Intelligent Recognition of Coastal Outfall Drainage Based on Sentinel-2/MSI Imagery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
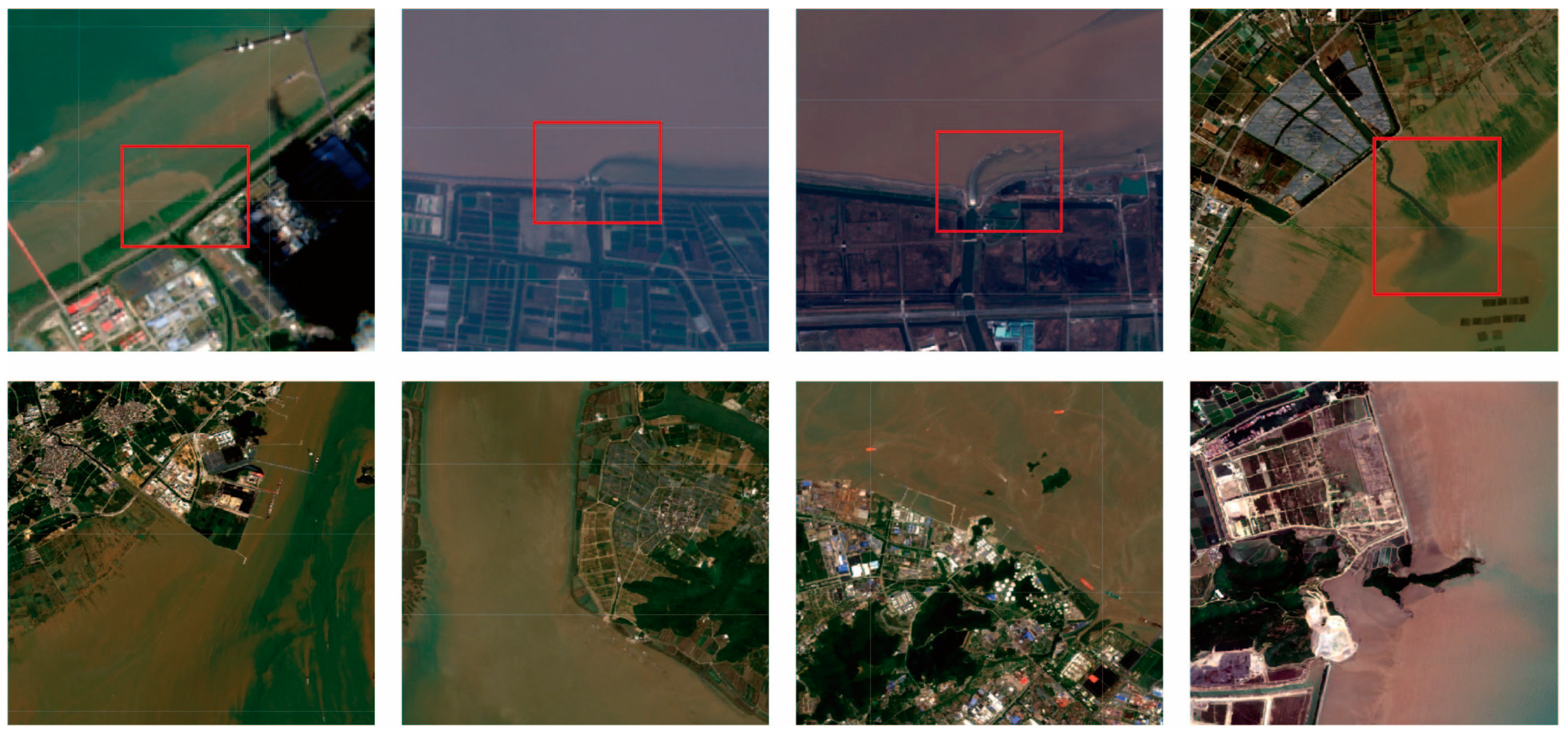
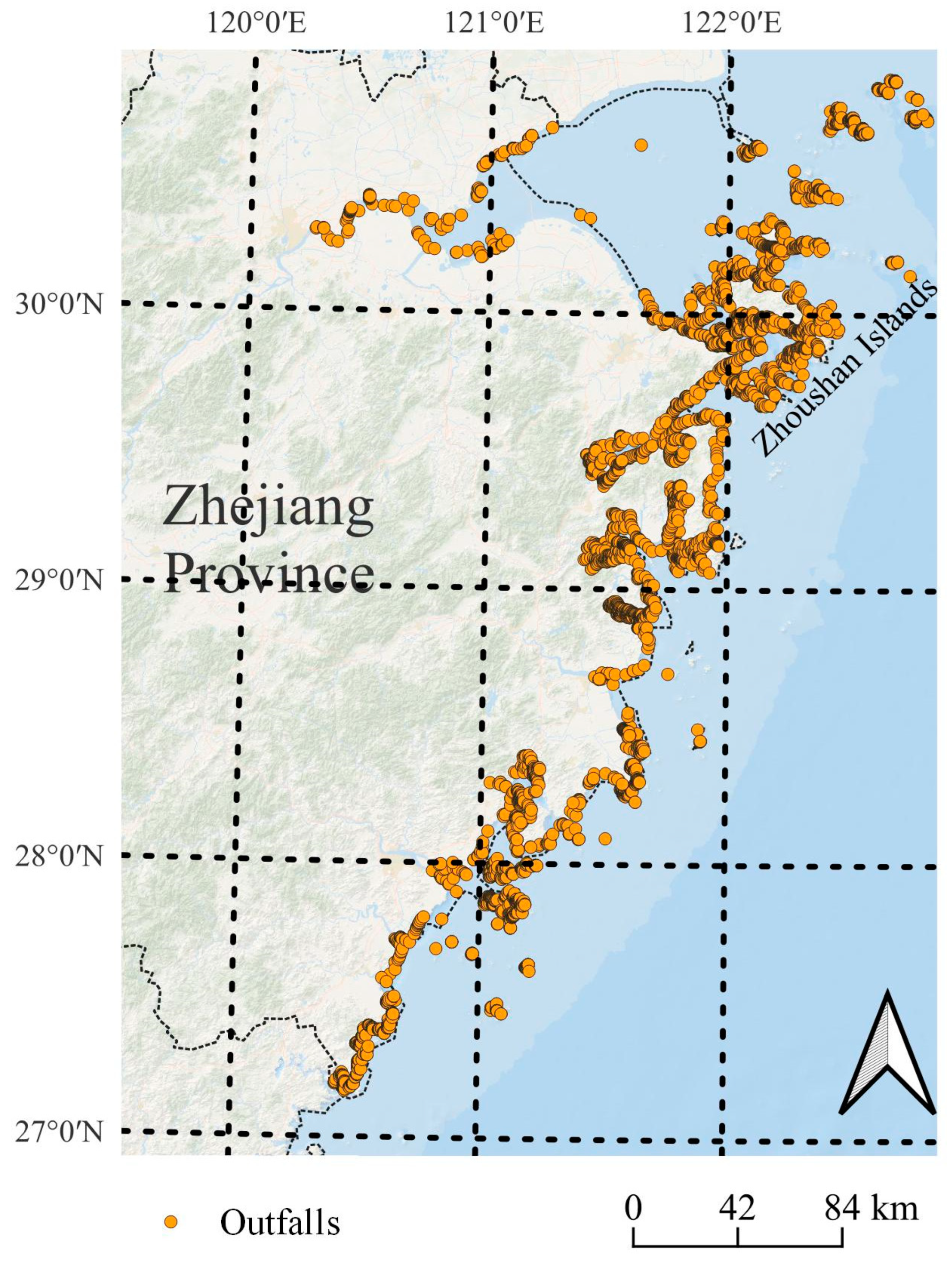
2.1. Data Preparation
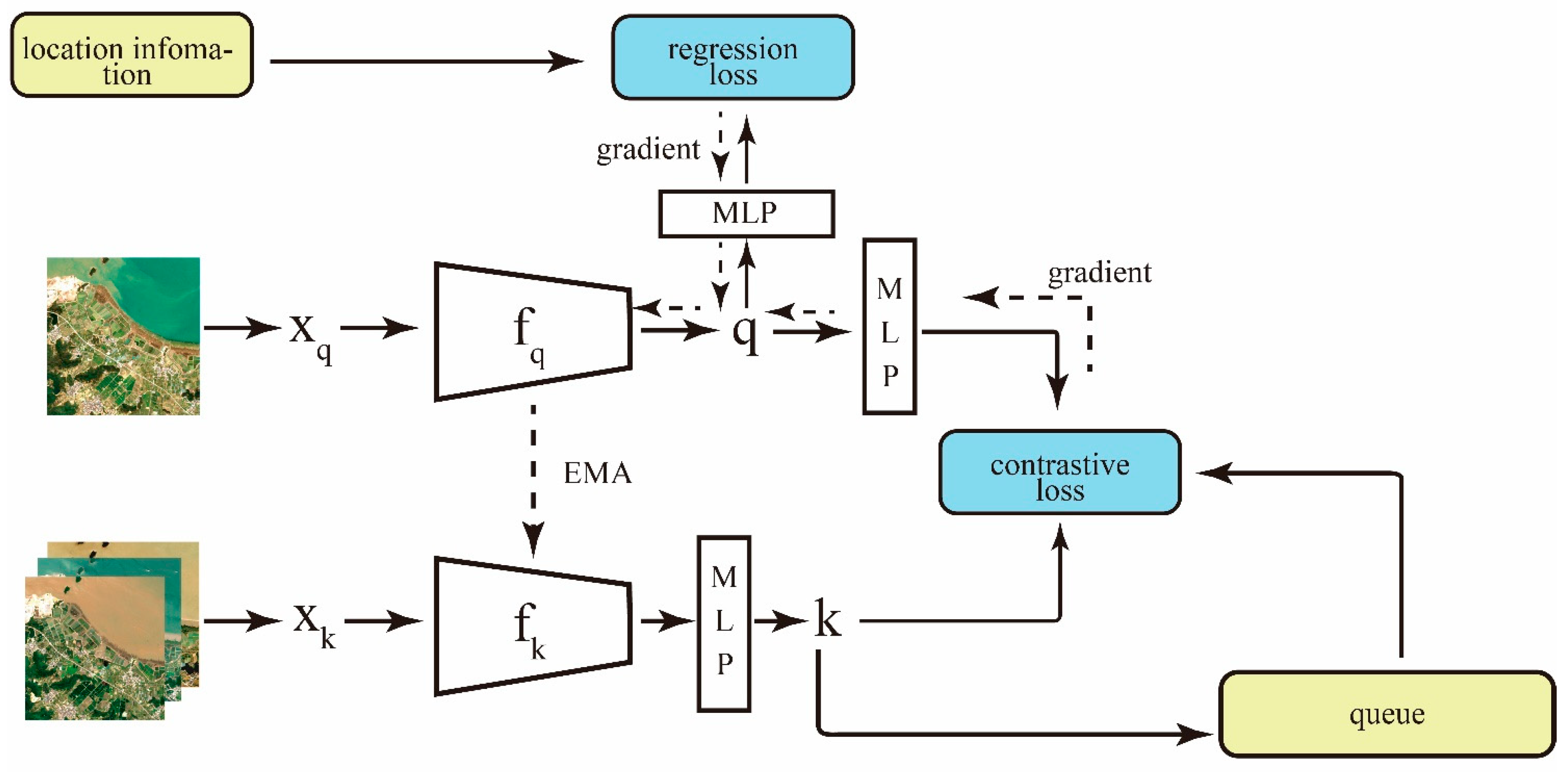
2.2. Establishment of the Intelligent Recognition Model
- (1)
- Training Framework
- (2)
- Positive Sample Pair Generation
- (3)
- Feature Assessment and Visualization
- (4)
- Evaluation of Model Performances
3. Results and Discussion
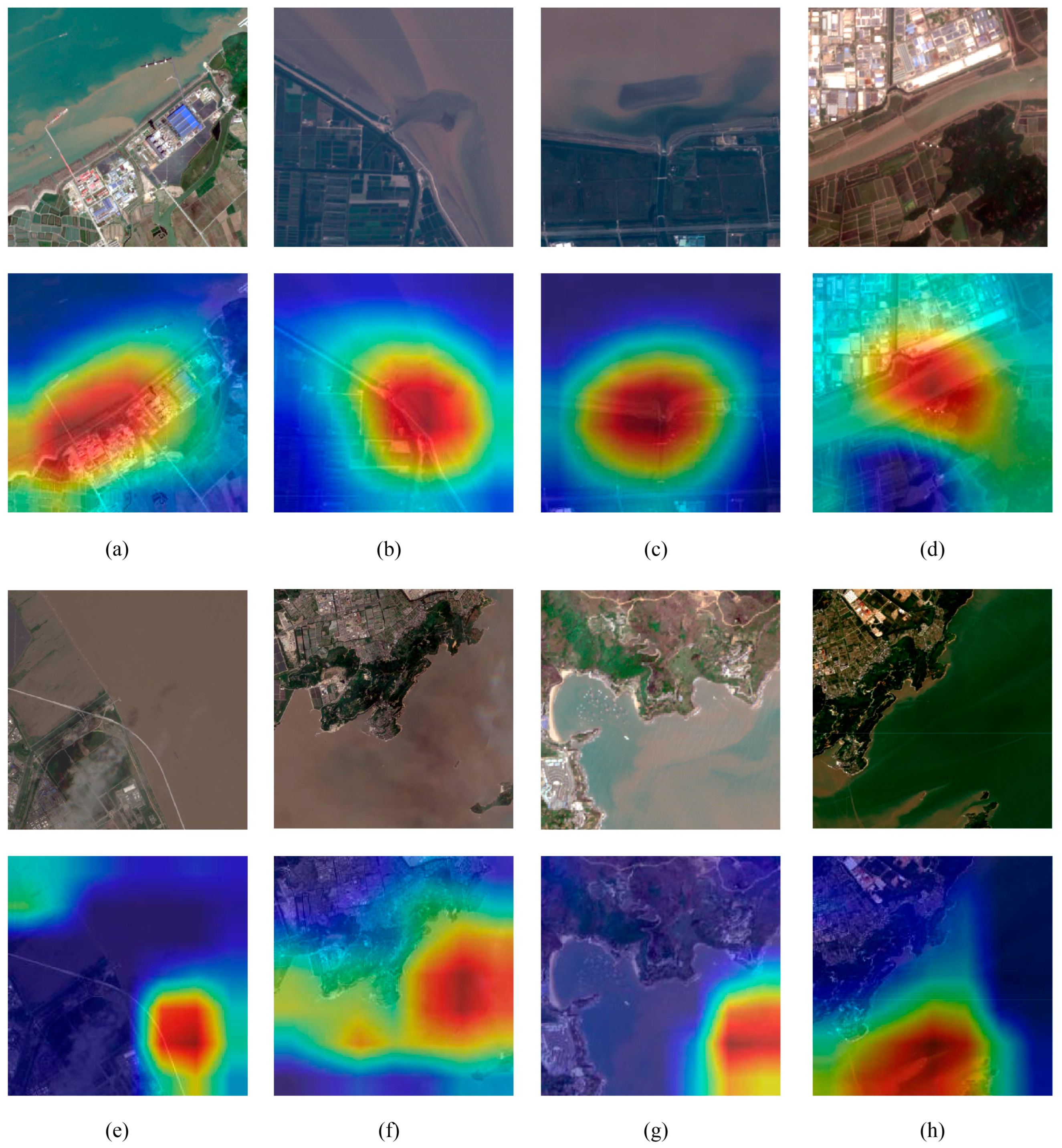
3.1. Visual Results from the Encoding Model
3.2. Pretraining Enhancement and Baseline Model Evaluation
- (1)
- Supervised-only: This method involves training the encoder exclusively on supervised data, maintaining complete isolation from the unlabeled dataset.
- (2)
- Self-sup-only: This self-supervised training method abstains from incorporating geographical information, thereby excluding the parameter update via , and geographical location information is not utilized in selecting positive sample pairs. The generation of positive sample pairs adheres to the same strategy as MoCo-V2 [29].
- (3)
- Selfsup + Geoloss: This method builds upon the previous approach, employing for gradient calculation and subsequent parameter updates.
- (4)
- Selfsup + Geoloss + GeoSelect: This method extends method 3, incorporating the sample pair selection mechanism, as discussed in Section 3.2.
| Methods | Encoder | Accuracy (%) | F1-Score (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supervised-only | Resnet50 | 79.73 | 75.68 |
| Selfsup-only | Resnet50 | 84.23 | 81.67 |
| Selfsup + Geoloss | Resnet50 | 88.29 | 86.17 |
| Selfsup + Geoloss + GeoSelect | Resnet50 | 90.54 | 88.52 |
3.3. Impact of Distance Threshold on Encoder Performance
3.4. Analysis of Classification Outcomes
4. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Q.; Yang, Z. Industrial water pollution, water environment treatment, and health risks in China. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zou, T.; Lai, Y. Novel method for industrial sewage outfall detection: Water pollution monitoring based on web crawler and remote sensing interpretation techniques. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 312, 127640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wu, C.; Yang, H.; Zhu, H.; Chen, M.; Yang, J. An Improved Deep Learning Approach for Retrieving Outfalls Into Rivers From UAS Imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Huang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, X.; Han, W.; Wang, L. UAV-ODS: A Real-time Outfall Detection System Based on UAV Remote Sensing and Edge Computing. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Unmanned Systems (ICUS), Guangzhou, China, 28–30 October 2022; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Ballasiotes, A.D. Mapping Untreated and Semi-Treated Wastewater Effluent off the Coast of Gaza with Sentinel-1 Time Series Data. Master’s Thesis, Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; He, X.; Bai, Y.; Tan, Y.; Zhu, B.; Wang, D.; Ou, M.; Gong, F.; Zhu, Q.; Huang, H. Automatic detection of suspected sewage discharge from coastal outfalls based on Sentinel-2 imagery. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 853, 158374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondur, V.; Zamshin, V.; Zamshina, A.S.; Vorobyev, V. Registering from space the features of deep wastewater outfalls into coastal water areas due to discharge collector breaks. Izv. Atmos. Ocean. Phys. 2020, 56, 979–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Shen, H.; Li, T.; Li, Z.; Li, S.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, H.; Tan, W.; Yang, Q.; Wang, J. Deep learning in environmental remote sensing: Achievements and challenges. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 241, 111716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, K.; Penatti, O.A.; Dos Santos, J.A. Towards better exploiting convolutional neural networks for remote sensing scene classification. Pattern Recognit. 2017, 61, 539–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhichri, H.; Alswayed, A.S.; Bazi, Y.; Ammour, N.; Alajlan, N.A. Classification of remote sensing images using EfficientNet-B3 CNN model with attention. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 14078–14094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, P.; Pham, M.-T.; Courty, N. Self-Supervised Learning for Scene Classification in Remote Sensing: Current State of the Art and Perspectives. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, P.; Caron, M.; Lefaudeux, B.; Xu, M.; Wang, P.; Pai, V.; Singh, M.; Liptchinsky, V.; Misra, I.; Joulin, A. Self-supervised pretraining of visual features in the wild. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.01988. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Fan, H.; Wu, Y.; Xie, S.; Girshick, R. Momentum contrast for unsupervised visual representation learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 9729–9738. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; He, K. Exploring simple siamese representation learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 15750–15758. [Google Scholar]
- Grill, J.-B.; Strub, F.; Altché, F.; Tallec, C.; Richemond, P.; Buchatskaya, E.; Doersch, C.; Avila Pires, B.; Guo, Z.; Gheshlaghi Azar, M. Bootstrap your own latent-a new approach to self-supervised learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 21271–21284. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Albrecht, C.M.; Braham, N.A.A.; Mou, L.; Zhu, X.X. Self-supervised learning in remote sensing: A review. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2206.13188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, G.; Lao, N.; He, Y.; Song, J.; Ermon, S. CSP: Self-Supervised Contrastive Spatial Pre-Training for Geospatial-Visual Representations. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.01118. [Google Scholar]
- Ayush, K.; Uzkent, B.; Meng, C.; Tanmay, K.; Burke, M.; Lobell, D.; Ermon, S. Geography-aware self-supervised learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 10181–10190. [Google Scholar]
- Phiri, D.; Simwanda, M.; Salekin, S.; Nyirenda, V.R.; Murayama, Y.; Ranagalage, M. Sentinel-2 data for land cover/use mapping: A review. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; He, X.; Lian, G.; Bai, Y.; Yang, Y.; Gong, F.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Li, T.; Jin, X. Monitoring and spatial traceability of river water quality using Sentinel-2 satellite images. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 894, 164862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, I.; Fernández, R.; Escalante, O.M.; Mamán, L.; Navarro, G. New capabilities of Sentinel-2A/B satellites combined with in situ data for monitoring small harmful algal blooms in complex coastal waters. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafeez, S.; Wong, M.S.; Abbas, S.; Asim, M. Evaluating landsat-8 and sentinel-2 data consistency for high spatiotemporal inland and coastal water quality monitoring. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Yao, X.; Chen, D. Simcse: Simple contrastive learning of sentence embeddings. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.08821. [Google Scholar]
- Oord, A.v.d.; Li, Y.; Vinyals, O. Representation learning with contrastive predictive coding. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.03748. [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhay, A.; Sarkar, A.; Howlader, P.; Balasubramanian, V.N. Grad-cam++: Generalized gradient-based visual explanations for deep convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 12–15 March 2018; pp. 839–847. [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-cam: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 618–626. [Google Scholar]
- Springenberg, J.T.; Dosovitskiy, A.; Brox, T.; Riedmiller, M. Striving for simplicity: The all convolutional net. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6806. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Fan, H.; Girshick, R.; He, K. Improved baselines with momentum contrastive learning. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.04297. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Kornblith, S.; Norouzi, M.; Hinton, G. A simple framework for contrastive learning of visual representations. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Online, 12–18 July 2020; pp. 1597–1607. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S. An image is worth 16×16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; He, X.; Bai, Y.; Gong, F.; Li, T.; Wang, D. Intelligent Recognition of Coastal Outfall Drainage Based on Sentinel-2/MSI Imagery. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 423. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16020423
Li H, He X, Bai Y, Gong F, Li T, Wang D. Intelligent Recognition of Coastal Outfall Drainage Based on Sentinel-2/MSI Imagery. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(2):423. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16020423
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Hongzhe, Xianqiang He, Yan Bai, Fang Gong, Teng Li, and Difeng Wang. 2024. "Intelligent Recognition of Coastal Outfall Drainage Based on Sentinel-2/MSI Imagery" Remote Sensing 16, no. 2: 423. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16020423
APA StyleLi, H., He, X., Bai, Y., Gong, F., Li, T., & Wang, D. (2024). Intelligent Recognition of Coastal Outfall Drainage Based on Sentinel-2/MSI Imagery. Remote Sensing, 16(2), 423. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16020423






