Abstract
Due to the significant discrepancies in the distribution of ships in nearshore and offshore areas, the wide range of their size, and the randomness of target orientation in the sea, traditional detection models in the field of computer vision struggle to achieve performance in SAR image ship target detection comparable to that in optical image detection. This paper proposes an oriented ship target detection model based on the YOLO11 algorithm, Neural Swin Transformer-YOLO11 (NST-YOLO11). The proposed model integrates an improved Swin Transformer module called Neural Swin-T and a Cross-Stage connected Spatial Pyramid Pooling-Fast (CS-SPPF) module. By introducing a spatial/channel unified attention mechanism with neuron suppression in the spatial domain, the information redundancy generated by the local window self-attention module in the Swin Transformer Block is cut off. Furthermore, the idea of cross-stage partial (CSP) connections is applied to the fast spatial pyramid pooling (SPPF) module, effectively enhancing the ability to retain information in multi-scale feature extraction. Experiments conducted on the Rotated Ship Detection Dataset in SAR Images (RSDD-SAR) and the SAR Ship Detection Dataset (SSDD+) and comparisons with other oriented detection models demonstrate that the proposed NST-YOLO11 achieves state-of-the-art detection performance, demonstrate outstanding generalization ability and robustness of the proposed model.
1. Introduction
Operating in the microwave band, synthetic aperture radar (SAR) offers distinct advantages over optical remote sensing systems, covering its all-time, all-weather characteristics as well as the capability to penetrate clouds and fog. Since the emergence of SAR in the 1950s, its extensive applications have been evident across both military and civilian fields [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8] (e.g., battlefield reconnaissance, precise guidance for seekers, terrain mapping, and urban management). Maritime surveillance [9], in particular, emerged as a pivotal mission in both domains. Driven by military security concerns [10] and the imperative for maintaining maritime activities [11], the detection of ship targets has become significant, yet challenging. Ships are usually sparsely distributed in the open sea but densely packed near the coast [12], further complicated by strong clutter interference inshore. This variability poses a significant challenge for SAR image interpretation systems to efficiently deliver accurate detection results.
SAR automatic target recognition (SAR ATR) [13], a challenging task introduced in the last century, aims to spot and recognize the targets of interest from an enormous amount of remote sensing data gained from high-resolution SAR systems using not only amplitude information but all obtained features (phase, frequency, polarization and so on). The standard procedure for SAR ATR is as follows: prescreen (locates candidate targets), discriminate (rejects false alarm), and classify (recognizes targets by type). Some early attempts [14,15] involved excavating features from SAR images based on image processing and statistical analysis or attaining pattern recognition based on scattering center extraction. Undeniably, accurate and effective signal processing methods can still achieve relatively satisfying results today [16], but those traditional approaches mean a huge consumption of time, human resources, and theoretical analyses. A paradigm shift for hand-crafted feature selection and discrimination is surely to come.
Over the past two decades, deep learning techniques, with convolutional neural networks (CNNs) as leading representatives, have achieved remarkable success in the field of computer vision (CV). Researchers have been utilizing state-of-the-art deep learning methodologies for SAR ship detection tasks. However, due to the complex texture, abstract feature presentation of SAR images and unique microwave characteristics, those detection models are far from reaching a practical level in comparison to deploying them on optical images [5]. Obstacles are, in the perspective of a ship’s distribution in the SAR images, targets usually oriented randomly, which diminishes the accuracy of detection when using non-rotatable rectangular bounding boxes; the wide variation in ship sizes, ranging from around 60 ft (trawler) to 1000 ft (aircraft carrier) [17], renders traditional anchor box detection methods ineffective. The fixed scaling design not only fails to accommodate this size diversity but also leads to considerable computational redundancies. The abovementioned challenges indicate that deep learning methods should be better adapted to the related field, not simply using what we had already in the CV field.
To enhance the detection capability of multi-scale SAR ship targets in complex coastal environments, this paper proposes an improved Transformer module based on neural spatial suppression (Neural Swin Transformer [18]) and a cross-stage pyramid feature pooling module with fast connections (CS-SPFF), utilizing the You Only Look Once 11 (YOLO11) architecture to complete the task of oriented bounding box object detection. Specifically, the Neural Swin Transformer (NST) module efficiently extracts feature maps that capture both local and global information through the Transformer structure and assigns importance weights to each component based on the inhibitory rule of important neurons on neighboring neurons in neuroscience, improving the representation efficiency of the Swin-T module; inspired by CSPDarkNet [19], the fast pyramid spatial pooling module is added with residual connections, effectively reducing the loss of information extraction during pooling. We conducted module ablation experiments on the Rotated Ship Detection Dataset in SAR images (RSDD-SAR) [20] and SAR Ship Detection Dataset (SSDD+) [21], and compared the performance with most of the current SAR ship target-oriented detection models, achieving the best performance in both nearshore and offshore detection tasks; a comparison of the detection results of some data from different models is presented, reflecting the excellent extraction capability of the proposed model for multi-scale targets and the perception ability of nearshore terrain. Overall, the main contributions of this paper are as follows:
- 1.
- Illustrated the existing challenges on the arbitrary-oriented ship detection in SAR images by analyzing different deep learning methods and common mechanisms employed in the field;
- 2.
- Proposed a CNN model, NST-YOLO11, integrating Neural Swin Transformer (Neural Swin-T) and Cross-Stage connection Spatial Pyramid Pooling-Fast (CS-SPPF) based on YOLO11;
- 3.
- Summarized the performance of the proposed model for arbitrary-oriented ship detection in SAR images on RSDD-SAR and SSDD in recent years and achieved state-of-the-art detection results on these two datasets. SOTA results were also achieved in the subsets of RSDD-SAR divided by nearshore and offshore scenes.
The organization of the remaining sections of the article is as follows: Section 2 introduces related work. Section 3 provides a detailed description of the proposed model and its improvement methods. Section 4 presents comparative experiments and ablation studies of the proposed model. Section 5 discusses the results and visualizes the advantages of the model. Finally, Section 6 summarizes the work presented in this article.
2. Related Work
2.1. Deep Learning-Based Bounding-Box SAR Ship Detection Models
Researchers have come up with a series of novel detection models based on deep learning, which mostly fall into two categories: one-stage and two-stage detectors. Some typical models from the former type are the YOLO series [19,22,23,24,25,26], FCOS [27], SSD [28], and DEtection TRansformer (DETR) [29]. Unlike the other one-stage detectors, Transformer-based [30] detection models (DETR [29] included) attach a Transformer encoder–decoder to a conventional CNN backbone, thus greatly improving the detection performance in exchange for a blooming number of parameters. Two-stage detectors include Fast R-CNN [31], R-FCN [32], Faster R-CNN [33], and Mask R-CNN [34]. To conclude, one-stage detectors are commonly faster than two-stage detectors because of their smaller and simpler network structures, while two-stage detectors would win the battle of precision. The promising attention mechanisms enable CNN models to comprehend SAR ship images from multi-scale and terrain-aware perspectives to a new extent.
Considering the multi-scale feature of dispersed ships in SAR images, it is widely accepted that there should be a network structure aimed at extracting information at different scales. The feature pyramid network (FPN) [35] is one suitable form. The lateral connection from top to bottom transfers object information with decreasing scales, which efficiently pays attention to targets of varied sizes. Research [36,37,38,39,40,41] has focused on improving FPN to meet the various needs of, for example, efficiency, detailed features, or lightweight models.
2.2. SAR Ship Detection Models Using Attention Mechanism
As the attention mechanism becomes a heated topic, relevant effective models have opened up a new field, previously dominated by CNNs. The CFAR-YOLO model, put forward by Xue Wen et al. [42], incorporates frequency domain information into the channel attention mechanism, receiving a satisfying detection result combined with its handcrafted feature extraction module. Inspired by the imaging mechanism of SAR, Xiangdong Tan et al. [43] employ an amplitude gradient guided feature extraction module to obtain attention from the range-compressed domain, thus enhancing the feature extraction process for ship targets in azimuth gates. Emphasizing spatial and frequency features in SAR images, Shiyu Wang et al. [44] fuse the spatial and frequency texture information into feature maps using haar wavelet transform and a shortcut convolutional block attention module (CBAM) [45] in a double-backbone network. Chunjie Zhang et al. [46] utilized a nested path aggregation attention module before an anchor-free key-point detection head, thereby obtaining a higher resolution layer with fine-grained SAR ship features in complex scenes. Those comparable attention methodologies seize global features and their correlations implicitly, thus enhancing the model detection performance in complex scenes.
2.3. Arbitrary-Oriented and Anchor-Free SAR Ship Detection Models
How detection models generate bounding boxes of the targets makes a major contribution to determining the location and orientation of the ships in SAR images [47]. Zhongzhen Sun et al. [48] put this thought into practice in the arbitrary-oriented bounding box model with a bi-directional feature fusion architecture for ship targets with multiple resolutions to be captured precisely. The model extracts multi-scale features and classifies angle information as a whole, generating bounding boxes that fit ship targets with the direction attached. In [49], a multilevel feature fusion module (MFFM) with atrous convolution for expanding the receptive field is proposed. With MFFM being the backbone, a decoupled detection head for object classification and angle regression is followed. In addition to the adoption of the oriented bounding box, anchor-free methodologies also gain evident advantages over anchor-based, in computation, latency, and even sometimes precision. The anchor-based algorithms require an artificial design of the scale and ratio of the bounding box, showing a lack of flexibility and efficiency. By regressing on the center coordinate, height and width of the object, the anchor-free method cuts off the redundancy and owns its speedy feature. This is instructive for the new YOLO series [24,26] to refine their detection heads. HuiYao Wan et al. [50] proposed an anchor-free model using MobileNetV2S as the backbone and adopted a decoupled detection head, beating its original YOLOX model by 0.005 mAP on the SSDD dataset. The two approaches innovated the generation of rotated bounding boxes, leaving great potential for exploring the use of CNN-based models in arbitrary-oriented SAR ship target detection tasks.
3. Methodology
Inspired by YOLO11 by Ultralytics, this paper proposes a single-stage oriented detection model that integrates Vision Transformer (ViT) with a neuron spatial suppression attention mechanism. Based on the cross-stage partial (CSP) idea, improvements are made to the spatial pyramid pooling-fast (SPPF), aiming to enhance the model’s efficient global perception capability for multi-scale targets.
3.1. Overall Structure of NST-YOLO11
The overall structure of NST-YOLO11 is shown in Figure 1. The model employs the original CSPDarkNet (first left column of the backbone network) followed by Neural Swin-T and CS-SPPF as the backbone network to enhance its representational ability, hoping to output more comprehensive and complete feature maps for information extraction. In the upper part of Figure 1, some fundamental elements (C3k2, C3, Bottleneck and Conv) of YOLO11 are shown. Generally, Neural Swin-T evolves from the Swin Transformer network. Considering the spatial suppression capability of important neurons in the neuroscience field, an energy function is designed to assign higher attention weights to such special neurons, effectively reducing some redundancy generated by focusing on local information in the Swin Transformer. Inspired by CSPDarkNet and [24], CS-SPPF makes max-pooling layers connected in series and concatenated with the original input as cross-scale feature maps for subsequent processing, improving pooling efficiency by reusing feature maps. Next, going through the feature-fusion neck, features are input into an anchor-free decoupled multi-scale oriented detection head. The use of the decoupled head avoids the confusion caused by the same branch performing classification and oriented box regression tasks, effectively improving training efficiency and target detection capability.
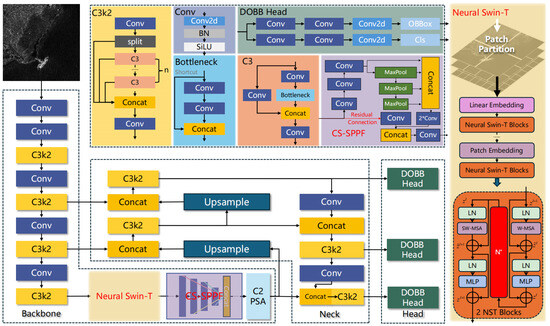
Figure 1.
Overall Structure of NST-YOLO11. Module names in red represent the proposed modification.
3.2. Swin Transformer Module with Neural Attention (Neural Swin-T)
Swin Transformer [51], introduced by Microsoft Research Asia in 2021, represents a groundbreaking visual processing algorithm that builds upon the Transformer architecture. The core component of Swin-T is the Swin-T Blocks. The window-based self-attention module lacks connections between blocks, which diminishes the model’s performance. To introduce cross-window connections while maintaining computational efficiency, the paper proposed a sliding window partitioning method that allows for the adjustment of partition settings between consecutive Swin-T Blocks. As depicted in Figure 2, the first Swin-T block kept its multi-head self-attention module to be a regular one, that is to say, a input feature map will be evenly partitioned into four windows. Differently, the following block adopted a shifted windowing configuration by offsetting the windows by from the original window. The feature going through these consecutive Swin Transformer blocks could be expressed by:
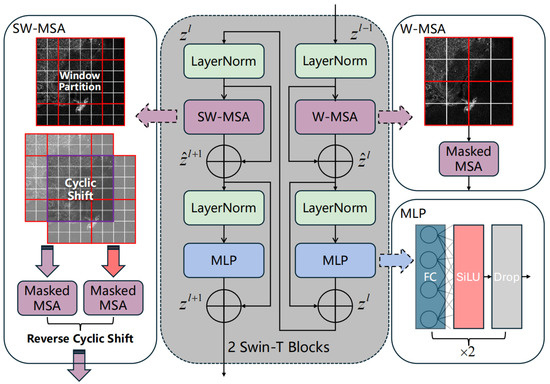
Figure 2.
Two Swin Transformer Blocks connected through alternating use of W-MSA and SW-MSA.
Drawing inspiration from neuroscience, where neural network units can be analogized to activated or inactive neurons, Ref. [52] introduces an energy function. This function is designed to assess the significance of individual neurons, playing a crucial role in unifying channel and spatial attention mechanisms. By utilizing this function, the model effectively assigns appropriate 3D weights to the neurons, thereby enhancing the overall performance of the neural network in processing visual data. The energy is described as
, are the linear transformations of t and , while t and are, respectively, the input object neuron and the other neurons in . i is the index in the spatial domain, and represents the number of neurons in this channel. To ascertain the linear separability of a neuron t from others within each channel, the approach involves minimizing the equation presented in Equation (2). This process involves simplifying the formula by employing binary labels and incorporating a regularization term. The resulting energy function is
For each pixel, there are energy equations to be solved. Fortunately, the analytical solution could be rendered
where
Thus, we put the minimum energy as
Equation (7) indicates that the lower the energy level, the more distinct neuron t is from its neighboring neurons, thus signifying a higher level of importance.
By synthesizing energy values e of each feature map, the importance indicator is gained. The feature maps are assigned to their corresponding weights:
Following the outlined procedures, the feature map is processed through an attention mechanism that incorporates neuron suppression in the spatial domain. Notably, this process is parameter-free, requiring only the setting of a single hyperparameter.
Within the Swin Transformer Block’s feature map progression, the features emerging after the W-MSA module exhibit a stronger focus on local attention while lacking global attention across windows. To mitigate the issue of local attention redundancy in smaller scenes, the neuron spatial suppression attention mechanism is integrated after the W-MSA. This module assigns weights to the features, enhancing their representation, as depicted in Figure 3.
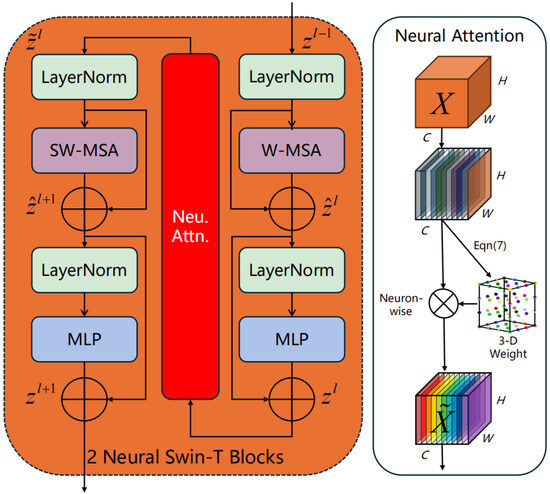
Figure 3.
Structure of the Neural Swin Transformer Block and the proposed attention module.
In detail, the neural attention module utilized a value that increases linearly:
where is the number of Neural Swin Transformer Blocks in the NST module (the number of Swin-T Blocks is equal to in the Swin-T module), this determines the length of the module and the depth of feature extraction.
3.3. Cross-Stage Connection Spatial Pyramid Pooling-Fast Module (CS-SPPF)
Since being proposed by Kaiming He et al. [53], the spatial pyramid pooling module has become the most commonly used multi-scale feature extraction module in the YOLO series algorithms. YOLOv8 [26] improved SPP by converting the separate pooling processes of different scales into continuous max-pooling, significantly improving efficiency. Influenced by the cross-stage design of the backbone network CSPDarkNet, we incorporate the SPPF module with residual connections as cross-stage processing, adding extra convolution layers to match the feature dimension before and after the concatenation, effectively reducing the loss of information extraction by the pooling layer and retaining most of the original features. The structure of CS-SPPF is shown in Figure 4.
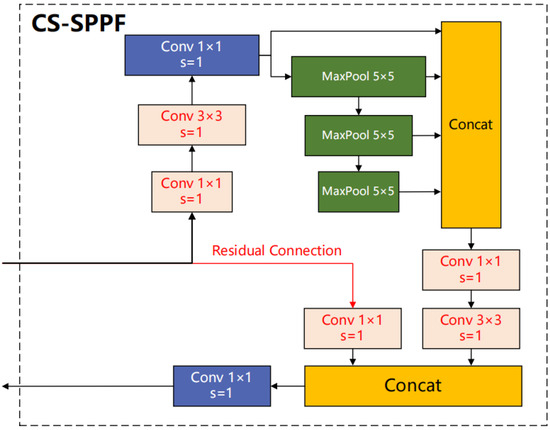
Figure 4.
Structure of the cross-stage connection spatial pyramid pooling-fast module.
3.4. Decoupled Detection Head Based on Anchor-Free Oriented Bounding Box (DOBB Head)
For the task of SAR ship detection using oriented bounding boxes addressed in this paper, the detection head is tasked with two primary sub-tasks: localizing the targets and classifying them. The nature of these tasks differs significantly—localization benefits from edge information in the image, whereas classification relies on texture and semantic details. This dichotomy makes it challenging for a traditional coupled head to optimize effectively under dual constraints, often leading to suboptimal weight configurations and potential issues like spatial misalignment.
To address this, the proposed detection head is designed as a decoupled structure, with separate pathways for localization and classification. This design enhances the head’s efficiency in interpreting feature maps. As illustrated in Figure 5b, are, respectively, the kernel size, stride, padding pixels and output channels of the convolutional module. In the OBBox branch, the term indicates that the x, y, w, h, and r (angle) parameters of the generated oriented bounding boxes are each distributed within their respective normal intervals. In the context of the Distributed Focal Loss (DFLoss) function, these parameters are assigned normalized probabilities, reflecting their likelihood of occurrence within the defined intervals. This normalization is crucial for effectively training the model to predict the spatial attributes of the bounding boxes. In the classification branch, , which obviously represents the probability of the predicted target belonging to each category.
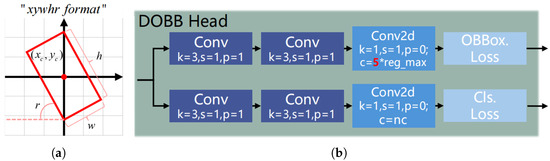
Figure 5.
Structure of the decoupled OBB head (b) and the OBB format (a).
Furthermore, as discussed in Section 2, anchor-based detection methods struggle with multi-scale targets in terms of both accuracy and efficiency. The proposed detection head, therefore, employs an anchor-free approach defined by “xywhr” coordinates, which represent the center coordinates, width, height, and rotation angle of the bounding box. By regressing these parameters, the model can directly predict rotation boxes tailored to the target’s dimensions, as shown in Figure 5a. For loss calculation, these rotation boxes are converted into the format required by DFLoss, which involves corner point coordinates. The schematic in Figure 5 outlines the structure of this decoupled detection head and the format of the anchor-free rotation boxes.
3.5. Merged Loss Function Focused on Classification and Regression
The decoupled detection head yields two primary outputs: categorical classifications and oriented bounding box coordinates. The composite loss function, which governs the optimization of these outputs, is formulated as:
where represent weights for three loss functions, and emphasis on classification or coordination could be adjusted through these weights.
To evaluate the effect of classification, a binary cross-entropy function is adopted:
where N stands for the number of images in a batch, and is the prediction of the image in comparison to the ground truth . As for the single-class detection task in this paper, w could be ignored.
In assessing the loss associated with the detection of oriented bounding boxes, the model utilizes two key loss functions: Distributed Focal Loss (DFLoss) and Complete Intersection over Union Loss (CIoU Loss). The DFLoss is:
Here, we focus on describing the tightness of the oriented bounding box around the ground truth. In this context, denotes , which represents the probability of the true value, y, occurring at the specific point . This probability is determined under the assumption that y follows a Gaussian distribution, confined within the interval . This approach allows the model to estimate the likelihood of the true value falling within specific ranges, which is essential for accurately predicting the position of the targets.
On the other hand, the CIoU loss function is based on the Intersection over Union (IoU) of the oriented bounding box:
which quantifies the overlap between the predicted bounding box and the ground truth. The CIoU function, however, enhances this by incorporating three key geometric considerations: the area of overlap, the distance between the centers of the two boxes, and the discrepancy in their aspect ratios as follows
where the parameters that describe the aspect ratio are
where h and w represent the length and width of the oriented bounding box, and represents the ground truth.
3.6. Optimizer
For the training of the proposed model, we employ Adam with Weight Decay Fix (AdamW) [54], which is well-suited for large-scale problems involving massive amounts of data. AdamW decouples weight decay from the gradient update step, applying weight decay directly to the model parameters rather than to the gradients. This modification is believed to lead to better convergence and generalization compared to the original Adam optimizer.
4. Experiments and Results
4.1. Datasets
This paper uses the Rotated Ship Detection Dataset in SAR Images (RSDD-SAR) [20] and the SAR Ship Detection Dataset (SSDD+) [21] as the experimental datasets. RSDD-SAR comprises 84 scenes from Gaofen-3 imagery, 41 scenes from TerraSAR-X, and 2 uncropped large images, totaling 127 scenes. These scenes are sliced into 7000 images with a resolution of 512 × 512, featuring 10,263 instances of ships. SSDD+, on the other hand, integrates 1160 images from RadarSat-2, TerraSAR-X, and Sentinel-1 data, spanning resolutions from 1 to 15 m in four polarizations, and the resolution is comparable to RSDD-SAR. The types of ships vary, but in the context of ship detection tasks, we categorize them into one single group. Detailed descriptions of RSDD-SAR and SSDD+ are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Detailed descriptions of RSDD-SAR and SSDD+.
Currently, the mainstream detection methods for SAR ship targets based on oriented bounding boxes [48,49,55,56,57,58,59] predominantly utilize these two datasets, achieving remarkable performance with Average Precision (AP) values exceeding . However, when it comes to more stringent metrics like or , which are indicators of model confidence in detection results, there is still potential for improvement. and specifically focus on detecting objects in difficult or low-confidence scenarios, making them crucial for evaluating the robustness of detection models.
4.2. Implementation Details
In this section, we delve into the specifics of the experiments performed using the proposed model on RSDD-SAR and SSDD+. The focus will be on three key areas: the design and selection of hyperparameters, the evaluation metrics, and the experimental environment and framework.
4.2.1. Design and Selection of Hyperparameters
This section gives details on the hyperparameters set during the training of the proposed model, as shown in Table 2. Ablation studies performed with YOLO11 have the same configurations.

Table 2.
Hyperparameter settings For YOLOs’ training on RSDD-SAR and SSDD+.
Considering the substantial variations in scale between RSDD-SAR and SSDD+, distinct batch sizes were employed during the training phase to optimize the learning process.
4.2.2. Evaluation Metrics
This study employs a set of standard evaluation metrics commonly used in object detection tasks, including Precision, Recall, and Average Precision (AP). These metrics are essential for assessing the performance of detection models. In the following comparison and evaluation, we focus on Average Precision at a confidence level of 0.5 () and 0.5 to 0.95 ().
4.2.3. Experimental Environment and Framework
The experimental hardware configuration is as follows: Intel Core™ i9-13900K CPU @ 3.0 GHz, NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4080 16 GB GPU, Windows 11 system. The experiment is run on the PyTorch framework, with CUDA12.2 accelerating computation.
Since YOLO11 was utilized as the baseline model, the training and validation processes of the proposed model were conducted using Ultralytics 8.3.1, and training configurations are given in Section 4.2.1.
Additionally, other models were trained on MMRotate 0.3.4, an open-source toolbox for rotated object detection based on PyTorch. MMRotate supports training and validation using MSR2N [60], R-FCOS [61], R-Faster RCNN [33], S2ANet [62] and so on, providing original settings and comprehensive evaluation metrics for these oriented object detection models. We conducted these models’ training and validation based on their default configuration, respectively (under version 0.3.4).
4.3. Comparisons with State-of-the-Art on SSDD+
In this section, we evaluate the performance of the proposed model on SSDD+ by comparing it against several recently proposed SAR ship detection models, including MSR2N [60], YOLO-FA [63], R-FCOS [61], R-Faster RCNN [33], S2ANet [62], FADet [55], BL-Net [57], NPA2Net [46], SAD-Det [64], and BiFA-YOLO [48]. The comparison is based on precision, recall, and . Additionally, model size quantified by the number of parameters is taken into account, as shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Performance comparison of oriented bounding box detection models on SSDD+.
The detection results indicate that our proposed model outperforms other models across all metrics, including precision, recall, and AP50, while also maintaining a relatively low parameter amount, closely following BiFA-YOLO and S2ANet. In Figure 6, the first column reveals that S2ANet, R-Faster R-CNN, and R-FCOS performed poorly in detecting the weak target signals in the center of the image, with the baseline model YOLO11m and the proposed model showing similar detection capabilities. However, in the second column, the former three models exhibited varying degrees of missed alarms, while the baseline model had one instance of false alarms. NST-YOLO11 accurately identified all targets beyond all the others. In the subsequent columns with nearshore scenarios, R-Faster R-CNN and the baseline model were less effective in mitigating ground clutter, whereas S2ANet and R-FCOS incorrectly merged adjacent targets into one. Our model effectively minimized false alarms due to ground clutter and demonstrated superior performance in dense target detection, albeit with some localization errors in expectation of further improvement.

Figure 6.
Detection results of NST-YOLO11 and other models on SSDD+: (a) ground truth, (b) S2ANet, (c) R-Faster R-CNN, (d) R-FCOS, (e) YOLO11m, (f) NST-YOLO11. Different colors indicate the detection results from specific models, except for green representing the ground truth.
4.4. Comparison with State-of-the-Art in the Nearshore/Offshore Scenarios on RSDD-SAR
Table 4 presents a comparison of the proposed NST-YOLO11’s performance on RSDD-SAR, using the metric across entire, nearshore, and offshore scenarios, with FADet [55], FcaNet [58], R-RetinaNet [59], R-FCOS [27], R-Faster RCNN [33], EPE [65], SAD-Det [64], and NPA2Net [46]. Our model consistently outperforms other models, achieving optimal performance in both complex nearshore scenes and sparser offshore images. Notably, it reaches 87.43% in nearshore and 98.96% in offshore scenarios. The smaller discrepancy between these two metrics underscores the model’s enhanced robustness to nearshore geographical influences.

Table 4.
Performance comparison of the oriented bounding box models in the nearshore/offshore scenarios on RSDD-SAR.
On the expansive RSDD-SAR, NST-YOLO11 exhibits a marked improvement in detection performance. Despite having the lowest parameter count among the compared models, it delivers superior results in both entire and offshore, as well as inshore detection scenarios. The proposed model achieves an impressive , surpassing the previous performance of . In the challenging nearshore environment, the proposed model maintains a high AP50 value of , significantly outperforming other models. Additionally, in the simpler offshore context, the model maintains a strong lead with an AP50 of .
4.5. Ablation Experiments
In this section, we evaluate the efficacy of our proposed enhancements through ablation studies on the RSSD-SAR and SSDD+ datasets using the NST-YOLO11 model. We specifically analyze three modifications based on YOLO11m:
- Incorporation of the SPPF module with cross-stage connections.
- Addition of the Swin-T module following the backbone network.
- Integration of attention mechanisms, informed by neuron suppression in the spatial domain, into the Swin-T module.
The evaluation metrics include Precision, Recall, , and . The findings from these experiments are presented in Table 5.

Table 5.
Ablation experiments of the proposed NST-YOLO11 on RSDD-SAR and SSDD+.
It is observed that the metrics of the various models are already quite similar. The excessive focus on increasing might lead to overfitting. However, our proposed model demonstrates a more significant advantage in the metric, indicating a deeper understanding of target characteristics and higher confidence in detection results, leading to more robust detections. On RSDD-SAR, the incorporation of the Swin-T module led to the suboptimal score of , likely due to the enhanced ability of the self-attention mechanism in generating oriented bounding boxes, as evidenced by improvements in the precision metric. The CS-SPPF module, despite adding approximately 8M parameters, effectively improved the recall metric, affirming its capability of detecting multi-scale targets. Furthermore, the Neural Swin-T modifications enhanced model performance without additional parameters, particularly in the precision metric, suggesting that the intended reduction in local attention redundancy in smaller scenes has been realized. On SSDD+, similar trends were observed in the performance of each module. Interestingly, the Neural Swin-T module showed a slight decrement in performance compared to Swin-T on this smaller dataset, hinting at untapped potential for the Neural Swin-T approach on larger datasets.
4.6. Transfer Experiment with SSDD+ Trained Model on RSDD-SAR
The deep learning method’s tendency to fit high-dimensional data can often lead to challenging non-convex optimization issues. To assess the generalization capabilities of our model in real-world scenarios, we conduct comparative experiments on RSDD-SAR using models trained on SSDD+, including S2ANet [62], R-Faster R-CNN [33], R-FCOS [27], YOLO11m, and the NST-YOLO11. This aims to showcase the robust performance of our proposed model across varying imaging conditions, radar parameters, and geographical distributions. The detection outcomes for each model are illustrated in Figure 7.
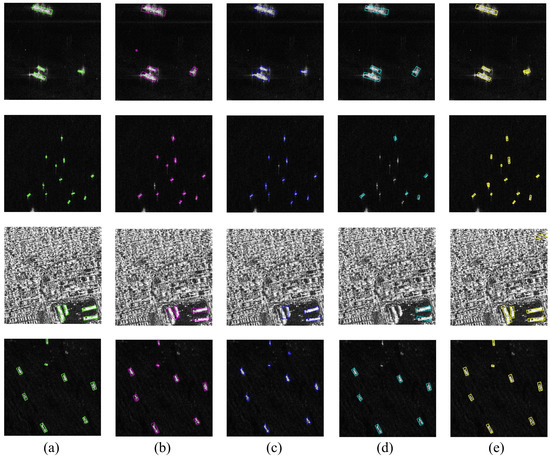
Figure 7.
Detection results of SSDD+ trained NST-YOLO11 and other models on RSDD-SAR: (a) ground truth, (b) S2ANet, (c) R-Faster R-CNN, (d) R-FCOS, (e) NST-YOLO11. Different colors indicate the detection results from specific models, except for green representing the ground truth.
5. Visualization and Discussion
We evaluate the proposed model’s fine performance in multi-scale SAR ship detection tasks by comparing it with several state-of-the-art oriented bounding box detection models on SSDD+ and RSDD. Figure 6 presents the detection outcomes of three other models, the original YOLO11m, and our proposed model. Our model demonstrates enhanced capabilities in detecting weak and small targets compared to others, and it provides more precise bounding boxes with reduced false alarms in complex nearshore scenarios, as evidenced by the original YOLO11m comparison. This is further supported by the metrics in Table 4. On RSDD, we divided the experiments into entire, inshore, and offshore scenarios to assess the model’s performance across varying task complexities. NST-YOLO11 consistently achieved the best results in all three scenarios, with scores of , , and , and topped Table 5 with a parameter size of only , indicating its excellent balance of detection accuracy and computational efficiency.
To validate the effectiveness of our improvement modules, we conducted ablation studies on RSDD-SAR and SSDD+. By combining the introduced modules and their intermediate versions, we observed consistent improvements over the original model. On RSDD-SAR, the CS-SPPF module, enhanced with residual connections, significantly increased the Recall metric to and (with Swin-T), indicating a more comprehensive detection. With the original Swin-T module, we noted the suboptimal score of , a testament to the advanced attention capabilities. Furthermore, incorporating the Neural Swin-T module led to a precision of without adding any trainable parameter and notably improved the model’s performance on the challenging metric, reaching . This validates the attention mechanism’s effectiveness in identifying crucial neurons. The better results on RSDD-SAR, we assumed, compared to SSDD+ likely stem from Swin-T’s self-attention module, which demonstrates greater potential for improvement on larger datasets.
To gain a clearer insight into the contributions of each module, we employed the method GradCAM++ [66] on RSDD-SAR to visualize the attention distributions of the models when each module was introduced individually. Feature maps are acquired from the input of medium DOBB Head (P4). This visualization is presented in Figure 8.

Figure 8.
Visualizations with GradCAM++ on ablation models and the proposed model: (a) images, (b) YOLO11m, (c) YOLO11m+Swin-T, (d) YOLO11m+Swin-T+CS-SPPF, (e) NST-YOLO11.
6. Conclusions
Our proposed model significantly enhances oriented SAR ship detection. It begins by refining target indication accuracy through an oriented detection model, which in turn optimizes the model’s feature perception for targets. The CS-SPPF module further boosts the detection of small targets, ensuring more comprehensive results and fewer missed detections. The Neural Swin-T module, incorporating a neuron spatial suppression attention mechanism, enhances detection accuracy without adding trainable parameters, outperforming the standard Swin-T. Experimental results on SSDD+ and RSDD demonstrate SOTA achievements across metrics like precision, recall, and . In nearshore and offshore scenarios, our model surpasses other oriented bounding box detectors, as indicated by . NST-YOLO11’s advancements are particularly notable in complex nearshore scenes and with multi-scale, arbitrary-oriented targets. However, variations in dataset size reveal the “data hunger” issue, suggesting room for improvement; the hyperparameter in the neural attention module requires in-depth determination with respect to the features of SAR images, experiments for search might be helpful for adapting the proposed model to another domain; a general exploration of the proposed method’s application to other datasets (i.e., optical or hyperspectral remote sensing images) could provide a more comprehensive insight into the limitations of the proposed method. Due to the dataset we selected for experiments, NST-YOLO11’s classification results may only reach the basic category level, and it may be quite challenging for more detailed sub-category classification, which requires further improvement in the dataset and model. In conclusion, while NST-YOLO11 has demonstrated significant advancements in detecting complex nearshore scenes and multi-scale, arbitrary-oriented targets, it is clear that there are several areas where further research and development are necessary. As research progresses, addressing these challenges will be crucial in order to enhance the robustness and versatility of NST-YOLO11, ultimately leading to more accurate and reliable detection capabilities across a broader range of applications and scenarios.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.A.; methodology, Y.H.; software, Y.H. and D.W.; validation, Y.H. and B.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of this manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan under Grant 2024JJ10002, the Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars of Hunan Province under Grant 2022JJ10062, and the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 62271492.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Li, J.; Chen, J.; Cheng, P.; Yu, Z.; Yu, L.; Chi, C. A Survey on Deep-Learning-Based Real-Time SAR Ship Detection. IEEE J. Sel. Topics Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2023, 16, 3218–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Song, Y.; Huang, J.; An, D.; Chen, L. SAR Target Classification Based on Multiscale Attention Super-Class Network. IEEE J. Sel. Topics Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 9004–9019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; An, D.; Ge, B.; Zhou, Z. Detection, Parameters Estimation, and Imaging of Moving Targets Based on Extended Post-Doppler STAP in Multichannel WasSAR-GMTI. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5223515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Wang, D.; An, D. Impact of SAR Image Quantization Method on Target Recognition With Neural Networks. IEEE J. Sel. Topics Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2025, 18, 308–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; An, D.; Li, J.; Chen, L.; Feng, D.; Song, Y.; Zhou, Z. The Dual-Band SAR Image Fusion-Based Foliage-Penetrating Target Detection Method. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5226513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, B.; An, D.; Liu, J.; Chen, L.; Feng, D.; Song, Y.; Zhou, Z. Three-Dimensional Parameter Estimation of Moving Target for Multichannel Airborne Wide-Angle Staring SAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5201115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xiong, R.; Yu, H.; Xu, G.; Xing, M. Nonparametric Full-Aperture Autofocus Imaging for Microwave Photonic SAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5214815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, M.; Yu, H.; Xing, M. Full-Aperture Processing of Airborne Microwave Photonic SAR Raw Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5218812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renga, A.; Graziano, M.D.; D’Errico, M.; Moccia, A.; Cecchini, A. SAR-based sea traffic monitoring: A reliable approach for Maritime Surveillance. In Proceedings of the SAR Image Analysis, Modeling, and Techniques XI, Prague, Czech Republic, 19–22 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Graziano, M.D. Preliminary Results of Ship Detection Technique by Wake Pattern Recognition in SAR Images. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchandt, S.; Runge, H.; Kotenkov, A.; Breit, H.; Steinbrecher, U. Extraction of traffic flows and surface current information using Terrasar-X Along-track interferometry data. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Cape Town, South Africa, 12–17 July 2009; Volume 2, pp. II-17–II-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, X.; Gao, G.; Lang, H.; Liu, G.; Cao, C.; Song, Y.; Guan, Y.; Dai, Y. Development and Application of Ship Detection and Classification Datasets: A review. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2024, 12, 12–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, L.M.; Owirka, G.J.; Netishen, C.M. Performance of a High-Resolution Polarimetric SAR Automatic Target Recognition System. Linc. Lab. J. 1993, 6, 11–24. [Google Scholar]
- Potter, L.C.; Moses, R.L. Attributed scattering centers for SAR ATR. IEEE Trans. Image. Process. 1997, 6, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, G. Statistical Modeling of SAR Images: A Survey. Sensors 2010, 10, 775–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, J.C.; Luo, Y.; Wang, D.; Liang, J.; Zhang, Q. Saliency-Based SAR Target Detection via Convolutional Sparse Feature Enhancement and Bayesian Inference. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5202015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Leng, X.; Sun, Z.; Ji, K. Construction and Recognition Performance Analysis of Wide-swath SAR Maritime Large Moving Ships Dataset. J. Radars. 2022, 11, 347–362. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, D.; Huang, W.; An, D. A ViT Merged Oriented-Detector with Neuron Attention for Ship Detection in SAR Images. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 7th International Conference on Electronic Information and Communication Technology (ICEICT), Xi’an, China, 30 July–2 August 2024; pp. 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochkovskiy, A.; Wang, C.Y.; Liao, H.Y.M. YOLOv4: Optimal Speed and Accuracy of Object Detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.10934. [Google Scholar]
- Congan, X.; Hang, S.; Jianwei, L.; Yu, L.; Libo, Y.; Long, G.; Wenjun, Y.; Taoyang, W. RSDD-SAR: Rotated Ship Detection Dataset in SAR Images. J. Radars 2022, 11, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Xu, X.; Wang, B.; Zhan, X.; Xu, Y.; Ke, X.; Zeng, T.; Su, H.; et al. SAR Ship Detection Dataset (SSDD): Official Release and Comprehensive Data Analysis. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You Only Look Once: Unified, Real-Time Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit, (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLOv3: An Incremental Improvement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.02767. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Li, L.; Jiang, H.; Weng, K.; Geng, Y.; Li, L.; Ke, Z.; Li, Q.; Cheng, M.; Nie, W.; et al. YOLOv6: A Single-Stage Object Detection Framework for Industrial Applications. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2209.02976. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.Y.; Bochkovskiy, A.; Liao, H.Y.M. YOLOv7: Trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2207.02696. [Google Scholar]
- Reis, D.; Kupec, J.; Hong, J.; Daoudi, A. Real-Time Flying Object Detection with YOLOv8. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.09972. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Z.; Shen, C.; Chen, H.; He, T. FCOS: A Simple and Strong Anchor-Free Object Detector. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 44, 1922–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.Y.; Berg, A.C. SSD: Single Shot MultiBox Detector. In Computer Vision–ECCV 2016: Proceedings of the 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; Volume 9905, pp. 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carion, N.; Massa, F.; Synnaeve, G.; Usunier, N.; Kirillov, A.; Zagoruyko, S. End-to-End Object Detection with Transformers. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.12872.,. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.; Polosukhin, I. Attention Is All You Need. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.03762. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R. Fast R-CNN. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1440–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Li, Y.; He, K.; Sun, J. R-FCN: Object Detection via Region-based Fully Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS 2016), Barcelona, Spain, 5–10 December 2016; Volume 29. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollar, P.; Girshick, R. Mask R-CNN. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 42, 386–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.Y.; Dollar, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature Pyramid Networks for Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 936–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Xu, H.; Tian, T.; Gao, P.; Li, L.; Zhao, T.; Zhang, N.; Tian, J. SEFEPNet: Scale Expansion and Feature Enhancement Pyramid Network for SAR Aircraft Detection With Small Sample Dataset. IEEE J. Sel. Topics Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 3365–3375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Chen, P.; Zhang, Y. A Multiscale Feature Pyramid SAR Ship Detection Network With Robust Background Interference. IEEE J. Sel. Topics Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2023, 16, 9904–9915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Hou, G.; Xin, Z.; Liao, G.; Huang, P.; Tai, Y. Detection of SAR Image Multiscale Ship Targets in Complex Inshore Scenes Based on Improved YOLOv5. IEEE J. Sel. Topics Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 5804–5823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhan, R.; Wang, W.; Zhang, J. LMSD-YOLO: A Lightweight YOLO Algorithm for Multi-Scale SAR Ship Detection. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Luo, R.; Xing, J.; Li, Z.; Yuan, Z.; Cai, X. Geospatial Transformer Is What You Need for Aircraft Detection in SAR Imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5225715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, R.; Yu, Y. A Lightweight SAR Ship Detector Using End-to-End Image Preprocessing Network and Channel Feature Guided Spatial Pyramid Pooling. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2024, 21, 4003605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Yao, T.; Tang, Y. A CFAR-Enhanced Ship Detector for SAR Images Based on YOLOv5s. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Leng, X.; Luo, R.; Sun, Z.; Ji, K.; Kuang, G. YOLO-RC: SAR Ship Detection Guided by Characteristics of Range-Compressed Domain. IEEE J. Sel. Topics Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 18834–18851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Cai, Z.; Yuan, J. Automatic SAR Ship Detection Based on Multifeature Fusion Network in Spatial and Frequency Domains. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 4102111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. CBAM: Convolutional Block Attention Module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; Volume 11211, pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, P.; Wang, H.; Jin, Y. NPA2Net: A Nested Path Aggregation Attention Network for Oriented SAR Ship Detection. IEEE J. Sel. Topics Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 9772–9789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, S.; Ren, H.; Hu, J.; Zou, L.; Wang, X. Multi-Level Feature-Refinement Anchor-Free Framework with Consistent Label-Assignment Mechanism for Ship Detection in SAR Imagery. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Leng, X.; Lei, Y.; Xiong, B.; Ji, K.; Kuang, G. BiFA-YOLO: A Novel YOLO-Based Method for Arbitrary-Oriented Ship Detection in High-Resolution SAR Images. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Liu, Q.; Yu, W.; Lv, J. A Single-Stage Arbitrary-Oriented Detector Based on Multiscale Feature Fusion and Calibration for SAR Ship Detection. IEEE J. Sel. Topics Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 8179–8198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.; Chen, J.; Huang, Z.; Xia, R.; Wu, B.; Sun, L.; Yao, B.; Liu, X.; Xing, M. AFSar: An Anchor-Free SAR Target Detection Algorithm Based on Multiscale Enhancement Representation Learning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5219514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin Transformer: Hierarchical Vision Transformer using Shifted Windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 9992–10002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, R.Y.; Li, L.; Xie, X. SimAM: A Simple, Parameter-Free Attention Module for Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Online, 18–24 July 2021; Volume 139, pp. 11863–11874. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Spatial Pyramid Pooling in Deep Convolutional Networks for Visual Recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 37, 1904–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loshchilov, I.; Hutter, F. Decoupled Weight Decay Regularization. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1711.05101. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, H.; Chen, J.; Huang, Z.; Du, W.; Xu, F.; Wang, F.; Wu, B. Orientation Detector for Ship Targets in SAR Images Based on Semantic Flow Feature Alignment and Gaussian Label Matching. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5218616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Su, H.; Gao, L.; Wu, J.; Yan, W. Rotated SAR Ship Detection based on Gaussian Wasserstein Distance Loss. Mob. Netw. Appl. 2023, 28, 1842–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, X.; Liu, C.; Shi, J.; Wei, S.; Ahmad, I.; Zhan, X.; Zhou, Y.; Pan, D.; Li, J.; et al. Balance learning for ship detection from synthetic aperture radar remote sensing imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 182, 190–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, L.; Zhao, C.; Wang, N.; Chen, J. Rotating Target Detection of SAR Image Based on Multi-scale Attentino Module for Inshore Ships. In IGARSS 2023—Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Pasadena, CA, USA, 16–21 July 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 7034–7037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Pan, Z.; Jia, X.; Zhang, L.; Deng, Y. A Novel CNN-Based Detector for Ship Detection Based on Rotatable Bounding Box in SAR Images. IEEE J. Sel. Topics Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 1938–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Yang, R.; Zhang, Z. MSR2N: Multi-Stage Rotational Region Based Network for Arbitrary-Oriented Ship Detection in SAR Images. Sensors 2020, 20, 2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; An, W.; Li, S.; Wei, G.; Zou, B. An Improved FCOS Method for Ship Detection in SAR Images. IEEE J. Sel. Topics Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 8910–8927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Ding, J.; Li, J.; Xia, G.S. Align Deep Features for Oriented Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5602511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, W.; Wang, X.; Li, G.; He, Y. Frequency-Adaptive Learning for SAR Ship Detection in Clutter Scenes. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5215514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Yu, C.; Zhao, S.; Song, H. An Anchor-Free Method Based on Transformers and Adaptive Features for Arbitrarily Oriented Ship Detection in SAR Images. IEEE J. Sel. Topics Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 2012–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, L.; Xiao, J. Ellipse Polar Encoding for Oriented SAR Ship Detection. IEEE J. Sel. Topics Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 3502–3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhay, A.; Sarkar, A.; Howlader, P.; Balasubramanian, V.N. Grad-CAM++: Generalized Gradient-Based Visual Explanations for Deep Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 12–15 March 2018; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).