Cereal B-Glucans: The Impact of Processing and How It Affects Physiological Responses
Abstract
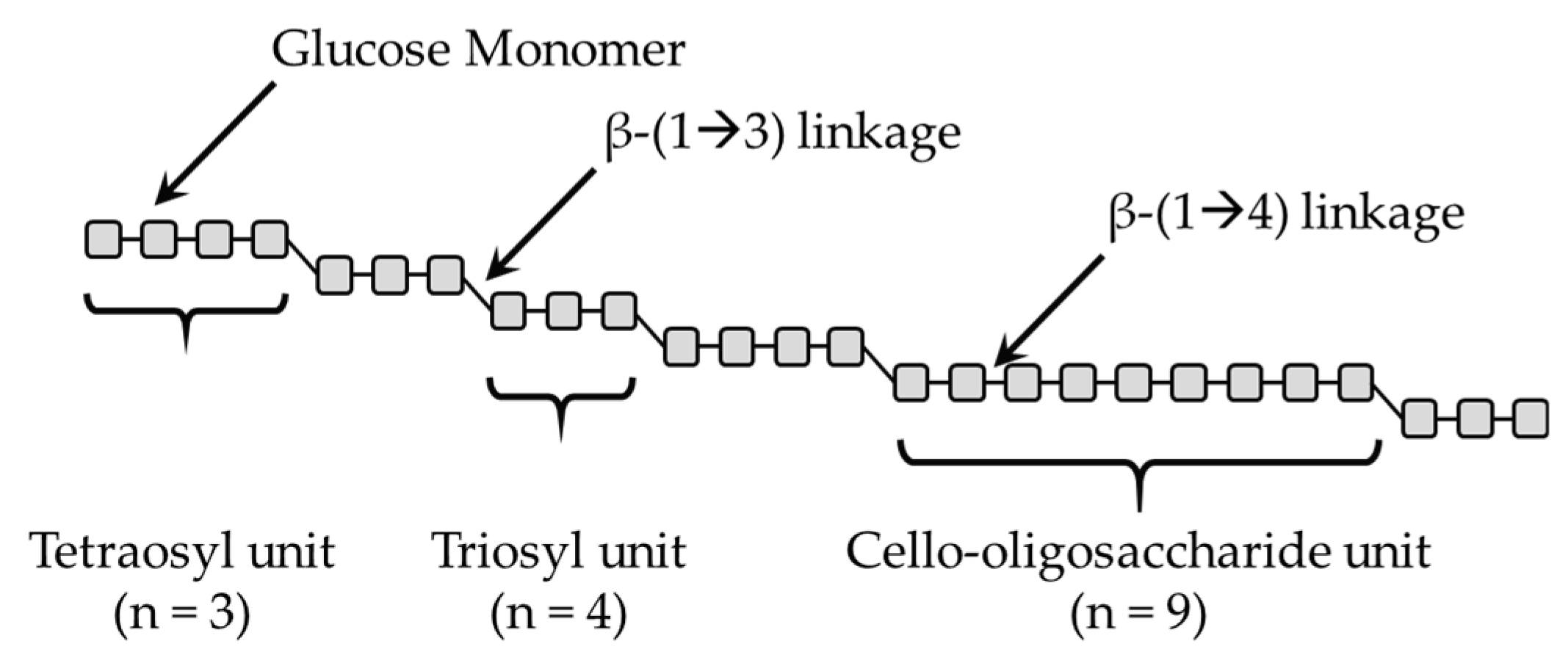
1. Introduction
2. The Effect of β-Glucans on Glucose Metabolism
2.1. The Effect of Molecular Weight of Cereal β-Glucans on Glucose Response
2.2. The Effect of Cereal β-Glucans’ Extractability on Glucose Response
2.3. The Effect of Food Matrix on the Impact of Cereal β-Glucans on Glucose Response
3. The Effect of β-Glucans on Lipid Metabolism
3.1. The Effect of Molecular Weight of Cereal β-Glucans on Lipid Response
3.2. The Effect of Food Matrix of Cereal β-Glucans on Lipid Response
4. The Impact of Cooking and Industrial Processing on the Physicochemical Properties of Cereal β-Glucans
4.1. Breadmaking and Preparations with Enzymes
4.2. Domestic Cooking and Storage of β-Glucan Formulations
4.3. Extrusion Cooking
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products; Nutrition and Allergies (NDA). Scientific Opinion on Dietary Reference Values for Carbohydrates and Dietary Fibre. EFSA J. 2010, 8, 1462. [Google Scholar]
- Institute of Medicine (IOM). Dietary Reference Intakes for Energy, Carbohydrate, Fiber, Fat, Fatty Acids, Cholesterol, Protein and Amino Acids (Macronutrients); The National Academic Press: Washington DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Scientific Advisory Committee on Nutrition (SACN). Carbohydrates and Health Report; TSO (The Stationery Office): London, UK, 2015.
- Joint WHO/FAO Expert Consultation. Diet, Nutrition and the Prevention of Chronic Diseases; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Izydorczyk, M.S.; Macri, L.J.; MacGregor, L.W. Structure and physicochemical properties of barley non-starch polysaccharides—I. Water extractable β-Glucans and arabinoxylans. Carbohydr. Polym. 1998, 35, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosh, S.M.; Brummer, Y.; Wood, P.J.; Wang, Q.; Weisz, J. Evaluation of structure in the formation of gels by structurally diverse (1->3)(1->4)-b-D-glucans from four cereal and one lichen species. Carbohydr. Pol. 2004, 57, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.C.; White, P.J. Enzymatic analysis of b-glucan content in different oat genotypes. Cereal Chem. 1993, 70, 539–542. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Cui, S.W.; Kakuda, Y. Extraction, fractionation, structural and physical characterization of wheat b-D-glucans. Carbohydr. Pol. 2005, 63, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, P.J. REVIEW: Oat and Rye β-Glucan: Properties and Function. Cereal Chem. 2010, 87, 315–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, Q.; Zheng, J. Structure and Characteristic of β-Glucan in Cereal: A Review. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2015, 39, 3145–3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, P.J. Relationships between solution properties of cereal β-glucan and physiological effects—A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2002, 13, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Du, B.; Xu, B. A critical review on production and industrial applications of beta-glucans. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 52, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Önning, G. Cereal beta-glucans: Use in foods to improve functionality and health. Food Sci. Technol. 2005, 19, 20–22. [Google Scholar]
- Lazaridou, A.; Biliaderis, C.G. Molecular aspects of cereal β-glucan functionality: Physical properties, technological applications and physiological effects. J. Cereal Sci. 2007, 46, 101–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Sheng, X.; Shi, A.; Hu, H.; Yang, Y.; Liu, L.; Fei, L.; Liu, H. β-Glucans: Relationships between modification, conformation and functional activities. Molecules 2017, 22, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozbulut, R.; Sanlier, N. Promising effects of β-glucans on glyceamic control in diabetes. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 83, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveria Silva, V.; Oliveria de Moura, N.; Rodrigues de Oliveria, L.J.; Peconick, A.P.; Pereira, L.J. Promising Effects of Beta-Glucans on Metabolism and on the Immune Responses: Review Article. Am. J. Immun. 2017, 13, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieder, A.; Samuelsen, A.B. Do cereal mixed-linked beta-glucans possess immune-modulating activities? Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2012, 56, 536–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kupetz, M.; Procopio, S.; Sacher, B.; Becker, T. Critical review of the methods of β-glucan analysis and its significance in the beer filtration process. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2015, 241, 725–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products; Nutrition and Allergies (NDA). Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of health claims related to beta-glucans from oats and barley and maintenance of normal blood LDL-cholesterol concentrations, increase in satiety leading to a reduction in energy intake, reduction of post-prandial glycaemic responses, and “digestive function” pursuant to Article 13(1) of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006. EFSA J. 2011, 9, 2207. [Google Scholar]
- Mälkki, Y.; Virtanen, E. Gastrointestinal Effects of Oat Bran and Oat Gum A review. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2001, 34, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battilana, P.; Ornstein, K.; Minehira, K.; Schwarz, J.M.; Acheson, K.; Schneiter, P.; Burri, J.; Jequier, E.; Tappy, L. Mechanisms of action of beta-glucan in postprandial glucose metabolism in healthy men. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2001, 55, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwong, M.G.; Wolever, T.M.; Brummer, Y.; Tosh, S.M. Increasing the viscosity of oat beta-glucan beverages by reducing solution volume does not reduce glycaemic responses. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 110, 1465–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostman, E.; Rossi, E.; Larsson, H.; Brighenti, F.; Björck, I. Glucose and insulin responses in healthy men to barley bread with different levels of (1→3;1→4)-β-glucans; predictions using fluidity measurements of in vitro enzyme digests. J. Cereal Sci. 2006, 43, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regand, A.; Chowdhury, Z.; Tosh, S.M.; Wolever, T.M.S.; Wood, P. The molecular weight, solubility and viscosity of oat beta-glucan affect human glycemic response by modifying starch digestibility. Food Chem. 2011, 129, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regand, A.; Tosh, S.M.; Wolever, T.M.; Wood, P.J. Physicochemical properties of beta-glucan in differently processed oat foods influence glycemic response. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2009, 57, 8831–8838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thondre, P.S.; Henry, C.J.K. Effect of a low molecular weight, high-purity B-glucan on in vitro digestion and glycemic response. Int. J. Food. Sci. Nutr. 2011, 62, 678–684. [Google Scholar]
- Thondre, P.S.; Shafat, A.; Clegg, M.E. Molecular weight of barley beta-glucan influences energy expenditure, gastric emptying and glycaemic response in human subjects. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 110, 2173–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anttila, H.; Tuula, S.-S.; Hannu, S. Viscosity of beta-glucan in oat products. Agric. Food. Sci. 2008, 13, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Ellis, P.R. Oat B-glucan: Physico-chemical characteristics in relation to its blood-glucose and cholesterol-lowering properties. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 112, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriartey, S.; Temelli, F.; Vasanthan, T. Effect of formulation and processing treatments on viscosity and solubility of extractable barley B-glucan in bread dough evaluated under in vitro conditions. Cereal Chem. 2010, 87, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan-Pidhainy, X.; Brummer, Y.; Tosh, S.M.; Wolever, T.M.; Wood, P.J. Reducing Beta-Glucan Solubility in Oat Bran Muffins by Freeze-Thaw Treatment Attenuates Its Hypoglycemic Effect. Cereal Chem. 2002, 13, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamel, T.H.; Abdel-Aal, E.S.M.; Ames, N.P.; Duss, R.; Tosh, S.M. Enzymatic extraction of beta-glucan from oat bran cereals and oat crackers and optimization of viscosity measurement. J. Cereal Sci. 2014, 59, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biörklund, M.; Van Rees, A.; Mensink, R.P.; Önning, G. Changes in serum lipids and postprandial glucose and insulin concentrations after consumption of beverages with beta-glucans from oats or barley: A randomised dose-controlled trial. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 59, 1272–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braaten, J.T.; Scott, F.W.; Wood, P.J.; Riedel, K.D.; Wolynetz, M.S.; Brule, D.; Collins, M.W. High beta-glucan oat bran and oat gum reduce postprandial blood glucose and insulin in subjects with and without type 2 diabetes. Diabet. Med. 1994, 11, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casiraghi, M.C.; Garsetti, M.; Testolin, G.; Brighenti, F. Post-prandial responses to cereal products enriched with barley beta-glucan. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2006, 25, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granfeldt, Y.; Nyberg, L.; Bjorck, I. Muesli with 4 g oat beta-glucans lowers glucose and insulin responses after a bread meal in healthy subjects. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 62, 600–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartvigsen, M.L.; Gregersen, S.; Laerke, H.N.; Holst, J.J.; Knudsen, K.B.; Hermansen, K. Effects of concentrated arabinoxylan and beta-glucan compared with refined wheat and whole grain rye on glucose and appetite in subjects with the metabolic syndrome: A randomized study. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 68, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souki-Rincón, A.; Almarza, J.; Mengual, E.; Cano-Peñaloza, R.; Fuenmayor, E.; Aguirre, M.; Reyna-Villasmil, N.; Cano-Ponce, C.; Araujo, S.; Mengual lett, E.; et al. Arepas made from beta-glucans enriched corn flour produced low metabolic responses in healthy subjects. Revista Latinoamericana de Hipertensión 2008, 3, 211–215. [Google Scholar]
- EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products; Nutrition and Allergies (NDA). Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of a health claim related to oat beta-glucan and lowering blood cholesterol and reduced risk of (coronary) heart disease pursuant to Article 14 of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006. EFSA J. 2010, 8, 1885. [Google Scholar]
- Food and Drug Administration. Food Labelling: Healh Claims; Soluble Fiber from Certain Foods and Risk of Coronary Heart Disease; Federal Register: Washington, WA, USA, 2008; Volume 73.
- Ellegard, L.; Andersson, H. Oat bran rapidly increases bile acid excretion and bile acid synthesis: An ileostomy study. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 61, 938–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, J.; Sundberg, B.; Kamal-Eldin, A.; Vessby, B.; Aman, P. Yeast-leavened oat breads with high or low molecular weight beta-glucan do not differ in their effects on blood concentrations of lipids, insulin, or glucose in humans. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 1384–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keenan, J.M.; Goulson, M.; Shamliyan, T.; Knutson, N.; Kolberg, L.; Curry, L. The effects of concentrated barley beta-glucan on blood lipids in a population of hypercholesterolaemic men and women. Br. J. Nutr. 2007, 97, 1162–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Harding, S.V.; Eck, P.; Thandapilly, S.J.; Gamel, T.H.; Abdel-Aal, E.S.M.; Crow, G.H.; Tosh, S.M.; Ames, N.P. High-Molecular-Weight Beta-Glucan Decreases Serum Cholesterol Differentially Based on the CYP7A1 rs3808607 Polymorphism in Mildly Hypercholesterolemic Adults. J. Nutr. 2016, 146, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolever, T.M.; Tosh, S.M.; Gibbs, A.L.; Brand-Miller, J.; Duncan, A.M.; Hart, V.; Lamarche, B.; Thomson, B.A.; Duss, R.; Wood, P.J. Physicochemical properties of oat beta-glucan influence its ability to reduce serum LDL cholesterol in humans: A randomized clinical trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 92, 723–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundy, M.M.; Fardet, A.; Tosh, S.M.; Rich, G.T.; Wilde, P.J. Processing of oat: The impact on oat’s cholesterol lowering effect. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 1328–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerckhoffs, D.A.; Hornstra, G.; Mensink, R.P. Cholesterol-lowering effect of beta-glucan from oat bran in mildly hypercholesterolemic subjects may decrease when beta-glucan is incorporated into bread and cookies. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 78, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naumann, E.; VaN Rees, A.B.; Önning, G.; Öste, R.; Wydra, M.; Mensink, R.P. Beta-Glucan incorporated into a fruit drink effectively lowers serum LDL-cholesterol concentrations. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 83, 601–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondanelli, M.; Opizzi, A.; Monteferrario, F.; Klersy, C.; Cazzola, R.; Cestaro, B. Beta-glucan- or rice bran-enriched foods: A comparative crossover clinical trial on lipidic pattern in mildly hypercholesterolemic men. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 65, 864–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theuwissen, E.; Mensink, R.P. Simultaneous intake of beta-glucan and plant stanol esters affects lipid metabolism in slightly hypercholesterolemic subjects. J. Nutr. 2007, 137, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aman, P.; Rimsten, L.; Andersson, R. Molecular Weight Distribution of β-Glucan in Oat-Based. Foods Cereal Chem. 2004, 81, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivelä, R.; Nyström, L.; Salovaara, H.; Sontag-Strohm, T. Role of oxidative cleavage and acid hydrolysis of oat beta-glucan in modelled beverage conditions. J. Cereal Sci. 2009, 50, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beer, M.U.; Wood, P.J.; Weisz, J.; Fillion, N. Effect of cooking and storage on the amount and molecular weight of (1->3) (1->4)-β-D-Glucan extracted from oat products by an In vitro digetsion system. Cereal Chem. 1997, 74, 705–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, A.A.M.; Armö, E.; Grangeon, E.; Fredriksson, H.; Andersson, R.; Åman, P. Molecular weight and structure units of (1→3, 1→4)-β-glucans in dough and bread made from hull-less barley milling fractions. J. Cereal Sci. 2004, 40, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, A.A.; Rüegg, N.; Aman, P. Molecular weight distribution and content of water-extractable β-glucan in rye crisp bread. J. Cereal Sci. 2008, 47, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleary, L.J.; Andersson, R.; Brennan, C.S. The behaviour and susceptibility to degradation of high and low molecular weight barley β-glucan in wheat bread during baking and In vitro digestion. Food Chem. 2007, 102, 889–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronda, F.; Perez-Quirce, S.; Lazaridou, A.; Biliaderis, C.G. Effect of barley and oat β-glucan concentrates on gluten-free rice-based doughs and bread characteristics. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 48, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djurle, S.; Andersson, A.A.M.; Andersson, R. Effects of baking on dietary fibre, with emphasis on β-glucan and resistant starch, in barley breads. J. Cereal Sci. 2018, 79, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comino, P.; Collins, H.; Lahnstein, J.; Gidley, M.J. Effects of diverse food processing conditions on the structure and solubility of wheat, barley and rye endosperm dietary fibre. J. Food Eng. 2016, 169, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosh, S.M.; Brummer, Y.; Wolever, T.M.; Wood, P.J. Glycemic response to oat bran muffins treated to vary molecular weight of β-glucan. Cereal Chem. 2008, 85, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, L.; Tuomainen, P.; Anttila, H.; Rita, H.; Virkki, L. Effect of processing on the etxractability of oat β-glucan. Food Chem. 2007, 105, 1439–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaosong, J.; Vasanthan, T. Effect of extrusion cooking on the primary structure and water solubility of β-glucan from regular and waxy barley. Cereal Chem. 2000, 77, 396–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosh, S.M.; Brummer, Y.; Miller, S.S.; Regand, A.; Defelice, C.; Duss, R.; Thomas, M.S.; Wood, P.J. Processing affects the physicochemical properties of beta-glucan in oat bran cereal. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 7723–7730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Bai, X.; Zhang, Z. Extrusion process improves the functionality of soluble dietary fiber in oat bran. J. Cereal Sci. 2011, 54, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Gujral, H.S. Extrusion of Hulled Barley Affecting β-Glucan and Properties of Extrudates. Food Bioprocess Tech. 2013, 6, 1374–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pentikainen, S.; Karhunen, L.; Flander, L.; Katina, K.; Meynier, A.; Aymard, P.; Vinoy, S.; Poutanen, K. Enrichment of biscuits and juice with oat beta-glucan enhances postprandial satiety. Appetite 2014, 75, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, E.J.; Tosh, S.M.; Batterham, M.J.; Tapsell, L.C.; Huang, X.F. Oat beta-glucan increases postprandial cholecystokinin levels, decreases insulin response and extends subjective satiety in overweight subjects. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2009, 53, 1343–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlebowicz, J.; Darwiche, G.; Björgell, O.; Almér, L.O. Effect of muesli with 4 g oat beta-glucan on postprandial blood glucose, gastric emptying and satiety in healthy subjects: A randomized crossover trial. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2008, 27, 470–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clegg, M.E.; Thondre, P.S. Molecular weight of barley beta-glucan does not influence satiety or energy intake in healthy male subjects. Appetite 2014, 83, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, H.P.; Boers, H.M.; Haddeman, E.; Melnikov, S.M.; Qvyjt, F. No effect of added beta-glucan or of fructooligosaccharide on appetite or energy intake. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 89, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, R.L.; Dang, X.Y.; Dong, J.L.; Hu, X.Z. Effects of oat beta-glucan and barley beta-glucan on fecal characteristics, intestinal microflora, and intestinal bacterial metabolites in rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 11301–11308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choromanska, A.; Kulbacka, J.; Rembialkowska, N.; Pilat, J.; Oledzki, R.; Harasym, J.; Saczko, J. Anticancer properties of low molecular weight oat beta-glucan - An in vitro study. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 80, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parzonko, A.; Makarewicz-Wujec, M.; Jaszewska, E.; Harasym, J.; Kozłowska-Wojciechowska, M. Pro-apoptotic properties of (1,3) (1,4)-beta-D-glucan from Avena sativa on human melanoma HTB-140 cells in vitro. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 72, 757–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayachandran, M.; Chen, J.; Chung, S.S.M.; Xu, B. A critical review on the impacts of β-glucans on gut microbiota and human health. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2018, 61, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angeli, J.P.; Ribeiro, L.R.; Gonzaga, M.L.C.; Soares, S.D.A.; Ricardo, M.P.S.N.; Tsuboy, M.S.; Stidl, R.; Knasmueller, S.; Linhares, R.E.; Mantovani, M.S. Protective effects of beta-glucan extracted from Agaricus brasiliensis against chemically induced DNA damage in human lymphocytes. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2006, 22, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angeli, J.P.; Ribeiro, L.R.; Bellini, M.F.; Mantovanil, M.S. Anti-clastogenic effect of beta-glucan extracted from barley towards chemically induced DNA damage in rodent cells. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2006, 25, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, R.J.; Ribeiro, L.R.; da Silva, A.F.; Matuo, R.; Mantovani, M.S. Evaluation of antimutagenic activity and mechanisms of action of beta-glucan from barley, in CHO-k1 and HTC cell lines using the micronucleus test. Toxicol. In Vitro 2006, 20, 1225–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, M.S.; Lee, S.; Lee, K.Y.; Lee, H.G. Structural and biological characterization of aminated-derivatized oat beta-glucan. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 5554–5558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuri, C.H.; Estrada, A.; Van Kessel, A.; Gajadhar, A.; Redmond, M.; Laarveld, B.A. Immunomodulatory effects of oat beta-glucan administered intragastrically or parenterally on mice infected with Eimeria vermiformis. Microbiol. Immunol. 1998, 42, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Bian, Z.; Xu, B. Skin health promotion effects of natural beta-glucan derived from cereals and microorganisms: A review. Phytother. Res. 2014, 28, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Type of Processing | Effect of Processing |
|---|---|
| Enzymatic Processing (e.g., Breadmaking) | Large Mw reduction |
| Increased extractability | |
| Gelling domain reached | |
| Cooking & Extrusion | Large Mw reduction under extreme cooking conditions (i.e., low moisture, high heat) |
| Increased extractability | |
| Freezing & Freeze‒Thaw Cycles | Decreased extractability due to aggregation |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Henrion, M.; Francey, C.; Lê, K.-A.; Lamothe, L. Cereal B-Glucans: The Impact of Processing and How It Affects Physiological Responses. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1729. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081729
Henrion M, Francey C, Lê K-A, Lamothe L. Cereal B-Glucans: The Impact of Processing and How It Affects Physiological Responses. Nutrients. 2019; 11(8):1729. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081729
Chicago/Turabian StyleHenrion, Muriel, Célia Francey, Kim-Anne Lê, and Lisa Lamothe. 2019. "Cereal B-Glucans: The Impact of Processing and How It Affects Physiological Responses" Nutrients 11, no. 8: 1729. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081729
APA StyleHenrion, M., Francey, C., Lê, K.-A., & Lamothe, L. (2019). Cereal B-Glucans: The Impact of Processing and How It Affects Physiological Responses. Nutrients, 11(8), 1729. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081729





