Comparing Three Approaches of Evapotranspiration Estimation in Mixed Urban Vegetation: Field-Based, Remote Sensing-Based and Observational-Based Methods
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Need for Evapotranspiration (ET) Estimates for Urban Landscapes
1.2. Soil Water Balance
1.3. The WUCOLS Method
1.4. Remote Sensing Method
1.5. The Present Study
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.1.1. Soil Water Balance Components
2.1.2. Precipitation and Irrigation Data
2.1.3. Soil Moisture Content Measurement Using Neutron Probes
2.1.4. Drainage Measurement Using Lysimeters
2.1.5. Monitoring of Water Table Heights and Surface Runoff
2.2. Water Use Classification of Landscape Plants (WUCOLS)
2.3. MODIS ET Method
3. Results
3.1. SWB Components
3.2. WUCOLS ET Estimate
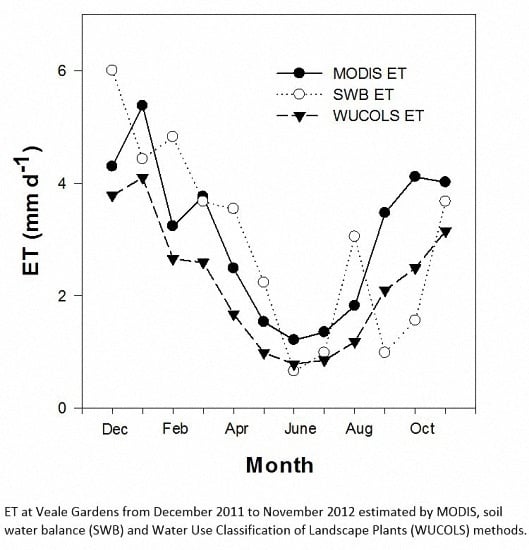
3.3. MODIS Estimate and Comparison of Methods
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Population Reference Bureau. World Population Data Sheet; Bureau, U.P.R., Ed.; Population Reference Bureau: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Mirzaei, P.A.; Haghighat, F. Approaches to study urban heat island—Abilities and limitations. Build. Environ. 2010, 45, 2192–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, M.; Oster, J.D. Crop and irrigation management strategies for saline-sodic soils and waters aimed at environmentally sustainable agriculture. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 323, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Järvi, L.; Grimmond, C.S.B.; Christen, A. The surface urban energy and water balance scheme (suews): Evaluation in los angeles and vancouver. J. Hydrol. 2011, 411, 219–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatta-Kassinos, D.; Kalavrouziotis, I.K.; Koukoulakis, P.H.; Vasquez, M.I. The risks associated with wastewater reuse and xenobiotics in the agroecological environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 3555–3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meli, S.; Porto, M.; Belligno, A.; Bufo, S.A.; Mazzatura, A.; Scopa, A. Influence of irrigation with lagooned urban wastewater on chemical and microbiological soil parameters in a citrus orchard under mediterranean condition. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 285, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, R.D.R.; Will, G.D.; Dawes, L.A.; Gardner, E.A.; Lyons, D.J. Phosphorus as a limiting factor on sustainable greywater irrigation. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 456–457, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabari, H. Evaluation of reference crop evapotranspiration equations in various climates. Water Resour. Manag. 2010, 24, 2311–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.; Pereira, L.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop Evapotranspiration-Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements-Fao Irrigation and Drainage Paper 56; FAO, Ed.; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1998; Volume 300. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, V.G.; Mein, R.G.; McMahon, T.A. Modelling the urban water cycle. Environ. Model. Softw. 2001, 16, 615–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri, H.; Beecham, S.; Anderson, S.; Hassanli, A.M.; Kazemi, F. Remote sensing techniques for predicting evapotranspiration from mixed vegetated surfaces. Urban Water J. 2015, 12, 380–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri, H.; Beecham, S.; Kazemi, F.; Hassanli, A.M. A review of ET measurement techniques for estimating the water requirements of urban landscape vegetation. Urban Water J. 2012, 10, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri, H.; Beecham, S.; Hassanli, A.M.; Ingleton, G. Variability of drainage and solute leaching in heterogeneous urban vegetation environ. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 4339–4347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaseef, N.R.; Yakir, D.; Rotenberg, E.; Schiller, G.; Cohen, S. Ecohydrology of a semi-arid forest: Partitioning among water balance components and its implications for predicted precipitation changes. Ecohydrology 2010, 3, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orfánus, T.; Eitzinger, J. Factors influencing the occurrence of water stress at field scale. Ecohydrology 2010, 3, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testi, L.; Villalobos, F.J.; Orgaz, F. Evapotranspiration of a young irrigated olive orchard in southern spain. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2004, 121, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizito, F.; Sène, M.; Dragila, M.I.; Lufafa, A.; Diedhiou, I.; Dossa, E.; Cuenca, R.; Selker, J.; Dick, R.P. Soil water balance of annual crop-native shrub systems in senegal's peanut basin: The missing link. Agric. Water Manag. 2007, 90, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, R.L. Using watershed water balance to evaluate the accuracy of eddy covariance evaporation measurements for three semiarid ecosystems. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2010, 150, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trambouze, W.; Bertuzzi, P.; Voltz, M. Comparison of methods for estimating actual evapotranspiration in a row-cropped vineyard. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1998, 91, 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri, H.; Beecham, S.; Hassanli, A.M.; Kazemi, F. Water requirements of urban landscape plants: A comparison of three factor-based approaches. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 57, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glenn, E.P.; Mexicano, L.; Garcia-Hernandez, J.; Nagler, P.L.; Gomez-Sapiens, M.M.; Tang, D.; Lomeli, M.A.; Ramirez-Hernandez, J.; Zamora-Arroyo, F. Evapotranspiration and water balance of an anthropogenic coastal desert wetland: Responses to fire, inflows and salinities. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 59, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri, H.; Beecham, S.; Anderson, S.; Nagler, P. High spatial resolution worldview-2 imagery for mapping ndvi and its relationship to temporal urban landscape evapotranspiration factors. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BOM. Annual Climate Summary; Commonwealth of Australia: Aelaide, Australia, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Keulen, H.V.; Seligman, N.G.; Benjamin, R.W. Simulation of water use and herbage growth in arid regions—A re-evaluation and further development of the model arid crop. Agric. Syst. 1981, 6, 159–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driessen, P.M. The water balance of a soil. In Modeling of Agricultural Production: Weather, Soils and Crops-Simulation Monographs, Pudoc; Keulen, H.V., Wolf, J., Eds.; Documentation-PUDOC: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1986; pp. 76–116. [Google Scholar]
- Sammis, T.; Sharma, P.; Shukla, M.K.; Wang, J.; Miller, D. A water-balance drip-irrigation scheduling model. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 113, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, J.; Mounzer, O.; Ruiz-Sánchez, M.C.; Abrisqueta, I.; Tapia, L.M.; Abrisqueta, J.M. Soil water balance trial involving capacitance and neutron probe measurements. Agric. Water Manag. 2009, 96, 905–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunusa, I.A.M.; Zeppel, M.J.B.; Fuentes, S.; Macinnis-Ng, C.M.O.; Palmer, A.R.; Eamus, D. An assessment of the water budget for contrasting vegetation covers associated with waste management. Hydrol. Process. 2010, 24, 1149–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evett, S.; Ibragimov, N.; Kamilov, B.; Esanbekov, Y.; Sarimsakov, M.; Shadmanov, J.; Mirhashimov, R.; Musaev, R.; Radjabov, T.; Muhammadiev, B. Neutron moisture meter calibration in six soils of uzbekistan affected by carbonate accumulation. Vadose Zone J. 2007, 6, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evett, S.R.; Tolk, J.A.; Howell, T.A. A depth control stand for improved accuracy with the neutron probe. Vadose Zone J. 2003, 2, 642–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyne, P.; Williams, D. Calibrating soil water monitoring devices. In Waterpak: A Guide for Irrigation Management in Cotton; Centre, A.C.R., Ed.; WATERpak: Narrabri, Australia, 2004; pp. 101–106. [Google Scholar]
- Ruprecht, J.K.; Schofield, N.J. In situ neutron moisture meter calibration in lateritic soils. Aust. J. Soil Res. 1990, 28, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Wierenga, P.J.; Graham, A.R.; Neuman, S.P. Neutron probe calibration in a vertically stratified vadose zone. Vadose Zone J. 2004, 3, 1400–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Walker, G.R.; Dawes, W.R. Water balance modelling: Concepts and applications. In Regional Water and Soil Assessment for Managing Sustainable Agriculture in China and Australia (ACIAR); Mcvicar, T.R., Li, R., Walker, J., Fitzpatrick, R.W., Liu, C., Eds.; Australian Centre for International Agricultural Research: Canberra, Australia, 2002; Volume 84, pp. 31–47. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, R.; Thomas, B.; Luitjes, K.; White, L. An Adaptive Management Framework for Reuse and Treated Wastewater from the Glenelg wwtp within the Adelaide Park Lands, Final Report; ARUP Water: Adelaide, Australia, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Pirone, M.; Papa, R.; Nicotera, M.V.; Urciuoli, G. Soil water balance in an unsaturated pyroclastic slope for evaluation of soil hydraulic behaviour and boundary conditions. J. Hydrol. 2015, 528, 63–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, L.R.; Jones, K.S. Wucols, Water Use Classification of Landscape Species: A Guide to the Water Needs of Landscape Plants; Department of Water Resources - Bulletins and Reports: Sacramento, CA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- NASA-MODIS; Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer. 2016. Available online: http://modis.gsfc.nasa.gov/ (accessed on 6 June 2016).
- Glenn, E.P.; Neale, C.M.U.; Hunsaker, D.J.; Nagler, P.L. Vegetation index-based crop coefficients to estimate evapotranspiration by remote sensing in agricultural and natural ecosystems. Hydrol. Process. 2011, 25, 4050–4062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huete, A.R. Vegetation indices, remote sensing and forest monitoring. Geogr. Compass 2012, 6, 513–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huete, A.R.; Glenn, E.P. Remote sensing of ecosystem structure and function. In Advances in Environmental Remote Sensing; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011; pp. 291–319. [Google Scholar]
- Glenn, E.P.; Nagler, P.L.; Huete, A.R. Vegetation index methods for estimating evapotranspiration by remote sensing. Surv. Geophys. 2010, 31, 531–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagler, P.; Glenn, E.; Nguyen, U.; Scott, R.; Doody, T. Estimating riparian and agricultural actual evapotranspiration by reference evapotranspiration and modis enhanced vegetation index. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, L.R.; Matheny, N.P.; Clark, J.R. A Guide to Estimating Irrigation Water Needs of Landscape Plantings in California, the Landscape Coefficient Method and Wucols III; University of California Cooperative Extension, California Department of Water Resources: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, G.; Cabrera, R.I. Growth and physiological responses of landscape plants to saline water irrigation. HortScience 2010, 45, 1605–1609. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, D. Remote Sensing Based Vegetation Indices Analysis to Improve Water Resources Management in Urban Environment. Aquat. Proced. 2015, 4, 1374–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Howell, T.A.; Jensen, M.E. Evapotranspiration information reporting: I. Factors governing measurement accuracy. Agric. Water Manag. 2011, 98, 899–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagler, P.L.; Cleverly, J.; Glenn, E.; Lampkin, D.; Huete, A.; Wan, Z. Predicting riparian evapotranspiration from modis vegetation indices and meteorological data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 94, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maselli, F.; Papale, D.; Chiesi, M.; Matteucci, G.; Angeli, L.; Raschi, A.; Seufert, G. Operational monitoring of daily evapotranspiration by the combination of modis ndvi and ground meteorological data: Application and evaluation in central italy. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 152, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Guan, H.; Gutiérrez-Jurado, H.A.; Simmons, C.T. Examination of water budget using satellite products over australia. J. Hydrol. 2014, 511, 546–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.D.; Belitz, K. A remote sensing approach for estimating the location and rate of urban irrigation in semi-arid climates. J. Hydrol. 2012, 414–415, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Hong, Y.; Khan, S.I.; Huang, M.; Vieux, B.; Caliskan, S.; Grout, T.; Baldocchi, D.D. Actual evapotranspiration estimation for different land use and land cover in urban regions using landsat 5 data. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2010, 4, 041873. [Google Scholar]





| Month | Precipitation (mm) | Irrigation (mm) | Drainage (mm) | Soil Moisture (mm) | ET SWB (mm) | ET WUCOLS (mm) | ET MODIS (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11 December | 22.0 | 119.28 | 0.34 | 1050.8 | 183 | 114 | 125 |
| 12 January | 26.6 | 145.08 | 0.08 | 1087.13 | 135 | 125 | 150 |
| 12 Feburary | 18.0 | 159.92 | 0.08 | 1118.274 | 147 | 81 | 96 |
| 12 March | 34.2 | 90.68 | 0.28 | 1131.22 | 112 | 79 | 105 |
| 12 April | 70.2 | 49.28 | 3.51 | 1139.25 | 108 | 51 | 68 |
| 12 May | 28.8 | 46.36 | 8.58 | 1138.13 | 68 | 30 | 42 |
| 12 June | 61.0 | 0 | 37.25 | 1142.31 | 20 | 24 | 31 |
| 12 July | 130.5 | 0 | 67.08 | 1175.27 | 30 | 26 | 42 |
| 12 Augest | 67.8 | 0 | 11.17 | 1138.68 | 93 | 36 | 59 |
| 12 September | 64.4 | 0 | 35.42 | 1138.46 | 29 | 64 | 110 |
| 12 October | 17.8 | 44.56 | 12.33 | 1141.12 | 47 | 76 | 106 |
| 12 November | 18.9 | 65.32 | 0.02 | 1113.8 | 112 | 96 | 154 |
| Total | 560 | 720 | 176 | - | 1084 | 802 | 1088 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nouri, H.; Glenn, E.P.; Beecham, S.; Chavoshi Boroujeni, S.; Sutton, P.; Alaghmand, S.; Noori, B.; Nagler, P. Comparing Three Approaches of Evapotranspiration Estimation in Mixed Urban Vegetation: Field-Based, Remote Sensing-Based and Observational-Based Methods. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8060492
Nouri H, Glenn EP, Beecham S, Chavoshi Boroujeni S, Sutton P, Alaghmand S, Noori B, Nagler P. Comparing Three Approaches of Evapotranspiration Estimation in Mixed Urban Vegetation: Field-Based, Remote Sensing-Based and Observational-Based Methods. Remote Sensing. 2016; 8(6):492. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8060492
Chicago/Turabian StyleNouri, Hamideh, Edward P. Glenn, Simon Beecham, Sattar Chavoshi Boroujeni, Paul Sutton, Sina Alaghmand, Behnaz Noori, and Pamela Nagler. 2016. "Comparing Three Approaches of Evapotranspiration Estimation in Mixed Urban Vegetation: Field-Based, Remote Sensing-Based and Observational-Based Methods" Remote Sensing 8, no. 6: 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8060492
APA StyleNouri, H., Glenn, E. P., Beecham, S., Chavoshi Boroujeni, S., Sutton, P., Alaghmand, S., Noori, B., & Nagler, P. (2016). Comparing Three Approaches of Evapotranspiration Estimation in Mixed Urban Vegetation: Field-Based, Remote Sensing-Based and Observational-Based Methods. Remote Sensing, 8(6), 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8060492