Oxidative Status before and after Renal Replacement Therapy: Differences between Conventional High Flux Hemodialysis and on-Line Hemodiafiltration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Assessment of Oxidative Damage and Antioxidant Defense
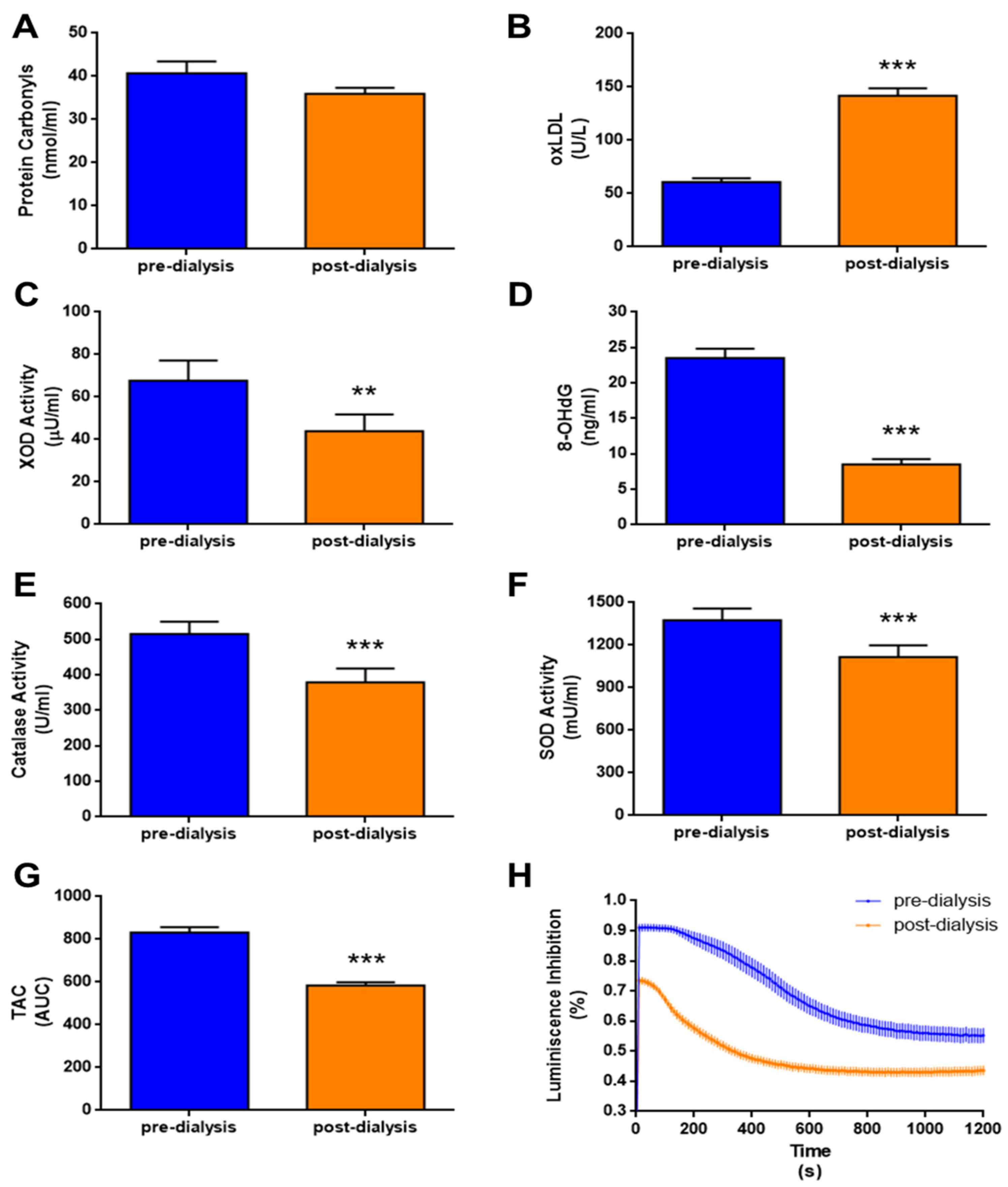
2.2.1. Oxidative Biomarkers
2.2.2. Antioxidant Biomarkers
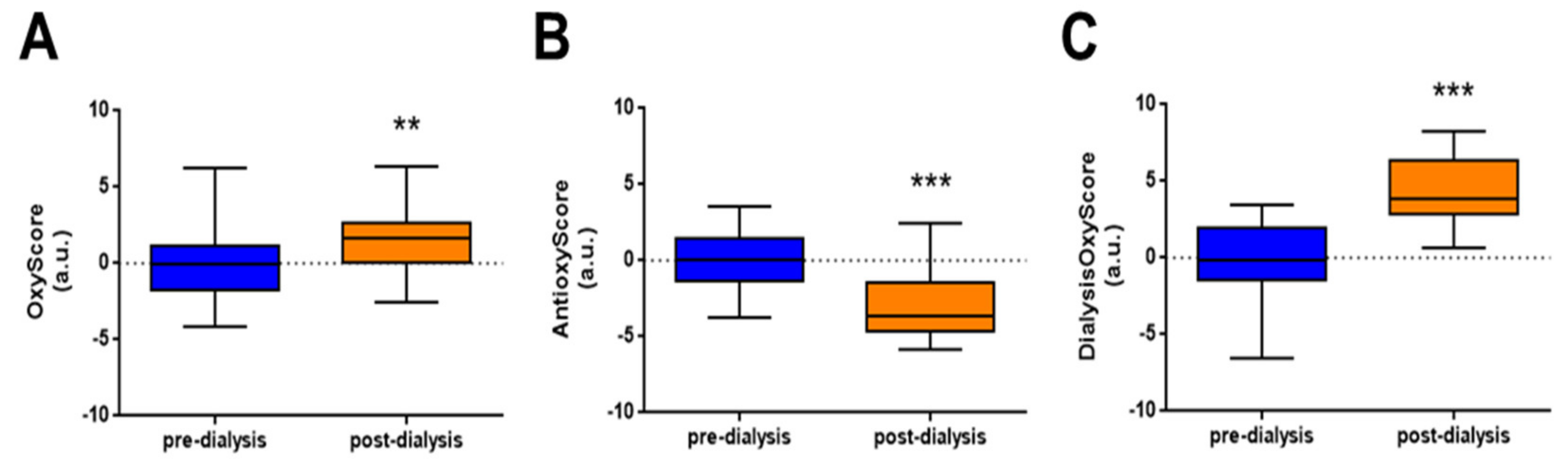
2.3. Calculation of OxyScore, AntioxyScore, and DialysisOxyScore
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Characteristics
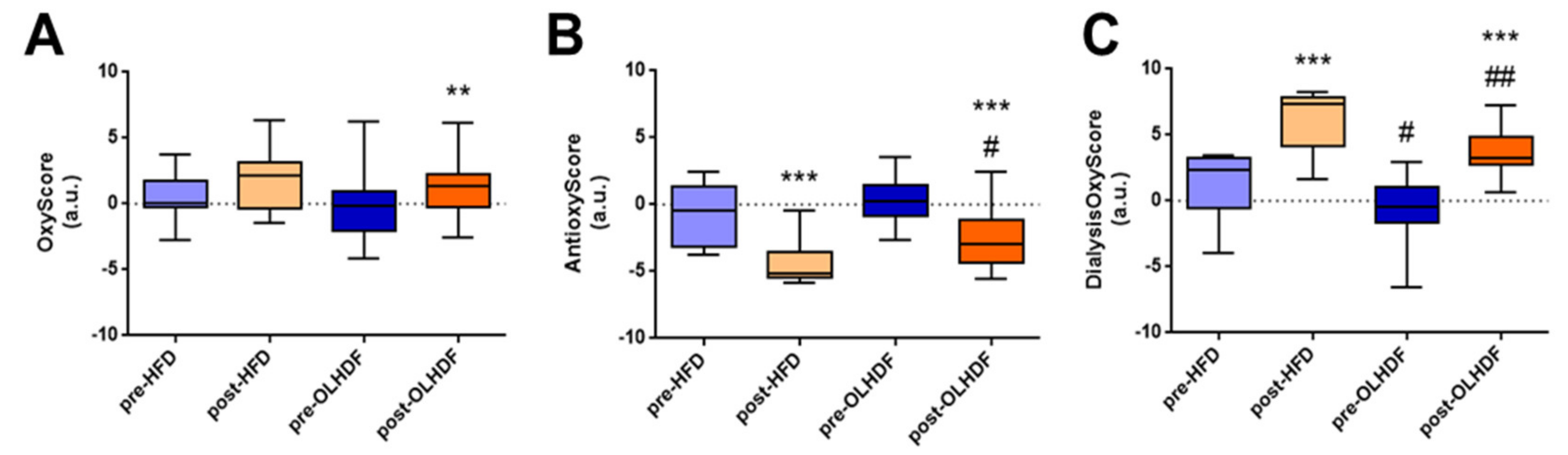
3.2. Dialysis Treatment Increases Oxidative Stress
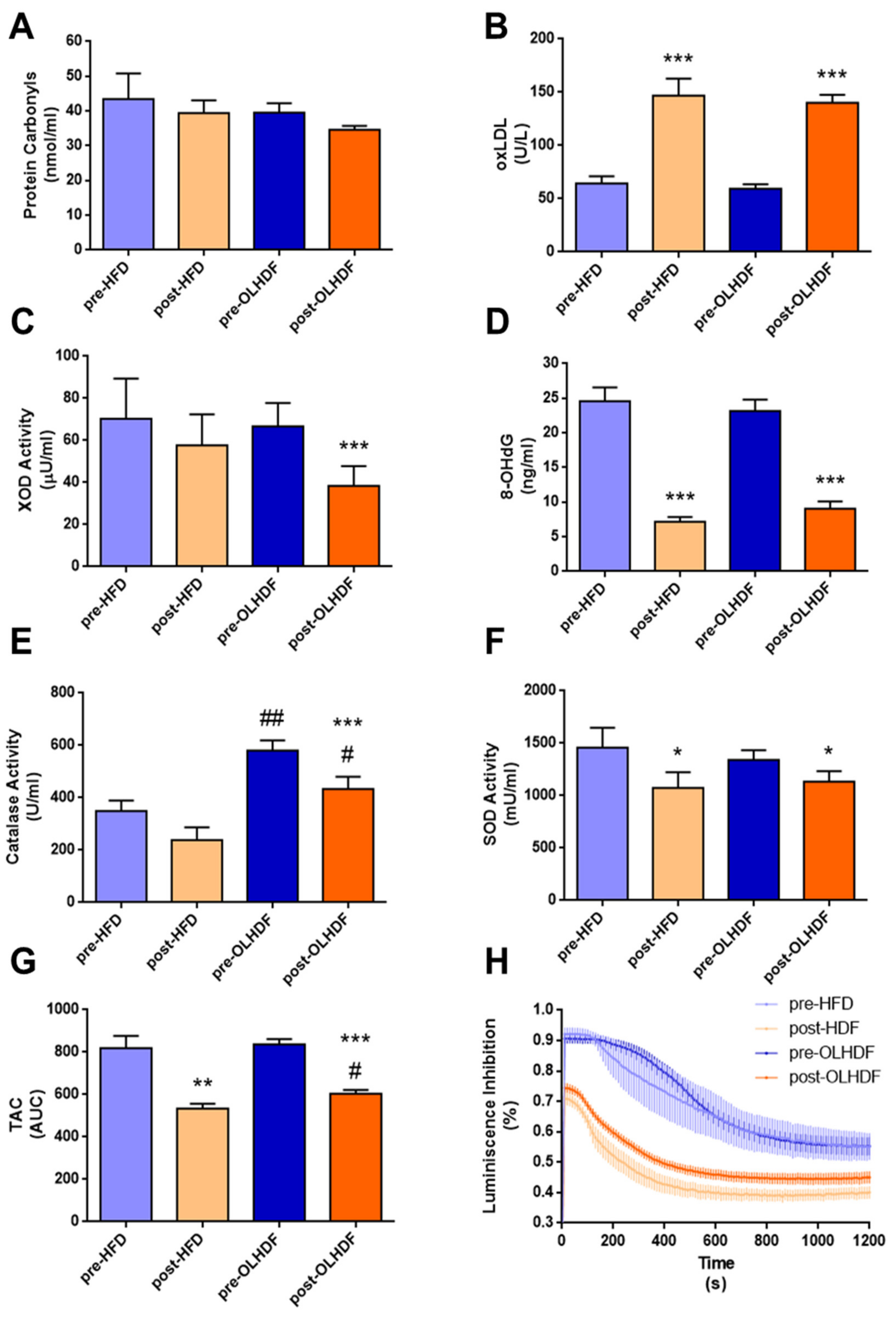
3.3. Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Defense Markers Are Different between HFD and OL-HDF Modalities
3.4. Global Oxidative Status (DialysisOxyScore) is Lower after OL-HDF Treatment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 8-OHdG | 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine |
| ACEi | Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor |
| ARB | Angiotensin receptor blocker |
| AUC | Area under the curve |
| BAP | Biological antioxidant potential |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| CKD | Chronic kidney disease |
| DBP | Diastolic blood pressure |
| DM | Diabetes mellitus |
| ESRD | End-stage renal disease |
| GFR | Glomerular filtration rate |
| HFD | High-flux dialysis |
| NAC | N-acetyl cysteine |
| NT-proBNP | N-terminal-pro hormone B-type natriuretic peptide |
| OL-HDF | On-line hemodiafiltration |
| oxLDL | Oxidized low density lipoprotein |
| RRTROS | Renal replacement therapyReactive oxygen species |
| SBP | Systolic blood pressure |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| RRT | Renal replacement therapy |
| TAC | Total antioxidant capacity |
| XOD | Xanthine oxidase |
References
- Gorostidi, M.; Santamaria, R.; Alcazar, R.; Fernandez Fresnedo, G.; Galceran, J.M.; Goicoechea, M.; Oliveras, A.; Portoles, J.; Rubio, E.; Segura, J.; et al. Spanish Society of Nephrology Document on KDIGO Guidelines for the Assessment and Treatment of Chronic Kidney Disease. Nefrologia 2014, 34, 302–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruilope, L.M.; Bakris, G.L. Renal Function and Target Organ Damage in Hypertension. Eur. Heart J. 2011, 32, 1599–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qureshi, A.R.; Alvestrand, A.; Divino Filho, J.C.; Gutierrez, A.; Heimburger, O.; Lindholm, B.; Bergstrom, J. Inflammation, Malnutrition, and Cardiac Disease as Predictors of Mortality in Hemodialysis Patients. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol 2002, 13, 28–36. [Google Scholar]
- Stenvinkel, P.; Alvestrand, A. Inflammation in End-Stage Renal Disease: Sources, Consequences, and Therapy. Semin. Dial. 2002, 15, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, S.A.; Bots, M.L.; Canaud, B.; Davenport, A.; Grooteman, M.P.; Kircelli, F.; Locatelli, F.; Maduell, F.; Morena, M.; Nube, M.J.; et al. Haemodiafiltration and Mortality in End-Stage Kidney Disease Patients: A Pooled Individual Participant Data Analysis from Four Randomized Controlled Trials. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2016, 31, 978–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strobel, N.A.; Fassett, R.G.; Marsh, S.A.; Coombes, J.S. Oxidative Stress Biomarkers as Predictors of Cardiovascular Disease. Int. J. Cardiol. 2011, 147, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griendling, K.K.; Touyz, R.M.; Zweier, J.L.; Dikalov, S.; Chilian, W.; Chen, Y.R.; Harrison, D.G.; Bhatnagar, A.; on Behalf of the American Heart Association Council on Basic Cardiovascular Sciences. Measurement of Reactive Oxygen Species, Reactive Nitrogen Species, and Redox-Dependent Signaling in the Cardiovascular System: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circ. Res. 2016, 119, e39–e75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzolino, M.; Mangano, M.; Stucchi, A.; Ciceri, P.; Conte, F.; Galassi, A. Cardiovascular Disease in Dialysis Patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2018, 33, iii28–iii34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulianiti, K.P.; Kaltsatou, A.; Mitrou, G.I.; Jamurtas, A.Z.; Koutedakis, Y.; Maridaki, M.; Stefanidis, I.; Sakkas, G.K.; Karatzaferi, C. Systemic Redox Imbalance in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 8598253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tbahriti, H.F.; Kaddous, A.; Bouchenak, M.; Mekki, K. Effect of Different Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease and Renal Replacement Therapies on Oxidant-Antioxidant Balance in Uremic Patients. Biochem. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 358985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himmelfarb, J.; Stenvinkel, P.; Ikizler, T.A.; Hakim, R.M. The Elephant in Uremia: Oxidant Stress as a Unifying Concept of Cardiovascular Disease in Uremia. Kidney Int. 2002, 62, 1524–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen Khoa, T.; Massy, Z.A.; De Bandt, J.P.; Kebede, M.; Salama, L.; Lambrey, G.; Witko Sarsat, V.; Drueke, T.B.; Lacour, B.; Thevenin, M. Oxidative Stress and Haemodialysis: Role of Inflammation and Duration of Dialysis Treatment. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2001, 16, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maraj, M.; Kusnierz Cabala, B.; Dumnicka, P.; Gala Blądzinska, A.; Gawlik, K.; Pawlica Gosiewska, D.; Ząbek Adamska, A.; Mazur Laskowska, M.; Ceranowicz, P.; Kuzniewski, M. Malnutrition, Inflammation, Atherosclerosis Syndrome (MIA) and Diet Recommendations among End-Stage Renal Disease Patients Treated with Maintenance Hemodialysis. Nutrients 2018, 10, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varan, H.I.; Dursun, B.; Dursun, E.; Ozben, T.; Suleymanlar, G. Acute Effects of Hemodialysis on Oxidative Stress Parameters in Chronic Uremic Patients: Comparison of Two Dialysis Membranes. Int. J. Nephrol. Renov. Dis. 2010, 3, 39–45. [Google Scholar]
- Liakopoulos, V.; Roumeliotis, S.; Gorny, X.; Eleftheriadis, T.; Mertens, P.R. Oxidative Stress in Patients Undergoing Peritoneal Dialysis: A Current Review of the Literature. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 3494867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roumeliotis, S.; Eleftheriadis, T.; Liakopoulos, V. Is Oxidative Stress an Issue in Peritoneal Dialysis? Semin. Dial. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, C.L.; Morgan, P.E.; Davies, M.J. Quantification of Protein Modification by Oxidants. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2009, 46, 965–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, L.; Plieth, C. Total Low-Molecular-Weight Antioxidants as a Summary Parameter, Quantified in Biological Samples by a Chemiluminescence Inhibition Assay. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 1627–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrier, L.; Dupuy, A.M.; Granger Vallee, A.; Chalabi, L.; Morena, M.; Canaud, B.; Cristol, J.P. FGF-23 Removal is Improved by on-Line High-Efficiency Hemodiafiltration Compared to Conventional High Flux Hemodialysis. J. Nephrol. 2013, 26, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veglia, F.; Cavalca, V.; Tremoli, E. OXY-SCORE: A Global Index to Improve Evaluation of Oxidative Stress by Combining Pro-And Antioxidant Markers. Methods Mol. Biol. 2010, 594, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RodrIguez SAnchez, E.; Navarro GarcIa, J.A.; Aceves Ripoll, J.; GonzAlez Lafuente, L.; Corbacho Alonso, N.; Martinez, P.; Calvo Bonacho, E.; Alvarez Llamas, G.; Barderas, M.G.; Ruilope, L.M.; et al. Lifetime Cardiovascular Risk is Associated with a Multimarker Score of Systemic Oxidative Status in Young Adults Independently of Traditional Risk Factors. Transl. Res. 2019, 212, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, R.A.; Ouseph, R.; McLeish, K.R. Effects of High-Flux Hemodialysis on Oxidant Stress. Kidney Int. 2003, 63, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chirakarnjanakorn, S.; Navaneethan, S.D.; Francis, G.S.; Tang, W.H. Cardiovascular Impact in Patients Undergoing Maintenance Hemodialysis: Clinical Management Considerations. Int. J. Cardiol. 2017, 232, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dursun, E.; Dursun, B.; Suleymanlar, G.; Ozben, T. Carbonyl Stress in Chronic Renal Failure: The Effect of Haemodialysis. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2005, 42, 64–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuchta, A.; Pacanis, A.; Kortas Stempak, B.; Cwiklinska, A.; Zietkiewicz, M.; Renke, M.; Rutkowski, B. Estimation of Oxidative Stress Markers in Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2011, 34, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, G.; Reggiani, F.; Cucchiari, D.; Astori, E.; Garavaglia, M.L.; Portinaro, N.M.; Saino, N.; Finazzi, S.; Milzani, A.; Badalamenti, S.; et al. Plasma Protein Carbonylation in Haemodialysed Patients: Focus on Diabetes and Gender. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 4149681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capusa, C.; Stoian, I.; Rus, E.; Lixandru, D.; Barbulescu, C.; Mircescu, G. Does Dialysis Modality Influence the Oxidative Stress of Uremic Patients? Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2012, 35, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninic, A.; Sopic, M.; Munjas, J.; Spasojevic Kalimanovska, V.; Kotur Stevuljevic, J.; Bogavac Stanojevic, N.; Ivanisevic, J.; Simic Ogrizovic, S.; Kravljaca, M.; Jelic Ivanovic, Z. Association Between Superoxide Dismutase Isoenzyme Gene Expression and Total Antioxidant Status in Patients with an End-Stage Renal Disease. Balkan Med. J. 2018, 35, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zargari, M.; Sedighi, O. Influence of Hemodialysis on Lipid Peroxidation, Enzymatic and Non-Enzymatic Antioxidant Capacity in Chronic Renal Failure Patients. Nephrourol. Mon. 2015, 7, e28526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, E.L.; Chen, C.H.; Huang, S.C.; Huang, Y.C. Higher Glutathione Demand may be Necessary for Assisting Haemodialysis Patients to Cope with Increased Oxidative Stress. Nephrology (Carlton) 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunleye, A.; Akinbodewa, A.A.; Adejumo, O.A.; Oluwafemi, T.T.; Akinfaderin, D.A. Changes in Antioxidant Status Associated with Haemodialysis in Chronic Kidney Disease. Ghana Med. J. 2018, 52, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindner, A.; Charra, B.; Sherrard, D.J.; Scribner, B.H. Accelerated Atherosclerosis in Prolonged Maintenance Hemodialysis. N Engl. J. Med. 1974, 290, 697–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchio, P.; Guerra Ojeda, S.; Vila, J.M.; Aldasoro, M.; Victor, V.M.; Mauricio, M.D. Targeting Early Atherosclerosis: A Focus on Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 8563845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stepniewska, J.; Dolegowska, B.; Popinska, M.; Salata, D.; Budkowska, M.; Golembiewska, E.; Myslak, M.; Domanski, M.; Marchelek Mysliwiec, M.; Ciechanowski, K. Prooxidative-Antioxidative Balance of Cells in Different Types of Renal Replacement Therapy. Blood Purif. 2014, 37, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clermont, G.; Lecour, S.; Lahet, J.; Siohan, P.; Vergely, C.; Chevet, D.; Rifle, G.; Rochette, L. Alteration in Plasma Antioxidant Capacities in Chronic Renal Failure and Hemodialysis Patients: A Possible Explanation for the Increased Cardiovascular Risk in These Patients. Cardiovasc. Res. 2000, 47, 618–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krueger, K.; Shen, J.; Maier, A.; Tepel, M.; Scholze, A. Lower Superoxide Dismutase 2 (SOD2) Protein Content in Mononuclear Cells Is Associated with Better Survival in Patients with Hemodialysis Therapy. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 7423249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusu, C.C.; Racasan, S.; Kacso, I.M.; Moldovan, D.; Potra, A.; Patiu, I.M.; Vladutiu, D.; Caprioara, M.G. Malondialdehyde Can Predict Survival in Hemodialysis Patients. Clujul. Med. 2016, 89, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, P.S.; Jeng, Y.; Wu, M.Y.; Pai, M.A.; Wu, T.K.; Liu, C.S.; Chen, C.H.; Kuo, Y.C.; Chien, S.W.; Chen, H.P. Serum Oxidized Albumin and Cardiovascular Mortality in Normoalbuminemic Hemodialysis Patients: A Cohort Study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, T.; Ohtake, T.; Okamoto, K.; Mochida, Y.; Ishioka, K.; Oka, M.; Maesato, K.; Ikee, R.; Moriya, H.; Hidaka, S.; et al. Serum Biological Antioxidant Potential Predicts the Prognosis of Hemodialysis Patients. Nephron Clin. Pract. 2011, 117, c230–c236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.H.; Hung, S.C.; Tarng, D.C. Serum Bilirubin Links UGT1A1*28 Polymorphism and Predicts Long-Term Cardiovascular Events and Mortality in Chronic Hemodialysis Patients. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 6, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canaud, B.; Cristol, J.; Morena, M.; Leray Moragues, H.; Bosc, J.; Vaussenat, F. Imbalance of Oxidants and Antioxidants in Haemodialysis Patients. Blood Purif. 1999, 17, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.S.; Hung, S.C.; Wei, Y.H.; Tarng, D.C. GST M1 Polymorphism Associates with DNA Oxidative Damage and Mortality Among Hemodialysis Patients. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suvakov, S.; Damjanovic, T.; Pekmezovic, T.; Jakovljevic, J.; Savic Radojevic, A.; Pljesa Ercegovac, M.; Radovanovic, S.; Simic, D.V.; Pljesa, S.; Zarkovic, M.; et al. Associations of GSTM1*0 and GSTA1*A Genotypes with the Risk of Cardiovascular Death Among Hemodialyses Patients. BMC Nephrol. 2014, 15, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ok, E.; Asci, G.; Toz, H.; Ok, E.S.; Kircelli, F.; Yilmaz, M.; Hur, E.; Demirci, M.S.; Demirci, C.; Duman, S.; et al. Mortality and Cardiovascular Events in Online Haemodiafiltration (OL-HDF) Compared with High-Flux Dialysis: Results from the Turkish OL-HDF Study. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2013, 28, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grooteman, M.P.; Van Den Dorpel, M.A.; Bots, M.L.; Penne, E.L.; Van Der Weerd, N.C.; Mazairac, A.H.; Den Hoedt, C.H.; Van Der Tweel, I.; Levesque, R.; Nube, M.J.; et al. Effect of Online Hemodiafiltration on All-Cause Mortality and Cardiovascular Outcomes. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 23, 1087–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klouche, K.; Amigues, L.; Morena, M.; Brunot, V.; Dupuy, A.M.; Jaussent, A.; Picot, M.C.; Besnard, N.; Daubin, D.; Cristol, J.P. On-Line Hemodiafiltration Did Not Induce an Overproduction of Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Cytokines in Intensive Care Unit-Acute Kidney Injury. BMC Nephrol. 2017, 18, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulop, T.; Tapolyai, M.B.; Zsom, L.; Molnar, M.Z.; Abdul Salim, S.; Ujhelyi, L.; Becs, G.; Balla, J.; Hamrahian, M. Successful Practice Transitioning Between Hemodialysis and Hemodiafiltration in Outpatient Units: Ten Key Issues for Physicians to Remember. Artif. Organs 2018, 42, 925–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, M.; Venkataraman, V.; Razavian, M.; Cooper, B.; Zoungas, S.; Ninomiya, T.; Webster, A.C.; Perkovic, V. Antioxidants for Chronic Kidney Disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 10, CD008176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q. Natural Forms of Vitamin E: Metabolism, Antioxidant, and Anti-Inflammatory Activities and Their Role in Disease Prevention and Therapy. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 72, 76–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boaz, M.; Smetana, S.; Weinstein, T.; Matas, Z.; Gafter, U.; Iaina, A.; Knecht, A.; Weissgarten, Y.; Brunner, D.; Fainaru, M.; et al. Secondary Prevention with Antioxidants of Cardiovascular Disease in Endstage Renal Disease (SPACE): Randomised Placebo-Controlled Trial. Lancet 2000, 356, 1213–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deicher, R.; Ziai, F.; Bieglmayer, C.; Schillinger, M.; Horl, W.H. Low Total Vitamin C Plasma Level is a Risk Factor for Cardiovascular Morbidity and Mortality in Hemodialysis Patients. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2005, 16, 1811–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jankowska, M.; Rutkowski, B.; Debska Slizien, A. Vitamins and Microelement Bioavailability in Different Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease. Nutrients 2017, 9, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
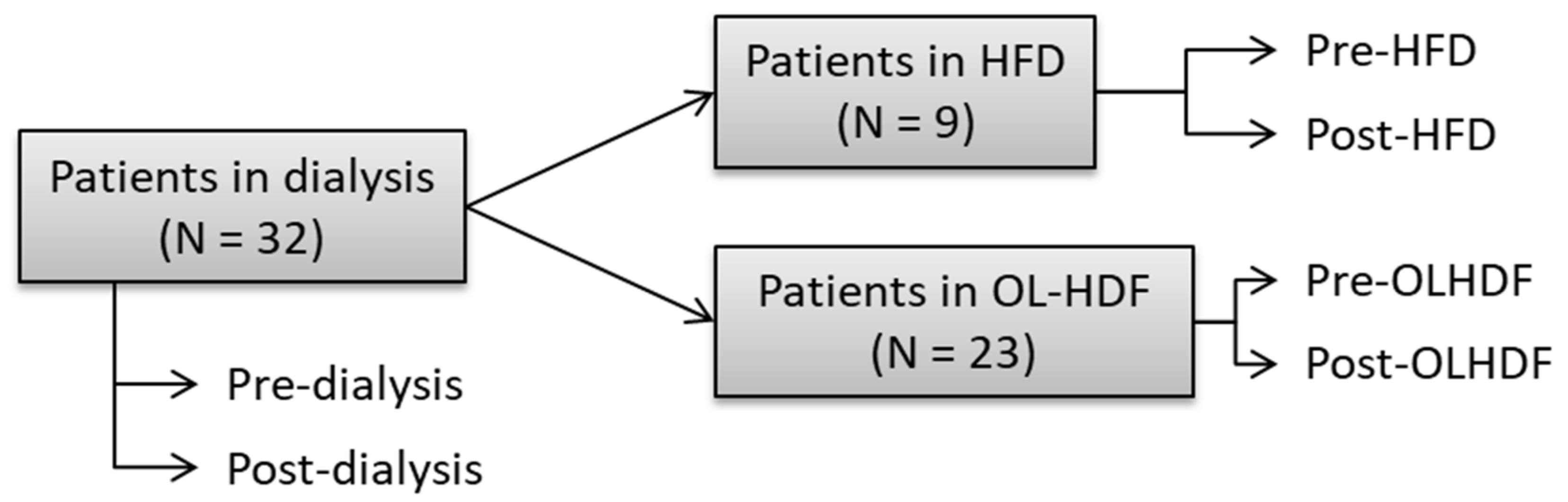
| All Patients (n = 32) | HFD Patients (n = 9) | OL-HDF Patients (n = 23) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic and clinical characteristics | ||||
| Age (years) | 60.0 ± 16.4 | 64.7 ± 22.0 | 58.2 ± 13.8 | 0.3224 |
| Sex (Men, %) | 50 | 11.1 | 65.2 | 0.0155 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 22.2 ± 3.9 | 19.6 ± 3.3 | 23.2 ± 3.7 | 0.0169 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 128.4 ± 23.0 | 126.2 ± 23.2 | 129.3 ± 23.4 | 0.7392 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 73.0 ± 16.7 | 67.8 ± 21.3 | 75.0 ± 14.6 | 0.2780 |
| Medical history | ||||
| Hypertension (%) | 78.1 | 77.7 | 78.2 | 0.9999 |
| Diabetes mellitus (%) | 22.8 | 22.2 | 21.8 | 0.9999 |
| Current smokers (%) | 12.5 | 0 | 17.4 | 0.3035 |
| Dialysis time (months) | 79.5 ± 74.3 | 31.4 ± 24.5 | 98.4 ± 79.1 | 0.0195 |
| Laboratory measurements | ||||
| NT-proBNP (pg/mL) | 6312 ± 10946 | 12668 ± 18811 | 4000 ± 5148 | 0.0534 |
| 25-Hydroxyvitamin D (ng/mL) | 10.0 ± 4.3 | 9.8 ± 3.2 | 10.1 ± 4.7 | 0.8696 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 145.8 ± 28.6 | 148.4 ± 25.1 | 144.7 ± 30.3 | 0.7473 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 143.3 ± 61.4 | 167.0 ± 52.5 | 134.0 ± 63.1 | 0.1753 |
| Serum creatinine (mg/dL) | 7.61 ± 2.22 | 7.16 ± 2.22 | 7.78 ± 2.25 | 0.4861 |
| Serum albumin (g/dL) | 4.05 ± 0.43 | 3.91 ± 0.24 | 4.10 ± 0.48 | 0.2592 |
| CaP | 38.87 ± 10.15 | 39.20 ± 7.27 | 38.74 ± 11.17 | 0.9095 |
| Kt/V | 1.63 ± 0.24 | 1.68 ± 0.25 | 1.61 ± 0.24 | 0.4628 |
| Potassium (mEq/L) | 5.15 ± 0.90 | 5.06 ± 0.78 | 5.19 ± 0.95 | 0.7248 |
| Bicarbonate (mEq/L) | 21.25 ± 2.94 | 21.22 ± 3.80 | 21.26 ± 2.63 | 0.9740 |
| Convection volume (L/session) | 29.32 ± 3.50 | |||
| Medication | ||||
| ACEi/ARB (%) | 25 | 22.2 | 26.1 | 0.9999 |
| Beta-blocker (%) | 40.6 | 55.6 | 34.8 | 0.4269 |
| Diuretics (%) | 9.4 | 0 | 13.0 | 0.5409 |
| Cinacalcet (%) | 9.4 | 0 | 13.0 | 0.5409 |
| Paracalcitol (%) | 38.7 | 55.6 | 31.8 | 0.2534 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Navarro-García, J.A.; Rodríguez-Sánchez, E.; Aceves-Ripoll, J.; Abarca-Zabalía, J.; Susmozas-Sánchez, A.; González Lafuente, L.; Bada-Bosch, T.; Hernández, E.; Mérida-Herrero, E.; Praga, M.; et al. Oxidative Status before and after Renal Replacement Therapy: Differences between Conventional High Flux Hemodialysis and on-Line Hemodiafiltration. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2809. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11112809
Navarro-García JA, Rodríguez-Sánchez E, Aceves-Ripoll J, Abarca-Zabalía J, Susmozas-Sánchez A, González Lafuente L, Bada-Bosch T, Hernández E, Mérida-Herrero E, Praga M, et al. Oxidative Status before and after Renal Replacement Therapy: Differences between Conventional High Flux Hemodialysis and on-Line Hemodiafiltration. Nutrients. 2019; 11(11):2809. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11112809
Chicago/Turabian StyleNavarro-García, José Alberto, Elena Rodríguez-Sánchez, Jennifer Aceves-Ripoll, Judith Abarca-Zabalía, Andrea Susmozas-Sánchez, Laura González Lafuente, Teresa Bada-Bosch, Eduardo Hernández, Evangelina Mérida-Herrero, Manuel Praga, and et al. 2019. "Oxidative Status before and after Renal Replacement Therapy: Differences between Conventional High Flux Hemodialysis and on-Line Hemodiafiltration" Nutrients 11, no. 11: 2809. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11112809
APA StyleNavarro-García, J. A., Rodríguez-Sánchez, E., Aceves-Ripoll, J., Abarca-Zabalía, J., Susmozas-Sánchez, A., González Lafuente, L., Bada-Bosch, T., Hernández, E., Mérida-Herrero, E., Praga, M., Ruilope, L. M., & Ruiz-Hurtado, G. (2019). Oxidative Status before and after Renal Replacement Therapy: Differences between Conventional High Flux Hemodialysis and on-Line Hemodiafiltration. Nutrients, 11(11), 2809. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11112809





