Comprehensive Assessment of Sustainable Development of Terrestrial Ecosystem Based on SDG 15—A Case Study of Guilin City
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
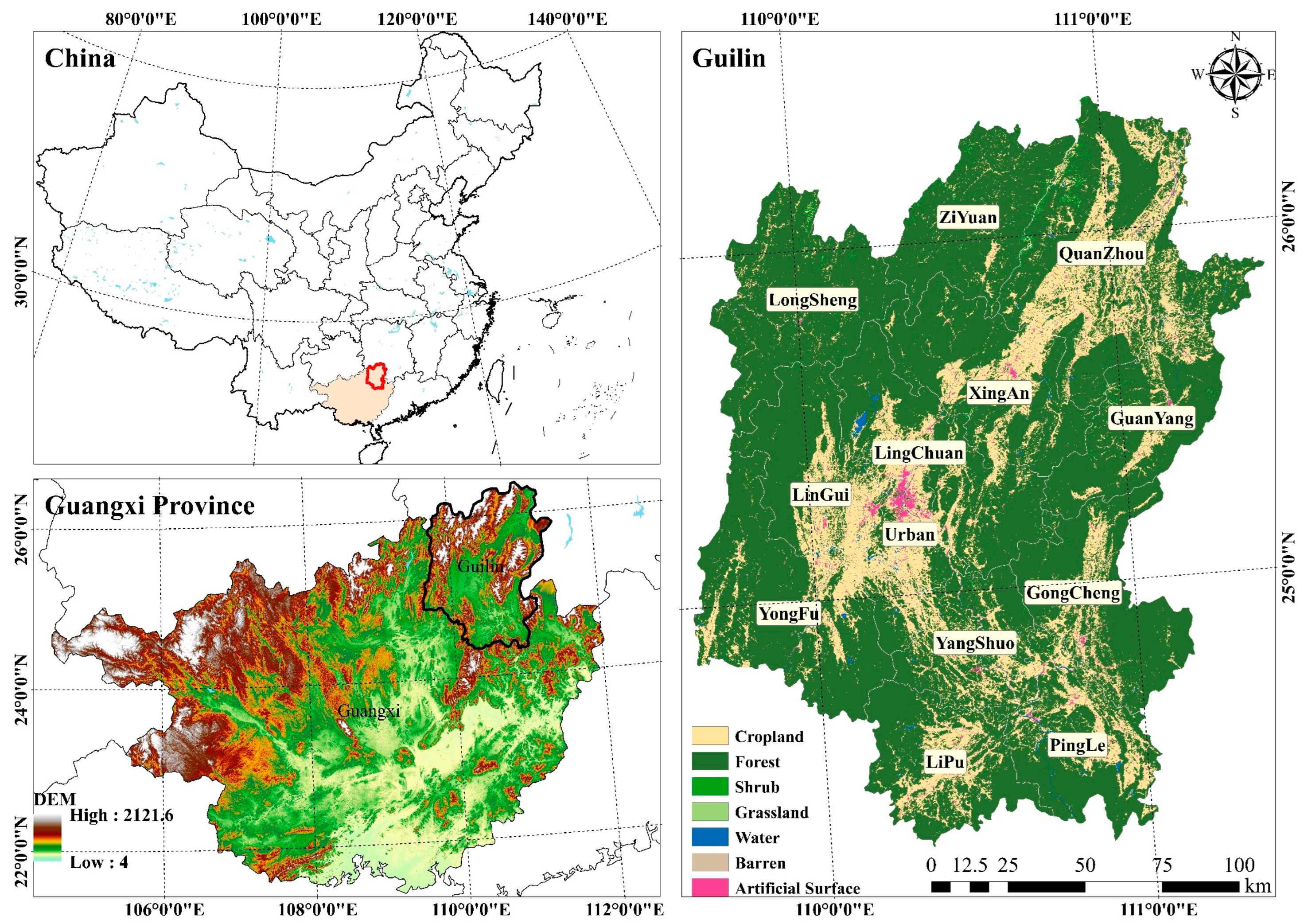
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources and Preprocessing
3. Methods
3.1. Scheme for Constructing the Evaluation Index System
3.1.1. Localization Connotation
3.1.2. Basis for the Selection of Indicators
3.2. Evaluation and Analysis Methods
3.2.1. Biodiversity Assessment
3.2.2. Land Degradation Neutrality
3.2.3. Assessment of Mountain Green Cover Index
3.3. Comprehensive Indicator Calculation
4. Results
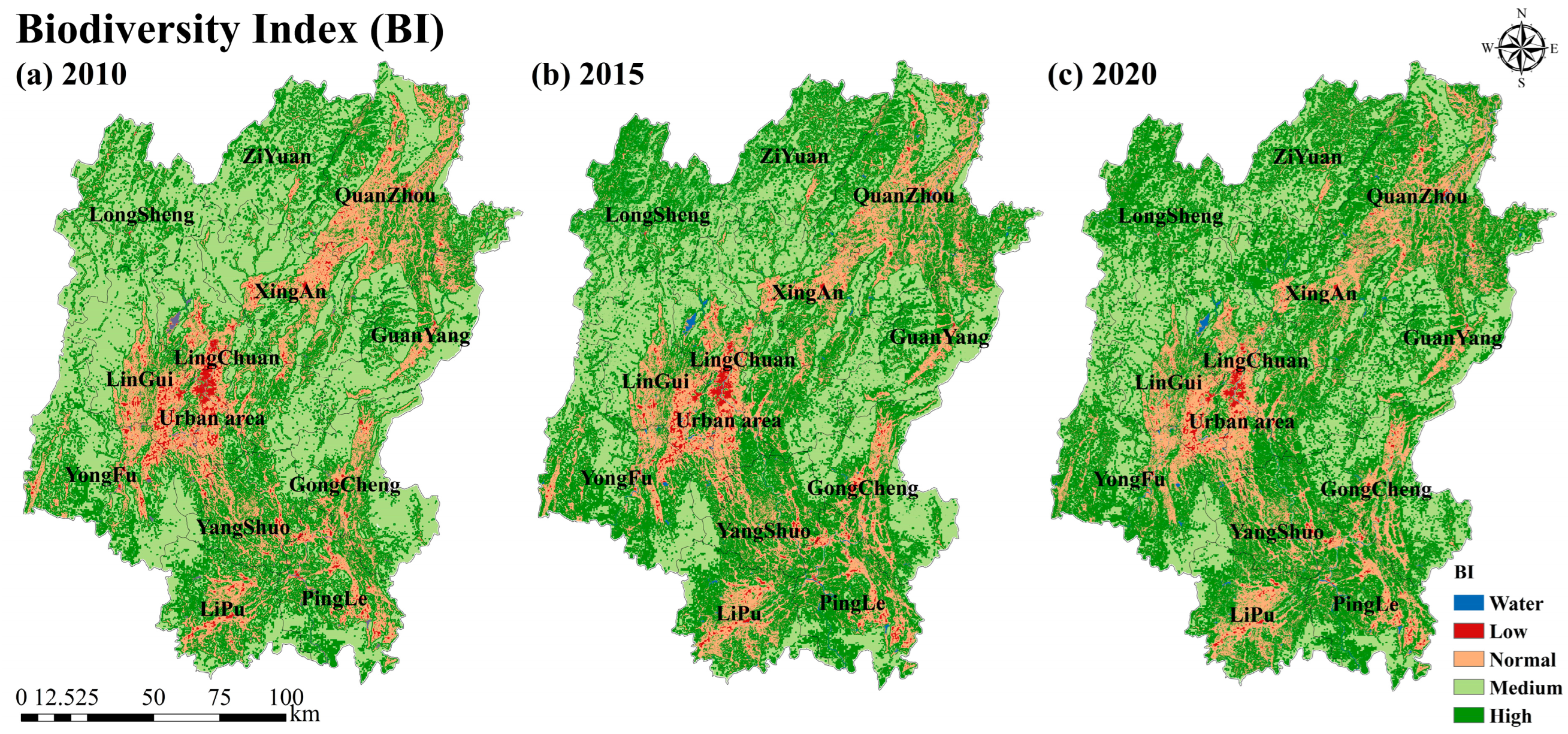
4.1. SDG 15.1.2 Biodiversity Index
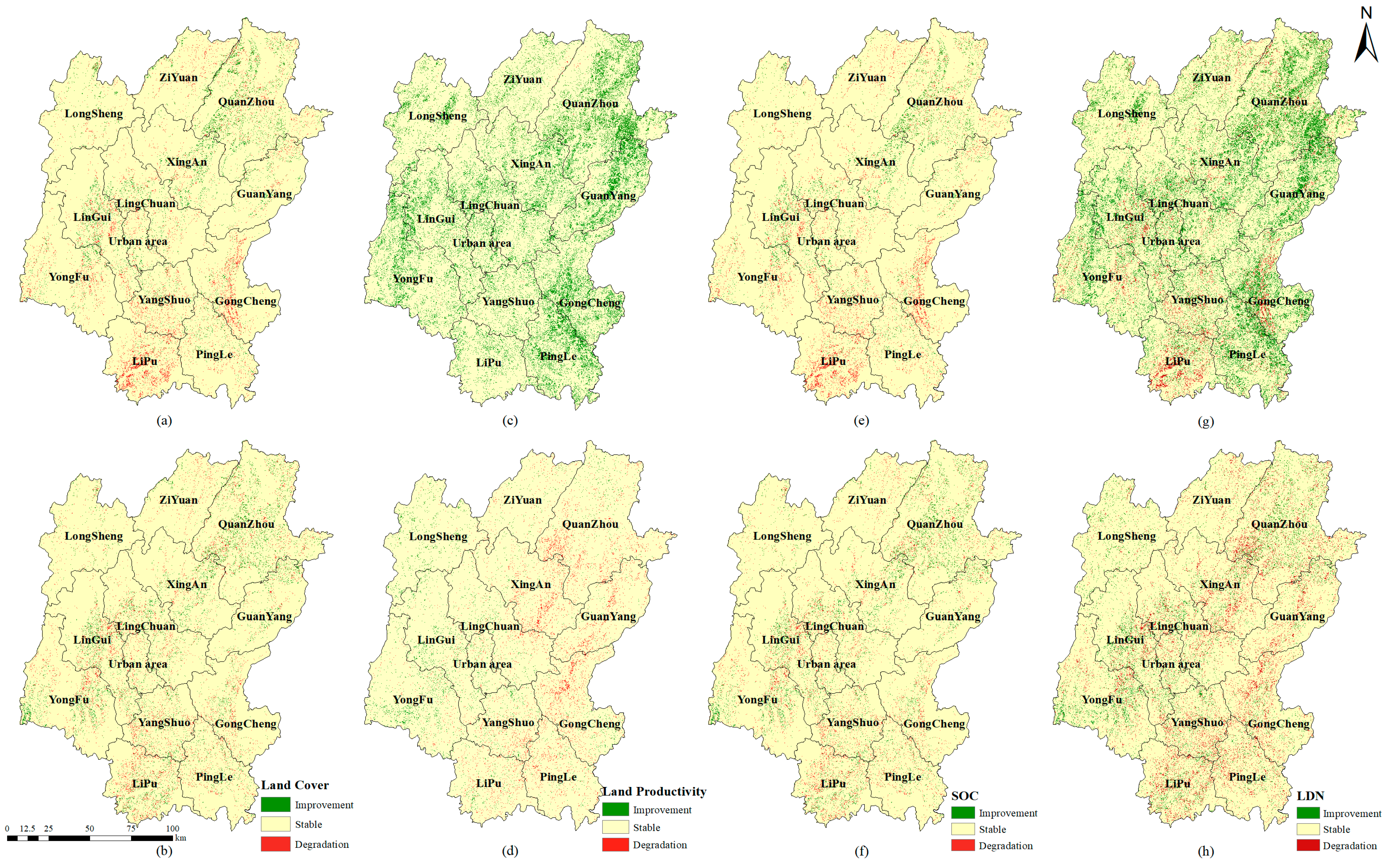
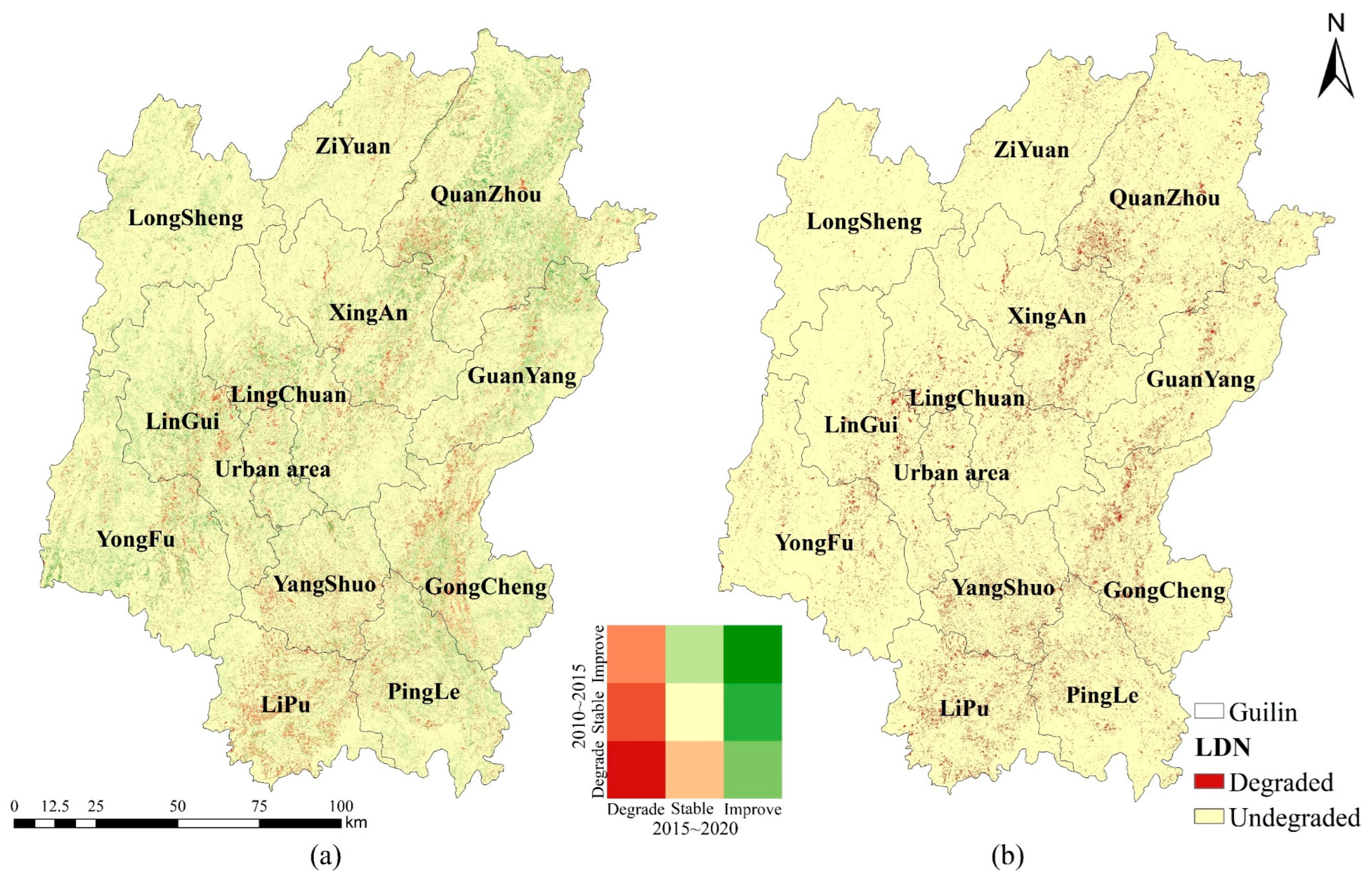
4.2. SDG 15.3.1 Land Degradation Neutrality
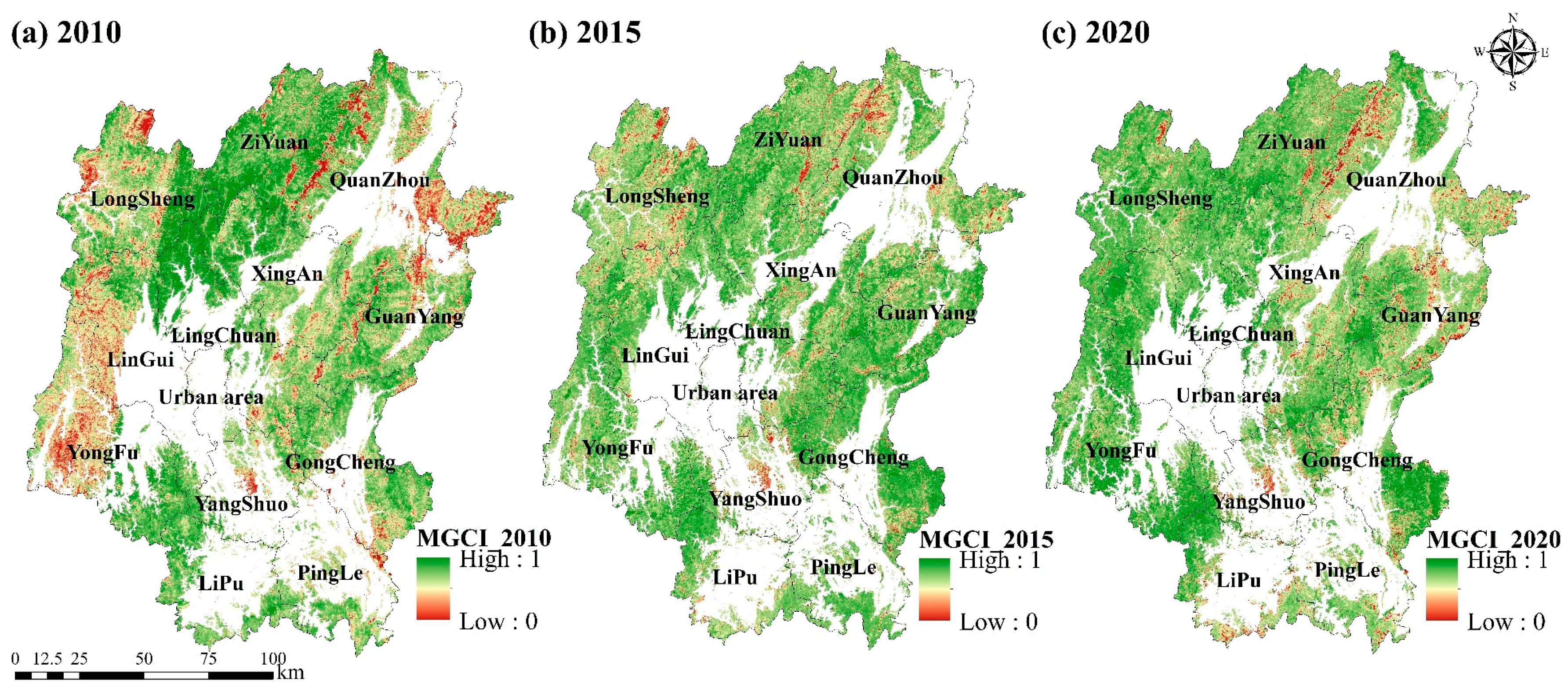
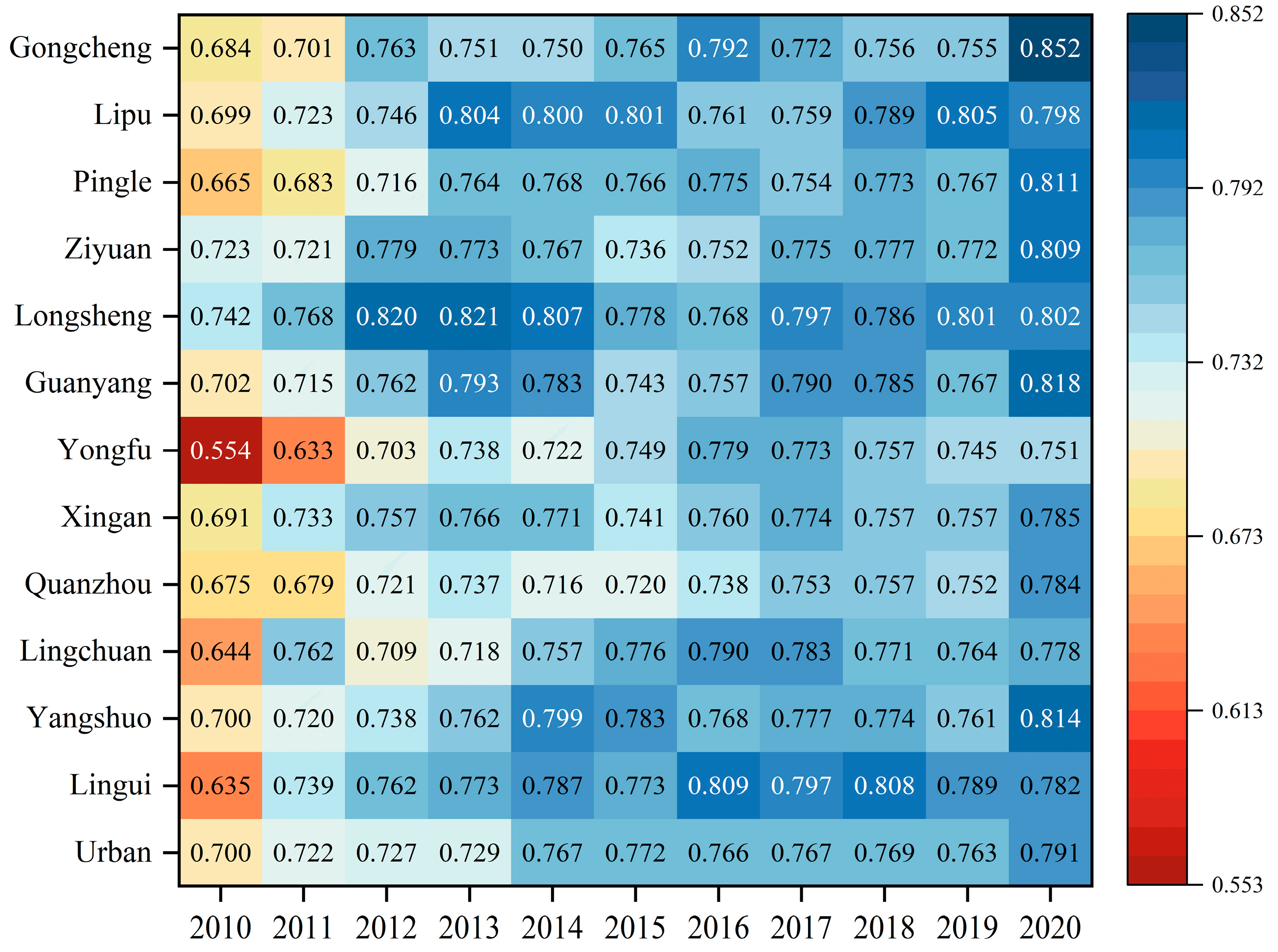
4.3. SDG 15.4.2 Mountain Green Cover Index
4.4. SDG 15 Comprehensive Assessment
5. Discussion
5.1. Importance of Localisation
5.2. Assessment of SDGs from a Geospatial Perspective
5.3. Coupled Coordination of Different SDGs
5.4. Optimizing Pathways for Regional Sustainability
- Strengthen biodiversity governance capacity: Remote sensing technology was employed to monitor and evaluate biodiversity levels in Guilin’s districts and counties. The results indicate that urban areas exhibited the lowest biodiversity due to being primarily built-up areas dominated by construction land, heavily impacted by human activities. Therefore, it’s necessary to enhance biodiversity protection measures, such as designating core conservation areas in ecologically sensitive areas in mountainous regions, implementing biodiversity monitoring programs to track the number of species and ecosystem health in the long term, and regulating tourism and human activities in important habitats to reduce disturbances, so as to improve the ecological environment’s quality, establish a more suitable terrestrial ecosystem for biological survival, and promote harmonious coexistence between humans and nature.
- Further strengthening terrestrial ecosystem conservation and ecological environmental protection. Implement the ecological protection and restoration project centered on the Li River, accelerate the construction of the ecological landscape restoration project at the Karst World Natural Heritage Site, and comprehensively enhance the urban and rural ecological environment. The results from the land degradation indicators in this study reveal that although Guilin has made progress in curbing land degradation, the newly degraded area has increased. Therefore, it is imperative to intensify ecological restoration and landscape resource conservation measures to achieve systematic protection and restoration of the environment.
5.5. Limitations and Future Directions
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A. The Meaning of Biodiversity Assessment Indicators and Their Calculation Methods
| Threat | Weight | Decay | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cropland | 8 | 0.7 | Liner |
| Water | 3 | 0.2 | Liner |
| Artificial Surface | 10 | 1 | Exponential |
| Forest | 6 | 0.5 | Exponential |
| Land Cover | Habitat | Cropland | Water | Artificial Surface | Forest |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cropland | 0.1 | 0 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.7 |
| Forest | 1 | 0.6 | 0.65 | 0.8 | 0.4 |
| Water | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.6 |
| Artificial Surface | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.1 | 0 |
| Grassland | 0.7 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.5 |
References
- United Nations. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Zhou, L.; Chi, Y. Review on Research of Spatial Pattern and Influencing Mechanisms of Terrestrial Ecosystem Stability. J. Agrometeorol. 2021, 42, 552–560. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, L.; He, H.; Ren, X.; Niu, Z.; Lv, Y.; Xu, Q.; Chang, Q.; Liu, W.; Li, P. Quality changes of China’s terrestrial ecosystem based on reference system. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 7100–7113. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldan, B.; Janoušková, S.; Hák, T. How to Understand and Measure Environmental Sustainability: Indicators and Targets. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 17, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-F.; Huang, H.-I.; Yeh, H.-R. Developing an Evaluation Model for Destination Attractiveness: Sustainable Forest Recreation Tourism in Taiwan. J. Sustain. Tour. 2010, 18, 811–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt-Traub, G.; Kroll, C.; Teksoz, K.; Durand-Delacre, D.; Sachs, J.D. National Baselines for the Sustainable Development Goals Assessed in the SDG Index and Dashboards. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, C.; Nejdawi, R.; El-Baba, J.; Hamati, K.; Metternicht, G.; Wiedmann, T. Indicator-Based Assessments of Progress towards the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): A Case Study from the Arab Region. Sustain. Sci. 2017, 12, 975–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Hackmann, H.; Gong, K. Big Data in Support of the Sustainable Development Goals: A Celebration of the Establishment of the International Research Center of Big Data for Sustainable Development Goals (CBAS). Big Earth Data 2021, 5, 259–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Ren, H.; Geng, W.; Peng, S.; Ye, F. Quantitative Measurement and Monitoring Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) with Geospatial Information. Geomat. World 2018, 25, 1–7. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, C.; Hou, Y.; Xin, F.; Mao, Z.; Xue, X. Study of the Spatio-Temporal Variation of Environmental Sustainability at National and Provincial Levels in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 150830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Jia, K.; Xia, M.; Zhao, W. Using Remote Sensing Data to Evaluate the Ecological Restoration in Taiyuan from the SDGs Perspective. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2023, 16, 4621–4645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Hu, B.; Zhang, Z. Impacts of Land Use Change on Ecosystem Service Value Based on SDGs Report--Taking Guangxi as an Example. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 133, 108366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Long, T.; He, G.; Guo, Y.; Yin, R.; Zhang, Z.; Xiao, H.; Li, M.; Cheng, B. Rapid Generation of Global Forest Cover Map Using Landsat Based on the Forest Ecological Zones. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2020, 14, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, N.C.; England, J.R.; Newnham, G.J.; Alexander, S.; Green, C.; Minelli, S.; Held, A. Developing Good Practice Guidance for Estimating Land Degradation in the Context of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals. Environ. Sci. Policy 2019, 92, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Giuliani, G.; Lehmann, A.; Jiang, Y.; Shao, X.; Li, L.; Zhao, H. Supporting SDG 15, Life on Land: Identifying the Main Drivers of Land Degradation in Honghe Prefecture, China, between 2005 and 2015. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Wang, C.; Yu, X.; Yin, S. Evaluating Trends of Land Productivity Change and Their Causes in the Han River Basin, China: In Support of SDG Indicator 15.3.1. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Gao, X.; Xiao, N.; Ji, S. Biodiversity Monitoring and Evaluation Using Remote Sensing Technology in Maduo County, Qinghai Province. Res. Environ. Sci. 2021, 34, 2419–2427. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Bai, J.; Chen, J. Measuring SDG 15 at the County Scale: Localization and Practice of SDGs Indicators Based on Geospatial Information. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shao, J.; Wang, S.; Wei, C. A Conceptual Analysis of Karst Ecosystem fragility. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2006, 26, 1–9. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Ma, J.; Yu, M.; He, G. Comprehensive disturbance evaluation of karst and its spatial characteristics in the Lijiang River Basin. Acta Ecol. Sinic. 2024, 44, 1404–1417. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, W.; Ma, J.; Wang, Y. Evaluation of ecological environment quality in Guilin City based on RSEl. J. Guangxi Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2023, 41, 200–212. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilin Economic and Social Statistical Yearbook 1999–2023. Available online: https://www.shujuku.org/statistical-yearbook-of-guilin.html (accessed on 23 November 2024).
- Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region People’s Government. Available online: https://www.guilin.gov.cn/glsj/ (accessed on 23 November 2024).
- National Catalogue Service for Geographic Information. Available online: https://www.webmap.cn/main.do?method=index (accessed on 23 November 2024).
- Yang, J.; Huang, X. The 30 m Annual Land Cover Dataset and Its Dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 3907–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenodo. Available online: https://zenodo.org/ (accessed on 23 November 2024).
- Geospatial Data Cloud. Available online: https://www.gscloud.cn/#page1/1 (accessed on 23 November 2024).
- Chen, J.; Peng, S.; Zhao, X.; Ge, Y.; Li, Z. Measuring regional progress towards SDGs by combining geospatial and statistical information. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2019, 48, 473–479. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KBA Data. Available online: https://www.keybiodiversityareas.org/kba-data (accessed on 16 December 2024).
- Fu, B.; Yu, D.; Lv, N. An indicator system for biodiversity and ecosystem services evaluation in China. Acta Ecol. Sinic. 2017, 37, 341–348. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, C.S.; Kurian, A.; Srivastava, G.; Singhal, J.; Varghese, A.O.; Padalia, H.; Ayyappan, N.; Rajashekar, G.; Jha, C.S.; Rao, P.V.N. Remote Sensing Enabled Essential Biodiversity Variables for Biodiversity Assessment and Monitoring: Technological Advancement and Potentials. Biodivers. Conserv. 2021, 30, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, D.; Xue, J.; Dai, H.; Sun, H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Gui, D. Analysis of spatial and temporal pattern changes and driving factors of Hotan Oasis. J. Desert Res. 2021, 41, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcgarigal, K.S.; Cushman, S.A.; Neel, M.C.; Ene, E. FRAGSTATS: Spatial Pattern Analysis Program for Categorical Maps; University of Massachusetts: Amherst, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, C.; Myint, S. A Comparison of Spatial Autocorrelation Indices and Landscape Metrics in Measuring Urban Landscape Fragmentation. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 121, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, B.A.; Field, R.; Cornell, H.V.; Currie, D.J.; Guégan, J.-F.; Kaufman, D.M.; Kerr, J.T.; Mittelbach, G.G.; Oberdorff, T.; O’Brien, E.M.; et al. Energy, Water, and Broad-Scale Geographic Patterns of Species Richness. Ecology 2003, 84, 3105–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lausch, A.; Bannehr, L.; Beckmann, M.; Boehm, C.; Feilhauer, H.; Hacker, J.M.; Heurich, M.; Jung, A.; Klenke, R.; Neumann, C.; et al. Linking Earth Observation and Taxonomic, Structural and Functional Biodiversity: Local to Ecosystem Perspectives. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 70, 317–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, J.H.; Caldarone, G.; Duarte, T.K.; Ennaanay, D.; Hannahs, N.; Mendoza, G.; Polasky, S.; Wolny, S.; Daily, G.C. Integrating Ecosystem-Service Tradeoffs into Land-Use Decisions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 7565–7570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wu, H.; Liu, S. The Research Progress of Terrestrial Wildlife Habitat Selection from Spatial Scale. J. Green Sci. Technol. 2015, 17, 5–8. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrado, M.; Sabater, S.; Chaplin-Kramer, B.; Mandle, L.; Ziv, G.; Acuña, V. Model Development for the Assessment of Terrestrial and Aquatic Habitat Quality in Conservation Planning. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 540, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Sun, W.; Xia, F.; Yang, Y.; Xie, Y. Can Habitat Quality Index Measured Using the InVEST Model Explain Variations in Bird Diversity in an Urban Area? Sustainability 2021, 13, 5747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Yu, D.; Qiu, J. Assessing Coupling Interactions in a Safe and Just Operating Space for Regional Sustainability. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Standard for the Assessment of Regional Biodiversity. Available online: https://english.mee.gov.cn/Resources/standards/Eco_Environment/201201/t20120106_222250.shtml (accessed on 3 July 2024).
- AbdelRahman, M.A.E. An Overview of Land Degradation, Desertification and Sustainable Land Management Using GIS and Remote Sensing Applications. Rend. Fis. Acc. Lincei 2023, 34, 767–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowie, A.L.; Orr, B.J.; Sanchez, V.M.C.; Chasek, P.; Crossman, N.D.; Erlewein, A.; Louwagie, G.; Maron, M.; Metternicht, G.I.; Minelli, S.; et al. Land in Balance: The Scientific Conceptual Framework for Land Degradation Neutrality. Environ. Sci. Policy 2018, 79, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, N.C.; Barger, N.N.; Metternicht, G.I.; England, J.R. A Land Degradation Interpretation Matrix for Reporting on UN SDG Indicator 15.3.1 and Land Degradation Neutrality. Environ. Sci. Policy 2020, 114, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric Tests Against Trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, C.; Ojha, C.S.P. Changes of Annual Precipitation and Probability Distributions for Different Climate Types of the World. Water 2019, 11, 2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Jia, K.; Liu, X.; Li, J.; Xia, M. Assessment of Land Degradation in Inner Mongolia between 2000 and 2020 Based on Remote Sensing Data. Geogr. Sustain. 2023, 4, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Chen, J.; Hou, J.; Zhou, G.; You, H.; Han, X. Study on sustainable development of carbon storage in Guilin coupled with InVEST and GeoSOS-FLUS model China. Environ. Sci. 2022, 42, 2799–2809. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, P.; Wang, Z.; Kuang, W.; Chen, J. Assessment of land degradation in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region from 2000 to 2020 based on SDG15.3.1. J. Spatiotemporal Inf. 2023, 30, 560–573. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Cheng, W.; Qian, J.; Li, B.; Zhang, B. Research on the Classification System of Digital Land Geomorphology of 1:1000000 in China. J. Geoinf. Sci. 2009, 11, 707–724. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, D.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, D.; Ge, J. Estimation of vegetation cover and analysis of landscape pattern base on Landsat data. Surv. Mapp. Sci. 2018, 43, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SDG Index and Dashboards Report for European Cities. Available online: https://www.sustainabledevelopment.report (accessed on 24 June 2024).
- Xue, L.; Weng, L. The Policy Opportunities and Challenges in China’s Implementation of 2030 Sustainable Development Goals. China Soft Sci. 2017, 32, 1–12. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Chen, J.; Ren, H.; Chen, H.; Zhao, X. Comprehensive Measurement of Localized Indicator Alignment and Practice Toward SDGs. Geomat. World 2022, 29, 48–55. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyers, B.; Stafford-Smith, M.; Erb, K.-H.; Scholes, R.J.; Selomane, O. Essential Variables Help to Focus Sustainable Development Goals Monitoring. Curr. Opin. Env. Sust. 2017, 26–27, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Feng, H.; Zou, B.; Wu, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Zhu, S.; Wang, Z. Evaluation on the SDGs of Innovation Demonstration Zone for National Sustainable Development Agenda in China: A Case Study of Chenzhou City. Geogr. GeoInf. Sci. 2022, 38, 104–109. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, D. Evaluation and Driving Factors of City Sustainability in Northeast China: An Analysis Based on Interaction among Multiple Indicators. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 67, 102721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Liang, D.; Sun, Z.; Chen, F.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Zhu, L.; Bian, J.; Wei, Y.; Huang, L.; et al. Measuring and Evaluating SDG Indicators with Big Earth Data. Sci. Bull. 2022, 67, 1792–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucia, L.D.; Slade, R.; Khan, J. Decision-Making Fitness of Methods to Understand Sustainable Development Goal Interactions. Nat. Sustain. 2022, 5, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Li, J.; Zeng, H.; Chen, J.; Zhao, J. Analysis of Hierarchical Analysis Weighting Method and Application Research. Math. Pract. Theory 2012, 42, 93–100. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Feng, X.; Tang, R. Analysis and Forecast of Coupling Coordination Development among the Regional Economy-Ecological Environment-Tourism Industry—A Case Study of Provinces Along the Yangtze Economic Zone. Econ. Geogr. 2016, 36, 186–193. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Target | SDG Indicator | Localization Indicator |
|---|---|---|
| Sustainable terrestrial ecosystems | 15.1.1 | Forest coverage rate |
| 15.1.2 | Biodiversity index, BI | |
| 15.2.1 | Proportion of expenditure on forest management | |
| 15.3.1 | Proportion of degraded land area | |
| 15.4.1 | Mountain biodiversity index, MBI | |
| 15.4.2 | Mountain green cover index, MGCI |
| Target | Standardized | Indicator | Weight |
|---|---|---|---|
| Biodiversity assessment | Species diversity | HQI | 0.35 |
| EVI | 0.15 | ||
| NPP | 0.2 | ||
| Ecosystem diversity | DIVISION | 0.1 | |
| Landscape diversity | SHDI | 0.1 | |
| CONTAG | 0.1 |
| Biodiversity Level | 2010 | 2015 | 2020 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pro/% | Pro/% | Pro/% | ||||
| High | 9908.64 | 36.33 | 11,236.51 | 41.20 | 13,515.16 | 49.56 |
| Medium | 12,177.31 | 44.65 | 11,692.94 | 42.87 | 11,422.06 | 41.88 |
| General | 4666.39 | 17.11 | 2859.21 | 10.48 | 2079.30 | 7.62 |
| Low | 518.95 | 1.91 | 404.43 | 1.48 | 256.1598 | 0.94 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, H.; Liu, G.; Muller, J.-P.; Sun, Z.; Yao, Y.; Chang, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Zhang, Y. Comprehensive Assessment of Sustainable Development of Terrestrial Ecosystem Based on SDG 15—A Case Study of Guilin City. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17010063
Pan H, Liu G, Muller J-P, Sun Z, Yao Y, Chang Y, Xiong Z, Zhang Y. Comprehensive Assessment of Sustainable Development of Terrestrial Ecosystem Based on SDG 15—A Case Study of Guilin City. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(1):63. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17010063
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Hongyu, Guang Liu, Jan-Peter Muller, Zhongchang Sun, Yuefeng Yao, Yao Chang, Zesen Xiong, and Yuchen Zhang. 2025. "Comprehensive Assessment of Sustainable Development of Terrestrial Ecosystem Based on SDG 15—A Case Study of Guilin City" Remote Sensing 17, no. 1: 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17010063
APA StylePan, H., Liu, G., Muller, J.-P., Sun, Z., Yao, Y., Chang, Y., Xiong, Z., & Zhang, Y. (2025). Comprehensive Assessment of Sustainable Development of Terrestrial Ecosystem Based on SDG 15—A Case Study of Guilin City. Remote Sensing, 17(1), 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17010063








