Thermal Profile Dynamics of a Central European River Based on Landsat Images: Natural and Anthropogenic Influencing Factors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Processing of Satellite Images
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
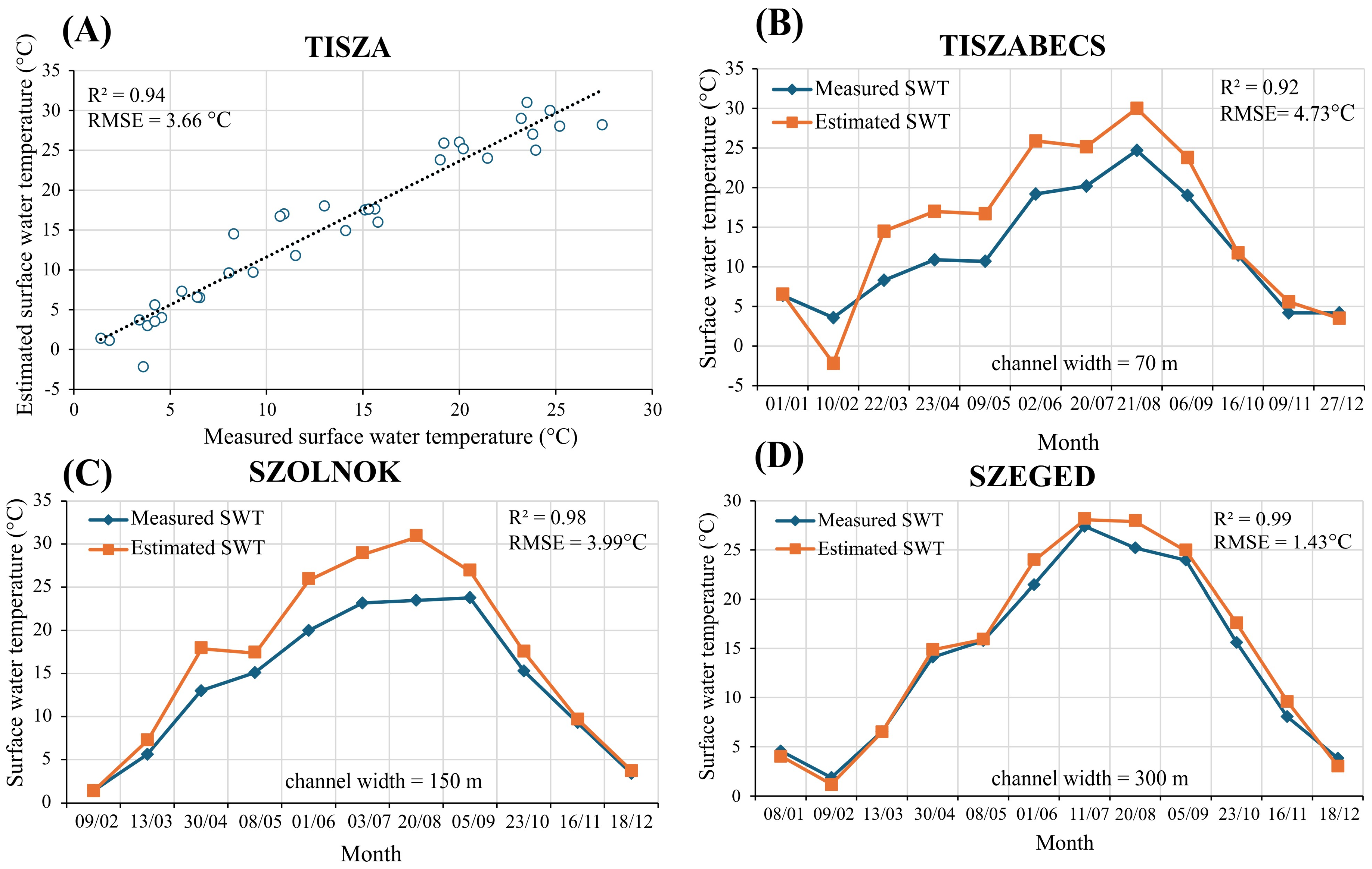
3.1. Validity of Landsat Surface Water Temperature (SWT) Estimates
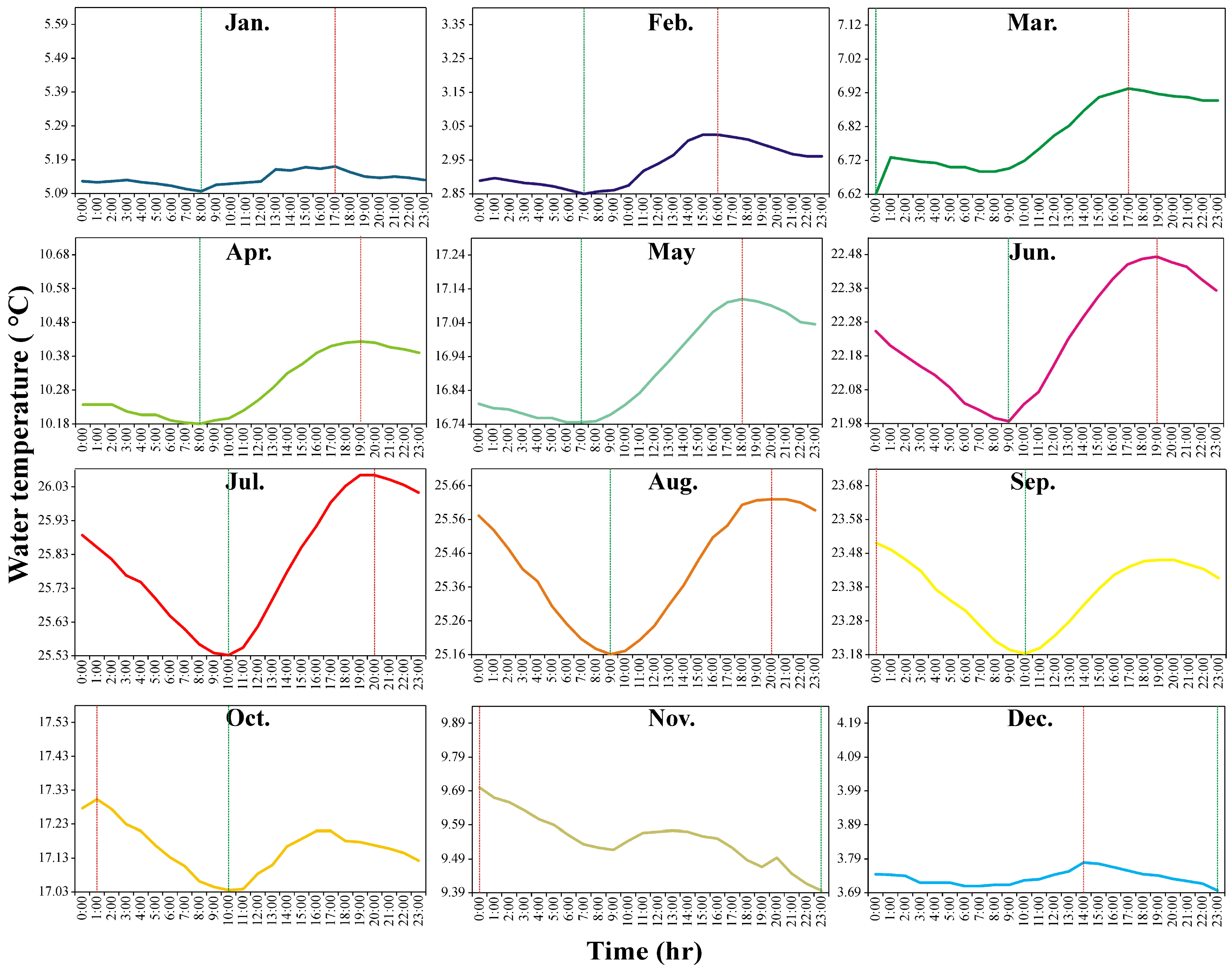
3.2. Water Temperature in the Tisza River and Its Daily Cycle (In Situ Data)
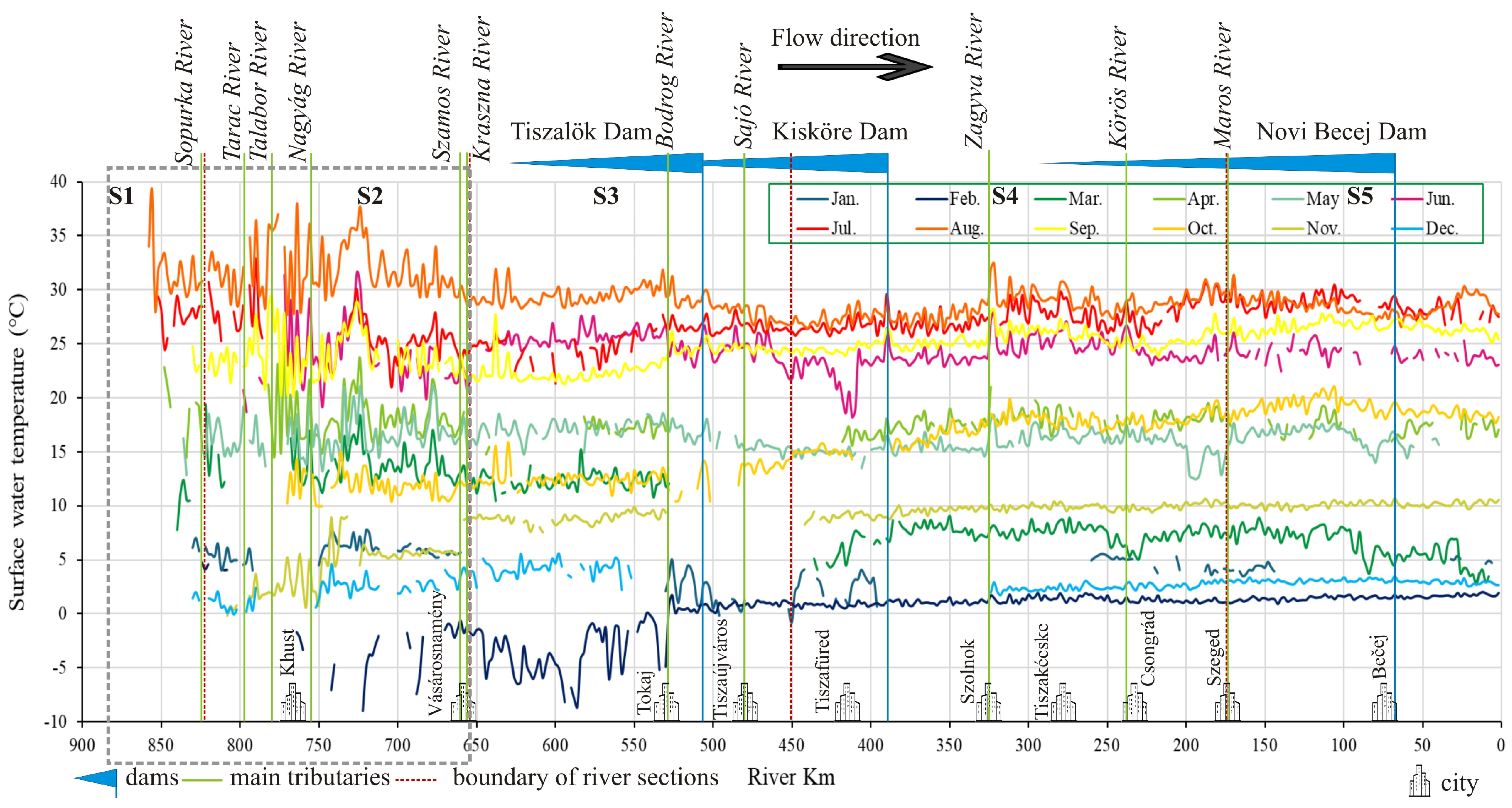
3.3. Longitudinal Thermal Profile of the Tisza River (Satellite Data)
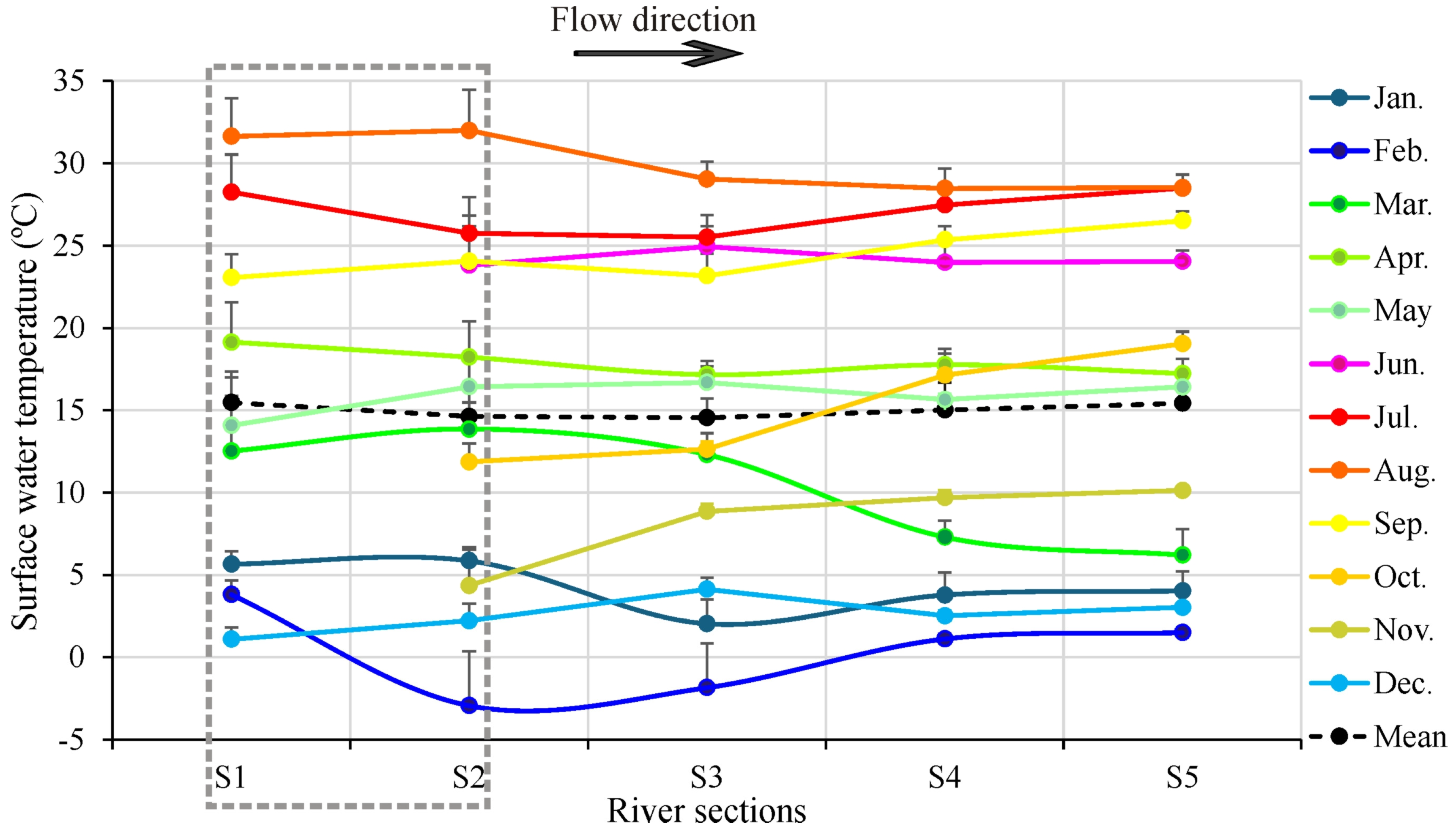
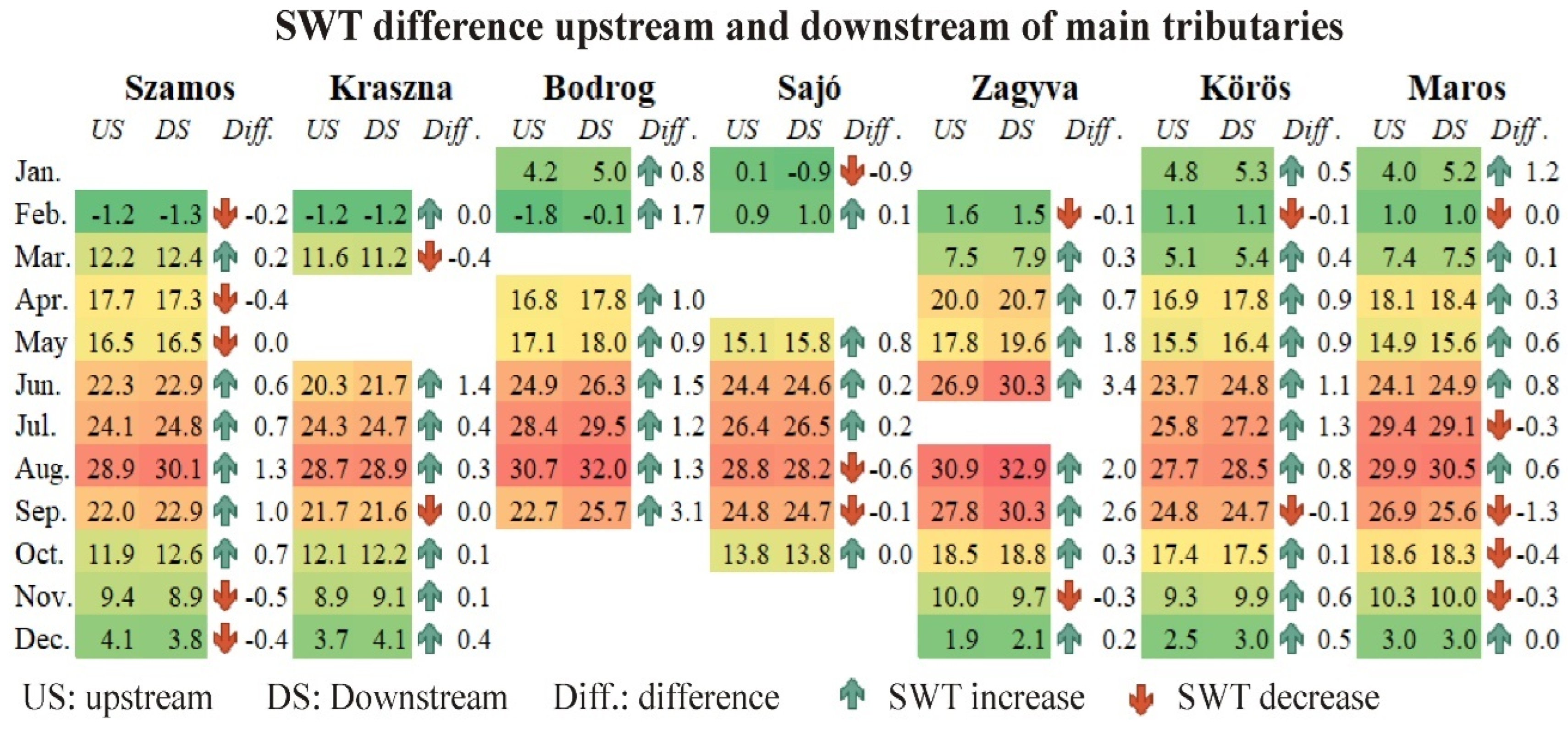
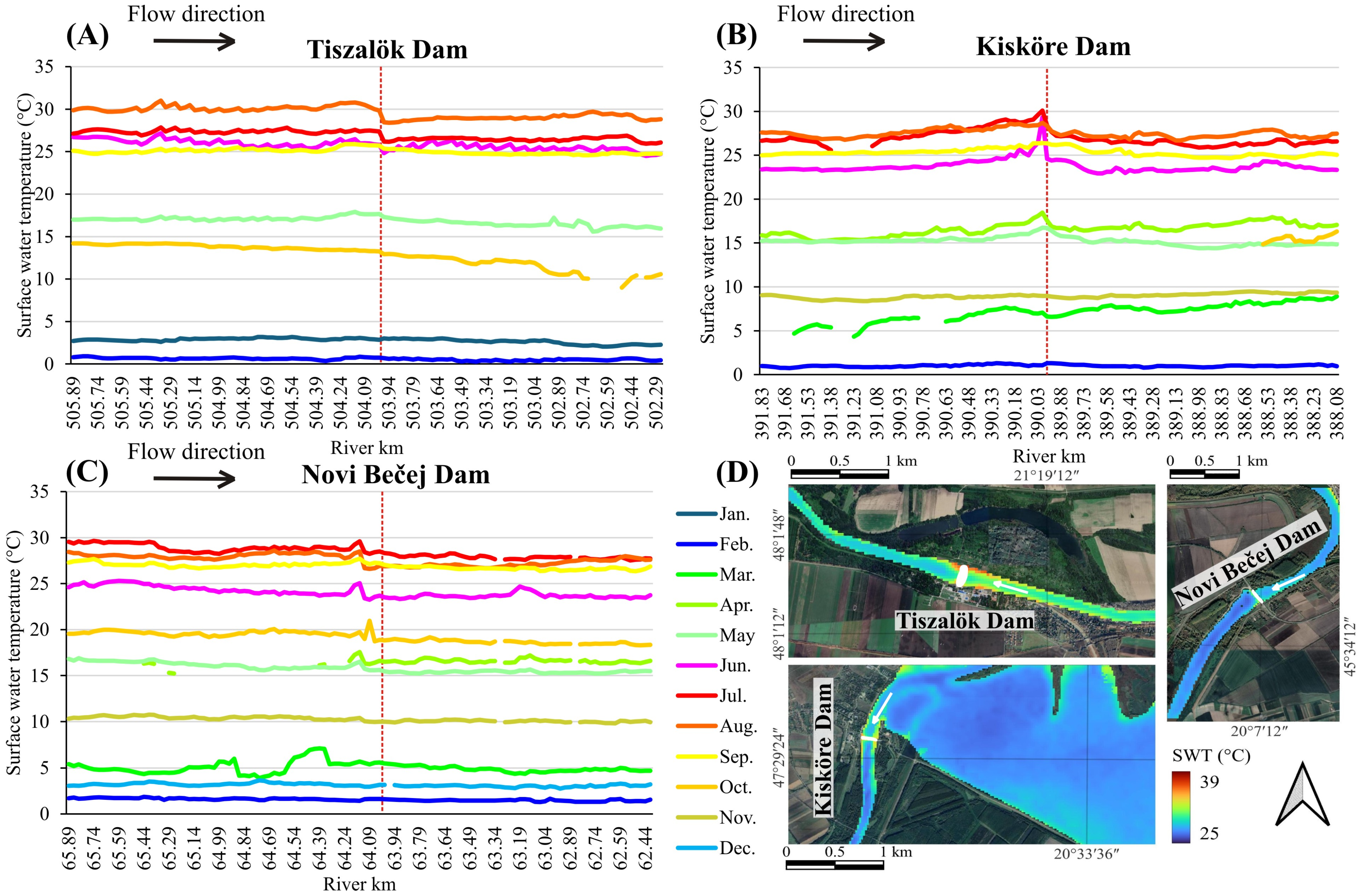
3.4. Influence of Tributaries and Dams on the Thermal Profile of the Tisza River
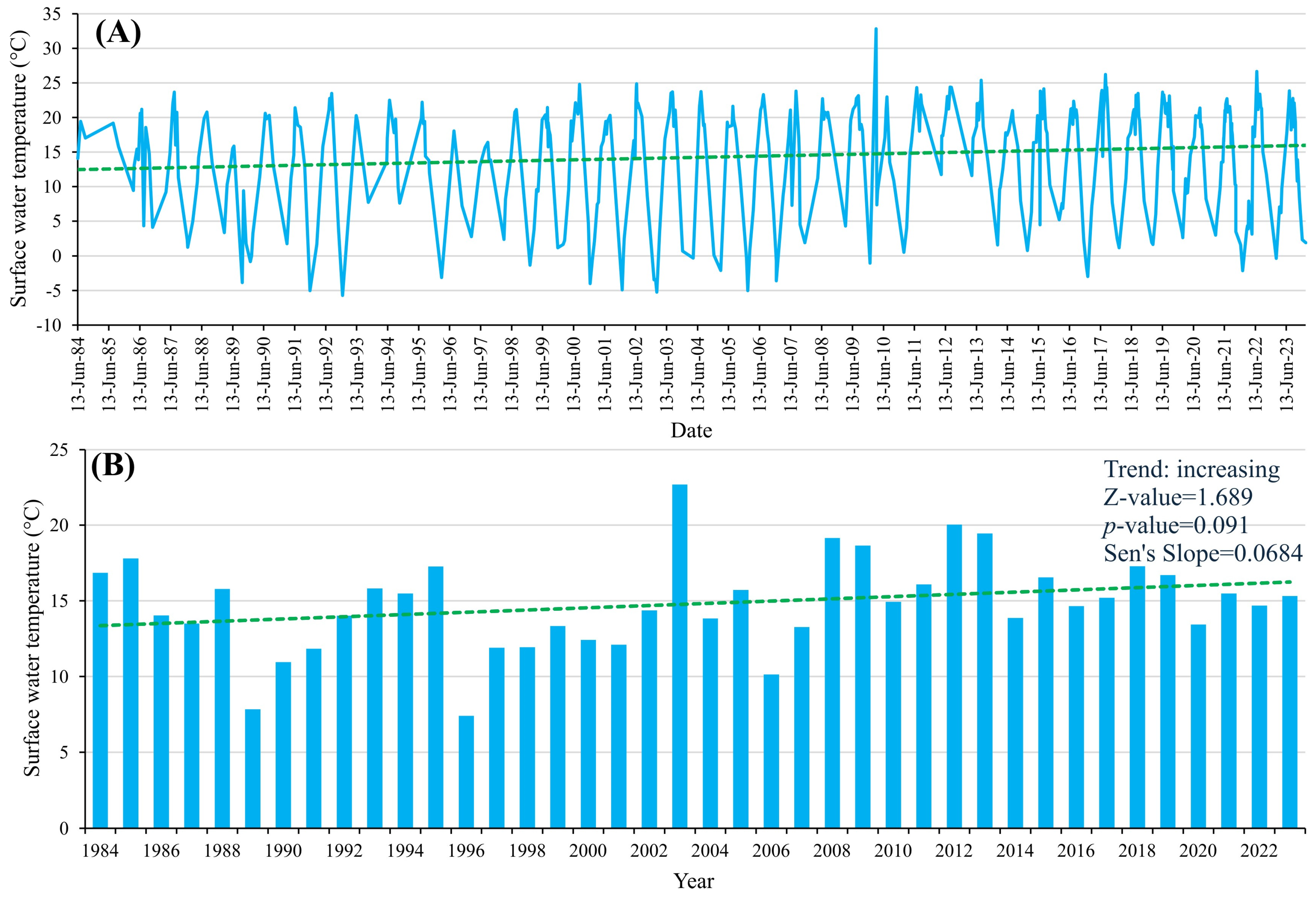
3.5. Influence of Climate Change on the Surface Water Temperature of the Tisza River (40 Years of Satellite Data)
4. Discussion
4.1. Assessment of Landsat Thermal Bands for Surface Water Temperature Evaluation of a Medium-Sized River (Tisza River)
4.2. Diurnal Temperature Cycle Dynamics in the Tisza River Throughout the Year
4.3. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of the Thermal Profile of the Tisza River at the Section Scale
4.4. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of the Thermal Profile of the Tisza River at a 2 km Scale
4.4.1. Influence of Urban Areas
4.4.2. Influence of Shading and Groundwater Inflow
4.4.3. Influence of Dams
4.4.4. Influence of Tributaries
4.5. Long-Term Evaluation of the Surface Water Temperature of the Tisza and Global Warming
4.6. Limitations of Landsat-Based SWT Estimates
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Month | Path | Row | Date | Month | Path | Row | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| January | 187 | 28 | 8 January 2023 | July | 187 | 28 | 11 July 2023 |
| 187 | 27 | 24 January 2023 | 187 | 27 | 3 July 2023 | ||
| 186 | 27 | 1 January 2023 | 186 | 27 | 20 July 2023 | ||
| 185 | 27 | 2 January 2023 | 185 | 27 | 29 July 2023 | ||
| February | 187 | 28 | 9 February 2023 | August | 187 | 28 | 20 August 2023 |
| 187 | 27 | 9 February 2023 | 187 | 27 | 20 August 2023 | ||
| 186 | 27 | 10 February 2023 | 186 | 27 | 21 August 2023 | ||
| 185 | 27 | 20 February 2023 | 185 | 27 | 22 August 2023 | ||
| March | 187 | 28 | 13 March 2023 | September | 187 | 28 | 5 September 2023 |
| 187 | 27 | 13 March 2023 | 187 | 27 | 5 September 2023 | ||
| 186 | 27 | 22 March 2023 | 186 | 27 | 6 September 2023 | ||
| 185 | 27 | 24 March 2023 | 185 | 27 | 7 September 2023 | ||
| April | 187 | 28 | 30 April 2023 | October | 187 | 28 | 23 October 2023 |
| 187 | 27 | 30 April 2023 | 187 | 27 | 23 October 2023 | ||
| 186 | 27 | 23 April 2023 | 186 | 27 | 16 October 2023 | ||
| 185 | 27 | 24 April 2023 | 185 | 27 | 17 October 2023 | ||
| May | 187 | 28 | 8 May 2023 | November | 187 | 28 | 16 November 2023 |
| 187 | 27 | 8 May 2023 | 187 | 27 | 16 November 2023 | ||
| 186 | 27 | 9 May 2023 | 186 | 27 | 11 September 2023 | ||
| 185 | 27 | 10 May 2023 | 185 | 27 | 26 November 2023 | ||
| June | 187 | 28 | 1 June 2023 | December | 187 | 28 | 18 December 2023 |
| 187 | 27 | 1 June 2023 | 187 | 27 | 18 December 2023 | ||
| 186 | 27 | 2 June 2023 | 186 | 27 | 27 December 2023 | ||
| 185 | 27 | 3 June 2023 | 185 | 27 | 20 December 2023 |


References
- Webb, B.W.; Hannah, D.M.; Moore, R.D.; Brown, L.E.; Nobilis, F. Recent advances in stream and river temperature research. Hydrol. Process. 2008, 22, 902–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Li, H.; Cai, X.; Chen, F.; Wang, L.; Yu, D.; Li, C.A. Long-term (2002–2017) impacts of Danjiangkou dam on thermal regimes of downstream Han River (China) using Landsat thermal infrared imagery. J. Hydrol. 2020, 589, 125135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, F.; Foody, G.M.; Du, H.; Ban, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Du, Y. Monitoring Thermal Pollution in Rivers Downstream of Dams with Landsat ETM+ Thermal Infrared Images. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Huang, X.; Liu, J.; Zheng, C.; He, X.; Liu, C. Spatiotemporal variation of river temperature as a predictor of groundwater/surface-water interactions in an arid watershed in China. Hydrogeol. J. 2015, 23, 999–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toffolon, M.; Piccolroaz, S. A hybrid model for river water temperature as a function of air temperature and discharge. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 114011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejia, F.H.; Torgersen, C.E.; Berntsen, E.K.; Maroney, J.R.; Connor, J.M.; Fullerton, A.H.; Ebersole, J.L.; Lorang, M.S. Longitudinal, lateral, vertical and temporal thermal heterogeneity in a large impounded river: Implications for cold-water refuges. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fullerton, A.H.; Torgersen, C.E.; Lawler, J.J.; Faux, R.N.; Steel, E.A.; Beechie, T.J.; Ebersole, J.L.; Leibowitz, S.G. Rethinking the longitudinal stream temperature paradigm: Region-wide comparison of thermal infrared imagery reveals unexpected complexity of river temperatures. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 29, 4719–4737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, M.; Rehana, S. Impact of climate change on river water temperature and dissolved oxygen: Indian riverine thermal regimes. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takács, K.; Kern, Z.; Pásztor, L. Long-term ice phenology records from eastern–central Europe. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2018, 10, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tassone, S.J.; Besterman, A.F.; Buelo, C.D.; Ha, D.T.; Walter, J.A.; Pace, M.L. Increasing heatwave frequency in streams and rivers of the United States. Limnol. Oceanogr. Lett. 2023, 8, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georges, B.; Michez, A.; Piegay, H.; Huylenbroeck, L.; Lejeune, P.; Brostaux, Y. Which environmental factors control extreme thermal events in rivers? A multi-scale approach (Wallonia, Belgium). PeerJ 2021, 9, e12494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qicai, L. Influence of dams on river ecosystem and its countermeasures. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2011, 3, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyedhashemi, H.; Moatar, F.; Vidal, J.-P.; Diamond, J.S.; Beaufort, A.; Chandesris, A.; Valette, L. Thermal signatures identify the influence of dams and ponds on stream temperature at the regional scale. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 766, 142667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csoma, J.; Szilágyi, J.; Zboray, K. Water, sediment and ice conditions of the reservoir of Tiszalök, Hungary (A tiszalöki duzzasztott tér víz-, hordalék- és jéglevonulási viszonyai.). Vízügyi Közlemények 1967, 49/2, 249–259. [Google Scholar]
- Schwanen, C.A.; Schwarzbauer, J. Structural Diversity of Organic Contaminants in a meso-scaled River System. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2022, 233, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aristi, I.; von Schiller, D.; Arroita, M.; Barceló, D.; Ponsatí, L.; García-Galán, M.J.; Sabater, S.; Elosegi, A.; Acuña, V. Mixed effects of effluents from a wastewater treatment plant on river ecosystem metabolism: Subsidy or stress? Freshw. Biol. 2015, 60, 1398–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jiang, G.; Tang, X.; Zuo, Y.; Hu, S.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, L. Detecting Geothermal Anomalies Using Multi-Temporal Thermal Infrared Remote Sensing Data in the Damxung–Yangbajain Basin, Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handcock, R.N.; Torgersen, C.E.; Cherkauer, K.A.; Gillespie, A.R.; Tockner, K.; Faux, R.N.; Tan, J. Thermal Infrared Remote Sensing of Water Temperature in Riverine Landscapes. In Fluvial Remote Sensing for Science and Management; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 85–113. [Google Scholar]
- Fricke, K.; Baschek, B. Temperature monitoring along the Rhine River based on airborne thermal infrared remote sensing: Estimation of in situ water temperatures and inflow detection compared to artificial satellite data. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2015, 9, 095067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torgersen, C.E.; Faux, R.N.; Mcintosh, B.A.; Poage, N.J.; Norton, D.J. Airborne thermal remote sensing for water temperature assessment in rivers and streams. Remote Sens. Environ. 2001, 76, 386–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinart, A.; Reinhold, M. Mapping surface temperature in large lakes with MODIS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lászlóffy, W. Tisza River: Construction and Water Management in the Tisza Water Regime. 1982. Available online: https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/030913338400800311 (accessed on 26 August 2024).
- Balint, Z.; Tóth, S. Flood protection in the Tisza Basin. In Proceedings of the Flood Risk Management: Hazards, Vulnerability and Mitigation Measures; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 185–197. [Google Scholar]
- Mohsen, A.; Balla, A.; Kiss, T. High Spatiotemporal Resolution Analysis on Suspended Sediment and Microplastic Transport of a Lowland River. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 902, 166188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leščešen, I.; Dolinaj, D.; Pantelić, M.; Telbisz, T.; Varga, G. Hydrological drought assessment of the Tisza river. J. Geogr. Inst. Jovan Cvijic SASA 2020, 70, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, T.; Gönczy, S.; Nagy, T.; Mesaroš, M.; Balla, A. Deposition and Mobilization of Microplastics in a Low-Energy Fluvial Environment from a Geomorphological Perspective. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipos, G.; Blanka, V.; Mezősi, G.; Kiss, T.; van Leeuwen, B. Effect of Climate Change on the Hydrological Character of River Maros, Hungary-Romania. J. Environ. Geogr. 2014, 7, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- János, T.; Bernadett, G.; Bódi, E.B.; Magyar, T.; Nagy, A. Evaluation of water demand supply on Tisza River Basin. In Proceedings of the 3rd World Irrigation Forum (WIF3), Bali, Indonesia, 1–7 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mohsen, A.; Kovács, F.; Kiss, T. Remote Sensing of Sediment Discharge in Rivers using Sentinel-2 Images and Machine-learning Algorithms. Hydrology 2022, 9, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICPDR. Analysis of the Tisza River Basin 2007; International Commission for the Protection of the Danube River, Vienna International Centre/D0412: Vienna, Austria, 2007; p. 136. [Google Scholar]
- János, F. Updated Integrated Tisza River Basin Management Plan; Interreg Europe: Lille, France, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lovász, G. Water temperatures of the Danube and Tisza Rivers in Hungary. Hung. Geogr. Bull. 2012, 61, 317–325. [Google Scholar]
- Fehér, Z.Z.; Rakonczai, J. Analysing the sensitivity of Hungarian landscapes based on climate change induced shallow groundwater fluctuation. Hung. Geogr. Bull. 2019, 68, 355–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliáš jun, P.; Dítě, D.; Dítě, Z. Halophytic Vegetation in the Pannonian Basin: Origin, Syntaxonomy, Threat, and Conservation. In Handbook of Halophytes: From Molecules to Ecosystems towards Biosaline Agriculture; Grigore, M.-N., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 287–324. [Google Scholar]
- Trásy-Havril, T.; Szkolnikovics-Simon, S.; Mádl-Szőnyi, J. How Complex Groundwater Flow Systems Respond to Climate Change Induced Recharge Reduction? Water 2022, 14, 3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ptak, M.; Choiński, A.; Piekarczyk, J.; Pryłowski, T. Applying Landsat Satellite Thermal Images in the Analysis of Polish Lake Temperatures. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2017, 26, 2159–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamaro, A.A.; Mariñelarena, A.; Torrusio, S.E.; Sala, S.E. Water surface temperature estimation from Landsat 7 ETM+ thermal infrared data using the generalized single-channel method: Case study of Embalse del Río Tercero (Córdoba, Argentina). Adv. Space Res. 2013, 51, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Wu, H.; Kimball, J.; Tao, J. Streamflow temperature estimation based on Landsat thermal infrared and optical bands data. In Proceedings of the AGU Fall Meeting 2021, New Orleans, LA, USA, 13–17 December 2021; p. H25F-1103. [Google Scholar]
- Teixeira Pinto, C.; Jing, X.; Leigh, L. Evaluation analysis of Landsat level-1 and level-2 data products using in situ measurements. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayler, K.; Zanter, K. Landsat 8 Collection 1 (C1) Land Surface Reflectance Code (LaSRC) Product Guide; LSDS-1368 Version; Department Interior United States Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2020; Volume 3.
- McFeeters, S.K. The use of the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) in the Delineation of Open Water Features. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsu, N. A threshold Selection Method from Gray-level Histograms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1979, 9, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ESA. Available online: https://step.esa.int/main/download/snap-download/ (accessed on 20 June 2021).
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric Tests Against Trend. Econom. J. Econom. Soc. 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M. Rank Correlation Measures. Charles Griffin Lond. 1975, 202, 15. [Google Scholar]
- IBM. Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) Software. Available online: https://www.ibm.com/analytics/us/en/technology/spss/ (accessed on 25 May 2022).
- Ali, S.A.; Parvin, F.; Ahmad, A. Retrieval of Land Surface Temperature from Landsat 8 OLI and TIRS: A Comparative Analysis Between Radiative Transfer Equation-Based Method and Split-Window Algorithm. Remote Sens. Earth Syst. Sci. 2023, 6, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niedrist, G.H. Substantial warming of Central European mountain rivers under climate change. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2023, 23, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanford, J.A.; Ward, J.V. Revisiting the serial discontinuity concept. Regul. Rivers: Res. Manag. Int. J. Devoted River Res. Manag. 2001, 17, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CityPopulation. Available online: https://www.citypopulation.de/en/ (accessed on 12 June 2024).
- Brosofske, K.D.; Chen, J.; Naiman, R.J.; Franklin, J.F. Harvesting effects on microclimatic gradients from small streams to uplands in western Washington. Ecol. Appl. 1997, 7, 1188–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keery, J.; Binley, A.; Crook, N.; Smith, J.W.N. Temporal and spatial variability of groundwater–surface water fluxes: Development and application of an analytical method using temperature time series. J. Hydrol. 2007, 336, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preece, R.M.; Jones, H.A. The effect of Keepit Dam on the temperature regime of the Namoi River, Australia. River Res. Appl. 2002, 18, 397–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casado, A.; Hannah, D.M.; Peiry, J.-L.; Campo, A.M. Influence of dam-induced hydrological regulation on summer water temperature: Sauce Grande River, Argentina. Ecohydrology 2013, 6, 523–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerimoglu, O.; Rinke, K. Stratification dynamics in a shallow reservoir under different hydro-meteorological scenarios and operational strategies. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 7518–7527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gizińska, J.; Sojka, M. How Climate Change Affects River and Lake Water Temperature in Central-West Poland—A Case Study of the Warta River Catchment. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itsukushima, R.; Ohtsuki, K.; Sato, T. Drivers of rising monthly water temperature in river estuaries. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2024, 69, 589–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Santis, D.; Del Frate, F.; Schiavon, G. Analysis of Climate Change Effects on Surface Temperature in Central-Italy Lakes Using Satellite Data Time-Series. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohsen, A.; Kiss, T.; Baranya, S.; Balla, A.; Kovács, F. Thermal Profile Dynamics of a Central European River Based on Landsat Images: Natural and Anthropogenic Influencing Factors. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3196. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16173196
Mohsen A, Kiss T, Baranya S, Balla A, Kovács F. Thermal Profile Dynamics of a Central European River Based on Landsat Images: Natural and Anthropogenic Influencing Factors. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(17):3196. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16173196
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohsen, Ahmed, Tímea Kiss, Sándor Baranya, Alexia Balla, and Ferenc Kovács. 2024. "Thermal Profile Dynamics of a Central European River Based on Landsat Images: Natural and Anthropogenic Influencing Factors" Remote Sensing 16, no. 17: 3196. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16173196
APA StyleMohsen, A., Kiss, T., Baranya, S., Balla, A., & Kovács, F. (2024). Thermal Profile Dynamics of a Central European River Based on Landsat Images: Natural and Anthropogenic Influencing Factors. Remote Sensing, 16(17), 3196. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16173196








