Formation of Lunar Swirls: Implication from Derived Nanophase Iron Abundance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data
2.1. Sample Data
2.2. Remote Sensing Data
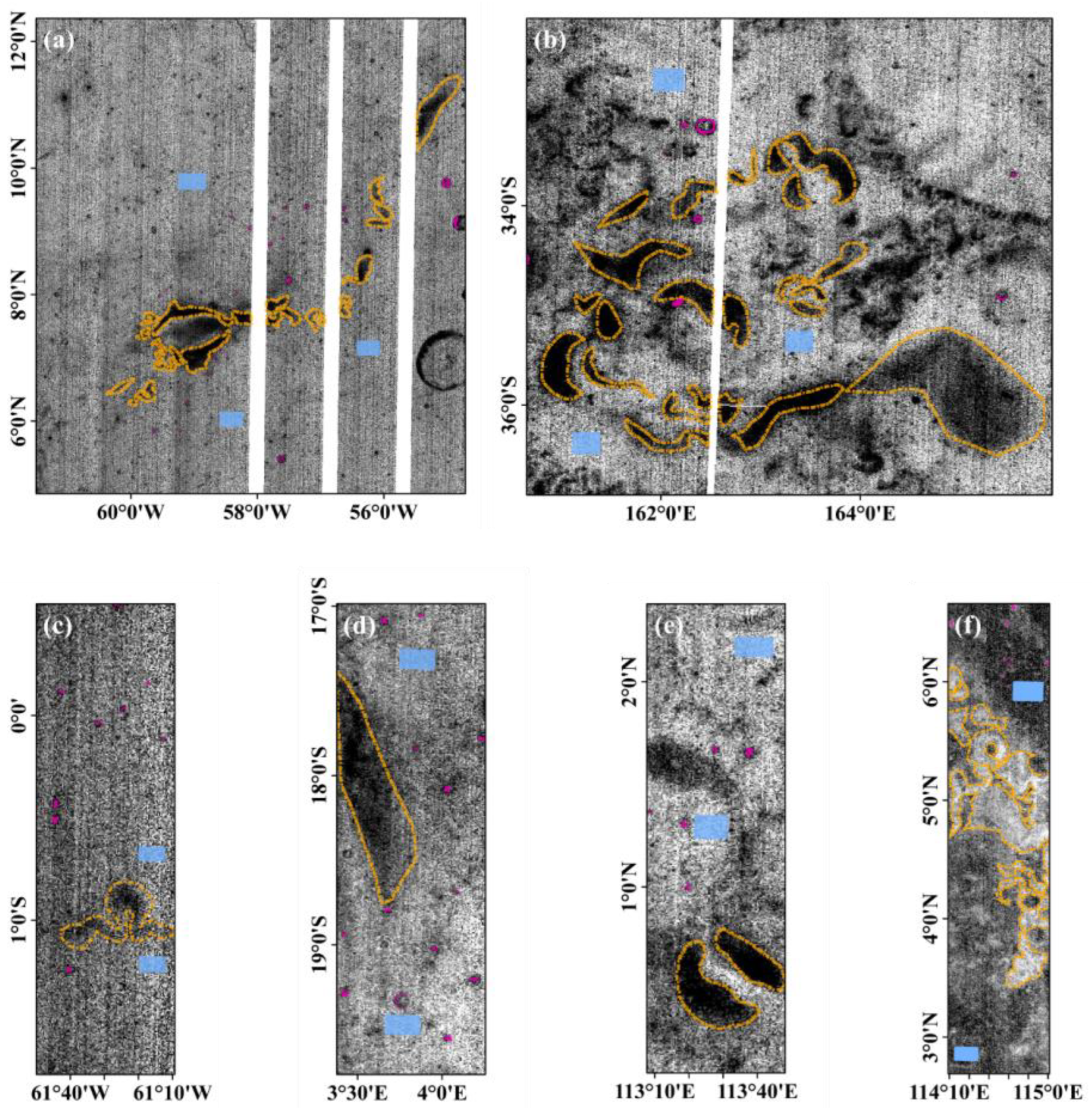
3. Study Area
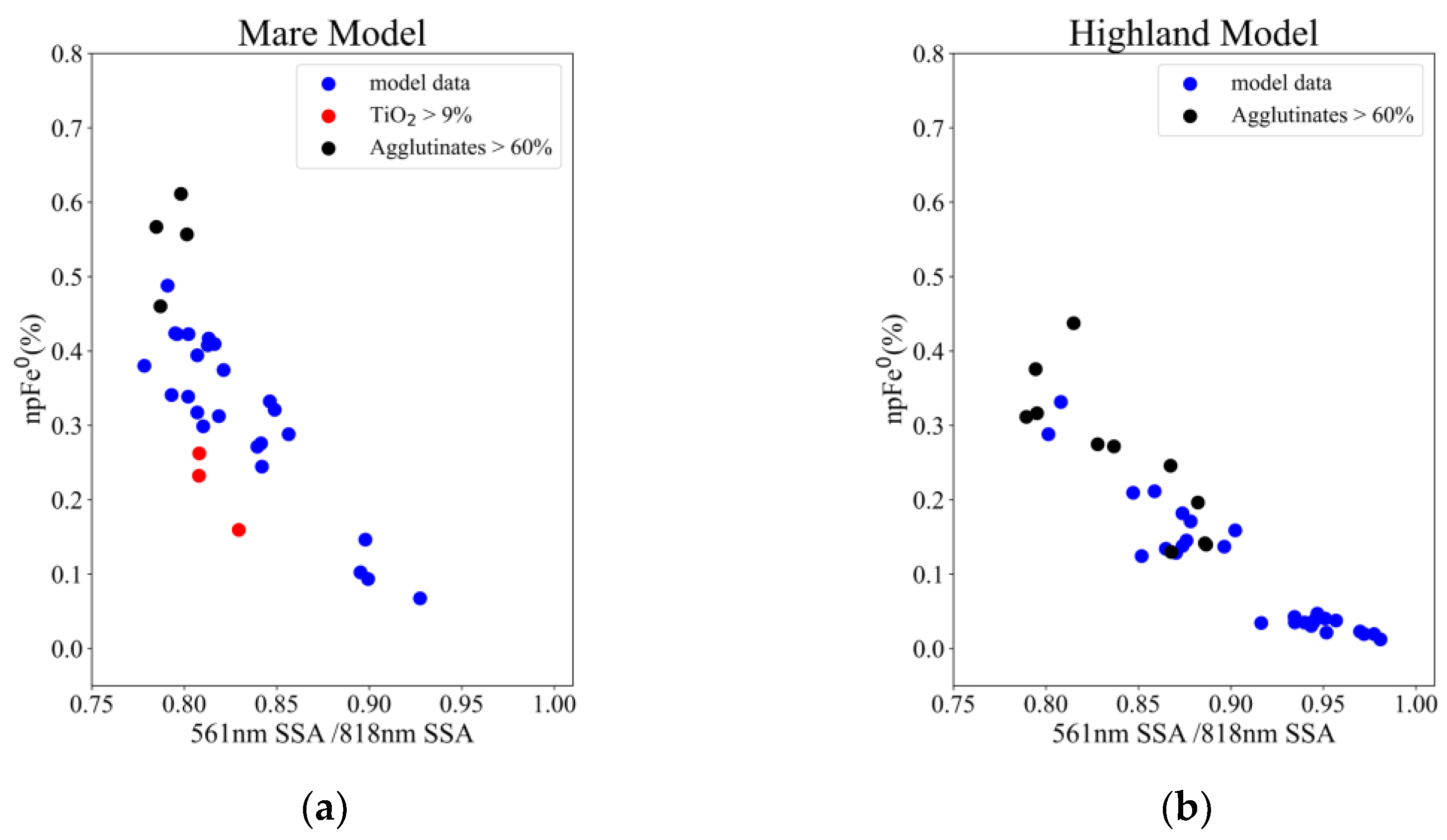
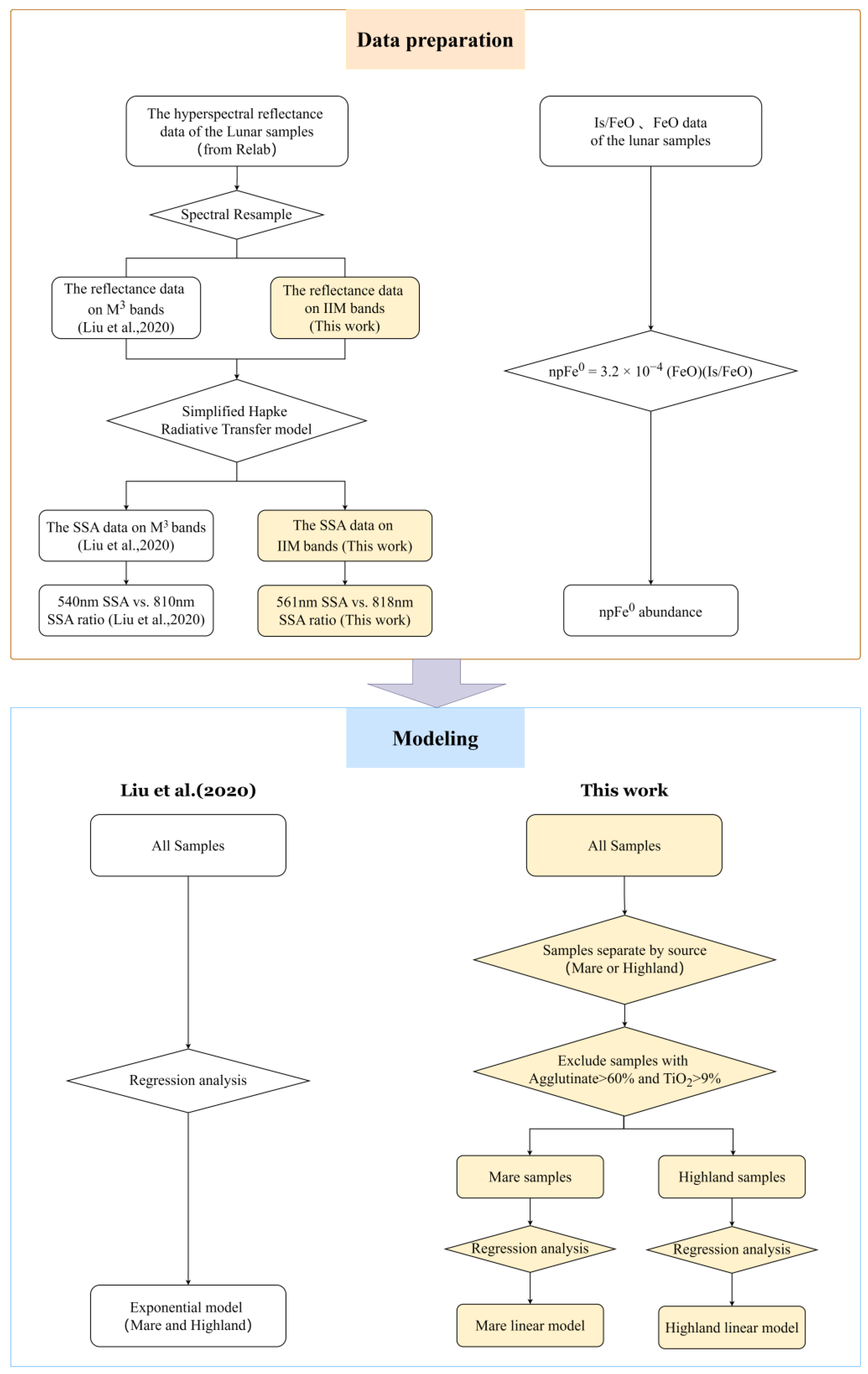
4. Method
4.1. Nanophase Iron Derivation Model
4.2. The IIM Data Processing
4.2.1. Sensor Response Inhomogeneity Correction
4.2.2. Reflectance Conversion
4.2.3. Bad Pixel and Bad Line Repair
4.3. Application to CE-1 IIM Data
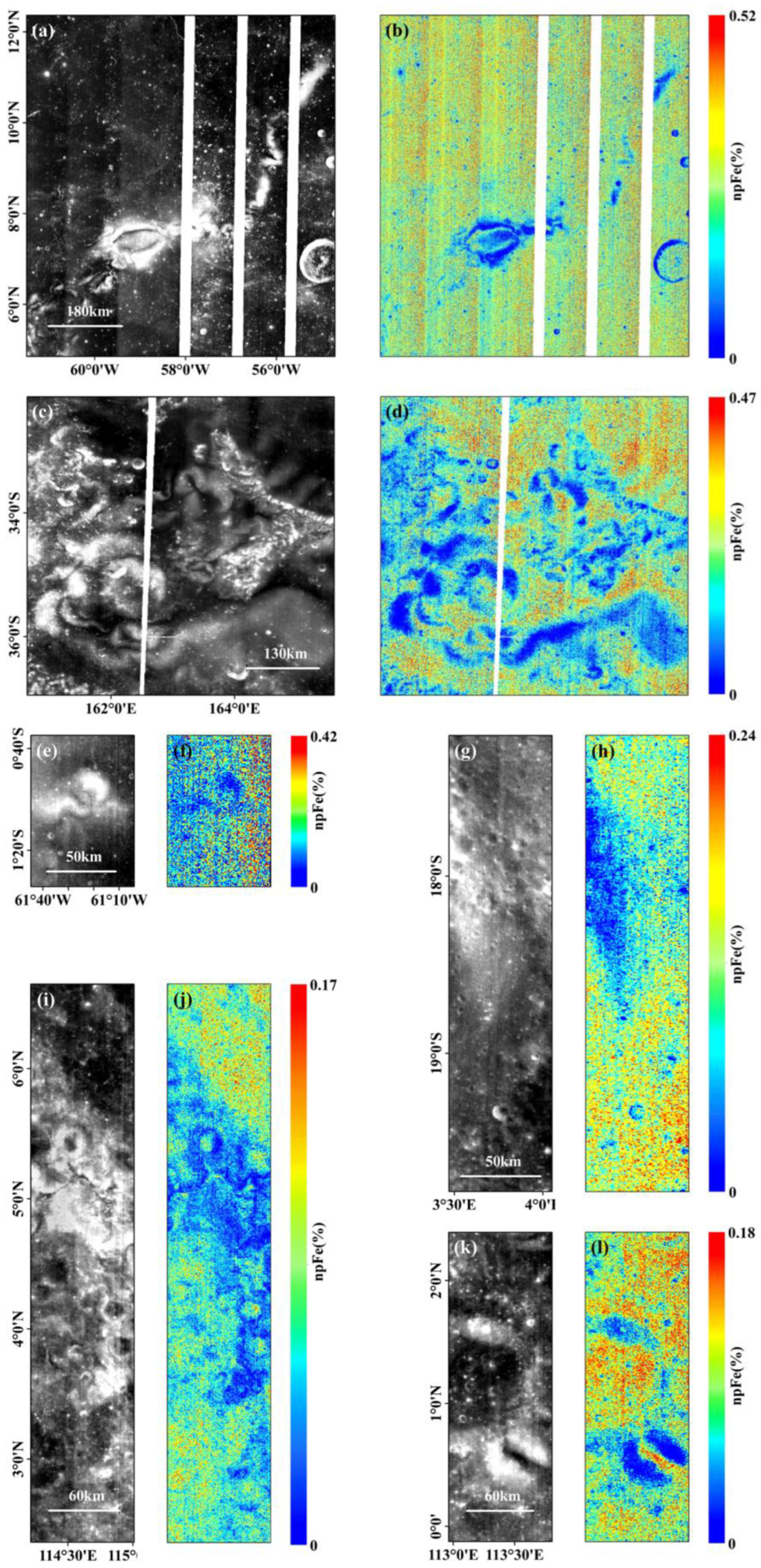
5. Results
6. Discussion
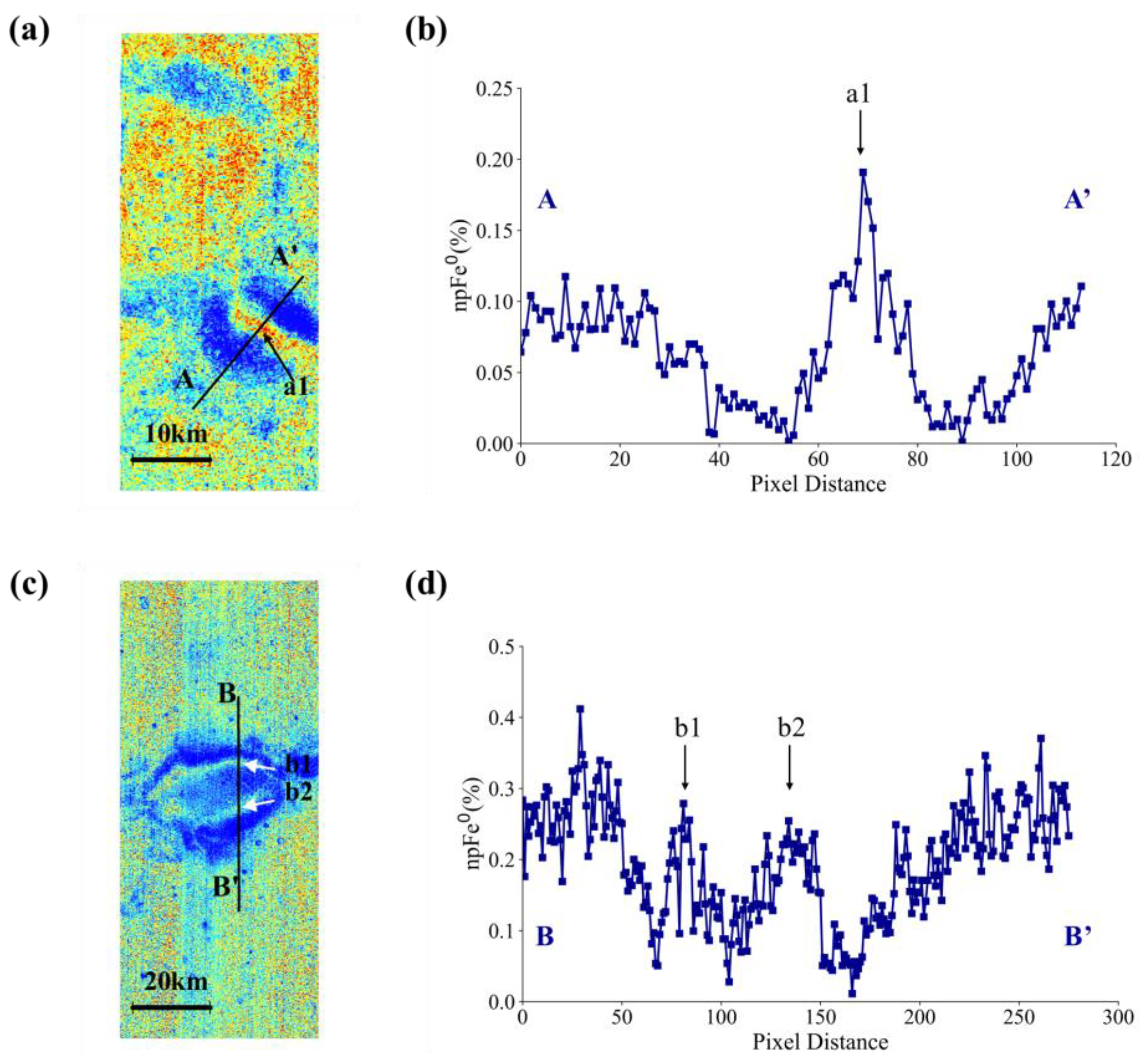
6.1. Dark Lane and Over-Maturation
6.2. Relation Between Nanophase Iron Abundance and Magnetic Anomaly Strength
6.3. Nanophase Iron Abundance Between On-Swirl Regions and Off-Swirl Fresh Craters
6.4. Formation Hypotheses of Lunar Swirls
6.5. Implication on Lunar Surface Water
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B

References
- Schultz, P.H.; Srnka, L.J. Cometary Collisions with the Moon and Mercury. Nature 1980, 284, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blewett, D.T.; Coman, E.I.; Hawke, B.R.; Gillis-Davis, J.J.; Purucker, M.E.; Hughes, C.G. Lunar Swirls: Examining Crustal Magnetic Anomalies and Space Weathering Trends. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2011, 116, E02002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hood, L.L.; Williams, C.R. The Lunar Swirls—Distribution and Possible Origins. In Proceedings of the 19th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 14–18 March 1989; p. 99. [Google Scholar]
- Denevi, B.W.; Robinson, M.S.; Boyd, A.K.; Blewett, D.T.; Klima, R.L. The Distribution and Extent of Lunar Swirls. Icarus 2016, 273, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemingway, D.J.; Garrick-Bethell, I.; Kreslavsky, M.A. Latitudinal Variation in Spectral Properties of the Lunar Maria and Implications for Space Weathering. Icarus 2015, 261, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrbolková, K.; Kohout, T.; Ďurech, J. Reflectance Spectra of Seven Lunar Swirls Examined by Statistical Methods: A Space Weathering Study. Icarus 2019, 333, 516–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrick-Bethell, I.; Head, J.W.; Pieters, C.M. Spectral Properties, Magnetic Fields, and Dust Transport at Lunar Swirls. Icarus 2011, 212, 480–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hood, L.L.; Schubert, G. Lunar Magnetic Anomalies and Surface Optical Properties. Science 1980, 208, 49–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieters, C.M.; Fischer, E.M.; Rode, O.; Basu, A. Optical Effects of Space Weathering: The Role of the Finest Fraction. J. Geophys. Res. 1993, 98, 20817–20824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieters, C.M.; Taylor, L.A.; Noble, S.K.; Keller, L.P.; Hapke, B.; Morris, R.V.; Allen, C.C.; McKAY, D.S.; Wentworth, S. Space Weathering on Airless Bodies: Resolving a Mystery with Lunar Samples. Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 2000, 35, 1101–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hapke, B. Space Weathering from Mercury to the Asteroid Belt. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2001, 106, 10039–10073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieters, C.M.; Noble, S.K. Space Weathering on Airless Bodies. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2016, 121, 1865–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Housley, R.M.; Cirlin, E.H.; Paton, N.E.; Goldberg, I.B. Solar Wind and Micrometeorite Alteration of the Lunar Regolith. In Proceedings of the 5th Lunar Science Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 18–22 March 1974; Pergamon Press: New York, NY, USA, 1974; Volume 5, pp. 2623–2642. [Google Scholar]
- Hapke, B.; Cassidy, W.; Wells, E. Effects of Vapor-Phase Deposition Processes on the Optical, Chemical, and Magnetic Properties of the Lunar Regolith. Moon 1975, 13, 339–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassidy, W.; Hapke, B. Effects of Darkening Processes on Surfaces of Airless Bodies. Icarus 1975, 25, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, L.P.; McKay, D.S. Discovery of Vapor Deposits in the Lunar Regolith. Science 1993, 261, 1305–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, L.P.; McKay, D.S. The Nature and Origin of Rims on Lunar Soil Grains. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1997, 61, 2331–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, S.K.; Pieters, C.M.; Taylor, L.A.; Morris, R.V.; Allen, C.C.; McKay, D.S.; Keller, L.P. The Optical Properties of the Finest Fraction of Lunar Soil: Implications for Space Weathering. Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 2001, 36, 31–42. [Google Scholar]
- Denevi, B.W.; Robinson, M.S.; Boyd, A.K.; Sato, H.; Hapke, B.W.; Hawke, B.R. Characterization of Space Weathering from Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter Camera Ultraviolet Observations of the Moon. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2014, 119, 976–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrix, A.; Greathouse, T.; Retherford, K.; Mandt, K.; Gladstone, G.; Kaufmann, D.; Hurley, D.; Feldman, P.; Pryor, W.; Stern, S.; et al. Lunar Swirls: Far-UV Characteristics. Icarus 2016, 273, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Li, L.; Wang, H.; Tang, B.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, Q.; Zhou, B.; Feng, Y. Global Hall MHD Simulations of the Solar Wind Implantation Flux on the Lunar Surface. Planet. Sci. J. 2023, 4, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, S.K.; Pieters, C.M.; Keller, L.P. An Experimental Approach to Understanding the Optical Effects of Space Weathering. Icarus 2007, 192, 629–642. [Google Scholar]
- Blewett, D.T.; Denevi, B.W.; Cahill, J.T.S.; Klima, R.L. Near-UV and Near-IR Reflectance Studies of Lunar Swirls: Implications for Nanosize Iron Content and the Nature of Anomalous Space Weathering. Icarus 2021, 364, 114472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trang, D.; Lucey, P.G. Improved Space Weathering Maps of the Lunar Surface through Radiative Transfer Modeling of Kaguya Multiband Imager Data. Icarus 2019, 321, 307–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, R.V. Origins and Size Distribution of Metallic Iron Particles in the Lunar Regolith. In Proceedings of the 11th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 17–21 March 1980; pp. 57–58. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Liu, B.; Ren, X.; Xu, R.; Li, C. An Empirical Model to Estimate Abundance of Nanophase Metallic Iron (npFe0) in Lunar Soils. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieters, C.M.; Taylor, L.A.; McKay, D.S.; Wentworth, S.; Morris, R.V.; Keller, L.P. Spectral Characterization of Lunar Mare Soils. In Proceedings of the Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 13–17 March 2000; Volume XXXI. Abstract #1865. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, L.A.; Pieters, C.M.; Keller, L.P.; Morris, R.V.; McKay, D.S. Lunar Mare Soils: Space Weathering and the Major Effects of Surface-Correlated Nanophase Fe. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2001, 106, 27985–27999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Xue, B.; Zhao, B.; Lucey, P.; Chen, J.; Xu, X.; Li, C.; Ouyang, Z. Global Estimates of Lunar Iron and Titanium Contents from the Chang’E-1 IIM Data. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Z.; Jiang, J.; Li, C.; Sun, H.; Zou, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, J.; Zhao, B.; Ren, X.; Yang, J.; et al. Preliminary Scientific Results of Chang E-1 Lunar Orbiter: Based on Payloads Detection Data in the First Phase. Chin. J. Space Sci. 2008, 28, 361–369. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, Z.C.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, G.; Liu, B.; Ren, X.; Mu, L.; Liu, J.; Li, C. Preliminary Results of TiO2 Mapping Using Imaging Interferometer Data From Chang’E-1. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2011, 56, 2082–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ling, Z.C.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.Z.; Zhang, W.; Bian, W.; Ren, X.; Mu, L.; Liu, J.; Li, C. Preliminary Results of FeO Mapping Using Imaging Interferometer Data From Chang’E-1. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2011, 56, 376–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yan, B.; Xiong, S.Q.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Dong, L.; Gan, F.; Yang, S.; Wang, R. Mapping Lunar Global Chemical Composition from Chang’E-1 IIM Data. Planet. Space Sci. 2012, 67, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucey, P.G.; Blewett, D.T.; Jolliff, B.L. Lunar Iron and Titanium Abundance Algorithms Based on Final Processing of Clementine Ultraviolet-Visible Images. J. Geophys. Res. 2000, 105, 20297–20305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, D.J.; Feldman, W.C.; Elphic, R.C.; Little, R.C.; Prettyman, T.H.; Maurice, S.; Lucey, P.G.; Binder, A.B. Iron Abundances on the Lunar Surface as Measured by the Lunar Prospector Gamma-Ray and Neutron Spectrometers. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 1830. [Google Scholar]
- Kramer, G.Y.; Besse, S.; Dhingra, D.; Nettles, J.; Klima, R.; Garrick-Bethell, I.; Clark, R.N.; Combe, J.; Head, J.W.; Taylor, L.A.; et al. M3 Spectral Analysis of Lunar Swirls and the Link Between Optical Maturation and Surface Hydroxyl Formation at Magnetic Anomalies. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunakawa, H.; Takahashi, F.; Shimizu, H.; Shibuya, H.; Matsushima, M. Surface Vector Mapping of Magnetic Anomalies over the Moon Using Kaguya and Lunar Prospector Observations. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2015, 120, 1160–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart-Alexander, D.E. Geologic Map of the Central Farside of the Moon; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1978; serious I-1047. [Google Scholar]
- Hood, L.L.; Zakharian, A.; Halekas, J.; Mitchell, D.L.; Lin, R.P.; Acuna, M.H.; Binder, A.B. Initial Mapping and Interpretation of Lunar Crustal Magnetic Anomalies Using Lunar Prospector Magnetometer Data. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 27825–27839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blewett, D.T.; Hawke, B.R.; Richmond, N.C.; Hughes, C.G. A Magnetic Anomaly Associated with an Albedo Feature near Airy Crater in the Lunar Nearside Highlands. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L24206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, H.E. Geologic Map of the Purback Quadrangle of the Moon; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1974; serious I-739. [Google Scholar]
- Wilhelms, D.E.; El-Baz, F. Geologic Map of the East Side of the Moon; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1977; serious I-948. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.Z. Sensitivity Analysis for Hapke’s Radiative Transfer Model. In Proceedings of the 44th Annual Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, The Woodlands, TX, USA, 18–22 March 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Li, L. An Empirical Approach to Estimating Mass Fraction of Submicroscopic Iron in Lunar Soils. In Proceedings of the 46th Annual Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, The Woodlands, TX, USA, 16–20 March 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Wang, R.; Gan, F.; Wang, Z. Minerals Mapping of the Lunar Surface with Clementine UVVIS/NIR Data Based on Spectra Unmixing Method and Hapke Model. Icarus 2010, 208, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemelin, M.; Morisset, C.E.; Germain, M.; Osinski, G.R.; Maurice, S.; Lucey, P.G. Ilmenite Mapping of the Lunar Regolith Over Mare Australe and Mare Ingenii Regions: An Optimized Multisource Approach Based on Hapke Radiative Transfer Theory. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2013, 118, 2582–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zou, Y.; Chen, J.; Xu, X.; Tang, Z.; Xu, A.; Yan, B.; Gan, F.; Zhang, X. A Preliminary Experience in the Use of Chang’E-1 IIM Data. Planet. Space Sci. 2010, 58, 1922–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Z.C.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.Z.; Li, B.; Wu, Z.C.; Ni, Y.H.; Sun, L.Z.; Chen, J. Lunar Global FeO and TiO2 Mapping Based on the Recalibrated Chang’E-1 IIM Dataset. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2016, 32, 87–98. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.Z.; Xu, X.S.; Xie, Z.D.; Tang, Z. Absolute Calibration of the Chang’E-1 IIM Camera and Its Preliminary Application. Sci. China Ser. G 2009, 52, 1842–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieters, C.M. The Moon as a Spectral Calibration Standard Enabled by Lunar Samples: The Clementine Example. Workshop New Views Moon II Underst. Moon Through Integr. Divers. Datasets 1999, 29, 47. [Google Scholar]
- Pieters, C.M.; Pratt, S. Earth-Based Near-Infrared Collection of Spectra for the Moon: A New PDS Data Set. In Proceedings of the Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 13–17 March 2000; Volume XXXI, p. 2059. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yan, B.; Gan, F.; Tang, Z.; Xu, A.; Zheng, Y.; Zou, Y. Global Absorption Center Map of the Mafic Minerals on the Moon as Viewed by CE-1 IIM Data. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 2010, 53, 2160–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieters, C.; Shkuratov, Y.; Kaydash, V.; Stankevich, D.; Taylor, L. Lunar Soil Characterization Consortium Analyses: Pyroxene and Maturity Estimates Derived from Clementine Image Data. Icarus 2006, 184, 83–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, H.; Robinson, M.S.; Lawrence, S.J.; Denevi, B.W.; Hapke, B.; Jolliff, B.L.; Hiesinger, H. Lunar Mare TiO2 Abundances Estimated from UV/Vis Reflectance. Icarus 2017, 296, 216–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemingway, D.; Garrick-Bethell, I. Magnetic Field Direction and Lunar Swirl Morphology: Insights from Airy and Reiner Gamma. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poppe, A.R.; Fatemi, S.; Garrick-Bethell, I.; Hemingway, D.; Holmström, M. Solar Wind Interaction with the Reiner Gamma Crustal Magnetic Anomaly: Connecting Source Magnetization to Surface Weathering. Icarus 2016, 266, 261–266. [Google Scholar]
- Coman, E.I.; Blewett, D.T.; Hawke, B.R.; Gillis-Davis, J.J.; Johns Hopkins Univ. Lunar Swirls: How Dark Are “Dark Lanes”? In Proceedings of the 42nd Annual Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, The Woodlands, TX, USA, 7–11 March 2011; Volume 42, p. 1096. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, E.; Sim, C.K.; Baek, S.M.; Jeong, M.; Choi, Y.J. Reddening and Darkening Trends of ON/Off Swirls and the Relationship with Magnetic Field Strength. Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn. 2021, 73, 1604–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemelin, M.; Lucey, P.G.; Miljković, K.; Gaddis, L.R.; Hare, T.; Ohtake, M. The Compositions of the Lunar Crust and Upper Mantle: Spectral Analysis of the Inner Rings of Lunar Impact Basins. Planet. Space Sci. 2019, 165, 230–243. [Google Scholar]
- Tai Udovicic, C.J.; Costello, E.S.; Ghent, R.R.; Edwards, C.S. New Constraints on the Lunar Optical Space Weathering Rate. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2020GL092198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Zhao, R.; Chang, C.; Yu, J.; Xiao, D.; Bai, H.; Zou, Z.; Yang, M.; Wang, W. Separate Effects of Irradiation and Impacts on Lunar Metallic Iron Formation Observed in Chang’e-5 Samples. Nat. Astron. 2024, 8, 1110–1118. [Google Scholar]
- Lucey, P.G.; Blewett, D.T.; Taylor, G.J.; Hawke, B.R. Imaging of Lunar Surface Maturity. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2000, 105, 20377–20386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieters, C.M.; Moriarty, D.P.; Garrick-Bethell, I. Atypical Regolith Processes Hold the Key to Enigmatic Lunar Swirls. In Proceedings of the 45th Annual Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, The Woodlands, TX, USA, 17–21 March 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wieczorek, M.A.; Weiss, B.P.; Stewart, S.T. An Impactor Origin for Lunar Magnetic Anomalies. Science 2012, 335, 1212–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jozwiak, L.M.; Blewett, D.T.; Denevi, B.W. Geomorphologic Analysis of Lunar Swirls: Assessment of Formation Mechanisms. In Proceedings of the 48th Annual Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, The Woodland, TX, USA, 20–24 March 2017; p. 1244, No. 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Lucey, P.G.; Song, E.; Donaldson Hanna, K.L.; Millan-Valle, L.F.; Bowles, N.E.; Thomas, I.R.; Gillis-Davis, J.J. Global Diviner Christiansen Feature Space Weathering Effects: Hypotheses, Experiment, and Mitigation. In Proceedings of the 44th Annual Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, The Woodlands, TX, USA, 18–22 March 2013; Volume 1719, p. 2890. [Google Scholar]
- Glotch, T.D.; Bandfield, J.L.; Lucey, P.G.; Hayne, P.O.; Greenhagen, B.T.; Arnold, J.A.; Ghent, R.R.; Paige, D.A. Formation of Lunar Swirls by Magnetic Field Standoff of the Solar Wind. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glotch, T.D.; Greenhagen, B.T.; Lucey, P.G.; Bandfield, J.L.; Hayne, P.O.; Allen, C.C.; Paige, D.A. Observations of Lunar Swirls by the Diviner Lunar Radiometer Experiment. In Proceedings of the 43rd Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, The Woodlands, TX, USA, 19–23 March 2012. No. JSC-CN-25794. [Google Scholar]
- Lucey, P.G.; Paige, D.A.; Greenhagen, B.T.; Bandfield, J.L.; Glotch, T.D. Composition of Diviner Christiansen Feature Position and Visible Albedo: Composition and Space Weathering Implications. In Proceedings of the 41st Annual Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, The Woodlands, TX, USA, 1–5 March 2010; Volume 41, p. 1600. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, L.A.; Pieters, C.M.; Patchen, A.; Taylor, D.S.; Morris, R.V.; Keller, L.P.; McKay, D.S. Mineralogical and Chemical Characterization of Lunar Highland Soils: Insights into the Space Weathering of Soils on Airless Bodies. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2010, 115, E02002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinet, P.C.; Shevchenko, V.V.; Chevrel, S.D.; Daydou, Y.; Rosemberg, C. Local and Regional Lunar Regolith Characteristics at Reiner Gamma Formation: Optical and Spectroscopic Properties from Clementine and Earth-Based Data. J. Geophys. Res. 2000, 105, 9457–9475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starukhina, L.V.; Shkuratov, Y.G. Swirls on the Moon and Mercury: Meteoroid Swarm Encounters as a Formation Mechanism. Icarus 2004, 167, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shkuratov, Y.; Kaydash, V.; Gerasimenko, S.; Opanasenko, N.; Velikodsky, Y.; Korokhin, V.; Videen, G.; Pieters, C. Probable Swirls Detected as Photometric Anomalies in Oceanus Procellarum. Icarus 2010, 208, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, T.; Soter, S. Cometary Impact and the Magnetization of the Moon. Planet. Space Sci. 1976, 24, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blewett, D.T.; Denevi, B.W.; Robinson, M.S.; Ernst, C.M.; Purucker, M.E.; Solomon, S.C. The Apparent Lack of Lunar-Like Swirls on Mercury: Implications for the Formation of Lunar Swirls and for the Agent of Space Weathering. Icarus 2010, 209, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, M.; Wöhler, C.; Bhatt, M.; Berezhnoy, A.A.; Grumpe, A.; Wohlfarth, K.; Bhardwaj, A.; Shevchenko, V.V. Processes Governing the VIS/NIR Spectral Reflectance Behavior of Lunar Swirls. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 639, A12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, M.; Wöhler, C.; Rogall, J.; Aravind, K.; Ganesh, S.; Bhardwaj, A. Unique Regolith Characteristics of the Lunar Swirl Reiner Gamma as Revealed by Imaging Polarimetry at Large Phase Angles. Astron. Astrophys. 2023, 674, A82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Garrick-Bethell, I. Surface Water at Lunar Magnetic Anomalies. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 14318–14327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieters, C.M.; Goswami, J.N.; Clark, R.N.; Annadurai, M.; Boardman, J.; Buratti, B.; Combe, J.-P.; Dyar, M.D.; Green, R.; Head, J.W.; et al. Character and Spatial Distribution of OH−/H2O on the Surface of the Moon Seen by M3 on Chandrayaan-1. Science 2009, 326, 568–572. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]



| Setting | Swirls | Magnetic Anomaly Strength (nT) * | Longitude | Latitude |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mare | Reiner Gamma | 22-strong | 302.5°E | 7.5°N |
| Mare Ingenii | 20-strong | 160°E | 33.5°S | |
| Rima Sirsalis | 1-weak | 300°E | 1°S | |
| Highland | Airy | 13-moderate | 3.5°E | 18°S |
| Firsov | 11-moderate | 114°E | 2.2°N |
| Swirls | Off-Swirl Fresh Craters npFe0(%) | On-Swirl Regions npFe0(%) | Off-Swirl Backgrounds npFe0(%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reiner Gamma | 0.05 | 0.15 | 0.27 |
| Mare Ingenii | 0.07 | 0.16 | 0.29 |
| Rima Sirsalis | 0.02 | 0.15 | 0.21 |
| Airy | 0.04 | 0.08 | 0.14 |
| Firsov | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, W.; Ren, X.; Liu, B.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, D. Formation of Lunar Swirls: Implication from Derived Nanophase Iron Abundance. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1324. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17081324
Zhao W, Ren X, Liu B, Xiao Y, Liu D. Formation of Lunar Swirls: Implication from Derived Nanophase Iron Abundance. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(8):1324. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17081324
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Wanqi, Xin Ren, Bin Liu, Yao Xiao, and Dawei Liu. 2025. "Formation of Lunar Swirls: Implication from Derived Nanophase Iron Abundance" Remote Sensing 17, no. 8: 1324. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17081324
APA StyleZhao, W., Ren, X., Liu, B., Xiao, Y., & Liu, D. (2025). Formation of Lunar Swirls: Implication from Derived Nanophase Iron Abundance. Remote Sensing, 17(8), 1324. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17081324






