Abstract
Satellite precipitation products (SPPs) have emerged as an alternative to estimate rainfall erosivity. However, prior studies showed that SPPs tend to underestimate rainfall erosivity but without reported bias-correction methods. This study evaluated the efficacy of two SPPs, namely, GPM_3IMERGHH (30-min and 0.1°) and GPM_3IMERGDF (daily and 0.1°), in estimating two erosivity indices in mainland China: the average annual rainfall erosivity (R-factor) and the 10-year event rainfall erosivity (10-yr storm EI), by comparing with that derived from gauge-observed hourly precipitation (Gauge-H). Results indicate that GPM_3IMERGDF yields higher accuracy than GPM_3IMERGHH, though both products generally underestimate these indices. The Percent Bias (PBIAS) is −55.48% for the R-factor and −56.38% for the 10-yr storm EI using GPM_3IMERGHH, which reduces to −10.86% and −32.99% with GPM_3IMERGDF. A bias-correction method was developed based on the systematic difference between SSPs and Gauge-H. A five-fold cross validation shows that with bias-correction, the accuracy of the R-factor and 10-yr storm EI for both SPPs improve considerably, and the difference between two SSPs is reduced. The PBIAS using GPM_3IMERGHH decreases to −0.06% and 0.01%, and that using GPM_3IMERGDF decreases to −0.33% and 0.14%, respectively, for the R-factor and 10-yr storm EI. The rainfall erosivity estimated with SPPs with bias-correction shows comparable accuracy to that obtained through Kriging interpolation using Gauge-H and is better than that interpolated from gauge-observed daily precipitation. Given their high temporal and spatial resolution, and timely updates, GPM_3IMERGHH and GPM_3IMERGDF are viable data products for rainfall erosivity estimation with bias correction.
1. Introduction
Soil erosion is one of the most severe environmental challenges in China [1]. Rainfall is the primary external force responsible for the detachment and transport of soil particles from soil masses, resulting in water-induced soil erosion [2]. The potential of rainfall to cause water-induced soil erosion is defined as the rainfall erosivity index in water erosion models, and the product of rainfall energy (E) and 30-min peak intensity (I30) during a storm is considered as the optimal indicator to estimate rainfall erosivity during a storm. The long-term (over 22 years) average of annual total EI30 is defined as the R-factor [3,4,5,6].
Given the high variability and randomness in rainfall intensity, the utilization of high-temporal-resolution precipitation data, such as breakpoint precipitation or minutely level measurements from rain gauges, should be the primary choice for accurately estimating rainfall erosivity [4,5,6,7,8]. However, these high-resolution datasets are frequently sparsely distributed and fail to represent the spatial distribution of rainfall. The deployment of gauge stations is limited by observational costs and practical feasibility, resulting in less dense networks. Furthermore, the higher the temporal resolution of precipitation data, the more challenging and less accessible they become. While gauge observations offer detailed site-specific measurements, their limited spatial distribution and inability to accurately represent spatial variations pose significant challenges [9].
Consequently, exploring alternative methods to depict the characteristics and changes of rainfall erosivity on both temporal and spatial scales becomes necessary. Temporally, models based on lower-resolution precipitation data, ranging from hourly to annual measurements, have been developed [7,8,10,11]. However, it is important to note that a decrease in temporal resolution typically results in reduced model accuracy [8]. Spatially, gridded datasets serve as an alternative to gauge observations, offering a more continuous spatial representation of precipitation. These datasets include gridded precipitation data derived from gauge-interpolation methods [12,13,14,15], and satellite or weather radar retrievals [9,16,17]. However, these datasets also have their limitations [18]. The interpolation-gridded products are not suitable to directly apply in erosivity estimation because the extreme values observed at gauges will be smoothed during the interpolation processes [18,19,20]. As Wang et al. [19] reported, the application of gridded datasets to estimate rainfall erosivity directly in China will lead to an underestimation of 15% to 40% in the R-factor and 25% to 50% in the 10-yr storm EI, respectively.
With the advancement of satellite remote sensing technology and precipitation retrieval algorithms, remote sensing precipitation products have emerged as a novel meteorological observation method, offering expansive spatial coverage. In comparison with gauge observations and interpolated products, which are often subject to delayed updates, satellite precipitation products are frequently updated, providing more timely data. These products are increasingly available at high temporal resolutions, including datasets with 3-h, hourly, and even 30-min intervals [21,22,23]. Consequently, remote sensing precipitation products have frequently been considered in hydrological and soil erosion studies in recent years [23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31].
Previous studies have widely explored the applicability of remote sensing precipitation in rainfall erosivity estimation, such as the level-3 satellite precipitation product released by the Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) [29,30,31,32], the IMERG series satellite inversion precipitation products produced by the Global Precipitation Measurement mission (GPM) [26,27,29], the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s Climate Precipitation Center morphing technique (CMORPH) [21,33,34], and Climate Hazards Group InfraRed Precipitation with Station Data (CHIRPS) [35,36].
On one hand, many studies have highlighted the strengths of remote sensing precipitation in capturing the spatial distribution of rainfall erosivity [26,29,30,31,34,37,38]. For example, Chen et al. [29] observed a high Pearson correlation coefficient of 0.98 and 0.97, respectively, between annual rainfall erosivity derived from gauge-interpolation results and the daily products of GPM IMERG-F and TRMM at a 0.25° spatial resolution over mainland China.
On the other hand, it has been noted that most remote sensing precipitation products, including TRMM and GPM, tend to underestimate rainfall erosivity [21,26,27,30,37,39]. However, it is crucial to recognize that estimation accuracy varies with the methodologies and datasets employed. For instance, Xing et al. [30] reported that the monthly, seasonal, and annual rainfall erosivity were underestimated by TRMM precipitation products by −26.5% to −32.2%. In contrast, Chen et al. [29] reported a much lower bias in rainfall erosivity estimates using TRMM precipitation products, ranging from 1.1% to 1.2%. This discrepancy may be attributed, at least in part, to differences in the methodologies used in the two studies. Xing et al. [30] based their comparison on rainfall erosivity calculated from 738 stations, while Chen et al. [29] utilized gridded rainfall erosivity data at a 0.25° spatial resolution, which was interpolated from 2417 stations across mainland China. The process of spatial interpolation from gauge observations to large-scale grids at 0.25° resolution can lead to some spatial smoothing of rainfall erosivity values [18,19,20]. Consequently, the evaluation results reported by Chen et al. [29] may not reflect the same level of underestimation as observed in the study by Xing et al. [30].
Overall, the potential of satellite precipitation products in estimating rainfall erosivity has been widely explored. The underestimation of rainfall erosivity estimated using satellite precipitation products has been noticed. Obviously, a bias-correction approach is needed before applying these kinds of satellite precipitation products in soil erosion studies [27]. However, corresponding methods have not been developed or reported in previous studies.
Additionally, previous studies have generally overlooked the assessment of the accuracy of the 10-yr storm EI estimated by satellite precipitation products. This index, known as extreme event rainfall erosivity (EI30) with a return period of 10 years, serves as a critical input in soil erosion models [5]. In the context of global warming, significant variations in the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events have been observed globally [40,41,42,43,44,45]. These changes have led to an increase in rainfall erosivity [46], potentially influencing the erosive index of the 10-yr storm EI [20]. Hence, when evaluating a satellite product for rainfall erosivity estimation, it is essential to consider not only the long-term annual average (R-factor) but also the 10-yr storm EI.
The objective of this study is to develop a sample framework for utilizing GPM satellite precipitation products, which offer high temporal and spatial resolution, comprehensive spatial coverage, and timely updates, to estimate two key rainfall erosivity indices for soil erosion models: the R-factor and 10-yr storm EI. To evaluate their accuracy, gauge-observed hourly precipitation data were collected from 2310 meteorological stations across mainland China. Then, the systematic biases between rainfall erosivity estimated from GPM products and gauge-observed hourly precipitation were addressed by developing these relationships for different water erosion regions. The coefficients from these relationships were subsequently applied as bias-correction factors.
2. Data and Method
2.1. Study Area
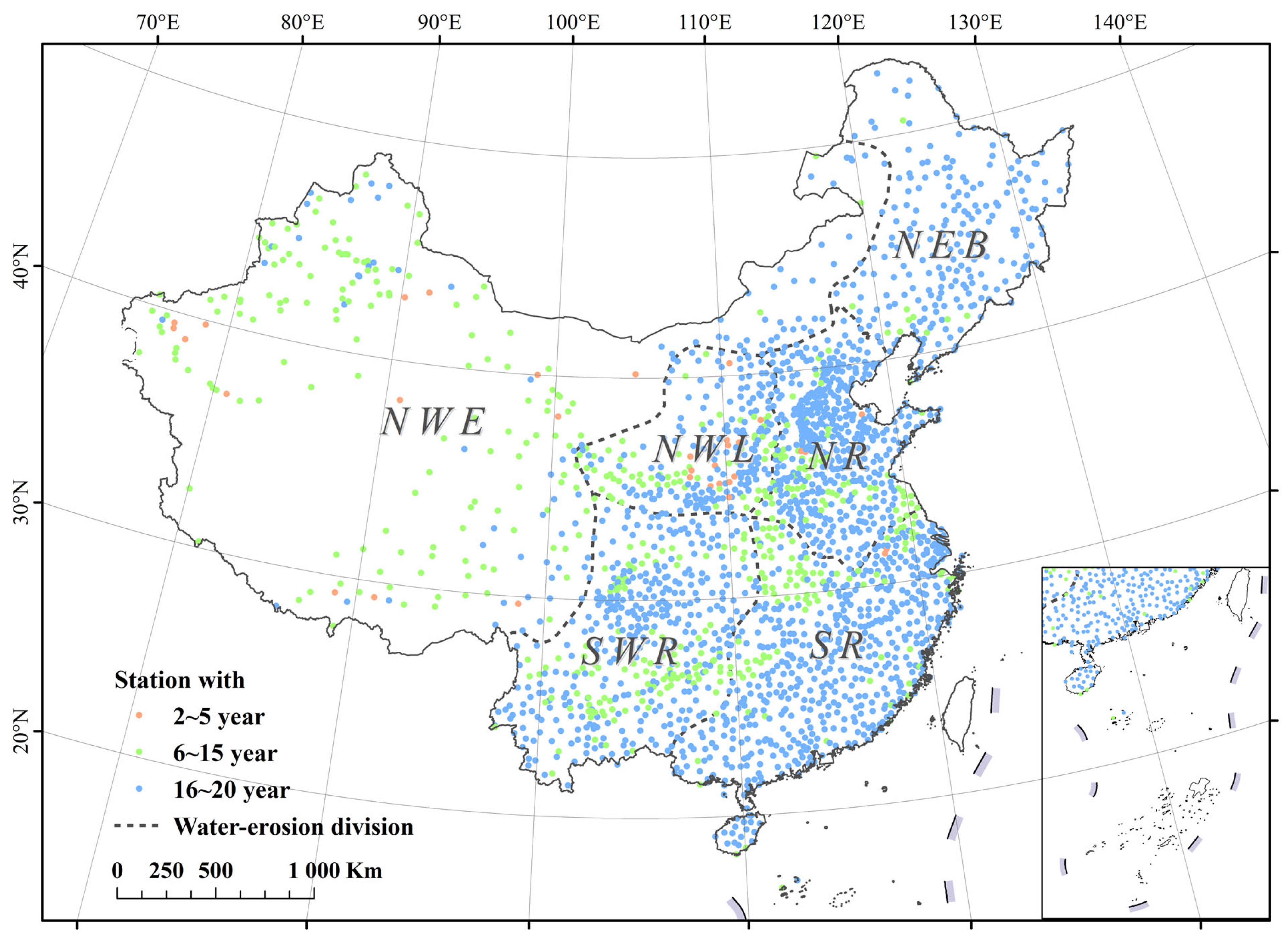
This study focuses on mainland China (Figure 1). Considering the variation in erosion driving factors and erosion characteristics across the entire study region, mainland China can be categorized into two major erosion zones: the eastern and southern regions experience water-induced soil erosion, leading to the classification of these areas as the water erosion region (WE); conversely, the western part, including the Tibet-Qinghai Plateau and northwestern China, is primarily influenced by wind and freeze–thaw processes, and is referred to as the non-water erosion region (NWE).
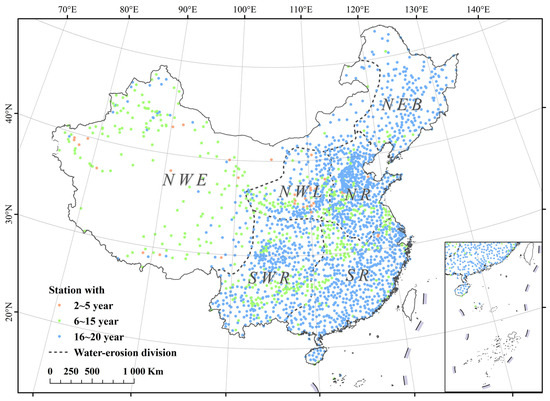
Figure 1.
Stations located in six soil erosion sub-zones in mainland China: (1) NWE, the non-water erosion region, which is mainly controlled by wind and freeze–thaw induced erosion; (2) NR, the northern rocky soil region; (3) SWR, the southwestern rocky mountain region; (4) SR, the southern red soil region; (5) NWL, the northwestern loess plateau region; and (6) NEB, the northeastern black soil region. The NR, SWR, SR, NWL, and NEB regions collectively form the water erosion zones (WE) of mainland China.
Further subdivision of the water erosion region results in five sub-erosion zones: (1) NR, the northern rocky soil region; (2) SWR, the southwestern rocky mountain region; (3) SR, the southern red soil region; (4) NWL, the northwestern loess plateau region; and (5) NEB, the northeastern black soil region (Figure 1).
2.2. Data Collection
Two satellite precipitation products, GPM_3IMERGHH (30-min resolution at 0.1°) and GPM_3IMERGDF (daily resolution at 0.1°), were obtained from the Global Precipitation Measurement mission (GPM) and downloaded from the NASA website (https://gpm.nasa.gov/data-access/downloads/gpm, accessed on 27 March 2024). These data cover the period from 2000 to 2020. Two rainfall erosivity indices, the long-term average of annual rainfall erosivity (R-factor) and extreme storm rainfall erosivity at 10-yr return level (10-yr storm EI), were calculated using these two satellite products for all grid cells within the study area.
To evaluate their accuracy, gauge-observed hourly precipitation data were collected from 2310 meteorological stations across mainland China. Grid cells from GPM precipitation that contained co-located meteorological stations were selected and extracted, and two rainfall erosivity indices of these grids were calculated and compared with corresponding values based on gauge-observed hourly precipitation located within the grid cells.
The gauge-observed hourly precipitation data were provided by the National Meteorological Information Center (NMIC) of the China Meteorological Administration (CMA), which are observed by siphon or tipping-bucket self-recording rain gauges and should not be used during the cold season to avoid damage to the instruments. Therefore, the hourly observation for most northern stations is only available through the warm season from May to September, but available throughout the year in southern China.
Hourly precipitation data have undergone basic quality control by CMA. Additionally, following the procedures in Wang et al. [45], a second quality control step was applied. Specifically, if the number of missing hours within a given year exceeded 5%, then the entire year was excluded from the analysis. Consequently, for each station, only the years within the 2000–2020 period that met the quality criteria were retained for further analysis. In other words, the data periods used for comparison varied among stations (as shown in Figure 1 and Table 1). Only the overlapping periods between the GPM products and gauge-observed hourly precipitation were considered for comparison and evaluation.

Table 1.
Station information in erosion zones within the study area.
It is important to note that the remaining data may still contain some missing hours, but the percentage of missing data was less than 5%. To mitigate potential underestimations resulting from these data gaps, linear interpolation was performed on the hourly data by comparing the data with corresponding daily precipitation data. Daily data were observed by sample rain gauges and were available throughout the year for all stations used. Daily data were used for the interpolation due to their longer series, fewer missing observations, and generally better data quality when compared to the hourly data. The interpolation procedure was as follows: (1) If the daily observed precipitation amount is zero, then the missing precipitation amount for the corresponding missing period in the hourly data is directly assigned as 0; (2) If the daily observed precipitation amount is not equal to zero, then the observed precipitation values within the hourly data are summed, and the difference between the accumulated hourly precipitation amount and the daily observed precipitation amount is calculated. For example, consider a day with two missing hours, and the daily observation records 20 mm of precipitation. If the total observed precipitation in the available hourly data for that day is 19 mm, the precipitation amount for each of the two missing hours would be set at 0.5 mm.
2.3. Rainfall Erosivity Estimations
Two rainfall erosivity indices (R-factor and 10-yr storm EI) were calculated using two satellite products for all grid cells within the study area in two ways: (1) utilizing the 30-min satellite precipitation product (GPM_3IMERGHH) and the RUSLE2 EI30 index, referred to as GPM-30-EI30; (2) utilizing the daily satellite precipitation product (GPM_3IMERGDF) and the daily erosivity model calibrated by Xie et al. [11], referred to as GPM-Daily-DR. Meanwhile, rainfall erosivity was also estimated using gauge-observed hourly precipitation data coupled with the RUSLE2 EI30 index (Gauge-H), and daily precipitation data coupled with the daily erosivity model (Gauge-DE), respectively.
For gauge-observed hourly precipitation data and the GPM satellite 30-min precipitation product (GPM_3IMERGHH), the continuous data series for each station was divided into individual storm events by the minimum dry inter-event time of 6 h [3,47]. Rainfall erosivity in this study was calculated for each storm using the rainfall erosivity equation recommended in RUSLE2 [6]. For a period mth with a constant rainfall intensity, the rainfall kinetic energy during the period is given as follows:
where is the rainfall intensity at the mth time, with a unit of mm h−1, and is the rainfall kinetic energy during the mth period, with a unit of . The total kinetic energy of a rainfall event is
where is the rainfall amount during the mth period, and n represents all periods with a constant rainfall intensity within a rainfall event. The product of the kinetic energy and the maximum 30-min rainfall intensity I30 is the rainfall erosivity of a rainfall event, with a unit of MJ mm ha−1 h−1. According to the definition of RUSLE2 [6], the sum of EI30 for all rainfall events in a year is the annual rainfall erosivity, with a unit of MJ mm ha−1 h−1. The average of long-term annual rainfall erosivity is defined as R-factor, with a unit of MJ mm ha−1 h−1 a−1.
The temporal resolution of GPM_3IMERGHH is 30 min; therefore, E and I30 can be estimated directly. But for hourly data, I30 cannot be directly obtained from the hourly observations. Yin et al. [7] reported that the Eh (rainfall energy obtained directly from hourly data), I1h (the maximum hourly intensity), and (EI30)h (rainfall intensity index obtained directly from hourly data) have systematic underestimations compared with E, I30, and EI30 that derived from breakpoint rainfall data. Therefore, Eh, I1h, and (EI30)h derived from hourly observations were adjusted by multiplying the adjustment factors of 1.105, 1.668, and 1.73 as suggested by Yin et al. [7], respectively, to approximate E, I30, and EI30.
For gauge-observed daily precipitation and the daily satellite precipitation product (GPM_3IMERGDF), rainfall erosivity was calculated using the daily model calibrated by Xie et al. [11] in China:
where n is the month from 1 to 12; d is the rainy day; and (MJ·mm·ha−1·h−1) and (mm) represent the daily precipitation and rainfall erosivity on the day of the month, respectively. The sum of around the year is the annual rainfall erosivity, and the long-term average over the study period is the R-factor.
When it comes to the 10-yr storm EI (MJ·mm·ha−1·h−1), for hourly observation and GPM_3IMERGHH, EI30 of each storm event can be determined. Then, the 10-yr storm EI can be calculated by the generalized extreme value distribution. For daily observations and GPM_3IMERGDF, only daily erosivity at the 10-year return level (referred to as 10-yr-daily EI) can be determined. But it has been found to have a strong linear correlation with 10-yr storm EI [48]. According to Yin et al. [48], 10-yr storm EI can be approximated by multiplying 1.17 by the 10-yr-daily EI. To simplify the expression, “R-factor in MJ mm ha−1 h−1 a−1” and “10-year storm EI in MJ mm ha−1 h−1” were simply denoted as “R-factor in SI units” and “10-year storm EI in SI units”.
2.4. Bias-Correction Method
In the Water Erosion region (WE) of mainland China, rainfall erosivity estimates derived from two GPM precipitation products, namely GPM-30-EI30 and GPM-Daily-DR, exhibit systematic biases when compared to estimates based on gauge-observed hourly precipitation. A power equation can be utilized to address these discrepancies:
where x represents the rainfall erosivity values derived from GPM-30-EI30 and GPM-Daily-DR, y represents rainfall erosivity estimated from hourly observations (denoted as Gauge-H), and a and b are parameters. Based on Equation (4), two bias-correction methods were developed and compared to mitigate these discrepancies.
The first method, referred to as “adjust1”, applies a uniform correction across the entire region by establishing and utilizing a correlation between GPM-derived rainfall erosivity and Gauge-H by Equation (4). The second method, referred to as “adjust2”, creates and applies separate correlations for each sub-zone in the region of WE by Equation (4), adapting bias corrections to individual areas.
The efficacy of the two bias-correction approaches was evaluated through a five-fold cross-validation process [49]. The study area, including 2058 stations within the WE region, was segmented into five equal folds. For each iteration, bias-correction equations were derived using four folds and subsequently applied to adjust the data in the remaining fold. The accuracy of these adjustments was assessed by calculating a series of statistical indices, as detailed in Section 2.5. This procedure was repeated across all five folds, and the mean of these statistical indices was employed to quantify the overall accuracy of the bias-correction approaches.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
R-factor and the 10-yr storm EI calculated by two GPM products through two algorithms were evaluated by comparing with that derived from Gauge-H. The evaluation indicators are the Absolute Error (AE, SI units), Relative Error (RE, %), Nash Efficiency Coefficient (NSE), the Correlation Coefficient (CC), the Percent Bias (PBIAS, %), and the Kling-Gupta Efficiency Coefficient (KGE):
in which and in Equations (5)–(9) are the observed and predicted values of a specific station; and in Equation (10) are the average observed and predicted values over all samples. KGE is a comprehensive index that reflects the correlation, variability, and bias between predicted and observed values, with ranges from −∞~1. The higher NSE and KGE suggest the better model estimation. The range for CC is −1 to 1, with −1 showcasing a perfect negative correlation, one indicating a perfect positive correlation, and zero denoting the absence of a linear relationship between the variables. A higher absolute value of CC indicates a stronger correlation. A negative PBIAS represents underestimation, and a positive PBIAS represents overestimation.
The rainfall erosivity estimated from two GPM precipitation products was compared with the interpolation erosivity maps generated by Kriging interpolation methods using gauge observations. The interpolation approach that calculates rainfall erosivity at the individual stations and then interpolates the data into a predefined grid is the most commonly used method [50]. The interpolation results are referred to as Gauge-H-Intp for hourly precipitation data and Gauge-DE-Intp for daily precipitation data, respectively. Additionally, a five-fold cross-validation approach was applied [49], and three indicators of NSE, PBIAS, and KGE were utilized. The satellite precipitation products and gauge-observed precipitation data were processed using MATLAB R2022a (for academic use), while the interpolation and figures were plotted using both RStudio and MATLAB.
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation of Rainfall Erosivity Derived from GPM Precipitation Products
3.1.1. General Accuracy over Mainland China
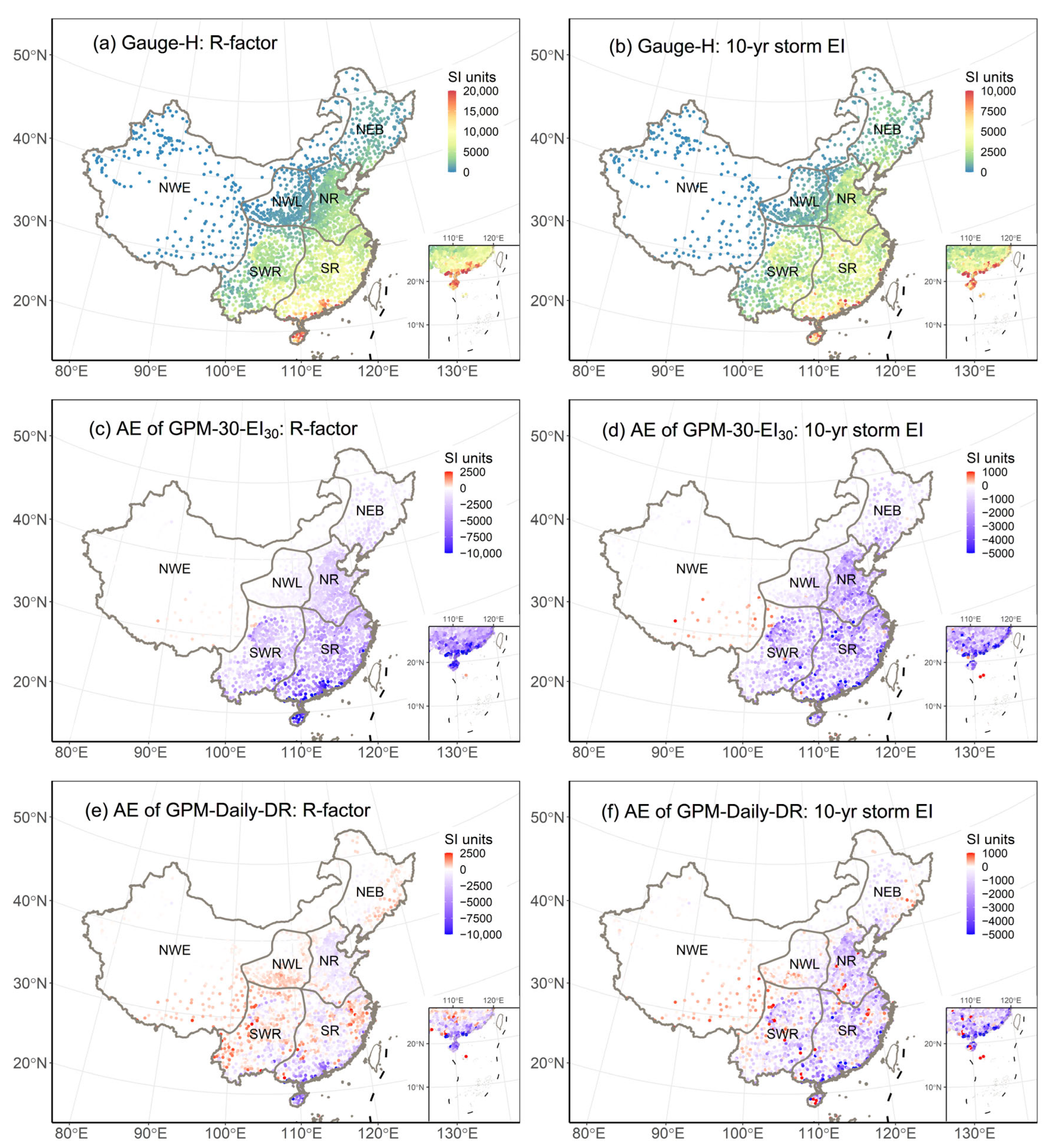
The spatial distribution of two erosivity indices, namely the R-factor and 10-yr storm EI, using gauge-observed hourly precipitation (referred to as Gauge-H), is illustrated in Figure 2a,b. The R-factor varies significantly across 2310 stations, ranging from 1.6 to 30,052.0 SI units. Similarly, the 10-yr storm EI exhibits a range from 2.3 to 20,999.9 SI units. Both indices display a spatial pattern similar to that of the annual precipitation in mainland China, reflecting the influence of the Asian Monsoon from the coastal to the inland areas.
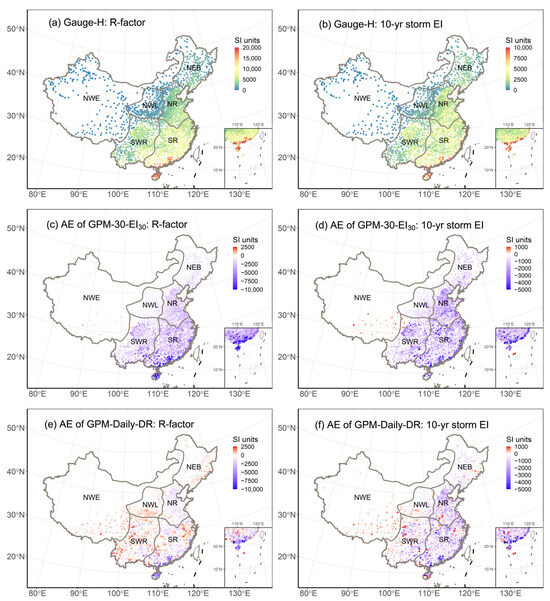
Figure 2.
Spatial distribution of R-factors (a) and 10-year storm EI (b) estimated from gauge-observed hourly precipitation (Gauge-H), and absolute errors (AEs) between these indices and those derived from GPM-30-EI30 (c,d) and GPM-Daily-DR (e,f).
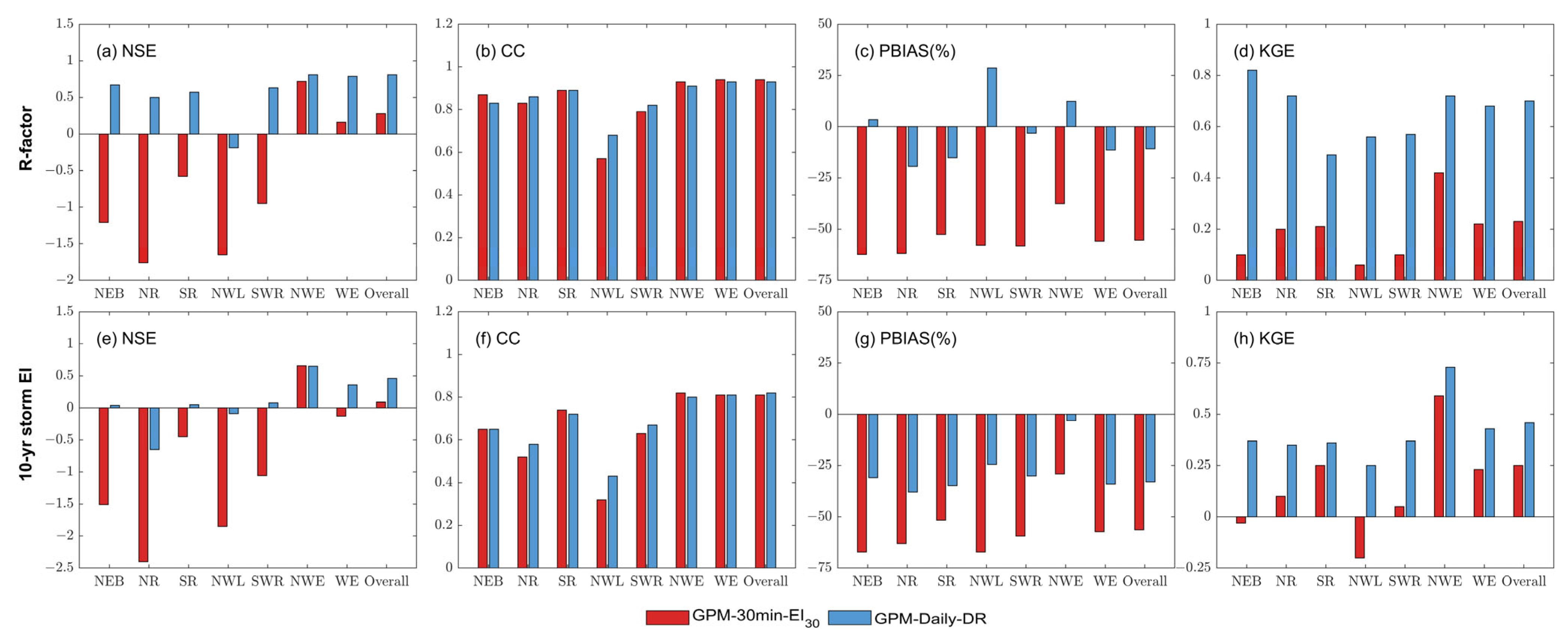
The evaluation results for the two rainfall erosivity indices computed using two GPM products with two different temporal resolutions and erosivity models (GPM-30-EI30 and GPM-Daily-DR) are represented in Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 4. Overall, GPM-Daily-DR exhibits better performance over GPM-30-EI30 in estimating the R-factor across mainland China, especially in the eastern and central regions primarily controlled by water-induced erosion processes (Figure 2c,e). The Nash-Sutcliffe Efficiency (NSE) and Kling-Gupta Efficiency Coefficient (KGE) of GPM-30-EI30 are as low as 0.28 and 0.23 for mainland China, whereas GPM-Daily-DR achieved a significantly higher NSE and KGE of 0.81 and 0.70 (Figure 4). Additionally, the Percent Bias (PBIAS) for GPM-30-EI30 was −55.48%, which is nearly five times higher than that derived from GPM-Daily-DR (PBIAS = −10.86%).
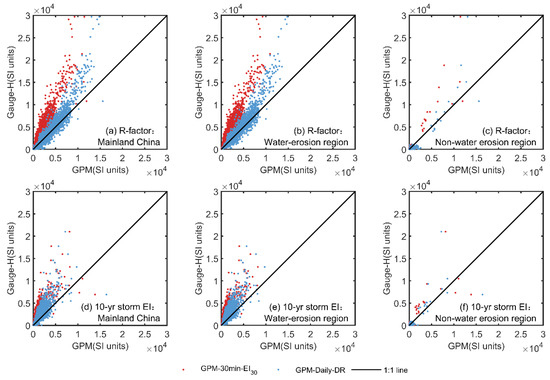
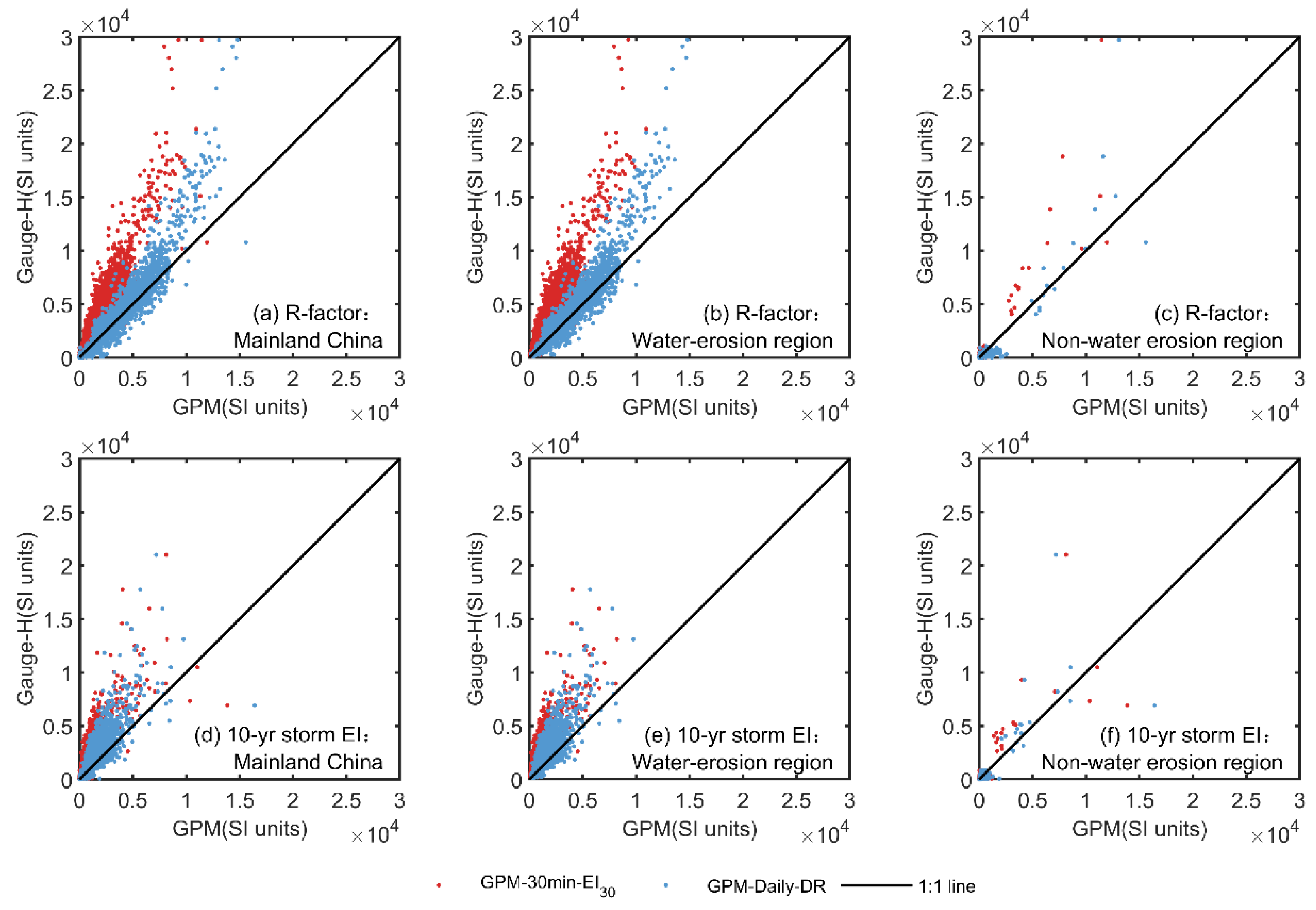
Figure 3.
Comparison of two erosivity indices (R-factors and 10-yr storm EI) estimated using gauge-observed hourly precipitation (Gauge-H) with estimates using GPM-30-EI30 and GPM-Daily-DR in mainland China (a,d), the Water Erosion region (b,e), and Non-Water Erosion region (c,f).
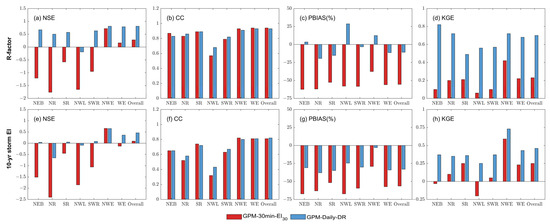
Figure 4.
Estimation accuracy comparison of GPM-30-EI30 and GPM-Daily-DR for two erosivity indices: R-factor (first row) and 10-year storm EI (second row). Overall indicates the results for mainland China.
Specifically, GPM-Daily-DR outperforms GPM-30-EI30 in locations where the R-factor estimation from Gauge-H data is below 10,000 SI units. It can be clearly observed from Figure 3a that the scatter points for GPM-Daily-DR align closely with the 1:1 line, particularly when Gauge-H data are below 10,000 SI units. In contrast, GPM-30-EI30 displays systematic biases deviating from the 1:1 line. This observation is corroborated by results presented in Figure 2. The Absolute Errors (AEs) between GPM-30-EI30 and Gauge-H display consistent negative values over the five sub-regions prone to water-induced erosion in eastern China (Figure 2c). In contrast, the AEs between GPM-Daily-DR and Gauge-H exhibit both negative and positive values (Figure 2e). For stations with R-factors exceeding 10,000 SI units, both products tend to underestimate (Figure 3a). It can be inferred from Figure 2 that these stations are mainly located in the southern part of the Southern Red Soil Region (SR).
As for the erosivity index of the 10-yr storm EI, the estimation accuracy of both products is unsatisfying. Figure 2d and Figure 3d show that both products tend to underestimate the 10-yr storm EI. This is further supported by Figure 4g, which shows that the PBIAS for both products is negative. Nevertheless, in comparison, the accuracy of GPM-Daily-DR is still superior to that of GPM-30-EI30 (Figure 4). The NSE and KGE of GPM-30-EI30 are as low as 0.09 and 0.25, whereas the use of GPM-Daily-DR yielded higher values of 0.46 and 0.46. The PBIAS using GPM-Daily-DR for mainland China is also smaller than that using GPM-30-EI30 (Figure 4g). It is noteworthy that both datasets are able to accurately represent the spatial distribution of two erosivity indices, as evidenced by the Correlation Coefficients (CC) shown in Figure 4. For both approaches and indices, the CC values are greater than 0.8 (Figure 4f).
3.1.2. Differences between Water Erosion and Non-Water Erosion Regions
The performance of two GPM products in the Water Erosion (WE) and Non-Water Erosion regions (NWE) shows great differences, and the estimation accuracy within the region of WE is basically consistent with that achieved for mainland China (Figure 3). This is mainly due to the fact that the majority of stations (2085 out of 2340) are situated in WE, where rainfall erosivity exhibits a wide-ranging variation from south to north. In contrast, there are only 252 stations situated in the region of NWE, and their R-factor and 10-yr storm EI estimates are influenced by regional climate dynamics. The scatter points predominantly cluster around the zero point, indicating that both gauge and GPM products yielded very small R-factors and 10-yr storm EI values (refer to Figure 3c,f). These clusters are primarily situated in northwestern China. A few scattered points are sparsely distributed within the range of 5000 to 30,000 SI units, primarily found in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. It is important to note that the NSE values in the region of NWE are higher than those in the region of WE (Figure 4a). However, higher NSE values in the NWE region do not necessarily indicate superior prediction accuracy compared to the WE region. Instead, they primarily reflect substantial erosivity differences between the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and arid northwestern China.
3.1.3. Regional Differences among Five Water Erosion Sub-Zones
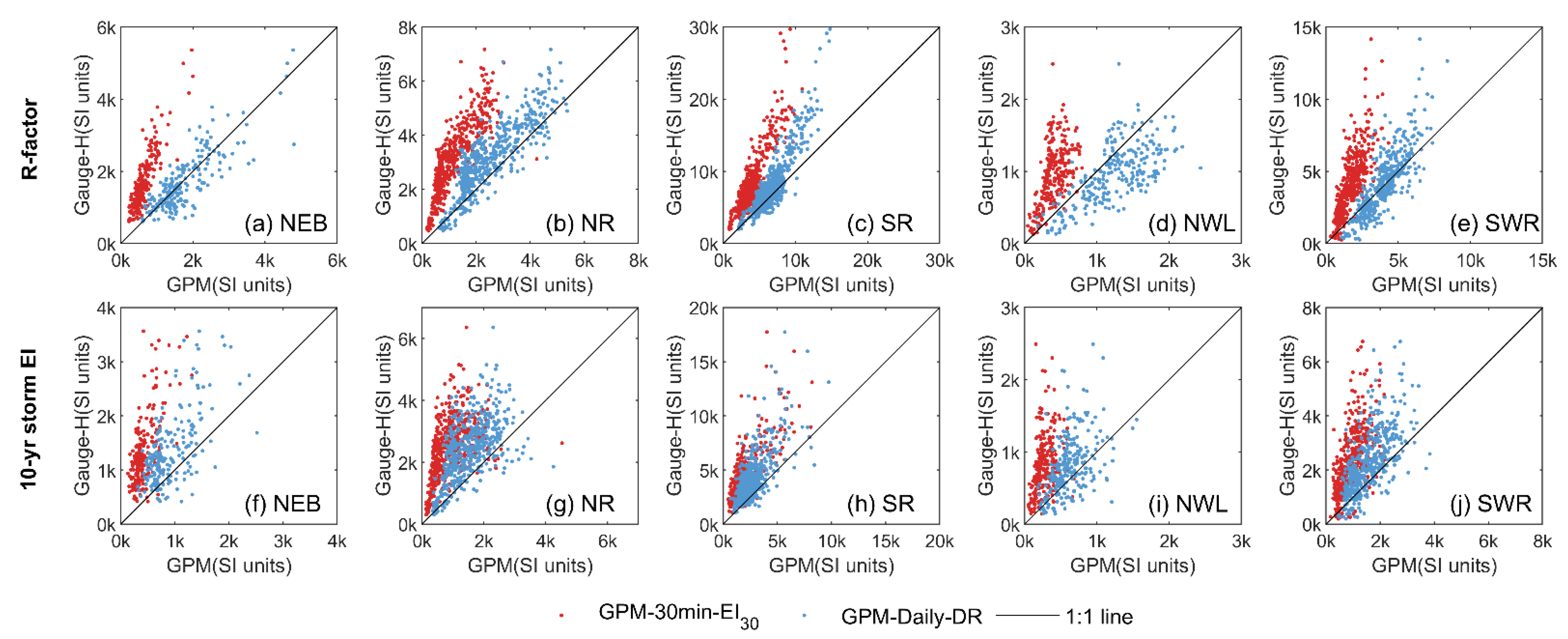
The region of WE can be further subdivided into five sub-regions based on the erosion characteristics, and it is noteworthy that the estimation accuracies vary among these different erosion regions. Firstly, GPM-Daily-DR consistently outperforms GPM-30-EI30 in all regions (Figure 4). NSE values for GPM-30-EI30 are predominantly negative across all five sub-regions. In contrast, NSE values for GPM-Daily-DR mostly exceed 0.5 in the majority of regions. The superiority of GPM-Daily-DR is evident in Figure 5, where the red points representing GPM-30-EI30 deviate from the 1:1 line, whereas most values for NEB, NR, SR, and SWR using GPM-Daily-DR (blue points) align closely with the 1:1 line. It is worth noting that the Northwestern Loess Plateau Region (NWL) exhibits the poorest accuracy among all regions, with the lowest NSE and CC values observed for both GPM-30-EI30 and GPM-Daily-DR (Figure 4).
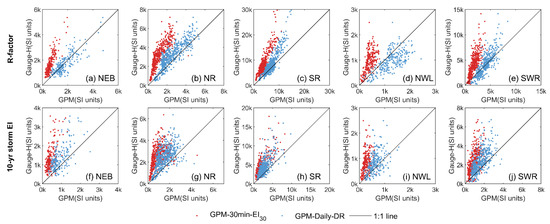
Figure 5.
Comparison of R-factors and 10-yr storm EI estimated using hourly gauge observations (Gauge-H) and two GPM products (GPM-30 min-EI30 and GPM-Daily-DR) in five Water Erosion sub-zones.
Compared to the estimation of the R-factor, the accuracy in estimating the 10-yr storm EI in these five erosion sub-zones is less satisfactory (Figure 4e–h). NSE values for WE using GPM-30-EI30 and GPM-Daily-DR are −0.13 and 0.36, respectively. Across all sub-regions, the NSE values are either below or near zero. Although GPM-Daily-DR performs slightly better than GPM-30-EI30 in estimating the 10-yr storm EI (Figure 5f–j), the accuracy remains notably low. Nevertheless, the spatial distribution of rainfall erosivity is still broadly preserved, as indicated by the Correlation Coefficients (CC) (Figure 4f).
Both GPM precipitation products tend to underestimate these two rainfall erosivity indices compared to those derived from hourly gauge observations (Figure 4 and Figure 5). The degree of underestimation is higher when using GPM-30-EI30 to estimate the R-factor compared to GPM-Daily-DR. Similarly, both GPM products exhibit underestimation in estimating 10-yr storm EI. Based on results achieved here, it can be concluded that GPM-30-EI30 is not suitable for the direct estimation of both the R-factor and the 10-yr storm EI, and GPM-Daily-DR is not suitable for the direct estimation of the extreme erosivity index, which will lead to significant uncertainties and biases.
3.2. Evaluation of the Bias-Correction Method
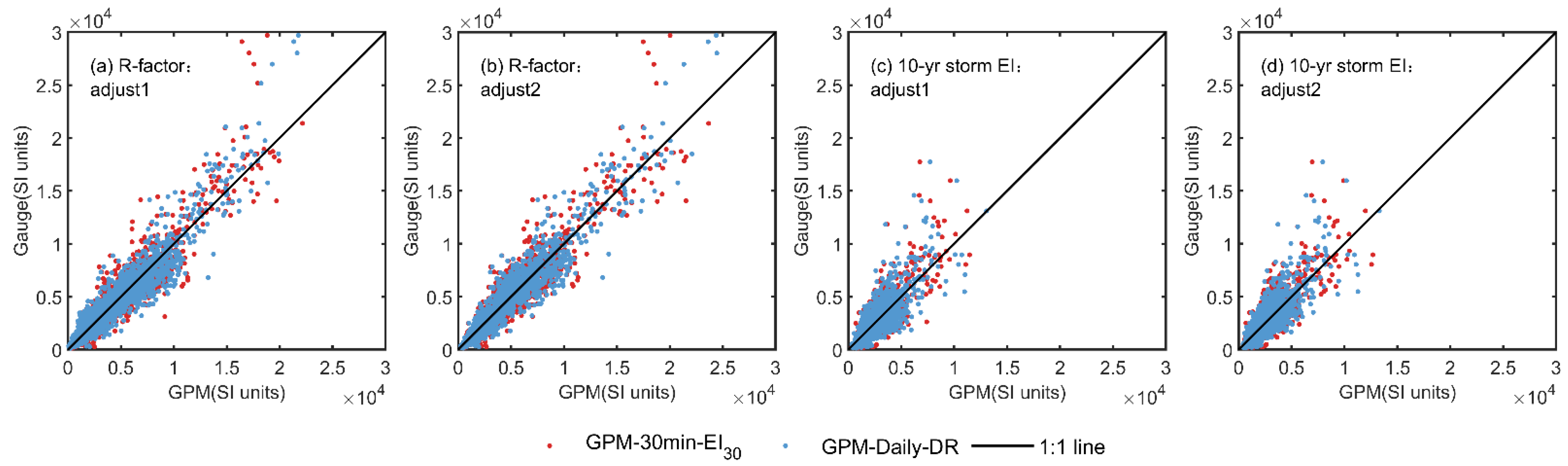
Rainfall erosivity estimated by GPM-30-EI30 and GPM-Daily-DR in the Water Erosion region (WE) shows systematic biases with that derived from gauge-observed hourly precipitation (Figure 3b,e). The biases can be addressed by a power relationship in Equation (4). Based on this equation, two bias-correction approaches named “adjust1” and “adjust2”, were developed and evaluated (Figure 6 and Table 2). The two methods demonstrate comparable accuracy when applied to the entire region of WE (Figure 6 and Figure 7), but “adjust2” slightly outperformed “adjust1” for both GPM products, showing higher Nash-Sutcliffe Efficiency (NSE) and Kling-Gupta Efficiency Coefficient (KGE) values, and lower Percent Bias (PBIAS) (Table 2).
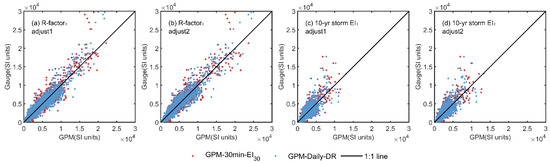
Figure 6.
Comparison of bias-corrected estimates in R-factors and 10-year storm EI from GPM-30-EI30 and GPM-Daily-DR versus gauge-observed hourly precipitation (Gauge-H) in the Water Erosion region, using two bias-correction methods (adjust1 and adjust2) through five-fold cross-validation.

Table 2.
Comparison of R-factors and 10-yr storm EI estimated using bias-corrected GPM-30-EI30 and GPM-Daily-DR versus gauge-observed hourly precipitation in Water Erosion region (WE), using two bias-correction methods (adjust1 and adjust2) through a five-fold cross validation.
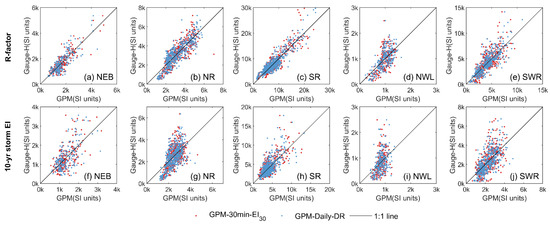
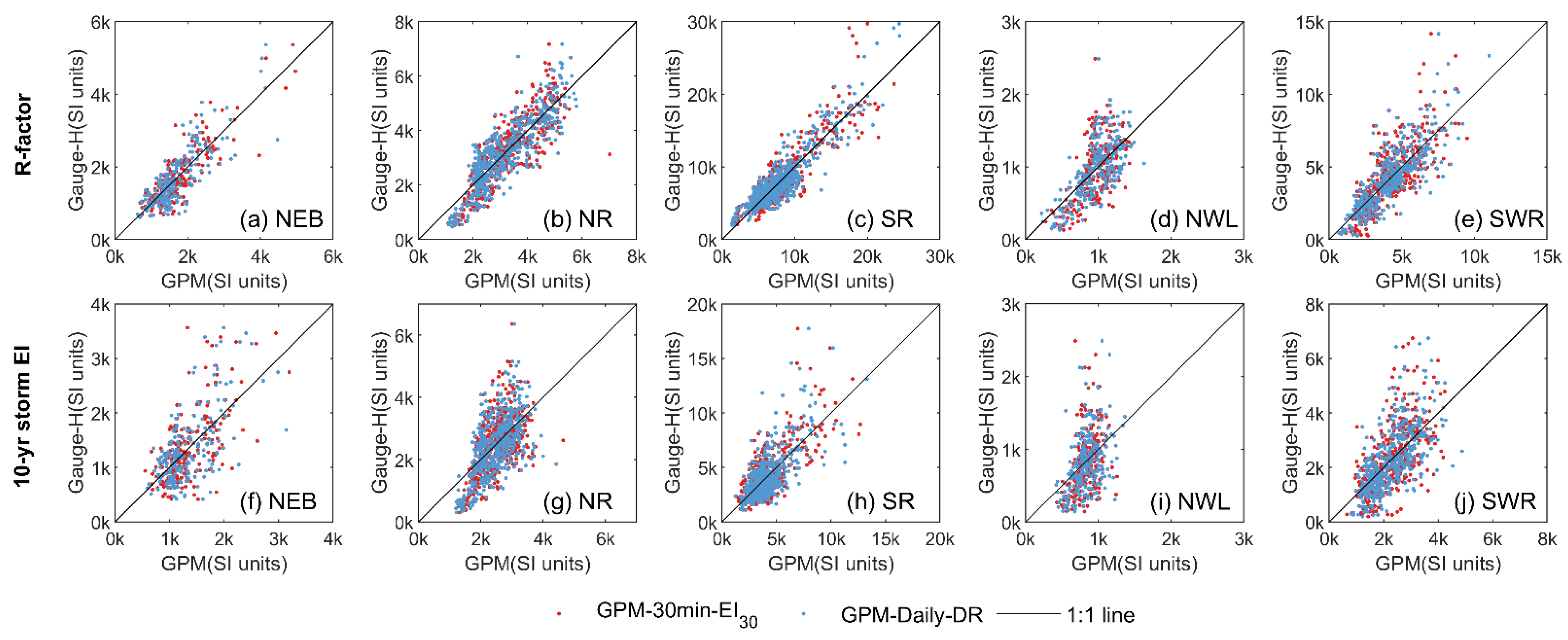
Figure 7.
Comparison of bias-corrected estimates in R-factors and 10-year storm EI from GPM-30-EI30 and GPM-Daily-DR versus gauge-observed hourly precipitation (Gauge-H) in five sub-zones within the Water Erosion region using adjust2 through five-fold cross-validation.
After bias-correction, an obvious improvement is observed (Table 2). Specifically, with the application of “adjust2”, the NSE for the R-factor derived from GPM-30-EI30 improves significantly, rising from 0.16 to an impressive 0.88. Similarly, for GPM-Daily-DR, the NSE improves from 0.79 to 0.90. The PBIAS for GPM-30-EI30 decreases from −55.48% to −0.06%, and for GPM-Daily-DR, it decreases from −10.86% to −0.33%.
These improvements are notable for the 10-yr storm EI as well, where the bias-correction leads to significant enhancements. Specifically, when “adjust2” is applied, the NSE for GPM-30-EI30 improves from 0.09 to 0.68, while for GPM-Daily-DR, it improves from 0.46 to 0.67. After the bias-correction procedure, GPM-30-EI30 and GPM-Daily-DR achieve comparable accuracy, with KGE values of 0.92 and 0.93, respectively. The PBIAS for GPM-30-EI30 and GPM-Daily-DR also decrease markedly, to as low as 0.01% and 0.14%, respectively. These results observed for R-factor and 10-yr storm EI indicate that the significant underestimation previously observed with the direct utilization of the two GPM products was greatly mitigated (Figure 4).
Improvements are observed across all five sub-zones in the Water Erosion region (Table 2, Figure 7). Before applying the bias-correction methods, the Nash-Sutcliffe Efficiency (NSE) of R-factors for all five sub-zones is below 0. These values then improve to positive NSE values for all sub-zones after bias correction. Specifically, the accuracy enhancements are notable in the Northwestern Loess Plateau Region (NWL), where NSE using GPM-30-EI30 and GPM-Daily-DR rose from negative values to 0.36 and 0.47, respectively, with the application of “adjust2”.
The fitted values of parameters a and b from Equation (4) are presented in Table 3. The fitting accuracy for both datasets is generally similar, with R2 values exceeding 0.62, except for the NWL region, which exhibits a lower fitting accuracy. The fitting accuracy for the 10-yr storm EI is lower compared to that of R-factor. Among all regions, the NWL region shows the poorest fitting accuracy for both GPM-30-EI30 and GPM-Daily-DR.

Table 3.
Equation parameters used to adjust the systematic biases of rainfall erosivity derived from two GPM precipitation products.
Based on the findings presented above, it can be concluded that both GPM-30-EI30 and GPM-Daily-DR hold potential for rainfall erosivity estimation. Both datasets can effectively benefit from the bias-correction procedure, resulting in comparable accuracy levels between GPM-30-EI30 and GPM-Daily-DR. Nonetheless, even after bias correction, GPM-Daily-DR consistently exhibits slightly superior performance when compared to GPM-30-EI30.
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison with Rainfall Erosivity Derived from Interpolation
In previous studies, one of the most commonly used methods to generate R-factor maps in a study area, including regions lacking gauge observations, has been to initially calculate the R-factor for individual stations and subsequently apply interpolation methods to extend these values to specific grid cells covering the entire study area [10,50,51,52,53]. This method can provide more accurate results when compared to using gridded precipitation products generated through the interpolation of daily precipitation data collected at specific locations. This is primarily because the R-factor, which represents a long-term average annual value, exhibits lower spatial variability than daily precipitation data [22,54]. However, the application of the interpolation procedure also introduces some uncertainty into the rainfall erosivity estimation. The interpolation accuracy primarily depends on the density of stations utilized and the interpolation method applied. For instance, in areas with sparse station coverage, the accuracy of estimated rainfall erosivity might be impacted [55].
This study compares rainfall erosivity estimated by GPM-30-EI30 and GPM-Daily-DR with results from the traditional Kriging interpolation method. Using a five-fold cross-validation, the study assesses the interpolation accuracy of erosivity based on gauge-observed hourly precipitation (Gauge-H-Intp) (Table 4). After bias correction, the accuracy of GPM-30-EI30 and GPM-Daily-DR proves comparable to that of Gauge-H-Intp. In the Water Erosion region (WE), the Kling-Gupta Efficiency (KGE) for R-factors estimated by GPM-30-EI30 and GPM-Daily-DR using the adjust2 method is 0.92 and 0.93, respectively, similar to Gauge-H-Intp’s 0.92. However, in sub-zones within WE, Gauge-H-Intp demonstrates higher accuracy than the bias-corrected estimates from GPM products, especially for the Northwestern Loess Plateau Region (NWL) (Table 4).

Table 4.
The interpolation accuracy of rainfall erosivity derived by gauge-observed hourly precipitation (Gauge-H-Intp) and daily precipitation (Gauge-DE-Intp) through a five-fold cross validation.
Although high-temporal-resolution precipitation data can accurately depict rainfall processes and capture intensity variations, they present considerable challenges in data collection, especially in areas with limited gauge records, such as in Africa [23,28]. Therefore, daily precipitation data and daily erosivity models have been widely employed for generating rainfall erosivity maps when high-spatiotemporal-resolution gauge observations are unavailable [53,56,57,58,59]. However, using daily data and daily erosivity models introduces more uncertainty into the mapping process for rainfall erosivity than does using hourly data for interpolation, as the models’ accuracy tends to decline when the adopted data resolution decreases from hourly to daily [8].
To illustrate, the study also evaluated interpolation results for daily data-derived rainfall erosivity using erosivity models [11] based on daily data (Gauge-DE-Intp) through five-fold cross-validation. Table 4 reveals that the interpolation results are notably lower when compared to the estimation accuracy derived from the two GPM datasets. The KGE of Gauge-DE-Intp is 0.74, which is significantly lower than the predictive accuracy of bias-corrected GPM-30-EI30 (KGE = 0.92) and GPM-Daily-DR (KGE = 0.93), as well as the interpolation results using hourly data (Gauge-H-Intp, KGE = 0.92).
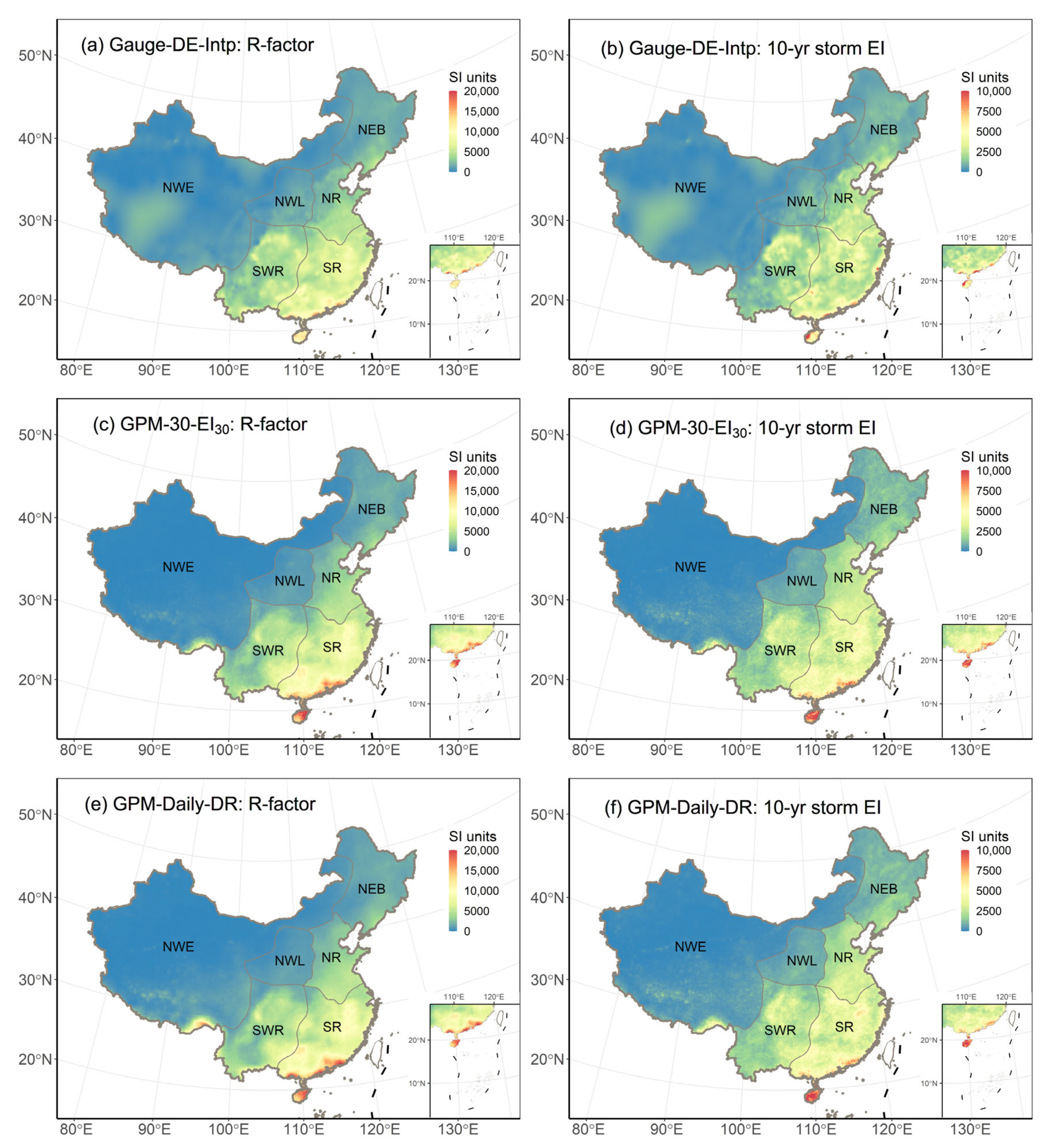
Figure 8 further compares the spatial distribution of rainfall erosivity estimated with Kriging interpolation methods based on daily precipitation (Gauge-DE-Intp) and bias-corrected GPM-30-EI30 and GPM-Daily-DR. The comparison reveals that the R-factors derived from GPM products exhibit a spatial distribution pattern identical to those derived from Gauge-DE-Intp. However, when considering the 10-yr storm EI, the erosivity maps generated using GPM products exhibit a smoother spatial pattern, whereas those produced by Gauge-DE-Intp display patches. This patchiness is evidently influenced by the locations of the stations used in the interpolation process, highlighting a key limitation of interpolation methods.
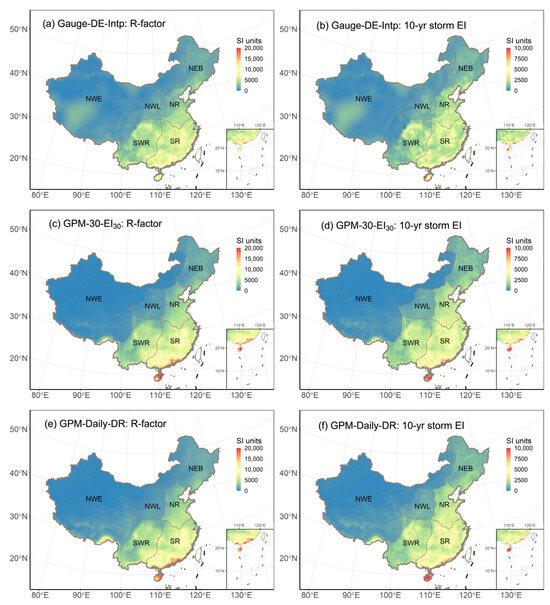
Figure 8.
Comparison of rainfall erosivity maps derived from interpolation method based on gauge-observed daily precipitation (Gauge-DE-Intp) and bias-corrected GPM-30-EI30 and GPM-Daily-DR with adjust2 (erosivity values in NWE are not adjusted).
Both GPM precipitation products demonstrate great potential for estimating R-factor and 10-yr storm EI, with accuracy levels comparable to those attained through the interpolation using hourly gauge observations and better than those derived from daily gauge observations.
4.2. Regional Differences
The estimation accuracy of rainfall erosivity indices derived from two GPM products shows obvious regional differences (Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5). Among all regions, the Northwestern Loess Plateau Region (NWL) exhibits the poorest accuracy, both before and after bias correction (Figure 6 and Figure 7). This phenomenon may be related to the lower precision of precipitation estimates within this region as provided by GPM products [22]. The NWL region is characterized by complex topography and significant elevation differences, ranging in elevation from 92 m to 5020 m [60]. The complex topography in this region may affect the accuracy of precipitation estimation, whereas the eastern regions of China, with higher precipitation intensity and relatively flatter topography, tend to have better precipitation estimation accuracy [31,45,61].
Moreover, it is noteworthy that the interpolation results derived from daily precipitation data and daily erosivity models (Gauge-DE-Intp) consistently demonstrate the lowest accuracy among the five regions. The average Nash-Sutcliffe Efficiency (NSE) value, determined through a five-fold cross-validation, is notably low at −0.51, while the NSE values for the other regions either equal or exceed 0.59 (Table 4). This discrepancy may be attributed to the limited data available for developing the daily models, with only two stations providing 1-min precipitation data used in the models’ calibration [11]. Therefore, the biases introduced by the daily erosivity model may be more pronounced in this region compared to others.
4.3. Comparison with Previous Studies
Satellite remote sensing precipitation products have emerged as alternative sources of gauge observations in the past decade and have been widely utilized in mapping rainfall erosivity [26,27,29,30,31,32,34,36]. Most studies have reported that these satellite products effectively capture the spatial distribution of rainfall erosivity [26,29,31,34], which is consistent with the results achieved in this study. However, the evaluation accuracy of rainfall erosivity magnitude derived from satellite products varies across studies, mainly due to differences in the satellite products used and the reference data employed in previous studies [26,29,31,34,36].
Particularly, in a study by Chen et al. [29], the performance of GPM_3IMERGDF in estimating erosivity was evaluated, which is one of the satellite products utilized in our study as well. Chen et al. [29] found good performance in rainfall erosivity estimation at the annual average, seasonal, and monthly scales. The Nash-Sutcliffe Efficiency (NSE) values for all eight river basins in China were above 0.89, which is higher than the direct evaluation results obtained in our study (Figure 4). It is important to note that the comparison in Chen et al. [29] between erosivity maps derived from satellite products and reference erosivity maps was conducted at a spatial resolution of 0.25°. The reference erosivity maps were interpolated using daily precipitation data and a daily erosivity model from 2471 stations to cover mainland China at a resolution of 0.25°, while the precipitation data from GPM was upscaled from 0.1° to 0.25°. This upscaling process may have resulted in the smoothing of rainfall erosivity derived from GPM precipitation data, partially explaining the discrepancies between the findings of Chen et al. [29] and the current study. Additionally, it is important to consider that the reference data used in Chen et al. [29] were interpolated maps generated from daily precipitation data and erosivity models. As discussed in Section 4.1, this interpolation procedure with daily precipitation may introduce higher uncertainty in rainfall erosivity estimation than using hourly rainfall erosivity. This may be the second factor leading to the differences between the results of Chen et al. [29] and the current study.
In previous studies, satellite precipitation products have been widely used for mapping the spatial distribution of rainfall erosivity. However, the results of this study demonstrated that the direct utilization of GPM data with a 30-min resolution (GPM-30-EI30) is inappropriate due to its low accuracy, resulting in obvious underestimation of both the R-factor and 10-yr storm EI. On the other hand, the estimation accuracy of GPM-Daily-DR is considerably higher than that of GPM-30-EI30, except for the Northwestern Loess Plateau Region (NWL). Despite these differences, both products show potential for improvement and can be bias-corrected (Table 2). Moreover, after applying bias correction, both GPM-30-EI30 and GPM-Daily-DR can be utilized for mapping rainfall erosivity, achieving accuracy comparable to the interpolation results based on hourly gauge observations (Table 4).
5. Conclusions
Remote sensing precipitation products have emerged as a new observation method and are widely used in rainfall erosivity estimation. However, previous studies have revealed that rainfall erosivity estimated using satellite precipitation products was underestimated, but corresponding bias-correction methods have not been reported. This study evaluated the potential of two satellite precipitation products—GPM_3IMERGHH (30-min resolution) and GPM_3IMERGDF (daily resolution), both at 0.1°—to estimate two important rainfall erosivity indices in mainland China: the R-factor and the 10-year storm EI. Due to the different temporal resolutions of these two datasets, different erosivity models were applied. For GPM_3IMERGHH, erosivity was estimated using the EI30 index (referred to as GPM-30-EI30); for the GPM_3IMERGDF, a daily erosivity model was used (referred to as GPM-Daily-DR). The following results were achieved:
(1) Both products can preserve the spatial pattern of rainfall erosivity when compared with that derived from gauge-observed hourly precipitation (Gauge-H). The correlation coefficients (CC) are greater than 0.93 for R-factors and greater than 0.81 for 10-yr storm EI, respectively. But both erosivity indices derived from GPM products tended to underestimate the two erosivity indices, and GPM-Daily-DR yielded higher accuracy compared to GPM-30-EI30. The Percent Bias (PBIAS) was −55.48% for the R-factor and −56.38% for the 10-yr storm EI when using GPM_3IMERGHH, and decreased to −10.86% and −32.99% when using GPM_3IMERGDF. This indicated that the direct utilization of GPM-30-EI30 for estimating both the R-factor and the 10-yr storm EI will lead to significant uncertainties and biases.
(2) Rainfall erosivity estimated by GPM products in the Water Erosion region (WE) of mainland China showed systematic biases compared to that derived from Gauge-H, and bias-correction methods were developed. The bias-correction methods could obviously improve the estimation accuracy of the two erosivity indices, and the differences between the two datasets were reduced. The PBIAS using GPM_3IMERGHH decreased to −0.06% and 0.01%, and that using GPM_3IMERGDF decreased to −0.33% and 0.14%, respectively, for the R-factor and 10-yr storm EI.
(3) Moreover, the rainfall erosivity estimated by both GPM products after bias correction showed accuracy comparable to those achieved through Kriging interpolation using Gauge-H (R-factor: PBIAS = 0.03%; 10-yr storm EI: PBIAS = −0.03%) and better than those derived from gauge-observed daily precipitation (R-factor: PBIAS = −6.9%; 10-yr storm EI: PBIAS = −16.77%).
Based on the results achieved here, it can be concluded that both GPM_3IMERGDF and GPM_3IMERGHH hold great potential for application in rainfall erosivity estimation after a bias-correction procedure. This research offers valuable insights and recommendations regarding the application of remote sensing precipitation products in the estimation of rainfall erosivity.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.W., B.Y. (Bofu Yu), X.Z. and Y.X.; Methodology, W.W., Y.J. and B.Y. (Bing Yin); Software, W.W. and Y.J.; Validation, Y.J.; Data curation, W.W.; Writing—original draft, W.W.; Writing—review & editing, W.W., B.Y. (Bofu Yu) and X.Z.; Visualization, Y.J.; Supervision, Y.X.; Funding acquisition, X.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Guangdong Major Project of Basic and Applied Basic Research (No. 2021B0301030007), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 42307424), the Open Research Fund of State Key Laboratory of Simulation and Regulation of Water Cycle in River Basin, China Institute of Water Resources and Hydropower Research (No. IWHR-SKL-KF202317).
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
This work utilized the Generative Pre-trained Transformer (GPT) tool provided by OpenAI for improving language, and has been revised by MDPI internal editor.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
References
- Zhen, L. The national census for soil erosion and dynamic analysis in China. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2013, 1, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekern, P.C. Rainfall intensity as a measure of storm erosivity. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1954, 18, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischmeier, W.H. A Rainfall Erosion Index for a Universal Soil-Loss Equation 1. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1959, 23, 246–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Predicting Rainfall-Erosion Losses from Cropland East of the Rocky Mountains: Guide for Selection of Practices for Soil and Water Conservation (No. 282); Agricultural Research Service, US Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1965.
- Renard, K.G.; Foster, G.R.; Weesies, G.A.; McCool, D.K.; Yoder, D.C. Predicting soil erosion by water: A guide to conservation planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE). In Agriculture Handbook; Agricultural Research Service, US Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- USDA-Agricultural Research Service. Science Documentation Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation Version 2; USDA-ARS: Washington, DC, USA, 2013.
- Yin, S.; Xie, Y.; Nearing, M.; Wang, C. Estimation of rainfall erosivity using 5- to 60-min fixed-interval rainfall data from China. CATENA 2007, 70, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Xie, Y.; Liu, B.; Nearing, M.A. Rainfall erosivity estimation based on rainfall data collected over a range of temporal resolutions. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 4113–4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, C.; Huffman, G. Global precipitation measurement. Meteorol. Appl. 2011, 18, 334–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Nearing, M.A.; Borrelli, P.; Xue, X. Rainfall erosivity: An overview of methodologies and applications. Vadose Zone J. 2017, 16, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Yin, S.-Q.; Liu, B.-Y.; Nearing, M.A.; Zhao, Y. Models for estimating daily rainfall erosivity in China. J. Hydrol. 2016, 535, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Chen, M.; Yang, S.; Yatagai, A.; Hayasaka, T.; Fukushima, Y.; Liu, C. A Gauge-based analysis of daily precipitation over East Asia. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 607–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Feng, M.; Zhang, H.; Gao, F. Interpolation methods of China daily precipitation data. J. Appl. Meteorol. Sci. 2010, 21, 279–286. [Google Scholar]
- Schamm, K.; Ziese, M.; Becker, A.; Finger, P.; Meyer-Christoffer, A.; Schneider, U.; Schröder, M.; Stender, P. Global gridded precipitation over land: A description of the new GPCC first guess daily product. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2014, 6, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Gao, X.J. A gridded daily observation dataset over China region and comparison with the other datasets. Chin. J. Geophys. 2013, 56, 1102–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Nelkin, E.J.; Wolff, D.B.; Adler, R.F.; Gu, G.; Hong, Y.; Bowman, K.P.; Stocker, E.F. The TRMM multisatellite precipitation analysis (TMPA): Quasi-global, multiyear, combined-sensor precipitation estimates at fine scales. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Joyce, R.; Yoo, S.; Yarosh, S.H.; Sun, Y.; Lin, F. NOAA Climate Data Record (CDR) of CPC Morphing Technique (CMORPH) High Resolution Global Precipitation Estimates, Version 1; NOAA National Centers for Environmental Information: Asheville, NC, USA, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Ou, T.; Chen, D.; Linderholm, H.W.; Jeong, J.-H. Evaluation of global climate models in simulating extreme precipitation in China. Tellus A Dyn. Meteorol. Oceanogr. 2013, 65, 19799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yin, S.; Yue, T.; Yu, B.; Wang, W. Rainfall erosivity estimation using gridded daily precipitation datasets. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2020, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yin, S.; He, Z.; Chen, D.; Wang, H.; Klik, A. Projections of rainfall erosivity in climate change scenarios for mainland China. CATENA 2023, 232, 107391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezak, N.; Borrelli, P.; Panagos, P. Exploring the possible role of satellite-based rainfall data in estimating inter- and intra-annual global rainfall erosivity. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 26, 1907–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Miao, C.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Q.; Su, J. Evaluation of the GPM IMERG product at the hourly timescale over China. Atmos. Res. 2023, 285, 106656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrieling, A.; Sterk, G.; de Jong, S.M. Satellite-based estimation of rainfall erosivity for Africa. J. Hydrol. 2010, 395, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musie, M.; Sen, S.; Srivastava, P. Comparison and evaluation of gridded precipitation datasets for streamflow simulation in data scarce watersheds of Ethiopia. J. Hydrol. 2019, 579, 124168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolopoulos, E.I.; Anagnostou, E.N.; Borga, M. Using high-resolution satellite rainfall products to simulate a major flash flood event in northern Italy. J. Hydrometeorol. 2013, 14, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Jain, M.K.; Gupta, V. A step towards mapping rainfall erosivity for India using high-resolution GPM satellite rainfall products. CATENA 2022, 212, 106067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Jain, M.K.; Gupta, V.; Saha, A. Understating the Uncertainty in Global Rainfall Erosivity Estimated Using Multiple Satellite Precipitation Datasets. In Proceedings of the AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts, Chicago, IL, USA, 12–16 December 2022; p. H42H-1390. [Google Scholar]
- Vrieling, A.; Hoedjes, J.C.; van der Velde, M. Towards large-scale monitoring of soil erosion in Africa: Accounting for the dynamics of rainfall erosivity. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2014, 115, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, M.; Wang, Z.; Gao, P.; Lai, C. Applicability of two satellite-based precipitation products for assessing rainfall erosivity in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 757, 143975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Z.; Duan, W.; Liu, M.; Wang, H.; Li, G.; Wang, J.; Fu, Q. Comparison of the four gridded precipitation products for estimating regional rainfall erosivity in China’s Mainland. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2023, 39, 100–109, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, Z.; Lin, Y. Suitability of TRMM products with different temporal resolution (3-hourly, daily, and monthly) for rainfall erosivity estimation. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wei, J.; Yin, J.; Qiao, Z.; Peng, W.; Peng, H. Multiscale comparative evaluation of the GPM and TRMM precipitation products against ground precipitation observations over Chinese Tibetan Plateau. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 14, 2295–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Joyce, R.; Wu, S.; Yoo, S.-H.; Yarosh, Y.; Sun, F.; Lin, R. Reprocessed, bias-corrected CMORPH global high-resolution precipitation estimates from 1998. J. Hydrometeorol. 2017, 18, 1617–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Han, H.; Kim, B.; Chen, H.; Lee, J.-H. Use of a high-resolution-satellite-based precipitation product in mapping continental-scale rainfall erosivity: A case study of the United States. CATENA 2020, 193, 104602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funk, C.; Peterson, P.; Landsfeld, M.; Pedreros, D.; Verdin, J.; Shukla, S.; Husak, G.; Rowland, J.; Harrison, L.; Hoell, A.; et al. The climate hazards infrared precipitation with stations—A new environmental record for monitoring extremes. Sci. Data 2015, 2, 150066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, W.; Ding, X.; Sun, W.; Mu, X. Improvement of satellite-based rainfall product CHIRPS in estimating rainfall erosivity on the Loess Plateau. Land Degrad. Dev. 2023, 34, 4517–4528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergni, L.; Parisi, A.; Todisco, F. Evaluation of the GPM IMERG half-hourly final precipitation product in the quantification of rainfall erosivity in central Italy. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Workshop on Metrology for Agriculture and Forestry (MetroAgriFor), Perugia, Italy, 3–5 November 2022; pp. 282–286. [Google Scholar]
- de Brito, C.S.; da Silva, R.M.; Santos, C.A.G.; Neto, R.M.B.; Coelho, V.H.R. Long-term basin-scale comparison of two high-resolution satellite-based remote sensing datasets for assessing rainfall and erosivity in a basin in the Brazilian semiarid region. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2022, 147, 1049–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenta, A.A.; Tsunekawa, A.; Haregeweyn, N.; Yasuda, H.; Tsubo, M.; Borrelli, P.; Kawai, T.; Belay, A.S.; Ebabu, K.; Berihun, M.L.; et al. Improving satellite-based global rainfall erosivity estimates through merging with gauge data. J. Hydrol. 2023, 620, 129555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenderink, G.; van Meijgaard, E. Increase in hourly precipitation extremes beyond expectations from temperature changes. Nat. Geosci. 2008, 1, 511–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenderink, G.; van Meijgaard, E. Linking increases in hourly precipitation extremes to atmospheric temperature and moisture changes. Environ. Res. Lett. 2010, 5, 025208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Yang, Z.; Yan, D.; Yin, J. Historical changes and future projection of extreme precipitation in China. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2017, 127, 393–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, C.; Sun, Q.; Borthwick, A.G.L.; Duan, Q. Linkage between hourly precipitation events and atmospheric temperature changes over China during the warm season. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, V.M.; Keim, B.D.; Black, A.W. Trend analysis of multiple extreme hourly precipitation time series in the southeastern United States. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2020, 59, 427–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yin, S.; Gao, G.; Papalexiou, S.; Wang, Z. Increasing trends in rainfall erosivity in the Yellow River basin from 1971 to 2020. J. Hydrol. 2022, 610, 127851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nearing, A.M. Potential changes in rainfall erosivity in the US with climate change during the 21st century. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2001, 56, 29–232. [Google Scholar]
- Huff, F.A. Time distribution of rainfall in heavy storms. Water Resour. Res. 1967, 3, 1007–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Xue, X.; Yue, T.; Xie, Y.; Gao, G. Spatiotemporal distribution and return period of rainfall erosivity in China. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2019, 35, 105–113, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.D.; Perez, A.; Lozano, J.A. Sensitivity analysis of k-fold cross validation in prediction error estimation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2009, 32, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, T.; Yin, S.; Xie, Y.; Yu, B.; Liu, B. Rainfall erosivity mapping over mainland China based on high-density hourly rainfall records. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2022, 14, 665–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulo-Martínez, M.; López-Vicente, M.; Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Beguería, S. Mapping rainfall erosivity at a regional scale: A comparison of interpolation methods in the Ebro Basin (NE Spain). Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 13, 1907–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P.; Meusburger, K.; Yu, B.; Klik, A.; Lim, K.J.; Yang, J.E.; Ni, J.; Miao, C.; Chattopadhyay, N.; et al. Global rainfall erosivity assessment based on high-temporal resolution rainfall records. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Guo, Q.; Zuo, C.; Shan, Z.; Ma, L.; Sun, G. Spatial distribution and temporal trends of rainfall erosivity in China’s mainland for 1951–2010. CATENA 2016, 147, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballabio, C.; Borrelli, P.; Spinoni, J.; Meusburger, K.; Michaelides, S.; Beguería, S.; Klik, A.; Petan, S.; Janeček, M.; Olsen, P.; et al. Mapping monthly rainfall erosivity in Europe. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 1298–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliver, M.A.; Webster, R. A tutorial guide to geostatistics: Computing and modelling variograms and kriging. CATENA 2014, 113, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Yu, B. Spatial and seasonal distribution of rainfall erosivity in Australia. Soil Res. 2002, 40, 887–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Liu, Q.; Ma, L.; Ding, S.; Xu, S.; Wu, C.; Liu, P. Spatiotemporal variations in rainfall erosivity during the period of 1960–2011 in Guangdong Province, southern China. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2017, 128, 113–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; He, Y.; Xu, J.; van Noordwijk, M.; Lu, X. Spatial and temporal variation in rainfall erosivity in a Himalayan watershed. CATENA 2014, 121, 248–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Xiong, K.; Xiao, H. Multi-time scale variability of rainfall erosivity and erosivity density in the karst region of southern China, 1960–2017. CATENA 2021, 197, 104977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Miao, C.; Xi, Y.; Duan, Q.; Lei, X.; Li, H. Analysis of precipitation characteristics on the loess plateau between 1965 and 2014, based on high-density gauge observations. Atmos. Res. 2018, 213, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, G.; Zhang, X.; Meng, Q.; Gu, P.; Liu, T. Evaluation of the performance of multi-source precipitation data in southwest China. Water 2021, 13, 3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).