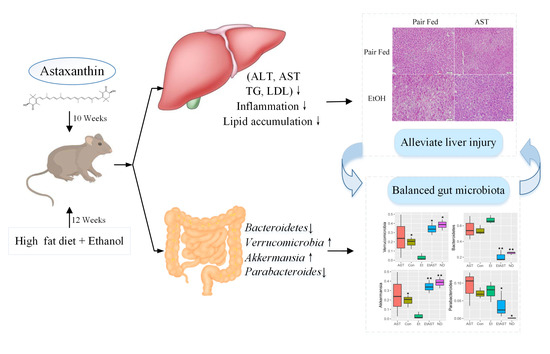
Astaxanthin Prevents Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Modulating Mouse Gut Microbiota
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Experimentation
2.2. Biochemical Analyses
2.3. Hepatic Triglyceride Staining
2.4. Quantification of Genes Expression in Liver Tissue
2.5. Fecal DNA Extraction
2.6. Amplification and Sequencing of the 16S rRNA Genes
2.7. Bioinformatics and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Astaxanthin Protects Mice from High-Fat Diet and Ethanol-Induced Liver Lesions
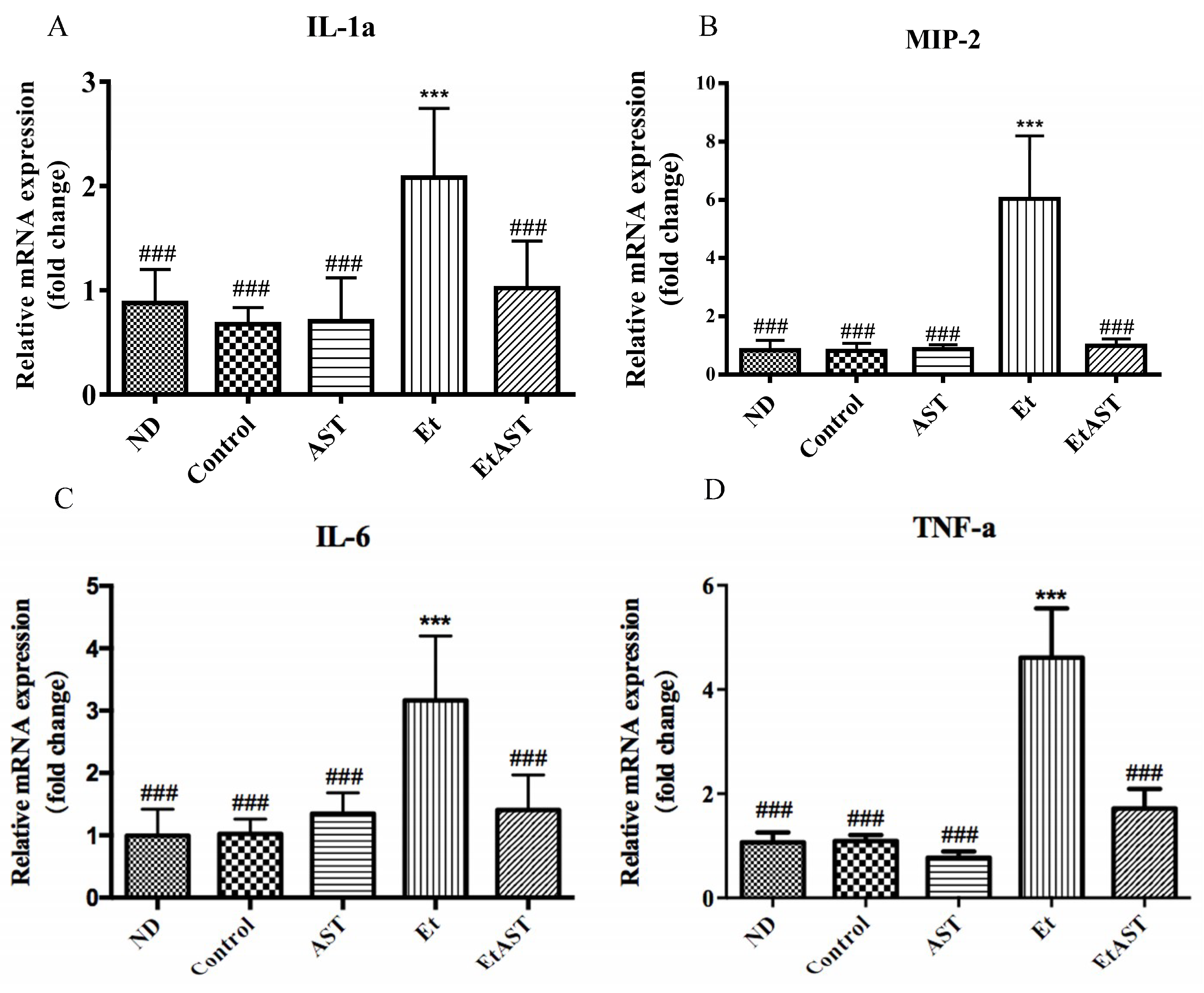
3.2. Astaxanthin Can Relieve Liver Injury Through the Regulation of Inflammatory Genes Expression in Mice
3.3. Astaxanthin Alters the Profiles of Gut Microbiota in Ethanol-Fed Mice
3.4. Astaxanthin Regulates the Gut Microbiota Composition in Ethanol Feeding Mice
3.5. Associations of the Bacterial Abundance Altered by Astaxanthin with the AFLD Phenotype
3.6. Predicted Metabolic Functions of the Metagenome in Gut Microbiota
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AST | astaxanthin |
| AFLD | alcoholic fatty liver disease |
| IL-1α | interleukin-1 alpha |
| MIP-2 | macrophage inflammatory protein 2 |
| ND | normal diet |
| Et | ethanol |
| ALT | alanine aminotransferase |
| TG | triacylglycerol |
| LDL | low-density lipoprotein |
| LW | liver weight |
| BW | body weight |
| Con | control |
| PCoA | principle coordinate analysis |
| OTUs | operational taxonomic units |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
References
- O’Shea, R.S.; Dasarathy, S.; McCullough, A.J. Alcoholic liver disease. Hepatology 2010, 51, 307–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menon, K.V.; Gores, G.J.; Shah, V.H. Pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of alcoholic liver disease. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2001, 76, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacSween, R.N.; Burt, A.D. Histologic spectrum of alcoholic liver disease. Semin. Liver Dis. 1986, 6, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussein, G.; Sankawa, U.; Goto, H.; Matsumoto, K.; Watanabe, H. Astaxanthin, a carotenoid with potential in human health and nutrition. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.P.; Peng, J.; Yin, K.; Wang, J.H. Potential health-promoting effects of astaxanthin: A high-value carotenoid mostly from microalgae. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2011, 55, 150–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sila, A.; Kamoun, Z.; Ghlissi, Z.; Makni, M.; Nasri, M.; Sahnoun, Z.; Nedjar-Arroume, N.; Bougatef, A. Ability of natural astaxanthin from shrimp by-products to attenuate liver oxidative stress in diabetic rats. Pharmacol. Rep. 2015, 67, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, M.; Chen, K.; Lu, J.; Cheng, P.; Xu, L.; Dai, W.; Wang, F.; He, L.; Zhang, Y.; Chengfen, W.; et al. Protective effect of astaxanthin on liver fibrosis through modulation of TGF-beta1 expression and autophagy. Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, 954502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobori, M.; Takahashi, Y.; Sakurai, M.; Ni, Y.; Chen, G.; Nagashimada, M.; Kaneko, S.; Ota, T. Hepatic Transcriptome Profiles of Mice with Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Treated with Astaxanthin and Vitamin E. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takemoto, M.; Yamaga, M.; Furuichi, Y.; Yokote, K. Astaxanthin Improves Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Werner Syndrome with Diabetes Mellitus. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2015, 63, 1271–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.; Wu, C.; Kim, J.; Kim, B.; Lee, S.J. Astaxanthin reduces hepatic lipid accumulations in high-fat-fed C57BL/6J mice via activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) alpha and inhibition of PPAR gamma and Akt. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2016, 28, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, Y.; Nagashimada, M.; Zhuge, F.; Zhan, L.; Nagata, N.; Tsutsui, A.; Nakanuma, Y.; Kaneko, S.; Ota, T. Astaxanthin prevents and reverses diet-induced insulin resistance and steatohepatitis in mice: A comparison with vitamin E. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Battson, M.L.; Lee, D.M.; Weir, T.L.; Gentile, C.L. The gut microbiota as a novel regulator of cardiovascular function and disease. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2015, 56, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, J.C.; Loo, W.M.; Goh, K.L.; Sugano, K.; Chan, W.K.; Chiu, W.Y.; Choi, M.G.; Gonlachanvit, S.; Lee, W.J.; Lee, W.J.; et al. Asian consensus on the relationship between obesity and gastrointestinal and liver diseases. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 31, 1405–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dao, M.C.; Clement, K. Gut microbiota and obesity: Concepts relevant to clinical care. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2018, 48, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, P.; Torralba, M.; Tan, J.; Embree, M.; Zengler, K.; Starkel, P.; van Pijkeren, J.P.; DePew, J.; Loomba, R.; Ho, S.B.; et al. FoutsandB. Schnabl. Supplementation of saturated long-chain fatty acids maintains intestinal eubiosis and reduces ethanol-induced liver injury in mice. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leclercq, S.; De Saeger, C.; Delzenne, N.; de Timary, P.; Starkel, P. Role of inflammatory pathways, blood mononuclear cells, and gut-derived bacterial products in alcohol dependence. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 76, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lippai, D.; Bala, S.; Catalano, D.; Kodys, K.; Szabo, G. Micro-RNA-155 deficiency prevents alcohol-induced serum endotoxin increase and small bowel inflammation in mice. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2014, 38, 2217–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dao, M.C.; Everard, A.; Aron-Wisnewsky, J.; Sokolovska, N.; Prifti, E.; Verger, E.O.; Kayser, B.D.; Levenez, F.; Chilloux, J.; Hoyles, L. Akkermansia muciniphila and improved metabolic health during a dietary intervention in obesity: Relationship with gut microbiome richness and ecology. Gut 2016, 65, 426–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Requena, T.; Martinez-Cuesta, M.C.; Pelaez, C. Diet and microbiota linked in health and disease. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 688–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.T.; Kotani, K. Astaxanthin as a Potential Protector of Liver Function: A. Review. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2016, 8, 701–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieber, C.S.; DeCarli, L.M.; Sorrell, M.F. Experimental methods of ethanol administration. Hepatology 1989, 10, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, D.; Li, Y.; He, L.; Tang, Y.; Li, X.; Shen, Q.; Yin, D.; Peng, Y. The protective effect of astaxanthin on fetal alcohol spectrum disorder in mice. Neuropharmacology 2014, 84, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Pena, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Edgar, R.C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2460–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Neuman, M.G.; French, S.W.; Zakhari, S.; Malnick, S.; Seitz, H.K.; Cohen, L.B.; Salaspuro, M.; Voinea-Griffin, A.; Barasch, A.; Kirpich, I.A.; et al. Alcohol, microbiome, life style influence alcohol and non-alcoholic organ damage. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2017, 102, 162–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scarpellini, E.; Forlino, M.; Lupo, M.; Rasetti, C.; Fava, G.; Abenavoli, L.; De Santis, A. Gut Microbiota and Alcoholic Liver Disease. Rev. Recent Clin. Trials 2016, 11, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.; Farruggia, C.; Ku, C.S.; Pham, T.X.; Yang, Y.; Bae, M.; Wegner, C.J.; Farrell, N.J.; Harness, E.; Park, Y.K.; et al. Astaxanthin inhibits inflammation and fibrosis in the liver and adipose tissue of mouse models of diet-induced obesity and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2017, 43, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhuvaneswari, S.; Arunkumar, E.; Viswanathan, P.; Anuradha, C.V. Astaxanthin restricts weight gain, promotes insulin sensitivity and curtails fatty liver disease in mice fed a obesity-promoting diet. Process Biochem. 2010, 45, 1406–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, M.; Park, Y.K.; Lee, J.Y. Food components with antifibrotic activity and implications in prevention of liver disease. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2017, 55, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fard, M.T.; Arulselvan, P.; Karthivashan, G.; Adam, S.K.; Fakurazi, S. Bioactive extract from Moringa oleifera inhibits the pro-inflammatory mediators in lipopolysaccharide stimulated macrophages. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2015, 11, 556–563. [Google Scholar]
- Malik, A.; Kanneganti, T.D. Function and regulation of IL-1alpha in inflammatory diseases and cancer. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 281, 124–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, C.C.; Liu, Y.N.; Hu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Z. Macrophage inflammatory protein-2 as mediator of inflammation in acute liver injury. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 3043–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, S.V.; Pedersen, O. The Human Intestinal Microbiome in Health and Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 2369–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmody, R.N.; Gerber, G.K.; Jr Luevano, J.M.; Gatti, D.M.; Somes, L.; Svenson, K.L.; Turnbaugh, P.J. Diet dominates host genotype in shaping the murine gut microbiota. Cell Host Microbe 2015, 17, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llopis, M.; Cassard, A.M.; Wrzosek, L.; Boschat, L.; Bruneau, A.; Ferrere, G.; Puchois, V.; Martin, J.C.; Lepage, P.; Le Roy, T.; et al. Intestinal microbiota contributes to individual susceptibility to alcoholic liver disease. Gut 2016, 65, 830–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, A.W.; Fouts, D.E.; Brandl, J.; Starkel, P.; Torralba, M.; Schott, E.; Tsukamoto, H.; Nelson, K.E.; Brenner, D.A.; Schnabl, B. Enteric dysbiosis associated with a mouse model of alcoholic liver disease. Hepatology 2011, 53, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, P.P.; Gyongyosi, B.; Satishchandran, A.; Iracheta-Vellve, A.; Ambade, A.; Kodys, K.; Catalano, D.; Ward, D.V.; Szabo, G. Alcohol-related changes in the intestinal microbiome influence neutrophil infiltration, inflammation and steatosis in early alcoholic hepatitis in mice. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174544. [Google Scholar]
- Neyrinck, A.M.; Etxeberria, U.; Taminiau, B.; Daube, G.; Van Hul, M.; Everard, A.; Cani, P.D.; Bindels, L.B.; Delzenne, N.M. Rhubarb extract prevents hepatic inflammation induced by acute alcohol intake, an effect related to the modulation of the gut microbiota. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surana, N.K.; Kasper, D.L. The yin yang of bacterial polysaccharides: Lessons learned from B. fragilis PSA. Immunol. Rev. 2012, 245, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, L.; Thiele, O.E.; Geis, A.L.; Chan, J.L.; Fu, K.; DeStefano, S.C.E.; Dejea, C.M.; Fathi, P.; Chen, J.; Finard, B.B.; et al. Bacteroides fragilis Toxin Coordinates a Pro-carcinogenic Inflammatory Cascade via Targeting of Colonic Epithelial Cells. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 23, 203–214.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shin, N.R.; Whon, T.W.; Bae, J.W. Proteobacteria: Microbial signature of dysbiosis in gut microbiota. Trends Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derrien, M.; Vaughan, E.E.; Plugge, C.M.; de Vos, W.M. Akkermansia muciniphila gen. nov., sp. nov., a human intestinal mucin-degrading bacterium. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 1469–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Lin, S.; Vanhoutte, P.M.; Woo, C.W.; Xu, A. Akkermansia Muciniphila Protects Against Atherosclerosis by Preventing Metabolic Endotoxemia-Induced Inflammation in Apoe−/− Mice. Circulation 2016, 133, 2434–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grander, C.; Adolph, T.E.; Wieser, V.; Lowe, P.; Wrzosek, L.; Gyongyosi, B.; Ward, D.V.; Grabherr, F.; Gerner, R.R.; Pfister, A.; et al. Recovery of ethanol-induced Akkermansia muciniphila depletion ameliorates alcoholic liver disease. Gut 2018, 67, 891–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derrien, M.; Belzer, C.; de Vos, W.M. Akkermansia muciniphila and its role in regulating host functions. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 106, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Lv, L.; Shi, D.; Ye, J.; Fang, D.; Guo, F.; Li, Y.; He, X.; Li, L. Protective Effect of Akkermansia muciniphila against Immune-Mediated Liver Injury in a Mouse Model. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ottman, N.; Geerlings, S.Y.; Aalvink, S.; de Vos, W.M.; Belzer, C. Action and function of Akkermansia muciniphila in microbiome ecology, health and disease. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2017, 31, 637–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Power, K.A.; Lu, J.T.; Monk, J.M.; Lepp, D.; Wu, W.; Zhang, C.; Liu, R.; Tsao, R.; Robinson, L.E.; Wood, G.A.; et al. Purified rutin and rutin-rich asparagus attenuates disease severity and tissue damage following dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2016, 60, 2396–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastrocola, R.; Ferrocino, I.; Liberto, E.; Chiazza, F.; Cento, A.S.; Collotta, D.; Querio, G.; Nigro, D.; Bitonto, V.; Cutrin, J.C.; et al. Fructose liquid and solid formulations differently affect gut integrity, microbiota composition and related liver toxicity: A comparative in vivo study. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2018, 55, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanislawski, M.A.; Lozupone, C.A.; Wagner, B.D.; Eggesbo, M.; Sontag, M.K.; Nusbacher, N.M.; Martinez, M.; Dabelea, D. Gut microbiota in adolescents and the association with fatty liver: The EPOCH study. Pediatr. Res. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Everard, A.; Belzer, C.; Geurts, L.; Ouwerkerk, J.P.; Druart, C.; Bindels, L.B.; Cani, P.D. Cross-talk between Akkermansia muciniphila and intestinal epithelium controls diet-induced obesity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 9066–9071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Macpherson, A.J.; Heikenwalder, M.; Ganal-Vonarburg, S.C. The Liver at the Nexus of Host-Microbial Interactions. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 20, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaulmann, A.; Bohn, T. Carotenoids, inflammation, and oxidative stress—Implications of cellular signaling pathways and relation to chronic disease prevention. Nutr. Res. 2014, 34, 907–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speranza, L.; Pesce, M.; Patruno, A.; Franceschelli, S.; de Lutiis, M.A.; Grilli, A.; Felaco, M. Astaxanthin Treatment Reduced Oxidative Induced Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines Secretion in U937: SHP-1 as a Novel Biological Target. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 890–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]





© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Liu, M.; Fu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, L.; Zheng, X.; Liu, J. Astaxanthin Prevents Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Modulating Mouse Gut Microbiota. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1298. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10091298
Liu H, Liu M, Fu X, Zhang Z, Zhu L, Zheng X, Liu J. Astaxanthin Prevents Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Modulating Mouse Gut Microbiota. Nutrients. 2018; 10(9):1298. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10091298
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Huilin, Meihong Liu, Xueqi Fu, Ziqi Zhang, Lingyu Zhu, Xin Zheng, and Jingsheng Liu. 2018. "Astaxanthin Prevents Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Modulating Mouse Gut Microbiota" Nutrients 10, no. 9: 1298. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10091298