Attenuation of UVB-Induced Photo-Aging by Polyphenolic-Rich Spatholobus Suberectus Stem Extract Via Modulation of MAPK/AP-1/MMPs Signaling in Human Keratinocytes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Preparation of Plant Extracts
2.2. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Analysis
2.3. Elastase Inhibition Assay and Combination Index
2.4. Cell Culture, UVB-Irradiation and Cell Viability Assay
2.5. ROS Generation Assay
2.6. RNA Extraction and Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
2.7. Preparation of Protein Lysates and Western Blotting
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. HPLC Analysis of Stem of Spatholobus Suberectus (SS)
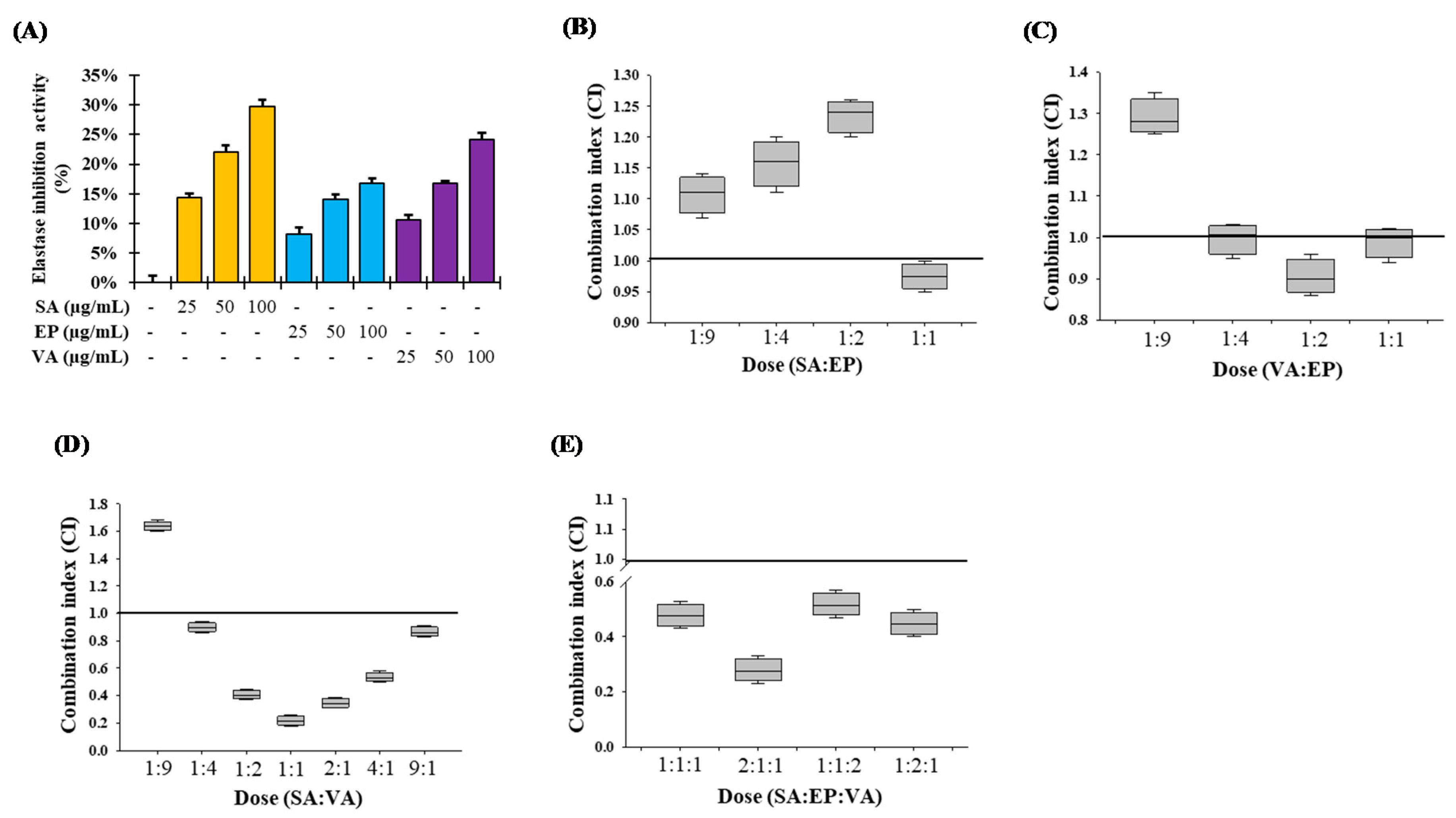
3.2. Inhibition of Elastase Activity by SS Stem
3.3. The Effet of SS on Cell Viability of Human Keratinocytes (HaCaT) Cells
3.4. Suppression of UVB-Stimulated Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Generation by SS
3.5. Regulation of UVB-Induced Matrix Metalloproteinases (MMPs) Expression by SS
3.6. Effects of SSE on the Expression of COL1A1, ELN and HAS2
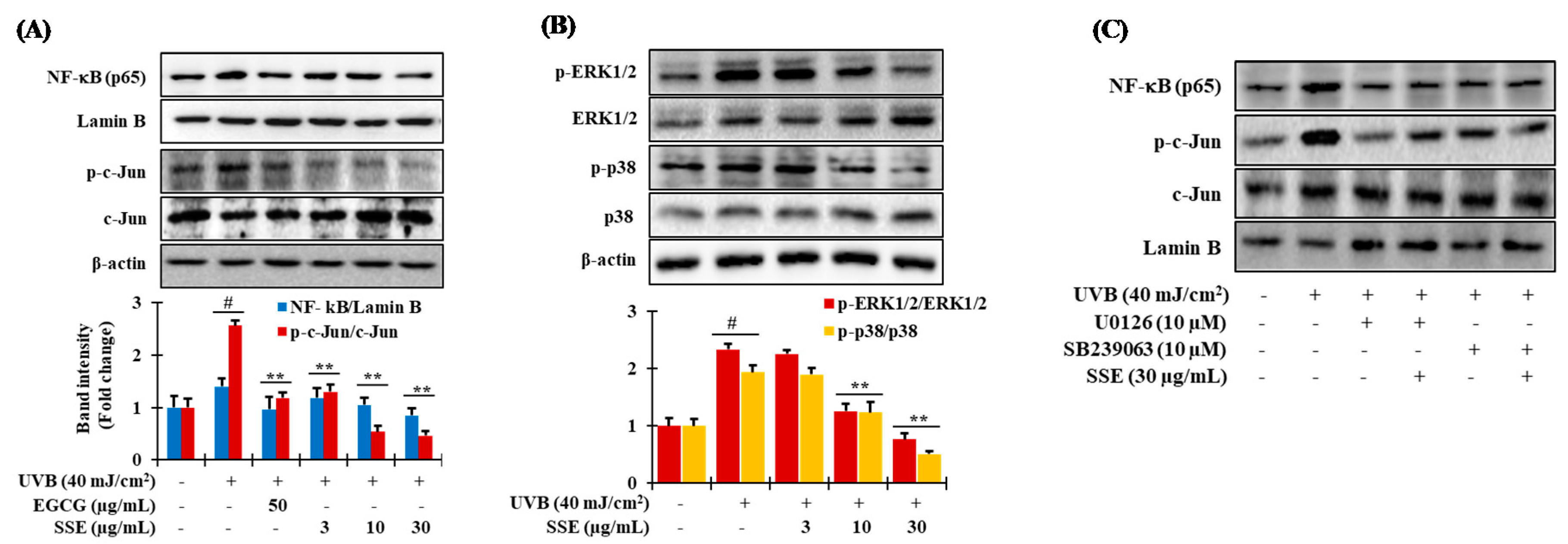
3.7. Downregulation of NF-κB and AP-1 by SSE
3.8. Effects of SSE on the Phosphorylation of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) Proteins
3.9. Combination Studies of the Major Components of SSE on Elastase Inhibition Activity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kammeyer, A.; Luiten, R.M. Oxidation events and skin aging. Ageing Res. Rev. 2015, 21, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cela, E.M.; Friedrich, A.; Paz, M.L.; Vanzulli, S.I.; Leoni, J.; Gonzalez Maglio, D.H. Time-course study of different innate immune mediators produced by UV-irradiated skin: Comparative effects of short and daily versus a single harmful UV exposure. Immunology 2015, 145, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, K.P.; Douki, T.; Sarkany, R.P.E.; Acker, S.; Herzog, B.; Young, A.R. The UV/visible radiation boundary region (385–405 nm) damages skin cells and induces “dark” cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers in human skin in vivo. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tewari, A.; Grys, K.; Kollet, J.; Sarkany, R.; Young, A.R. Upregulation of MMP12 and its activity by UVA1 in human skin: Potential implications for photoaging. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 2598–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varani, J.; Spearman, D.; Perone, P.; Fligiel, S.E.; Datta, S.C.; Wang, Z.Q.; Shao, Y.; Kang, S.; Fisher, G.J.; Voorhees, J.J. Inhibition of type I procollagen synthesis by damaged collagen in photoaged skin and by collagenase-degraded collagen in vitro. Am. J. Pathol. 2001, 158, 931–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catania, J.M.; Chen, G.; Parrish, A.R. Role of matrix metalloproteinases in renal pathophysiologies. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2007, 292, F905–F911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woessner, J.F. Matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in connective tissue remodeling. FASEB J. 1991, 5, 2145–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wlaschek, M.; Tantcheva-Poor, I.; Naderi, L.; Ma, W.; Schneider, L.A.; Razi-Wolf, Z.; Schuller, J.; Scharffetter-Kochanek, K. Solar UV irradiation and dermal photoaging. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2001, 63, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, G.J.; Datta, S.C.; Talwar, H.S.; Wang, Z.Q.; Varani, J.; Kang, S.; Voorhees, J.J. Molecular basis of sun-induced premature skin ageing and retinoid antagonism. Nature 1996, 379, 335–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Park, W.S.; Baek, J.I.; Lee, B.S.; Yoo, D.S.; Park, S.J. Continuous irradiation with a 633-nm light-emitting diode exerts an anti-aging effect on human skin cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2015, 35, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weston, C.R.; Davis, R.J. The JNK signal transduction pathway. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2002, 12, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anggakusuma; Yanti; Hwang, J.K. Effects of macelignan isolated from Myristica fragrans Houtt. on UVB-induced matrix metalloproteinase-9 and cyclooxygenase-2 in HaCaT cells. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2010, 57, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, R.; Cui, Y.; Fisher, G.J.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Schneider, L.M.; Majmudar, G. A comparative study of the effects of retinol and retinoic acid on histological, molecular, and clinical properties of human skin. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2016, 15, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varani, J.; Warner, R.L.; Gharaee-Kermani, M.; Phan, S.H.; Kang, S.; Chung, J.H.; Wang, Z.Q.; Datta, S.C.; Fisher, G.J.; Voorhees, J.J. Vitamin A antagonizes decreased cell growth and elevated collagen-degrading matrix metalloproteinases and stimulates collagen accumulation in naturally aged human skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2000, 114, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Xuan, L. New phenolic constituents from the stems of Spatholobus suberectus. Helv. Chim. Acta 2006, 89, 1241–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.H.; Lin, Y.P.; Hsu, F.L.; Zhan, G.R.; Yen, K.Y. Bioactive constituents of Spatholobus suberectus in regulating tyrosinase-related proteins and mRNA in HEMn cells. Phytochemistry 2006, 67, 1262–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.R.; Wang, A.Q.; Lin, L.G.; Qiu, H.C.; Wang, Y.T.; Wang, Y. In vitro study on anti-hepatitis C virus activity of Spatholobus suberectus Dunn. Molecules 2016, 21, 1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.J.; Jo, I.Y.; Bu, Y.; Park, J.W.; Maeng, S.; Kang, H.; Jang, W.; Hwang, D.S.; Lee, W.; Min, K.; et al. Antiplatelet effects of Spatholobus suberectus via inhibition of the glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptor. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 134, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Meng, C.W.; Zhou, Q.M.; Chen, J.P.; Xiong, L. Cytotoxic evaluation against breast cancer cells of isoliquiritigenin analogues from Spatholobus suberectus and their synthetic derivatives. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 248–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyama, T.; Wada-Takahashi, S.; Takamichi, M.; Watanabe, K.; Yoshida, A.; Yoshino, F.; Miyamoto, C.; Maehata, Y.; Sugiyama, S.; Takahashi, S.S.; et al. Reactive oxygen species scavenging activity of Jixueteng evaluated by electron spin resonance (ESR) and photon emission. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2014, 9, 1755–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, N.K.; Lee, S.G.; Lee, D.S.; Park, P.H.; Lee, I.S.; Jeong, G.S. Spatholobus suberectus inhibits osteoclastogenesis and stimulates chondrogenesis. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2014, 42, 1123–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, J.; Guo, J.P.; Jin, M.; Chen, Z.Q.; Wang, X.W.; Li, J.W. Antiviral effects of aqueous extract from Spatholobus suberectus Dunn. Against coxsackievirus B3 in mice. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2011, 17, 764–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Liu, C.; Liu, X.; Guo, Y. Protective effect of Spatholobus suberectus on brain tissues in cerebral ischemia. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2016, 8, 3963–3969. [Google Scholar]
- Brito, S.M.; Coutinho, H.D.; Talvani, A.; Coronel, C.; Barbosa, A.G.; Vega, C.; Figueredo, F.G.; Tintino, S.R.; Lima, L.F.; Boligon, A.A.; et al. Analysis of bioactivities and chemical composition of Ziziphus joazeiro Mart. using HPLC-DAD. Food Chem. 2015, 186, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraunsoe, J.A.; Claridge, T.D.; Lowe, G. Inhibition of human leukocyte and porcine pancreatic elastase by homologues of bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 9090–9096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, T.C. Theoretical basis, experimental design, and computerized simulation of synergism and antagonism in drug combination studies. Pharmacol. Rev. 2006, 58, 621–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigel, E.G.; Lebwohl, M.; Rigel, A.C.; Rigel, D.S. Daily UVB exposure levels in high-school students measured with digital dosimeters. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2003, 49, 1112–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Alam, M.B.; Lee, S.H. Protection of UVB-induced photoaging by Fuzhuan-Brick tea aqueous extract via MAPKs/Nrf2-mediated down-regulation of MMP-1. Nutrients 2018, 11, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohm, M.; Schulte, U.; Kalden, H.; Luger, T.A. Alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone modulates activation of NF-κB and AP-1 and secretion of interleukin-8 in human dermal fibroblasts. Ann. NY. Acad. Sci. 1999, 885, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, Y.; Cheong, Y.-K.; Kim, N.-H.; Chung, H.-T.; Kang, D.G.; Pae, H.-O. Mitogen-activated protein kinases and reactive oxygen species: How can ROS activate MAPK pathways? J. Signal Transduct. 2011, 2011, 792639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouinard, N.; Valerie, K.; Rouabhia, M.; Huot, J. UVB-mediated activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase enhances resistance of normal human keratinocytes to apoptosis by stabilizing cytoplasmic p53. Biochem. J. 2002, 365, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabe, J.H.; Mamelak, A.J.; McElgunn, P.J.; Morison, W.L.; Sauder, D.N. Photoaging: Mechanisms and repair. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2006, 55, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, T.; Qin, Z.; Xia, W.; Shao, Y.; Voorhees, J.J.; Fisher, G.J. Matrix-degrading metalloproteinases in photoaging. J. Investig. Dermatol. Symp. Proc. 2009, 14, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, T.; Tian, Y.; Ren, Q.; Wei, L.; Li, X.; Cai, Q. Red light interferes in UVA-induced photoaging of human skin fibroblast cells. Photochem. Photobiol. 2014, 90, 1349–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, G.J.; Kang, S.; Varani, J.; Bata-Csorgo, Z.; Wan, Y.; Datta, S.; Voorhees, J.J. Mechanisms of photoaging and chronological skin aging. Arch. Dermatol. 2002, 138, 1462–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.J.; Moh, S.H.; Son, D.H.; You, S.; Kinyua, A.W.; Ko, C.M.; Song, M.; Yeo, J.; Choi, Y.H.; Kim, K.W. Gallic acid promotes wound healing in normal and hyperglucidic conditions. Molecules 2016, 21, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maity, N.; Nema, N.K.; Abedy, M.K.; Sarkar, B.K.; Mukherjee, P.K. Exploring Tagetes erecta Linn flower for the elastase, hyaluronidase and MMP-1 inhibitory activity. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 137, 1300–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojo de la Vega, M.; Krajisnik, A.; Zhang, D.D.; Wondrak, G.T. Targeting NRF2 for improved skin barrier function and photoprotection: Focus on the achiote-derived apocarotenoid bixin. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittayapruek, P.; Meephansan, J.; Prapapan, O.; Komine, M.; Ohtsuki, M. Role of Matrix metalloproteinases in photoaging and photocarcinogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J. Matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases are essential for the inflammatory response in cancer cells. J. Signal Transduct. 2010, 2010, 985132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.; Park, S.J.; Kim, I.H.; Choi, Y.H.; Nam, T.J. Protective effect of porphyra-334 on UVA-induced photoaging in human skin fibroblasts. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 34, 796–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Lauer, M.E.; Anand, S.; Mack, J.A.; Maytin, E.V. Hyaluronan synthase 2 protects skin fibroblasts against apoptosis induced by environmental stress. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 32253–32265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, K.; Asamitsu, K.; Uranishi, H.; Iddamalgoda, A.; Ito, K.; Kojima, H.; Okamoto, T. Protecting skin photoaging by NF-κB inhibitor. Curr. Drug Metab. 2010, 11, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwok, B.H.; Koh, B.; Ndubuisi, M.I.; Elofsson, M.; Crews, C.M. The anti-inflammatory natural product parthenolide from the medicinal herb Feverfew directly binds to and inhibits I-κB kinase. Chem. Biol. 2001, 8, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-H.; Wu, P.-Y.; Wen, K.-C.; Lin, C.-Y.; Chiang, H.-M. Protective effects and mechanisms of Terminalia catappa L. methenolic extract on hydrogen-peroxide-induced oxidative stress in human skin fibroblasts. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 18, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kwon, K.-R.; Alam, M.B.; Park, J.-H.; Kim, T.-H.; Lee, S.-H. Attenuation of UVB-Induced Photo-Aging by Polyphenolic-Rich Spatholobus Suberectus Stem Extract Via Modulation of MAPK/AP-1/MMPs Signaling in Human Keratinocytes. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1341. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11061341
Kwon K-R, Alam MB, Park J-H, Kim T-H, Lee S-H. Attenuation of UVB-Induced Photo-Aging by Polyphenolic-Rich Spatholobus Suberectus Stem Extract Via Modulation of MAPK/AP-1/MMPs Signaling in Human Keratinocytes. Nutrients. 2019; 11(6):1341. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11061341
Chicago/Turabian StyleKwon, Kyoo-Ri, Md Badrul Alam, Ji-Hyun Park, Tae-Ho Kim, and Sang-Han Lee. 2019. "Attenuation of UVB-Induced Photo-Aging by Polyphenolic-Rich Spatholobus Suberectus Stem Extract Via Modulation of MAPK/AP-1/MMPs Signaling in Human Keratinocytes" Nutrients 11, no. 6: 1341. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11061341
APA StyleKwon, K.-R., Alam, M. B., Park, J.-H., Kim, T.-H., & Lee, S.-H. (2019). Attenuation of UVB-Induced Photo-Aging by Polyphenolic-Rich Spatholobus Suberectus Stem Extract Via Modulation of MAPK/AP-1/MMPs Signaling in Human Keratinocytes. Nutrients, 11(6), 1341. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11061341






