Modeling the Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Gross Domestic Product in China Using Extended Temporal Coverage Nighttime Light Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials
3. Methods
3.1. Correction of the DMSP-OLS Data
3.1.1. Intercalibration
3.1.2. Intra-Annual Composition
3.1.3. Inter-Annual Series Correction
3.2. Correction of the NPP-VIIRS Data
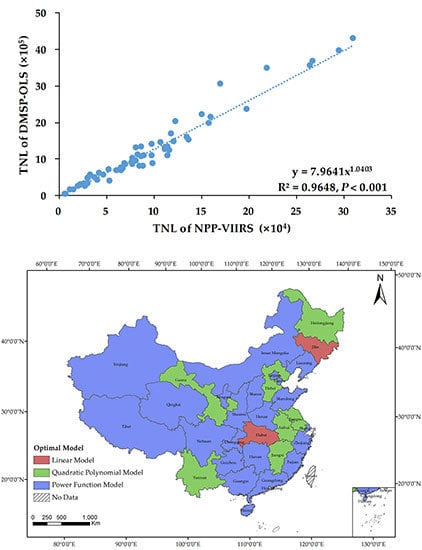
3.3. Temporal Coverage Extension of the Nighttime Light Data
3.4. Modeling the Spatiotemporal Dynamics of the GDP
4. Results
4.1. Extended Temporal Coverage Results for the Nighttime Light Data
4.2. Modeling Results for the Spatiotemporal Dynamics of the GDP
4.2.1. Modeling Results at the Country Level
4.2.2. Modeling Results at the Provincial Level
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Henderson, J.V.; Storeygard, A.; Weil, D.N. Measuring economic growth from outer space. Am. Econ. Rev. 2012, 102, 994–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, T.; Powell, R.L.; Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K.E.; Sutton, P.C.; Anderson, S. Shedding light on the global distribution of economic activity. Open Geogr. J. 2010, 3, 148–161. [Google Scholar]
- Feige, E.L.; Urban, I. Measuring underground (unobserved, non-observed, unrecorded) economies in transition countries: Can we trust GDP ? J. Compar. Econ. 2008, 36, 287–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, W.; Peng, J. Exploring factors affecting the relationship between light consumption and GDP based on DMSP/OLS nighttime satellite imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 134, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Yu, B.; Huang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Yin, B.; Chen, Z.; Chen, L.; Wu, J. Evaluating the ability of NPP-VIIRS nighttime light data to estimate the gross domestic product and the electric power consumption of China at multiple scales: A comparison with DMSP-OLS data. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 1705–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics of the People’s Republic of China. Available online: http://www.stats.gov.cn/tjzs/cjwtjd/201407/t20140714_580886.html (accessed on 11 November 2016).
- Henderson, V.; Storeygard, A.; Weil, D.N. A bright idea for measuring economic growth. Am. Econ. Rev. 2011, 101, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Nordhaus, W.D. Using luminosity data as a proxy for economic statistics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 8589–8594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K.E.; Kihn, E.A.; Kroehl, H.W.; Davis, E.R.; Davis, C.W. Relation between satellite observed visible-near infrared emissions, population, economic activity and electric power consumption. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1997, 18, 1373–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doll, C.H.; Muller, J.-P.; Elvidge, C.D. Night-time imagery as a tool for global mapping of socioeconomic parameters and greenhouse gas emissions. Ambio 2000, 29, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Imhoff, M.L.; Baugh, K.E.; Hobson, V.R.; Nelson, I.; Safran, J.; Dietz, J.B.; Tuttle, B.T. Night-time lights of the world: 1994–1995. ISPRS J. Photogram. Remote Sens. 2001, 56, 81–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebener, S.; Murray, C.; Tandon, A.; Elvidge, C.C. From wealth to health: Modelling the distribution of income per capita at the sub-national level using night-time light imagery. Int. J. Health Geogr. 2005, 4, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutton, P.C.; Elvidge, C.D.; Ghosh, T. Estimation of gross domestic product at sub-national scales using nighttime satellite imagery. Int. J. Ecol. Econ. Stats. 2007, 8, 5–21. [Google Scholar]
- An Estimate of Gross Domestic Product (GDP) Derived from Satellite Data. Available online: https://ngdc.noaa.gov/eog/dmsp/download_gdp.html (accessed on 18 October 2016).
- Elvidge, C.D.; Hsu, F.C.; Baugh, K.E.; Ghosh, T. National trends in satellite observed lighting: 1992–2012. In Global Urban Monitoring and Assessment through Earth Observation; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; pp. 97–118. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, N.; Currit, N.; Samson, E. Net primary production and gross domestic product in China derived from satellite imagery. Ecol. Econ. 2011, 70, 921–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Zhou, C.; Pei, T.; Haynie, S.; Fan, J. Quantitative estimation of urbanization dynamics using time series of DMSP/OLS nighttime light data: A comparative case study from China’s cities. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 124, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baugh, K.; Hsu, F.-C.; Elvidge, C.D.; Zhizhin, M. Nighttime lights compositing using the VIIRS day-night band: Preliminary results. Proc. Asia Pac. Adv. Netw. 2013, 35, 70–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Zhizhin, M.; Hsu, F.C.; Baugh, K.E. VIIRS nightfire: Satellite pyrometry at night. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 4423–4449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K.E.; Zhizhin, M.; Hsu, F.-C. Why VIIRS data are superior to DMSP for mapping nighttime lights. Proc. Asia Pac. Adv. Netw. 2013, 35, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, C.; Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K. Urban Remote Sensing Event (JURSE), 2013 Joint. In Mapping Urban Structure and Spatial Connectivity with VIIRS and OLS Night Light Imagery, Urban Remote Sensing Event (JURSE); IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 230–233. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Tian, H.; Liu, M.; Zhuang, D.; Melillo, J.M.; Zhang, Z. China’s changing landscape during the 1990s: Large-scale land transformations estimated with satellite data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L02405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Tian, H.; Zhou, G.; Ge, H. Regional mapping of human settlements in southeastern China with multisensor remotely sensed data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3668–3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Normile, D. China’s living laboratory in urbanization. Science 2008, 319, 740–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Xu, H.; Chen, X.; Li, C. Potential of NPP-VIIRS nighttime light imagery for modeling the regional economy of China. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 3057–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, G. The suitability of different nighttime light data for GDP estimation at different spatial scales and regional levels. Sustainability 2017, 9, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, C.; Pozzi, F.; Elvidge, C. Spatial analysis of global urban extent from DMSP-OLS night lights. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 96, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Version 4 DMSP-OLS Nighttime Lights Time Series. Available online: https://ngdc.noaa.gov/eog/DMSP/downloadV4composites.html (accessed on 12 October 2016).
- Baugh, K.; Elvidge, C.; Ghosh, T.; Ziskin, D. Development of a 2009 stable lights product using DMSP-OLS data. Proc. Asia Pac. Adv. Netw. 2010, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Radiance Calibrated Nighttime Lights. Available online: https://ngdc.noaa.gov/eog/DMSP/download_radcal.html (accessed on 20 October 2016).
- Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K.E.; Dietz, J.B.; Bland, T.; Sutton, P.C.; Kroehl, H.W. Radiance calibration of DMSP-OLS low-light imaging data of human settlements. Remote Sens. Environ. 1999, 68, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziskin, D.; Baugh, K.; Hsu, F.-C.; Elvidge, C.D. Methods used for the 2006 radiance lights. Proc. Asia Pac. Adv. Netw. 2010, 30, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; He, S.; Peng, J.; Li, W.; Zhong, X. Intercalibration of DMSP-OLS night-time light data by the invariant region method. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 7356–7368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Chen, Y.; Yu, B.; Xu, T.; Yang, C.; Li, L.; Huang, C.; Chen, Z.; Liu, R.; Wu, J. Detecting spatiotemporal dynamics of global electric power consumption using DMSP-OLS nighttime stable light data. Appl. Energy 2016, 184, 450–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VIIRS DNB Cloud Free Composites. Available online: https://ngdc.noaa.gov/eog/VIIRS/download_monthly.html (accessed on 3 December 2016).
- Dou, Y.; Liu, Z.; He, C.; Yue, H. Urban land extraction using VIIRS nighttime light data: An evaluation of three popular methods. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Ma, Q.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Q. Modeling the spatiotemporal dynamics of electric power consumption in mainland China using saturation-corrected DMSP/OLS nighttime stable light data. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2013, 7, 993–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; He, C.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, Q.; Yang, Y. Extracting the dynamics of urban expansion in China using DMSP-OLS nighttime light data from 1992 to 2008. Landscape Urban Plan. 2012, 106, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Zhou, Y.; Samson, E.L. Correcting incompatible dn values and geometric errors in nighttime lights time-series images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 2039–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Ziskin, D.; Baugh, K.E.; Tuttle, B.T.; Ghosh, T.; Pack, D.W.; Erwin, E.H.; Zhizhin, M. A fifteen year record of global natural gas flaring derived from satellite data. Energies 2009, 2, 595–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Graus, W.; Worrell, E.; Huang, B. Estimating CO2 (carbon dioxide) emissions at urban scales by DMSP/OLS (Defense Meteorological Satellite Program’s Operational Linescan System) nighttime light imagery: Methodological challenges and a case study for China. Energy 2014, 71, 468–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, Y. Urban mapping using DMSP/OLS stable night-time light: A review. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Seto, K.C. Mapping urbanization dynamics at regional and global scales using multi-temporal DMSP/OLS nighttime light data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2320–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Yu, B.; Hu, Y.; Huang, C.; Chen, Y.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wu, J. Modeling and mapping total freight traffic in China using NPP-VIIRS nighttime light composite data. Gisci. Remote Sens. 2015, 52, 274–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Weng, Q. Detecting urban-scale dynamics of electricity consumption at Chinese cities using time-series DMSP-OLS (Defense Meteorological Satellite Program-Operational Linescan System) nighttime light imageries. Energy 2016, 100, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, C. Modeling the population of China using DMSP operational linescan system nighttime data. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sensing 2001, 67, 1037–1047. [Google Scholar]
- Townsend, A.C.; Bruce, D.A. The use of night-time lights satellite imagery as a measure of Australia’s regional electricity consumption and population distribution. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 31, 4459–4480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, W.; Gao, J.; Yang, X. Estimation of gross domestic product using multi-sensor remote sensing data: A case study in Zhejiang province, East China. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 7260–7275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, J. Estimating census district populations from satellite imagery: Some approaches and limitations. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 2071–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Development Research Center of the State Council of China. Coordinated Regional Development Strategy and Policy Reports; Development Research Center of the State Council of China: Beijing, China, 2005.
- Zhou, Y.; Ma, T.; Zhou, C.; Xu, T. Nighttime light derived assessment of regional inequality of socioeconomic development in China. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 1242–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Yang, X.; Gao, B.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Y. Application of DMSP/OLS nighttime light images: A meta-analysis and a systematic literature review. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 6844–6866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Safran, J.; Tuttle, B.; Sutton, P.; Cinzano, P.; Pettit, D.; Arvesen, J.; Small, C. Potential for global mapping of development via a nightsat mission. GeoJournal 2007, 69, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Ma, T.; Zhou, C.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, T. Comparative estimation of urban development in China’s cities using socioeconomic and DMSP/OLS night light data. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 7840–7856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Qu, G.; Wang, W. Estimating land development time lags in China using DMSP/OLS nighttime light image. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 882–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Huang, X.; Yang, H.; Chuai, X.; Li, Y.; Qu, J.; Zhang, Z. Situation and determinants of household carbon emissions in Northwest China. Habit. Int. 2016, 51, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, X.; Yang, H.; Zhong, T. Environmental effects of land-use/cover change caused by urbanization and policies in Southwest China Karst area–A case study of Guiyang. Habit. Int. 2014, 44, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Huang, X.; Yang, H.; Chuai, X.; Wu, C. Convergence of carbon intensity in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Habit. Int. 2017, 60, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Yang, H.; Huang, X.; Chuai, X.; Wu, C. Multi-sectoral decomposition in decoupling industrial growth from carbon emissions in the developed Jiangsu Province, China. Energy 2015, 82, 414–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Yang, H.; Wang, L.; Huang, X.; Zeng, C.; Wu, H.; Ma, X.; Song, X.; Wei, Y. Optimization of industry structure based on water environmental carrying capacity under uncertainty of the Huai River Basin within Shandong Province, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 4594–4604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H. China must continue the momentum of green law. Nature 2014, 509, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Satellite | Year | a | b | Satellite | Year | a | b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F10 | 1992 | 0.214 | 2.110 | F15 | 2001 | 0.197 | 2.155 |
| F10 | 1993 | 0.255 | 2.000 | F15 | 2002 | 0.206 | 2.105 |
| F10 | 1994 | 0.238 | 2.028 | F15 | 2003 | 0.329 | 1.845 |
| F12 | 1994 | 0.196 | 2.160 | F15 | 2004 | 0.321 | 1.842 |
| F12 | 1995 | 0.200 | 2.128 | F15 | 2005 | 0.283 | 1.916 |
| F12 | 1996 | 0.200 | 2.128 | F15 | 2006 | 0.288 | 1.898 |
| F12 | 1997 | 0.194 | 2.146 | F15 | 2007 | 0.294 | 1.887 |
| F12 | 1998 | 0.181 | 2.188 | F16 | 2004 | 0.233 | 2.024 |
| F12 | 1999 | 0.163 | 2.278 | F16 | 2005 | 0.268 | 1.934 |
| F14 | 1997 | 0.253 | 1.976 | F16 | 2006 | 0.256 | 1.965 |
| F14 | 1998 | 0.242 | 2.000 | F16 | 2007 | 0.219 | 2.049 |
| F14 | 1999 | 0.248 | 1.980 | F16 | 2008 | 0.226 | 2.033 |
| F14 | 2000 | 0.242 | 2.000 | F16 | 2009 | 0.216 | 2.083 |
| F14 | 2001 | 0.213 | 2.079 | F18 | 2010 | 0.154 | 2.326 |
| F14 | 2002 | 0.233 | 2.016 | F18 | 2011 | 0.201 | 2.132 |
| F14 | 2003 | 0.243 | 1.988 | F18 | 2012 | 0.185 | 2.169 |
| F15 | 2000 | 0.194 | 2.151 | F18 | 2013 | 0.185 | 2.165 |
| Province | 2012 | 2013 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DMSP-OLS TNL | Extended TNL | RE (%) | DMSP-OLS TNL | Extended TNL | RE (%) | |
| Beijing | 868,571.94 | 869,042.45 | 0.05 | 905,903.10 | 951,355.48 | 5.02 |
| Tianjin | 703,545.22 | 746,497.03 | 6.11 | 768,575.13 | 835,504.21 | 8.71 |
| Hebei | 2,032,137.66 | 1,556,920.89 | −23.39 | 2,238,316.98 | 1,937,483.21 | −13.44 |
| Shanxi | 1,342,767.96 | 1,089,614.71 | −18.85 | 1,457,144.20 | 1,350,146.02 | −7.34 |
| Inner Mongolia | 1,317,047.05 | 1,015,907.00 | −22.86 | 1,409,399.81 | 1,232,594.12 | −12.54 |
| Liaoning | 1,491,362.08 | 1,532,125.78 | 2.73 | 1,596,523.05 | 1,724,975.76 | 8.05 |
| Jilin | 749,307.58 | 832,034.67 | 11.04 | 855,678.48 | 963,947.10 | 12.65 |
| Heilongjiang | 1,314,178.27 | 1,411,571.96 | 7.41 | 1,523,745.99 | 1,741,625.34 | 14.30 |
| Shanghai | 816,233.48 | 1,110,917.84 | 36.10 | 887,388.60 | 1,239,955.79 | 39.73 |
| Jiangsu | 3,680,608.49 | 3,509,035.95 | −4.66 | 4,308,393.36 | 4,096,784.55 | −4.91 |
| Zhejiang | 2,161,638.14 | 2,059,749.70 | −4.71 | 2,361,509.36 | 2,568,020.33 | 8.74 |
| Anhui | 1,079,116.60 | 1,085,624.14 | 0.60 | 1,346,950.22 | 1,450,477.27 | 7.69 |
| Fujian | 1,117,935.29 | 1,033,994.16 | −7.51 | 1,306,931.81 | 1,423,318.60 | 8.91 |
| Jiangxi | 477,494.68 | 364,004.28 | −23.77 | 635,416.26 | 517,184.56 | −18.61 |
| Shandong | 3,062,092.93 | 2,193,081.00 | −28.38 | 3,490,370.24 | 2,856,238.90 | −18.17 |
| Henan | 1,709,321.21 | 1,502,155.22 | −12.12 | 1,999,349.99 | 2,028,319.28 | 1.45 |
| Hubei | 723,142.54 | 644,961.65 | −10.81 | 1,023,120.28 | 968,570.70 | −5.33 |
| Hunan | 506,236.28 | 369,085.71 | −27.09 | 763,774.88 | 804,439.05 | 5.32 |
| Guangdong | 3,579,626.22 | 3,479,545.87 | −2.80 | 3,970,102.44 | 3,890,371.65 | −2.01 |
| Guangxi | 586,690.31 | 401,061.07 | −31.64 | 707,193.83 | 810,857.53 | 14.66 |
| Hainan | 259,255.69 | 232,785.55 | −10.21 | 283,777.66 | 257,632.97 | −9.21 |
| Chongqing | 342,311.97 | 319,365.17 | −6.70 | 430,971.42 | 488,065.43 | 13.25 |
| Sichuan | 804,809.15 | 1,059,718.49 | 31.67 | 1,098,418.44 | 1,452,896.88 | 32.27 |
| Guizhou | 261,801.09 | 324,743.63 | 24.04 | 411,543.14 | 654,998.85 | 59.16 |
| Yunnan | 890,418.66 | 854,610.21 | −4.02 | 970,447.49 | 1,017,251.10 | 4.82 |
| Tibet | 54,268.23 | 64,777.11 | 19.36 | 59,741.55 | 74,223.86 | 24.24 |
| Shaanxi | 1,111,777.06 | 1,124,106.54 | 1.11 | 1,263,576.61 | 1,409,005.17 | 11.51 |
| Gansu | 498,009.42 | 448,341.41 | −9.97 | 578,400.64 | 574,393.24 | −0.69 |
| Qinghai | 158,669.97 | 135,821.67 | −14.40 | 178,478.81 | 172,379.87 | −3.42 |
| Ningxia | 310,587.95 | 272,089.48 | −12.40 | 337,160.76 | 359,709.51 | 6.69 |
| Xinjiang | 1,101,950.18 | 1,235,927.81 | 12.16 | 1,235,204.49 | 1,471,523.52 | 19.13 |
| MARE (%) | − | − | 13.83 | − | − | 12.97 |
| Year | Percentage of Absolute RE (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| High Accuracy (%) | Moderate Accuracy (%) | Inaccuracy (%) | |
| 2012 | 83.87 | 16.13 | 0.00 |
| 2013 | 90.32 | 6.45 | 3.23 |
| Year | Statistical GDP (Billion RMB) | Modeling in Time Series | Modeling in Provincial Units | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estimated GDP (Billion RMB) | RE (%) | Estimated GDP (Billion RMB) | RE (%) | R2 | ||
| 1992 | 2719.45 | 2436.05 | −10.42 | 1916.55 | −29.52 | 0.56 |
| 1993 | 3567.32 | 3952.71 | 10.80 | 2233.19 | −37.40 | 0.65 |
| 1994 | 4863.75 | 5637.04 | 15.90 | 2851.05 | −41.38 | 0.64 |
| 1995 | 6133.99 | 6646.20 | 8.35 | 3898.66 | −36.44 | 0.67 |
| 1996 | 7181.36 | 6896.10 | −3.97 | 4531.75 | −36.90 | 0.66 |
| 1997 | 7971.50 | 7371.36 | −7.53 | 5116.33 | −35.82 | 0.68 |
| 1998 | 8519.55 | 8392.86 | −1.49 | 5777.19 | −32.19 | 0.71 |
| 1999 | 9056.44 | 8936.78 | −1.32 | 6276.96 | −30.69 | 0.73 |
| 2000 | 10,028.01 | 10,413.99 | 3.85 | 7113.27 | −29.07 | 0.75 |
| 2001 | 11,086.31 | 11,724.99 | 5.76 | 8109.49 | −26.85 | 0.77 |
| 2002 | 12,171.74 | 15,158.81 | 24.54 | 9997.43 | −17.86 | 0.85 |
| 2003 | 13,742.20 | 18,636.02 | 35.61 | 11,487.16 | −16.41 | 0.88 |
| 2004 | 16,184.02 | 21,122.73 | 30.52 | 14,319.63 | −11.52 | 0.88 |
| 2005 | 18,731.89 | 22,111.01 | 18.04 | 17,517.64 | −6.48 | 0.90 |
| 2006 | 21,943.85 | 25,153.04 | 14.62 | 20,978.78 | −4.40 | 0.91 |
| 2007 | 27,023.23 | 27,015.07 | −0.03 | 25,342.82 | −6.22 | 0.91 |
| 2008 | 31,951.55 | 28,151.61 | −11.89 | 29,321.33 | −8.23 | 0.89 |
| 2009 | 34,908.14 | 30,168.28 | −13.58 | 32,669.75 | −6.41 | 0.86 |
| 2010 | 41,303.03 | 37,571.10 | −9.04 | 39,417.30 | −4.57 | 0.88 |
| 2011 | 48,930.06 | 42,197.08 | −13.76 | 45,750.55 | −6.50 | 0.88 |
| 2012 | 54,036.74 | 45,448.23 | −15.89 | 50,701.78 | −6.17 | 0.86 |
| 2013 | 59,524.44 | 53,284.03 | −10.48 | 57,181.25 | −3.94 | 0.88 |
| 2014 | 64,397.40 | 68,086.46 | 5.73 | 70,282.66 | 9.14 | 0.82 |
| 2015 | 68,550.58 | 78,015.00 | 13.81 | 75,757.34 | 10.51 | 0.81 |
| MARE (%) | − | − | 11.96 | − | 18.94 | − |
| Province | Linear | Quadratic | Power | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | MARE (%) | R2 | MARE (%) | R2 | MARE (%) | |
| Beijing | 0.93 | 51.00 | 0.99 | 11.55 | 0.99 | 10.94 |
| Tianjin | 0.96 | 53.69 | 0.99 | 12.15 | 0.99 | 7.91 |
| Hebei | 0.99 | 16.06 | 0.99 | 8.43 | 0.99 | 9.52 |
| Shanxi | 0.96 | 36.28 | 0.96 | 31.85 | 0.96 | 16.90 |
| Inner Mongolia | 0.99 | 15.97 | 0.99 | 18.94 | 0.98 | 15.28 |
| Liaoning | 0.98 | 12.84 | 0.98 | 12.59 | 0.97 | 11.28 |
| Jilin | 0.95 | 16.41 | 0.98 | 20.85 | 0.95 | 17.93 |
| Heilongjiang | 0.92 | 22.12 | 0.97 | 13.64 | 0.92 | 19.63 |
| Shanghai | 0.89 | 20.19 | 0.91 | 27.32 | 0.94 | 20.05 |
| Jiangsu | 0.98 | 19.89 | 0.99 | 12.68 | 0.97 | 13.34 |
| Zhejiang | 0.97 | 18.46 | 0.97 | 15.31 | 0.97 | 13.28 |
| Anhui | 0.97 | 20.33 | 0.99 | 11.35 | 0.96 | 15.34 |
| Fujian | 0.98 | 13.39 | 0.98 | 23.85 | 0.98 | 10.87 |
| Jiangxi | 0.95 | 24.98 | 0.96 | 23.46 | 0.93 | 23.95 |
| Shandong | 0.94 | 34.92 | 0.97 | 12.74 | 0.98 | 12.65 |
| Henan | 0.98 | 15.87 | 0.98 | 16.45 | 0.98 | 12.25 |
| Hubei | 0.95 | 16.89 | 0.96 | 25.38 | 0.95 | 17.00 |
| Hunan | 0.93 | 23.29 | 0.94 | 28.08 | 0.93 | 22.91 |
| Guangdong | 0.94 | 45.17 | 0.97 | 17.53 | 0.98 | 11.98 |
| Guangxi | 0.97 | 16.67 | 0.97 | 21.14 | 0.97 | 13.00 |
| Hainan | 0.98 | 13.60 | 0.98 | 12.34 | 0.99 | 7.76 |
| Chongqing | 0.94 | 21.25 | 0.96 | 27.61 | 0.94 | 19.86 |
| Sichuan | 0.90 | 32.38 | 0.96 | 27.32 | 0.95 | 19.15 |
| Guizhou | 0.92 | 35.19 | 0.97 | 25.73 | 0.95 | 19.81 |
| Yunnan | 0.98 | 21.45 | 0.99 | 10.35 | 0.98 | 10.46 |
| Tibet | 0.97 | 16.67 | 0.97 | 25.67 | 0.98 | 12.58 |
| Shaanxi | 0.98 | 11.92 | 0.98 | 21.00 | 0.98 | 10.93 |
| Gansu | 0.96 | 22.42 | 0.99 | 13.83 | 0.94 | 19.75 |
| Qinghai | 0.98 | 13.29 | 0.99 | 17.91 | 0.98 | 12.25 |
| Ningxia | 0.96 | 16.30 | 0.98 | 23.97 | 0.97 | 16.12 |
| Xinjiang | 0.88 | 31.73 | 0.96 | 36.76 | 0.94 | 17.58 |
| Mean | 0.95 | 23.57 | 0.97 | 19.61 | 0.96 | 14.91 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, X.; Ma, M.; Yang, H.; Ge, W. Modeling the Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Gross Domestic Product in China Using Extended Temporal Coverage Nighttime Light Data. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 626. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9060626
Zhu X, Ma M, Yang H, Ge W. Modeling the Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Gross Domestic Product in China Using Extended Temporal Coverage Nighttime Light Data. Remote Sensing. 2017; 9(6):626. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9060626
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Xiaobo, Mingguo Ma, Hong Yang, and Wei Ge. 2017. "Modeling the Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Gross Domestic Product in China Using Extended Temporal Coverage Nighttime Light Data" Remote Sensing 9, no. 6: 626. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9060626
APA StyleZhu, X., Ma, M., Yang, H., & Ge, W. (2017). Modeling the Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Gross Domestic Product in China Using Extended Temporal Coverage Nighttime Light Data. Remote Sensing, 9(6), 626. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9060626