A Review of Deep Learning-Based Remote Sensing Image Caption: Methods, Models, Comparisons and Future Directions
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Different scales. Remote sensing images are typically acquired from a distance, whereas natural images are typically taken closer to the item. As a result, objects in remote sensing images are not only greater in size but also harder to distinguish.
- Different object distribution. Objects in natural images are often located in the center of the image, while the distribution of objects in remote sensing images is extremely complex and likely to be in the corners of the picture.
- Different number of objects. Natural images often have only a few key figures or animals, while remote sensing images usually involve a huge number of buildings.
- Different viewpoints of the shot, making it challenging to discern between foreground and background. The foreground and background of a natural image are instantly recognizable by human eyes, and we can naturally find the main subject and construct sentences. In contrast, remote sensing images are recorded in God’s perspective [22], where the main objects in the image are similar in size to the background or are directly hidden from it, making them difficult to find for humans and even harder for machines.
2. Methods
- The results presented in the paper are unreasonable or significantly deviate from findings reported in peers’ papers.
- Full-text access to certain articles could not be obtained from their respective publishers.
- Only image caption applications in remote sensing are included, while traditional image caption tasks are not.
- Papers that employ auxiliary tasks for generating remote sensing image captions may be included. However, those utilizing remote sensing image captions to assist other tasks will be excluded.
- Regarding papers on remote sensing image retrieval, understanding, interpretation, analysis and other related topics, we cannot judge by a simple paper title, we will check the evaluation metrics used in experimental results. Papers which use evaluation metrics that do not belong to this area may fall outside this paper’s scope.
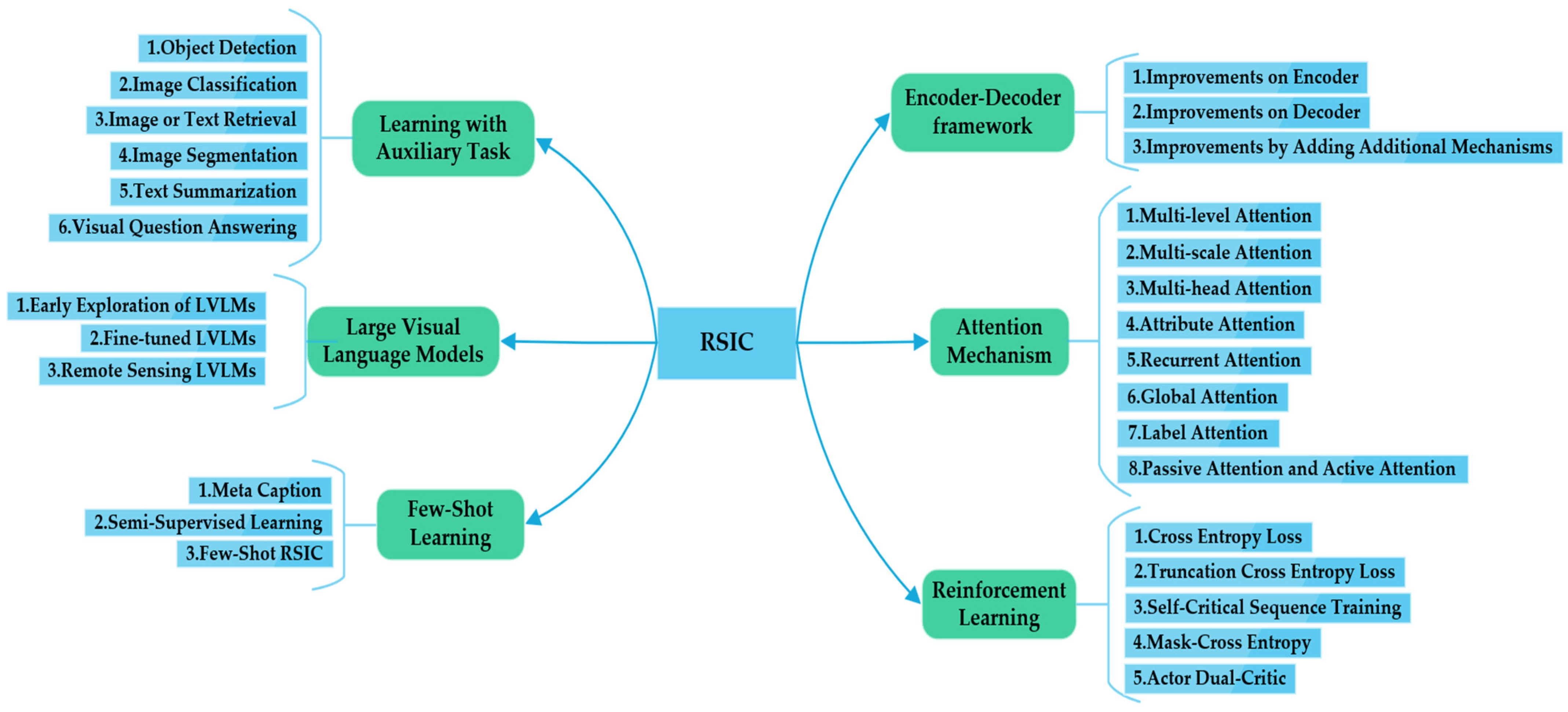
3. Review of RSIC Based on Deep Learning
3.1. Encoder–Decoder Framework
3.1.1. Improvements on Encoder
3.1.2. Improvements on Decoder
3.1.3. Improvements by Adding Additional Mechanisms
3.2. Attention Mechanism
3.2.1. Multi-Level Attention
3.2.2. Multi-Scale Attention
3.2.3. Multi-Head Attention
3.2.4. Attribute Attention
3.2.5. Recurrent Attention
3.2.6. Global Attention
3.2.7. Label Attention
3.2.8. Passive Attention and Active Attention
3.3. Reinforcement Learning
3.3.1. Cross Entropy Loss
3.3.2. Truncation Cross Entropy Loss
3.3.3. Self-Critical Sequence Training
3.3.4. Mask-Cross Entropy
3.3.5. Actor Dual-Critic
| Models | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| CE [37] | Most frequently used; effectively improves performance | Overfitting; exposure bias |
| TCE [118] | Solving the overfitting problem of CE; generate more flexible and concise captions | After the probability of truncating words decreases, other words may not be able to learn accurately, either |
| SCST [120] | Using metrics to motivate the model to generate sentences with higher rewards | Sentence diversity is neglected |
| Mask-CE [123] | Solved the overfitting problem of CE; combined with the advantages of SCST; improved the accuracy and diversity of caption generation | When keywords are masked, it relies more on the prediction of the model |
| ADC [129] | The generated sentences have stronger semantic relevance | Easy to lead to local optimal solutions and difficult convergence |
3.4. Learning with Auxiliary Task
3.4.1. Object Detection
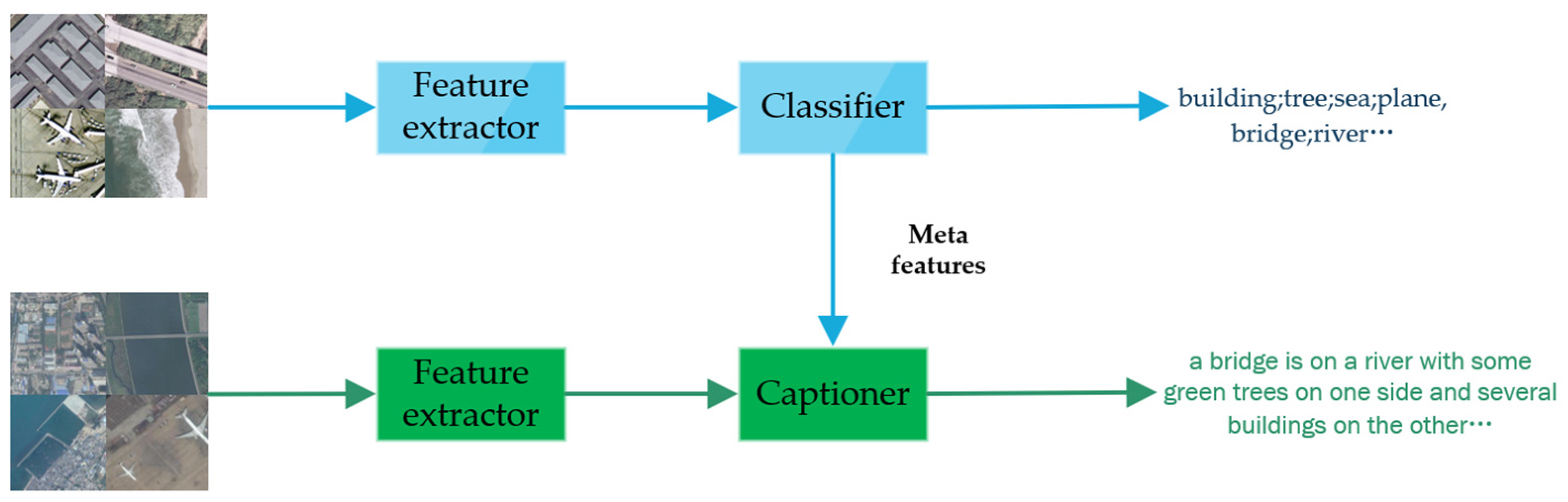
3.4.2. Image Classification
3.4.3. Image or Text Retrieval
3.4.4. Image Segmentation
3.4.5. Text Summarization
3.4.6. Visual Question Answering
| Authors | Auxiliary Task | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shi et al. [16] | Object detection | Investigate the feasibility of RSIC | Simple model-FCN |
| Li et al. [81] | Object detection | Enrich feature and semantic information by extracting object-level features | There is a deviation of dataset between the auxiliary task and original task, fewer categories |
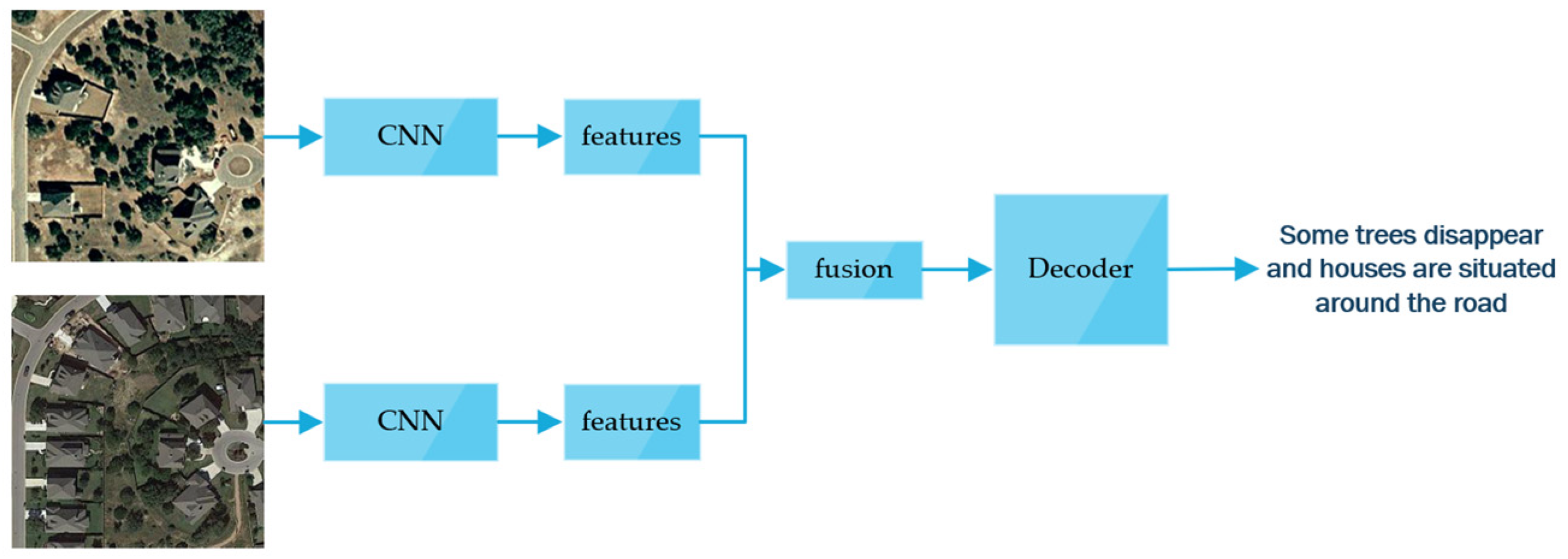
| Liu et al. [135] | Change detection | The pseudo-labels strengthen the recognition and accurate location of the change of targets, and improve the accuracy of change caption | Require pretrained model; highly reliant on the precision of the change-detection model |
| Li et al. [137] | Change detection | Precisely identify the key areas of visual change | Require pretrained model; highly reliant on the precision of the change-detection model |
| Ni et al. [138] | Change detection | The numerical accuracy of the caption has been enhanced | Only valid for partial multi-quantity caption, mostly templated |
| Long et al. [139] | Multi-label classification | Generate more accurate captions about the object information | Require double training time; no real-time interaction |
| Zhao et al. [140] | Image classification | The probability obtained through classification enriches image features | Use pretrained models; generate less comprehensive captions |
| Kumar et al. [141] | Multi-label classification | Training two tasks simultaneously reduces computation time | Less interaction between the two tasks; ignoring the real-time impact |
| Kanadala et al. [142] | Multi-label classification | Reduces computation time; enables joint training for real-time interaction | Unable to generate fine-grained RSIC based on practical application scenarios |
| Ye et al. [143] | Image classification | Solved the problem of sparse RSIC datasets | Meta-learning may produce inaccurate captions in some situations |
| Yang et al. [144] | Image and text retrieval | Reduce global semantic errors caused by a single word error | The model structure is simple and adopts a CNN + RNN model |
| Wang et al. [146] | Text retrieval | Overcome long-term information dilution in RNN; reflect the controllability of captions | More fixed topic words lead to more fixed captions; sometimes result in meaningless captions |
| Li et al. [51] | Text retrieval | Not restricted by predefined labels; employ more refined and accurate semantic information | The risk of semantic misalignment between the retrieved word and the actual content; still some errors in semantic refinement |
| Zhao et al. [22] | Image segmentation | Optimize attention through segmentation proposals; focus on highly structured semantic content | Only applicable to high-resolution remote sensing images; The number of segmentation proposals is fixed |
| Cul et al. [147] | Image segmentation | Reduce the accumulated error; construct a new attention-correction mechanism to improve the location accuracy | Used in landslide caption; hard to judge the type and depth of landslide. The landslide covered by vegetation cannot be recognized. |
| Sumbul et al. [148] | Text summarization | Eliminate redundancy; enrich vocabulary; more suitable for complex scenarios | Introducing complex text consumes an amount of time and space |
| Murali et al. [150] | VQA | Solve the problem of similarity and indistinguishable in remote sensing images; obtain more information | The VQA model requires additional training and is no less complex than the RSIC task |
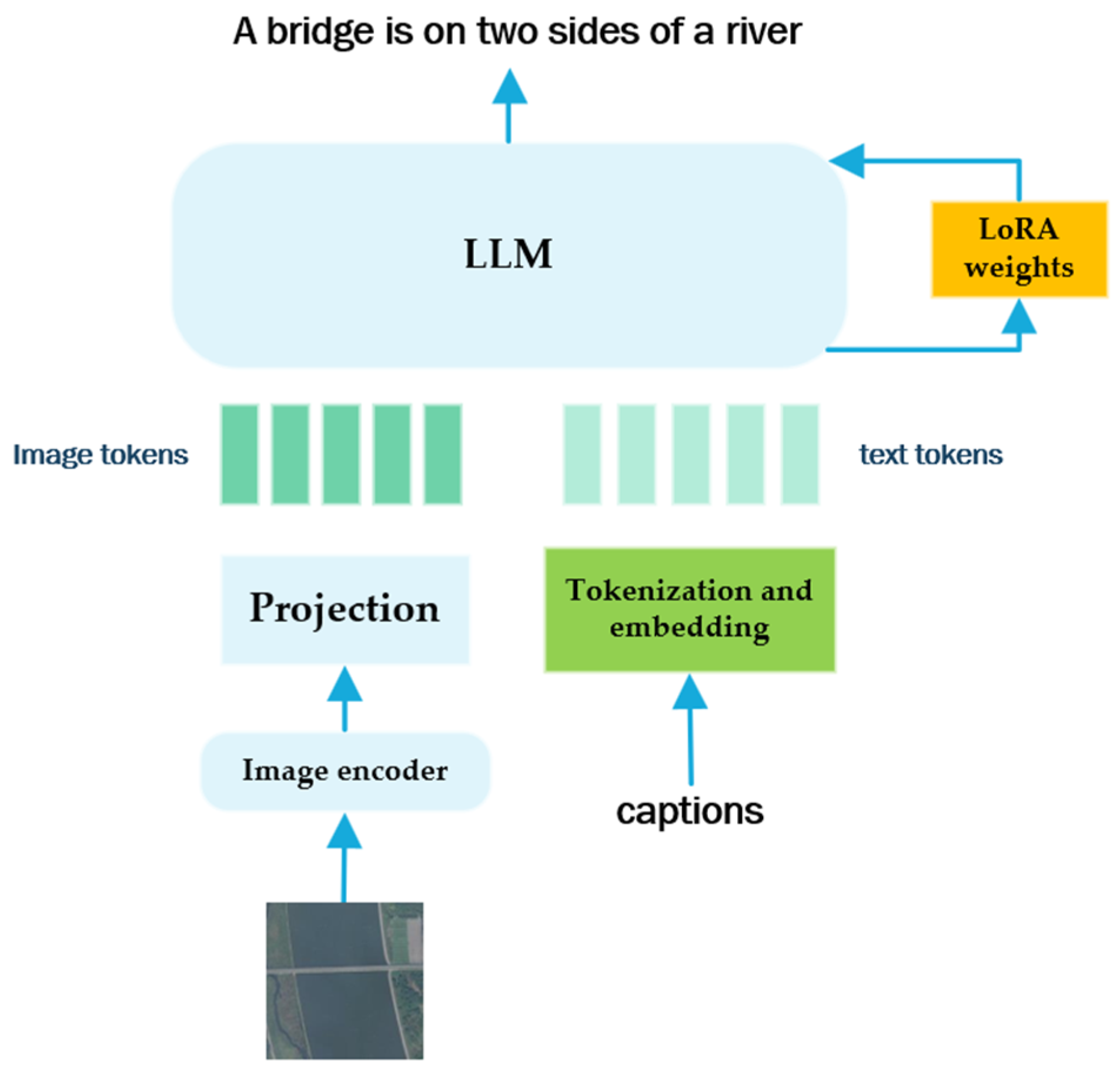
3.5. Large Visual Language Models
3.5.1. Early Exploration of LVLMs
3.5.2. Fine-Tuned LVLMs
3.5.3. LVLMs with Huge Data
3.6. Few-Shot Learning
3.6.1. Meta Caption
3.6.2. Semi-Supervised Learning
3.6.3. Few-Shot RSIC
4. Datasets and Evaluation Metrics of RSIC
4.1. Datasets
4.1.1. Sydney-Captions Dataset
4.1.2. UCM-Captions Dataset
4.1.3. RSICD
4.1.4. NWPU-Captions
4.1.5. LEVIR-CC
4.1.6. LEVIR-CCD
4.1.7. Dubai CCD
4.2. Evaluation Metrics
4.2.1. BLEU
4.2.2. METEOR
4.2.3. ROUGE
4.2.4. CIDEr
4.2.5. SPICE
4.2.6.
5. Discussion
5.1. Analysis of State-of-the-Art Models on Different Datasets
5.1.1. Analysis on Sydney-Captions
5.1.2. Analysis of UCM-Captions
5.1.3. Analysis on RSICD
5.2. Pros and Cons of Different Methods
6. Future Directions
- (1)
- Large and high-quality datasets
- (2)
- Opportunities for Regional Features
- (3)
- Opportunities and Challenges of LVLMs
- (4)
- Remote Sensing Image Change Caption
- (5)
- Diffusion model
- (6)
- Deeper alignment between image and text
- (7)
- More application scenarios
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, A.; Rauf, A.; Ozturk, I.; Wu, J.; Zhao, X.; Du, H. The key to sustainability: In-depth investigation of environmental quality in G20 countries through the lens of renewable energy, economic complexity and geopolitical risk resilience. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 352, 120045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, B.; Chanussot, J.; Hong, D.; Yao, J.; Gao, L. Progress and challenges in intelligent remote sensing satellite systems. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 1814–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selva, M.; Santurri, L.; Baronti, S. Improving hypersharpening for WorldView-3 data. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 16, 987–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sefercik, U.G.; Alkan, M.; Jacobsen, K.; Atalay, C.; Buyuksalih, G. Quality analysis of Worldview-4 DSMs generated by least squares matching and semiglobal matching. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2021, 15, 034515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hestrio, Y.F.; Soleh, M.; Hidayat, A.; Afida, H.; Gunawan, H.; Maryanto, A. Satellite data receiving antenna system for pleiades neo observation satellite. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1763, 012019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Han, J.; Lu, X. Remote sensing image scene classification: Benchmark and state of the art. Proc. IEEE 2017, 105, 1865–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Li, J.; Luo, Z.; Li, J.; Chen, C. Remote sensing image scene classification based on an enhanced attention module. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 18, 1926–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Qi, Z.; Shi, Z. Remote sensing image change detection with transformers. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 5607514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Liu, M.; Li, S.; Liu, X.; Wang, F.; Zhang, L. A deeply supervised attention metric-based network and an open aerial image dataset for remote sensing change detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 5604816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Bashir, S.M.A.; Khan, M.; Ullah, Q.; Wang, R.; Song, Y.; Guo, Z.; Niu, Y. Remote sensing image super-resolution and object detection: Benchmark and state of the art. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 197, 116793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Dhanaraj, M.; Karnam, S.; Chachlakis, D.G.; Ptucha, R.; Markopoulos, P.P.; Saber, E. YOLOrs: Object detection in multimodal remote sensing imagery. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 14, 1497–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, C.; Duan, C.; Su, J.; Wang, L.; Atkinson, P.M. Multiattention network for semantic segmentation of fine-resolution remote sensing images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 5607713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H. Semantic segmentation with attention mechanism for remote sensing images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 5403913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ding, L.; Chen, C.; Liu, Y. Similarity-based unsupervised deep transfer learning for remote sensing image retrieval. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 7872–7889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, J.; Li, Q.; Li, Q.; Liu, B.; Qiu, G. Enhancing remote sensing image retrieval using a triplet deep metric learning network. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 41, 740–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Zou, Z. Can a machine generate humanlike language descriptions for a remote sensing image? IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 3623–3634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recchiuto, C.T.; Sgorbissa, A. Post-disaster assessment with unmanned aerial vehicles: A survey on practical implementations and research approaches. J. Field Robot. 2018, 35, 459–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Ruan, C.; Zhong, S.; Li, J.; Yin, Z.; Lian, X. Risk assessment of storm surge disaster based on numerical models and remote sensing. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 68, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Wang, X.; Johnson, B.A.; Tian, Q.; Wang, Y.; Verrelst, J.; Mu, X.; Gu, X. Remote sensing algorithms for estimation of fractional vegetation cover using pure vegetation index values: A review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 159, 364–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, L.; Chawla, I.; Mishra, A.K. A review of remote sensing applications in agriculture for food security: Crop growth and yield, irrigation, and crop losses. J. Hydrol. 2020, 586, 124905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wentz, E.A.; Anderson, S.; Fragkias, M.; Netzband, M.; Mesev, V.; Myint, S.W.; Quattrochi, D.; Rahman, A.; Seto, K.C. Supporting global environmental change research: A review of trends and knowledge gaps in urban remote sensing. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 3879–3905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Shi, Z.; Zou, Z. High-resolution remote sensing image captioning based on structured attention. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 5603814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zang, S.; Zhang, B.; Li, S.; Wu, C. A review of remote sensing image classification techniques: The role of spatio-contextual information. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 47, 389–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Gao, S.; Zhu, Y.; Ma, C. A survey of remote sensing image classification based on CNNs. Big Earth Data 2019, 3, 232–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuia, D.; Volpi, M.; Copa, L.; Kanevski, M.; Munoz-Mari, J. A survey of active learning algorithms for supervised remote sensing image classification. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2011, 5, 606–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotaridis, I.; Lazaridou, M. Remote sensing image segmentation advances: A meta-analysis. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 173, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lv, H.; Deng, R.; Zhuang, S. A comprehensive survey of optical remote sensing image segmentation methods. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 46, 501–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H. Review of remote sensing image segmentation techniques. Int. J. Adv. Res. Comput. Eng. Technol. (IJARCET) 2015, 4, 1667–1674. [Google Scholar]
- Khelifi, L.; Mignotte, M. Deep learning for change detection in remote sensing images: Comprehensive review and meta-analysis. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 126385–126400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afaq, Y.; Manocha, A. Analysis on change detection techniques for remote sensing applications: A review. Ecol. Inform. 2021, 63, 101310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, T.; Wang, L.; Yin, D.; Sun, K.; Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Li, D. Deep learning for change detection in remote sensing: A review. Geo-Spat. Inf. Sci. 2023, 26, 262–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B. A systematic survey of remote sensing image captioning. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 154086–154111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashmal, L.; Bazi, Y.; Melgani, F.; Al Rahhal, M.M.; Al Zuair, M.A. Language Integration in Remote Sensing: Tasks, datasets, and future directions. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Magazine 2023, 11, 63–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinyals, O.; Toshev, A.; Bengio, S.; Erhan, D. Show and tell: A neural image caption generator. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3156–3164. [Google Scholar]
- Albawi, S.; Mohammed, T.A.; Al-Zawi, S. Understanding of a convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Engineering and Technology (ICET), Antalya, Turkey, 21–23 August 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Salehinejad, H.; Sankar, S.; Barfett, J.; Colak, E.; Valaee, S. Recent advances in recurrent neural networks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1801.01078. [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein, R.Y.; Kroese, D.P. The Cross-Entropy Method: A Unified Approach to Combinatorial Optimization, Monte-Carlo Simulation, and Machine Learning; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2004; Volume 133. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Huang, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, X. Word–sentence framework for remote sensing image captioning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 59, 10532–10543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, B.; Li, X.; Tao, D.; Lu, X. Deep semantic understanding of high resolution remote sensing image. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Computer, Information and Telecommunication Systems (CITS), Kunming, China, 6–8 July 2016; pp. 1–5, IEEE. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Wang, B.; Zheng, X.; Li, X. Exploring models and data for remote sensing image caption generation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 56, 2183–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanal, W.; Hajiarbabi, M. Captioning remote sensing images using transformer architecture. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Information and Communication (ICAIIC), Bali, Indonesia, 20–23 February 2023; pp. 413–418. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, X.; Liu, B.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, J. Remote sensing image caption generation via transformer and reinforcement learning. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020, 79, 26661–26682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, B.; Xi, J.; Bai, X.; Ersoy, O.K.; Cong, M.; Gao, S.; Zhao, Z. Remote Sensing Image Captioning with Sequential Attention and Flexible Word Correlation. IEEE Geosci. Remote. Sens. Lett. 2024, 21, 6004505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geetha, G.; Kirthigadevi, T.; Ponsam, G.; Karthik, T.; Safa, M. Image Captioning Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs). J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1712, 012015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Newsam, S. Densenet for dense flow. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Beijing, China, 17–20 September 2017; pp. 790–794. [Google Scholar]
- Jastrzębski, S.; Arpit, D.; Ballas, N.; Verma, V.; Che, T.; Bengio, Y. Residual connections encourage iterative inference. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1710.04773. [Google Scholar]
- Badhe, N.B.; Bharadi, V.A.; Giri, N.; Alegavi, S. Deep Attention Based DenseNet with Visual Switch Added BiLSTM for Caption Generation from Remote Sensing Images. Int. J. Intell. Eng. Syst. 2023, 16, 677–687. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.; Wang, Q.; Li, X. Denoising-based multiscale feature fusion for remote sensing image captioning. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 18, 436–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.J.; Li, K.; Fei-Fei, L. Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20 June 2009; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, X.; Liu, B.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, J.; Liu, M. Remote sensing image captioning via variational autoencoder and reinforcement learning. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2020, 203, 105920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhao, W.; Du, X.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, S. Cross-modal retrieval and semantic refinement for remote sensing image captioning. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, A. Supervised Sequence Labelling with Recurrent Neural Networks; Springer Nature: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 37–45. [Google Scholar]
- Dey, R.; Salem, F.M. Gate-variants of gated recurrent unit (GRU) neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 60th International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems (MWSCAS), Boston, MA, USA, 6–9 August 2017; pp. 1597–1600. [Google Scholar]
- Chouaf, S.; Hoxha, G.; Smara, Y.; Melgani, F. Captioning changes in bi-temporal remote sensing images. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium IGARSS, Brussels, Belgium, 11–16 July 2021; pp. 2891–2894. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 30; Guyon, I., Von Luxburg, U., Bengio, S., Wallach, H., Fergus, R., Vishwanathan, S., Garnett, R., Eds.; Neural Information Processing Systems Foundation, Inc.: La Jolla, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sutskever, I.; Vinyals, O.; Le, Q.V. Sequence to sequence learning with neural networks. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 27; Ghahramani, Z., Welling, M., Cortes, C., Lawrence, N., Weinberg, K.Q., Eds.; Neural Information Processing Systems Foundation, Inc.: La Jolla, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Li, B.; Xiao, T.; Zhu, J.; Li, C.; Wong, D.F.; Chao, L.S. Learning deep transformer models for machine translation. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.01787. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Lapata, M. Text summarization with pretrained encoders. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1908.08345. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Zhu, L.; Liu, P.; Yang, Y. Entangled transformer for image captioning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 8928–8937. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Yao, P.; Guo, L.; Zhang, W. Boosted transformer for image captioning. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suthaharan, S.; Suthaharan, S. Support vector machine. In Machine Learning Models and Algorithms for Big Data Classification: Thinking with Examples for Effective Learning; Springer Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 207–235. [Google Scholar]
- Rosset, S.; Zhu, J.; Hastie, T. Margin maximizing loss functions. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 16; Thrun, S., Saul, L., Schölkopf, B., Eds.; Neural Information Processing Systems Foundation, Inc.: La Jolla, CA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Belgiu, M.; Drăguţ, L. Random forest in remote sensing: A review of applications and future directions. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 114, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoxha, G.; Chouaf, S.; Melgani, F.; Smara, Y. Change captioning: A new paradigm for multitemporal remote sensing image analysis. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5627414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
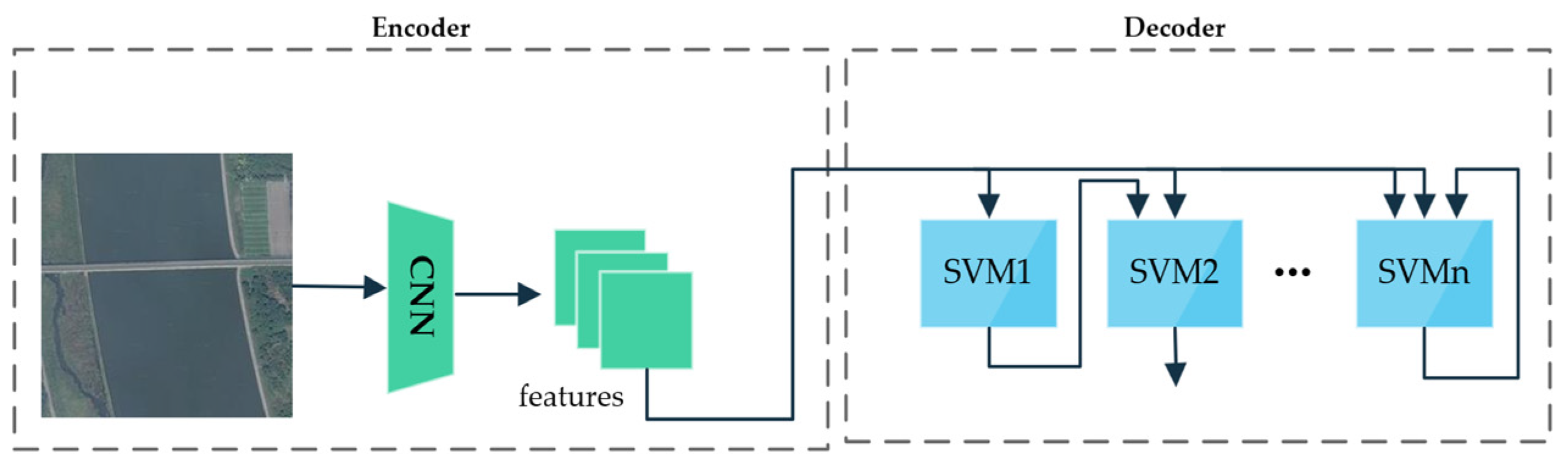
- Hoxha, G.; Melgani, F. A novel SVM-based decoder for remote sensing image captioning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 5404514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, K.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yu, H.; Sun, X. Boosting memory with a persistent memory mechanism for remote sensing image captioning. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, Z.; Ma, A.; Zhong, Y. Capformer: Pure transformer for remote sensing image caption. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 17–22 July 2022; pp. 7996–7999. [Google Scholar]
- Han, K.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Chen, X.; Guo, J.; Liu, Z.; Tang, Y.; Xiao, A.; Xu, C.; Xu, Y. A survey on vision transformer. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 45, 87–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. aXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.04805. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Zhao, R.; Shi, Z. Remote-sensing image captioning based on multilayer aggregated transformer. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 6506605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Q.; Chen, S.; Li, X. Multi-scale cropping mechanism for remote sensing image captioning. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 28 July–2 August 2019; pp. 10039–10042. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos, R.; Martins, B. Using neural encoder-decoder models with continuous outputs for remote sensing image captioning. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 24852–24863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, J.; Ma, A.; Zhong, Y. TypeFormer: Multiscale transformer with type controller for remote sensing image caption. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 6514005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoxha, G.; Scuccato, G.; Melgani, F. Improving image captioning systems with postprocessing strategies. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5612013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galassi, A.; Lippi, M.; Torroni, P. Attention in natural language processing. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2020, 32, 4291–4308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Ba, J.; Kiros, R.; Cho, K.; Courville, A.; Salakhudinov, R.; Zemel, R.; Bengio, Y. Show, attend and tell: Neural image caption generation with visual attention. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 6–11 July 2015; pp. 2048–2057. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, P.; He, X.; Buehler, C.; Teney, D.; Johnson, M.; Gould, S.; Zhang, L. Bottom-up and top-down attention for image captioning and visual question answering. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 6077–6086. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.; Wang, W.; Chen, J.; Wei, X.Y. Attention on attention for image captioning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 4634–4643. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.; Xiong, C.; Parikh, D.; Socher, R. Knowing when to look: Adaptive attention via a visual sentinel for image captioning. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 375–383. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Diao, W.; Yan, M.; Gao, X.; Sun, X. VAA: Visual aligning attention model for remote sensing image captioning. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 137355–137364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
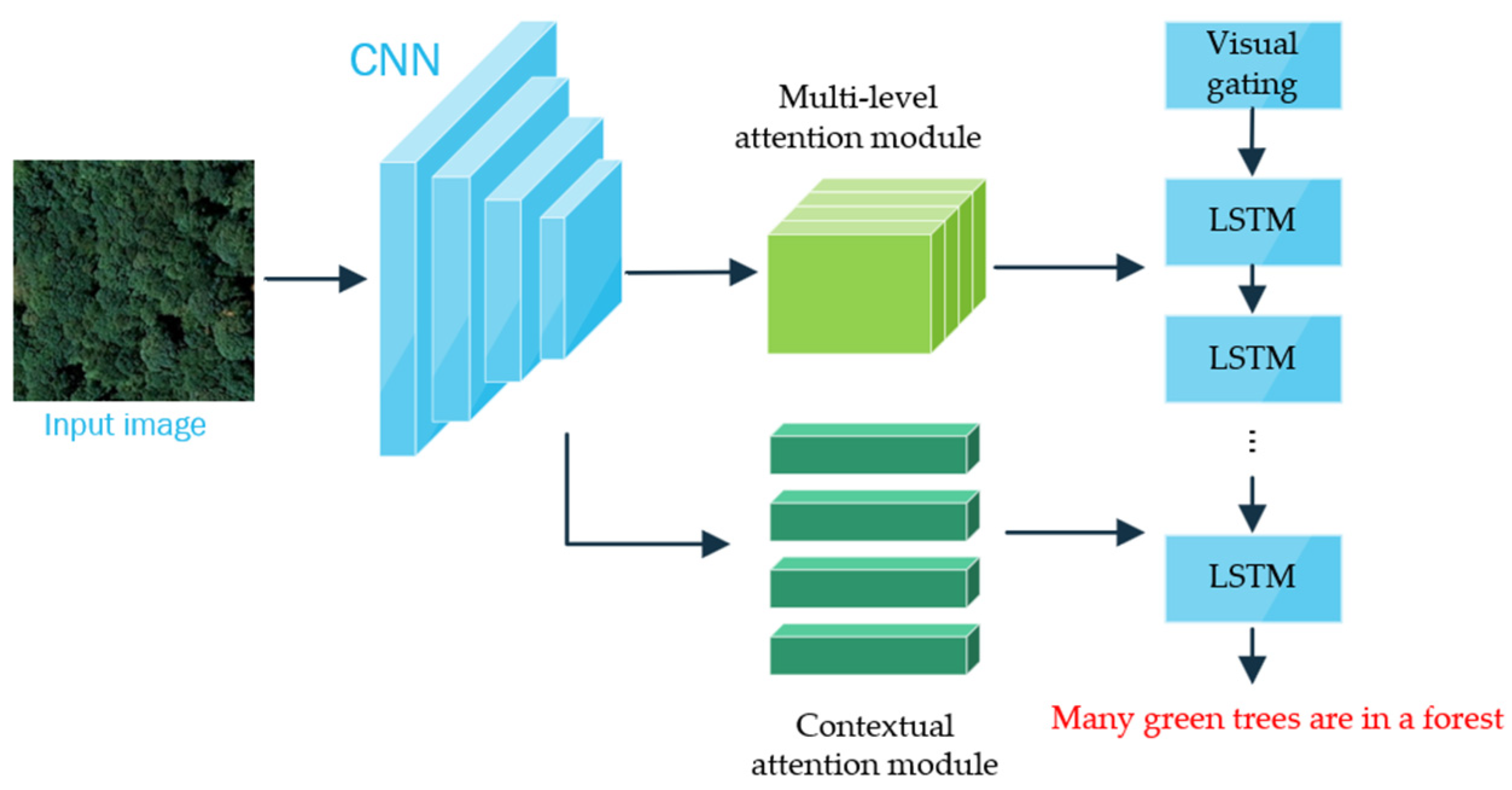
- Li, Y.; Fang, S.; Jiao, L.; Liu, R.; Shang, R. A multi-level attention model for remote sensing image captions. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, X.; Tang, X.; Jiao, L. Learning consensus-aware semantic knowledge for remote sensing image captioning. Pattern Recognit. 2024, 145, 109893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Huang, H.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, Z. NWPU-captions dataset and MLCA-net for remote sensing image captioning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5629419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Shao, Z.; Cheng, Q.; Huang, X.; Wu, X.; Li, G.; Tan, L. MC-Net: Multi-scale contextual information aggregation network for image captioning on remote sensing images. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2023, 16, 4848–4866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, F.; Wu, Z.; Cheng, X.; Jiao, L. Multi-source interactive stair attention for remote sensing image captioning. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Qi, H.; Dai, J.; Ji, X.; Wei, Y. Fully convolutional instance-aware semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision And Pattern Recognition, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2359–2367. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Jiang, Z.; Yuan, Y. Instance-aware remote sensing image captioning with cross-hierarchy attention. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2020-2020 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Online, 26 September–2 October 2020; pp. 980–983. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Zhao, R.; Shi, Z. Multiscale methods for optical remote-sensing image captioning. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 18, 2001–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, X.; Sun, X. Multiscale multiinteraction network for remote sensing image captioning. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 2154–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Carass, A.; Zuo, L.; Dewey, B.E.; Prince, J.L. Self domain adapted network. In Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2020: 23rd International Conference, Lima, Peru, October 4–8, 2020, Proceedings, Part I 23; Springer International Publishing: Berlin, Germany, 2020; pp. 437–446. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, Q. Exploring multi-level attention and semantic relationship for remote sensing image captioning. IEEE Access 2019, 8, 2608–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Gu, Y.; Ye, X.; Tian, J.; Wang, S.; Zhang, H.; Hou, B.; Jiao, L. Multi-view attention network for remote sensing image captioning. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium IGARSS, Brussels, Belgium, 11–16 July 2021; pp. 2349–2352. [Google Scholar]
- Zia, U.; Riaz, M.M.; Ghafoor, A. Transforming remote sensing images to textual descriptions. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 108, 102741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornia, M.; Stefanini, M.; Baraldi, L.; Cucchiara, R. Meshed-memory transformer for image captioning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 10578–10587. [Google Scholar]
- Gajbhiye, G.O.; Nandedkar, A.V. Generating the captions for remote sensing images: A spatial-channel attention-based memory-guided transformer approach. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2022, 114, 105076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, R.; Cao, W.; Zhang, W.; Zhi, G.; Sun, X.; Li, S.; Li, J. From Plane to Hierarchy: Deformable Transformer for Remote Sensing Image Captioning. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote. Sens. 2023, 16, 7704–7717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, L.; Jiao, L.; Liu, F.; Liu, X.; Yang, S. TrTr-CMR: Cross-Modal Reasoning Dual Transformer for Remote Sensing Image Captioning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5643912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, L.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Xiao, L. Prior Knowledge-Guided Transformer for Remote Sensing Image Captioning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2023, 61, 4706213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Wang, J.; Meng, R.; Yang, Y.; Xiao, L. A Multiscale Grouping Transformer With CLIP Latents for Remote Sensing Image Captioning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2024, 62, 4703515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Xiong, W. Exploring region features in remote sensing image captioning. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2024, 127, 103672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Li, Z.; Song, B.; Chi, Y. TSFE: Two-Stage Feature Enhancement for Remote Sensing Image Captioning. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Xiong, W. Cooperative Connection Transformer for Remote Sensing Image Captioning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2024, 62, 5607314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Wang, Y.; Yap, K.H. Interactive change-aware transformer network for remote sensing image change captioning. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Gao, J.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, Q. Single-Stream Extractor Network With Contrastive Pre-Training for Remote-Sensing Change Captioning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2024, 62, 5624514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yang, J.; Qi, Z.; Zou, Z.; Shi, Z. Progressive scale-aware network for remote sensing image change captioning. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2023–2023 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Pasadena, CA, USA, 16–21 July 2023; pp. 6668–6671. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Tang, X.; Zhou, H.; Li, C. Description Generation for Remote Sensing Images Using Attribute Attention Mechanism. Remote. Sens. 2019, 11, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Jia, Y.; Chen, J.; Ji, X. GAF-Net: Global view guided attribute fusion network for remote sensing image captioning. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 22409–22431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Gu, J.; Li, C.; Wang, X.; Tang, X.; Jiao, L. Recurrent attention and semantic gate for remote sensing image captioning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 5608816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Yan, M.; Gao, X.; Fu, K.; Sun, X. Global visual feature and linguistic state guided attention for remote sensing image captioning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 5615216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Huang, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, X. GLCM: Global–Local Captioning Model for Remote Sensing Image Captioning. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2022, 53, 6910–6922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Diao, W.; Zhang, W.; Yan, M.; Gao, X.; Sun, X. LAM: Remote sensing image captioning with label-attention mechanism. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.; Wu, Z.; Jin, H.; Li, X. Remote Sensing Image Captioning with Multi-Scale Feature and Small Target Attention. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2024–2024 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Athens, Greece, 7–12 July 2024; pp. 7436–7439. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Wang, B.; Zheng, X. Sound active attention framework for remote sensing image captioning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 58, 1985–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul, Z.K.; Al-Talabani, A.K. Mel frequency cepstral coefficient and its applications: A review. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 122136–122158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Parkes, D.C.; Chen, Y. Policy teaching through reward function learning. In Proceedings of the 10th ACM Conference on Electronic Commerce, Stanford, CA, USA, 6–10 July 2009; pp. 295–304. [Google Scholar]
- Arulkumaran, K.; Deisenroth, M.P.; Brundage, M.; Bharath, A.A. Deep reinforcement learning: A brief survey. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2017, 34, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Huang, W.; Wang, Q. Truncation cross entropy loss for remote sensing image captioning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 59, 5246–5257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Goyal, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Dollár, P. Focal loss for dense object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2980–2988. [Google Scholar]
- Rennie, S.J.; Marcheret, E.; Mroueh, Y.; Ross, J.; Goel, V. Self-critical sequence training for image captioning. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 7008–7024. [Google Scholar]
- Ranzato, M.A.; Chopra, S.; Auli, M.; Zaremba, W. Sequence level training with recurrent neural networks. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1511.06732. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, R. A better variant of self-critical sequence training. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.09971. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Z.; Gou, S.; Guo, Z.; Mao, S.; Li, R. A mask-guided transformer network with topic token for remote sensing image captioning. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drenkow, N.; Sani, N.; Shpitser, I.; Unberath, M. A systematic review of robustness in deep learning for computer vision: Mind the gap? arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.00639. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Sung, F.; Liu, F.; Xiang, T.; Gong, S.; Yang, Y.; Hospedales, T.M. Actor-critic sequence training for image captioning. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.09601. [Google Scholar]
- Creswell, A.; White, T.; Dumoulin, V.; Arulkumaran, K.; Sengupta, B.; Bharath, A.A. Generative adversarial networks: An overview. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2018, 35, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, X.; Cao, Y.; Yuan, X.; Kang, Y.; Song, W. Disastergan: Generative adversarial networks for remote sensing disaster image generation. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfau, D.; Vinyals, O. Connecting generative adversarial networks and actor-critic methods. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1610.01945. [Google Scholar]
- Chavhan, R.; Banerjee, B.; Zhu, X.X.; Chaudhuri, S. A novel actor dual-critic model for remote sensing image captioning. In Proceedings of the 2020 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Milan, Italy, 10–15 January 2020; pp. 4918–4925. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, Y.; Chen, Y.; Shi, X. A multi-task approach for improving biomedical named entity recognition by incorporating multi-granularity information. In Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: ACL-IJCNLP 2021; Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL): Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2021; pp. 4804–4813. [Google Scholar]
- Ruder, S. An overview of multi-task learning in deep neural networks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.05098. [Google Scholar]
- Toshniwal, S.; Tang, H.; Lu, L.; Livescu, K. Multitask learning with low-level auxiliary tasks for encoder-decoder based speech recognition. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.01631. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q. Three challenges in data mining. Front. Comput. Sci. China 2010, 4, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Chen, K.; Qi, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zou, Z.; Shi, Z. Pixel-level change detection pseudo-label learning for remote sensing change captioning. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Athens, Greece, 7–12 July 2024; pp. 8405–8408. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, M.; Yang, G.; Zhang, H. Transition is a process: Pair-to-video change detection networks for very high resolution remote sensing images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2022, 32, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Sun, B.; Li, S. Detection Assisted Change Captioning for Remote Sensing Image. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Athens, Greece, 7–12 July 2024; pp. 10454–10458. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, Z.; Zong, Z.; Ren, P. Incorporating object counts into remote sensing image captioning. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2024, 17, 2392847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Yang, W.; Chen, D.; Wei, F. DFEN: Dual feature enhancement network for remote sensing image caption. Electron. 2023, 12, 1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.C.; Hemalatha, M.; Narayan, S.B.; Nandhini, P. Region driven remote sensing image captioning. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2019, 165, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandala, H.; Saha, S.; Banerjee, B.; Zhu, X.X. Exploring transformer and multilabel classification for remote sensing image captioning. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 6514905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Wang, S.; Gu, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, R.; Hou, B.; Giunchiglia, F.; Jiao, L. A joint-training two-stage method for remote sensing image captioning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 4709616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Ni, Z.; Ren, P. Meta captioning: A meta learning based remote sensing image captioning framework. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2022, 186, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoxha, G.; Melgani, F.; Slaghenauffi, J. A new CNN-RNN framework for remote sensing image captioning. In Proceedings of the 2020 Mediterranean and Middle-East Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (M2GARSS), Tunis, Tunisia, 9–11 March 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhary, C.L.; Goyal, A.; Vasnani, B.K. Experimental assessment of beam search algorithm for improvement in image caption generation. J. Appl. Sci. Eng. 2019, 22, 691–698. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Zheng, X.; Qu, B.; Lu, X. Retrieval topic recurrent memory network for remote sensing image captioning. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 256–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; He, X.; Yao, M.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Hao, Y.; Wu, W.; Zhao, H.; Chen, X.; Cui, W. Landslide image captioning method based on semantic gate and bi-temporal LSTM. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumbul, G.; Nayak, S.; Demir, B. SD-RSIC: Summarization-driven deep remote sensing image captioning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 59, 6922–6934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobry, S.; Marcos, D.; Murray, J.; Tuia, D. RSVQA: Visual question answering for remote sensing data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 8555–8566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murali, N.; Shanthi, A.P. Remote sensing image captioning via multilevel attention-based visual question answering. In Innovations in Computational Intelligence and Computer Vision: Proceedings of ICICV 2021; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2022; pp. 465–475. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, K.; Yang, J.; Loy, C.C.; Liu, Z. Learning to prompt for vision-language models. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2022, 130, 2337–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achiam, J.; Adler, S.; Agarwal, S.; Ahmad, L.; Akkaya, I.; Aleman, F.L.; Almeida, D.; Altenschmidt, J.; Altman, S.; Anadkat, S.; et al. Gpt-4 technical report. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.08774. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Li, C.; Li, Y.; Lee, Y.J. Improved Baselines with Visual Instruction Tuning. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.03744. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Zhu, D.; Shen, X.; Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, P.; Krishnamoorthi, R.; Chandra, V.; Xiong, Y.; Elhoseiny, M. Minigpt-v2: Large language model as a unified interface for vision-language multi-task learning. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.09478. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Sun, Q. Towards Automatic Satellite Images Captions Generation Using Large Language Models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.11392. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Tworek, J.; Jun, H.; Yuan, Q.; Pinto, H.P.D.O.; Kaplan, J.; Edwards, H.; Burda, Y.; Joseph, N.; Brockman, G.; et al. Evaluating large language models trained on code. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.03374. [Google Scholar]
- Pettie, S.; Ramachandran, V. An optimal minimum spanning tree algorithm. JACM 2002, 49, 16–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.; Yuan, W.; Luo, J.; Zhang, W.; Lu, L. VLCA: Vision-language aligning model with cross-modal attention for bilingual remote sensing image captioning. J. Syst. Eng. Electron. 2023, 34, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Hsiang, J. Patent claim generation by fine-tuning OpenAI GPT-2. World Pat. Inf. 2020, 62, 101983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, R.; Melgani, F.; Junior, J.M.; Gonçalves, W.N. NLP-Based Fusion Approach to Robust Image Captioning. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 11809–11822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Yuan, J.; Wen, C.; Lu, X.; Li, X. Rsgpt: A remote sensing vision language model and benchmark. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.15266. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, W.; Li, J.; Li, D.; Tiong, A.M.H.; Zhao, J.; Wang, W.; Li, B.; Fung, P.N.; Hoi, S. Instructblip: Towards general-purpose vision-language models with instruction tuning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2024, 36, 49250–49267. [Google Scholar]
- Bazi, Y.; Bashmal, L.; Al Rahhal, M.M.; Ricci, R.; Melgani, F. RS-LLaVA: A Large Vision-Language Model for Joint Captioning and Question Answering in Remote Sensing Imagery. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, E.J.; Shen, Y.; Wallis, P.; Allen-Zhu, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Chen, W. LoRA: Low-Rank Adaptation of Large Language Models. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2106.09685. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, J.D.; Magalhães, J.; Tuia, D.; Martins, B. Large Language Models for Captioning and Retrieving Remote Sensing Images. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.06475. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Li, C.; Wu, Q.; Lee, Y.J. Visual instruction tuning. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 36; Oh, A., Naumann, T., Globerson, A., Saenko, K., Hardt, M., Levine, S., Eds.; Neural Information Processing Systems Foundation, Inc.: La Jolla, CA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, S.; Fu, C.; Zhao, S.; Li, K.; Sun, X.; Xu, T.; Chen, E. A survey on multimodal large language models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2306.13549. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Yuan, Y. Skyeyegpt: Unifying remote sensing vision-language tasks via instruction tuning with large language model. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.09712. [Google Scholar]
- Kuckreja, K.; Danish, M.S.; Naseer, M.; Das, A.; Khan, S.; Khan, F.S. Geochat: Grounded large vision-language model for remote sensing. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 17–21 June 2024; pp. 27831–27840. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Wong, C.; Zhang, S.; Usuyama, N.; Liu, H.; Yang, J.; Naumann, T.; Poon, H.; Gao, J. Llava-med: Training a large language-and-vision assistant for biomedicine in one day. In Advances in Neural Information Processing 36; Oh, A., Naumann, T., Globerson, A., Saenko, K., Hardt, M., Levine, S., Eds.; Neural Information Processing Systems Foundation, Inc.: La Jolla, CA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, J.; Du, B.; Xu, M.; Liu, L.; Tao, D.; Zhang, L. Samrs: Scaling-up remote sensing segmentation dataset with segment anything model. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 36; Oh, A., Naumann, T., Globerson, A., Saenko, K., Hardt, M., Levine, S., Eds.; Neural Information Processing Systems Foundation, Inc.: La Jolla, CA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Chiang, W.L.; Li, Z.; Lin, Z.; Sheng, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, L.; Zhuang, S.; Zhuang, Y.; Gonzalez, J.E. Vicuna: An Open-source Chatbot Impressing Gpt-4 with 90%* Chatgpt Quality. Available online: https://vicuna.lmsys.org (accessed on 14 April 2023).
- Zhang, W.; Cai, M.; Zhang, T.; Zhuang, Y.; Mao, X. Earthgpt: A universal multi-modal large language model for multi-sensor image comprehension in remote sensing domain. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5917820. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Chen, D.; Guan, Z.; Zhou, X.; Zhu, J.; Ye, Q.; Fu, L.; Zhou, J. Remoteclip: A vision language foundation model for remote sensing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5917820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Zhang, W.; Fu, K.; Li, X.; Deng, C.; Wang, H.; Sun, X. Exploring a fine-grained multiscale method for cross-modal remote sensing image retrieval. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2204.09868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, P.; Singh, R.; Sharma, A. Deep learning-based object detection in low-altitude UAV datasets: A survey. Image Vis. Comput. 2020, 104, 104046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Chen, K.; Zhang, H.; Qi, Z.; Zou, Z.; Shi, Z. Change-Agent: Toward Interactive Comprehensive Remote Sensing Change Interpretation and Analysis. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2024, 62, 5635616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yao, Q.; Kwok, J.T.; Ni, L.M. Generalizing from a few examples: A survey on few-shot learning. ACM Comput. Surv. 2020, 53, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Jiang, M.; Zhao, Q. Self-distillation for few-shot image captioning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Online, 5–9 January 2021; pp. 545–555. [Google Scholar]
- Allen-Zhu, Z.; Li, Y. Towards understanding ensemble, knowledge distillation and self-distillation in deep learning. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2012.09816. [Google Scholar]
- Barraco, M.; Stefanini, M.; Cornia, M.; Cascianelli, S.; Baraldi, L.; Cucchiara, R. CaMEL: Mean teacher learning for image captioning. In Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Montreal, QC, Canada, 21–25 August 2022; pp. 4087–4094. [Google Scholar]
- Laina, I.; Rupprecht, C.; Navab, N. Towards unsupervised image captioning with shared multimodal embeddings. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 7414–7424. [Google Scholar]
- Rusu, A.A.; Rao, D.; Sygnowski, J.; Vinyals, O.; Pascanu, R.; Osindero, S.; Hadsell, R. Meta-learning with latent embedding optimization. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.05960. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Du, X.; Xia, L.; Li, S. Self-learning for few-shot remote sensing image captioning. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Xia, L.; Du, X.; Li, S. FRIC: A framework for few-shot remote sensing image captioning. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2024, 17, 2337240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plummer, B.A.; Wang, L.; Cervantes, C.M.; Caicedo, J.C.; Hockenmaier, J.; Lazebnik, S. Flickr30k entities: Collecting region-to-phrase correspondences for richer image-to-sentence models. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 2641–2649. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft coco: Common objects in context. In Computer Vision–ECCV 2014: 13th European Conference, Zurich, Switzerland, September 6–12, 2014, Proceedings, Part V; Springer International Publishing: Berlin, Germany, 2014; pp. 740–755. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Zhao, R.; Chen, H.; Zou, Z.; Shi, Z. Remote sensing image change captioning with dual-branch transformers: A new method and a large scale dataset. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5633520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masek, J.G.; Honzak, M.; Goward, S.N.; Liu, P.; Pak, E. Landsat-7 ETM+ as an observatory for land cover: Initial radiometric and geometric comparisons with Landsat-5 Thematic Mapper. Remote Sens. Environ. 2001, 78, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Newsam, S. Bag-of-visual-words and spatial extensions for land-use classification. In Proceedings of the 18th SIGSPATIAL International Conference on Advances in Geographic Information Systems, San Jose, CA, USA, 2–5 November 2010; pp. 270–279. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Du, B.; Zhang, L. Saliency-guided unsupervised feature learning for scene classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 53, 2175–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Shi, Z. A spatial-temporal attention-based method and a new dataset for remote sensing image change detection. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papineni, K.; Roukos, S.; Ward, T.; Zhu, W.J. Bleu: A method for automatic evaluation of machine translation. In Proceedings of the 40th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 6–12 July 2002; pp. 311–318. [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee, S.; Lavie, A. METEOR: An automatic metric for MT evaluation with improved correlation with human judgments. In Proceedings of the ACL Workshop on Intrinsic and Extrinsic Evaluation Measures for Machine Translation and/or Summarization, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 29 June 2005; pp. 65–72. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.Y.; Och, F.J. Looking for a few good metrics: ROUGE and its evaluation. In Proceedings of the 4th NTCIR Workshop, Tokyo, Japan, 2–4 June 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Vedantam, R.; Lawrence Zitnick, C.; Parikh, D. Cider: Consensus-based image description evaluation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 4566–4575. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, P.; Fernando, B.; Johnson, M.; Gould, S. Spice: Semantic propositional image caption evaluation. In Computer Vision–ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, October 11–14, 2016, Proceedings, Part V; Springer International Publishing: Berlin, Germany, 2016; pp. 382–398. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, B.; Linder, F.; Mebane, W.R., Jr. Active learning approaches for labeling text: Review and assessment of the performance of active learning approaches. Political Anal. 2020, 28, 532–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, V.; Sumanathilaka, T.G.D.K. A Survey on Image Captioning Using Object Detection and NLP. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Advanced Research in Computing, Belihuloya, Sri Lanka, 21–24 February 2024; pp. 270–275. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, F.; Yu, Z.; Zhao, H.; Wang, T.; Bai, T. Integrating grid features and geometric coordinates for enhanced image captioning. Appl. Intell. 2024, 54, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Liu, J.; Zhu, X.; Yao, P.; Lu, S.; Lu, H. Normalized and geometry-aware self-attention network for image captioning. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 10327–10336. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Y.; Duan, J.; Xu, K.; Cai, Y.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, Y. A survey on large language model (llm) security and privacy: The good, the bad, and the ugly. High-Confid. Comput. 2024, 4, 100211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.; Zhang, B.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Li, C.; Yao, J.; Yokoya, N.; Li, H.; Ghamisi, P.; Jia, X.; et al. SpectralGPT: Spectral remote sensing foundation model. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2024, 46, 5227–5244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Ghamisi, P. Changes to captions: An attentive network for remote sensing change captioning. IEEE Trans. Image Processing 2023, 32, 6047–6060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhao, R.; Chen, J.; Qi, Z.; Zou, Z.; Shi, Z. A decoupling paradigm with prompt learning for remote sensing image change captioning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5622018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Jian, P.; Mao, Z.; Zhao, Y. Change Captioning for Satellite Images Time Series. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2024, 21, 6006905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Lei, L.; Guan, D.; Kuang, G.; Li, Z.; Liu, L. Locality Preservation for Unsupervised Multimodal Change Detection in Remote Sensing Imagery. In IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.; Guan, D.; Li, B.; Chen, Z.; Li, X. Change smoothness-based signal decomposition method for multimodal change detection. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 2507605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Xu, Y.; Huang, Z. VCC-DiffNet: Visual Conditional Control Diffusion Network for Remote Sensing Image Captioning. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Li, Z.; Zhang, L. Bootstrapping interactive image-text alignment for remote sensing image captioning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5607512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Li, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, Q. HCNet: Hierarchical Feature Aggregation and Cross-Modal Feature Alignment for Remote Sensing Image Captioning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5624711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, A.; Baise, L.G.; Koch, M.; Moaveni, B.; Chatterjee, S.; Aimaiti, Y. Pixel-based classification method for earthquake-induced landslide mapping using remotely sensed imagery, geospatial data and temporal change information. Nat. Hazards 2024, 120, 5163–5200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amitrano, D.; Di Martino, G.; Di Simone, A.; Imperatore, P. Flood Detection with SAR: A Review of Techniques and Datasets. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Yao, Y. Mountain Vegetation Classification Method Based on Multi-Channel Semantic Segmentation Model. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, P.; Chen, C.; Zhang, D.; Sang, Y.; Zhang, L. Semantic segmentation of deep learning remote sensing images based on band combination principle: Application in urban planning and land use. Comput. Commun. 2024, 217, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, G.; Tonderski, A.; Petersson, C.; Åström, K.; Svensson, L. Lidarclip or: How I learned to talk to point clouds. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2024; pp. 7438–7447. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Lei, L.; Li, Z.; Kuang, G. Similarity and dissimilarity relationships based graphs for multimodal change detection. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2024, 208, 70–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Li, P.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, J. A survey on deep learning for multimodal data fusion. Neural Comput. 2020, 32, 829–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| CNN | GFLOPs | Params |
|---|---|---|
| ResNet-50 [41] | 4.1 | 25.6 M |
| ResNet-101 [42] | 7.6 | 44.5 M |
| VGG-16 [43] | 15.5 | 138 M |
| VGG-19 [44] | 19.6 | 143 M |
| DenseNet121 [45] | 8 | 8 M |
| Dataset | Image | Captions | Category | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sydney-Captions [39] | 613 | 3065 | 7 | Minimum quantity |
| UCM-Captions [39] | 2100 | 10,500 | 21 | The simplest captions |
| RSICD [40] | 10,921 | 24,233 | 30 | Less than 5 captions per image, randomly supplemented |
| NWPU-Captions [83] | 31,500 | 157,500 | 45 | The largest in quantity, variety and vocabulary |
| LEVIR CC [188] | 20,154 | 50,385 | 5 | Five captions for a pair of images, reflecting changes in the image |
| LEVIR-CCD [64] | 1000 | 2500 | 13 | A small dataset annotated by annotators with RS background |
| Dubai CCD [64] | 1000 | 2500 | 6 | The image size is small |
| Evaluation Metrics | Advantages | Disadvantages | Application Scenarios |
|---|---|---|---|
| BLEU [193] | Easy to calculate | Does not consider semantic fluency or synonyms | Machine translation; image caption |
| METEOR [194] | Takes into account word meaning and grammatical structure | Too many hyperparameters; lack of suitability for multiple datasets | Machine translation; image caption |
| ROUGE [195] | Measures the repeatability and importance of words | Sensitive to length differences | Automatic summarization; image caption |
| CIDEr [196] | Considers semantic meaning, context and visual content | Complex calculations | Image caption |
| SPICE [188] | Focuses more on semantics; more consistent with humans | Ignores grammatical correctness | Image caption |
| [106] | Overall model evaluation | Less frequently utilized | Image caption |
| Methods | Models | BLEU-1 | BLEU-2 | BLEU-3 | BLEU-4 | METEOR | ROUGE | CIDEr | SPICE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Encoder– Decoder | Word-sentence [35] | 0.7891 | 0.7094 | 0.6317 | 0.5625 | 0.4181 | 0.6922 | 2.0411 | |
| DMSFF [48] | 0.8324 | 0.7489 | 0.6591 | 0.5851 | 0.7218 | 3.1898 | |||
| SVMs [62] | 0.7787 | 0.6835 | 0.6023 | 0.5305 | 0.3643 | 0.6746 | 2.2222 | ||
| PMM [66] | 0.8160 | 0.5560 | 0.4150 | 0.7360 | 2.3650 | 0.4300 | |||
| Attention mechanism | MLA [81] | 0.8057 | 0.7189 | 0.6448 | 0.5822 | 0.4665 | 0.7472 | 2.2028 | 0.4005 |
| VSCA [82] | 0.7908 | 0.7200 | 0.6605 | 0.6088 | 0.4031 | 0.7354 | 2.6788 | 0.4637 | |
| MC-Net [84] | 0.8340 | 0.7500 | 0.6780 | 0.6070 | 0.4060 | 0.7390 | 2.5640 | 0.4560 | |
| MSISAM [85] | 0.7643 | 0.6919 | 0.6283 | 0.5725 | 0.3946 | 0.7172 | 2.8122 | ||
| CHA [87] | 0.8170 | 0.7420 | 0.6570 | 0.5910 | 0.7210 | 2.2910 | |||
| MSMI [89] | 0.8420 | 0.7570 | 0.6720 | 0.6010 | 0.4210 | 0.7330 | 2.8510 | 0.4450 | |
| MAN [92] | 0.7723 | 0.5617 | 0.4020 | 0.7284 | 2.6137 | ||||
| Adaptive [93] | 0.8220 | 0.7410 | 0.6620 | 0.5940 | 0.3970 | 2.7050 | |||
| SCAMET [95] | 0.8072 | 0.7136 | 0.6431 | 0.5846 | 0.4614 | 0.7258 | 2.3570 | ||
| Deformable [96] | 0.8373 | 0.7771 | 0.7198 | 0.6659 | 0.4548 | 0.7860 | 3.0369 | 0.4839 | |
| TrTr-CMR [97] | 0.8270 | 0.6994 | 0.6002 | 0.5199 | 0.3803 | 0.7220 | 2.2728 | ||
| PKGT [99] | 0.8317 | 0.7783 | 0.7248 | 0.6824 | 0.4528 | 0.7706 | 2.8476 | 0.4405 | |
| MGT [100] | 0.8668 | 0.8087 | 0.7588 | 0.7122 | 0.4770 | 0.7970 | 3.2776 | 0.4809 | |
| RAT [101] | 0.8610 | 0.7900 | 0.7270 | 0.6700 | 0.4460 | 0.7870 | 2.8580 | ||
| TSFE [102] | 0.8279 | 0.7606 | 0.6951 | 0.6290 | 0.4228 | 0.7713 | 2.6561 | ||
| CCT [103] | 0.8660 | 0.7990 | 0.7470 | 0.6910 | 0.4600 | 0.7910 | 2.8670 | ||
| AA [107] | 0.8143 | 0.7351 | 0.6586 | 0.5806 | 0.4111 | 0.7195 | 2.3021 | ||
| GAF-Net [108] | 0.7950 | 0.7330 | 0.6590 | 0.6260 | 0.4580 | 0.7300 | 2.7720 | ||
| RASG [109] | 0.8000 | 0.7217 | 0.6531 | 0.5909 | 0.3908 | 0.7218 | 2.6311 | 0.4301 | |
| GVFGA [110] | 0.7681 | 0.6846 | 0.6145 | 0.5504 | 0.3866 | 0.7030 | 2.4522 | 0.4532 | |
| GLCM [111] | 0.8041 | 0.7305 | 0.6745 | 0.6259 | 0.4421 | 0.6965 | 2.4337 | ||
| LAM [112] | 0.7365 | 0.6440 | 0.5835 | 0.5348 | 0.3693 | 0.6827 | 2.3513 | 0.4351 | |
| STA [113] | 0.7910 | 0.7030 | 0.5920 | 0.5790 | 2.3060 | ||||
| SAA [114] | 0.7155 | 0.6323 | 0.5469 | 0.4660 | 0.3132 | 0.6035 | 1.8027 | 0.3865 | |
| Reinforcement learning | TCE [118] | 0.7937 | 0.7304 | 0.6717 | 0.6193 | 0.4430 | 0.7130 | 2.4042 | |
| SCST [120] | 0.8016 | 0.7095 | 0.6314 | 0.5724 | 0.4183 | 0.7262 | 2.5392 | ||
| Mask-CE [123] | 0.8338 | 0.7572 | 0.6772 | 0.5980 | 0.4346 | 0.7660 | 2.6982 | ||
| Other auxiliary tasks | Object Count [138] | 0.8659 | 0.8532 | 0.7625 | 0.7162 | 0.5936 | 0.7660 | 2.6887 | 0.7355 |
| DFEN [139] | 0.7980 | 0.6970 | 0.6140 | 0.5420 | 0.3730 | 0.7230 | 2.0090 | 0.4490 | |
| JTTS [142] | 0.6518 | 0.4327 | 0.7474 | 2.8102 | 0.4729 | ||||
| Meta capton [143] | 0.8531 | 0.7915 | 0.7344 | 0.6800 | 0.4303 | 0.7417 | 2.6660 | 0.4359 | |
| CRSR [51] | 0.7994 | 0.7440 | 0.6987 | 0.6602 | 0.4150 | 0.7488 | 2.8900 | 0.4845 | |
| SAM [22] | 0.7795 | 0.7019 | 0.6392 | 0.5861 | 0.3954 | 0.7299 | 2.3791 | ||
| SD-RSIC [148] | 0.7610 | 0.6660 | 0.5860 | 0.5170 | 0.3660 | 0.6570 | 1.6900 | ||
| LLM | RSGPT [161] | 0.8226 | 0.7528 | 0.6857 | 0.6223 | 0.4137 | 0.7477 | 2.7308 | |
| RS-CapRet [165] | 0.7820 | 0.5450 | 2.3900 | 0.4230 | |||||
| SkyEyeGPT [168] | 0.9185 | 0.8564 | 0.8088 | 0.7740 | 0.4662 | 0.7774 | 1.8106 | ||
| Few-shot learning | SFRC [184] | 0.8256 | 0.7449 | 0.6678 | 0.5939 | 0.4349 | 0.7560 | 2.6388 | 0.4445 |
| FRIC [185] | 0.8239 | 0.7347 | 0.6582 | 0.5883 | 0.4241 | 0.7315 | 2.5539 | 0.4481 |
| Methods | Models | BLEU-1 | BLEU-2 | BLEU-3 | BLEU-4 | METEOR | ROUGE | CIDEr | SPICE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Encoder– Decoder | Word-sentence [35] | 0.7931 | 0.7237 | 0.6671 | 0.6202 | 0.4395 | 0.7132 | 2.7871 | |
| DMSFF [48] | 0.8306 | 0.7589 | 0.6972 | 0.6345 | 0.7318 | 3.2956 | |||
| SVMs [65] | 0.7653 | 0.6947 | 0.6417 | 0.5942 | 0.3702 | 0.6877 | 2.9228 | ||
| PMM [66] | 0.8620 | 0.7120 | 0.4820 | 0.8250 | 3.6540 | 0.5360 | |||
| Attention mechanism | MLA [81] | 0.8864 | 0.8233 | 0.7735 | 0.7271 | 0.5222 | 0.8441 | 3.3074 | 0.5021 |
| VSCA [82] | 0.8900 | 0.8416 | 0.7987 | 0.7575 | 0.4931 | 0.8478 | 3.8314 | 0.5227 | |
| MLCA-Net [83] | 0.8260 | 0.7700 | 0.7170 | 0.6680 | 0.4350 | 0.7720 | 3.2400 | 0.4730 | |
| MC-Net [84] | 0.8450 | 0.7840 | 0.7320 | 0.6790 | 0.4490 | 0.7860 | 3.3550 | 0.5200 | |
| MSISAM [85] | 0.8727 | 0.8096 | 0.7551 | 0.7039 | 0.4652 | 0.8258 | 3.7129 | ||
| CHA [87] | 0.8230 | 0.7680 | 0.7100 | 0.6590 | 0.7560 | 3.1920 | |||
| MSMI [89] | 0.8430 | 0.7750 | 0.7110 | 0.6510 | 0.4530 | 0.7850 | 3.3810 | 0.5240 | |
| MAN [92] | 0.8480 | 0.6642 | 0.4562 | 0.8065 | 3.3172 | ||||
| Adaptive [93] | 0.8390 | 0.7690 | 0.7150 | 0.6750 | 0.4460 | 3.2310 | |||
| SCAMET [95] | 0.8460 | 0.7772 | 0.7262 | 0.6812 | 0.5257 | 0.8166 | 3.3773 | ||
| Deformable [96] | 0.8230 | 0.7700 | 0.7228 | 0.6792 | 0.4439 | 0.7839 | 3.4629 | 0.4825 | |
| TrTr-CMR [97] | 0.8156 | 0.7091 | 0.6220 | 0.5469 | 0.3978 | 0.7442 | 2.4742 | ||
| PKGT [99] | 0.9048 | 0.8704 | 0.8410 | 0.8139 | 0.5466 | 0.8657 | 4.2749 | 0.5701 | |
| MGT [100] | 0.9128 | 0.8811 | 0.8537 | 0.8295 | 0.5601 | 0.8877 | 4.4839 | 0.5839 | |
| RAT [101] | 0.8950 | 0.8530 | 0.8110 | 0.7660 | 0.5030 | 0.8580 | 3.7930 | ||
| TSFE [102] | 0.8985 | 0.8546 | 0.8126 | 0.7645 | 0.4893 | 0.8800 | 3.6701 | ||
| CCT [103] | 0.9220 | 0.8900 | 0.8640 | 0.8330 | 0.5730 | 0.8830 | 4.1560 | ||
| GAF-Net [108] | 0.8690 | 0.8380 | 0.7870 | 0.7530 | 0.4790 | 0.8100 | 3.7760 | ||
| RASG [109] | 0.8518 | 0.7925 | 0.7432 | 0.6976 | 0.4571 | 0.8072 | 3.3887 | ||
| GVFGA [110] | 0.8319 | 0.7657 | 0.7102 | 0.6596 | 0.4436 | 0.7845 | 3.3270 | 0.4853 | |
| GLCM [111] | 0.8182 | 0.7540 | 0.6986 | 0.6468 | 0.4619 | 0.7524 | 3.0279 | ||
| LAM [112] | 0.8570 | 0.8120 | 0.7750 | 0.7430 | 0.5100 | 0.8260 | 3.7580 | 0.5350 | |
| STA [113] | 0.8170 | 0.7790 | 0.6130 | 0.6060 | 3.1990 | ||||
| SAA [114] | 0.7828 | 0.7276 | 0.6759 | 0.6333 | 0.3803 | 0.6864 | 2.9057 | 0.4194 | |
| Reinforcement learning | TCE [118] | 0.8210 | 0.7622 | 0.7140 | 0.6700 | 0.4775 | 0.7567 | 2.8547 | |
| SCST [120] | 0.8382 | 0.7901 | 0.7443 | 0.7011 | 0.4464 | 0.7763 | 3.5653 | ||
| Mask-CE [123] | 0.8936 | 0.8517 | 0.8057 | 0.7650 | 0.5138 | 0.8585 | 3.8992 | ||
| ADC [129] | 0.8533 | 0.7568 | 0.6785 | 0.6117 | 0.8324 | 0.8087 | 4.8650 | ||
| Other auxiliary tasks | Object Count [138] | 0.9233 | 0.9152 | 0.8863 | 0.8596 | 0.6235 | 0.8875 | 4.3622 | 0.6126 |
| DFEN [139] | 0.8510 | 0.7840 | 0.7280 | 0.6770 | 0.4590 | 0.8050 | 3.1770 | 0.5010 | |
| JTTS [142] | 0.7376 | 0.4906 | 0.8364 | 3.7102 | 0.5231 | ||||
| Meta capton [143] | 0.9185 | 0.8876 | 0.8603 | 0.8347 | 0.5401 | 0.8758 | 4.3311 | 0.5710 | |
| CRSR [51] | 0.9060 | 0.8561 | 0.8122 | 0.7681 | 0.4956 | 0.8586 | 3.8069 | 0.5201 | |
| SAM [22] | 0.8538 | 0.8035 | 0.7572 | 0.7149 | 0.4632 | 0.8141 | 3.3489 | ||
| SD-RSIC [148] | 0.7480 | 0.6640 | 0.5980 | 0.5380 | 0.3900 | 0.6950 | 2.1320 | ||
| LLM | RSGPT [161] | 0.8612 | 0.7914 | 0.7231 | 0.6574 | 0.4221 | 0.7834 | 3.3323 | |
| RS-LLaVA [165] | 0.9000 | 0.8488 | 0.8030 | 0.7603 | 0.4921 | 0.8578 | 3.5561 | ||
| RS-CapRet [168] | 0.8330 | 0.6450 | 3.4290 | 0.5250 | |||||
| Few-shot learning | SFRC [184] | 0.8856 | 0.8143 | 0.7778 | 0.7149 | 0.4706 | 0.8167 | 3.7595 | 0.5098 |
| FRIC [185] | 0.8665 | 0.8162 | 0.7683 | 0.7226 | 0.4771 | 0.8163 | 3.5589 | 0.5128 |
| Methods | Models | BLEU-1 | BLEU-2 | BLEU-3 | BLEU-4 | METEOR | ROUGE | CIDEr | SPICE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Encoder– Decoder | Word-sentence [35] | 0.7240 | 0.5861 | 0.4923 | 0.4250 | 0.3197 | 0.6260 | 2.0629 | |
| SA-FWC [43] | 0.7200 | 0.6000 | 0.5100 | 0.4300 | 0.3700 | 0.6500 | 2.8300 | ||
| VRTMM [50] | 0.7813 | 0.6721 | 0.5645 | 0.5123 | 0.3737 | 0.5713 | 2.7150 | ||
| SVMs [65] | 0.6112 | 0.4277 | 0.3153 | 0.2411 | 0.2303 | 0.4588 | 0.6825 | ||
| PMM [66] | 0.7360 | 0.4540 | 0.3730 | 0.6600 | 2.6340 | 0.4770 | |||
| Attention mechanism | MLA [81] | 0.8058 | 0.6778 | 0.5866 | 0.5163 | 0.4718 | 0.7237 | 2.7716 | 0.4786 |
| VSCA [82] | 0.7965 | 0.6856 | 0.5964 | 0.5224 | 0.3745 | 0.6833 | 2.9343 | 0.4914 | |
| MLCA-Net [83] | 0.7570 | 0.6430 | 0.5390 | 0.4610 | 0.3510 | 0.6460 | 2.3560 | 0.4440 | |
| MC-Net [84] | 0.7280 | 0.6060 | 0.5110 | 0.4330 | 0.3600 | 0.6410 | 2.4540 | 0.4630 | |
| MSISAM [85] | 0.7836 | 0.6679 | 0.5774 | 0.5042 | 0.3672 | 0.6730 | 2.8436 | ||
| CHA [87] | 0.7700 | 0.6490 | 0.5320 | 0.4710 | 0.6510 | 2.3630 | |||
| MSMI [89] | 0.7930 | 0.6810 | 0.5770 | 0.4980 | 0.3740 | 0.6820 | 2.7930 | 0.4910 | |
| MAN [92] | 0.7272 | 0.4436 | 0.3690 | 0.6575 | 2.5276 | ||||
| Adaptive [93] | 0.7980 | 0.6470 | 0.5690 | 0.4890 | 0.2850 | 2.4040 | |||
| SCAMET [95] | 0.7681 | 0.6309 | 0.5352 | 0.4611 | 0.4572 | 0.6979 | 2.4681 | ||
| Deformable [96] | 0.7581 | 0.6416 | 0.5585 | 0.4923 | 0.3550 | 0.6523 | 2.5814 | 0.4579 | |
| TrTr-CMR [97] | 0.6201 | 0.3937 | 0.2671 | 0.1932 | 0.2399 | 0.4895 | 0.7518 | ||
| PKGT [99] | 0.6967 | 0.5830 | 0.5045 | 0.4431 | 0.3332 | 0.6078 | 2.7401 | 0.4691 | |
| MGT [100] | 0.7027 | 0.5980 | 0.5208 | 0.4601 | 0.3417 | 0.6227 | 2.8510 | 0.4807 | |
| TSFE [102] | 0.8054 | 0.7064 | 0.6208 | 0.5486 | 0.3793 | 0.7020 | 3.0570 | ||
| CCT [103] | 0.7980 | 0.6930 | 0.6080 | 0.5330 | 0.3830 | 0.6920 | 2.8810 | ||
| GAF-Net [108] | 0.7920 | 0.6760 | 0.5820 | 0.5100 | 0.4020 | 0.7100 | 2.7920 | ||
| RASG [109] | 0.7729 | 0.6651 | 0.5782 | 0.5062 | 0.3626 | 0.6691 | 2.7549 | 0.4719 | |
| GVFGA [110] | 0.6779 | 0.5600 | 0.4781 | 0.4165 | 0.3285 | 0.5929 | 2.6012 | 0.4683 | |
| GLCM [111] | 0.7767 | 0.6492 | 0.5642 | 0.4937 | 0.3627 | 0.6779 | 2.5491 | ||
| LAM [112] | 0.6756 | 0.5549 | 0.4714 | 0.4077 | 0.3261 | 0.5848 | 2.6285 | 0.4671 | |
| STA [113] | 0.8130 | 0.6810 | 0.5410 | 0.4960 | 2.6950 | ||||
| SAA [114] | 0.6196 | 0.4819 | 0.3902 | 0.3195 | 0.2733 | 0.5143 | 1.6386 | 0.3598 | |
| Reinforcement learning | TCE [118] | 0.7608 | 0.6358 | 0.5471 | 0.4791 | 0.3425 | 0.6687 | 2.4665 | |
| SCST [120] | 0.7704 | 0.6549 | 0.5632 | 0.4882 | 0.3698 | 0.6696 | 2.6840 | ||
| Mask-CE [123] | 0.8042 | 0.6996 | 0.6136 | 0.5414 | 0.3937 | 0.7058 | 2.9839 | ||
| ADC [129] | 0.7397 | 0.5526 | 0.4635 | 0.4102 | 0.2213 | 0.7131 | 2.2430 | ||
| Other auxiliary tasks | Object Count [138] | 0.8221 | 0.7480 | 0.6999 | 0.6285 | 0.5289 | 0.7408 | 2.7522 | 0.5429 |
| DFEN [139] | 0.7660 | 0.6360 | 0.5380 | 0.4630 | 0.3730 | 0.6850 | 2.6050 | 0.4770 | |
| JTTS [142] | 0.5135 | 0.3773 | 0.6823 | 2.7958 | 0.4877 | ||||
| Meta capton [143] | 0.7067 | 0.5936 | 0.5119 | 0.4471 | 0.3394 | 0.6082 | 2.7425 | 0.4772 | |
| CRSR [51] | 0.8192 | 0.7171 | 0.6307 | 0.5574 | 0.4015 | 0.7134 | 3.0687 | 0.5276 | |
| SAM [22] | 0.7016 | 0.5614 | 0.4648 | 0.3934 | 0.3291 | 0.5706 | 1.7031 | ||
| SD-RSIC [148] | 0.6440 | 0.4740 | 0.3690 | 0.3000 | 0.2490 | 0.5230 | 0.7940 | ||
| VLLM | RSGPT [161] | 0.7032 | 0.5423 | 0.4402 | 0.3683 | 0.3010 | 0.5334 | 1.0294 | |
| RS-CapRet [165] | 0.7410 | 0.4550 | 2.6050 | 0.4840 | |||||
| SkyEyeGPT [168] | 0.8773 | 0.7770 | 0.6890 | 0.6199 | 0.3623 | 0.6354 | 0.8937 | ||
| Few-shot learning | SFRC [184] | 0.8009 | 0.6952 | 0.6084 | 0.5345 | 0.3882 | 0.6974 | 2.8727 | 0.5096 |
| FRIC [185] | 0.7925 | 0.6853 | 0.5977 | 0.5238 | 0.3912 | 0.6981 | 2.8830 | 0.5133 |
| Methods | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Encoder–Decoder | It serves as the foundation for all models and is highly susceptible enhancement | Limited capacity for improvement |
| Attention mechanism | It can help us more accurately focus on and utilize image features | High sensitivity to the resolution of images, and traditional dataset images tend to be blurry, which may lead to overfitting |
| Reinforcement learning | Enhanced model performance without the need for additional datasets | Increased demand for computing power |
| Learning with auxiliary tasks | More accurate object and attribute information, fewer errors | Most of them rely on pre-trained models, and double model training |
| LVLMs | It can be used in multi-tasks without training | High cost |
| Few-shot learning | It reduces reliance on datasets | Hard to achieve sota performance, and the effect is not obvious on small datasets. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, K.; Li, P.; Wang, J. A Review of Deep Learning-Based Remote Sensing Image Caption: Methods, Models, Comparisons and Future Directions. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4113. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16214113
Zhang K, Li P, Wang J. A Review of Deep Learning-Based Remote Sensing Image Caption: Methods, Models, Comparisons and Future Directions. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(21):4113. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16214113
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Ke, Peijie Li, and Jianqiang Wang. 2024. "A Review of Deep Learning-Based Remote Sensing Image Caption: Methods, Models, Comparisons and Future Directions" Remote Sensing 16, no. 21: 4113. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16214113
APA StyleZhang, K., Li, P., & Wang, J. (2024). A Review of Deep Learning-Based Remote Sensing Image Caption: Methods, Models, Comparisons and Future Directions. Remote Sensing, 16(21), 4113. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16214113






