Surface-Dependent Meteorological Responses to a Taklimakan Dust Event During Summer near the Northern Slope of the Tibetan Plateau
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data
2.1.1. Satellite Observation Data
2.1.2. Reanalysis Data
2.1.3. Ground-Based Observation Data
2.2. Model Description and Experimental Setup
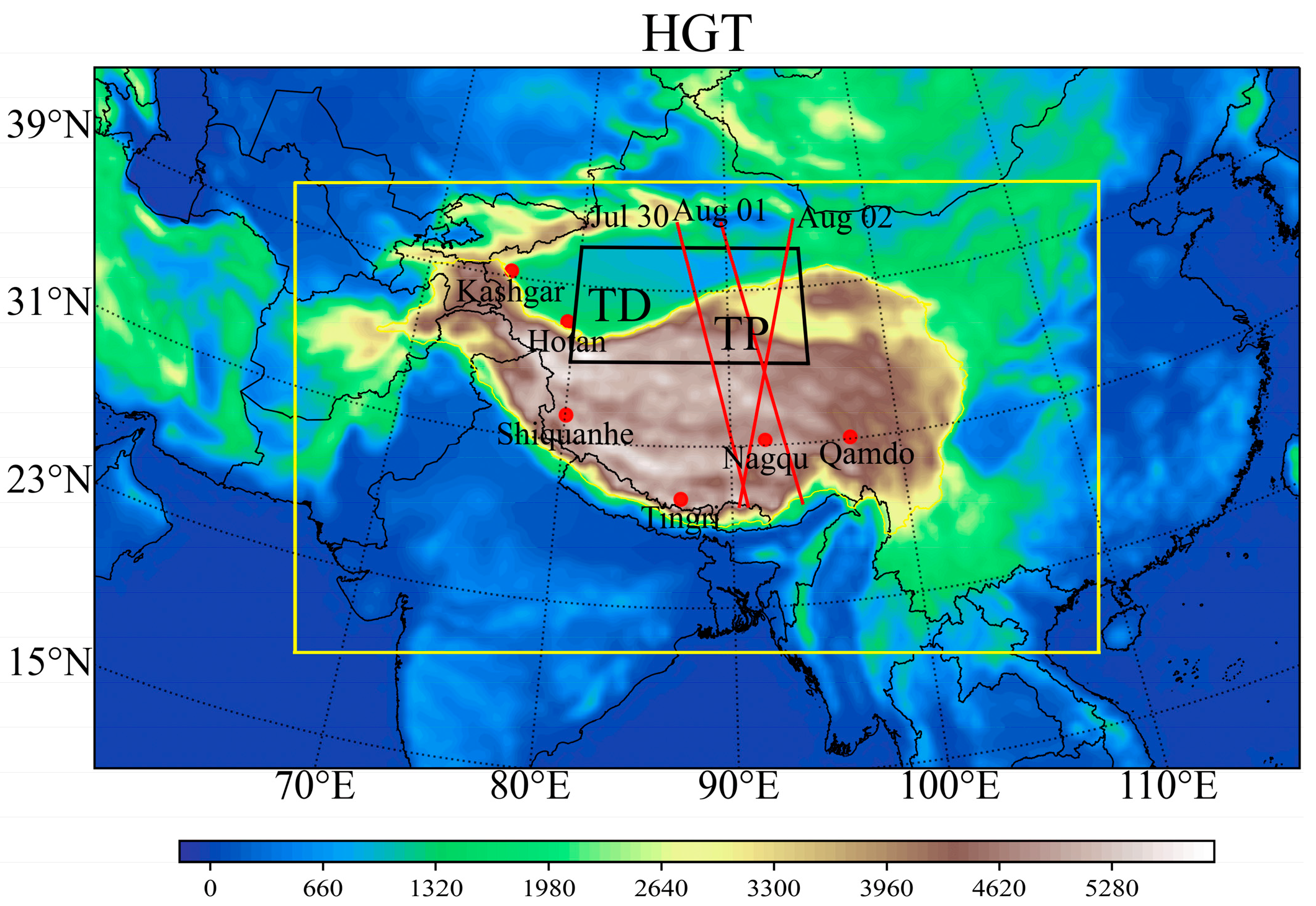
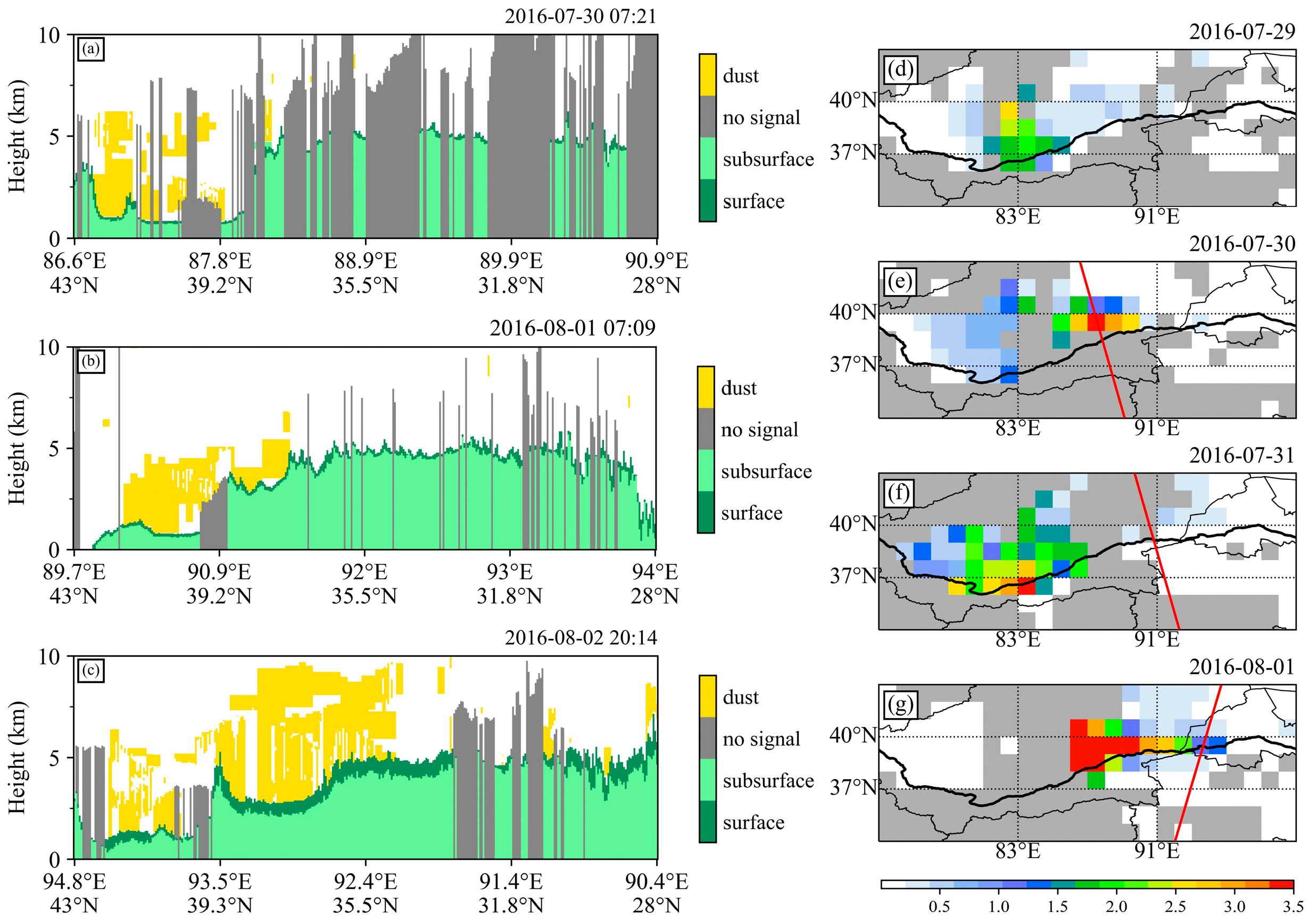
3. A Satellite-Observed Dust Transport Process
4. Simulation of Dust Transportation Process
4.1. Model Evaluation
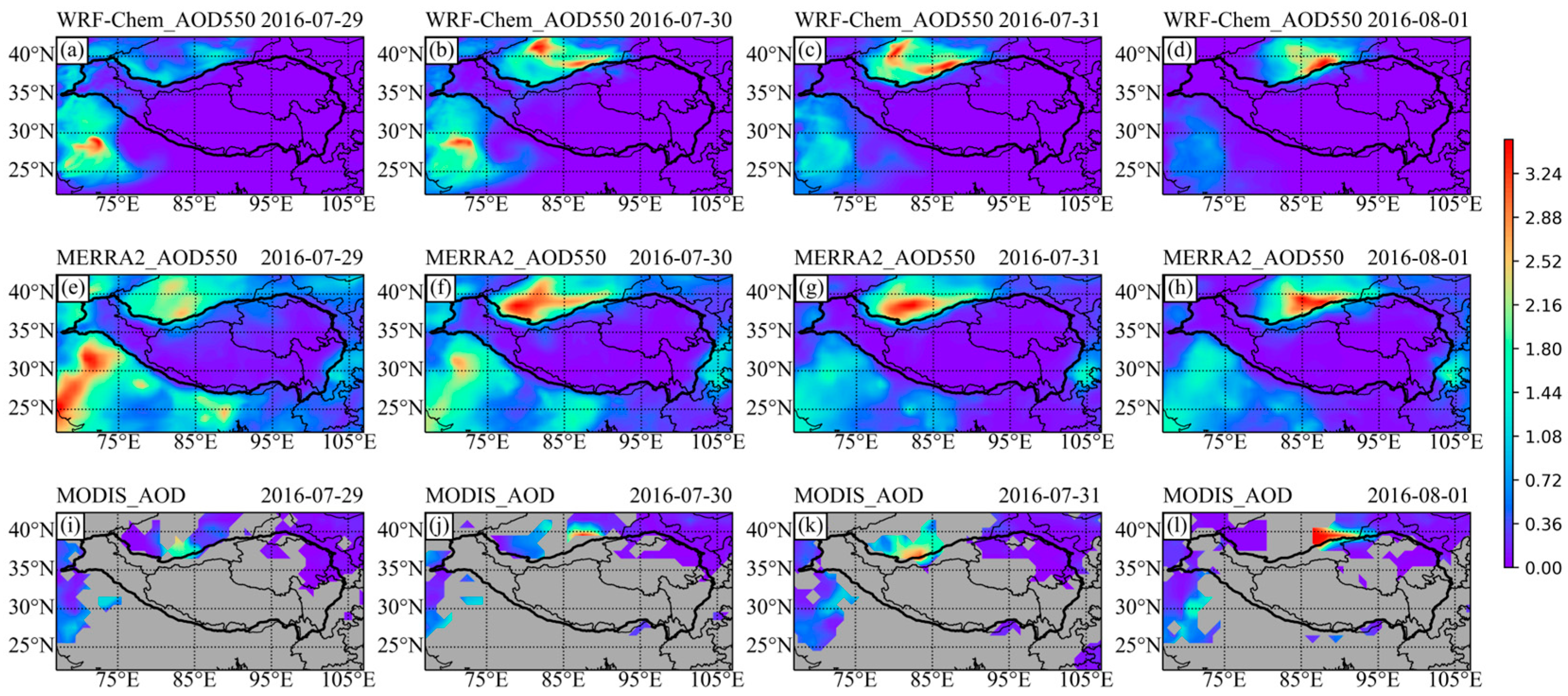
4.1.1. AOD Evaluation
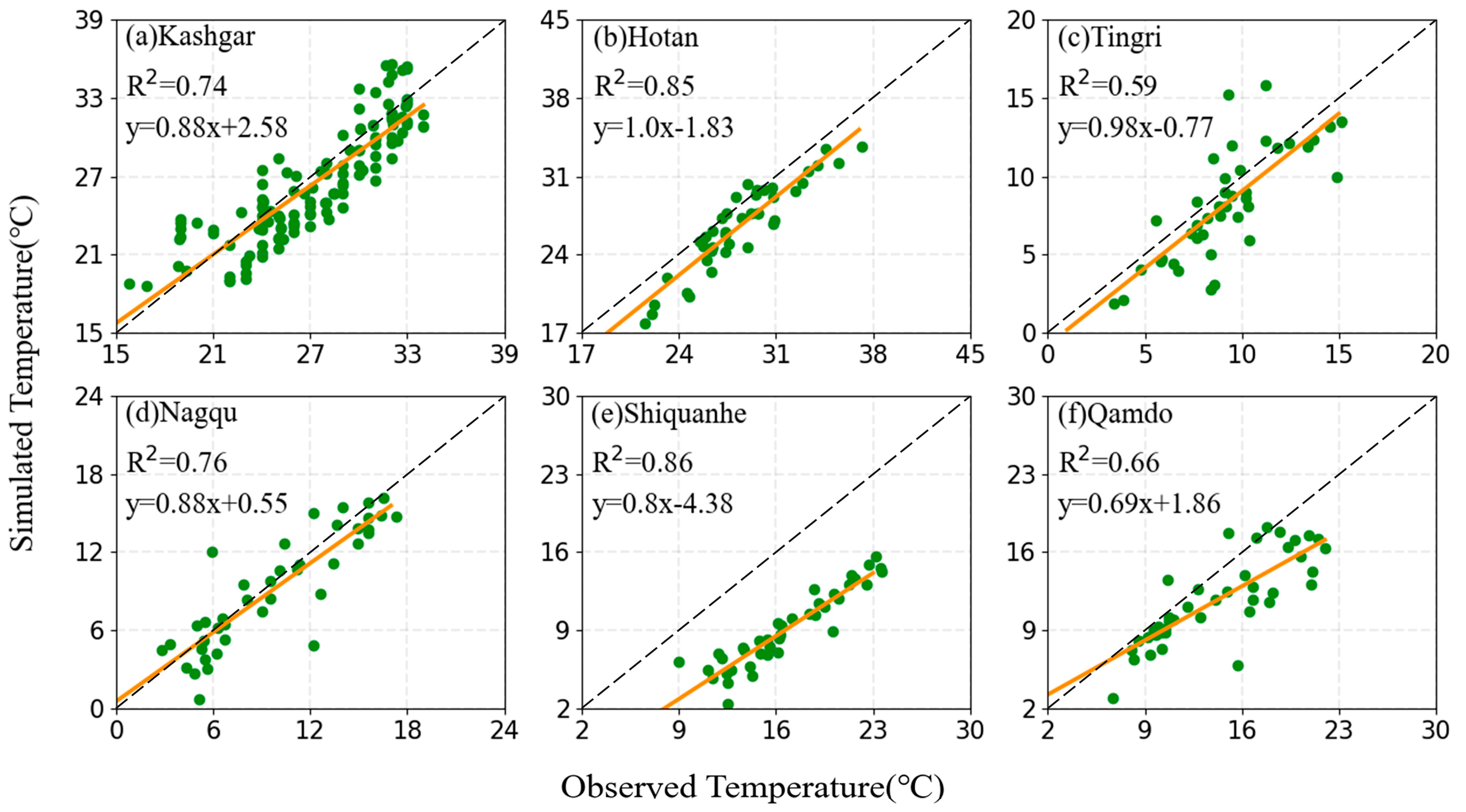
4.1.2. 2 m Temperature Evaluation
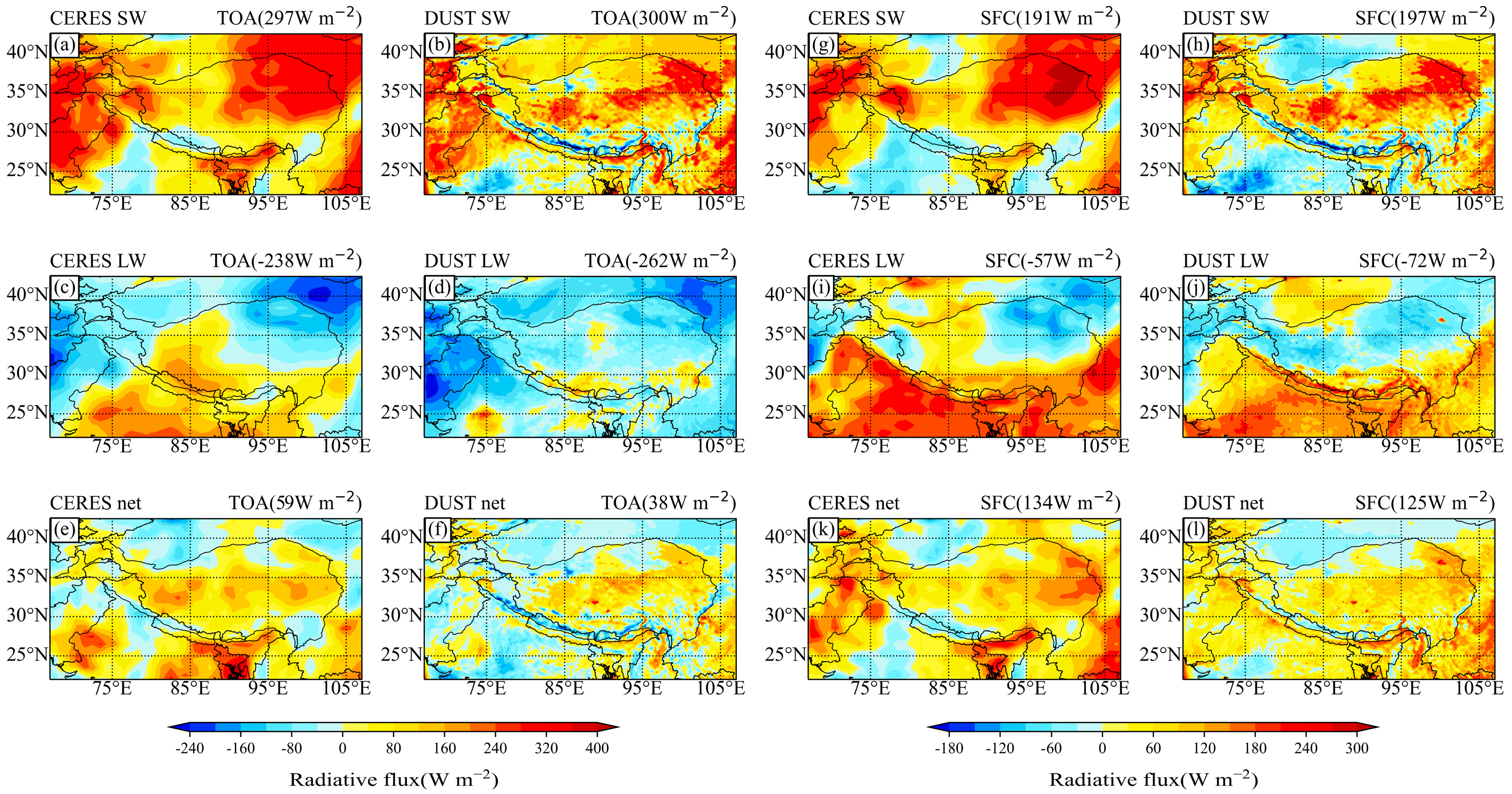
4.1.3. Radiation Flux Comparison
4.2. Dust Transport from the TD to the TP
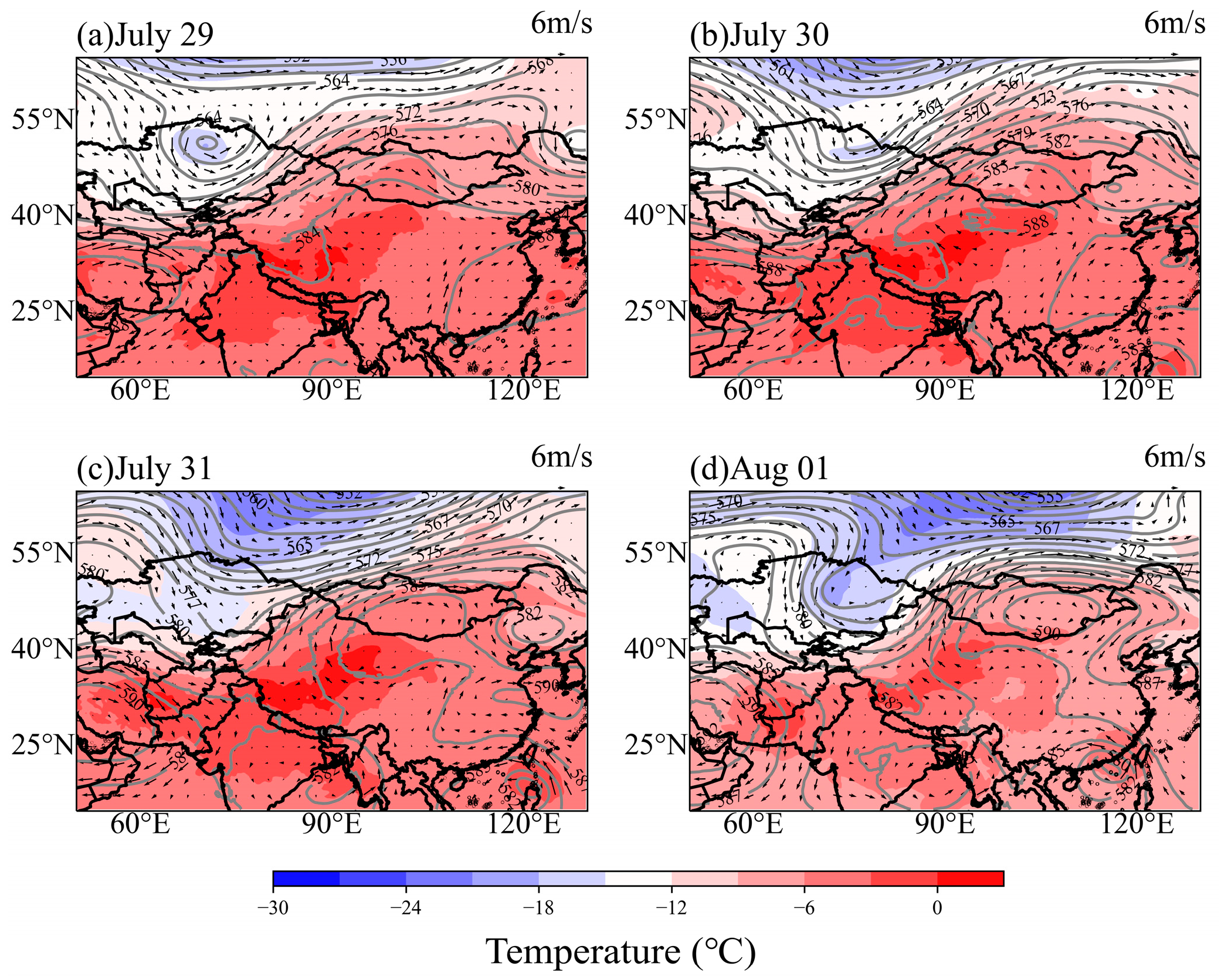
4.2.1. Meteorological Background of Dust Transport to the TP
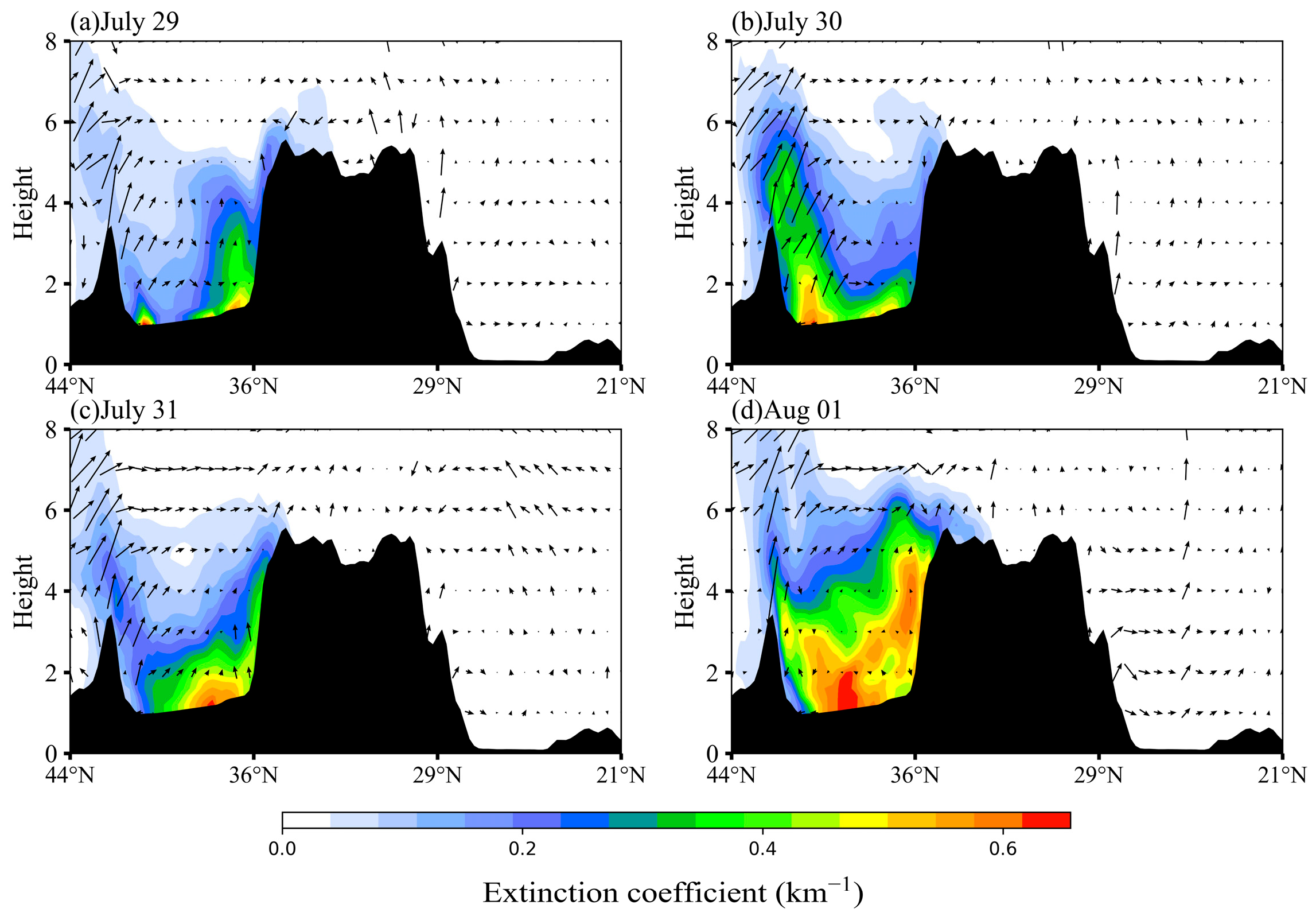
4.2.2. Simulation of the Dust Transport
5. Results
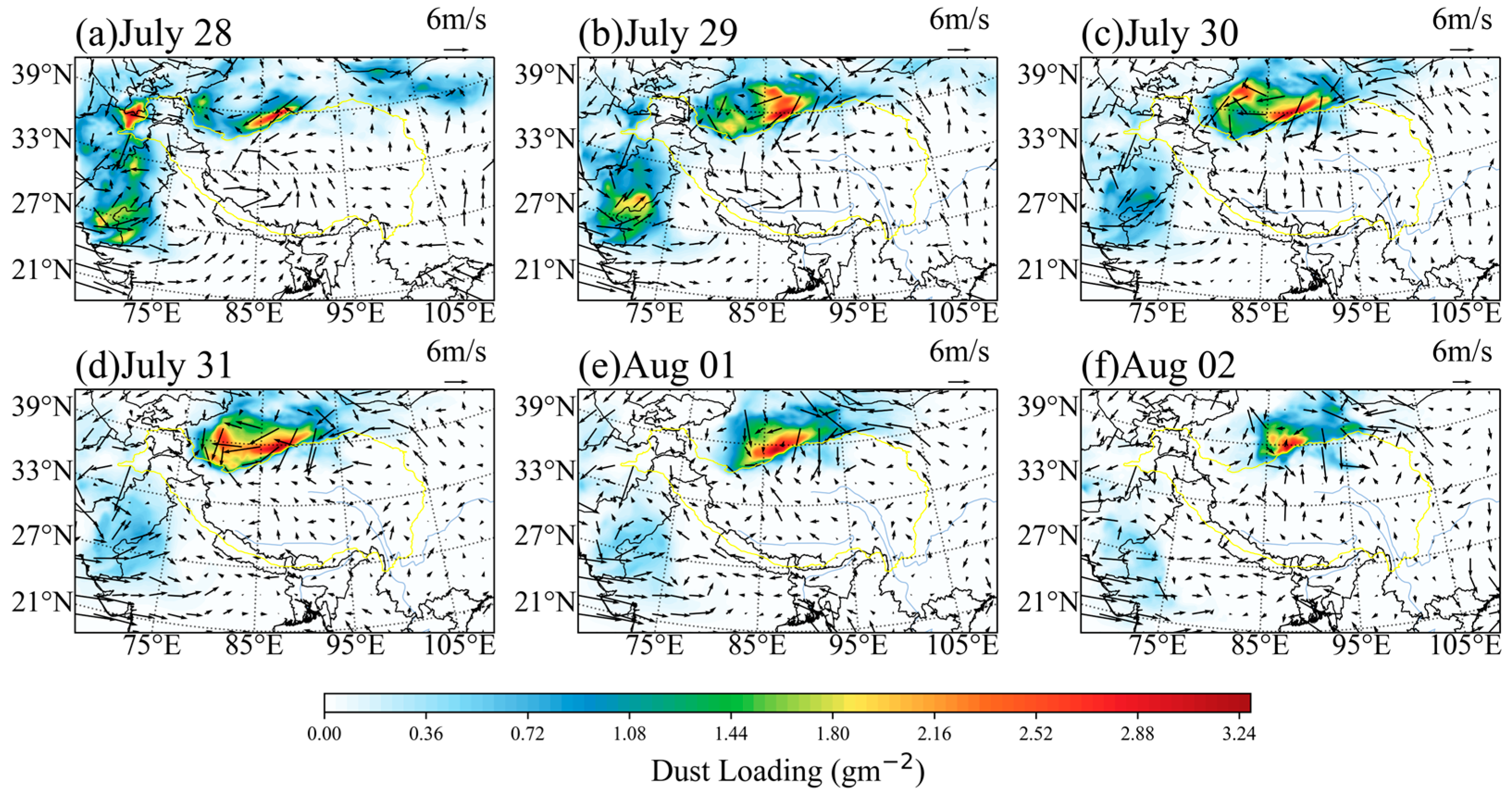
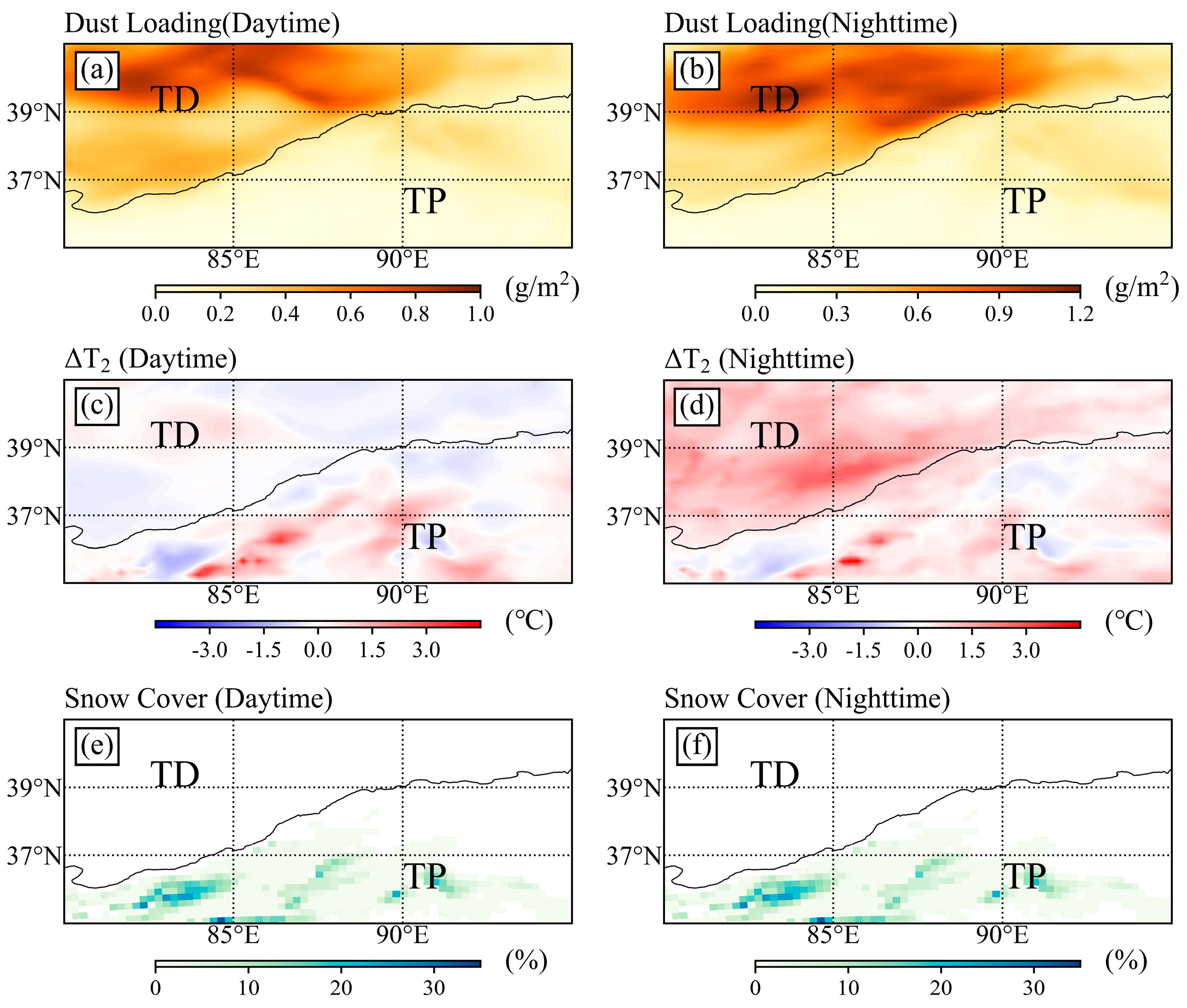
5.1. Dust Loading and Dust Concentration
5.2. Surface Temperature Response to Dust
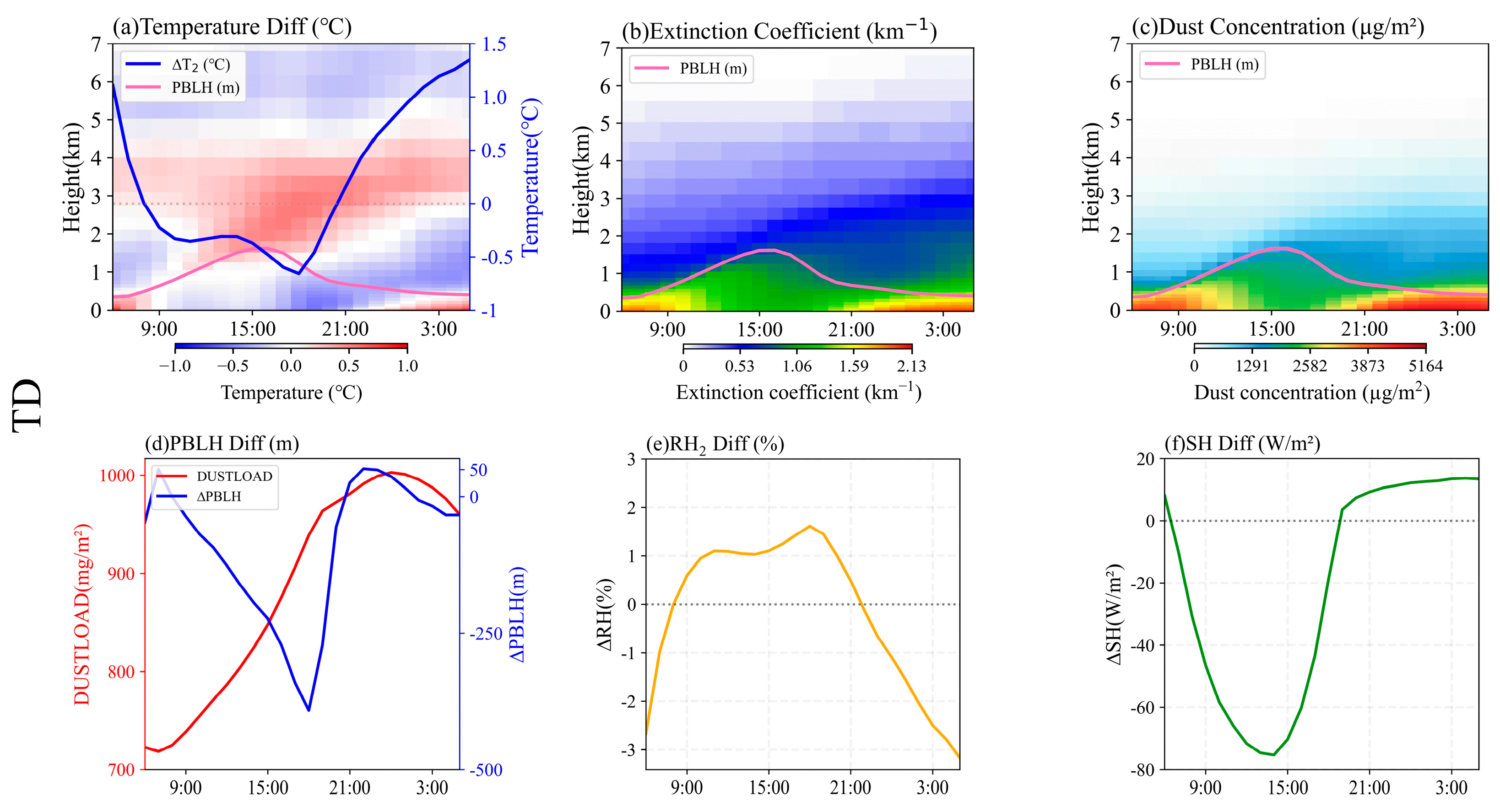
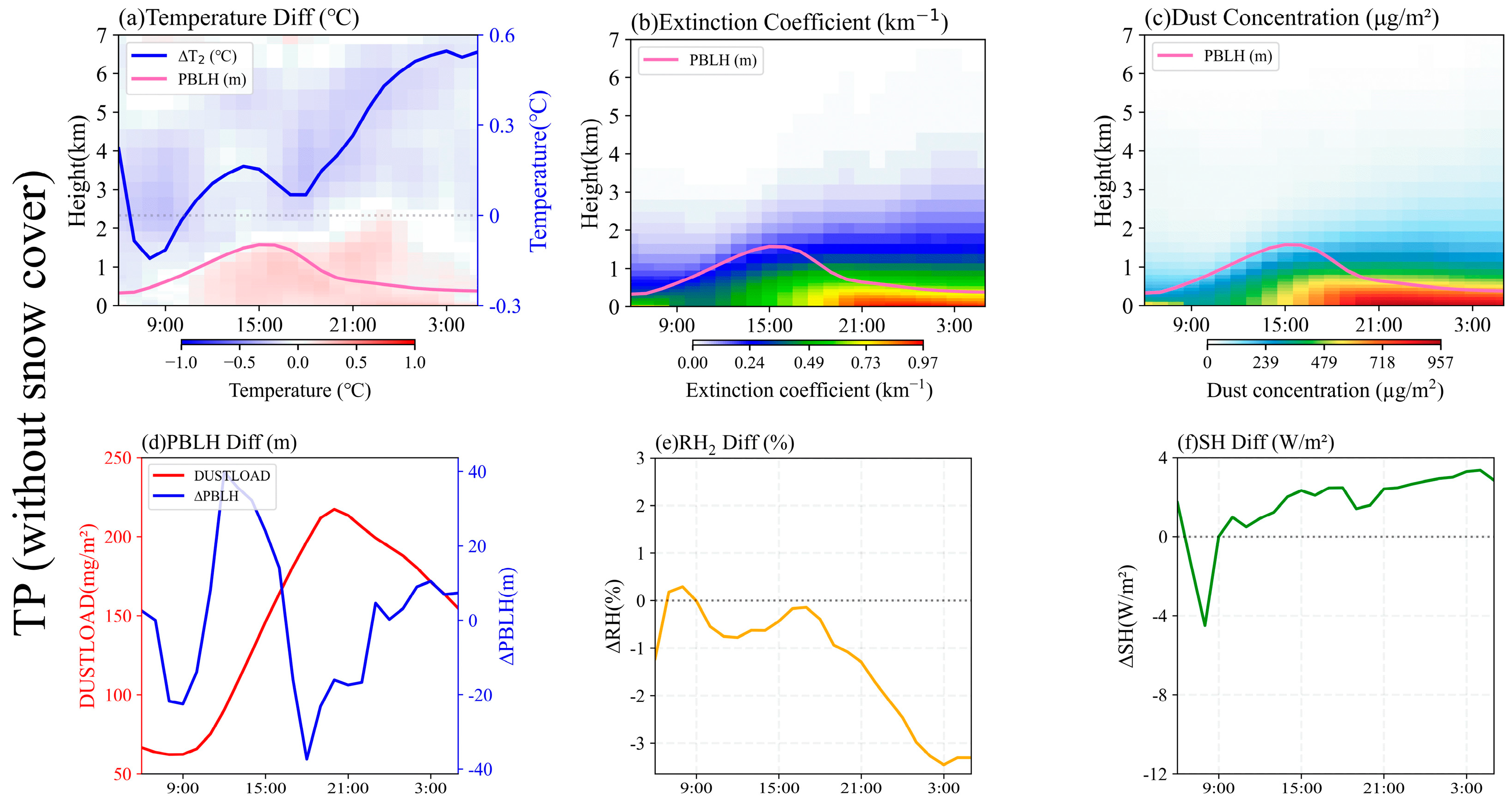
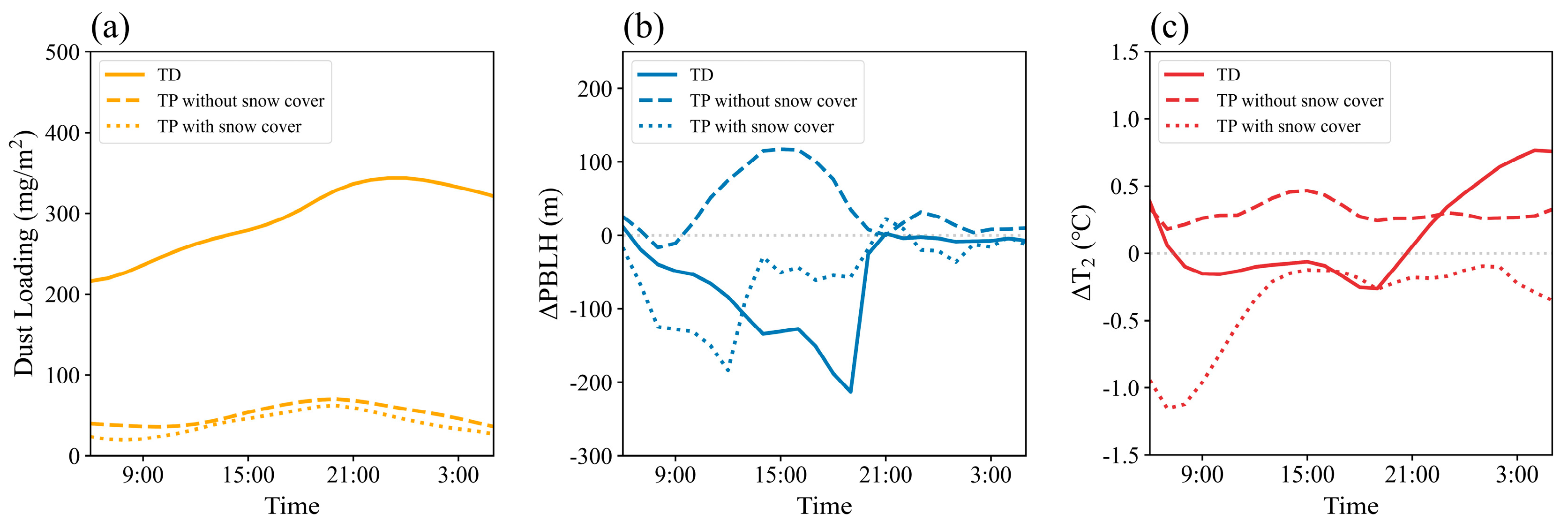
5.3. Responses of Meteorological Elements to Dust over Different Surface Types
5.3.1. Responses of Meteorological Elements in the TD
5.3.2. Responses of Meteorological Elements in the TP Without Snow Cover
5.3.3. Responses of Meteorological Elements in the TP with Snow Cover
5.4. A Dust Process in June
6. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kok, J.F.; Ridley, D.A.; Zhou, Q.; Miller, R.L.; Zhao, C.; Heald, C.L.; Ward, D.S.; Albani, S.; Haustein, K. Smaller desert dust cooling effect estimated from analysis of dust size and abundance. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 274–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wang, T.; Wang, W.; Li, Z.; Yan, H. Climate effects of dust aerosols over East Asian arid and semiarid regions. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 11–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knippertz, P.; Todd, M.C. Mineral dust aerosols over the Sahara: Meteorological controls on emission and transport and implications for modeling. Rev. Geophys. 2012, 50, RG1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Su, S.; Yin, Z.; Sun, C.; Xie, X.; Wang, T.; Yasheng, D.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y. Quantitatively assessing the contributions of dust aerosols to direct radiative forcing based on remote sensing and numerical simulation. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizza, U.; Avolio, E.; Morichetti, M.; Di Liberto, L.; Bellini, A.; Barnaba, F.; Virgili, S.; Passerini, G.; Mancinelli, E. On the Interplay between Desert Dust and Meteorology Based on WRF-Chem Simulations and Remote Sensing Observations in the Mediterranean Basin. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xia, X.; Zong, X.; Fan, X.; Chen, H.; Li, J. Dust Properties and Radiative Impacts at a Suburban Site during 2004–2017 in the North China Plain. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; He, Q. On the Association between Fine Dust Concentrations from Sand Dunes and Environmental Factors in the Taklimakan Desert. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creamean, J.M.; Suski, K.J.; Rosenfeld, D.; Cazorla, A.; DeMott, P.J.; Sullivan, R.C.; White, A.B.; Ralph, F.M.; Minnis, P.; Comstock, J.M.; et al. Dust and biological aerosols from the Sahara and Asia influence precipitation in the western US. Science 2013, 339, 1572–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsarpalis, K.; Katsafados, P.; Papadopoulos, A.; Mihalopoulos, N. Assessing desert dust indirect effects on cloud microphysics through a cloud nucleation scheme: A case study over the Western Mediterranean. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Huang, X.; Ding, A.; Fu, C. Dust-induced radiative feedbacks in north China: A dust storm episode modeling study using WRF-Chem. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 129, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Gong, S.; Chen, Y.; Shi, G.; Li, W. Radiative feedback of dust aerosols on the East Asian dust storms. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, D23214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Lei, Z.; Lijing, C.; Qi, G. Influence of the dust aerosols on meteorological fields during dust storm. Plateau Meteorol. 2017, 36, 1422–1432. [Google Scholar]
- Stanelle, T.; Vogel, B.; Vogel, H.; Bäumer, D.; Kottmeier, C. Feedback between dust particles and atmospheric processes over West Africa during dust episodes in March 2006 and June 2007. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 10771–10788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; An, J.; Qu, Y.; Xie, F.; Ma, S. Dust radiation effect on the weather and dust transport over the Taklimakan Desert, China. Atmos. Res. 2023, 284, 106600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemaître, C.; Flamant, C.; Cuesta, J.; Raut, J.C.; Chazette, P.; Formenti, P.; Pelon, J. Radiative heating rates profiles associated with a springtime case of Bodélé and Sudan dust transport over West Africa. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 8131–8150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, X.; Chen, H.; Hu, X.M.; Gao, L. Dust-planetary boundary layer interactions amplified by entrainment and advections. Atmos. Res. 2022, 278, 106359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Huang, J.; Li, J.; Jia, R.; Jiang, N.; Kang, L.; Ma, X.; Xie, T. Comparison of dust emissions, transport, and deposition between the Taklimakan Desert and Gobi Desert from 2007 to 2011. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2017, 60, 1338–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Duan, A.; Wang, T.; Wan, R.; Liu, X.; Li, W.; Wang, Z.; Liang, X. The Influence of Mechanical and Thermal Forcing by the Tibetan Plateau on Asian Climate. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 770–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Huang, J.; Zhao, C.; Qian, Y.; Leung, L.R.; Yang, B. Modeling the transport and radiative forcing of Taklimakan dust over the Tibetan Plateau: A case study in the summer of 2006. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 797–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Chen, S. The Tibetan Plateau as dust aerosol transit station in middle troposphere over northern East Asia: A case study. Atmos. Res. 2022, 280, 106416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.; Liu, Y.; Chen, B.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, J. Source and transportation of summer dust over the Tibetan Plateau. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 123, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, J.; Wang, T.; Li, J.; Yan, H.; He, Y. Aerosol-cloud interactions over the Tibetan Plateau: An overview. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2022, 234, 104216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Ma, Y.; Yang, K.; You, C. Tibetan Plateau impacts on global dust transport in the upper troposphere. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 4745–4756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Huang, J.; Zhao, C.; Jin, Q.; Ma, Y.; Yang, B. Modeling dust sources, transport, and radiative effects at different altitudes over the Tibetan Plateau. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 1507–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Minnis, P.; Yi, Y.; Tang, Q.; Wang, X.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Ayers, K.; Trepte, C.; Winker, D. Summer dust aerosols detected from CALIPSO over the Tibetan Plateau. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L18805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, D.; Huang, J.; Vaughan, M.; Uno, I.; Sugimoto, N.; Kittaka, C.; Trepte, C.; Wang, Z.; Hostetler, C.; et al. Airborne dust distributions over the Tibetan Plateau and surrounding areas derived from the first year of CALIPSO lidar observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 5045–5060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sato, Y.; Jia, R.; Xie, Y.; Huang, J.; Nakajima, T. Modeling study on the transport of summer dust and anthropogenic aerosols over the Tibetan Plateau. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 12581–12594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; He, Q.; Ge, X.; Abbas, A. Spatiotemporal distribution of aerosols over the Tibet Plateau and Tarim Basin (1980–2020). J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 374, 133958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Xia, X.; Che, H.; Wang, J.; Cong, Z.; Zhao, T.; Kang, S.; Zhang, X.; Yu, X.; Zhang, Y. Spatiotemporal variation of aerosol and potential long-range transport impact over the Tibetan Plateau, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 14637–14656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Hua, S.; Alam, K.; Dai, T.; Cheng, Y. Tibetan Plateau driven impact of Taklimakan dust on northern rainfall. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 234, 117583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Huang, J.; Hua, S.; Jia, R. Impact of dust-polluted convective clouds over the Tibetan Plateau on downstream precipitation. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 209, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Q.; Xu, Z.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Y.-F.; Zheng, H.; Shi, C.; Zhang, S.; Xie, C.; Yang, Z.-L. Evaluation and Intercomparison of Multiple Snow Water Equivalent Products over the Tibetan Plateau. J. Hydrometeorol. 2019, 20, 2043–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Luo, S.; Hao, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y. Observations of East Qinghai-Xizang Plateau Snow Cover Effects on Surface Energy and Water Exchange in Different Seasons. Plateau Meteorol. 2021, 40, 455–471. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, X.; Liu, X.; Che, H.; Xie, X.; Li, X.; Shi, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhao, T.; Liu, Y. Radiative feedbacks of dust in snow over eastern Asia in CAM4-BAM. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 12683–12698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Chen, S.; Chen, Y.; Gong, Y.; Lou, G.; Cheng, S.; Bi, H. Influence of Dust Aerosols on Snow Cover Over the Tibetan Plateau. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 839691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yuan, R.; Singh, V.P.; Xu, C.Y.; Fan, K.; Shen, Z.; Wang, G.; Zhao, J. Dynamic vulnerability of ecological systems to climate changes across the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 134, 108483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Wang, X.; Pang, G.; Wan, G.; Liu, Z. The Tibetan Plateau cryosphere: Observations and model simulations for current status and recent changes. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2019, 190, 353–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, P.; Wang, J.; Chen, X.; Ruan, J.; Ye, X.; Alavi, A.H. Next-generation remote sensing and prediction of sand and dust storms: State-of-the-art and future trends. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 42, 5277–5316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Wang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Hong, C.; Zhou, S. Simulation and evaluation of dust emissions with WRF-Chem (v3. 7.1) and its relationship to the changing climate over East Asia from 1980 to 2015. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 167, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Yahya, K.; Wu, S.Y.; Grell, G. Implementation and initial application of new chemistry-aerosol options in WRF/Chem for simulating secondary organic aerosols and aerosol indirect effects for regional air quality. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 115, 716–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kok, J.F.; Storelvmo, T.; Karydis, V.A.; Adebiyi, A.A.; Mahowald, N.M.; Evan, A.T.; He, C.; Leung, D.M. Mineral dust aerosol impacts on global climate and climate change. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, P.; Mejia, J.F. Impact of transported dust aerosols on precipitation over the Nepal Himalayas using convection-permitting WRF-Chem simulation. Atmos. Environ. X 2022, 15, 100179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, S.; Guo, Z.; Zhou, H.; Chen, Y.; Kang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Huang, G.; Liu, T.; Chen, C.; et al. The influence of dusts on radiation and temperature over the eastern Asia with a regional climate model. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 792, 148351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.; Liu, Y.; Hua, S.; Zhu, Q.; Shao, T. Estimation of the aerosol radiative effect over the Tibetan Plateau based on the lat-est CALIPSO product. J. Meteorol. Res. 2018, 32, 707–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Ma, X.; Wu, S.; Sha, T. Dust emission and transport in Northwest China: WRF-Chem simulation and comparisons with multi-sensor observations. Atmos. Res. 2020, 241, 104978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winker, D.M.; Hostetler, C.A.; Hunt, W.H. Cloud-Aerosol LIdar with Orthogonal Polarization (CALIOPE). In Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Toulouse, France, 21–25 July 2003; pp. 1514–1516. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, N.C.; Tsay, S.C.; King, M.D.; Herman, J.R. Deep blue retrievals of Asian aerosol properties during ACE-Asia. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 3180–3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NASA; LARC; SD; ASDC. CERES and GEO-Enhanced TOA, Within-Atmosphere and Surface Fluxes, Clouds and Aerosols 1-Hourly Terra-Aqua Edition 4A. 2017. Available online: https://asdc.larc.nasa.gov/project/CERES/CER_SYN1deg-1Hour_Terra-Aqua-MODIS_Edition4A (accessed on 1 November 2024).
- Doelling, D.R.; Loeb, N.G.; Keyes, D.F.; Nordeen, M.L.; Morstad, D.; Nguyen, C.; Wielicki, B.A.; Young, D.F.; Sun, M. Geostationary enhanced temporal interpolation for CERES flux products. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2013, 30, 1072–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randles, C.; Da Silva, A.; Buchard, V.; Colarco, P.; Darmenov, A.; Govindaraju, R.; Smirnov, A.; Holben, B.; Ferrare, R.; Hair, J.; et al. The MERRA-2 aerosol reanalysis, 1980 onward. Part I: System description and data assimilation evaluation. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 6823–6850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grell, G.A.; Peckham, S.E.; Schmitz, R.; McKeen, S.A.; Frost, G.; Skamarock, W.C.; Eder, B. Fully coupled “online” chemistry within the WRF model. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 6957–6975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fast, J.D.; Gustafson Jr, W.I.; Easter, R.C.; Zaveri, R.A.; Barnard, J.C.; Chapman, E.G.; Grell, G.A.; Peckham, S.E. Evolution of ozone, particulates, and aerosol direct radiative forcing in the vicinity of Houston using a fully coupled meteorology-chemistry-aerosol model. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111, D21305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.H.; Sun, W.Y. A one-dimensional time dependent cloud model. J. Meteorol. Soc. Japan. Ser. II 2002, 80, 99–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacono, M.J.; Delamere, J.S.; Mlawer, E.J.; Shephard, M.W.; Clough, S.A.; Collins, W.D. Radiative forcing by long-lived greenhouse gases: Calculations with the AER radiative transfer models. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113, D13103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Dudhia, J. Coupling an advanced land surface–hydrology model with the Penn State–NCAR MM5 modeling system. Part I: Model implementation and sensitivity. Mon. Weather Rev. 2001, 129, 569–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.Y.; Noh, Y.; Dudhia, J. A new vertical diffusion package with an explicit treatment of entrainment processes. Mon. Weather. Rev. 2006, 134, 2318–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grell, G.A.; Dévényi, D. A generalized approach to parameterizing convection combining ensemble and data assimilation techniques. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewson, M.; McGowan, H.; Phinn, S. Comparing remotely sensed and modelled aerosol properties for a region of low aerosol optical depth. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 22–27 July 2012; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 2512–2515. [Google Scholar]
- Gillette, D.A.; Passi, R. Modeling dust emission caused by wind erosion. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1988, 93, 14233–14242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, M.A.; Young, S.A.; Winker, D.M.; Powell, K.A.; Omar, A.H.; Liu, Z.; Hu, Y.; Hostetler, C.A. Fully automated analysis of space-based lidar data: An overview of the CALIPSO retrieval algorithms and data products. Laser Radar Tech. Atmos. Sens. 2004, 5575, 16–30. [Google Scholar]
- Winker, D.; Vaughan, M.; Hunt, B. The CALIPSO mission and initial results from CALIOP. In Proceedings of the Lidar Remote Sensing for Environmental Monitoring VII, Goa, India, 12 December 2006; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2006; Volume 6409, p. 640902. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Shen, H.; Weng, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Dou, P.; Zhang, L. Cloud and cloud shadow detection for optical satellite imagery: Features, algorithms, validation, and prospects. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2022, 188, 89–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, T.; Chen, S.; Huang, J.; Wu, D.; Lu, H.; Zhang, G.; Ma, X.; Chen, Z.; Luo, Y.; Ma, X. Influence of dynamic and thermal forcing on the meridional transport of Taklimakan Desert dust in spring and summer. J. Clim. 2019, 32, 749–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Yang, Y.; Fan, H.; Huang, J.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Kang, S.; Cong, Z.; Letu, H.; Menenti, M. Aerosol characteristics and impacts on weather and climate over the Tibetan Plateau. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2020, 7, 492–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.U.; Choe, A.; Park, M.S. A simulation of Asian dust events observed from 20 to 29 December 2009 in Korea by using ADAM2. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2013, 49, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, C. Impact of dust radiation effect on simulations of temperature and wind–A case study in Taklimakan Desert. Atmos. Res. 2022, 273, 106163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Shi, G.; Zhang, X.; Gong, S.; Tan, S.; Chen, B.; Che, H.; Li, T. Mesoscale modelling study of the interactions between aerosols and PBL meteorology during a haze episode in China Jing–Jin–Ji and its near surrounding region–Part 2: Aerosols’ radiative feedback effects. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 3277–3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.; Tegen, I. Climate response to soil dust aerosols. J. Clim. 1998, 11, 3247–3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usha, K.; Nair, V.S.; Babu, S.S. Deciphering the Role of Aerosol-Induced Snow Albedo Feedback on Dust Emission Over the Tibetan Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2022, 127, e2021JD036384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, W.K.; Kim, K.M. Impact of snow darkening by deposition of light-absorbing aerosols on snow cover in the Himalayas–Tibetan Plateau and influence on the Asian summer monsoon: A possible mechanism for the Blanford hypothesis. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Dataset | Source | Time Resolution | Spatial Resolution | Data Ranges (2016) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAL_LID_L2_VFM-Standard-V4-20 | CALIPSO | 5.92 s | 30 m (vertical) 333 m (horizontal) | 7.30–8.02 |
| MOD08_D3 | MODIS | 1 day | 1° × 1° | 7.29–8.01 |
| CERES_EBAF_Ed4.1 | CERES | 1 h | 1° × 1° | 7.30–8.02 |
| tavg1_2d_aer_Nx | MERRA-2 | 1 h | 0.5 ° × 0.625 ° | 7.29–8.01 |
| ERA5 | ECMWF ERA5 | 1 h | 0.25° × 0.25° | 7.29–8.01 |
| Ground-based Observation | CMA | 1 h | _ | 7.29–8.02 |
| Physics Schemes | Description |
|---|---|
| Microphysics | Lin et al. Scheme [53] |
| Longwave radiation | Rapid radiation transfer model (RRTMG) [54] |
| Shortwave radiation | Rapid radiation transfer model (RRTMG) [54] |
| Land surface | Unified Noah land surface model [55] |
| Planet boundary layer | Yonsei University scheme [56] |
| Cumulus parameterization | Grell 3D Ensemble scheme [57] |
| Chemistry | GOCART coupled with RACM-KPP [58] |
| Dust Emission | GOCART [59] |
| Horizontal resolution | 20 (km) |
| Time step | 80 (s) |
| T2 (°C) | PBLH (m) | RH2 (%) | SH (W/m2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TD | Daytime | −0.40 | −198.38 (16.36%) | 1.15 (4.21%) | −52.84 |
| Nighttime | 0.87 | 9.72 (1.91%) | −1.49 (3.84%) | 12.09 | |
| TP (without snow cover) | Daytime | 0.09 | 3.70 (0.32%) | −0.38 (0.78%) | 2.03 |
| Nighttime | 0.47 | 1.37 (0.54%) | −2.66 (3.83%) | 2.86 | |
| TP (with snow cover) | Daytime | −0.98 | −200.94 (23.20%) | 8.11 (12.19%) | −18.22 |
| Nighttime | −0.43 | 23.59 (9.22%) | 3.30 (3.70%) | −0.91 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, B.; Ji, H.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, M.; Qiu, R.; Luo, H.; An, W.; Tian, P.; et al. Surface-Dependent Meteorological Responses to a Taklimakan Dust Event During Summer near the Northern Slope of the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1561. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17091561
Wang B, Ji H, Zhang Z, Liang J, Zhang L, Li M, Qiu R, Luo H, An W, Tian P, et al. Surface-Dependent Meteorological Responses to a Taklimakan Dust Event During Summer near the Northern Slope of the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(9):1561. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17091561
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Binrui, Hongyu Ji, Zhida Zhang, Jiening Liang, Lei Zhang, Mengqi Li, Rui Qiu, Hongjing Luo, Weiming An, Pengfei Tian, and et al. 2025. "Surface-Dependent Meteorological Responses to a Taklimakan Dust Event During Summer near the Northern Slope of the Tibetan Plateau" Remote Sensing 17, no. 9: 1561. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17091561
APA StyleWang, B., Ji, H., Zhang, Z., Liang, J., Zhang, L., Li, M., Qiu, R., Luo, H., An, W., Tian, P., & Amonov, M. O. (2025). Surface-Dependent Meteorological Responses to a Taklimakan Dust Event During Summer near the Northern Slope of the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sensing, 17(9), 1561. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17091561






