Discriminative Feature Metric Learning in the Affinity Propagation Model for Band Selection in Hyperspectral Images
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
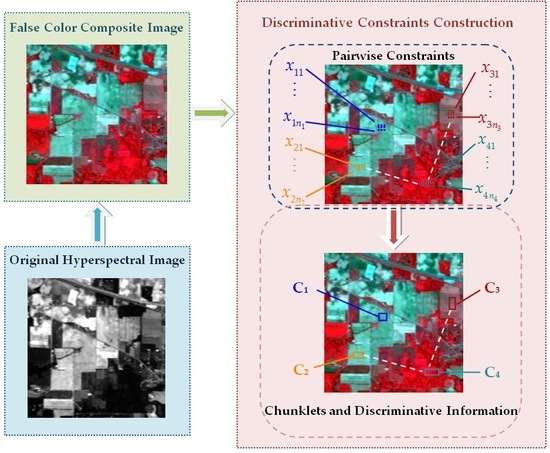
2.1. Construction of Discriminative Constraints
- Spectral similarity: HSI pixels that are similar in the feature space have a high probability of belonging to the same class (and vice versa).
- Spatial correlation: HSI pixels that are spatially near each other have a high probability of belonging to the same class, while pixels that are far away from each other in the spatial domain may belong to different classes.
2.2. Learning Discriminative Feature Metric
2.3. Discriminative Feature Metric-Based Affinity Propagation
| Proposed Discriminative Feature Metric-Based Affinity Propagation |
| Input: Hyperspectral dataset X, Discriminative Constraints C and D. Output: Representative bands set Y Procedure:
The damping factor is used in over-relaxation methods to avoid numerical oscillations when computing responsibilities and availabilities with simple updating rules. The two types of messages could be damped according to the following equations:
|
3. Experimental Results
3.1. Dataset Description
3.2. Experimental Design
- Maximum variance-based principal component analysis (MVPCA) [10]: MV criteria used to prioritize bands;
- AP [12]: standard AP with the negative Euclidean distance;
- Adaptive AP (AAP) [14]: AP with the negative spectral angle mapper (SAM) and an exemplar number determination procedure for getting fixed selected band numbers;
- ERCA-based AP (pairwise feature metric (PFM)-AP): the similarity of bands used in AP is based on the optimization criterion of ERCA with pairwise constraints.
- FLDA-based AP (LFM-AP): the similarity in AP is based on FLDA with class labels.
3.3. Results
3.3.1. Accuracy Compared to the Number of Selected Bands
3.3.2. Comparison of Accuracy Compared to the Number of Chunklets
3.3.3. Comparison of Accuracy with Discriminative Information
3.3.4. Sensitivity Analysis
- , which affects the convergence speed; and
- DFTS, which determines the number of selected bands (i.e., representative bands).
4. Discussion
4.1. Clustering-Based Methods versus Ranking-Based Methods
4.2. BS Performance Compared to Different Prior Information
4.3. BS Performance Compared to the Amount of Prior Information
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, R.B. Introduction to Hyperspectral Imaging; TNTmips, MicroImages: Lincoln, NE, USA, 2012; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Duda, R.O.; Hart, P.E.; Stork, D.G. Pattern Classification, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons Press: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, G. On the mean accuracy of statistical pattern recognizers. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1968, 14, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruzzone, L.; Demir, B. A review of modern approaches to classification of remote sensing data. In Land Use and Land Cover Mapping in Europe; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; Volume 18, pp. 127–143. [Google Scholar]
- Plaza, A.; Benediktsson, J.A.; Boardman, J.W.; Brazile, J.; Bruzzone, L.; Camps-Valls, G.; Chanussot, J.; Fauvel, M.; Gamba, P.; Gualtieri, A. Recent advances in techniques for hyperspectral image processing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, S110–S122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cover, T.M.; Thomas, J.A. Elements of Information Theory, 2nd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Dopido, I.; Villa, A.; Plaza, A.; Gamba, P. A quantitative and comparative assessment of unmixing-based feature extraction techniques for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2012, 5, 421–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serpico, S.B.; Bruzzone, L. A new search algorithm for feature selection in hyperspectral remote sensing images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1994, 39, 1360–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Jiang, M.; Li, W.; Liu, Y. A symmetric sparse representation based band selection method for hyperspectral imagery classification. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-I.; Du, Q.; Sun, T.L.; Althouse, M.L. A joint band prioritization and band-deccorelation approach to band selection for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1999, 37, 2631–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-I.; Wang, S. Constrained band selection for hyperspectral imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 1575–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, J.F.; Dueck, D. Clustering by passing messages between data points. Science 2007, 315, 972–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Y.; Yao, F.; Jia, S. Band selection for hyperspectral imagery using affinity propagation. IET Comput. Vis. 2009, 3, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.J.; Sheng, Y.H.; Du, P.J.; Liu, K. Adaptive affinity propagation with spectral angle mapper for semi-supervised hyperspectral band selection. Appl. Opt. 2012, 51, 2656–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, B.; Gunn, S.R.; Damper, R.I.; Nelson, J.D.B. Band selection for hyperspectral image classification using mutual information. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2006, 3, 522–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, M. Dimensionality reduction of multimodal labeled data by local fisher discriminant analysis. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2007, 8, 1027–1061. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-usó, A.; Pla, F.; Sotoca, J.M.; García-sevilla, P. Clustering based hyperspectral band selection using information measures. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 4158–4171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Geng, X.; Ji, L.; Lu, Y. A new band selection method for hyperspectral image based on data quality. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 2697–2703. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, R.; Gao, Y.; Hong, R.; Liu, Q. Spectral-spatial constraint hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 1811–1824. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, G.; Zhu, F.; Xiang, S.; Wang, Y. Semisupervised hyperspectral image classification via discriminant analysis and robust regression. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 9, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shental, N.; Hertz, T.; Weinshall, D.; Pavel, M. Adjustment learning and relevant component analysis. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Copenhagen, Denmark, 28–31 May 2002; pp. 776–790. [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Hillel, A.; Hertz, T.; Shental, N.; Weinshall, D. Learning distance functions using equivalence relations. In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML-03), Washington, DC, USA, 21–24 August 2003; pp. 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Hillel, A.; Hertz, T.; Shental, N.; Weinshall, D. Learning a Mahalanobis metric from equivalence constraints. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2005, 6, 937–965. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Liu, S.; Bruzzone, L.; Guan, R.C. A semisupervised feature metric based band selection method for hyperspectral image classification. In Proceedings of the 4th Workshop on Hyperspectral Image and Signal Processing: Evolution in Remote Sensing, Shanghai, China, 4–7 July 2012; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Liu, S.C.; Bruzzone, L.; Guan, R.C.; Du, P.J. A feature-metric-based affinity propagation technique to feature selection for Hyperspectral Image Classification. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 10, 1152–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoi, S.C.H.; Liu, W.; Lyu, M.R.; Ma, W.Y. Learning distance metrics with contextual constraints for image retrieval. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Washington, DC, USA, 17–22 June 2006; pp. 2072–2078. [Google Scholar]
- Yeung, D.Y.; Chang, H. Extending the relevant component analysis algorithm for metric learning using both positive and negative equivalence constraints. Pattern Recognit. 2006, 39, 1007–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLachlan, G.J. Discriminant Analysis and Statistical Pattern Recognition; John Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Mika, S.; Ratsch, G.; Weston, J.; Scholkopf, B.; Muller, K. Fisher discriminant analysis with kernels. In Proceedings of the IEEE Signal Processing Society Workshop, Madison, WI, USA, 25 August 1999; pp. 41–48. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.-I.; Ji, B.-H. Fisher’s linear spectral mixture analysis. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 2292–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q. Modified fisher’s linear discriminant analysis for hyperspectral imagery. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2007, 4, 503–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Prasad, S.; Fowler, J.E.; Bruce, L.M. Locality-preserving dimensionality reduction and classification for hyperspectral image analysis. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 1185–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgardner, M.F.; Biehl, L.L.; Landgrebe, D.A. 220 Band AVIRIS Hyperspectral Image Data Set: June 12, 1992 Indian Pine Test Site 3; Purdue University Research Repository: West Lafayette, Indiana, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, J.F.; Dueck, D. Affinity Propagation FAQ. Available online: http://www.psi.toronto.edu/affinitypropagation/faq.html (accessed on 26 May 2017).
- Frey, J.F.; Dueck, D. Affinity Propagation. Available online: http://www.psi.toronto.edu/index.php?q=affinity%20propagation (accessed on 26 May 2017).







| Acronyms | Description | Acronyms | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ID | Information divergence | LFM-AP | Label feature metric-based affinity propagation |
| NG | Non-Gaussianity | PFM-AP | Pairwise feature metric-based affinity propagation |
| MVPCA | Maximum variance-based principal component analysis | DFM-AP | Discriminative feature metric-based affinity propagation |
| AP | Affinity propagation | SVM | Support vector machine |
| AAP | Adaptive affinity propagation | AOA | Average overall accuracy |
| FM-AP | Feature metric-based affinity propagation | SD | Standard deviation |
| Datasets | SD | MVPCA | ID | AP | AAP | LFM-AP | FM-AP | PAM-AP | DFM-AP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NB | ||||||||||
| Indian Pines | 10 | 1.642 | 1.426 | 1.382 | 2.368 | 2.667 | 2.005 | 1.061 | 1.045 | |
| 20 | 1.746 | 1.526 | 1.458 | 0.767 | 2.985 | 1.106 | 1.304 | 2.006 | ||
| 40 | 1.996 | 1.129 | 2.126 | 1.831 | 2.480 | 0.910 | 1.398 | 2.205 | ||
| 60 | 1.582 | 1.468 | 2.308 | 2.116 | 1.427 | 0.689 | 1.399 | 1.878 | ||
| Xuzhou | 10 | 1.860 | 1.757 | 2.363 | 2.972 | 2.437 | 1.661 | 6.476 | 1.812 | |
| 20 | 1.969 | 1.812 | 2.007 | 2.045 | 2.954 | 1.874 | 3.624 | 1.972 | ||
| 40 | 1.783 | 1.826 | 1.964 | 2.510 | 2.972 | 1.985 | 3.085 | 1.596 | ||
| 60 | 1.813 | 1.719 | 2.174 | 2.747 | 2.700 | 1.956 | 3.135 | 1.989 | ||
| Dataset | AOA | Discriminative Information (# Times the Number of Original Negative Constraints) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NB | 0.5 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ||
| Indian Pines | 12 | 57.39 | 60.18 | 59.70 | 60.69 | 57.87 | |
| 20 | 59.60 | 60.11 | 60.21 | 62.23 | 60.90 | ||
| 30 | 60.09 | 60.12 | 62.27 | 61.97 | 60.46 | ||
| 40 | 61.06 | 61.39 | 62.04 | 62.13 | 60.47 | ||
| 50 | 61.52 | 60.63 | 62.23 | 63.04 | 60.98 | ||
| 60 | 62.18 | 61.06 | 62.11 | 63.45 | 60.14 | ||
| Xuzhou | 8 | 58.46 | 89.08 | 89.27 | 89.58 | 90.15 | |
| 20 | 88.02 | 89.79 | 90.41 | 90.93 | 91.07 | ||
| 30 | 90.18 | 91.82 | 92.67 | 91.02 | 91.93 | ||
| 40 | 91.60 | 93.65 | 93.52 | 93.95 | 93.82 | ||
| 50 | 90.15 | 90.72 | 92.59 | 92.23 | 92.73 | ||
| 60 | 92.07 | 92.43 | 91.86 | 92.52 | 93.37 | ||
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, C.; Tan, Y.; Bruzzone, L.; Lu, L.; Guan, R. Discriminative Feature Metric Learning in the Affinity Propagation Model for Band Selection in Hyperspectral Images. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 782. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9080782
Yang C, Tan Y, Bruzzone L, Lu L, Guan R. Discriminative Feature Metric Learning in the Affinity Propagation Model for Band Selection in Hyperspectral Images. Remote Sensing. 2017; 9(8):782. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9080782
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Chen, Yulei Tan, Lorenzo Bruzzone, Laijun Lu, and Renchu Guan. 2017. "Discriminative Feature Metric Learning in the Affinity Propagation Model for Band Selection in Hyperspectral Images" Remote Sensing 9, no. 8: 782. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9080782
APA StyleYang, C., Tan, Y., Bruzzone, L., Lu, L., & Guan, R. (2017). Discriminative Feature Metric Learning in the Affinity Propagation Model for Band Selection in Hyperspectral Images. Remote Sensing, 9(8), 782. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9080782