Developing Strategies for Carbon Neutrality Through Restoration of Ecological Spatial Networks in the Thal Desert, Punjab
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials
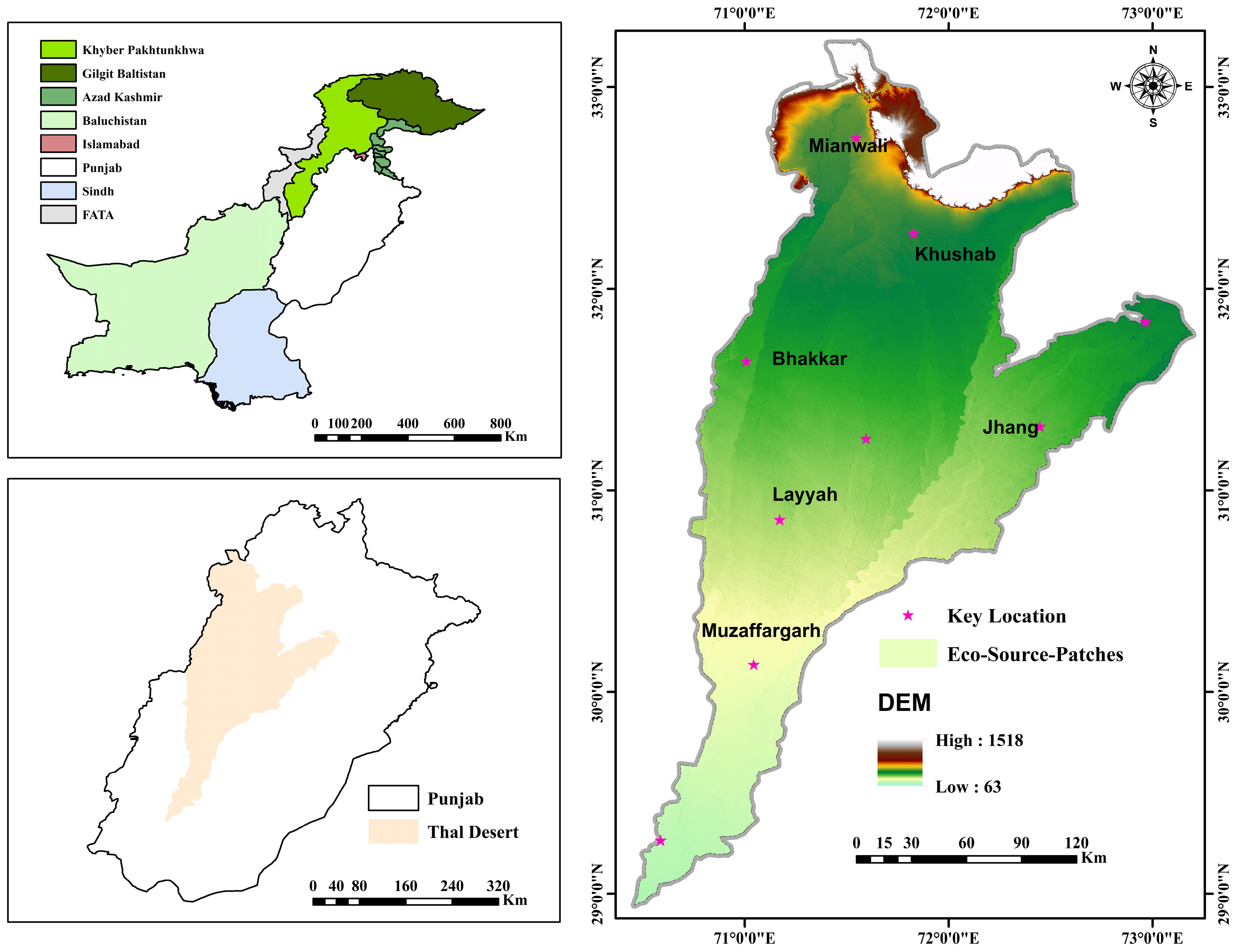
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Source and Processing
3. Methods
3.1. Construction of Ecological Spatial Network
3.1.1. Ecological Source Identification
3.1.2. Construction of an Ecological Corridor
3.2. Topological Indicators for Optimizing Spatial Network
3.2.1. Degree
3.2.2. Clustering Coefficient
3.2.3. Betweenness
3.2.4. Coreness
3.3. Ecological Network Gravity
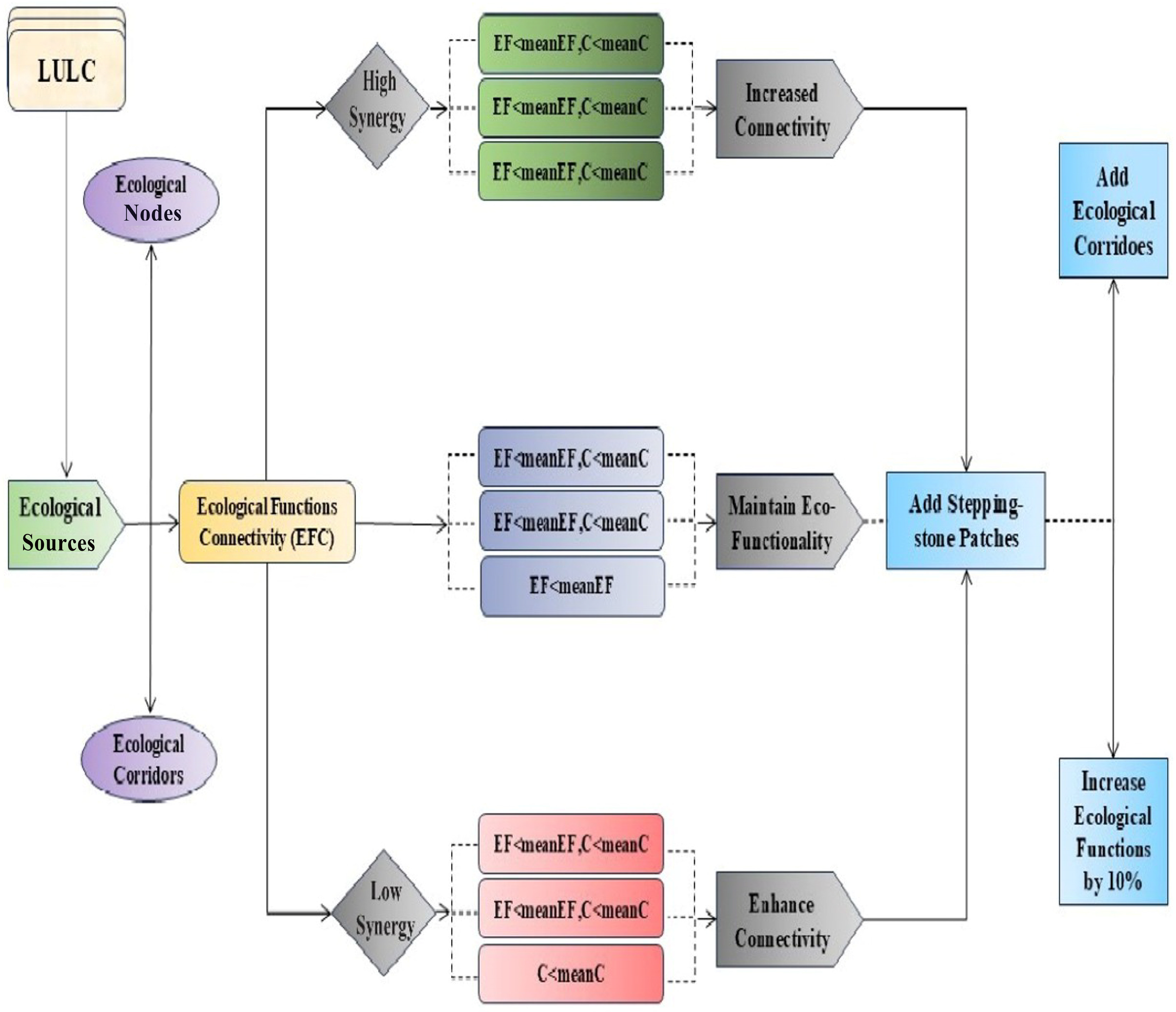
3.4. EFCT Optimization Model
3.5. Calculating Carbon Sequestration Accuracy
3.6. Robustness of Ecological Spatial Network
4. Results
4.1. Extraction and Analyzing Ecological Spatial Network
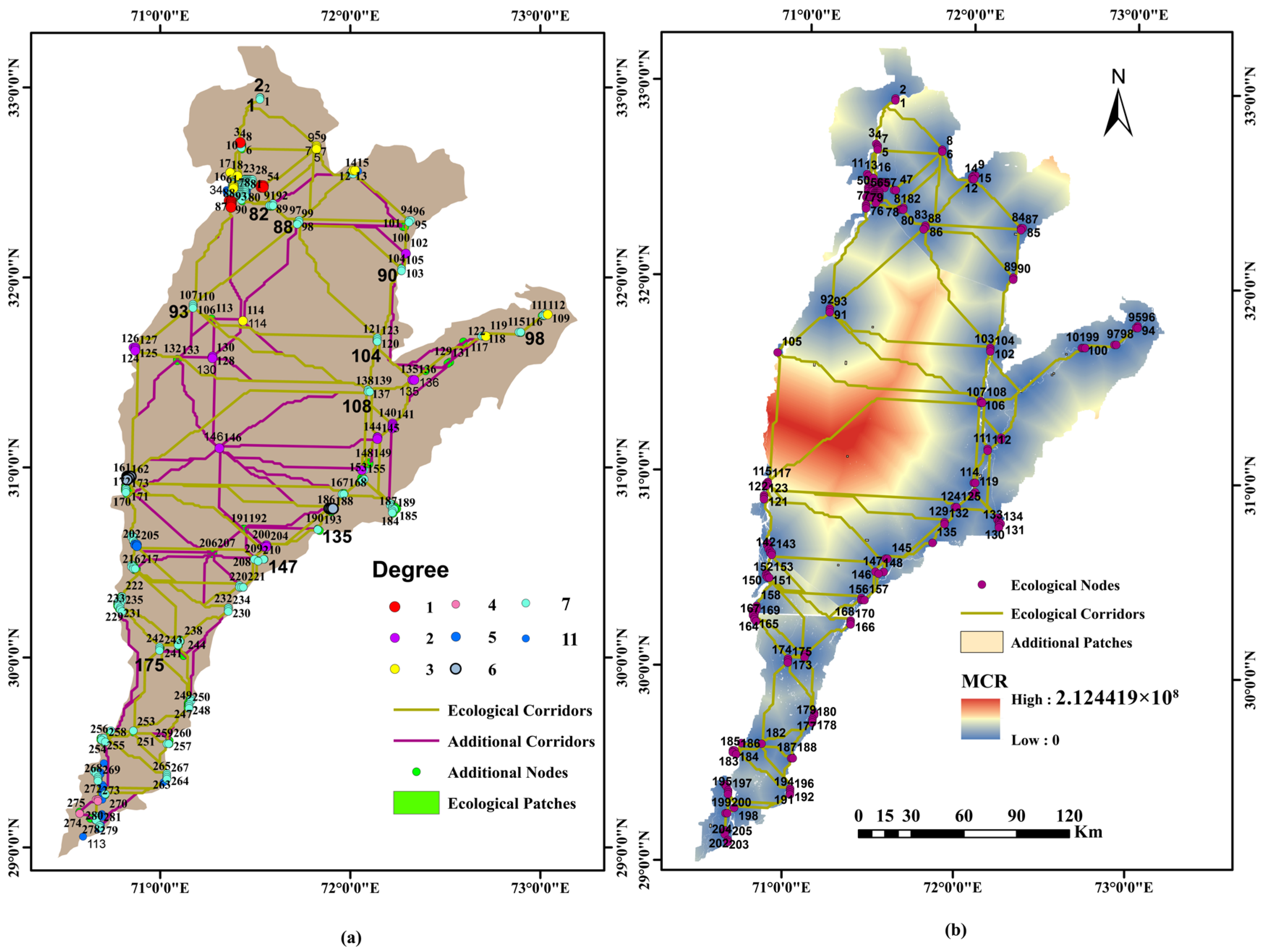
4.1.1. Screening of Ecological Sources
4.1.2. Analyzing Ecological MCR Surface
4.2. Ecological Spatial Network in the Thal Desert
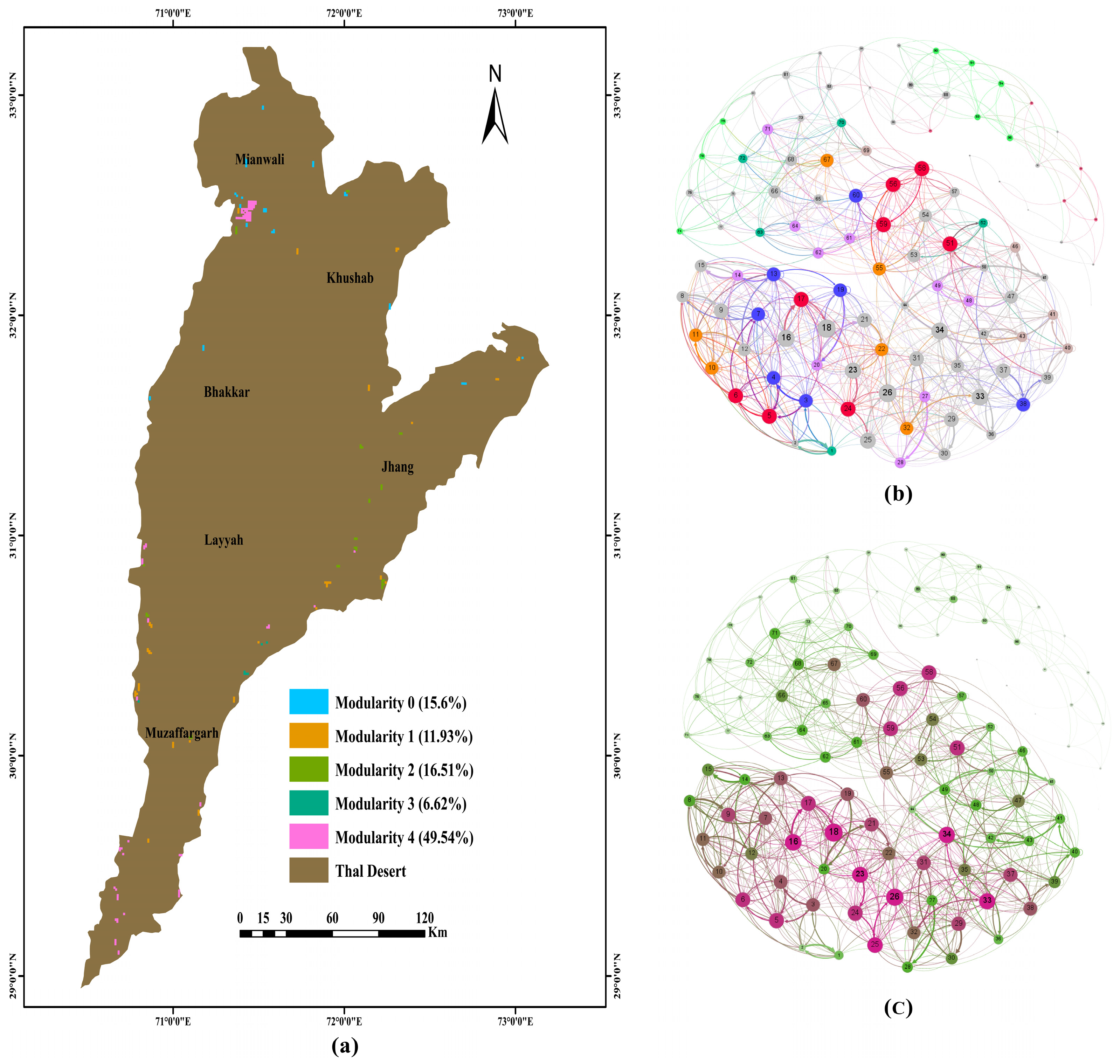
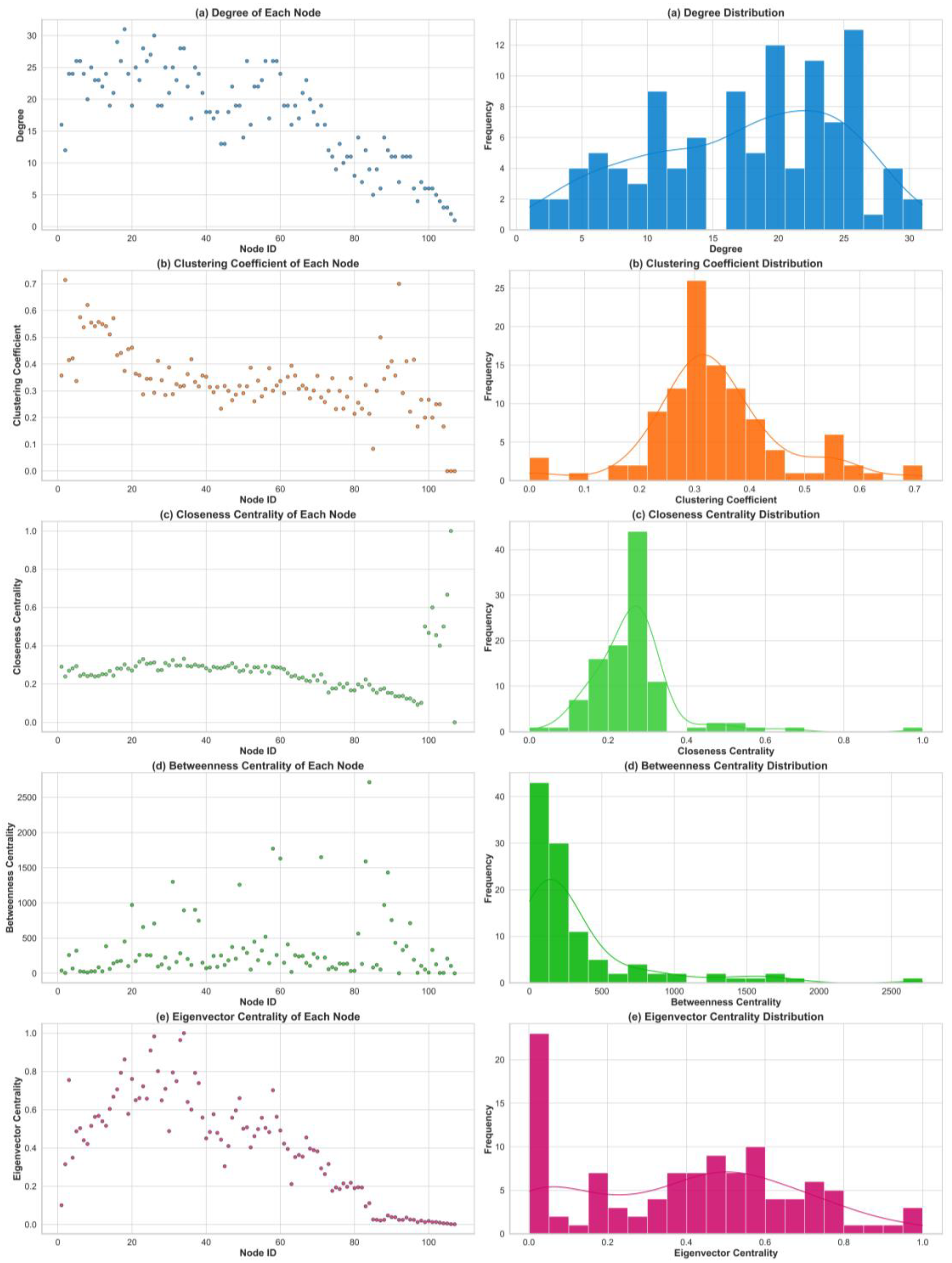
4.3. Analyzing Topological Indicators to Optimize ESNs
4.4. The Impact of Evaluation on Optimization
4.5. Analyzing and Comparison of Various Optimization Approaches
4.6. Assessing Carbon Sink vs. Source
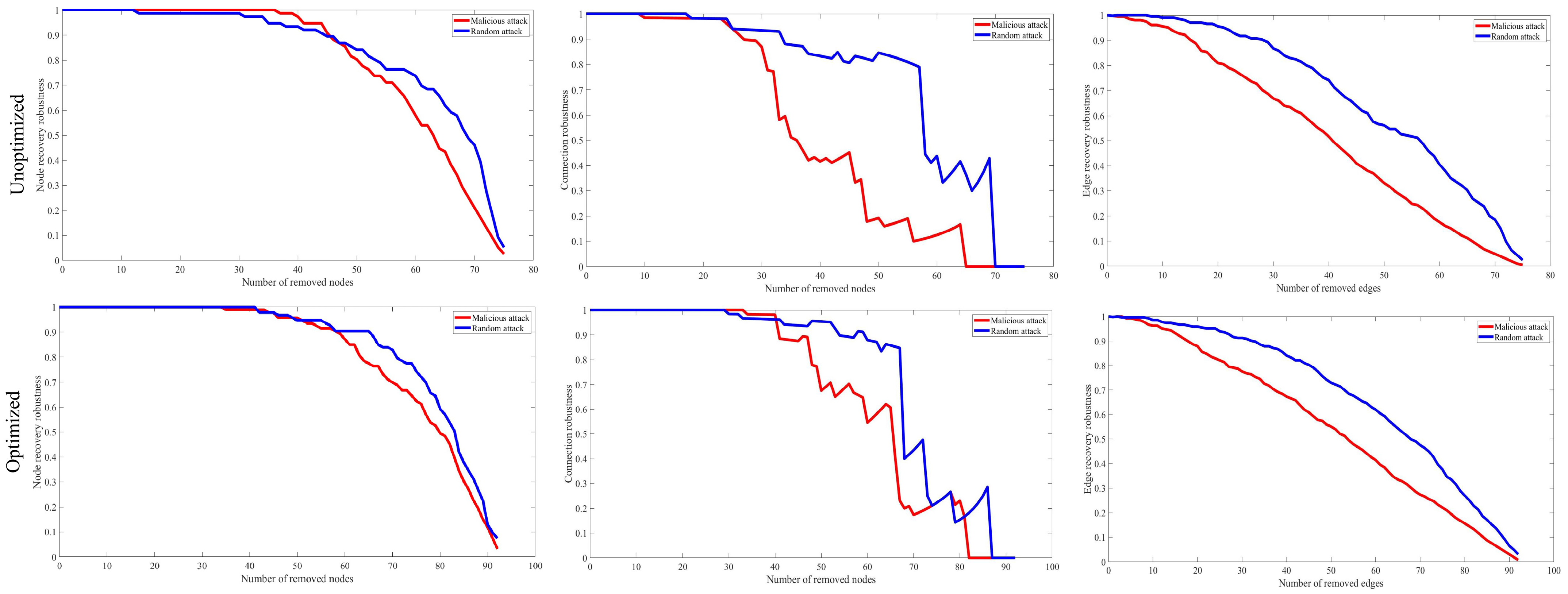
4.7. Robustness Comparison in Thal Desert
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mora, C.; Spirandelli, D.; Franklin, E.C.; Lynham, J.; Kantar, M.B.; Miles, W.; Smith, C.Z.; Freel, K.; Moy, J.; Louis, L.V. Broad threat to humanity from cumulative climate hazards intensified by greenhouse gas emissions. Nat. Clim. Change 2018, 8, 1062–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoro, K.O.; Daramola, M.O. CO2 emission sources, greenhouse gases, and the global warming effect. In Advances in Carbon Capture; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 3–28. [Google Scholar]
- Gurney, K.R.; Liang, J.; Roest, G.; Song, Y.; Mueller, K.; Lauvaux, T. Under-reporting of greenhouse gas emissions in US cities. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Li, H.; Huang, Y. The complex ecological network’s resilience of the Wuhan metropolitan area. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 130, 108101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.M.; Lowe, J.A.; Bowerman, N.H.; Gohar, L.K.; Huntingford, C.; Allen, M.R. Equivalence of greenhouse-gas emissions for peak temperature limits. Nat. Clim. Change 2012, 2, 535–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreyra Marinucci, X. Carbon Offsetting in the Framework of Net Zero Carbon Buildings. Politecnico di Torino. 2023. Available online: https://webthesis.biblio.polito.it/26266/ (accessed on 10 February 2024).
- Niu, D.; Wu, G.; Ji, Z.; Wang, D.; Li, Y.; Gao, T. Evaluation of provincial carbon neutrality capacity of China based on combined weight and improved TOPSIS model. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Feng, Z.; Song, Y.; Li, M.; Zhang, P. Carbon sequestration potential of forest vegetation in China from 2003 to 2050: Predicting forest vegetation growth based on climate and the environment. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 252, 119715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, Z.; Dong, S.; Wei, M.; Zhou, J. Spatial and temporal changes in vegetation and desertification (1982–2018) and their responses to climate change in the Ulan Buh Desert, Northwest China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2021, 143, 1643–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, M.; Kazmi, J.H.; Tariq, A. Traditional ecological knowledge based indicators for monitoring rangeland conditions in Thal and Cholistan Desert, Pakistan. Environ. Chall. 2023, 13, 100754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, J.F.; Smith, D.M.S.; Lambin, E.F.; Turner, B.; Mortimore, M.; Batterbury, S.P.; Downing, T.E.; Dowlatabadi, H.; Fernández, R.J.; Herrick, J.E. Global desertification: Building a science for dryland development. Science 2007, 316, 847–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Odorico, P.; Rosa, L.; Bhattachan, A.; Okin, G.S. Desertification and land degradation. Dryland Ecohydrol. 2019, 573–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, M.V. Interactions between climate and desertification. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2007, 142, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Huan, Y.; Wang, L.; Lan, Y.; Liang, T.; Shi, B.; Zhang, Q. Linking ecosystem services and circuit theory to identify priority conservation and restoration areas from an ecological network perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 873, 162261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahbaz, M.; Rafiq, M.K.; Khan, T.N. Arid Land Development and Combating Desertification in Pakistan. Combat. Desertif. Asia Afr. Middle East Proven Pract. 2013, 231–248. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, G.; Wen, Y.; Zhang, M.; Gu, Y.; Xiong, W.; Wang, Z.; Niu, S. The status and development proposal of carbon sources and sinks monitoring satellite system. Carbon Neutrality 2022, 1, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, K. Carbon Sequestration in Forest Ecosystems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kuss, F.R. A review of major factors influencing plant responses to recreation impacts. Environ. Manag. 1986, 10, 637–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walmsley, A. Greenways and the making of urban form. Landsc. Urban Plan. 1995, 33, 81–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Du, Y.; Meersmans, J.; Qiu, S. Linking ecosystem services and circuit theory to identify ecological security patterns. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Zhou, L.; Sun, D.; Yuan, B.; Hu, F. Evaluating the impact of urban expansion on the habitat quality and constructing ecological security patterns: A case study of Jiziwan in the Yellow River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 145, 109544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.-M.; Ma, Y.-F.; Wang, J.-L.; You, X.-Y. Landscape pattern analysis and ecological network planning of Tianjin City. Urban For. Urban Green. 2019, 46, 126479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, L.; Zhong, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Ji, Y.; Song, P.; Wang, Q. An optimized evaluation method of an urban ecological network: The case of the Minhang District of Shanghai. Urban For. Urban Green. 2021, 62, 127158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zou, J. Spatial identification and optimization of ecological network in desert-oasis area of Yellow River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 147, 109999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Yu, Q.; Pei, Y.; Wang, G.; Yue, D. Optimization of landscape spatial structure aiming at achieving carbon neutrality in desert and mining areas. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 322, 129156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Fang, M.; Yu, Q.; Niu, T.; Liu, H.; Wang, F.; Xu, C.; Ai, M.; Zhang, J. Study of spatialtemporal changes in Chinese forest eco-space and optimization strategies for enhancing carbon sequestration capacity through ecological spatial network theory. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 859, 160035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puth, L.M.; Wilson, K.A. Boundaries and corridors as a continuum of ecological flow control: Lessons from rivers and streams. Conserv. Biol. 2001, 15, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Liu, C.; Ni, B.; Lian, H. Ecological Network Resilience of Shiyang River Basin: An Arid Inland Watershed of Northwest China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2024, 34, 951–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.; Liu, S.; An, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, M. Spatio-temporal dynamics of landscape connectivity and ecological network construction in Long Yangxia basin at the upper Yellow river. Land 2020, 9, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Yue, D.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Yu, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, N. The optimization of urban ecological infrastructure network based on the changes of county landscape patterns: A typical case study of ecological fragile zone located at Deng Kou (Inner Mongolia). J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 163, S54–S67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Yue, D.; Wang, Y.; Kai, S.; Fang, M.; Ma, H.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, Y. Optimization of ecological node layout and stability analysis of ecological network in desert oasis: A typical case study of ecological fragile zone located at Deng Kou County (Inner Mongolia). Ecol. Indic. 2018, 84, 304–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.P.; Chen, W.B. Construction and evaluation of ecological network in Poyang Lake Eco-economic Zone, China. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao J. Appl. Ecol. 2016, 27, 1611–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Liu, Y.; Luo, X. Integrating the MCR and DOI models to construct an ecological security network for the urban agglomeration around Poyang Lake, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 141868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Huang, J.; Ji, C.; Li, Z.A. Construction of a landscape ecological network for a large-scale energy and chemical industrial base: A case study of Ningdong, China. Land 2021, 10, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Wang, J.; Fang, Y.; Zhai, T.; Cheng, H. An integrated approach towards spatial identification of restored and conserved priority areas of ecological network for implementation planning in metropolitan region. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 69, 102865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Yu, Q.; Niu, T.; Fang, M.; Guo, H.; Liu, H.; Li, S.; Zhang, J. Restoration and renewal of ecological spatial network in mining cities for the purpose of enhancing carbon Sinks: The case of Xuzhou, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 143, 109313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Guo, C.-H.; Chen, X.-J.; Jia, L.-Q.; Guo, X.-N.; Chen, R.-S.; Zhang, M.-S.; Chen, Z.-Y.; Wang, H.-D. Carbon peak and carbon neutrality in China: Goals, implementation path and prospects. China Geol. 2021, 4, 720–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yuan, X.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, M. Integrating ecosystem services and landscape connectivity to construct and optimize ecological security patterns: A case study in the central urban area Chongqing municipality, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 43138–43154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ureta, J.C.; Clay, L.; Motallebi, M.; Ureta, J. Quantifying the landscape’s ecological benefits—An analysis of the effect of land cover change on ecosystem services. Land 2020, 10, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Zhao, H.; Liu, Y. Urban ecological corridors construction: A review. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Zheng, H. Energy security and sustainable design of urban systems based on ecological network analysis. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 129, 107903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Yi, S. An integrated approach to constructing ecological security patterns and identifying ecological restoration and protection areas: A case study of Jingmen, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 137, 108723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Wong, C.P.; Jiang, B.; Hughes, A.C.; Wang, M.; Wang, Q. Developing China’s Ecological Redline Policy using ecosystem services assessments for land use planning. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Wang, J.; Sun, L.; Lv, C. Construction and optimization of green space ecological networks in urban fringe areas: A case study with the urban fringe area of Tongzhou district in Beijing. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 276, 124266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Wang, Z. Construction and optimization strategy of ecological security pattern based on ecosystem services and landscape connectivity: A case study of Guizhou Province, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 45123–45139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shuai, N.; Hu, Y.; Gao, M.; Guo, Z.; Bai, Y. Construction and optimization of ecological networks in karst regions based on multi-scale nesting: A case study in Guangxi Hechi, China. Ecol. Inform. 2023, 74, 101963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Ling, H.; Zhang, G.; Yan, J.; Deng, M.; Wang, G.; Xu, S. Variations in the dissolved carbon concentrations of the shallow groundwater in a desert inland river basin. J. Hydrol. 2021, 602, 126774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yi, Y.; Yue, Y.; Cui, B. Reducing the likelihood of carbon loss from wetlands by improving the spatial connections between high carbon patches. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 267, 121819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.V.; Setia, R.; Sahoo, S.; Prasad, A.; Pateriya, B. Evaluation of NDWI and MNDWI for assessment of waterlogging by integrating digital elevation model and groundwater level. Geocarto Int. 2015, 30, 650–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Cao, H.; Sun, W.; Chen, X. Quantitative evaluation of the rebuilding costs of ecological corridors in a highly urbanized city: The perspective of land use adjustment. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 141, 109130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qu, Z.; Zhong, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, R.; Yi, Y.; Zhang, G.; Li, X.; Liu, J. Delimitation of ecological corridors in a highly urbanizing region based on circuit theory and MSPA. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 142, 109258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knaapen, J.P.; Scheffer, M.; Harms, B. Estimating habitat isolation in landscape planning. Landsc. Urban Plan. 1992, 23, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Ye, Y.; Song, B.; Wang, R. Evaluation of urban suitable ecological land based on the minimum cumulative resistance model: A case study from Changzhou, China. Ecol. Model. 2015, 318, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Li, W.; Li, D.; Li, C.; Huang, G.; Liu, H. Suitability analysis of heritage corridor in rapidly urbanizing region: A case study of Taizhou City. Geogr. Res. 2005, 24, 69–76. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, K.; Li, D.; Liu, H. The negative approach to urban growth planning of Beijing, China. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2011, 54, 123–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adriaensen, F.; Chardon, J.; De Blust, G.; Swinnen, E.; Villalba, S.; Gulinck, H.; Matthysen, E. The application of ‘least-cost’modelling as a functional landscape model. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2003, 64, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadini, F.; Zio, E.; Petrescu, C.-A. Using centrality measures to rank the importance of the components of a complex network infrastructure. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Critical Information Infrastructures Security, Italy, 13–15 October 2008; pp. 155–167. [Google Scholar]
- Jasny, B.R.; Zahn, L.M.; Marshall, E. Connections INTRODUCTION. Science 2009, 325, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Yu, Q.; Niu, T.; Fang, M.; Guo, H.; Liu, H.; Li, S. Study on the landscape space of typical mining areas in Xuzhou City from 2000 to 2020 and optimization strategies for carbon sink enhancement. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yu, Q.; Qiu, S.; Xu, C.; Ma, J.; Liu, H. Study on the relationship between topological characteristics of ecological spatial network and soil conservation function in southeastern Tibet, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, K.; Yu, Q.; Yue, D.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, L.; Liu, Z.; Niu, T.; Sun, X. Simulation of a forest-grass ecological network in a typical desert oasis based on multiple scenes. Ecol. Model. 2019, 413, 108834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsikadelis, J.T. Derivation of Newton’s law of motion from Kepler’s laws of planetary motion. Arch. Appl. Mech. 2018, 88, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Guo, J. Cartographic generalization of urban street networks based on gravitational field theory. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 2014, 28, 1450133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekkanen, J.; Timonen, K.L.; Ruuskanen, J.; Reponen, A.; Mirme, A. Effects of ultrafine and fine particles in urban air on peak expiratory flow among children with asthmatic symptoms. Environ. Res. 1997, 74, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergstrand, J.H. The gravity equation in international trade: Some microeconomic foundations and empirical evidence. Rev. Econ. Stat. 1985, 67, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wong, K.K. The influence of cultural distance on China inbound tourism flows: A panel data gravity model approach. Asian Geogr. 2012, 29, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Niu, T.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wu, H. Relationship between topological structure and ecosystem services of forest grass ecospatial network in China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosche, T.; Rothlauf, F.; Heinzl, A. Gravity models for airline passenger volume estimation. J. Air Transp. Manag. 2007, 13, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Xie, M.; Liu, G. Spatial linkage of regional innovation output based on gravity model: A case study in Zhejiang Province. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2014, 34, 1320–1326. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Meerow, S.; Newell, J.P.; Lindquist, M. Enhancing landscape connectivity through multifunctional green infrastructure corridor modeling and design. Urban For. Urban Green. 2019, 38, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadstock, D.; Ji, Q.; Managi, S.; Zhang, D. Pathways to carbon neutrality: Challenges and opportunities. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 169, 105472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Yu, G.; Liu, L.; Hu, S.; Chapin III, F.S. Climate change, human impacts, and carbon sequestration in China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2018, 115, 4015–4020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacala, S.W.; Hurtt, G.C.; Baker, D.; Peylin, P.; Houghton, R.A.; Birdsey, R.A.; Heath, L.; Sundquist, E.T.; Stallard, R.; Ciais, P. Consistent land-and atmosphere-based US carbon sink estimates. Science 2001, 292, 2316–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Ashraf, M.I.; Gulzar, S.; Akmal, M. Estimation of forest carbon stocks in temperate and subtropical mountain systems of Pakistan: Implications for REDD+ and climate change mitigation. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haseeb, M.; Tahir, Z.; Mehmood, S.A.; Gill, S.A.; Farooq, N.; Butt, H.; Iftikhar, A.; Maqsood, A.; Abdullah-Al-Wadud, M.; Tariq, A. Enhancing Carbon Sequestration through Afforestation: Evaluating the Impact of Land Use and Cover Changes on Carbon Storage Dynamics. Earth Syst. Environ. 2024, 8, 1563–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Were, D.; Kansiime, F.; Fetahi, T.; Cooper, A.; Jjuuko, C. Carbon sequestration by wetlands: A critical review of enhancement measures for climate change mitigation. Earth Syst. Environ. 2019, 3, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waleed, M.; Sajjad, M.; Shazil, M.S. Urbanization-led land cover change impacts terrestrial carbon storage capacity: A high-resolution remote sensing-based nation-wide assessment in Pakistan (1990–2020). Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2024, 105, 107396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafoor, G.Z.; Sharif, F.; Shahid, M.G.; Shahzad, L.; Rasheed, R.; Khan, A.U.H. Assessing the impact of land use land cover change on regulatory ecosystem services of subtropical scrub forest, Soan Valley Pakistan. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 10052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.; Zhang, H. Economic value of wetland ecosystem services in the Heihe National Nature Reserve of Zhangye. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2015, 35, 972–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sydow, M.; Owsianiak, M.; Szczepaniak, Z.; Framski, G.; Smets, B.F.; Ławniczak, Ł.; Lisiecki, P.; Szulc, A.; Cyplik, P.; Chrzanowski, Ł. Evaluating robustness of a diesel-degrading bacterial consortium isolated from contaminated soil. New Biotechnol. 2016, 33, 852–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravard, C.; Charroin, L.; Touati, C. Optimal design and defense of networks under link attacks. J. Math. Econ. 2017, 68, 62–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Liu, J. A memetic algorithm for enhancing the robustness of scale-free networks against malicious attacks. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2014, 410, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Li, Y.; Xu, L. Identification of green infrastructure networks based on ecosystem services in a rapidly urbanizing area. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 300, 126945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Yang, Z.; Xu, X. Ecological corridors analysis based on MSPA and MCR model—A case study of the Tomur World Natural Heritage Region. Sustainability 2020, 12, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Wei, X.; Liu, W.; Zhang, F.; Li, Z. Spatial and temporal analysis of carbon sources and sinks through land use/cover changes in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration region. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2019, 110, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Hartemink, A.E.; Zhang, Y. Climate and land-use change effects on soil carbon stocks over 150 years in Wisconsin, USA. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Yang, R.; Dong, Y.-X.; Liu, Y.-X.; Qiu, L.-R. The influence of rapid urbanization and land use changes on terrestrial carbon sources/sinks in Guangzhou, China. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 70, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnick, D.A.; Ryan, S.J.; Beier, P.; Cushman, S.A.; Dieffenbach, F.; Epps, C.W.; Gerber, L.; Hartter, J.; Jenness, J.S.; Kintsch, J. The role of landscape connectivity in planning and implementing conservation and restoration priorities. Issues Ecol. 2012, 16, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Travers, E.; Härdtle, W.; Matthies, D. Corridors as a tool for linking habitats–Shortcomings and perspectives for plant conservation. J. Nat. Conserv. 2021, 60, 125974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.; Yin, H.; Nakagoshi, N.; Zong, Y. Urban green space network development for biodiversity conservation: Identification based on graph theory and gravity modeling. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2010, 95, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podobnik, B.; Lipic, T.; Horvatic, D.; Majdandzic, A.; Bishop, S.R.; Eugene Stanley, H. Predicting the lifetime of dynamic networks experiencing persistent random attacks. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Shi, X.; Sun, Y.; Cui, J.; Shao, S. Have China’s provinces achieved their targets of energy intensity reduction? Reassessment based on nighttime lighting data. Energy Policy 2019, 128, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Jin, G. Exploring the optimization of spatial patterns for carbon sequestration services based on multi-scenario land use/cover changes in the changchun-Jilin-Tumen region, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 438, 140788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Lu, J.; Han, J. Studying the spatiotemporal variations of the ecological network and carbon utilization efficiency in Southeast Tibet based on complex network theory. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Xu, D.; Hu, S.; Shi, M. Ecological network optimization in urban central district based on complex network theory: A case study with the urban central district of Harbin. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.B.; Gifford, R.M. Soil carbon stocks and land use change: A meta analysis. Glob. Change Biol. 2002, 8, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, R.S.C.; Sales, A.T.; Primo, D.C.; de Albuquerque, E.R.G.M.; de Jesus, K.N.; Pareyn, F.G.C.; da Silva Santana, M.; dos Santos, U.J.; Martins, J.C.R.; Althoff, T.D. Soil and vegetation carbon stocks after land-use changes in a seasonally dry tropical forest. Geoderma 2021, 390, 114943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalal, R.C.; Thornton, C.M.; Allen, D.E.; Kopittke, P.M. A study over 33 years shows that carbon and nitrogen stocks in a subtropical soil are increasing under native vegetation in a changing climate. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 772, 145019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
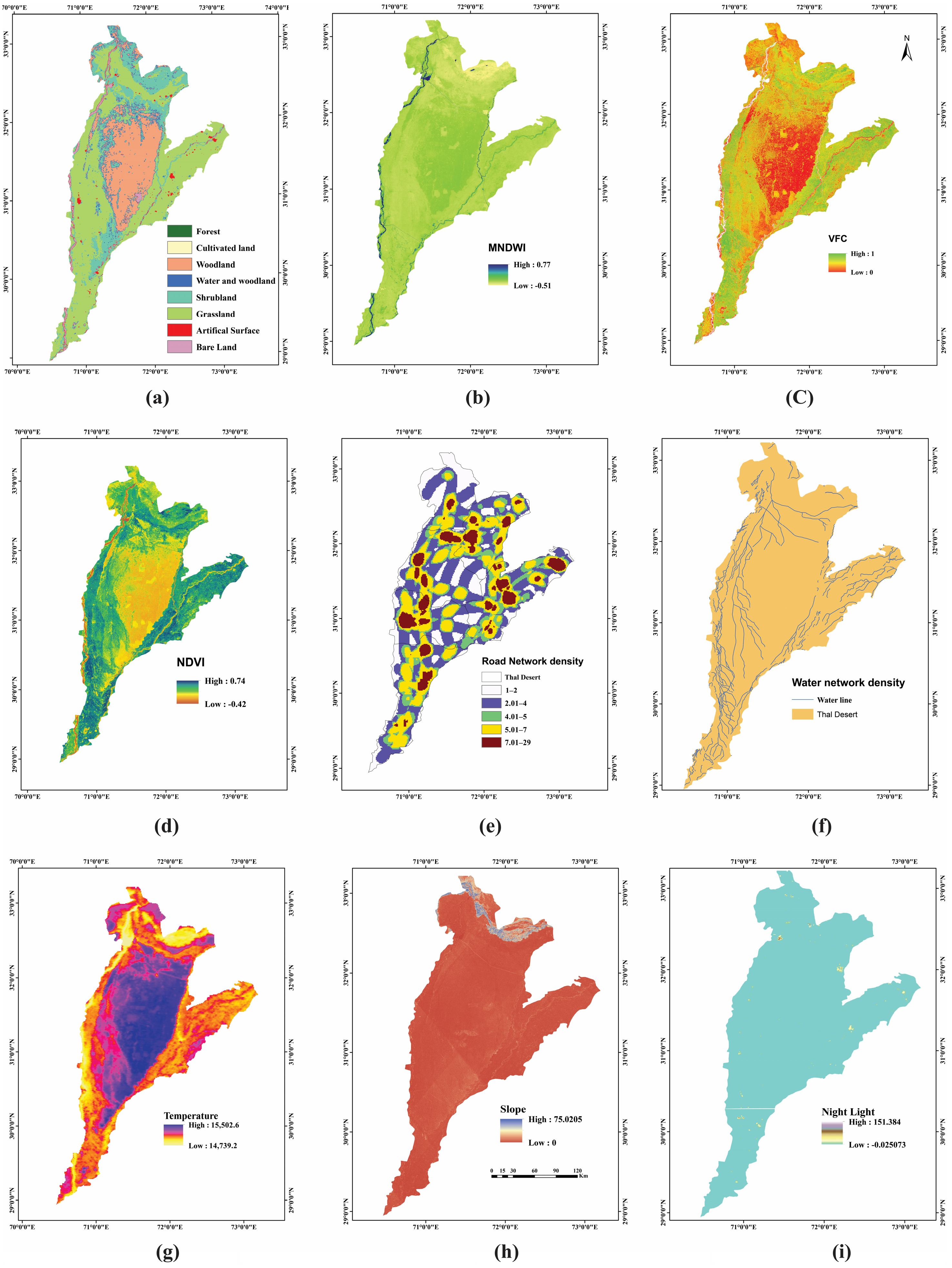




| Data | Type | Resolution | Year | Sources |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Land Cover Type Yearly Global | Raster | 500 m | 2000–2022 | https://lpdaac.usgs.gov/products/mcd12q1v006/, accessed on 5 August 2023 |
| DEM | Raster | 30 m | 2021 | https://code.earthengine.google.com/, accessed on 5 August 2023 |
| NDVI | Raster | 250 m | 2021 | https://code.earthengine.google.com/, accessed on 5 August 2023 |
| MNDWI | Raster | 250 m | 2021 | https://code.earthengine.google.com/, accessed on 5 August 2023 |
| VFC | Raster | 250 m | 2021 | https://code.earthengine.google.com/, accessed on 5 August 2023 |
| Water network density | Vector | _ | 2021 | http://www.OpenStreetMap.org/, accessed on 5 August 2023 |
| Road network density | Vector | _ | 2021 | http://www.OpenStreetMap.org/, accessed on 5 August 2023 |
| Mean annual temperature | Raster | 1000 m | 2000–2022 | https://code.earthengine.google.com/, accessed on 5 August 2023 |
| Slope | Raster | 30 m | 2021 | https://code.earthengine.google.com/, accessed on 5 August 2023 |
| Population Density | Raster | 1000 m | 2000–2022 | https://www.worldpop.org/datacatalog/, accessed on 5 August 2023 |
| Nighttime Light | Raster | 463.83 m | 200–2022 | https://code.earthengine.google.com/, accessed on 5 August 2023 |
| Administrative divisions | Vector | _ | 2021 | https://diva-gis.org/data.html, accessed on 5 August 2023 |
| Types of Patches | Target Species in Thal | Total Area Threshold (km2) | Criteria/Additional Metrics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Forest Patches | Acacia senegal, Prosopis cineraria (Jand) Date Palm (Phoenix dactylifera), Ziziphus mauritiana (Ber), Tamarix aphylla (Farash), Wan (Salvadora oleoides), Desert Marigold (Baileya multiradiata), Salsola spp. (Prickly Russian Thistle) | 10 | N/L |
| Water and wet patches | Fimbristylis dichotoma, Cyperus rotundus, Phragmites karka, Typha spp. Arthrocnemum indicum, Saccharum spontaneum, Saccharum bengalense, Suaeda fruticosa | 20 | MNDWI > 0.25 and buffered 70 m outwards |
| Grassland Patches | Cenchrus ciliaris (Dhaman Grass), Lasiurus scindicus (Sewan Grass), Saccharum bengalense (Munji Grass), Cymbopogon jwarancusa (Khabal Grass), Panicum turgidum (Bhurt Grass), Desmostachya bipinnata (Dab Grass), Leptochloa fusca (Kallar Grass) | 15 | NDVI-based Grass cover > 40%, buffered 50 m outwards |
| Factor | Weight | Grade | Value | Factor | Weight | Grade | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DEM | 0.01 | 1 | 63–230 | Night Light | 0.05 | 1 | 0.02–1.75 |
| 5 | 230–411 | 5 | 1.75–10.06 | ||||
| 10 | 411–641 | 10 | 10.06–29.06 | ||||
| 15 | 641–851 | 15 | 29.06–76.56 | ||||
| 20 | 851–1518 | 20 | 76.56–151.38 | ||||
| Slope | 0.04 | 20 | 0–2.3535 | VFC | 0.16 | 1 | 0–0.16 |
| 15 | 2.33–6.47 | 5 | 0.16–0.38 | ||||
| 10 | 6.47–14.41 | 10 | 0.58–0.80 | ||||
| 5 | 14.41–25.59 | 15 | 0.58–0.80 | ||||
| 20 | 25.59–75.02 | 20 | 0.8078–1 | ||||
| NDVI | 0.6 | 1 | 0.42–0.02 | Population Density | 0.06 | 1 | 90–205 |
| 5 | 0.02–0.17 | 5 | 205–274 | ||||
| 10 | 0.17–0.29 | 10 | 274–333 | ||||
| 15 | 0.29–0.41 | 15 | 333–482 | ||||
| 20 | 0.41–0.74 | 20 | 482–813 | ||||
| MNDWI | 0.12 | 1 | 0.51–0.29 | Land Surface Temperature | 0.19 | 1 | 14–15 |
| 5 | 0.29–0.17 | 5 | 15–15.16 | ||||
| 10 | 0.17–0.06 | 10 | 15.16–15.26 | ||||
| 15 | 0.06–0.36 | 15 | 15.22–15.38 | ||||
| 20 | 0.36–0.77 | 20 | 15.38–15.50 | ||||
| Road Density | 0.03 | 20 | 0–3.44 | Distance Settlement | 0.4 | 1 | 0–24,669 |
| 15 | 3.44–6.88 | 5 | 24.66–49.33 | ||||
| 10 | 6.88–10.32 | 10 | 49.33–74.01 | ||||
| 5 | 10.32–13.77 | 15 | 74.01–98.67 | ||||
| 1 | 13.77–17.21 | 20 | 98.7–123 | ||||
| Water Density | 0.08 | 1 | 0.01–0.16 | LULC | 0.28 | 1 | Forest Land |
| 5 | 0.16–0.38 | 5 | Shrubland | ||||
| 10 | 0.38–0.58 | 10 | Grassland | ||||
| 15 | 0.58–0.80 | 15 | Water–Wetland | ||||
| 20 | 0.8078–1 | 20 | Barren land |
| Land Use Type | Carbon Sequestration Coefficient (t/hm2 a) | Justification Literature |
|---|---|---|
| Forestland | 0.69 | [72] |
| Watershed | 0.49 | [79] |
| Wetland | 0.35 | [79] |
| Types of Energy | CO2 (kg) | CH4 (g) | N2O (g) | CO2e (kg) | CO2e (Gk) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electrical | 146,051 | 4.269 | 0.75 | 146,056 | 0.15 |
| Petroleum | 527,309 | 2112 | 1913 | 531,334 | 0.534 |
| Natural Gass | 80,020 | 7.131 | 0.14 | 80,027 | 0.087 |
| LPG | 17,829 | 0.14 | 0.002 | 17,829 | 0.024 |
| Diesel | 291.15 | 0.039 | 0.0002 | 291.19 | 0.0003 |
| Status | Ecological Patch Carbon Sink | Ecological Corridor Carbon Sink | Total Carbon Sink |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unoptimized | 210.2968 | 125.9372 | 336.234 |
| Optimized | 222.1377 | 173.29278 | 395.43048 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nawaz, T.; Ansari, M.G.I.; Yu, Q.; Avirmed, B.; Iftikhar, F.; Yu, W.; Zhao, J.; Khan, M.A.; Khan, M.M. Developing Strategies for Carbon Neutrality Through Restoration of Ecological Spatial Networks in the Thal Desert, Punjab. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17030431
Nawaz T, Ansari MGI, Yu Q, Avirmed B, Iftikhar F, Yu W, Zhao J, Khan MA, Khan MM. Developing Strategies for Carbon Neutrality Through Restoration of Ecological Spatial Networks in the Thal Desert, Punjab. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(3):431. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17030431
Chicago/Turabian StyleNawaz, Tauqeer, Muhammad Gohar Ismail Ansari, Qiang Yu, Buyanbaatar Avirmed, Farhan Iftikhar, Wang Yu, Jikai Zhao, Muhammad Anas Khan, and Muhammad Mudassar Khan. 2025. "Developing Strategies for Carbon Neutrality Through Restoration of Ecological Spatial Networks in the Thal Desert, Punjab" Remote Sensing 17, no. 3: 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17030431
APA StyleNawaz, T., Ansari, M. G. I., Yu, Q., Avirmed, B., Iftikhar, F., Yu, W., Zhao, J., Khan, M. A., & Khan, M. M. (2025). Developing Strategies for Carbon Neutrality Through Restoration of Ecological Spatial Networks in the Thal Desert, Punjab. Remote Sensing, 17(3), 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17030431







