment
4.2. Test Results and Comparison
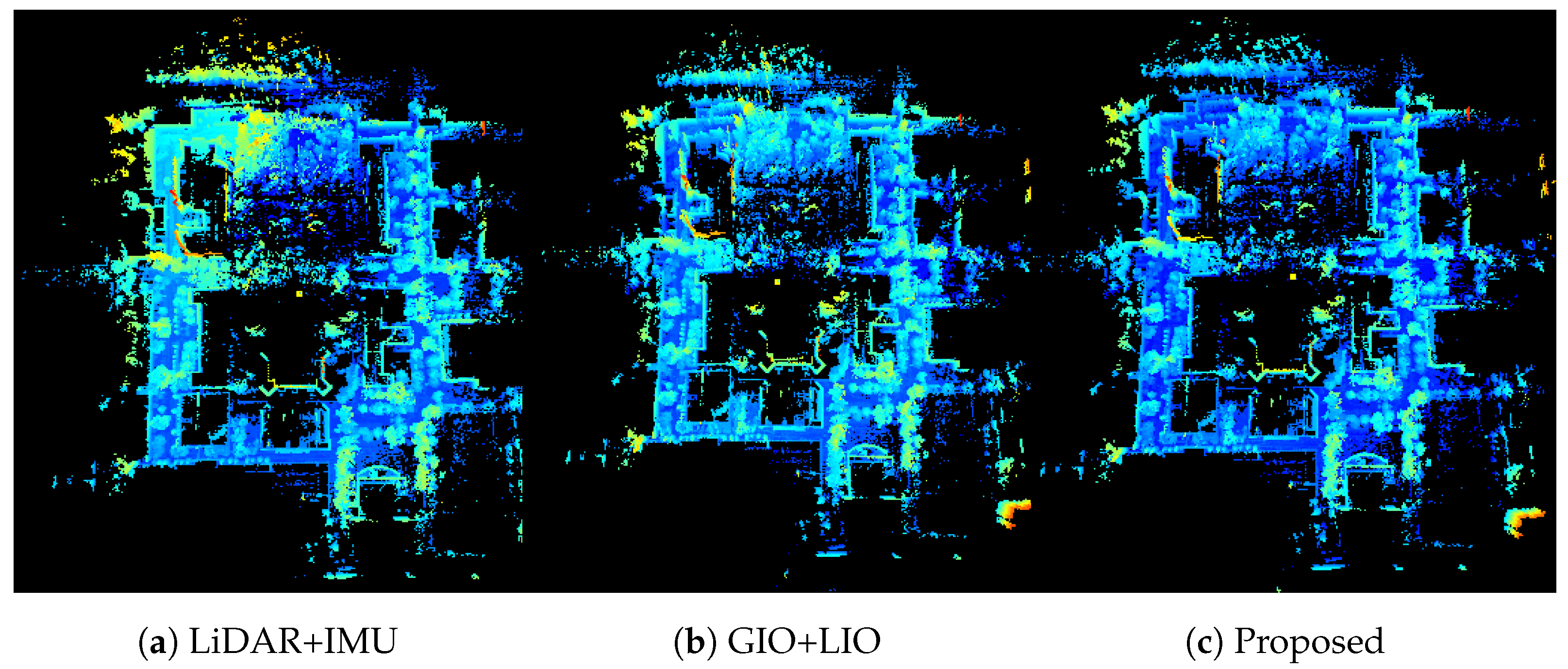
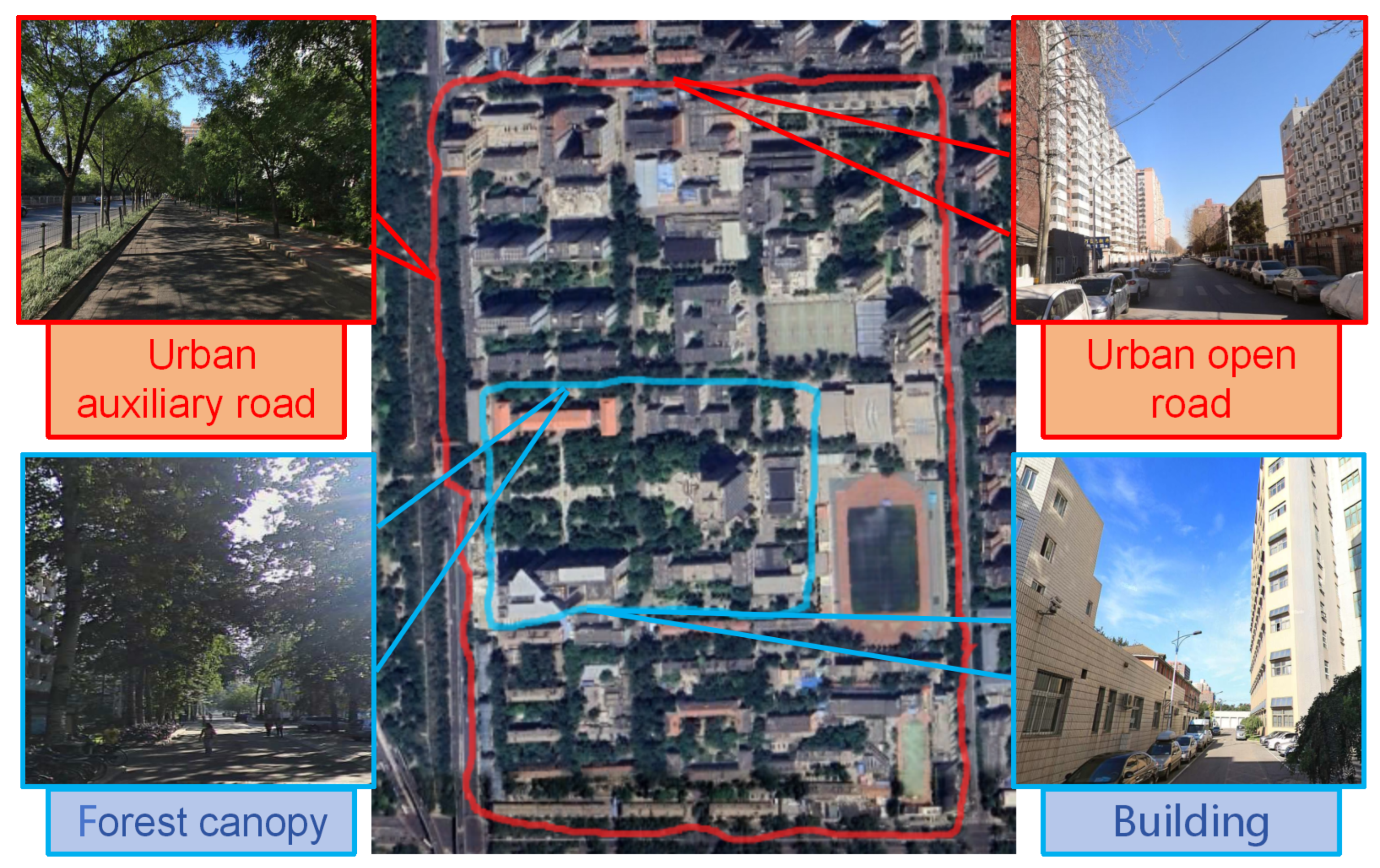
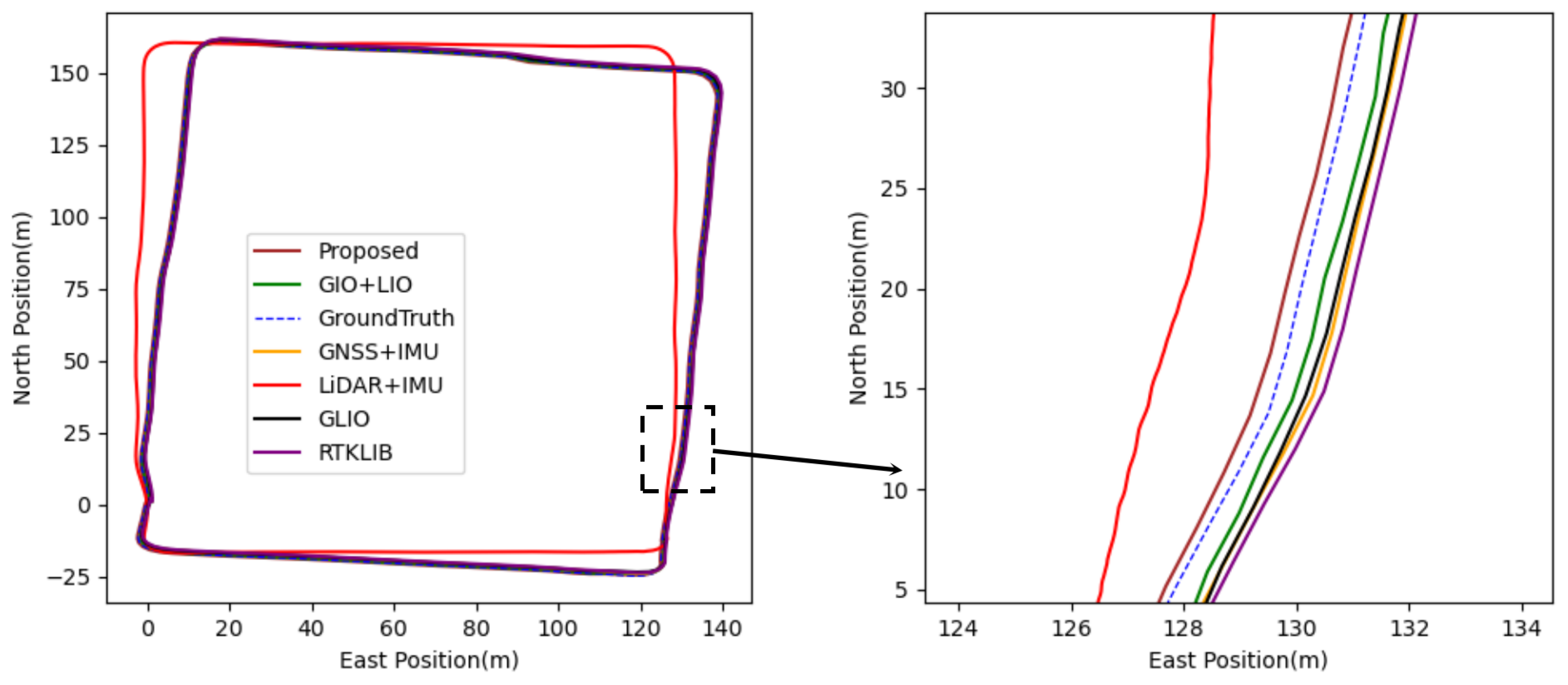
4.2.1. Testing of UrbanLoco
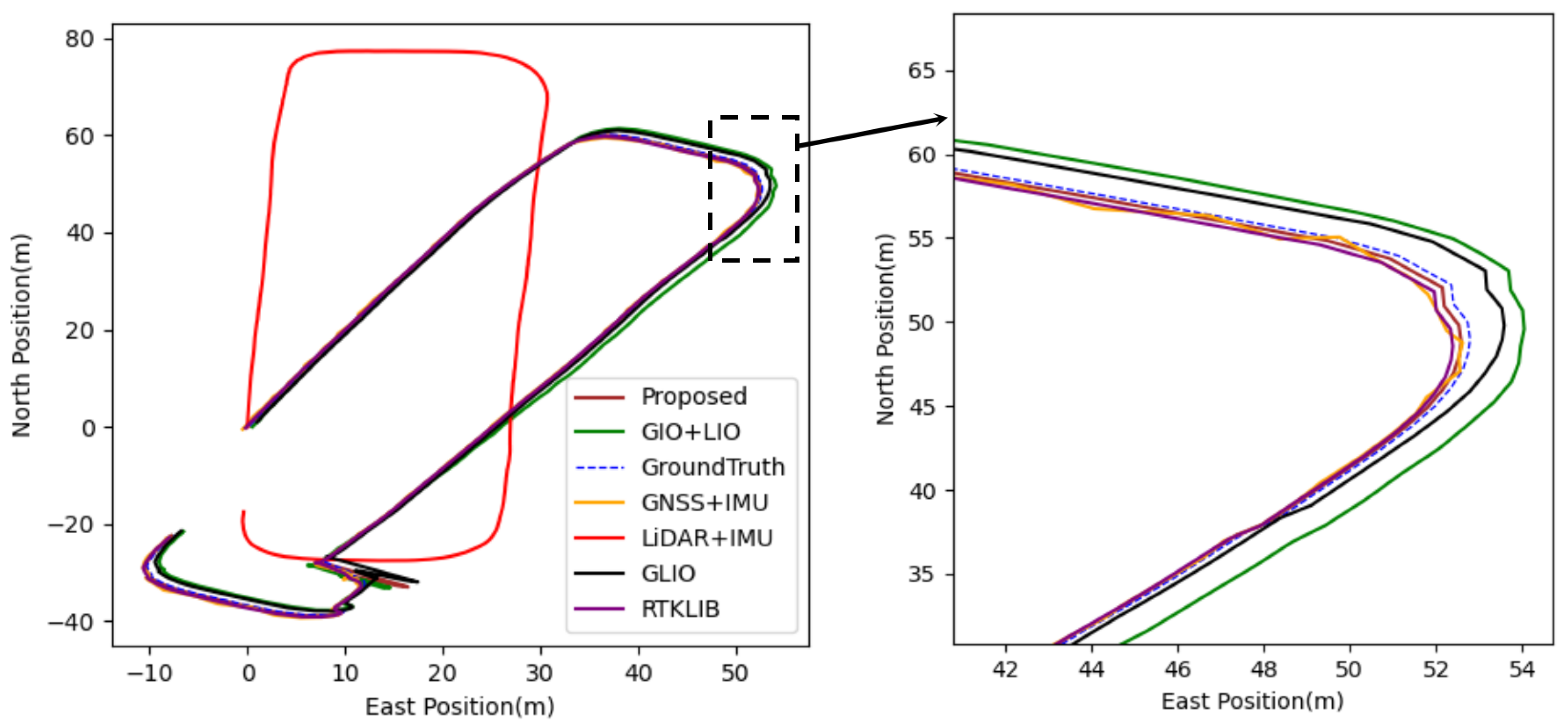
4.2.2. Testing of Actual Dataset
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
- Algorithm Optimization: Enhance the computational efficiency and robustness of factor graph optimization algorithms to adapt to more complex environments;
- Multi-Sensor Fusion: Explore the integration of additional sensors, such as visual sensors, to further improve positioning accuracy and environmental perception;
- Real-Time Applications: Develop real-time sensor fusion systems suitable for practical applications, such as autonomous driving and drone navigation.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cao, S.; Lu, X.; Shen, S. GVINS: Tightly coupled GNSS-visual-inertial fusion for smooth and consistent state estimation. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2022, 38, 2004–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhuang, Y.; Hu, X.; Gao, Z.; Hu, J.; Chen, L.; El-Sheimy, N. Toward location-enabled IoT (LE-IoT): IoT positioning techniques, error sources, and error mitigation. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 4035–4062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, C.; Liu, H.; Tang, J.; Chen, Y.; Kaartinen, H.; Kukko, A.; Zhu, L.; Liang, X.; Chen, L.; Hyyppä, J. GNSS/INS/LiDAR-SLAM positioning method for highly accurate forest stem mapping. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, T.; Englot, B.; Meyers, D. Lio-sam: Tightly-coupled lidar inertial odometry via smoothing and map. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 24 October 2020–24 January 2021; pp. 5135–5142. [Google Scholar]
- Barfoot, T.D. State Estimation for Robotics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2017; pp. 205–284. [Google Scholar]
- Crosara, L.; Ardizzon, F.; Tomasin, S. Worst-Case Spoofing Attack and Robust Countermeasure in Satellite Navigation Systems. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2023, 19, 2039–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, S. An Anti-Spoofing Model Based on MVM and MCCM for a Loosely-Coupled GNSS/INS/LiDAR Kalman Filter. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2023, 9, 1744–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radoš, K.; Brkić, M.; Begušić, D. Recent Advances on Jamming and Spoofing Detection in GNSS. Sensors 2024, 24, 4210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Liu, B.; Feng, C.; Vallespi-Gonzalez, C.; Wellington, C. 3D Point Cloud Processing and Learning for AutonomousDriving: Impacting Map Creation, Localization, and Perception. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2020, 38, 68–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Niu, Q. Multi-Sensor Fusion in Automated Driving: A Survey. IEEE Access 2019, 8, 2847–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Lee, I. Localization of a car based on multi-sensor fusion. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2018, 42, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, G.; Yang, X.; Cai, R.; Li, H.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, H.; Song, S. Robust and precise vehicle localization based on multi-sensor fusion in diverse city scenes. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Brisbane, Australia, 21–25 May 2018; pp. 4670–4677. [Google Scholar]
- Schütz, A.; Sánchez-Morales, D.E.; Pany, T. Precise positioning through a loosely-coupled sensor fusion of GNSS-RTK, INS and LiDAR for autonomous driving. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/ION Position, Location and Navigation Symposium, Portland, OR, USA, 20–23 April 2020; pp. 219–225. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, T. Advanced receiver autonomous integrity monitoring in tightly integrated GNSS/inertial systems. In Proceedings of the 2020 DGON Inertial Sensors and Systems, Braunschweig, Germany, 15–16 September 2020; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Pei, L.; Xiang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Xia, S.; Tao, L.; Yu, W. P 3-LOAM: PPP/LiDAR loosely coupled SLAM with accurate covariance estimation and robust RAIM in urban canyon environment. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 21, 6660–6671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Ye, H.; Pranata, C.E.; Han, J.; Zhang, S.; Liu, M. Lins: A LiDAR-inertial state estimator for robust and efficient navigation. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Paris, France, 31 May 2020–31 August 2020; pp. 8899–8906. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, S.; Lai, J.; Lyu, P.; Cen, Y.; Sun, X.; Wang, B. Performance Enhancement of Tightly Coupled GNSS/IMU Integration Based on Factor Graph with Robust TDCP Loop Closure. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 25, 2437–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouybari, A.; Bagherbandi, M.; Nilfouroushan, F. Numerical Analysis of GNSS Signal Outage Effect on EOPs Solutions Using Tightly Coupled GNSS/IMU Integration: A Simulated Case Study in Sweden. Sensors 2023, 14, 6361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, W. 3D LiDAR aided GNSS and its tightly coupled integration with INS via factor graph optimization. In Proceedings of the 33rd International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation, Online, 21–25 September 2020; pp. 1649–1672. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, H.; Qi, J.; Ji, K. A tightly coupled LiDAR-IMU SLAM in off-road environment. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Vehicular Electronics and Safety, Cairo, Egypt, 21 November 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, H.; Liu, D.; Ren, J.; Huang, T.; Yang, H. LiDAR-IMU Tightly-Coupled SLAM Method Based on IEKF and Loop Closure Detection. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 6986–7001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellaert, F. Factor graphs and GTSAM: A hands-on introduction. Ga. Inst. Technol. 2012, 2, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, G.; Wang, W.; Zhong, Y. A new direct filtering approach to INS/GNSS integration. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2018, 77, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, J.; Hu, D. A new technique for INS/GNSS attitude and parameter estimation using online optimization. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2014, 62, 2642–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Bian, H.; Wang, R. An INS/GNSS integrated navigation in GNSS denied environment using recurrent neural network. Def. Technol. 2020, 16, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelaziz, N.; El-Rabbany, A. An integrated ins/lidar slam navigation system for gnss-challenging environments. Sensors 2022, 22, 4327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Chen, Y.; Niu, X. LiDAR scan matching aided inertial navigation system in GNSS-denied environments. Sensors 2015, 15, 16710–16728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zhang, F. FAST-LIO: A Fast, Robust LiDAR-Inertial Odometry Package by Tightly-Coupled Iterated Kalman Filter. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 3317–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wu, W.; Zhang, S.; Wu, C.; Zhong, R. A GNSS/LiDAR/IMU Pose Estimation System Based on Collaborative Fusion of Factor Map and Filtering. Remote Sens. 2023, 3, 790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Xia, C. Targetless extrinsic calibration of LiDAR-IMU system using raw GNSS observations for vehicle applications. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 1003311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wen, W.; Huang, F.; Chen, X.; Hsu, L.T. Continuous GNSS-RTK aided by LiDAR/inertial odometry with intelligent GNSS selection in urban canyons. In Proceedings of the 34th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation, St. Louis, MO, USA, 20–24 September 2021; pp. 4198–4207. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Li, B.; Yang, L.; He, L.; He, J. Tightly coupled gnss, ins and visual odometry for accurate and robust vehicle positioning. In Proceedings of the 2022 5th International Symposium on Autonomous Systems, Hangzhou, China, 22 April 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wang, S.; Li, S.; Zhou, Y.; Xia, C.; Shen, Z. Enhancing RTK Performance in Urban Environments by Tightly Integrating INS and LiDAR. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2023, 8, 9845–9856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.; Lai, J.; Lyu, P.; Wang, B.; Sun, X.; Yu, W. An Enhanced Adaptable Factor Graph for Simultaneous Localization and Calibration in GNSS/IMU/Odometer Integration. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2023, 9, 11346–11357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Ji, K.; Zhao, J. Tightly-coupled multi-sensor fusion for localization with LiDAR feature maps. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Xi’an, China, 18 October 2021; pp. 5215–5221. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.U.; Won, J.H. Adaptive Kalman Filter Based LiDAR aided GNSS/IMU Integrated Navigation System for High-Speed Autonomous Vehicles in Challenging Environments. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Technical Meeting of The Institute of Navigation, Long Beach, CA, USA, 23–25 January 2024; pp. 1095–1102.
- Ai, M.; Asl Sabbaghian Hokmabad, I.; Elhabiby, M.; El-Sheimy, N. A novel LiDAR-GNSS-INS Two-Phase Tightly Coupled integration scheme for precise navigation. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2024, 10, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Wang, J.; Pang, C.; Lan, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Fang, Z. A LiDAR-IMU-GNSS fused mapping method for large-scale and high-speed scenarios. Measurement 2024, 225, 113976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Sha, J.; Li, H.; Wang, Y. A Robust and Fast GNSS-Inertial-LiDAR Odometry With INS-Centric Multiple Modalities by IESKF. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 73, 8501312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wen, W.; Hsu, L.T. GLIO: Tightly-Coupled GNSS/LiDAR/IMU Integration for Continuous and Drift-free State Estimation of Intelligent Vehicles in Urban Areas. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2023, 1, 1412–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noureldin, A.; Karamat, T.B.; Georgy, J. Fundamentals of Inertial Navigation, Satellite-Based Positioning and Their Integration; Springer Science + Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2012; pp. 65–123. [Google Scholar]
- Crassidis, J.L. Sigma-point Kalman filtering for integrated GPS and inertial navigation. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2006, 42, 750–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijeth, G.; Gatti, R.R. Review on Robot Operating System. Self-Powered Cyber Phys. Syst. 2023, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, W.; Zhou, Y.; Fahandezh-Saadi, S.; Bai, X.; Zhan, W.; Tomizuka, M.; Hsu, L.T. UrbanLoco: A Full Sensor Suite Dataset for Mapping and Localization in Urban Scenes. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Paris, France, 15 September 2020; pp. 2310–2316. [Google Scholar]
- Vázquez-Ontiveros, J.R.; Padilla-Velazco, J.; Gaxiola-Camacho, J.R.; Vázquez-Becerra, G.E. Evaluation and Analysis of the Accuracy of Open-Source Software and Online Services for PPP Processing in Static Mode. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



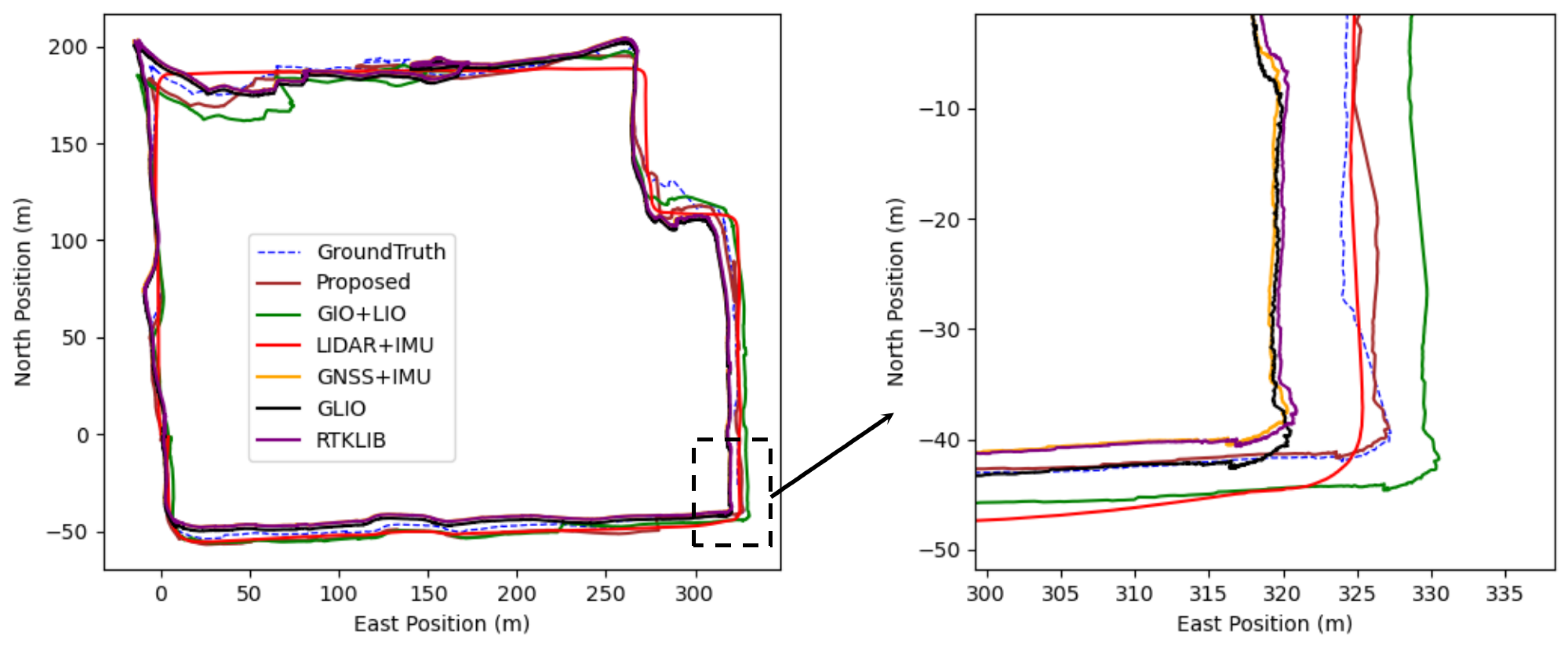

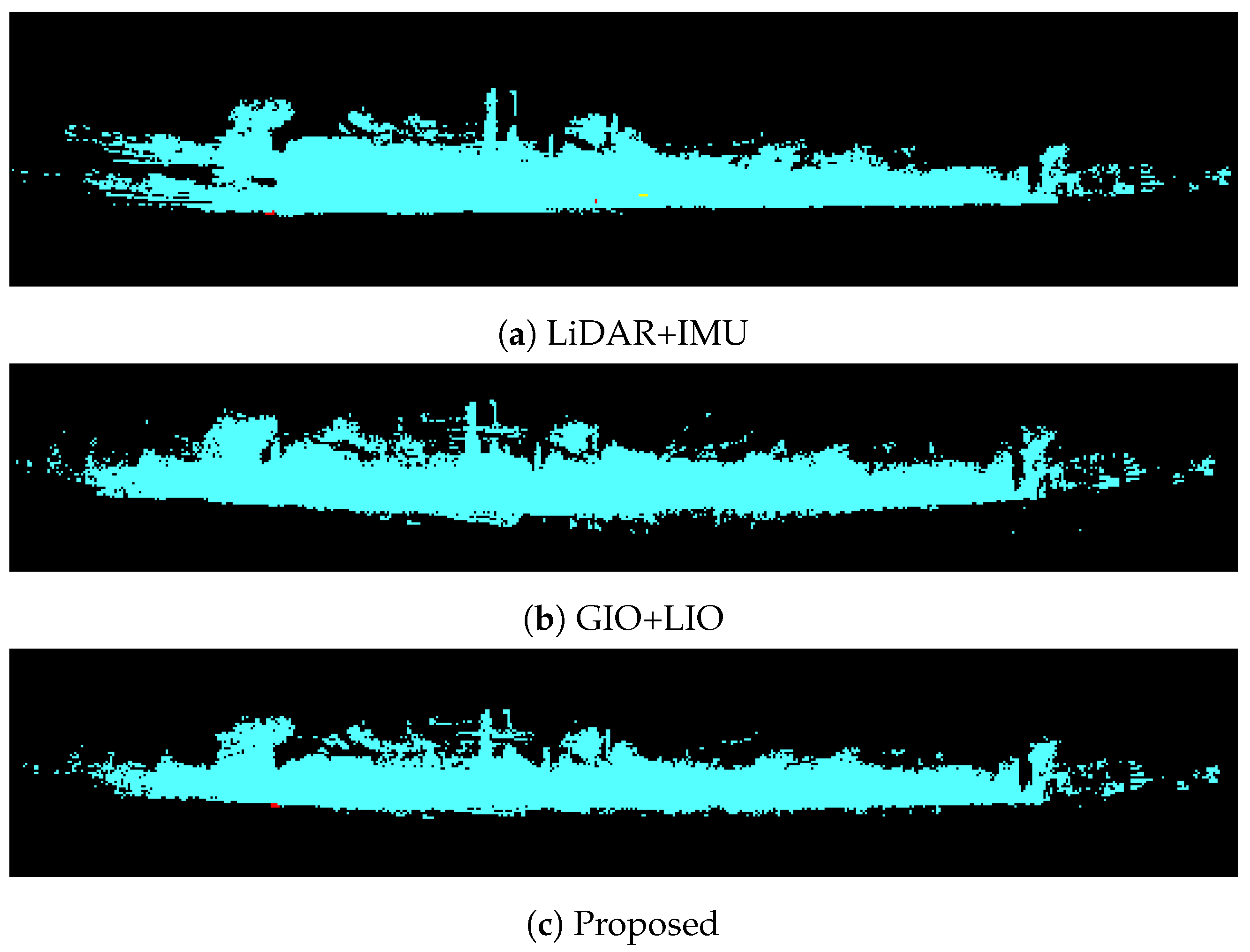
| Performance Index | Config |
|---|---|
| GNSS signal selection | BDS: B1I+B2I+B3I GPS: L1 C/A+L2 P (Y)/L2 C+L5 GLONASS: L1+L2 Galileo: E1+E5a+E5b QZSS: L1+L2+L5 |
| Update frequency | 20 Hz |
| Data format | NMEA 0183 |
| IMU Sensors | Bias Instability | Random Walk | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gyro. (/h) | Acc. (ug) | Angular () | Velocity (m/s/) | |
| Wheeltec N200WP | 5.0 | 400 | 0.60 | / |
| FSS-IMU16460 | 3.0 | 35 | 0.30 | 0.05 |
| Horizontal Position Error (m) | Vertical Position Error (m) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | Maximum Error | RMSE | Maximum Error | |
| RTKLIB | 1.99 | 5.47 | 6.14 | 12.02 |
| GNSS+IMU | 1.63 | 2.82 | 1.76 | 3.17 |
| LiDAR+IMU | 4.32 | 11.28 | 7.15 | 14.83 |
| GIO+LIO | 1.56 | 2.13 | 1.35 | 2.36 |
| GLIO | 1.61 | 2.55 | 1.13 | 2.93 |
| Proposed | 1.44 | 2.09 | 0.86 | 1.31 |
| Horizontal Position Error (m) | Vertical Position Error (m) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | Maximum Error | RMSE | Maximum Error | |
| RTKLIB | 0.92 | 1.78 | 1.83 | 3.27 |
| GNSS+IMU | 1.29 | 2.02 | 0.94 | 1.61 |
| LiDAR+IMU | 18.78 | 30.60 | 1.69 | 2.65 |
| GIO+LIO | 1.31 | 1.72 | 1.49 | 1.93 |
| GLIO | 1.26 | 1.80 | 0.66 | 1.62 |
| Proposed | 0.88 | 1.64 | 0.75 | 1.38 |
| Horizontal Position Error (m) | Vertical Position Error (m) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | Maximum Error | RMSE | Maximum Error | |
| RTKLIB | 3.59 | 4.86 | 2.63 | 9.44 |
| GNSS+IMU | 1.37 | 1.64 | 2.58 | 8.60 |
| LiDAR+IMU | 24.70 | 41.35 | 5.72 | 10.92 |
| GIO+LIO | 1.39 | 1.83 | 2.77 | 9.96 |
| GLIO | 1.08 | 1.69 | 1.39 | 3.23 |
| Proposed | 0.41 | 0.54 | 1.46 | 3.39 |
| Horizontal Position Error (m) | Vertical Position Error (m) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | Maximum Error | RMSE | Maximum Error | |
| RTKLIB | 7.27 | 30.54 | 7.92 | 13.65 |
| GNSS+IMU | 6.31 | 28.42 | 7.78 | 13.91 |
| LiDAR+IMU | 4.88 | 31.40 | 5.26 | 10.33 |
| GIO+LIO | 5.98 | 22.62 | 4.80 | 11.53 |
| GLIO | 4.75 | 27.99 | 3.51 | 8.84 |
| Proposed | 2.47 | 13.49 | 2.98 | 7.46 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zou, Z.; Wang, G.; Li, Z.; Zhai, R.; Li, Y. MFO-Fusion: A Multi-Frame Residual-Based Factor Graph Optimization for GNSS/INS/LiDAR Fusion in Challenging GNSS Environments. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3114. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16173114
Zou Z, Wang G, Li Z, Zhai R, Li Y. MFO-Fusion: A Multi-Frame Residual-Based Factor Graph Optimization for GNSS/INS/LiDAR Fusion in Challenging GNSS Environments. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(17):3114. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16173114
Chicago/Turabian StyleZou, Zixuan, Guoshuai Wang, Zhenshuo Li, Rui Zhai, and Yonghua Li. 2024. "MFO-Fusion: A Multi-Frame Residual-Based Factor Graph Optimization for GNSS/INS/LiDAR Fusion in Challenging GNSS Environments" Remote Sensing 16, no. 17: 3114. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16173114
APA StyleZou, Z., Wang, G., Li, Z., Zhai, R., & Li, Y. (2024). MFO-Fusion: A Multi-Frame Residual-Based Factor Graph Optimization for GNSS/INS/LiDAR Fusion in Challenging GNSS Environments. Remote Sensing, 16(17), 3114. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16173114







