A Continuous B2b-PPP Model Considering Interruptions in BDS-3 B2b Orbits and Clock Corrections as Well as Signal-in-Space Range Error Residuals
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Precise Orbits and Clock Generation Based on B2b Corrections
2.2. B2b Orbits and Clock Corrections Prediction Model
2.3. Assessment of B2b SISRE for BDS-3 and GPS
2.4. B2b-PPP Observation Model Incorporating SISRE Residuals
2.5. Stochastic Model of SISRE
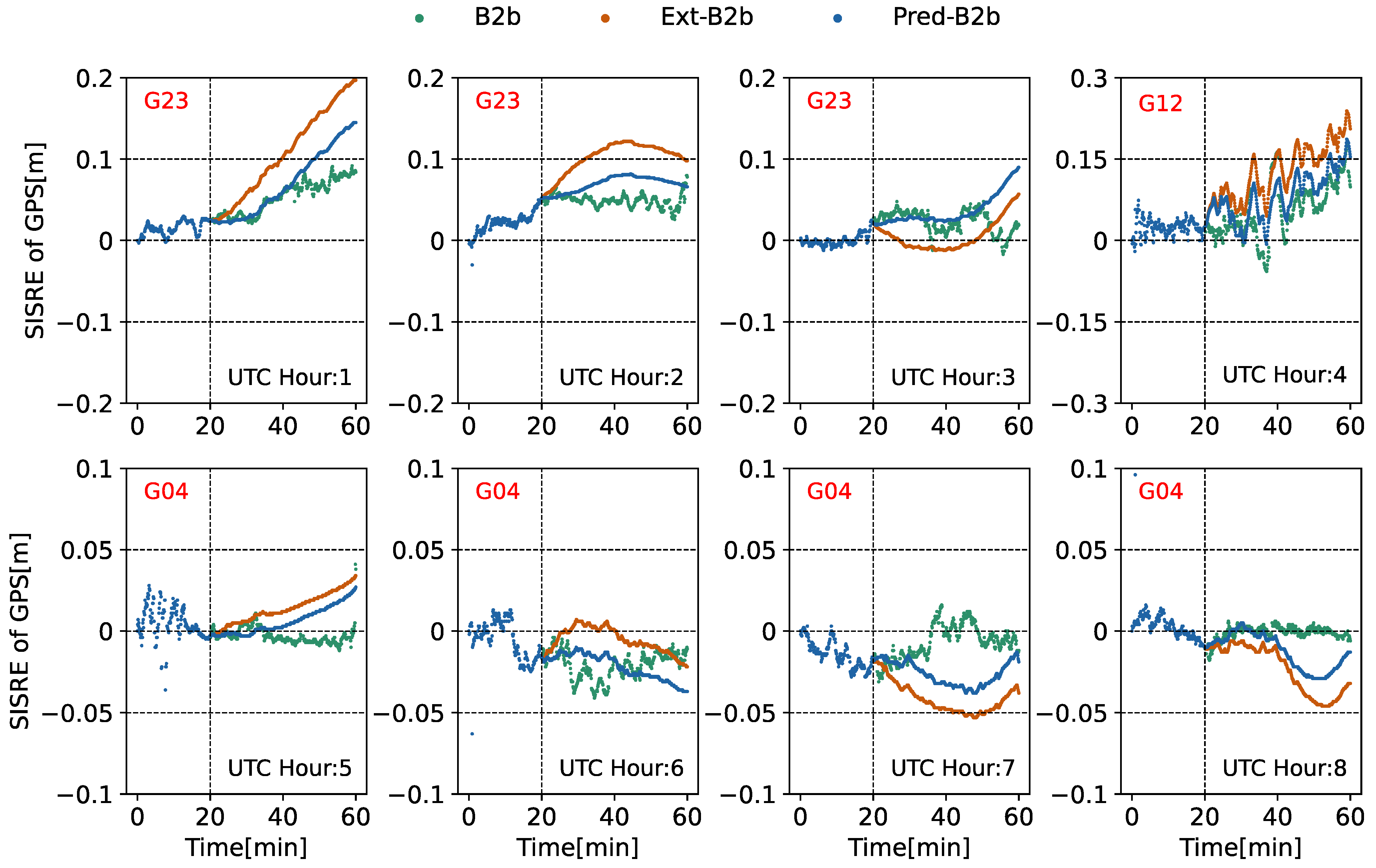
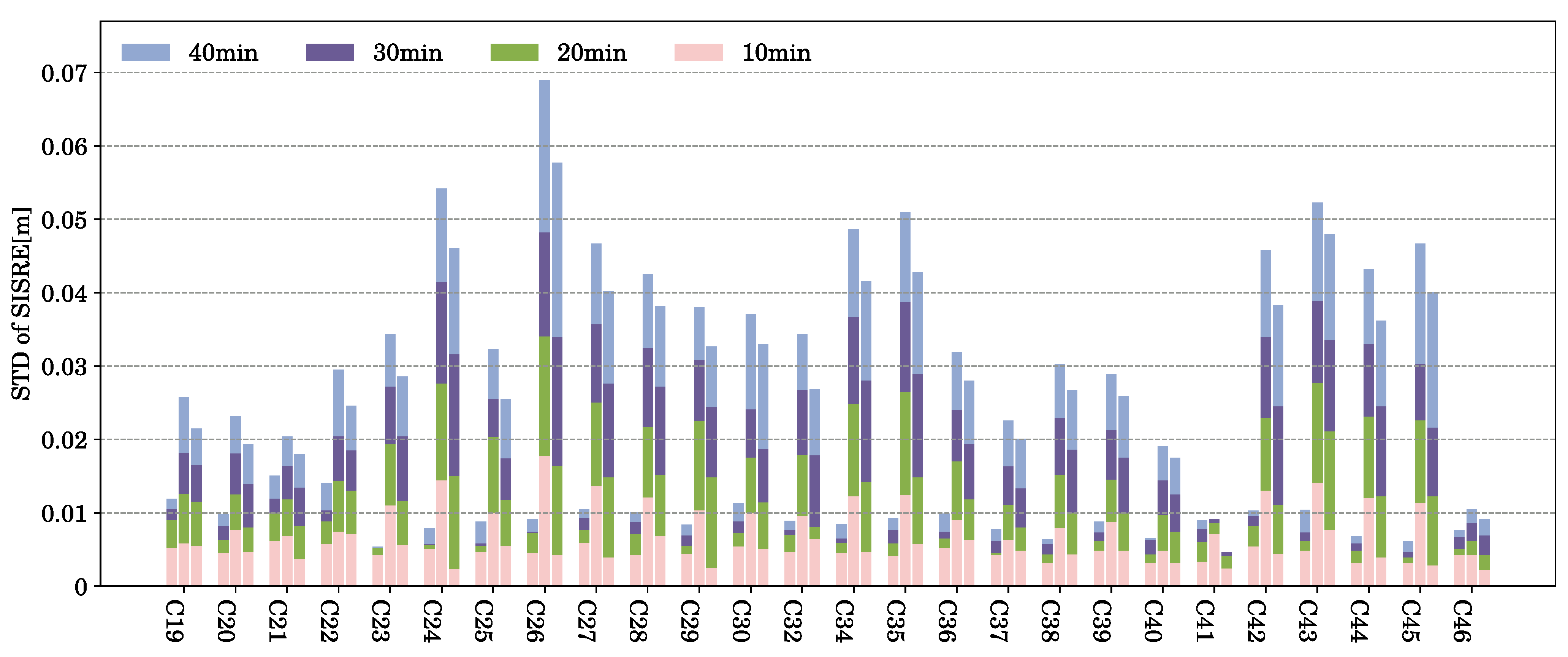
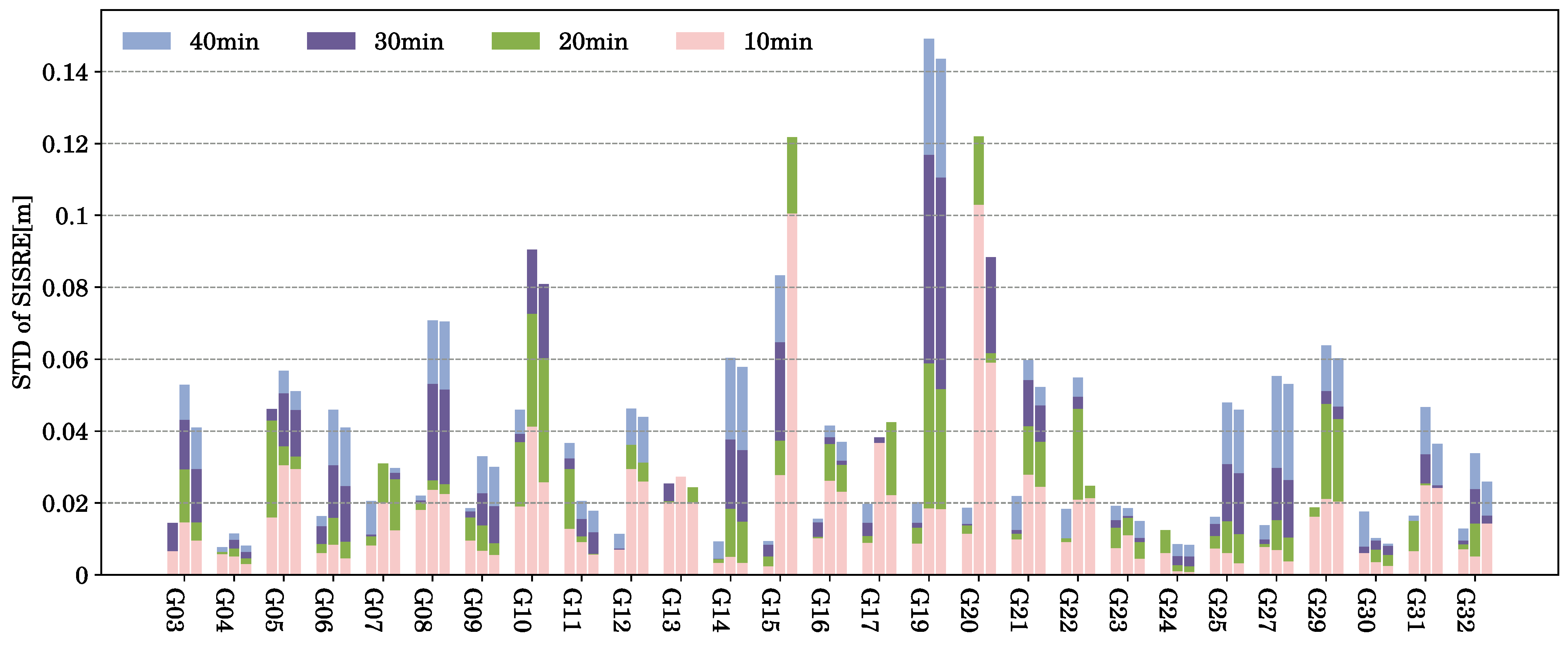
3. Analysis of SISRE Under Different Interruption Scenarios
4. Analysis of Positioning Results
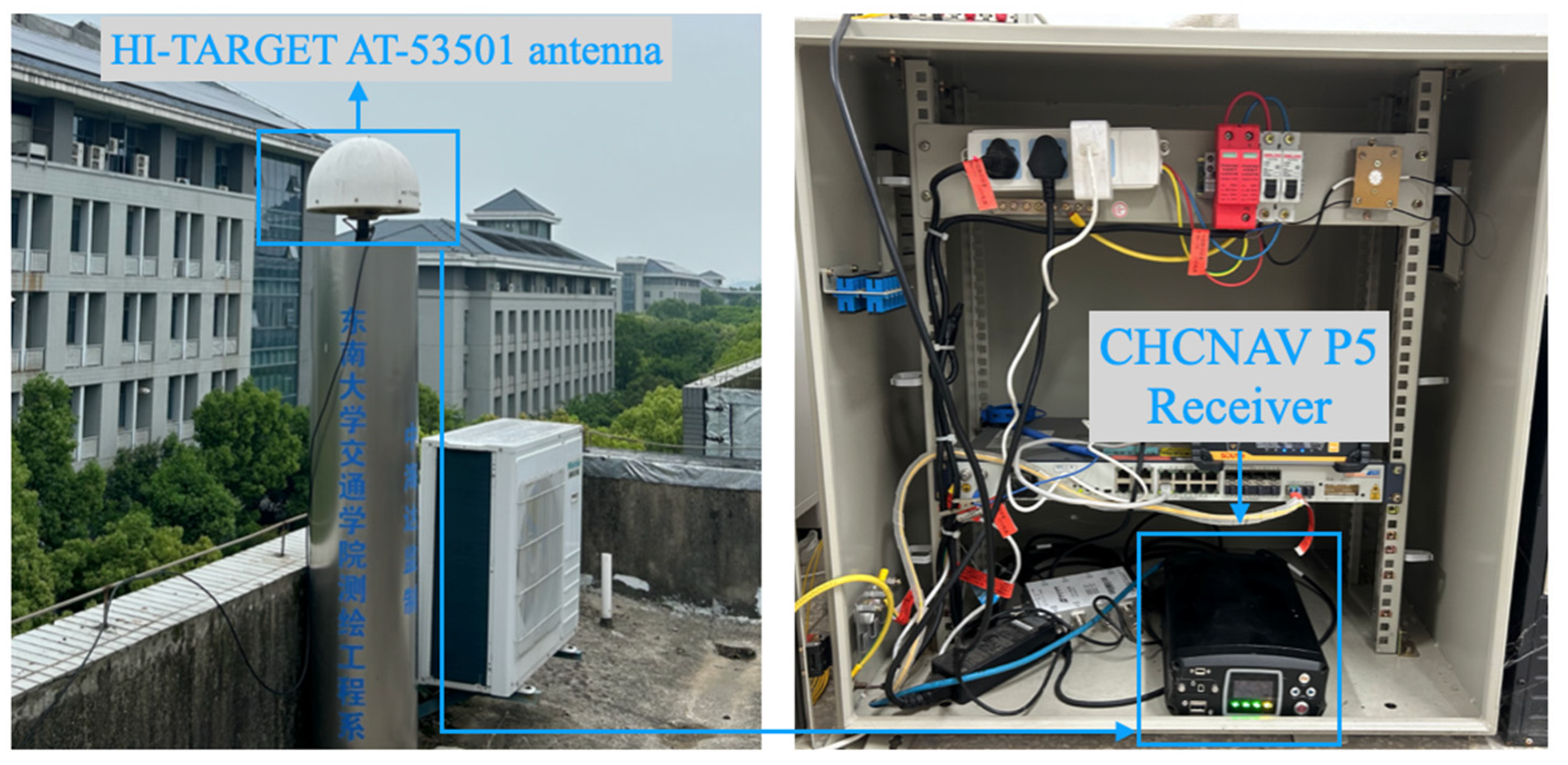
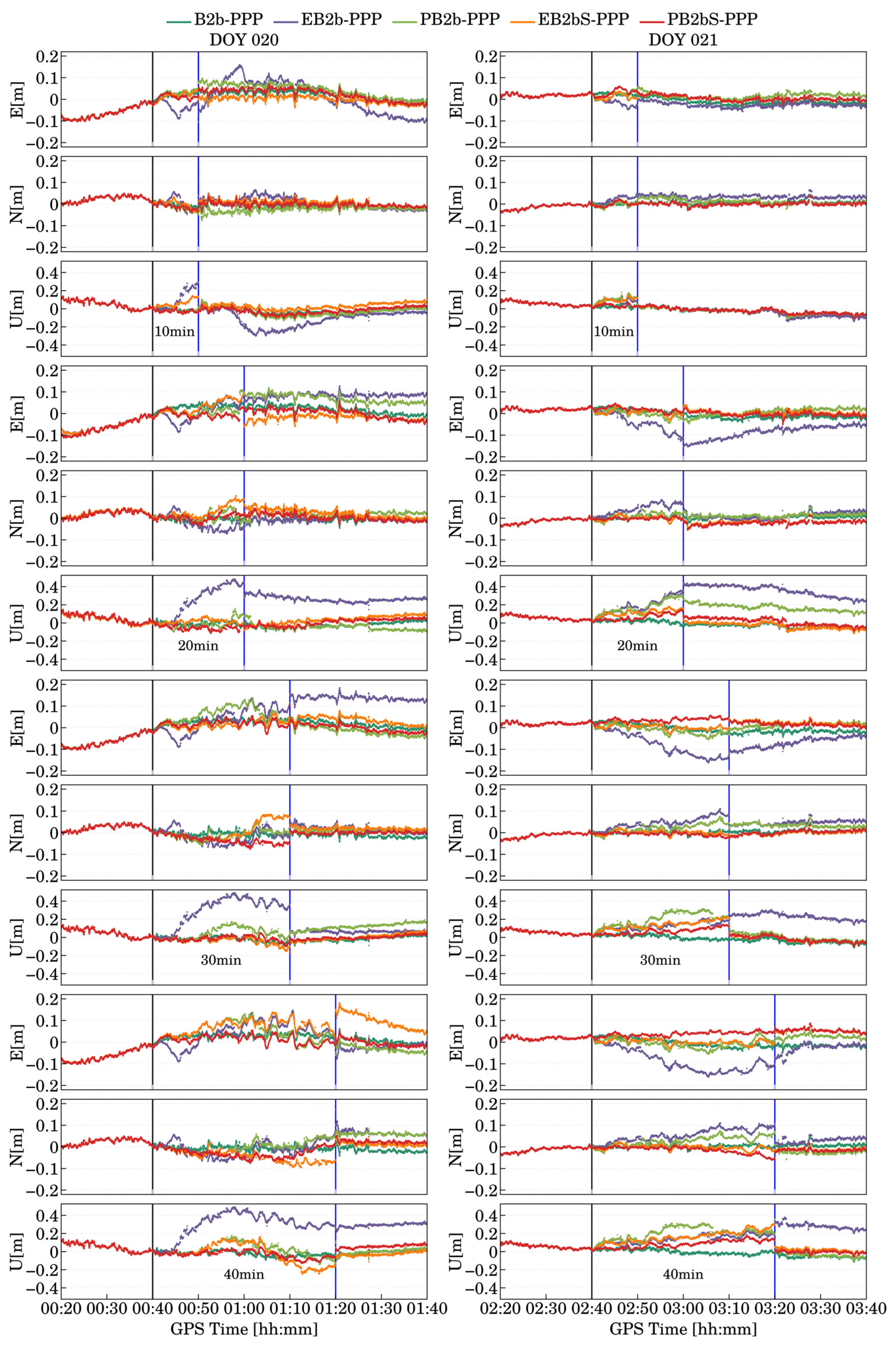
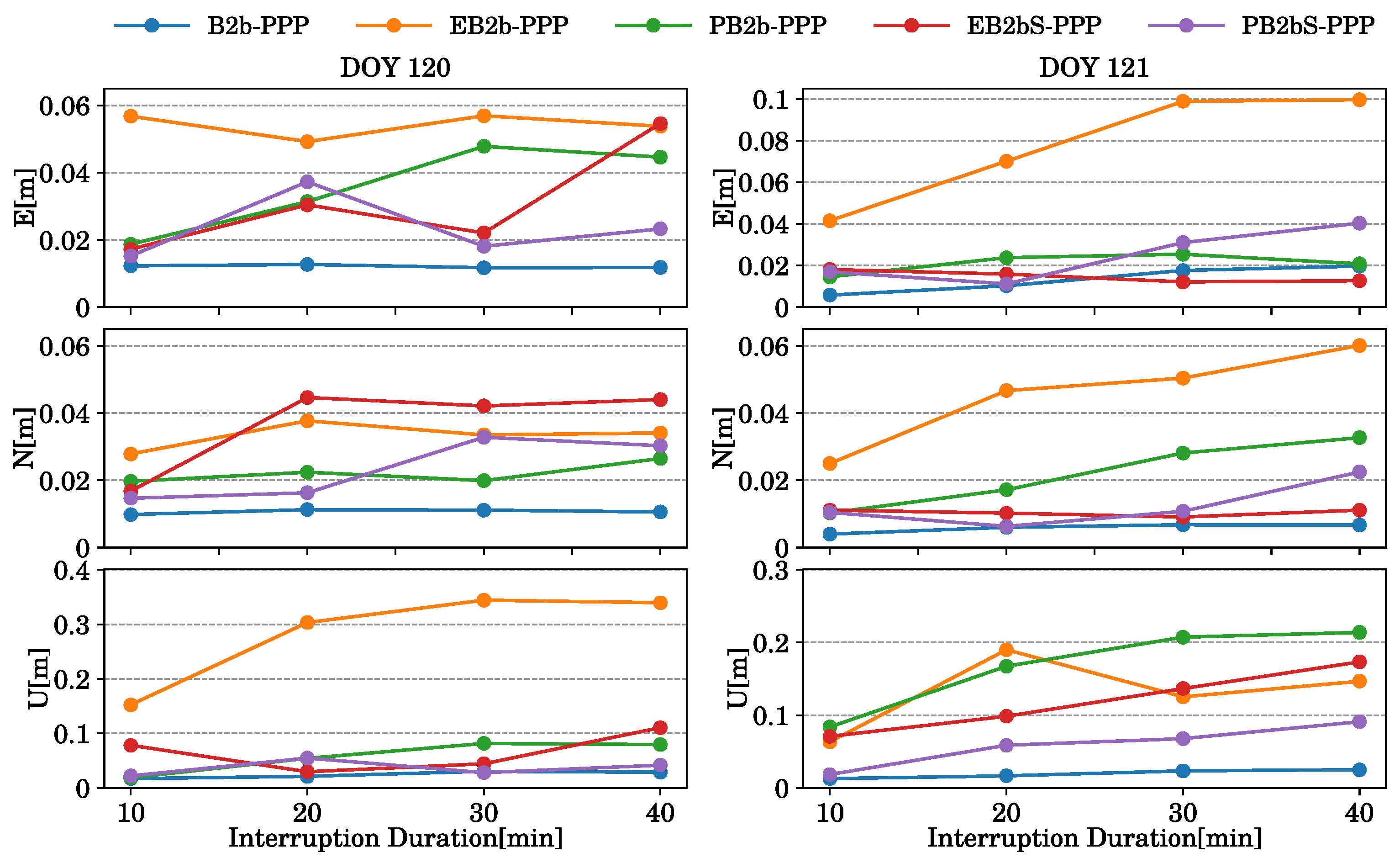
4.1. Analysis of Positioning Preformance Under a Simulated Kinematic Experiment with Different Interruption Durations
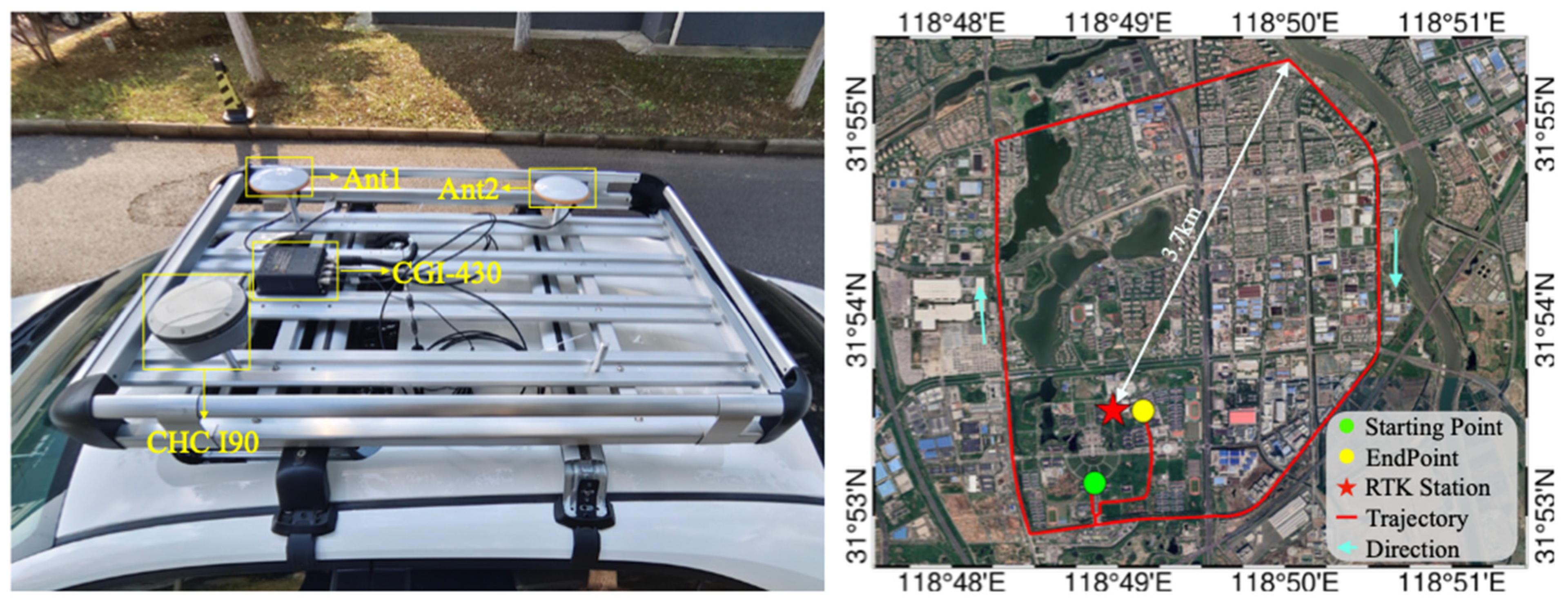
4.2. Analysis of Positioning Performance Under Kinematic Experiment with Different Interruption Durations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Malys, S.; Jensen, P.A. Geodetic point positioning with GPS carrier beat phase data from the CASA UNO experiment. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1990, 17, 651–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zumberge, J.; Heflin, M.; Jefferson, D.; Watkins, M.; Webb, F.H. Precise point positioning for the efficient and robust analysis of GPS data from large networks. J. Geophys. Res. Solid. Earth 1997, 102, 50055017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.; Meng, X.; Jiang, W. Multi-constellation GNSS precise point positioning with multi-frequency raw observations and dual-frequency observations of ionospheric-free linear combination. Satell. Navig. 2020, 1, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Pan, S.; Gao, C.; Gao, W.; Xia, Y. BDS/GPS/LEO triple-frequency uncombined precise point positioning and its performance in harsh environments. Measurement 2020, 151, 107216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, P.; Sun, F.; Wang, K.; Xiao, K.; Shang, X.; Liu, J. Positioning performance analysis of real-time BDS-3 PPP-B2b/INS tightly coupled integration in urban environments. Adv. Space Res. 2023, 72, 4008–4020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, R.; Gao, C.; Meng, X.; Xu, Z.; Liu, Q.; Chen, Q.; An, X. Lightweight seamless lane-level positioning with the integration of BDS-3 PPP-B2b and VINS: A case study using smartphone. GPS Solut. 2024, 28, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CSNO. BeiDou Navigation Satellite System Signal in Space Interface Control Document Precise Point Positioning Service Signal PPP-B2b (Version 1.0). 2020. Available online: http://www.beidou.gov.cn/xt/gfxz/202008/P020200803362062482940.pdf (accessed on 5 January 2025).
- Liu, Y.; Yang, C.; Zhang, M. Comprehensive Analyses of PPP-B2b Performance in China and Surrounding Areas. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Chen, L.; Shen, N.; Wang, L.; Jiao, Z.; Chen, R. Decoding PPP corrections from BDS B2b signals using a software-defined receiver: An initial performance evaluation. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 21, 7871–7883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Lou, Y.; Song, W.; Sun, W.; Zou, X.; Gong, X. Initial assessment of BDS-3 precise point positioning service on GEO B2b signal. Adv.Space Res. 2022, 69, 690–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Wang, L.; Fu, W.; Han, Y.; Li, T.; Li, W.; Chen, R. Real-time single-frequency precise point positioning using BDS-3 PPP-B2b corrections. Measurement 2022, 205, 112178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Cao, X.; Lyu, D.; He, Z.; Xiao, G.; Shen, F. An investigation of PPP time transfer via BDS-3 PPP-B2b service. GPS Solut. 2023, 27, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Gong, H.; Peng, J.; Tang, C.; Huang, X.; Sun, G. Performance assessment of real-time precise point positioning using BDS PPP-B2b service signal. Adv. Space Res. 2021, 68, 3242–3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Lou, Y.; Zhang, W.; Jan, D.; He, H.; Chai, J.; Ouyang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zou, X. Evaluation of real-time kinematic positioning performance of the BDS-3 PPP service on B2b signal. GPS Solut. 2023, 27, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, J. Performance evaluation of BDS-3 PPP-B2b precise point positioning service. GPS Solut. 2021, 25, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Union. Galileo High Accuracy Service Signal-InSpace Interface Control Document (HAS SIS ICD) Issue 1.0. 2022. Available online: https://www.gsc-europa.eu/sites/default/files/sites/all/files/Galileo_HAS_SIS_ICD_v1.0.pdf (accessed on 5 January 2025).
- European Union. Galileo High Accuracy Service Service Definition Document (HAS SDD) Issue 1.0. 2023. Available online: https://www.gsc-europa.eu/sites/default/files/sites/all/files/Galileo-HAS-SDD_v1.0.pdf (accessed on 5 January 2025).
- Yang, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Mao, Y.; Sun, B.; Ren, X. Featured Services and Performance of BDS-3. Sci. Bull. 2021, 66, 2135–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ding, Q.; Gao, W.; Li, J.; Xu, Y.; Sun, B. Principle and performance of BDSBAS and PPP-B2b of BDS-3. Satell. Navig. 2022, 3, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Mao, Y.; Sun, B. Basic performance and future developments of BeiDou global navigation satellite system. Satell. Navig. 2020, 1, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Liu, J.; Hu, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, G.; Ju, B. Initial Assessment of the BDS-3 PPP-B2b RTS compared with the CNES RTS. GPS Solut. 2021, 25, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Nie, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, L. An Improved BDS-3 PPP-B2b Positioning Approach by Estimating Signal in Space Range Errors. GPS Solut. 2023, 27, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Shang, R.; Gao, C.; Gao, W.; Liu, Q.; Long, F.; Xu, D. Temporal Characteristics Based Outlier Detection and Prediction Methods for PPP-B2b Orbit and Clock Corrections. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, H.; Meng, G.; Li, B. Zero-reconvergence PPP for real-time low-earth satellite orbit determination in case of data interruption. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 4705–4715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhou, K.; Zhang, J.; Qiu, C.; Li, H.; Xin, S. Real-Time Precise Point Positioning during Outages of the PPP-B2b Service. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenbruck, O.; Steigenberger, P.; Hauschild, A. Multi-GNSS signal-in-space range error assessment—Methodology and results. Adv. Space Res. 2018, 61, 3020–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlin, L.; Hauschild, A.; Montenbruck, O. Precise point positioning with GPS and Galileo broadcast ephemerides. GPS Solut. 2021, 25, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Wei, N.; Li, M.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, J. BDS-3 and GPS/Galileo integrated PPP using broadcast ephemerides. GPS Solut. 2022, 26, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Hu, X.; Chen, J.; Liu, L.; Zhou, S.; Guo, R.; Li, X.; He, F.; Liu, J.; Yang, J. Orbit determination, clock estimation and performance evaluation of BDS-3 PPP-B2b service. J. Geod. 2022, 96, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Wang, M.; Liu, C.; Meng, X.; Ji, R. Long-term performance analysis of BDS-3 precise point positioning (PPP-B2b) service. GPS Solut. 2023, 27, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; He, Y.; Yi, W.; Song, W.; Cao, C.; Chen, M. Method for evaluating real-time GNSS satellite clock offset products. GPS Solut. 2017, 21, 1417–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Y.; Zheng, F.; Gu, S.; Wang, C.; Guo, H.; Feng, Y. Multi-GNSS precise point positioning with raw single-frequency and dual-frequency measurement models. GPS Solut. 2016, 20, 849–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Dong, D.; Li, P.; Li, X.; Schuh, H. Influence of stochastic modeling for inter-system biases on multi-GNSS undifferenced and uncombined precise point positioning. GPS Solut. 2019, 23, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takasu, T.; Yasuda, A. Development of the low-cost RTK-GPS receiver with an open source program package RTKLIB. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on GPS/GNSS. International Convention Center, Jeju, Republic of Korea, 12–17 July 2009; Volume 1. Available online: https://gpspp.sakura.ne.jp/paper2005/isgps_2009_rklib.pdf (accessed on 5 January 2025).
- Saastamoinen, J. Atmospheric correction for the troposphere and stratosphere in radio ranging satellites. The use of artificial satellites for geodesy, American Geophysics Union. Geophys. Monogr. Ser. 1972, 15, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhm, J.; Niell, A.; Tregoning, P.; Schuh, H. Global Mapping Function (GMF): A new empirical mapping function based on numerical weather model data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L07304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebischung, P.; Schmid, R. IGS14/igs14.atx: A new framework for the IGS products. In Proceedings of the AGU Fall Meeting, San Francisco, CA, USA, 12–16 December 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kouba, J. A Guide to Using International GNSS Service (IGS) Products. 2009. Available online: https://files.igs.org/pub/resource/pubs/UsingIGSProductsVer21_cor.pdf (accessed on 5 February 2025).
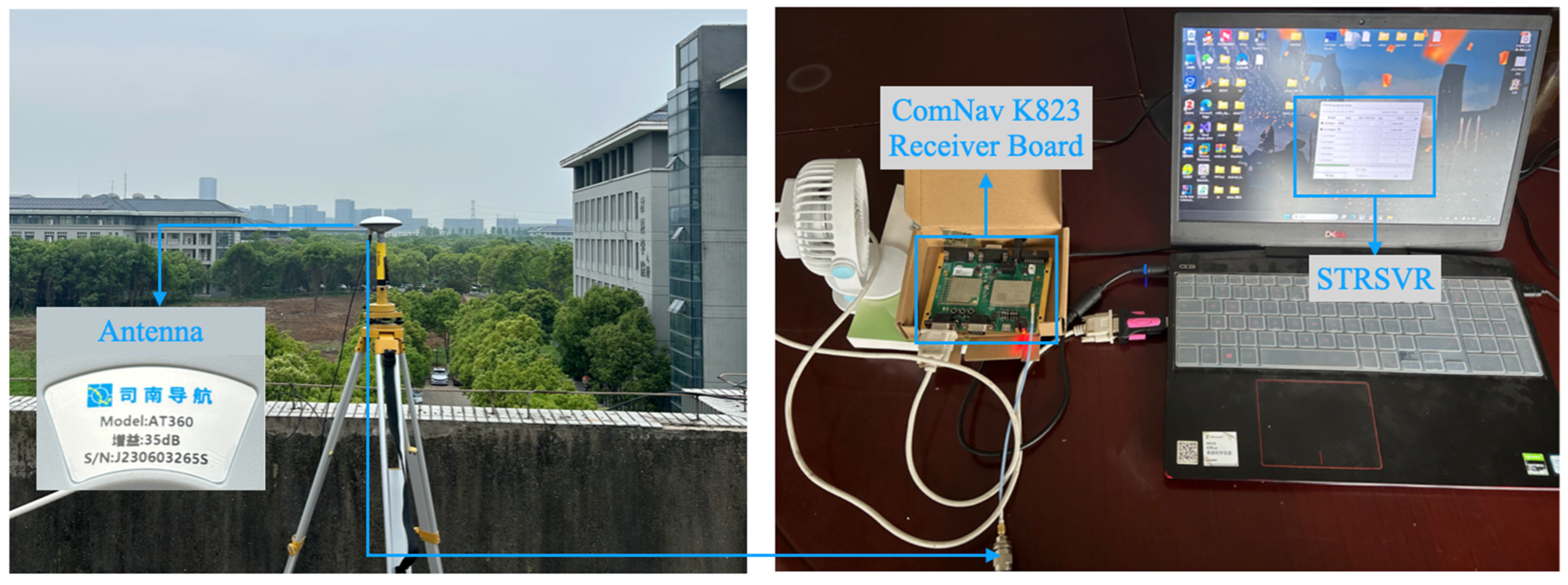


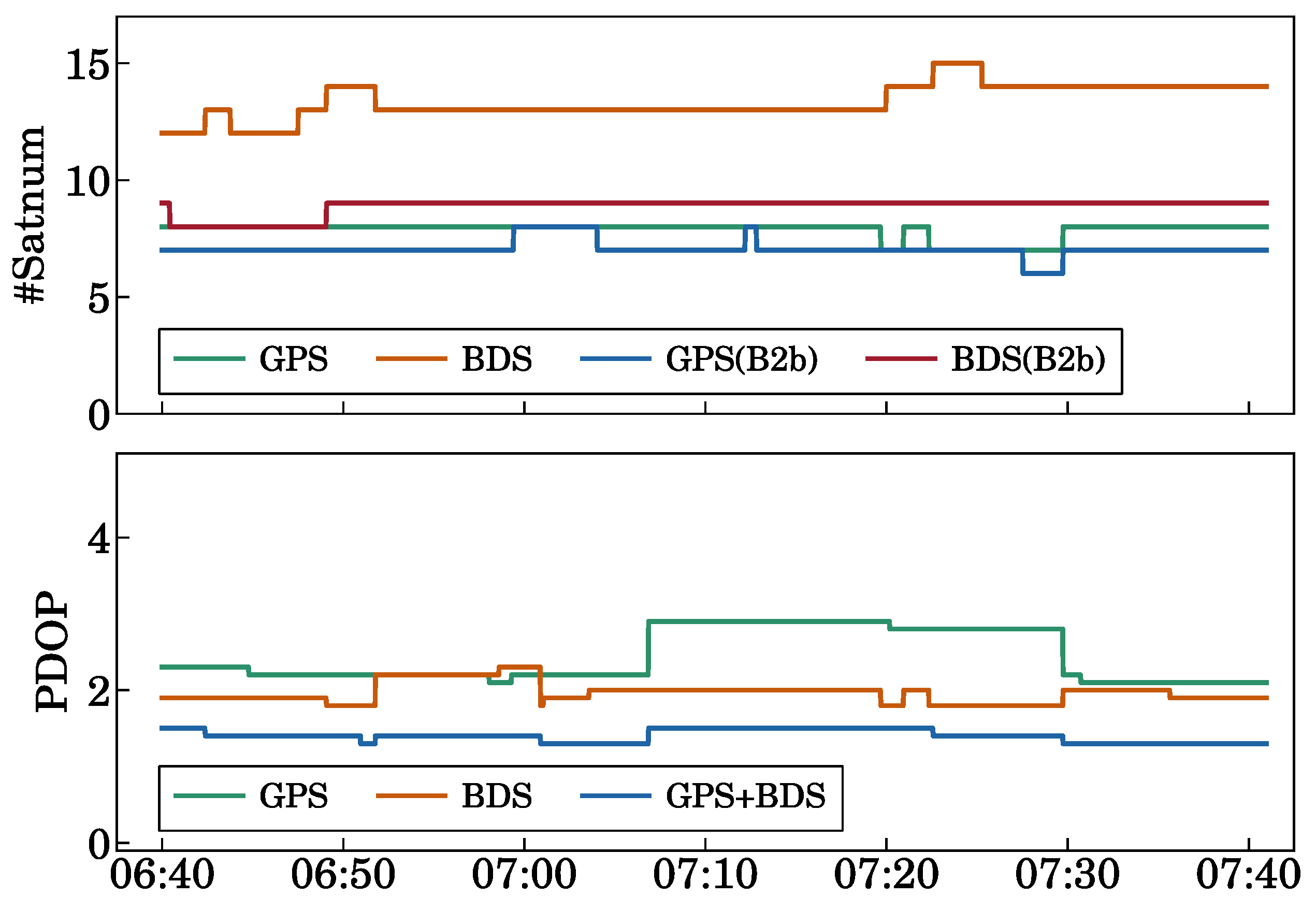
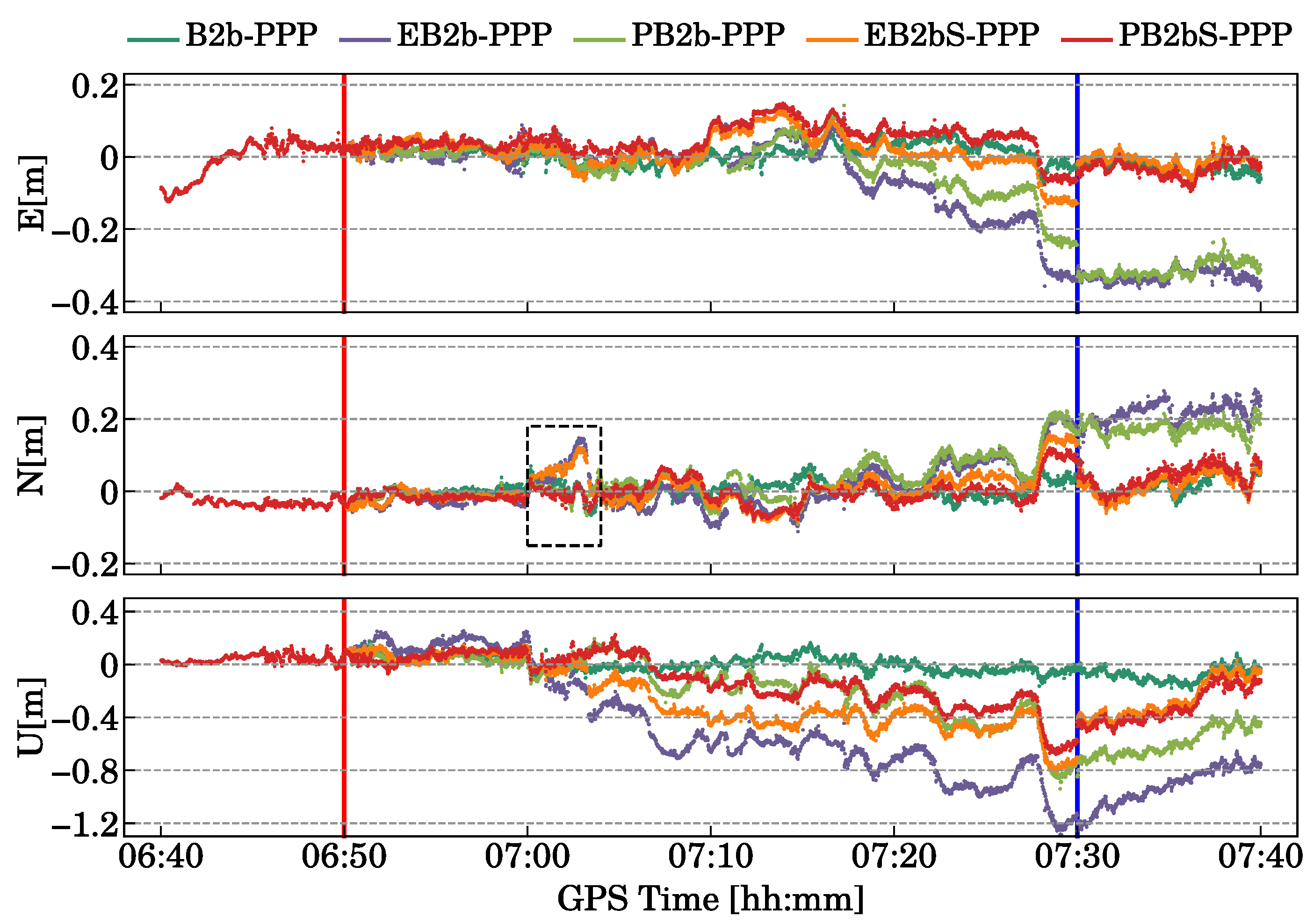
| Item | Processing Strategies |
|---|---|
| Observations | Dual frequency pseudo-range and carrier phase IF combinations |
| GNSS Signals | GPS (L1, L2), BDS-3 (B1I, B3I) |
| Satellite orbits and clock | (1) CNAV1, LNAV + B2b (B2b-PPP) (2) CNAV1, LNAV + Ext-B2b (EB2b-PPP) (3) CNAV1, LNAV + Pred-B2b (PB2b-PPP) (4) CNAV1, LNAV + Ext-B2b + SISRE (EB2bS-PPP) (5) CNAV1, LNAV + Pred-B2b + SISRE (PB2bS-PPP) |
| DCB | The DCB products from B2b [7] |
| SISRE | Estimated as random walk |
| Cutoff elevation | 10° |
| Ambiguities | float |
| Atmospheric delays | ZHD is corrected by the Saastamoinen model [35] and mapping function is from GMF [36] |
| Satellite PCO/PCV | igs14.atx [37] |
| Relativistic effect | Model corrected [38] |
| Phase windup | Model corrected [38] |
| Tide model | Solid tide and Ocean tide model corrected [38] |
| Receiver clock | Estimated as white noise, and the GPS and BDS-3 measurements are processed distinctively |
| Receiver position | White noise |
| Estimation | Kalman filter |
| PPP Model | RMS of E/N/U Position Errors (cm) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 min | 20 min | 30 min | 40 min | |||||||||
| E | N | U | E | N | U | E | N | U | E | N | U | |
| B2b-ppp | 1.2 | 1 | 1.7 | 1.3 | 1 | 1.9 | 1.2 | 1 | 2.8 | 1.2 | 1 | 2.7 |
| EB2b-ppp | 2.5 | 2.7 | 10.7 | 4.5 | 3.4 | 17.5 | 5.6 | 3.2 | 15.7 | 5.2 | 3.4 | 13.7 |
| PB2b-ppp | 1.7 | 1.4 | 1.5 | 2.5 | 2 | 5.1 | 3.5 | 2 | 6.1 | 3.9 | 2.6 | 7.1 |
| EB2bS-ppp | 1.7 | 1.7 | 3.9 | 3 | 3 | 2.3 | 1.8 | 4.1 | 3.5 | 3.3 | 2.6 | 11 |
| PB2bS-ppp | 1.3 | 1.1 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 2.5 | 1.5 | 1.9 | 2.8 | 1.9 | 2.1 | 3.9 |
| PPP Model | RMS of E/N/U Position Errors (cm) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 min | 20 min | 30 min | 40 min | |||||||||
| E | N | U | E | N | U | E | N | U | E | N | U | |
| B2b-ppp | 0.6 | 0.4 | 1.3 | 1 | 0.6 | 1.7 | 1.8 | 0.7 | 2.4 | 2 | 0.7 | 2.5 |
| EB2b-ppp | 1.6 | 1.6 | 2.8 | 4 | 2.5 | 9.1 | 5.4 | 2.6 | 4.3 | 5.1 | 2.9 | 4.7 |
| PB2b-ppp | 1.4 | 0.9 | 3.3 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 7.6 | 1.9 | 2 | 7.8 | 2 | 2.1 | 6.9 |
| EB2bS-ppp | 1.2 | 1.1 | 2.9 | 1.3 | 1 | 3.5 | 1.2 | 0.9 | 4.6 | 1.2 | 1 | 6.3 |
| PB2bS-ppp | 1.6 | 1 | 1.6 | 1.1 | 0.5 | 3.7 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 3.4 | 1 | 1.5 | 4.1 |
| PPP Model | RMS of E/N/U Position Errors (cm) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 min | 20 min | 30 min | 40 min | |||||||||
| E | N | U | E | N | U | E | N | U | E | N | U | |
| B2b-ppp | 2.2 | 6.3 | 18.8 | 3.7 | 6.4 | 15.1 | 3.3 | 5.9 | 15.5 | 3.3 | 6.1 | 14.1 |
| EB2b-ppp | 2.7 | 8.4 | 26.9 | 3.0 | 8.0 | 29.7 | 4.2 | 8.2 | 38.4 | 11.8 | 7.9 | 51.7 |
| PB2b-ppp | 1.6 | 7.2 | 16.8 | 3.4 | 6.4 | 16.0 | 3.9 | 6.3 | 14.0 | 8.3 | 6.4 | 22.6 |
| EB2bS-ppp | 1.8 | 7.7 | 19.5 | 3.1 | 6.8 | 17.5 | 3.8 | 7.4 | 22.3 | 4.9 | 6.9 | 27.1 |
| PB2bS-ppp | 2.2 | 7.4 | 18.1 | 2.2 | 7.0 | 17.4 | 5.6 | 9.8 | 14.6 | 4.4 | 7.1 | 18.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shang, R.; Xu, Z.; Gao, C.; Meng, X.; Gao, W.; Liu, Q. A Continuous B2b-PPP Model Considering Interruptions in BDS-3 B2b Orbits and Clock Corrections as Well as Signal-in-Space Range Error Residuals. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 618. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17040618
Shang R, Xu Z, Gao C, Meng X, Gao W, Liu Q. A Continuous B2b-PPP Model Considering Interruptions in BDS-3 B2b Orbits and Clock Corrections as Well as Signal-in-Space Range Error Residuals. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(4):618. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17040618
Chicago/Turabian StyleShang, Rui, Zhenhao Xu, Chengfa Gao, Xiaolin Meng, Wang Gao, and Qi Liu. 2025. "A Continuous B2b-PPP Model Considering Interruptions in BDS-3 B2b Orbits and Clock Corrections as Well as Signal-in-Space Range Error Residuals" Remote Sensing 17, no. 4: 618. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17040618
APA StyleShang, R., Xu, Z., Gao, C., Meng, X., Gao, W., & Liu, Q. (2025). A Continuous B2b-PPP Model Considering Interruptions in BDS-3 B2b Orbits and Clock Corrections as Well as Signal-in-Space Range Error Residuals. Remote Sensing, 17(4), 618. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17040618







