Characterizing Changes in Paddy Rice Flooding Time over the Sanjiang Plain Using Moderate-Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer Time Series
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
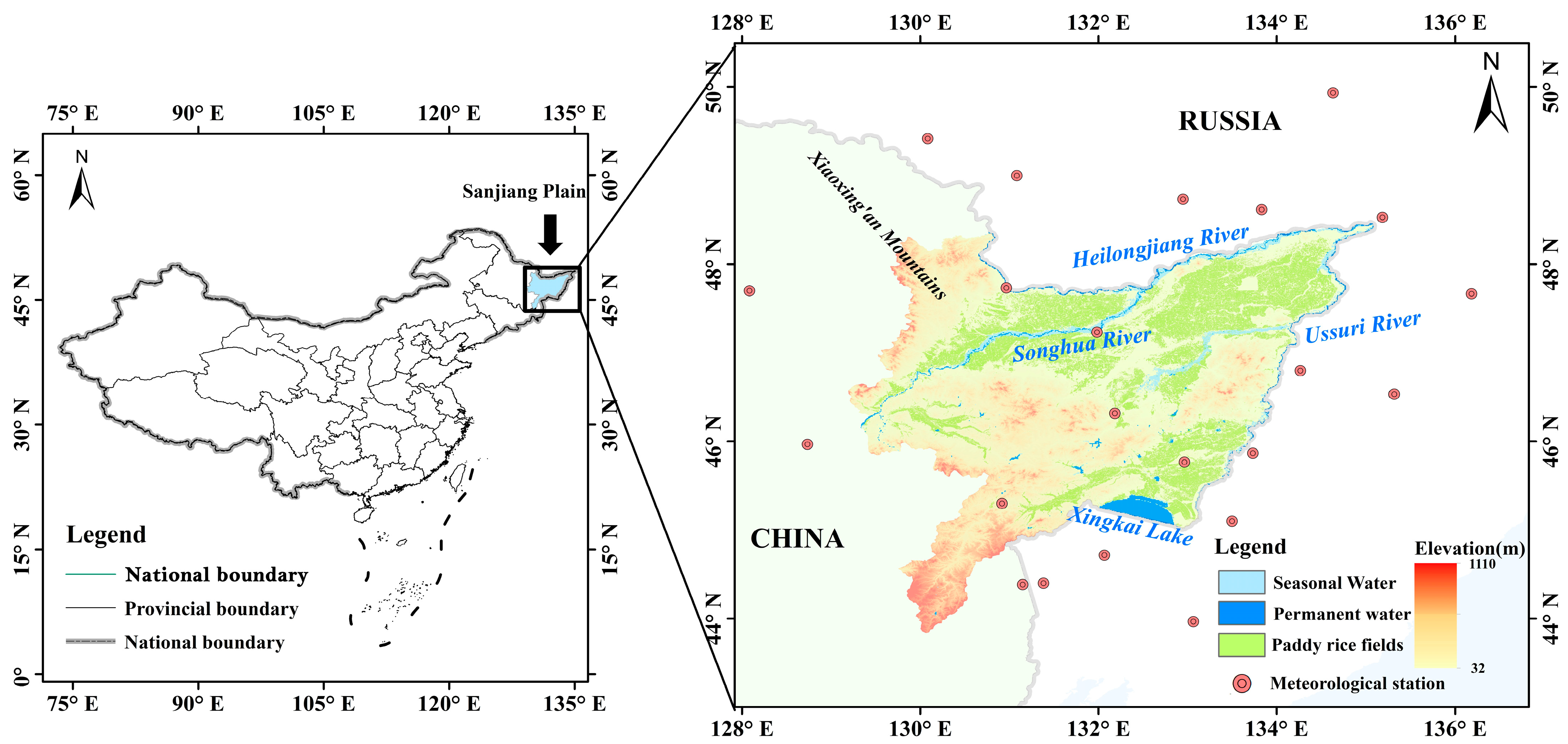
2.1. Study Area
2.2. MODIS Data
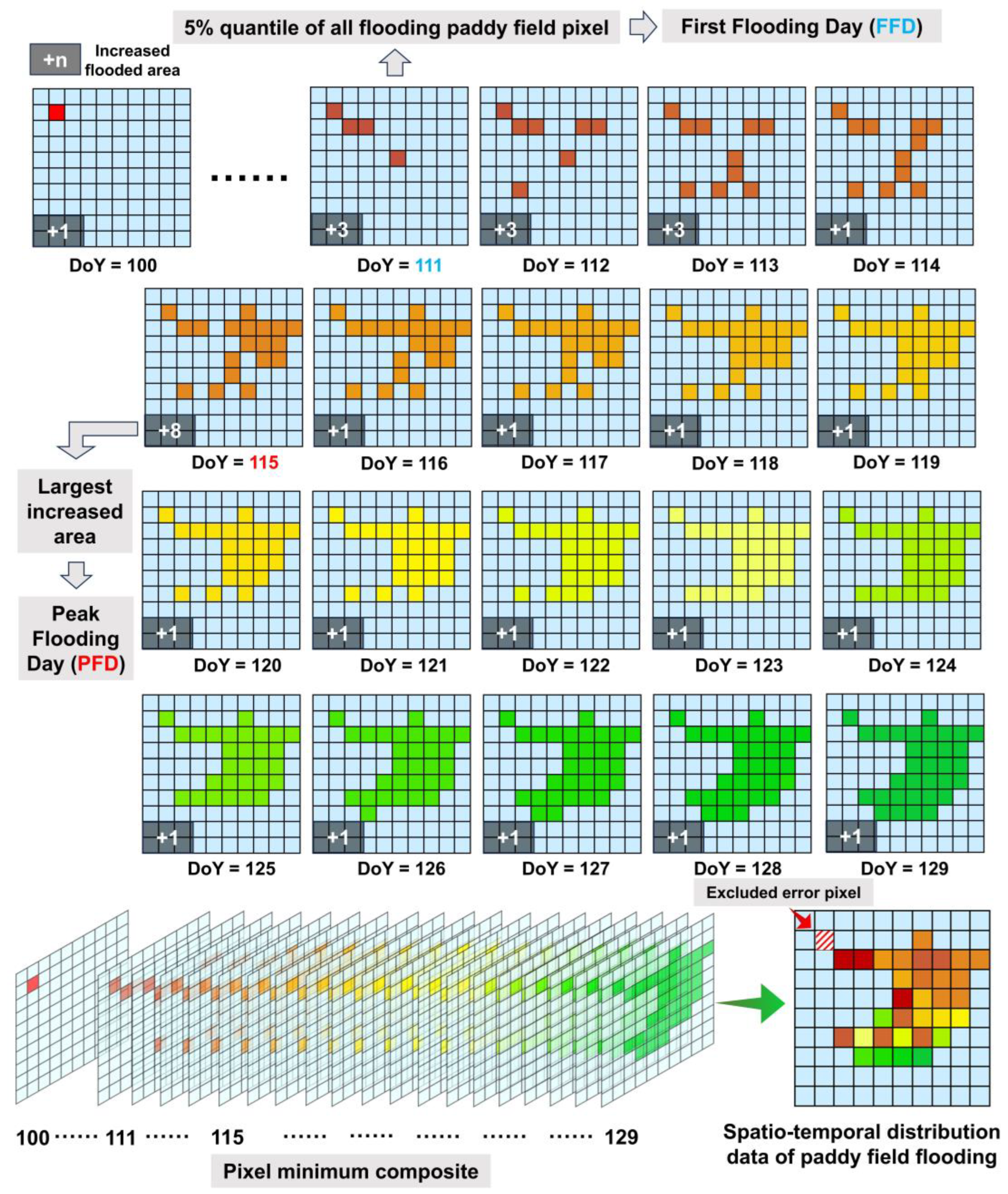
2.3. Identification of Rice Flooding Time
2.4. Elimination of Other Interfering Objects
2.4.1. Snow Cover Elimination
2.4.2. Water Elimination
2.4.3. Wetland Elimination
2.5. Daily Flooding Data Composite
2.6. Temperature Data and Processing
2.6.1. Land Surface Temperature
2.6.2. Air Temperature
3. Results
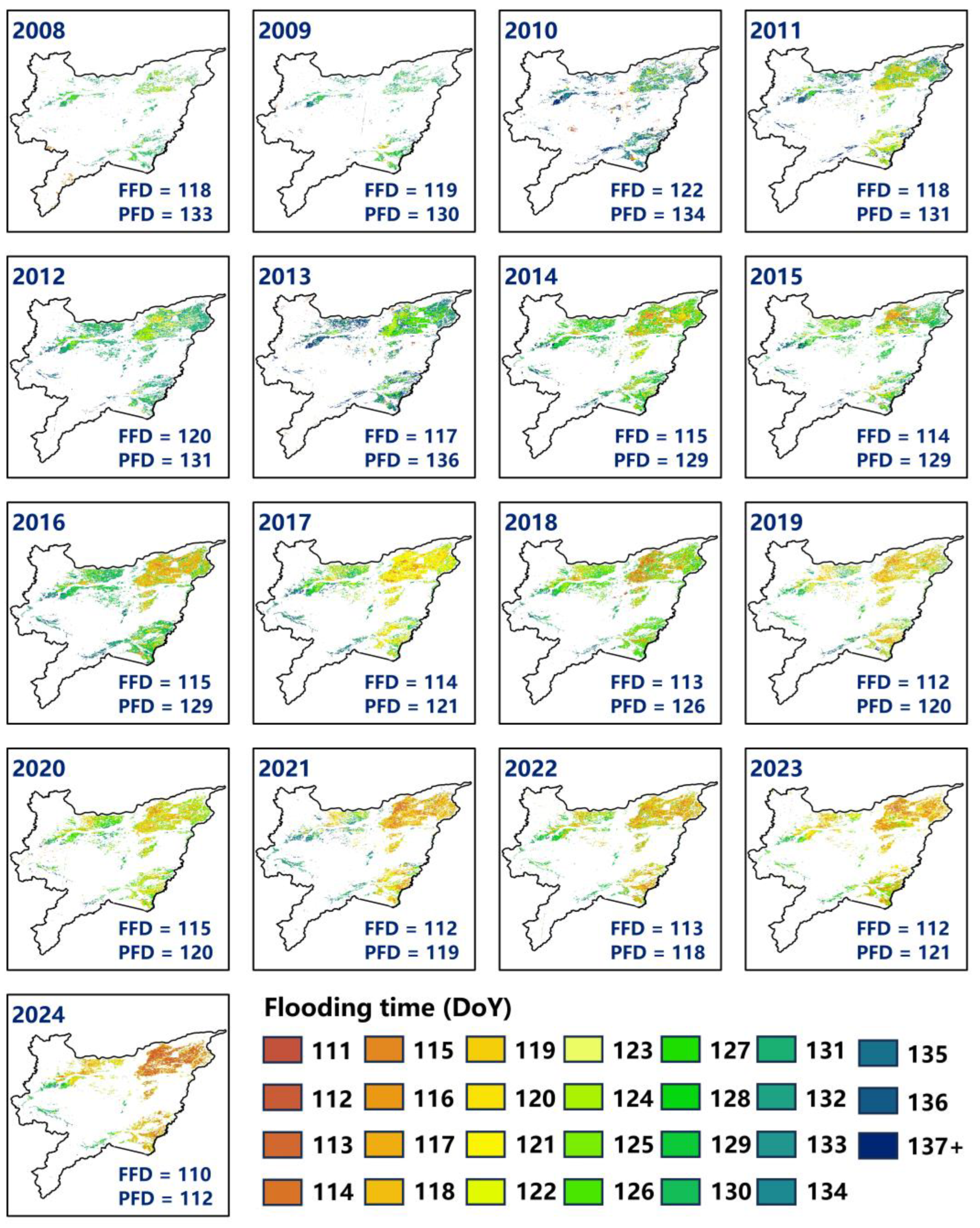
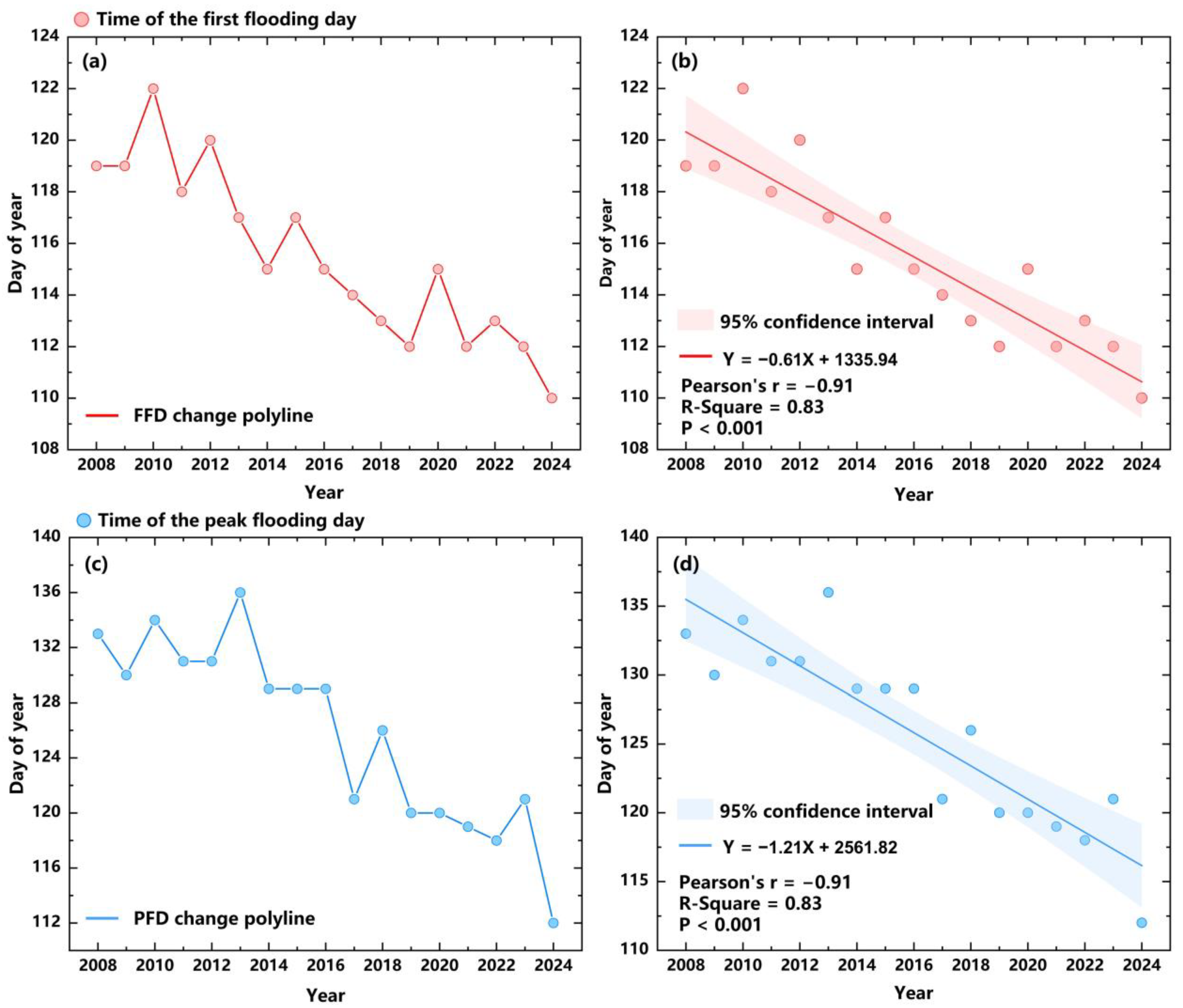
3.1. Spatio-Temporal Pattern of Flooding Time
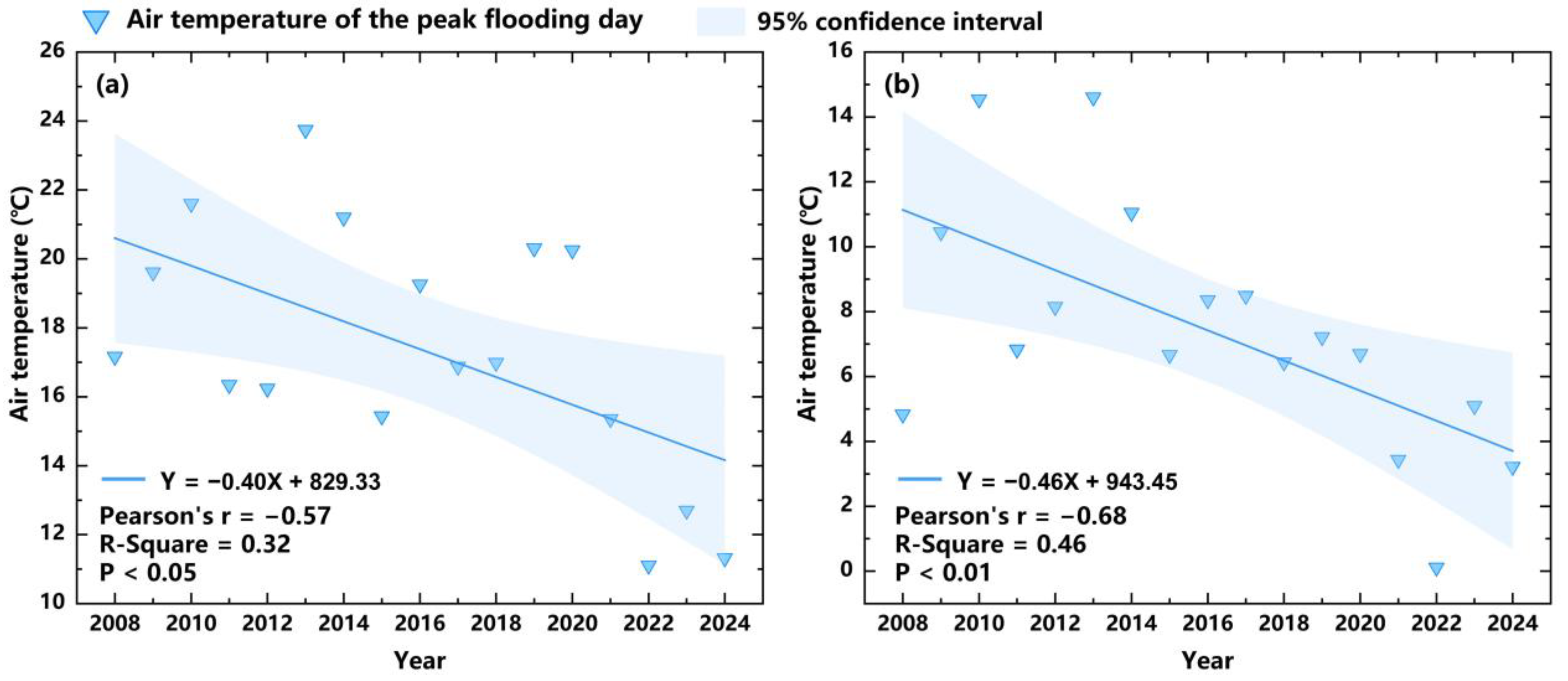
3.2. Changes in Temperature of PFD
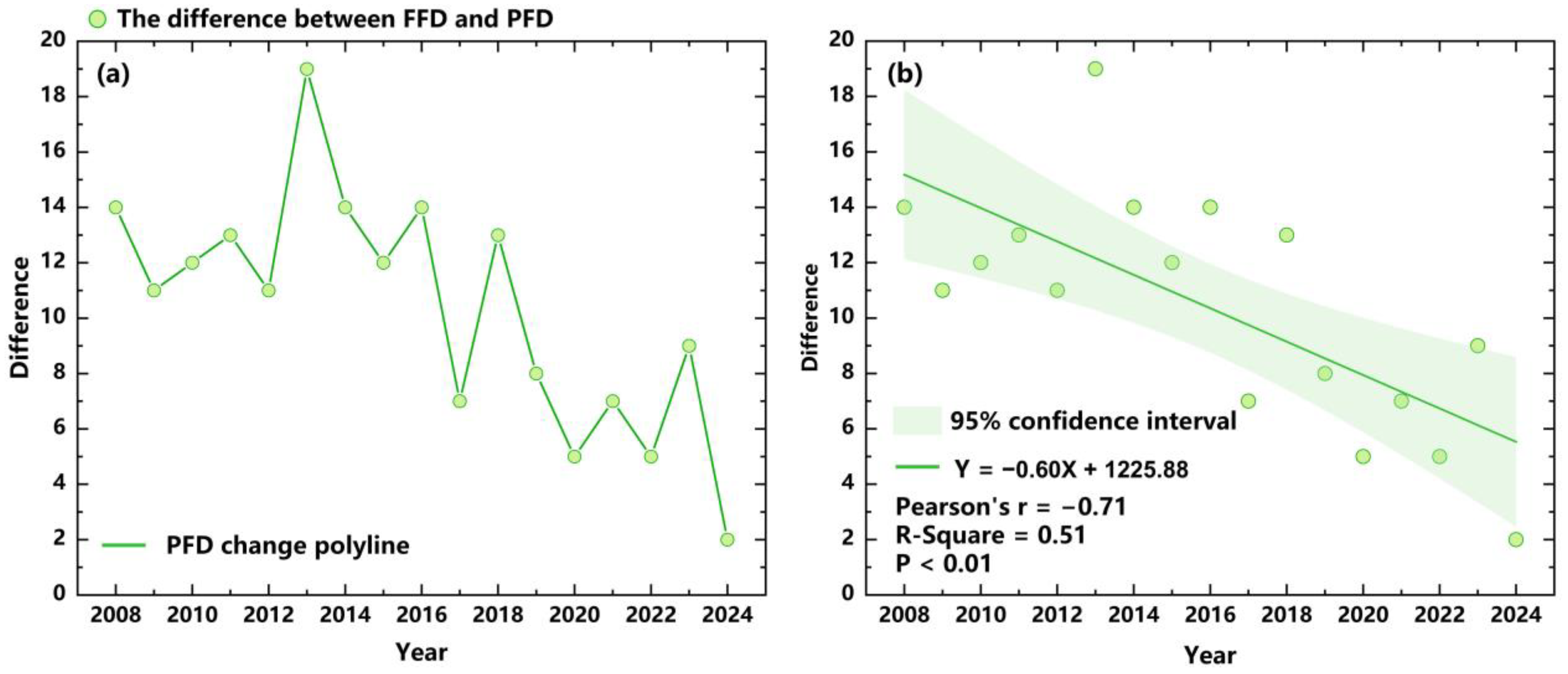
3.3. Analysis of Changes in Flooding Concentration
4. Discussion
4.1. Advantages and Limitations
4.2. Contrast Verification with 8-Day Results
4.3. Impact of Advancing Rice Flooding Time
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Normile, D. Reinventing Rice to Feed the World. Science 2008, 321, 330–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elert, E. Rice by the Numbers: A Good Grain. Nature 2014, 514, S50–S51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samad, M.; Merrey, D.; Vermillion, D.; Fuchs-Carsch, M.; Mohtadullah, K.; Lenton, R. Irrigation Management Strategies for Improving the Performance of Irrigated Agriculture. Outlook Agric. 1992, 21, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, F.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, W.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, D.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, M.; Liu, F. Single Rice Growth Period Was Prolonged by Cultivars Shifts, but Yield Was Damaged by Climate Change during 1981–2009 in China, and Late Rice Was Just Opposite. Glob. Change Biol. 2013, 19, 3200–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belesky, P. Regional Governance, Food Security and Rice Reserves in East Asia. Glob. Food Secur. 2014, 3, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, D.; Kar, S.K.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Shikha; Rakshit, A.; Tripathi, V.K.; Dubey, P.K.; Abhilash, P.C. Low Input Sustainable Agriculture: A Viable Climate-Smart Option for Boosting Food Production in a Warming World. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 115, 106412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilman, D.; Cassman, K.G.; Matson, P.A.; Naylor, R.; Polasky, S. Agricultural Sustainability and Intensive Production Practices. Nature 2002, 418, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Zhang, S.; Su, F. Variations in Ecosystem Services in Response to Paddy Expansion in the Sanjiang Plain, Northeast China. Int. J. Agric. Sustain. 2019, 17, 158–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Peng, S.; Liu, H.; Tao, Y.; Huang, J.; Cui, K.; Nie, L. The Possibility of Replacing Puddled Transplanted Flooded Rice with Dry Seeded Rice in Central China: A Review. Field Crops Res. 2017, 214, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhir-Yadav; Evangelista, G.; Faronilo, J.; Humphreys, E.; Henry, A.; Fernandez, L. Establishment Method Effects on Crop Performance and Water Productivity of Irrigated Rice in the Tropics. Field Crops Res. 2014, 166, 112–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassam, A.; Stoop, W.; Uphoff, N. Review of SRI Modifications in Rice Crop and Water Management and Research Issues for Making Further Improvements in Agricultural and Water Productivity. Paddy Water Environ. 2011, 9, 163–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Xiao, X.; Menarguez, M.A.; Zhang, G.; Qin, Y.; Thau, D.; Biradar, C.; Moore, B. Mapping Paddy Rice Planting Area in Northeastern Asia with Landsat 8 Images, Phenology-Based Algorithm and Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 185, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, X.; Boles, S.; Frolking, S.; Salas, W.; Moore III, B.; Li, C.; He, L.; Zhao, R. Observation of Flooding and Rice Transplanting of Paddy Rice Fields at the Site to Landscape Scales in China Using VEGETATION Sensor Data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 3009–3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Boles, S.; Frolking, S.; Salas, W.; Moore III, B.; Li, C.; He, L.; Zhao, R. Landscape-Scale Characterization of Cropland in China Using Vegetation and Landsat TM Images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 3579–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Boles, S.; Frolking, S.; Li, C.; Babu, J.Y.; Salas, W.; Moore, B. Mapping Paddy Rice Agriculture in South and Southeast Asia Using Multi-Temporal MODIS Images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 100, 95–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Boles, S.; Liu, J.; Zhuang, D.; Frolking, S.; Li, C.; Salas, W.; Moore, B. Mapping Paddy Rice Agriculture in Southern China Using Multi-Temporal MODIS Images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 95, 480–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.; Kang, S.; Jang, K.; Lee, H.; Hong, S.; Ko, D. Development of Variable Threshold Models for Detection of Irrigated Paddy Rice Fields and Irrigation Timing in Heterogeneous Land Cover. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 115, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Huang, J.; Huete, A.R.; Peng, D.; Zhang, F. Mapping Paddy Rice with Multi-Date Moderate-Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) Data in China. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 2009, 10, 1509–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.; Huete, A.R.; Huang, J.; Wang, F.; Sun, H. Detection and Estimation of Mixed Paddy Rice Cropping Patterns with MODIS Data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2011, 13, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Xiao, X.; Dong, J.; Kou, W.; Jin, C.; Qin, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, J.; Menarguez, M.A.; Biradar, C. Mapping Paddy Rice Planting Areas through Time Series Analysis of MODIS Land Surface Temperature and Vegetation Index Data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 106, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, R.; Tian, J.; Li, X.; Yin, D.; Li, J.; Gong, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, L.; Wu, D. An Enhanced Pixel-Based Phenological Feature for Accurate Paddy Rice Mapping with Sentinel-2 Imagery in Google Earth Engine. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 178, 282–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAOSTAT. Statistical Database of the Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations. 2018. Available online: https://www.fao.org (accessed on 1 November 2024).
- Li, X.; Chen, D.; Cao, X.; Luo, Z.; Webber, M. Assessing the Components of, and Factors Influencing, Paddy Rice Water Footprint in China. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 229, 105939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, Z.; Tang, P.; Li, Z.; Wu, W.; Yang, P.; You, L.; Tang, H. Change Analysis of Rice Area and Production in China during the Past Three Decades. J. Geogr. Sci. 2013, 23, 1005–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, T.; Yang, X.; Zhang, T.; Liu, Z.; Guo, E.; Liu, Z.; Qu, H.; Chen, X.; Wang, L.; et al. Rice Yield Potential, Gaps and Constraints during the Past Three Decades in a Climate-Changing Northeast China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 259, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-H.; Jang, T.; Hwang, S.; Jeong, H. Paddy Rice Adaptation Strategies to Climate Change: Transplanting Date Shift and BMP Applications. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 252, 106926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhuang, Q.; Luo, Y. Adaptation of Paddy Rice in China to Climate Change: The Effects of Shifting Sowing Date on Yield and Irrigation Water Requirement. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 228, 105890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-Y.; Yang, M.-D.; Tseng, W.-C.; Hsu, Y.-C.; Li, G.-S.; Lai, M.-H.; Wu, D.-H.; Lu, H.-Y. Assessment of Rice Developmental Stage Using Time Series UAV Imagery for Variable Irrigation Management. Sensors 2020, 20, 5354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Ouyang, W.; Liu, H.; Zhu, J.; Ma, Y.; Wu, Q.; Chen, J.; Zhang, D. Potential of Paddy Drainage Optimization to Water and Food Security in China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 171, 105624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, G.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Q. The evolution path of crop structure in the Sanjiang Plain in the 21st century. Res. Agric. Mod. 2019, 40, 736–744. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, A.; Lehmann, J.; Barriopedro, D.; Rahmstorf, S.; Coumou, D. Increasing Heat and Rainfall Extremes Now Far Outside the Historical Climate. NPJ Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 4, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; You, Q.; Zuo, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, Z.; Li, W.; Jiang, Z.; Ullah, S.; Tang, X.; Zhang, R.; et al. Compound Climate Extremes in China: Trends, Causes, and Projections. Atmos. Res. 2023, 286, 106675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, N.; Dong, J.; Huang, J.; Du, G.; Zhang, G.; He, Y.; Yang, T.; Di, Y.; Xiao, X. The 10-m Crop Type Maps in Northeast China during 2017–2019. Sci. Data 2021, 8, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pekel, J.-F.; Cottam, A.; Gorelick, N.; Belward, A.S. High-Resolution Mapping of Global Surface Water and Its Long-Term Changes. Nature 2016, 540, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Twedt, K.A.; Henderson, S.; Xiong, X.; Angal, A.; Geng, X. Nonlinear Detector Response of Aqua MODIS Land Imaging Bands. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Dong, X.; Xi, B.; Xin, X.; Liu, Q.; He, H.; Xie, X.; Li, L.; Yu, S. Retrieving High-Resolution Surface Photosynthetically Active Radiation from the MODIS and GOES-16 ABI Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 260, 112436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Chen, J.; Chen, F.; Xiang, G.; Luo, D.; Sun, L.; Hong, J.; Shu, S. Ocean Water Colour Retrieval Method Based on Directional Polarimetric Camera. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2024, 45, 5175–5191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Zhao, W.; Zhan, Q.; Xiong, D. Spatiotemporal Patterns of Land Surface Temperature Change in the Tibetan Plateau Based on MODIS/Terra Daily Product From 2000 to 2018. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 6501–6514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauf, U.; Qureshi, W.S.; Jabbar, H.; Zeb, A.; Mirza, A.; Alanazi, E.; Khan, U.S.; Rashid, N. A New Method for Pixel Classification for Rice Variety Identification Using Spectral and Time Series Data from Sentinel-2 Satellite Imagery. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 193, 106731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; Niu, H.; Guo, F.; Zhao, S.; Fan, L. Monitoring Irrigation Dynamics in Paddy Fields Using Spatiotemporal Fusion of Sentinel-2 and MODIS. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 263, 107409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Tenhunen, J.; Dinh, N.Q.; Reichstein, M.; Vesala, T.; Keronen, P. Similarities in Ground- and Satellite-Based NDVI Time Series and Their Relationship to Physiological Activity of a Scots Pine Forest in Finland. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 93, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huete, A.R.; Didan, K.; Shimabukuro, Y.E.; Ratana, P.; Saleska, S.R.; Hutyra, L.R.; Yang, W.; Nemani, R.R.; Myneni, R. Amazon Rainforests Green-up with Sunlight in Dry Season. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Huete, A.; Didan, K.; Miura, T. Development of a Two-Band Enhanced Vegetation Index without a Blue Band. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3833–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.K.; Riggs, G.A.; Salomonson, V.V. Development of Methods for Mapping Global Snow Cover Using Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1995, 54, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potapov, P.; Turubanova, S.; Hansen, M.C.; Tyukavina, A.; Zalles, V.; Khan, A.; Song, X.-P.; Pickens, A.; Shen, Q.; Cortez, J. Global Maps of Cropland Extent and Change Show Accelerated Cropland Expansion in the Twenty-First Century. Nat. Food 2021, 3, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Niu, Z.; Cheng, X.; Guo, J.; Liang, L. China’s Wetland Change (1990–2000) Determined by Remote Sensing | Science China Earth Sciences. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2010, 53, 1036–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Song, K.; Ma, W.; Ren, C.; Zhang, B.; Liu, D.; Chen, J.M.; Song, C. Loss and Fragmentation of Marshes in the Sanjiang Plain, Northeast China, 1954–2005. Wetlands 2011, 31, 945–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, D.; Wang, Z.; Du, B.; Li, L.; Tian, Y.; Jia, M.; Zeng, Y.; Song, K.; Jiang, M.; Wang, Y. National Wetland Mapping in China: A New Product Resulting from Object-Based and Hierarchical Classification of Landsat 8 OLI Images. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 164, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, M.F. The Application of Thin Plate Smoothing Splines to Continent-Wide Data Assimilation. Bur. Meteorol. Res. Rep. 1991, 27, 104–113. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, T.; Liu, J.; Qian, B.; Zhao, T.; Jing, Q. Estimating Winter Wheat Biomass by Assimilating Leaf Area Index Derived from Fusion of Landsat-8 and MODIS Data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 49, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Dong, J.; Zhang, G.; Yang, J.; Liu, R.; Wu, B.; Xiao, X. Improved Phenology-Based Rice Mapping Algorithm by Integrating Optical and Radar Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2024, 315, 114460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ticehurst, C.; Guerschman, J.P.; Chen, Y. The Strengths and Limitations in Using the Daily MODIS Open Water Likelihood Algorithm for Identifying Flood Events. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 11791–11809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ines, A.V.M.; Honda, K. On Quantifying Agricultural and Water Management Practices from Low Spatial Resolution RS Data Using Genetic Algorithms: A Numerical Study for Mixed-Pixel Environment. Adv. Water Resour. 2005, 28, 856–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchenko, V. Observability of Hybrid Discrete-Continuous Systems. Differ. Equ. 2013, 49, 1389–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.M.; Screen, J.A.; Deser, C.; Cohen, J.; Fyfe, J.C.; García-Serrano, J.; Jung, T.; Kattsov, V.; Matei, D.; Msadek, R.; et al. The Polar Amplification Model Intercomparison Project (PAMIP) Contribution to CMIP6: Investigating the Causes and Consequences of Polar Amplification. Geosci. Model Dev. 2019, 12, 1139–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolan, S.; Padhye, L.P.; Jasemizad, T.; Govarthanan, M.; Karmegam, N.; Wijesekara, H.; Amarasiri, D.; Hou, D.; Zhou, P.; Biswal, B.K.; et al. Impacts of Climate Change on the Fate of Contaminants through Extreme Weather Events. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 909, 168388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Guan, Y.; Wu, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, R.; Lin, K.; Wang, Y. Revealing the Dynamic Effects of Land Cover Change on Land Surface Temperature in Global Major Bay Areas. Build. Environ. 2025, 267, 112266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Liu, C.; Zhang, J.; Wang, G.; Bao, Z.; Jin, J. On the Attribution of Changing Water Surface Evaporation across China. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2022, 40, 100991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnell, N.W.; Lowe, J.A.; Challinor, A.J.; Osborn, T.J. Global and Regional Impacts of Climate Change at Different Levels of Global Temperature Increase. Clim. Change 2019, 155, 377–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Shin, H.; Han, J. Assessing Irrigation Efficiency Improvements in Paddy Fields Using Granular SWMM Simulations. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Zhuang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, W.; Xu, H.; Zhao, M.; Ma, D. Multi-Omics Approach Reveals the Contribution of OsSEH1 to Rice Cold Tolerance. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 13, 1110724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, N.; Nabi, H.G.; Qiao, L.; Li, W. The Molecular Mechanism of Cold-Stress Tolerance: Cold Responsive Genes and Their Mechanisms in Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Biology 2024, 13, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Yuan, J.; Guo, F.; Chen, Z. Preliminary Study on Water-Catching and Controlled Irrigation Technology of Rice. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2009, 25, 70–73. [Google Scholar]


| Year | Daily | 8-Day Composite |
|---|---|---|
| 2008 | 118 | 115–122 |
| 2009 | 119 | 115–122 |
| 2010 | 122 | 115–122 |
| 2011 | 118 | 107–114 |
| 2012 | 120 | 115–122 |
| 2013 | 117 | 115–122 |
| 2014 | 115 | 107–114 |
| 2015 | 114 | 115–122 |
| 2016 | 115 | 115–122 |
| 2017 | 114 | 107–114 |
| 2018 | 113 | 107–114 |
| 2019 | 112 | 107–114 |
| 2020 | 115 | 115–122 |
| 2021 | 112 | 107–114 |
| 2022 | 113 | 107–114 |
| 2023 | 112 | 107–114 |
| 2024 | 110 | 107–114 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ning, X.; Li, H.; Liu, R. Characterizing Changes in Paddy Rice Flooding Time over the Sanjiang Plain Using Moderate-Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer Time Series. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4683. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16244683
Ning X, Li H, Liu R. Characterizing Changes in Paddy Rice Flooding Time over the Sanjiang Plain Using Moderate-Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer Time Series. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(24):4683. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16244683
Chicago/Turabian StyleNing, Xiangyu, Huapeng Li, and Ruoqi Liu. 2024. "Characterizing Changes in Paddy Rice Flooding Time over the Sanjiang Plain Using Moderate-Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer Time Series" Remote Sensing 16, no. 24: 4683. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16244683
APA StyleNing, X., Li, H., & Liu, R. (2024). Characterizing Changes in Paddy Rice Flooding Time over the Sanjiang Plain Using Moderate-Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer Time Series. Remote Sensing, 16(24), 4683. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16244683






