A-DInSAR Monitoring of Landslide and Subsidence Activity: A Case of Urban Damage in Arcos de la Frontera, Spain
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area
2.1. Geography
2.2. Geological and Geotechnical Context
- Calcarenites and sandstones, commonly known as “Caliza Tosca” of Arcos de la Frontera, which constitute the upper part of the slope that faces the Guadalete River (with a slope angle of about 55°) and the crag where the old town is located.
- Silts, marls and sandstones, which outcrop in the middle part of the slope (18–23°) where La Verbena is located and also determine the substratum where Pueblos Blancos settles, below the artificial filling.
- Blue marls with narrow intercalations of sands, which develop typically smooth slope landscapes (<15°). They outcrop in the lower part of the slope facing the Guadalete River.
- White marls with siliciclastic sands, which outcrop in the east of the studied area.
2.3. Geotechnical Campaigns in La Verbena landslide
3. Arcos de la Frontera Landslide
3.1. Classification and Activity
3.2. Damage in La Verbena Area
4. Pueblos Blancos Site. The Case of the Differential Settlement of an Artificial Fill
5. A-DInSAR Monitoring
5.1. “ENVISAT 2010+” Project Images Processing
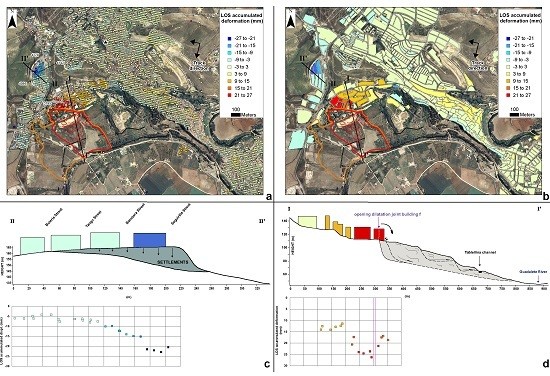
5.2. A-DInSAR Results
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Farina, P.; Colombo, D.; Fumagalli, A.; Marks, F.; Moretti, S. Permanent Scatterers for landslide investigations: outcomes from the ESA-SLAM project. Eng. Geol. 2006, 88, 200–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovenga, F.; Nutricato, R.; Refice, A.; Wasowski, J. Application of multi-temporal differential interferometry to slope instability detection in urban/peri-urban areas. Eng. Geol. 2006, 88, 218–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardino, P.; Costantini, M.; Franceschetti, G.; Iodice, A.; Pietranera, L.; Rizzo, V. Use of differential SAR interferometry in monitoring and modelling large slope instability at Maratea (Basilicata, Italy). Eng. Geol. 2003, 68, 31–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colesanti, C.; Wasowski, J. In Satellite SAR interferometry for wide-area slope hazard detection and site-specific monitoring of slow landslides. In Proceedings of the Ninth International Symposium on Landslides, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 28 June–2 July 2004; pp. 795–802. [Google Scholar]
- Colesanti, C.; Wasowski, J. Investigating landslides with space-borne Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) interferometry. Eng. Geol. 2006, 88, 173–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squarzoni, C.; Delacourt, C.; Allemand, P. Nine years of spatial and temporal evolution of the La Valette landslide observed by SAR interferometry. Eng. Geol. 2003, 68, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasowski, J.; Bovenga, F. Investigating landslides and unstable slopes with satellite Multi Temporal Interferometry: Current issues and future perspectives. Eng. Geol. 2014, 174, 103–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilley, G.E.; Bürgmann, R.; Ferretti, A.; Novali, F.; Rocca, F. Dynamics of slow-moving landslides from permanent scatterer analysis. Science 2004, 304, 1952–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera, G.; Gutiérrez, F.; García-Davalillo, J.; Guerrero, J.; Notti, D.; Galve, J.; Fernández-Merodo, J.; Cooksley, G. Multi-sensor advanced DInSAR monitoring of very slow landslides: The Tena Valley case study (Central Spanish Pyrenees). Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 128, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, D.L.; Hudnut, K.W.; Ingebritsen, S.; Phillips, S.P.; Peltzer, G.; Rogez, F.; Rosen, P. Detection of aquifer system compaction and land subsidence using interferometric synthetic aperture radar, Antelope Valley, Mojave Desert, California. Water Resour. Res. 1998, 34, 2573–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, G.; Fernández, J.; Tomás, R.; Cooksley, G.; Mulas, J. Advanced interpretation of subsidence in Murcia (SE Spain) using A-DInSAR data-modelling and validation. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 9, 647–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoffmann, J.; Zebker, H.A.; Galloway, D.L.; Amelung, F. Seasonal subsidence and rebound in Las Vegas Valley, Nevada, observed by synthetic aperture radar interferometry. Water Resour. Res. 2001, 37, 1551–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmanoğlu, B.; Dixon, T.H.; Wdowinski, S.; Cabral-Cano, E.; Jiang, Y. Mexico City subsidence observed with persistent scatterer InSAR. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2011, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomás, R.; Romero, R.; Mulas, J.; Marturiá, J.; Mallorqui, J.J.; López-Sánchez, J.; Herrera, G.; Gutiérrez, F.; González, P.; Fernández, J.; et al. Radar interferometry techniques for the study of ground subsidence phenomena: A review of practical issues through cases in Spain. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 163–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sillerico, E.; Ezquerro, P.; Marchamalo, M.; Herrera, G.; Duro, J.; Martínez, R. Monitoring ground subsidence in urban environments: M-30 tunnels under Madrid City (Spain). Ingeniería e Investigación 2015, 35, 30–35. [Google Scholar]
- Samsonov, S.V.; d’Oreye, N.; González, P.J.; Tiampo, K.F.; Ertolahti, L.; Clague, J.J. Rapidly accelerating subsidence in the Greater Vancouver region from two decades of ERS-ENVISAT-RADARSAT-2 DInSAR measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 143, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruden, D.M.; Varnes, D.J. Landslides: Investigation and Mitigation. Chapter 3-Landslide Types and Processes. Transportation Research Board Special Report; Transportation Research Board: Washington, DC, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Hungr, O.; Leroueil, S.; Picarelli, L. The Varnes classification of landslide types, an update. Landslides 2014, 11, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, J.A. Glossary of Geology, 5th ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; ISBN 3-540-27951-2. [Google Scholar]
- Comerci, V.; Vittori, E.; Cipolloni, C.; Di Manna, P.; Guerrieri, L.; Nisio, S.; Succhiarelli, C.; Ciuffreda, M.; Bertoletti, E. Geohazards monitoring in Roma from InSAR and in situ data: Outcomes of the PanGeo Project. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2015, 172, 2997–3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capes, R.; Teeuw, R. On safe ground? Analysis of European urban geohazards using satellite radar interferometry. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2017, 58, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, G.; Fernández, M.Á.; Tomás, R.; González-Nicieza, C.; López-Sánchez, J.M.; Vigil, A.Á. Forensic analysis of buildings affected by mining subsidence based on Differential Interferometry (Part III). Eng. Fail. Anal. 2012, 24, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciampalini, A.; Bardi, F.; Bianchini, S.; Frodella, W.; Del Ventisette, C.; Moretti, S.; Casagli, N. Analysis of building deformation in landslide area using multisensor PSInSAR™ technique. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2014, 33, 166–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianchini, S.; Pratesi, F.; Nolesini, T.; Casagli, N. Building deformation assessment by means of persistent scatterer interferometry analysis on a landslide-affected area: the Volterra (Italy) case study. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 4678–4701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bru, G.; Herrera, G.; Tomás, R.; Duro, J.; De la Vega, R.; Mulas, J. Control of deformation of buildings affected by subsidence using persistent scatterer interferometry. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2013, 9, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanabria, M.; Guardiola-Albert, C.; Tomás, R.; Herrera, G.; Prieto, A.; Sánchez, H.; Tessitore, S. Subsidence activity maps derived from DInSAR data: Orihuela case study. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2013, 1, 5365–5402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peduto, D.; Cascini, L.; Arena, L.; Ferlisi, S.; Fornaro, G.; Reale, D. A general framework and related procedures for multiscale analyses of DInSAR data in subsiding urban areas. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 105, 186–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notti, D.; Galve, J.P.; Mateos, R.M.; Monserrat, O.; Lamas-Fernández, F.; Fernández-Chacón, F.; Roldán-García, F.J.; Pérez-Peña, J.V.; Crosetto, M.; Azañón, J.M. Human-induced coastal landslide reactivation. Monitoring by PSInSAR techniques and urban damage survey (SE Spain). Landslides 2015, 12, 1007–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González Méndez, P.J. Medida y Caracterización de Deformaciones Usando Técnicas Geodésicas y de Teledetección. Aplicación en Volcanología y Sismotectónica. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Madrid, Spain, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- González, P.J.; Fernandez, J. Error estimation in multitemporal InSAR deformation time series, with application to Lanzarote, Canary Islands. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alonso-Ruiz, M.M.; García-Pulido, L.J. Estudio histórico-arqueológico de la muralla sureste de Arcos de la Frontera (Cádiz). Arqueología de la Arquitectura 2013, 10, e004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, J.; Pérez, L.M.; García, S.; Moral, J.P.; Paniagua, D.; Higueras, M.d.M.; Martínez, J.; Sánchez, Á. Geología Aplicada en el Entorno de Arcos de la Frontera; Sociedad Geológica de España: Salamanca, Spain, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Jerez, L.; Moreno, E.; Ganados, L.F.; Leyva, F. Mapa y Memoria Explicativa de la Hoja 1049 (Arcos de la Frontera); MAGNA. IGME: Madrid, Spain, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, J. Obras reales y recalces en arcillas expansivas y suelos colapsables. Available online: http://www.site.biz/descargas/Conferencias_pdf/Obras%20Reales%20y%20Recalces%20en%20Arcillas%20Expansivas%20y%20Suelos%20Colapsables.pdf (accessed on 31 July 2017).
- Uriel, S.; Oteo, C. Propiedades Geotécnicas de las Margas Azules de Sevilla. In Simposium Nacional Sobre Rocas Blandas; Comité Organizador del Simposio Nacional sobre Rocas Blandas: Madrid, Spain, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Tsige, M.; de Vallejo, L.G.; Doval, M.; Oteo, C.; Barba, C. Microfabric of Guadalquivir Blue Marls and Its Engineering Geological Significance; International Association of Engineers: Hong Kong, China, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Tsige, M.; de Vallejo, L.I.G.; Doval, M.; Mazo, C.O. Microfábrica y Mineralogía de las Arcillas Azules del Guadalquivir: Influencia en su Comportamiento Geotécnico; Ministerio de Fomento, Centro de Publicaciones: Madrid, Spain, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Alonso, E.; Gens, A. Aznalcollar dam failure. Part 1: Field observations and material properties. Géotechnique 2006, 56, 165–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oteo, C.S. Las margas azules del Guadalquivir y la inestabilidad de taludes. Rutas 2000, 77, 17–27. [Google Scholar]
- García, A. Informe Geológico Sobre el Terreno Afectado por el Canal de Tablellina (pk 1461 a pk 3434). Término Municipal de Arcos de la Frontera (Cádiz); Servicio Geológico de Obras Públicas: Madrid, Spain, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.H. Foundations on Expansive Soils; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; Volume 12. [Google Scholar]
- VORSEVI, S.A. Reconocimiento Geotécnico UE “La Verbena”; Technical Report; Sevilla, Spain, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- VORSEVI, S.A. Reconocimiento Geotécnico UE “La Verbena”; Technical Report; Sevilla, Spain, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Edartec Consultores S.L. (EDARTEC). Informe de Visita de Reconocimiento e Inspección n°3 (Technical Report); Edartec Consultores S.L. (EDARTEC): Sevilla, Spain, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- EXPERTA. Informe Sobre el Estudio de Patologías Existentes, Control de Movimiento de Fisuras y Control de Desplomes en Edificios de Viviendas en Pz. Ayuntamientos Democráticos n°2 y n°4. Arcos de la Frontera, Cádiz (Technical Report); EXPERTA: Sevilla, Spain, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- AEMET. Resumen Diario de Datos de Estaciones Principales. 2012. Available online: https://sede.aemet.gob.es/AEMET/es/GestionPeticiones/nuevaSolicitud (accessed on 26 June 2012).
- BOE. Real Decreto 112/1986 de 10 de Enero. N°24; Ministerio de Trabajo y Seguridad Social: Madrid, Spain, 1986; p. 3833. [Google Scholar]
- BOJA. Resolución de 8 de Enero de 2009. N°29; Junta de Andalucía: Sevilla, Spain, 2009; p. 49. [Google Scholar]
- Redacción. La Junta Arregla el Canal de Tablellina Para la Zona Regable de Guadalcacín; Diario de Cádiz: Cádiz, Spain, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Cañas, J. 200 Familias Bajo el Riesgo de un Alud de Lodo; El País: Madrid, Spain, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Dictum. Sentencia N° 153/2014. Audiencia Provincial de Cádiz (Legal Report); Jerez de la Frontera, Spain, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- BOPA. Proposición no de Ley Relativa a Plan Integral de Actuación en la Ladera de Arcos. N°672; Parlamento de Andalucía: Sevilla, Spain, 2011; p. 13. [Google Scholar]
- BOP. Anuncio Administración Local, de 6 de Abril. N°62; Diputación de Cádiz: Cádiz, Spain, 2010; p. 24. [Google Scholar]
- BOJA. Resolución de 23 de Junio de 2010, de la Delegación del Gobierno de Cádiz. N°133; Junta de Andalucía: Sevilla, Spain, 2010; p. 79. [Google Scholar]
- BOE. Real Decreto 173/2011, de 11 de Febrero. N° 43; Ministerio de Política Territorial y Administración Pública: Madrid, Spain, 2011; p. 19267. [Google Scholar]
- BOE. Real Decreto 1601/2011, de 4 de Noviembre. N° 269; Ministerio de Política Territorial y Administración Pública: Madrid, Spain, 2011; p. 116438. [Google Scholar]
- Benítez, J. Compromiso absoluto del Estado para seguir la obra de la Verbena. 2017. Available online: andaluciainformacion.es (accessed on 16 February 2017).
- Redacción. Emilio Yanes Diagnosticará los Problemas de Pueblos Blancos; Diario de Cádiz: Cádiz, Spain, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- del Real, E.M. Sistemas de Recalce de Cimentaciones en los Proyectos de Conservación de Edificios Patrimoniales en Andalucía. Revisión Crítica de Intervenciones Realizadas y de los Sistemas Empleados; Universidad de Sevilla: Sevilla, Spain, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Casu, F.; Manzo, M.; Lanari, R. A quantitative assessment of the SBAS algorithm performance for surface deformation retrieval from DInSAR data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 102, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanari, R.; Casu, F.; Manzo, M.; Zeni, G.; Berardino, P.; Manunta, M.; Pepe, A. An overview of the small baseline subset algorithm: A DInSAR technique for surface deformation analysis. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2007, 164, 637–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, A.; Bekaert, D.; Spaans, K.; Arıkan, M. Recent advances in SAR interferometry time series analysis for measuring crustal deformation. Tectonophysics 2012, 514, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanssen, R.F. Radar Interferometry: Data Interpretation and Error Analysis; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2001; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, O.; Mallorqui, J.J.; Broquetas, A. Linear and non-linear terrain deformation maps from a reduced set of interferometric SAR images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 2243–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usai, S. A least squares database approach for SAR interferometric data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanari, R.; Mora, O.; Manunta, M.; Mallorqui, J.J.; Berardino, P.; Sansosti, E. A small baseline DInSAR approach for investigating deformations on full resolution SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 1377–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Zan, F.; Zonno, M.; López-Dekker, P. Phase inconsistencies and multiple scattering in SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 6608–6616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Parameter | Weathered GBM | Unweathered GBM |
|---|---|---|
| Liquid Limit | 44.8 | 60 |
| Plasticity Index | 21.3 | 32.7 |
| In situ density (g/cm3) | 1.60 | 1.55 |
| Humidity (%) | 20.9 | 25.6 |
| Specific weight (g/cm3) | 2.75 | 2.74 |
| %CO3Ca | 34.88 | 28.57 |
| %SO3 | 0.74 | 0.19 |
| SAR Image | Acquisition Date | Perpendicular Baseline [m] |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 15 April 2011 | 151 |
| 2 | 15 May 2011 | 474 |
| 3 | 14 July 2011 | 61 |
| 4 | 13 August 2011 | 0 |
| 5 | 12 September 2011 | 133 |
| 6 | 12 October 2011 | 94 |
| 7 | 11 December 2011 | −210 |
| 8 | 10 January 2012 | 282 |
| 9 | 9 February 2012 | 156 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bru, G.; González, P.J.; Mateos, R.M.; Roldán, F.J.; Herrera, G.; Béjar-Pizarro, M.; Fernández, J. A-DInSAR Monitoring of Landslide and Subsidence Activity: A Case of Urban Damage in Arcos de la Frontera, Spain. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 787. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9080787
Bru G, González PJ, Mateos RM, Roldán FJ, Herrera G, Béjar-Pizarro M, Fernández J. A-DInSAR Monitoring of Landslide and Subsidence Activity: A Case of Urban Damage in Arcos de la Frontera, Spain. Remote Sensing. 2017; 9(8):787. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9080787
Chicago/Turabian StyleBru, Guadalupe, Pablo J. González, Rosa M. Mateos, Francisco J. Roldán, Gerardo Herrera, Marta Béjar-Pizarro, and José Fernández. 2017. "A-DInSAR Monitoring of Landslide and Subsidence Activity: A Case of Urban Damage in Arcos de la Frontera, Spain" Remote Sensing 9, no. 8: 787. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9080787
APA StyleBru, G., González, P. J., Mateos, R. M., Roldán, F. J., Herrera, G., Béjar-Pizarro, M., & Fernández, J. (2017). A-DInSAR Monitoring of Landslide and Subsidence Activity: A Case of Urban Damage in Arcos de la Frontera, Spain. Remote Sensing, 9(8), 787. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9080787