The Impact of Consecutive Tropical Cyclones on Changes in Environmental Factors and Phytoplankton Distributions in Overlapping Areas
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Data
2.1.1. Typhoon Tracks
2.1.2. Satellite Data
2.1.3. Reanalysis and Model Simulation Data
2.1.4. In Situ Data
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Calculation of Ekman Pumping Velocity
2.2.2. Calculation of Depth-Integrated Chl-a
3. Results
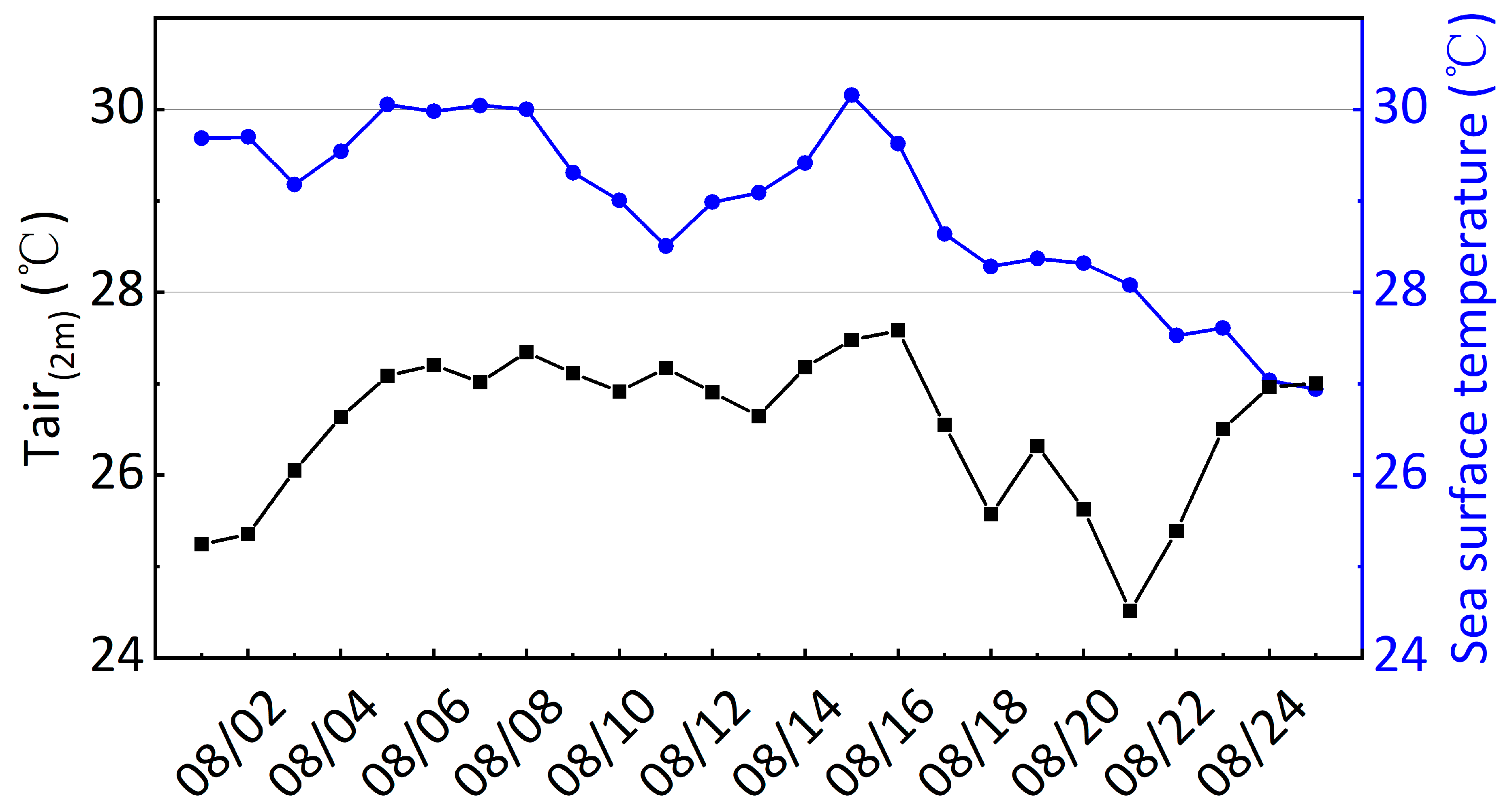
3.1. Temporal Variations in Temperature and Salinity
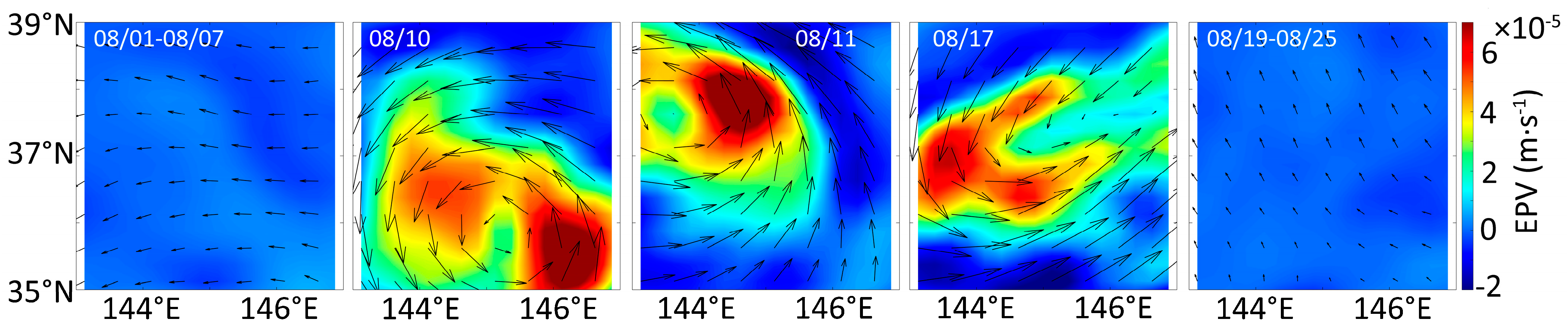
3.2. Variations in Wind, EPV, MLD, and Total Precipitation
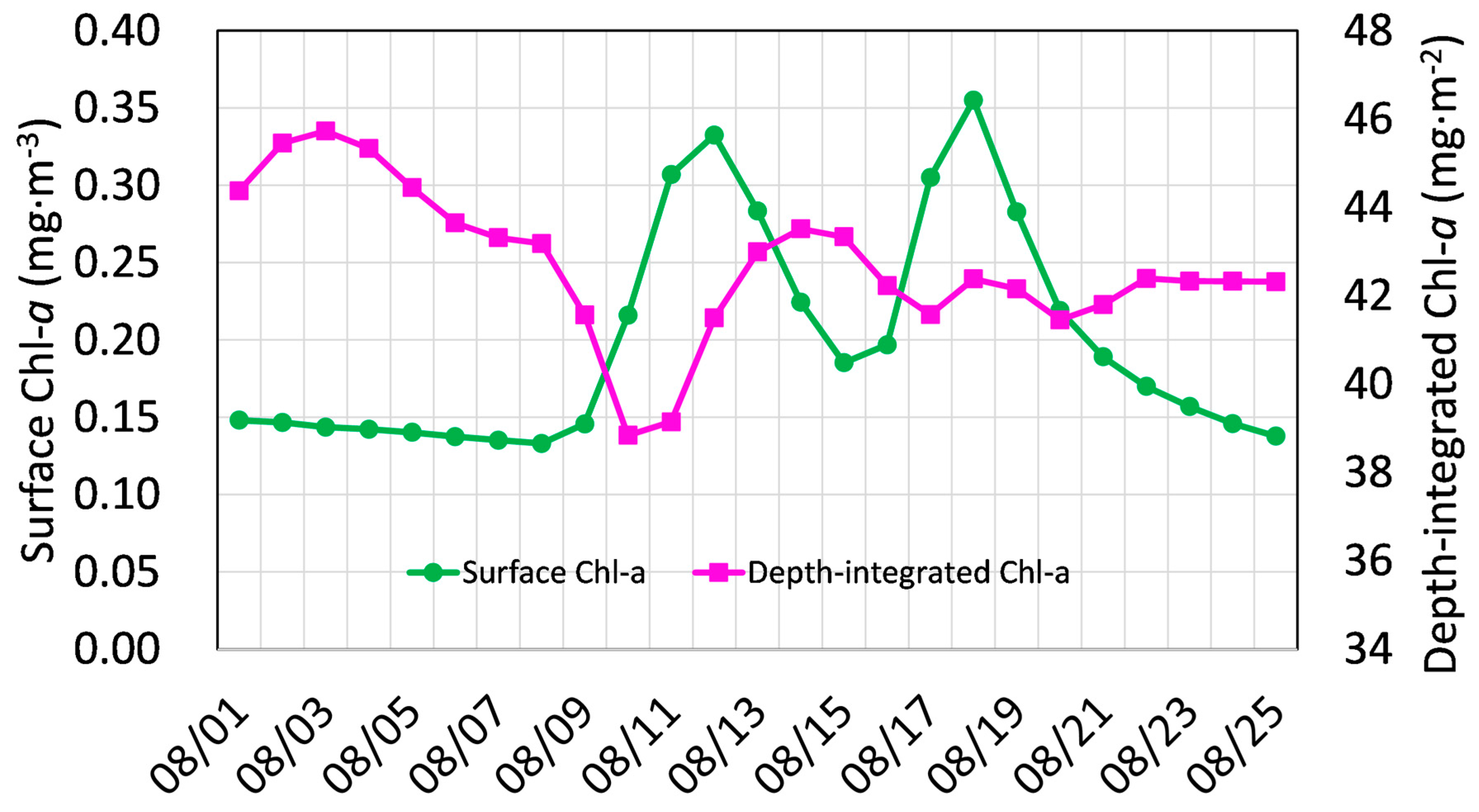
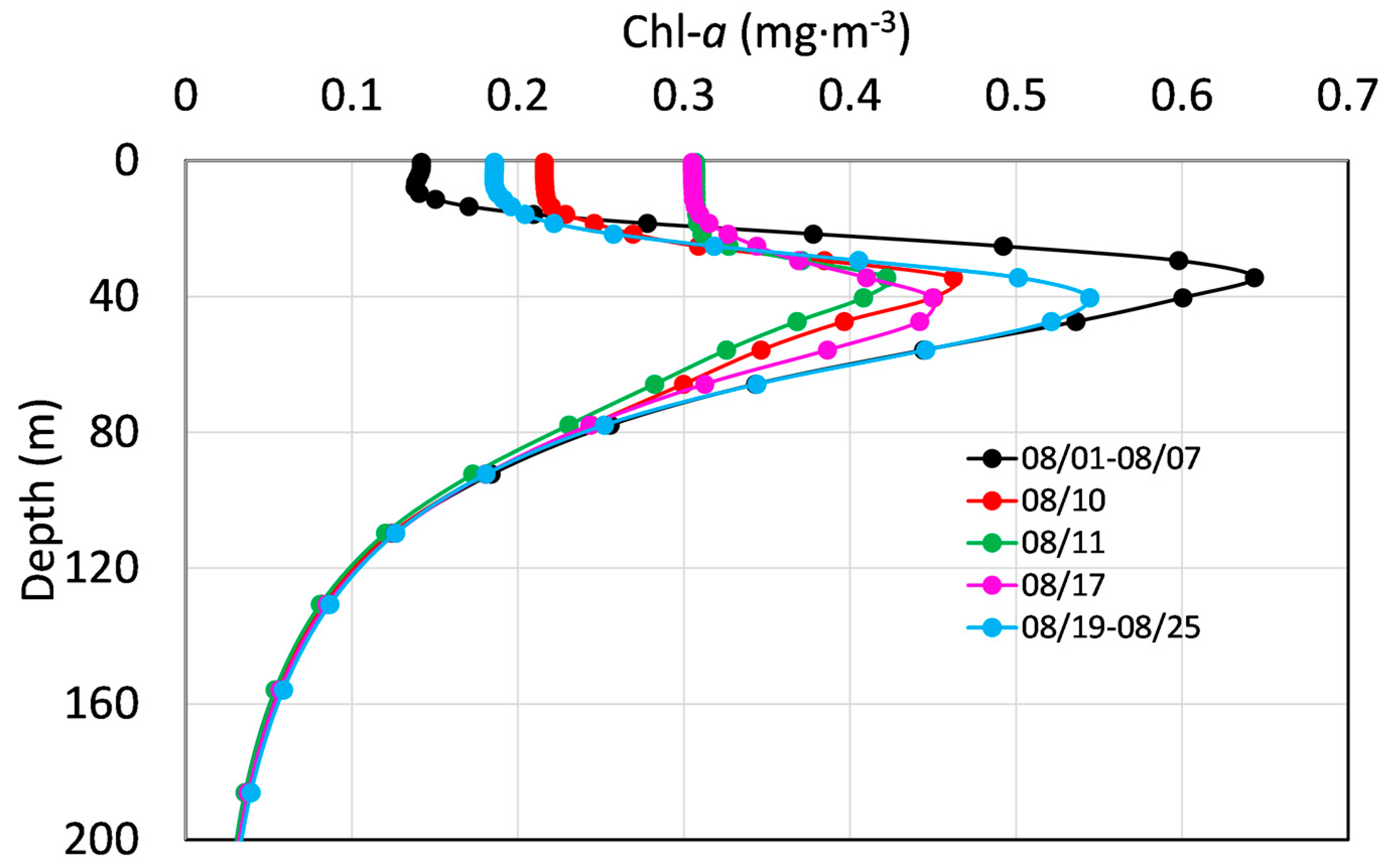
3.3. Variations in Phytoplankton Chl-a
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison of Environmental Factor Changes Caused by Two Typhoons
4.2. The Changes in Phytoplankton Chl-a Triggered by Successive Typhoons
4.3. Initial Exploration of Anomalous Sustained Cooling After the Passage of Two Typhoons
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Z.; England, M.H.; Groeskamp, S. Recent acceleration in global ocean heat accumulation by mode and intermediate waters. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, T.; Jia, F.; Cai, W.; Wu, L.; Gan, B.; Jing, Z.; Li, S.; McPhaden, M.J. Increased occurrences of consecutive La Niña events under global warming. Nature 2023, 619, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, K.; Lin, Y.; Chu, P.-S.; Yu, X.; Song, F. Seasonal advance of intense tropical cyclones in a warming climate. Nature 2023, 623, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Wu, L.; Mei, W.; Xie, S.-P. Ocean currents show global intensification of weak tropical cyclones. Nature 2022, 611, 496–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Tang, D.; Wang, Y. Comparison of phytoplankton blooms triggered by two typhoons with different intensities and translation speeds in the South China Sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 365, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Zhao, H.; Pan, J.; Devlin, A. Remote sensing observations of phytoplankton increases triggered by successive typhoons. Front. Earth Sci. 2017, 11, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, T.-L.; Wu, C.-R.; Oey, L.-Y. Typhoon Kai-Tak: An Ocean’s Perfect Storm. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2011, 41, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.-W.; Ho, C.-R.; Zheng, Q.; Kuo, N.-J.; Lo, Y.-T. Satellite observation and model simulation of upper ocean biophysical response to Super Typhoon Nakri. Cont. Shelf Res. 2010, 30, 1450–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, I.; Liu, W.T.; Wu, C.-C.; Wong, G.T.F.; Hu, C.; Chen, Z.; Liang, W.; Yang, Y.; Liu, K. New evidence for enhanced ocean primary production triggered by tropical cyclone. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, D.; Zhou, L.; Liu, X.; Ding, T.; Zhou, B. Upper ocean response to typhoon Kalmaegi (2014). J. Geophys.Res. Ocean. 2016, 121, 6520–6535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, J.F. Upper Ocean Response to a Hurricane. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1981, 11, 153–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, N.B. Cover The wake of Hurricane Felix. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 2893–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, W.J.; Dickey, T.D. Observations and analyses of upper ocean responses to tropical storms and hurricanes in the vicinity of Bermuda. J. Geophys.Res. Ocean. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, H.; Drennan, W.M.; Graber, H.C. Upper ocean cooling and air-sea fluxes under typhoons: A case study. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2017, 122, 7237–7252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cione, J.J.; Uhlhorn, E.W. Sea Surface Temperature Variability in Hurricanes: Implications with Respect to Intensity Change. Mon. Weather Rev. 2003, 131, 1783–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.; Chern, C.-S.; Wang, J. The upper ocean response to a moving typhoon. J. Oceanogr. 2008, 64, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-T.A.; Liu, C.-T.; Chuang, W.S.; Yang, Y.J.; Shiah, F.-K.; Tang, T.Y.; Chung, S. Enhanced buoyancy and hence upwelling of subsurface Kuroshio waters after a typhoon in the southern East China Sea. J. Mar. Syst. 2003, 42, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; He, Y.; Shen, H.; Qiu, Z. Submesoscale activity over the shelf of the northern South China Sea in summer: Simulation with an embedded model. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2010, 28, 1073–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Tang, D. Offshore and nearshore chlorophyll increases induced by typhoon winds and subsequent terrestrial rainwater runoff. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 333, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babin, S.M.; Carton, J.A.; Dickey, T.D.; Wiggert, J.D. Satellite evidence of hurricane-induced phytoplankton blooms in an oceanic desert. J. Geophys.Res. Ocean. 2004, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Yang, Y.J.; Xian, T.; Lu, Z.M.; Fu, Y.F. Strong enhancement of chlorophyll a concentration by a weak typhoon. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2010, 404, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Chen, F.; Zhang, S.; Pan, J.; Devlin, A.T.; Ning, H.; Zeng, W. Physical and Biochemical Responses to Sequential Tropical Cyclones in the Arabian Sea. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Pan Frsc, G.; Mortimer, R.; Zhao, H. Possible Mechanism of Phytoplankton Blooms at the Sea Surface after Tropical Cyclones. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, K.R.; Kruk, M.C.; Levinson, D.H.; Diamond, H.J.; Neumann, C.J. The International Best Track Archive for Climate Stewardship (IBTrACS): Unifying Tropical Cyclone Data. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2010, 91, 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halpern, D. Offshore Ekman transport and Ekman pumping off Peru during the 1997–1998 El Niño. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 19-1–19-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, H.; Han, G. Vertical and horizontal variations in phytoplankton chlorophyll a in response to a looping super typhoon. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2024, 69, 2085–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Han, G.; Zhang, S.; Wang, D. Two phytoplankton blooms near Luzon Strait generated by lingering Typhoon Parma. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosciences 2013, 118, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Zhao, J.; Ai, B.; Sun, S.; Zhang, G.-W.; Huang, W.; Wang, G. Assessing responses of phytoplankton to consecutive typhoons by combining Argo, remote sensing and numerical simulation data. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 790, 148086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, F.; Wang, Y.; Xing, X.; Yan, Y.; Xue, H.; Wells, M.; Boss, E. A limited effect of sub-tropical typhoons on phytoplankton dynamics. Biogeosciences 2021, 18, 849–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, M.D.; Vickery, P.J.; Reinhold, T.A. Reduced drag coefficient for high wind speeds in tropical cyclones. Nature 2003, 422, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarosz, E.; Mitchell, D.A.; Wang, D.W.; Teague, W.J. Bottom-Up Determination of Air-Sea Momentum Exchange Under a Major Tropical Cyclone. Science 2007, 315, 1707–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, W.; Wang, M. Observations of a Hurricane Katrina-induced phytoplankton bloom in the Gulf of Mexico. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.; Willey, J.; Go, M.; Peierls, B.L.; Pinckney, J.; Fogel, M. Rainfall stimulation of primary production in western Atlantic Ocean waters: Roles of different nitrogen sources and co-limiting nutrients. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1999, 176, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herut, B.; Krom, M.D.; Pan, G.; Mortimer, R. Atmospheric input of nitrogen and phosphorus to the Southeast Mediterranean: Sources, fluxes, and possible impact. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1999, 44, 1683–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, H. Spatial distribution of the summer subsurface chlorophyll maximum in the North South China Sea. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Shi, J.; Gao, H.; Guo, X.; Yao, X.; Gong, X. Contributions of physical and biogeochemical processes to phytoplankton biomass enhancement in the surface and subsurface layers during the passage of Typhoon Damrey. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosciences 2017, 122, 212–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ren, C.; Yuting, F.; Shi, H.; Pan Frsc, G.; Cooper, M.; Zhao, H. Different Responses of Chlorophyll a to the Passage of the Tropical Storm Wipha (2019) in the Coastal Waters of the Northern Beibu Gulf. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 887240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, S.; Wang, H.; Liu, G.; Huang, L.; Song, X. Chlorophyll a increase induced by surface winds in the northern South China Sea. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2012, 31, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Zhang, T.; Xu, C.; Xie, Q. Upper ocean response to typhoon Kujira (2015) in the South China Sea by multiple means of observation. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2020, 38, 314–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, Y. Phytoplankton Increases Induced by Tropical Cyclones in the South China Sea During 1998–2015. J. Geophys.Res. Ocean. 2018, 123, 2903–2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Pan, J.; Han, G.; Devlin, A.T.; Zhang, S.; Hou, Y. Effect of a fast-moving tropical storm Washi on phytoplankton in the northwestern South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2017, 122, 3404–3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siswanto, E.; Ishizaka, J.; Yokouchi, K. Estimating Chlorophyll-a Vertical Profiles from Satellite Data and the Implication for Primary Production in the Kuroshio Front of the East China Sea. J. Oceanogr. 2005, 61, 575–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, C.E.; Waite, A.M.; Thompson, P.A.; Pattiaratchi, C.B. Phytoplankton community structure and nitrogen nutrition in Leeuwin Current and coastal waters off the Gascoyne region of Western Australia. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2007, 54, 902–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, H.; Guan, Y.; Huang, J. Investigating different bio-responses of the upper ocean to Typhoon Haitang using Argo and satellite data. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2014, 59, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’asaro, E.A.; Black, P.G.; Centurioni, L.R.; Chang, Y.T.; Chen, S.S.; Foster, R.C.; Graber, H.C.; Harr, P.; Hormann, V.; Lien, R.-C.; et al. Impact of Typhoons on the Ocean in the Pacific. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 95, 1405–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, N.D.; Leben, R.R.; Balasubramanian, S. Hurricane-forced upwelling and chlorophyll a enhancement within cold-core cyclones in the Gulf of Mexico. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Sanford, T.B.; Imberger, J. Heat and turbulent kinetic energy budgets for surface layer cooling induced by the passage of Hurricane Frances (2004). J. Geophys.Res. Ocean. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Campbell, T.J.; Jin, H.; Gaberšek, S.; Hodur, R.M.; Martin, P. Effect of Two-Way Air–Sea Coupling in High and Low Wind Speed Regimes. Mon. Weather Rev. 2010, 138, 3579–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Xie, L.; Zheng, Q.; Zhang, S.; Li, M.; Li, J. Unusual coastal ocean cooling in the northern South China Sea by a katabatic cold jet associated with Typhoon Mujigea (2015). Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2019, 38, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
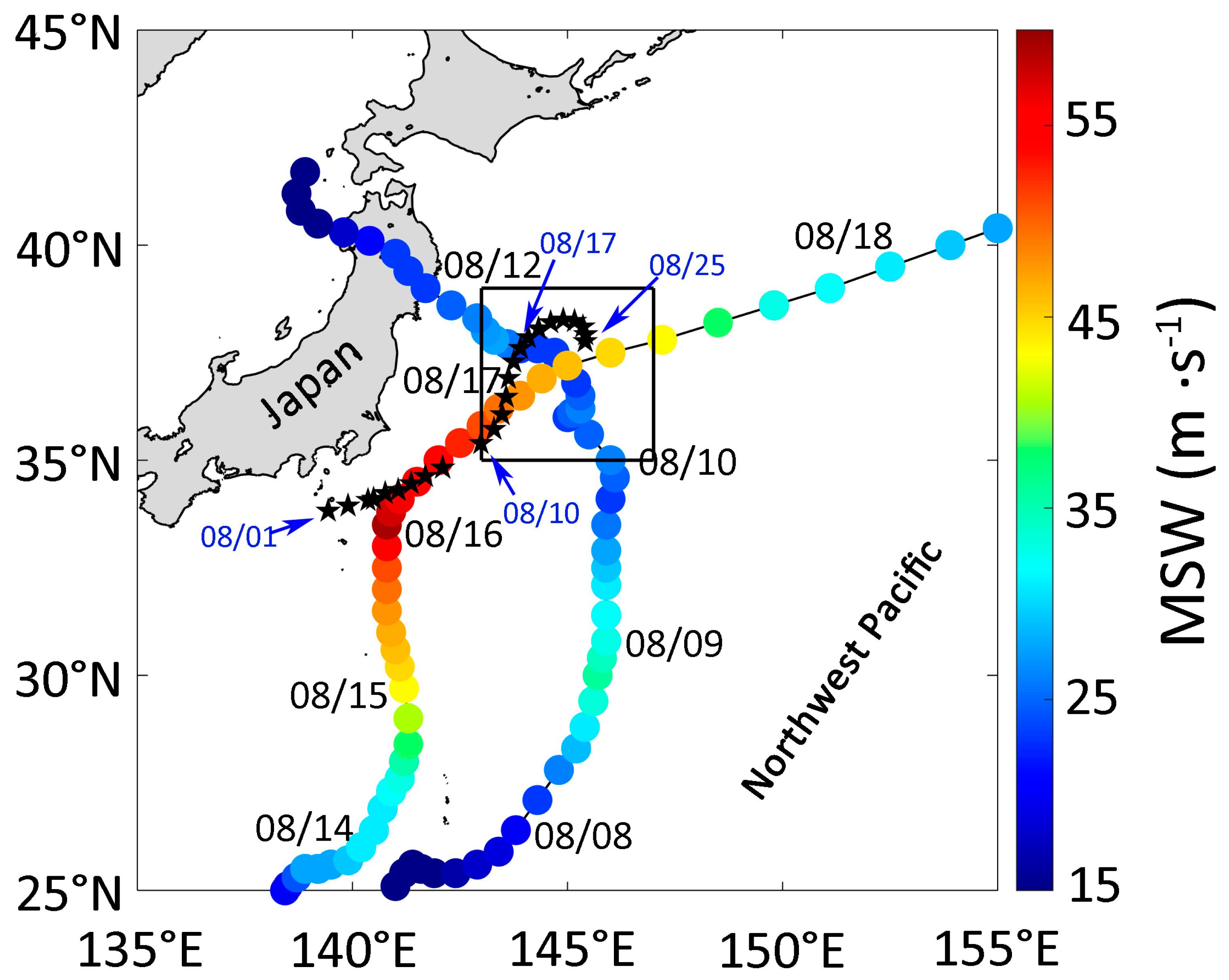
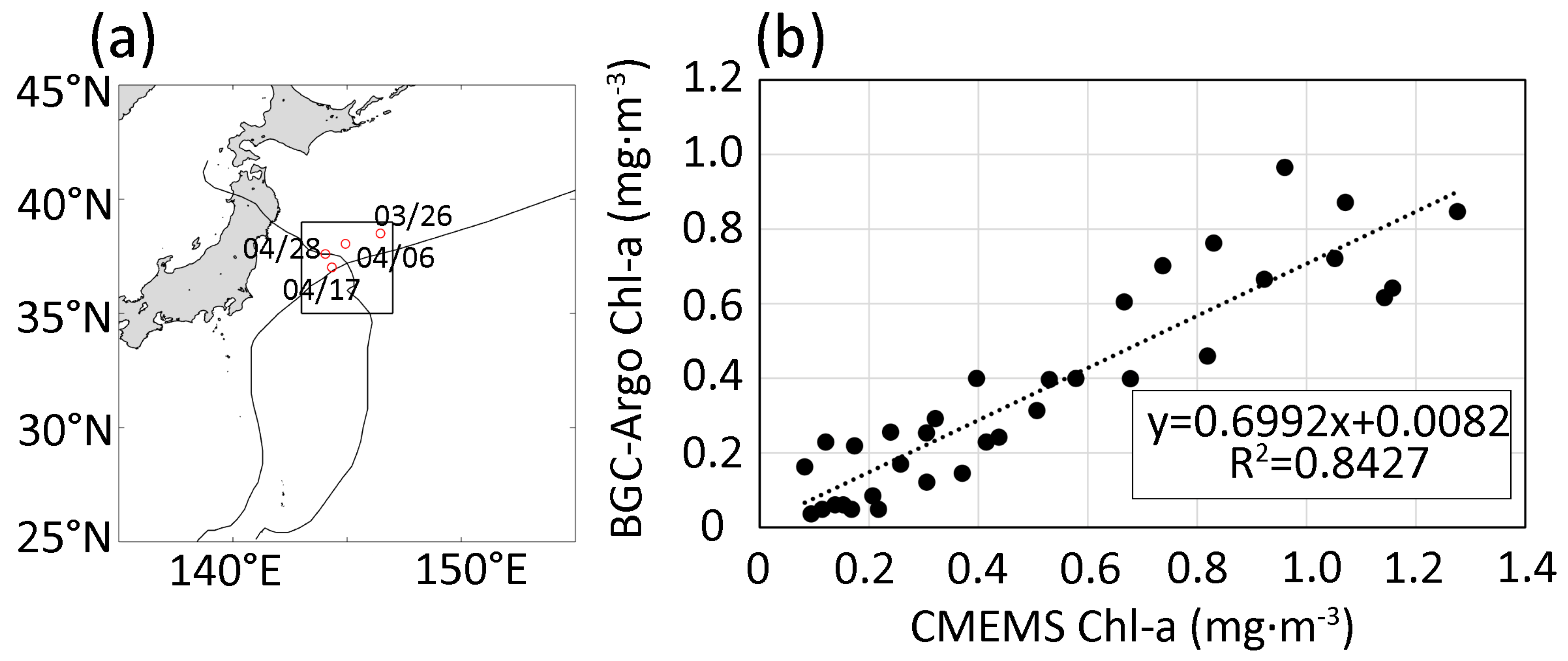
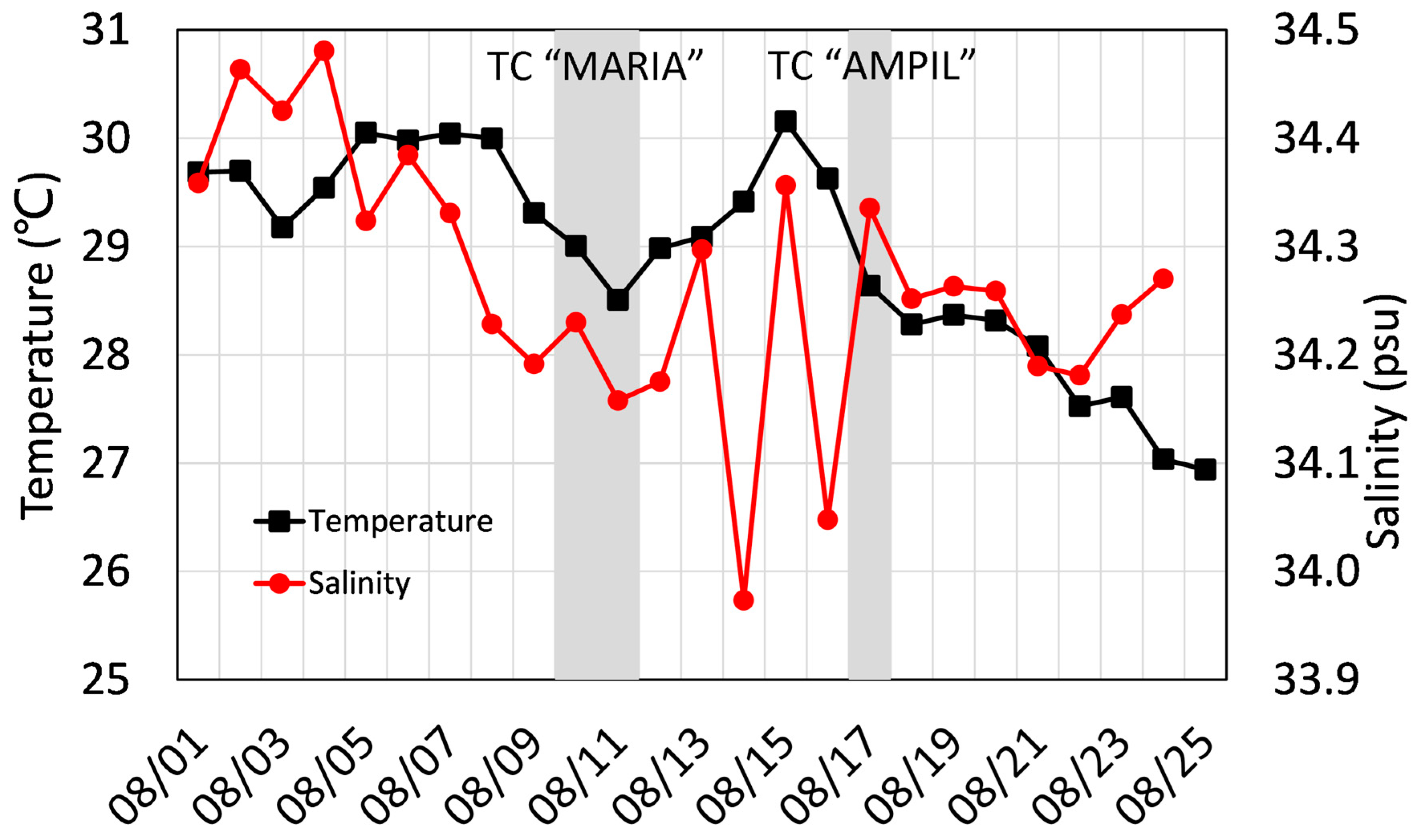
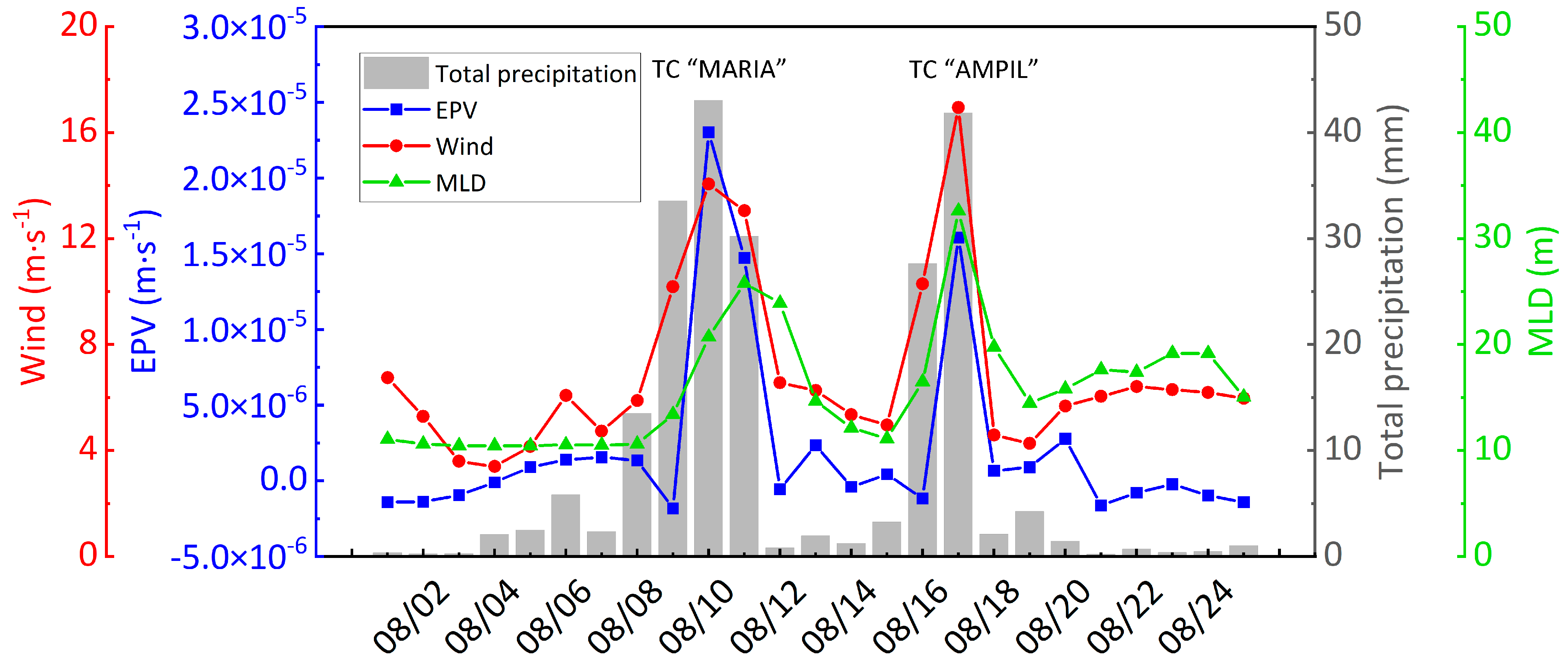
| Mean Translation Speed (m·s−1) | Mean MSW (m·s−1) | Duration (h) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| TC “MARIA” | 2.79 | 24.73 | 42 |
| TC “AMPIL” | 5.05 | 47.59 | 18 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Zhao, H.; Gao, H. The Impact of Consecutive Tropical Cyclones on Changes in Environmental Factors and Phytoplankton Distributions in Overlapping Areas. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4460. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16234460
Chen Y, Zhao H, Gao H. The Impact of Consecutive Tropical Cyclones on Changes in Environmental Factors and Phytoplankton Distributions in Overlapping Areas. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(23):4460. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16234460
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Ying, Hui Zhao, and Hui Gao. 2024. "The Impact of Consecutive Tropical Cyclones on Changes in Environmental Factors and Phytoplankton Distributions in Overlapping Areas" Remote Sensing 16, no. 23: 4460. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16234460
APA StyleChen, Y., Zhao, H., & Gao, H. (2024). The Impact of Consecutive Tropical Cyclones on Changes in Environmental Factors and Phytoplankton Distributions in Overlapping Areas. Remote Sensing, 16(23), 4460. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16234460





