Monitoring Thermal Exchange of Hot Water Mass via Underwater Acoustic Tomography with Inversion and Optimization Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Simulation Model and Method
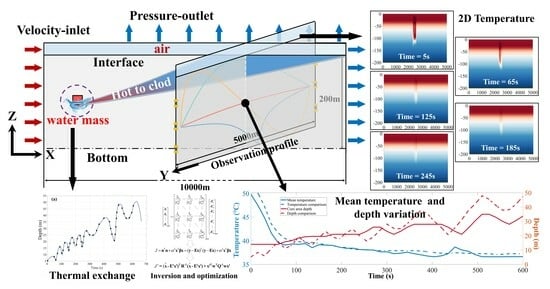
2.1. Simulation Model
2.2. Inversion Method
2.3. Optimization of Vertical Results
3. Thermal Exchange and Signal Identification
3.1. Thermal Exchange
3.2. Signal Identification in Acoustic Transmission Simulation
4. Results
4.1. Travel Time Variation
4.2. Inversion and Optimization Results
4.3. Comparison
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
- The sound speed of RSMEs between simulation results and inversion optimization results at whole core observation area is 2.23 m/s (equivalent to 0.4 °C temperature change), which is less than the error requirements. Furthermore, the curves fluctuations input and results are close and similar.
- The new proposed methods combined inversion and optimization, are based on the simulated hot water mass mode matrix, and are successfully used in the observation. The accuracy of results is verified the method effect.
- The signal transmission can be influenced by the hot water mass flotation and diffusion. Due to the small water temperature variation, the station deployment needs to consider the relationship between the signal loss and transmission distance.
- The application of acoustic tomography is an innovative way for thermal exchange observation, which is proved by the simulation comparison. The real sea scale variation needs further study and verification.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pearce, A.F.; Feng, M. The rise and fall of the “marine heat wave” off Western Australia during the summer of 2010/2011. J. Mar. Syst. 2013, 111, 139–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobday, A.J.; Alexander, L.V.; Perkins, S.E.; Smale, D.A.; Straub, S.C.; Oliver, E.C.J.; Benthuysen, J.A.; Burrows, M.T.; Donat, M.G.; Peng, M.; et al. A hierarchical approach to defining marine heatwaves. Prog. Oceanogr. 2016, 141, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scannell, H.A.; Johnson, G.C.; Thompson, L.; Lyman, J.M.; Riser, S.C. Subsurface Evolution and Persistence of Marine Heatwaves in the Northeast Pacific. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benthuysen, J.A.; Oliver, E.C.J.; Feng, M.; Marshall, A.G. Extreme Marine Warming Across Tropical Australia during Austral Summer 2015–2016. J. Geophys. Res.-Oceans 2018, 123, 1301–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.Q.; Zhang, L.; Meehl, G.A.; Kido, S.; Tozuka, T.; Li, Y.L.; McPhaden, M.J.; Hu, A.X.; Cazenave, A.; Rosenbloom, N.; et al. Sea level extremes and compounding marine heatwaves in coastal Indonesia. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varela, R.; Rodriguez-Diaz, L.; de Castro, M.; Gomez-Gesteira, M. Influence of Eastern Upwelling systems on marine heatwaves occurrence. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2021, 196, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentemann, C.L.; Fewings, M.R.; Garcia-Reyes, M. Satellite sea surface temperatures along the West Coast of the United States during the 2014–2016 northeast Pacific marine heat wave. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, E.C.J.; Benthuysen, J.A.; Darmaraki, S.; Donat, M.G.; Hobday, A.J.; Holbrook, N.J.; Schlegel, R.W.; Sen Gupta, A. Marine Heatwaves. In Annual Review of Marine Science; Carlson, C.A., Giovannoni, S.J., Eds.; Annual Review of Marine Science; Annual Reviews: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 2021; Volume 13, pp. 313–342. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.Y.; Shi, J.; Li, C. Two types of warm blobs in the Northeast Pacific and their potential effect on the El Nino. Int. J. Climatol. 2021, 41, 2810–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, B.; Zeng, L.L.; He, Y.K.; Wu, Z.W.; Chen, J. Properties and Drivers of Marine Heat Waves in the Northern South China Sea. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2022, 52, 917–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munk, W.; Wunsch, C. Ocean acoustic tomography—Scheme for large-scale monitoring. Deep. Sea Res. Part A Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 1979, 26, 123–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornuelle, B.; Munk, W.; Worcester, P. Ocean acoustic tomography from ships. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1989, 94, 6232–6250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, E.C.; Wang, Y.Y. Acoustic travel time computation based on pe solution. J. Comput. Acoust. 1993, 1, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behringer, D.; Birdsall, T.; Brown, M.; Cornuelle, B.; Heinmiller, R.; Knox, R.; Metzger, K.; Munk, W.; Spiesberger, J.; Spindel, R.; et al. A demonstration of ocean acoustic tomography. Nature 1982, 299, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.Z.; Kaneko, A.; Zhu, X.H.; Gohda, N. Tomographic mapping of a coastal upwelling and the associated diurnal internal tides in Hiroshima Bay, Japan. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2015, 120, 4288–4305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.J.; Li, G.M.; Feng, R.D.; Hu, Z.L.; Xu, P.; Huang, H.C. 3-D Water Temperature Distribution Observation via Coastal Acoustic Tomography Sensing Network. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawanisi, K.; Bahrainimotlagh, M.; Al Sawaf, M.B.; Razaz, M. High-frequency streamflow acquisition and bed level/flow angle estimates in a mountainous river using shallow-water acoustic tomography. Hydrol. Process. 2016, 30, 2247–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.M.; Hanifa, A.D.; Taniguchi, N.; Mutsuda, H.; Zhu, X.H.; Zhu, Z.N.; Zhang, C.Z.; Lin, J.; Kaneko, A. Coastal Acoustic Tomography of the Neko-Seto Channel with a Focus on the Generation of Nonlinear Tidal Currents-Revisiting the First Experiment. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackenzie, K.V. Nine-term equation for sound speed in the oceans. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1981, 70, 807–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.J.; Li, G.M.; Feng, R.D.; Hu, Z.L.; Xu, P.; Huang, H.C. Tomographic Mapping of Water Temperature and Current in a Reservoir by Trust-Region Method Based on CAT. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.J.; Feng, R.D.; Xu, P.; Hu, Z.L.; Huang, H.C.; Li, G.M. Flow current field observation with underwater moving acoustic tomography. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, P.C. Analysis of discrete ill-posed problems of the L-curve. SIAM Rev. 1992, 34, 561–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Station Pairs | Launch Angle (°) | Ray Length (m) | Travel Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50 m_50 m | −2.96 (blue ray) | 5045.919590 | 3.3144957 |
| −1 (red ray) | 5042.638983 | 3.314263 | |
| 4.54 (green ray) | 5050.544503 | 3.314902 | |
| 100 m_100 m | −5.57 (blue ray) | 5032.079960 | 3.3136260 |
| −1 (rad ray) | 5019.860809 | 3.3125639 | |
| 5.57 (green ray) | 5032.025004 | 3.313598 | |
| 150 m_150 m | −3.45 (blue ray) | 5010.278219 | 3.312462 |
| 1.63 (rad ray) | 5006.951102 | 3.312726 | |
| 3.46 (green ray) | 5010.304894 | 3.312469 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, S.; Yu, F.; Zhang, X.; Diao, Y.; Li, G.; Huang, H. Monitoring Thermal Exchange of Hot Water Mass via Underwater Acoustic Tomography with Inversion and Optimization Method. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1105. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16061105
Xu S, Yu F, Zhang X, Diao Y, Li G, Huang H. Monitoring Thermal Exchange of Hot Water Mass via Underwater Acoustic Tomography with Inversion and Optimization Method. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(6):1105. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16061105
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Shijie, Fengyuan Yu, Xiaofei Zhang, Yiwen Diao, Guangming Li, and Haocai Huang. 2024. "Monitoring Thermal Exchange of Hot Water Mass via Underwater Acoustic Tomography with Inversion and Optimization Method" Remote Sensing 16, no. 6: 1105. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16061105
APA StyleXu, S., Yu, F., Zhang, X., Diao, Y., Li, G., & Huang, H. (2024). Monitoring Thermal Exchange of Hot Water Mass via Underwater Acoustic Tomography with Inversion and Optimization Method. Remote Sensing, 16(6), 1105. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16061105