Dietary Inflammatory Index and Non-Communicable Disease Risk: A Narrative Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. DII Development
3. Methods
4. DII and Cancers
4.1. Colorectal Cancer (CRC)
4.2. Cancers of the Upper Aerodigestive Tract
4.3. Other Tobacco-Related Cancers
4.4. Other Digestive Tract Sites
4.5. Hormone-Sensitive Cancers
4.6. Lymphomas
5. DII and Cardiometabolic Health and Disease
5.1. DII and CVD Risk and CVD Mortality
5.2. DII and MetS
5.3. DII and Obesity
5.4. DII and T2DM or Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM)
6. DII and Respiratory Health
7. DII and Neurodevelopment
8. DII and Mental Health
9. DII and Musculoskeletal Health
10. DII and Intergenerational Health
11. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GBD 2016 Causes of Death Collaborators. Global, regional, and national age-sex specific mortality for 264 causes of death, 1980–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet 2017, 390, 1151–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, J.M.; Reeves, G.; Billman, G.E.; Sturmberg, J.P. Inflammation-Nature’s Way to Efficiently Respond to All Types of Challenges: Implications for Understanding and Managing “the Epidemic” of Chronic Diseases. Front. Med. 2018, 5, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calder, P.C.; Bosco, N.; Bourdet-Sicard, R.; Capuron, L.; Delzenne, N.; Doré, J.; Franceschi, C.; Lehtinen, M.J.; Recker, T.; Salvioli, S.; et al. Health relevance of the modification of low grade inflammation in ageing (inflammageing) and the role of nutrition. Ageing Res. Rev. 2017, 40, 95–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotamisligil, G.S. Inflammation, metaflammation and immunometabolic disorders. Nature 2017, 542, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micha, R.; Kalantarian, S.; Wirojratana, P.; Byers, T.; Danaei, G.; Elmadfa, I.; Ding, E.; Giovannucci, E.; Powles, J.; Smith-Warner, S.; et al. Estimating the global and regional burden of suboptimal nutrition on chronic disease: Methods and inputs to the analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 66, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willett, W.C.; Stampfer, M.J. Current evidence on healthy eating. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2013, 34, 77–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Arellano, A.; Martinez-Gonzalez, M.A.; Ramallal, R.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Hebert, J.R.; Corella, D.; Shivappa, N.; Forga, L.; Muñoz-Bravo, C.; Estruch, R.; et al. Dietary inflammatory index and all-cause mortality in large cohorts: The SUN and PREDIMED studies. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 1221–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazidi, M.; Shivappa, N.; Wirth, M.D.; Hebert, J.R.; Mikhailidis, D.P.; Kengne, A.P.; Banach, M. Dietary inflammatory index and cardiometabolic risk in US adults. Atherosclerosis 2018, 276, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-Y.; Kang, M.; Wilkens, L.R.; Shvetsov, Y.B.; Harmon, B.E.; Shivappa, N.; Wirth, M.D.; Hébert, J.R.; Haiman, C.A.; Le Marchand, L.; et al. The Dietary Inflammatory Index and All-Cause, Cardiovascular Disease, and Cancer Mortality in the Multiethnic Cohort Study. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivappa, N.; Godos, J.; Hébert, J.R.; Wirth, M.D.; Piuri, G.; Speciani, A.F.; Grosso, G. Dietary Inflammatory Index and Colorectal Cancer Risk—A Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivappa, N.; Godos, J.; Hébert, J.R.; Wirth, M.D.; Piuri, G.; Speciani, A.F.; Grosso, G. Dietary Inflammatory Index and Cardiovascular Risk and Mortality—A Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2018, 10, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivappa, N.; Schneider, A.; Hebert, J.R.; Koenig, W.; Peters, A.; Thorand, B. Association between dietary inflammatory index, and cause-specific mortality in the MONICA/KORA Augsburg Cohort Study. Eur. J. Public Health 2018, 28, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imamura, F.; Micha, R.; Khatibzadeh, S.; Fahimi, S.; Shi, P.; Powles, J.; Mozaffarian, D. Dietary quality among men and women in 187 countries in 1990 and 2010: A systematic assessment. Lancet Glob. Health 2015, 3, e132–e142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minihane, A.M.; Vinoy, S.; Russell, W.R.; Baka, A.; Roche, H.M.; Tuohy, K.M.; Teeling, J.L.; Blaak, E.E.; Fenech, M.; Vauzour, D.; et al. Low-grade inflammation, diet composition and health: Current research evidence and its translation. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 114, 999–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, J.R.; Shivappa, N.; Wirth, M.D.; Hussey, J.R.; Hurley, T.G. Perspective: The Dietary Inflammatory Index (DII)-Lessons Learned, Improvements Made, and Future Directions. Adv. Nutr. 2019, 10, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyson, C.C.; Nwankwo, C.; Lin, P.-H.; Svetkey, L.P. The Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) Eating Pattern in Special Populations. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2012, 14, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heroux, M.; Janssen, I.; Lam, M.; Lee, D.-C.; Hebert, J.R.; Sui, X.; Blair, S.N. Dietary patterns and the risk of mortality: Impact of cardiorespiratory fitness. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 39, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirth, M.D.; Hebert, J.R.; Shivappa, N.; Hand, G.A.; Hurley, T.G.; Drenowatz, C.; McMahon, D.; Shook, R.P.; Blair, S.N. Anti-inflammatory Dietary Inflammatory Index scores are associated with healthier scores on other dietary indices. Nutr. Res. 2016, 36, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugué, P.-A.; Hodge, A.M.; Brinkman, M.T.; Bassett, J.K.; Shivappa, N.; Hebert, J.R.; Hopper, J.L.; English, D.R.; Milne, R.L.; Giles, G.G. Association between selected dietary scores and the risk of urothelial cell carcinoma: A prospective cohort study. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 139, 1251–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Horn, L.; Appel, L.J. Did the PREDIMED Trial Test a Mediterranean Diet? N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 1353–1354. [Google Scholar]
- Buckland, G.; Travier, N.; Cottet, V.; Gonzalez, C.A.; Lujan-Barroso, L.; Agudo, A.; Trichopoulou, A.; Lagiou, P.; Trichopoulos, D.; Peeters, P.H.; et al. Adherence to the mediterranean diet and risk of breast cancer in the European prospective investigation into cancer and nutrition cohort study. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 132, 2918–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viscogliosi, G.; Cipriani, E.; Liguori, M.L.; Marigliano, B.; Saliola, M.; Ettorre, E.; Andreozzi, P. Mediterranean Dietary Pattern Adherence: Associations with Prediabetes, Metabolic Syndrome, and Related Microinflammation. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2013, 11, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, M.; Vierkant, R.A.; Kushi, L.H.; Sellers, T.A.; Vachon, C.M. Dietary patterns and breast density in the Minnesota Breast Cancer Family Study. Cancer Causes Control 2008, 19, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, M.; Chocano-Bedoya, P.; Schulze, M.B.; Mirzaei, F.; O’Reilly, E.J.; Okereke, O.I.; Hu, F.B.; Willett, W.C.; Ascherio, A. Inflammatory dietary pattern and risk of depression among women. Brain Behav. Immun. 2014, 36, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabung, F.K.; Smith-Warner, S.A.; Chavarro, J.E.; Wu, K.; Fuchs, C.S.; Hu, F.B.; Chan, A.T.; Willett, W.C.; Giovannucci, E.L. Development and Validation of an Empirical Dietary Inflammatory Index. J. Nutr. 2016, 146, 1560–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavicchia, P.P.; Steck, S.E.; Hurley, T.G.; Hussey, J.R.; Ma, Y.; Ockene, I.S.; Hébert, J.R. A New Dietary Inflammatory Index Predicts Interval Changes in Serum High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein. J. Nutr. 2009, 139, 2365–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivappa, N.; Steck, S.E.; Hurley, T.G.; Hussey, J.R.; Hebert, J.R. Designing and developing a literature-derived population-based dietary inflammatory index. Public Health Nutr. 2014, 17, 1689–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, J.R.; Ockene, I.S.; Hurley, T.G.; Luippold, R.; Well, A.D.; Harmatz, M.G. Development and testing of a seven-day dietary recall. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1997, 50, 925–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivappa, N.; Steck, S.E.; Hurley, T.G.; Hussey, J.R.; Ma, Y.; Ockene, I.S.; Tabung, F.; Hébert, J.R. A population-based dietary inflammatory index predicts levels of c-reactive protein (CRP) in the SEASONS Study. Public Health Nutr. 2014, 17, 1825–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirth, M.D.; Burch, J.; Shivappa, N.; Violanti, J.M.; Burchfiel, C.M.; Fekedulegn, D.; Andrew, M.E.; Hartley, T.A.; Miller, D.B.; Mnatsakanova, A.; et al. Association of a Dietary Inflammatory Index with Inflammatory Indices and the Metabolic Syndrome among Police Officers. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2014, 56, 986–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivappa, N.; Hebert, J.R.; Rietzschel, E.R.; De Buyzere, M.L.; Langlois, M.; Debruyne, E.; Marcos, A.; Huybrechts, I. Associations between dietary inflammatory index and inflammatory markers in the Asklepios Study. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 113, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tabung, F.K.; Steck, S.E.; Zhang, J.; Ma, Y.; Liese, A.D.; Agalliu, I.; Hingle, M.; Hou, L.; Hurley, T.G.; Jiao, L.; et al. Construct Validation of the Dietary Inflammatory Index among Postmenopausal Women. Ann. Epidemiol. 2015, 25, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivappa, N.; Hebert, J.R.; Marcos, A.; Diaz, L.-E.; Gomez, S.; Nova, E.; Michels, N.; Arouca, A.; González-Gil, E.; Frederic, G.; et al. Association between dietary inflammatory index and inflammatory markers in the HELENA study. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1600707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivappa, N.; Wirth, M.D.; Hurley, T.G.; Hebert, J.R. Association between the Dietary Inflammatory Index (DII) and telomere length and C-reactive protein from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1999–2002. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2016, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julia, C.; Assmann, K.E.; Shivappa, N.; Hebert, J.R.; Wirth, M.D.; Hercberg, S.; Touvier, M.; Kesse-Guyot, E. Long-term associations between inflammatory dietary scores in relation to long-term C-reactive protein status measured 12 years later: Findings from the Supplémentation en Vitamines et Minéraux Antioxydants (SU.VI.MAX) cohort. Br. J. Nutr. 2017, 117, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahid, F.; Shivappa, N.; Hekmatdoost, A.; Hebert, J.R.; Davoodi, S.H.; Sadeghi, M. Association between Maternal Dietary Inflammatory Index (DII) and abortion in Iranian women and validation of DII with serum concentration of inflammatory factors: Case-control study. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2017, 42, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirth, M.D.; Shivappa, N.; Davis, L.; Hurley, T.G.; Ortaglia, A.; Drayton, R.; Blair, S.N.; Hébert, J.R. Construct validation of the Dietary Inflammatory Index among African Americans. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2017, 21, 487–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahid, F.; Shivappa, N.; Faghfoori, Z.; Khodabakhshi, A.; Zayeri, F.; Hebert, J.R.; Davoodi, S.H. Validation of a Dietary Inflammatory Index (DII) and Association with Risk of Gastric Cancer: A Case-Control Study. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2018, 19, 1471–1477. [Google Scholar]
- Shivappa, N.; Wirth, M.D.; Murphy, E.A.; Hurley, T.G.; Hebert, J.R. Association between the Dietary Inflammatory Index (DII) and urinary enterolignans and C-reactive protein from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2003–2008. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 58, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodén, S.; Wennberg, M.; Van Guelpen, B.; Johansson, I.; Lindahl, B.; Andersson, J.; Shivappa, N.; Hebert, J.R.; Nilsson, L.M. Dietary inflammatory index and risk of first myocardial infarction; A prospective population-based study. Nutr. J. 2017, 16, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, C.M.; Shivappa, N.; Hébert, J.R.; Perry, I.J. Dietary Inflammatory Index and Biomarkers of Lipoprotein Metabolism, Inflammation and Glucose Homeostasis in Adults. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabung, F.K.; Steck, S.E.; Ma, Y.; Liese, A.D.; Zhang, J.; Caan, B.; Hou, L.; Johnson, K.C.; Mossavar-Rahmani, Y.; Shivappa, N.; et al. The association between dietary inflammatory index and risk of colorectal cancer among postmenopausal women: Results from the Women’s Health Initiative. Cancer Causes Control 2015, 26, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizil, M.; Tengilimoglu-Metin, M.M.; Gumus, D.; Sevim, S.; Turkoglu, I.; Mandiroglu, F. Dietary inflammatory index is associated with serum C-reactive protein and protein energy wasting in hemodialysis patients: A cross-sectional study. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2016, 10, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kotemori, A.; Sawada, N.; Iwasaki, M.; Yamaji, T.; Shivappa, N.; Hebert, J. Association between dietary inflammatory index and high-sensitive C-reactive protein levels in cancer screening in Japanese. Rev. D’Epidemiol. St. Publique 2018, 66, S347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.; Lee, K.W.; Brann, L.; Shivappa, N.; Hebert, J.R. Dietary inflammatory index is positively associated with serum high-sensitivity C-reactive protein in a Korean adult population. Nutrition 2018, 63–64, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirmajidi, S.; Izadi, A.; Saghafi-Asl, M.; Vahid, F.; Karamzad, N.; Amiri, P.; Shivappa, N.; Hébert, J.R. Inflammatory Potential of Diet: Association With Chemerin, Omentin, Lipopolysaccharide-Binding Protein, and Insulin Resistance in the Apparently Healthy Obese. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2019, 38, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirth, M.D.; Sevoyan, M.; Hofseth, L.; Shivappa, N.; Hurley, T.G.; Hébert, J.R. The Dietary Inflammatory Index is associated with elevated white blood cell counts in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Brain Behav. Immun. 2018, 69, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivappa, N.; Bonaccio, M.; Hebert, J.R.; Di Castelnuovo, A.; Costanzo, S.; Ruggiero, E.; Pounis, G.; Donati, M.B.; de Gaetano, G.; Iacoviello, L.; et al. Association of proinflammatory diet with low-grade inflammation: Results from the Moli-sani study. Nutrition 2018, 54, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Wirth, M.D.; Ortaglia, A.; Alvarado, C.R.; Shivappa, N.; Hurley, T.G.; Hebert, J.R. Design, Development and Construct Validation of the Children’s Dietary Inflammatory Index. Nutrients 2018, 10, 993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkwill, F.; Mantovani, A. Inflammation and cancer: Back to Virchow? Lancet 2001, 357, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Hao, X.; Li, J.; Wu, Z.; Chen, S.; Lin, J.; Li, X.; Dong, Y.; Na, Z.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Dose-response relation between dietary inflammatory index and human cancer risk: Evidence from 44 epidemiologic studies involving 1,082,092 participants. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 107, 371–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.-L.; Ren, Z.-J.; Zhang, Q.; Ren, P.-W.; Yang, B.; Liu, L.-R.; Dong, Q. Meta-analysis of the association between the inflammatory potential of diet and urologic cancer risk. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, C.; Zhou, C.; Zhuang, J.; Tang, S.; Yu, J.; Tian, J.; Feng, F.; Liu, L.; Zhang, T.; et al. Meta-analysis of the association between the dietary inflammatory index (DII) and breast cancer risk. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 73, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.-Y.; Gao, X.-P.; Zhu, S.; Liu, Y.-H.; Wang, L.-J.; Jing, C.-X.; Zeng, F.-F. Dietary inflammatory index and risk of gynecological cancers: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. J. Gynecol. Oncol. 2019, 30, e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawa, T.; Ohshima, H. Nitrative DNA damage in inflammation and its possible role in carcinogenesis. Nitric Oxide 2006, 14, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, J.J.; Schetter, A.J.; Yfantis, H.G.; Ridnour, L.A.; Horikawa, I.; Khan, M.A.; Robles, A.I.; Hussain, S.P.; Goto, A.; Bowman, E.D.; et al. Macrophages, Nitric Oxide and microRNAs Are Associated with DNA Damage Response Pathway and Senescence in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnishi, S.; Ma, N.; Thanan, R.; Pinlaor, S.; Hammam, O.; Murata, M.; Kawanishi, S. DNA Damage in Inflammation-Related Carcinogenesis and Cancer Stem Cells. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2013, 2013, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwer, J.G.; Makama, M.; Van Woudenbergh, G.J.; Vasen, H.F.; Nagengast, F.M.; Kleibeuker, J.H.; Kampman, E.; Van Duijnhoven, F.J. Inflammatory potential of the diet and colorectal tumor risk in persons with Lynch syndrome. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 106, ajcn152900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, M. Inflammation and cancer. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2018, 23, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawanishi, S.; Hiraku, Y.; Pinlaor, S.; Ma, N. Oxidative and nitrative DNA damage in animals and patients with inflammatory diseases in relation to inflammation-related carcinogenesis. Boil. Chem. 2006, 387, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.P.; Hofseth, L.J.; Harris, C.C. Radical causes of cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, M.; Rowley, D.A.; Schreiber, H. Inflammation as a tumor promoter in cancer induction. Semin. Cancer Boil. 2004, 14, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, J.R.; Backlund, M.G.; DuBois, R.N. Mechanisms of disease: Inflammatory mediators and cancer prevention. Nat. Clin. Pract. Oncol. 2005, 2, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.-H.; Lai, C.-S.; Dushenkov, S.; Ho, C.-T.; Dushenkov, V. Modulation of Inflammatory Genes by Natural Dietary Bioactive Compounds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 4467–4477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guffey, C.R.; Fan, D.; Singh, U.P.; Murphy, E.A. Linking obesity to colorectal cancer: Recent insights into plausible biological mechanisms. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2013, 16, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, L.; Ye, W.; Wen, Q.; Wang, J. Role of cancer-related inflammation in esophageal cancer. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 2013, 23, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugase, T.; Takahashi, T.; Serada, S.; Nakatsuka, R.; Fujimoto, M.; Ohkawara, T.; Hara, H.; Nishigaki, T.; Tanaka, K.; Miyazaki, Y.; et al. Suppressor of cytokine signaling-1 gene therapy induces potent antitumor effect in patient-derived esophageal squamous cell carcinoma xenograft mice. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 140, 2608–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohseni, R.; Abbasi, S.; Mohseni, F.; Rahimi, F.; Alizadeh, S. Association between Dietary Inflammatory Index and the Risk of Prostate Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Nutr. Cancer 2018, 71, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, S.; Issah, A.; Mohammadi, H.; Mirzaei, K. Associations between dietary inflammatory index and incidence of breast and prostate cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients 2018, 56, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namazi, N.; Larijani, B.; Azadbakht, L. Association between the dietary inflammatory index and the incidence of cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. Public Health 2018, 164, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, J.M.; Campbell, B.J. Inflammation and colorectal cancer: IBD-associated and sporadic cancer compared. Trends Mol. Med. 2002, 8, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toriola, A.T.; Cheng, T.Y.; Neuhouser, M.L.; Wener, M.H.; Zheng, Y.; Brown, E.; Miller, J.W.; Song, X.; Beresford, S.A.; Gunter, M.J.; et al. Biomarkers of inflammation are associated with colorectal cancer risk in women but are not suitable as early detection markers. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 132, 2648–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, R.N. Role of Inflammation and Inflammatory Mediators in Colorectal Cancer. Trans. Am. Clin. Clim. Assoc. 2014, 125, 358–373. [Google Scholar]
- Poullis, A.; Foster, R.; Shetty, A.; Fagerhol, M.K.; Mendall, M.A. Bowel Inflammation as Measured by Fecal Calprotectin: A Link between Lifestyle Factors and Colorectal Cancer Risk. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2004, 13, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dales, L.G.; Friedman, G.D.; Ury, H.K.; Grossman, S.; Williams, S.R. A case-control study of relationships of diet and other traits to colorectal cancer in american blacks. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1979, 109, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trichopoulos, D.; Polychronopoulou, A. Epidemiology, diet and colorectal cancer. Eur. J. Cancer Clin. Oncol. 1986, 22, 335–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wargovich, M.J.; Baer, A.R.; Hu, P.J.; Sumiyoshi, H. Dietary factors and colorectal cancer. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 1988, 17, 727–745. [Google Scholar]
- Accardi, G.; Shivappa, N.; Di Maso, M.; Hebert, J.R.; Fratino, L.; Montella, M.; La Vecchia, C.; Caruso, C.; Serraino, D.; Libra, M.; et al. Dietary inflammatory index and cancer risk in the elderly: A pooled-analysis of Italian case-control studies. Nutrition 2019, 63–64, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmon, B.E.; Wirth, M.D.; Boushey, C.J.; Wilkens, L.R.; Draluck, E.; Shivappa, N.; Steck, S.E.; Hofseth, L.; Haiman, C.A.; Le Marchand, L.; et al. The Dietary Inflammatory Index Is Associated with Colorectal Cancer Risk in the Multiethnic Cohort. J. Nutr. 2017, 147, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niclis, C.; Pou, S.A.; Shivappa, N.; Hébert, J.R.; Steck, S.E.; Díaz, M.D.P. Proinflammatory Dietary Intake is Associated with Increased Risk of Colorectal Cancer: Results of a Case-Control Study in Argentina Using a Multilevel Modeling Approach. Nutr. Cancer 2017, 70, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obón-Santacana, M.; Romaguera, D.; Gracia-Lavedan, E.; Molinuevo, A.; Molina-Montes, E.; Shivappa, N.; Hebert, J.R.; Tardón, A.; Castaño-Vinyals, G.; Moratalla, F.; et al. Dietary Inflammatory Index, Dietary Non-Enzymatic Antioxidant Capacity, and Colorectal and Breast Cancer Risk (MCC-Spain Study). Nutrients 2019, 11, 1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiee, P.; Shivappa, N.; Hébert, J.R.; Nasab, S.J.; Bahrami, A.; Hekmatdoost, A.; Rashidkhani, B.; Sadeghi, A.; Houshyari, M.; Hejazi, E. Dietary Inflammatory Index and Odds of Colorectal Cancer and Colorectal Adenomatous Polyps in a Case-Control Study from Iran. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, I.; Zhu, Y.; Woodrow, J.R.; Mulay, S.; Parfrey, P.S.; McLaughlin, J.R.; Hebert, J.R.; Shivappa, N.; Li, Y.; Zhou, X.; et al. Inflammatory diet and risk for colorectal cancer: A population-based case-control study in Newfoundland, Canada. Nutrition 2017, 42, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivappa, N.; Prizment, A.E.; Blair, C.K.; Jacobs, D.R.; Steck, S.E.; Hébert, J.R. Dietary Inflammatory Index (DII) and risk of colorectal cancer in Iowa Women’s Health Study. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2014, 23, 2383–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivappa, N.; Zucchetto, A.; Montella, M.; Serraino, D.; Steck, S.E.; La Vecchia, C.; Hebert, J.R. Inflammatory potential of diet and risk of colorectal cancer: A case-control study from Italy. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 114, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivappa, N.; Steck, S.E.; Shehadah, I.; Al-Jaberi, T.; Al-Nusairr, M.; Heath, D.; Hébert, J.R.; Hofseth, L.J.; Bani-Hani, K.E.; Tayyem, R. Dietary inflammatory index and odds of colorectal cancer in a case-control study from Jordan. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2017, 42, 744–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivappa, N.; Hebert, J.R.; Steck, S.E.; Safari, A.; Sedaghat, F.; Rashidkhani, B. Dietary Inflammatory Index and Odds of Colorectal Cancer in a Case-Control Study from Iran. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2018, 19, 1999–2006. [Google Scholar]
- Wirth, M.D.; Shivappa, N.; Steck, S.E.; Hurley, T.G.; Hebert, J.R. The Dietary Inflammatory Index is Associated with Colorectal Cancer in the National Institutes of Health-American Association of Retired Persons Diet and Health Study. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 113, 1819–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora-Ros, R.; Shivappa, N.; Steck, S.E.; Canzian, F.; Landi, S.; Alonso, M.H.; Hébert, J.R.; Moreno, V. Dietary inflammatory index and inflammatory gene interactions in relation to colorectal cancer risk in the Bellvitge colorectal cancer case-control study. Genes Nutr. 2015, 10, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, F.E.; Shivappa, N.; Tang, Y.; Mann, J.R.; Hebert, J.R. Association between diet-related inflammation, all-cause, all-cancer, and cardiovascular disease mortality, with special focus on prediabetics: Findings from NHANES III. Eur. J. Nutr. 2016, 56, 1085–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratjen, I.; Shivappa, N.; Schafmayer, C.; Burmeister, G.; Nothlings, U.; Hampe, J.; Hébert, J.R.; Lieb, W.; Schlesinger, S. Association between the dietary inflammatory index and all-cause mortality in colorectal cancer long-term survivors. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 144, 1292–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Tabung, F.K.; Zhang, J.; Murphy, E.A.; Shivappa, N.; Ockene, J.K.; Caan, B.; Kroenke, C.H.; Hébert, J.R.; Steck, S.E. Post-cancer diagnosis dietary inflammatory potential is associated with survival among women diagnosed with colorectal cancer in the Women’s Health Initiative. Eur. J. Nutr. 2019, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haslam, A.; Robb, S.W.; Hébert, J.R.; Huang, H.; Wirth, M.D.; Shivappa, N.; Ebell, M.H. The association between Dietary Inflammatory Index scores and the prevalence of colorectal adenoma. Public Health Nutr. 2017, 20, 1609–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sardo Molmenti, C.L.; Steck, S.E.; Thomson, C.A.; Hibler, E.A.; Yang, J.; Shivappa, N.; Greenlee, H.; Wirth, M.D.; Neugut, A.I.; Jacobs, E.T.; et al. Dietary Inflammatory Index and Risk of Colorectal Adenoma Recurrence: A Pooled Analysis. Nutr. Cancer 2017, 69, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruner, S.D.; Jobin, C. Intestinal microbiota in inflammatory bowel disease and carcinogenesis: Implication for therapeutics. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 99, 585–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, E.A.; Velázquez, K.T.; Herbert, K.M. Influence of High-Fat-Diet on Gut Microbiota: A Driving Force for Chronic Disease Risk. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2015, 18, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith-Brown, P.; Morrison, M.; Krause, L.; Davies, P.S.W. Dairy and plant based food intakes are associated with altered faecal microbiota in 2 to 3 year old Australian children. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wogan, G.N.; Hecht, S.S.; Felton, J.S.; Conney, A.H.; Loeb, L.A. Environmental and chemical carcinogenesis. Semin. Cancer Boil. 2004, 14, 473–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugade, A.A.; Bogner, P.N.; Thatcher, T.H.; Sime, P.J.; Phipps, R.P.; Thanavala, Y. Cigarette Smoke Exposure Exacerbates Lung Inflammation and Compromises Immunity to Bacterial Infection. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 5226–5235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shivappa, N.; Hebert, J.; Rosato, V.; Serraino, D.; La Vecchia, C. Inflammatory potential of diet and risk of laryngeal cancer in a case–control study from Italy. Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 61, S153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazul, A.L.; Shivappa, N.; Hébert, J.R.; Steck, S.E.; Rodriguez-Ormaza, N.; Weissler, M.; Olshan, A.F.; Zevallos, J.P. Proinflammatory diet is associated with increased risk of squamous cell head and neck cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 143, 1604–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivappa, N.; Hébert, J.R.; Zucchetto, A.; Montella, M.; Libra, M.; Garavello, W.; Rossi, M.; La Vecchia, C.; Serraino, D. Increased risk of nasopharyngeal carcinoma with increasing levels of diet-associated inflammation in an Italian case-control study. Nutr. Cancer 2016, 68, 1123–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, M.; Shivappa, N.; Ito, H.; Oze, I.; Abe, T.; Shimizu, Y.; Hasegawa, Y.; Kiyohara, C.; Nomura, M.; Ogawa, Y.; et al. Dietary inflammatory index and risk of upper aerodigestive tract cancer in Japanese adults. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 24028–24040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shivappa, N.; Hébert, J.R.; Rosato, V.; Garavello, W.; Serraino, D.; La Vecchia, C. Inflammatory potential of diet and risk of oral and pharyngeal cancer in a large case-control study from Italy. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 141, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzi, C.; Zhang, J.; Purdon, C.H.; Chapman, J.M.; Nitcheva, D.; Hebert, J.R.; Smith, E.W. Permeation and reservoir formation of 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone (NNK) and benzo[a]pyrene (BAP) across porcine esophageal tissue in the presence of ethanol and menthol. Carcinogenesis 2006, 27, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squier, C.A.; Mantz, M.J.; Wertz, P.W. Effect of menthol on the penetration of tobacco carcinogens and nicotine across porcine oral mucosa ex vivo. Nicotine Tob. Res. 2010, 12, 763–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shivappa, N.; Hebert, J.R.; Rashidkhani, B. Dietary Inflammatory Index and risk of esophageal squamous cell cancer in a case-control study from Iran. Nutr. Cancer 2015, 67, 1253–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivappa, N.; Zucchetto, A.; Serraino, D.; Rossi, M.; La Vecchia, C.; Hebert, J.R. Dietary inflammatory index and risk of esophageal squamous cell cancer in a case–control study from Italy. Cancer Causes Control 2015, 26, 1439–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Shivappa, N.; Lin, Y.; Lagergren, J.; Hebert, J.R. Diet-related inflammation and oesophageal cancer by histological type: A nationwide case-control study in Sweden. Eur. J. Nutr. 2016, 55, 1683–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivappa, N.; Hebert, J.R.; Anderson, L.A.; Shrubsole, M.J.; Murray, L.J.; Getty, L.B.; Coleman, H.G. Dietary inflammatory index and risk of reflux oesophagitis, Barrett’s oesophagus and oesophageal adenocarcinoma: A population-based case–control study. Br. J. Nutr. 2017, 117, 1323–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Shivappa, N.; Hebert, J.R.; Lee, A.H.; Xu, F.; Binns, C.W. Dietary inflammatory index and risk of oesophageal cancer in Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region, China. Br. J. Nutr. 2018, 119, 1068–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hodge, A.M.; Bassett, J.K.; Shivappa, N.; Hébert, J.R.; English, D.R.; Giles, G.G.; Severi, G. Dietary inflammatory index, Mediterranean diet score, and lung cancer: A prospective study. Cancer Causes Control 2016, 27, 907–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivappa, N.; Wang, R.; Hébert, J.R.; Jin, A.; Koh, W.-P.; Yuan, J.M. Association between inflammatory potential of diet and risk of lung cancer among smokers in a prospective study in Singapore. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodén, S.; Myte, R.; Wennberg, M.; Harlid, S.; Johansson, I.; Shivappa, N.; Hébert, J.R.; Van Guelpen, B.; Nilsson, L.M. The inflammatory potential of diet in determining cancer risk; A prospective investigation of two dietary pattern scores. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maisonneuve, P.; Shivappa, N.; Hebert, J.R.; Bellomi, M.; Rampinelli, C.; Bertolotti, R.; Spaggiari, L.; Palli, D.; Veronesi, G.; Gnagnarella, P. Dietary inflammatory index and risk of lung cancer and other respiratory conditions among heavy smokers in the COSMOS screening study. Eur. J. Nutr. 2015, 55, 1069–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shivappa, N.; Hebert, J.R.; Rosato, V.; Rossi, M.; Libra, M.; Montella, M.; Serraino, D.; La Vecchia, C. Dietary Inflammatory Index and Risk of Bladder Cancer in a Large Italian Case-Control Study. Urology 2017, 100, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivappa, N.; Hebert, J.R.; Mirsafa, F.; Rashidkhani, B. Increased Inflammatory Potential of Diet Is Associated with Increased Risk of Bladder Cancer in an Iranian Case-Control Study. Nutr. Cancer 2019, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivappa, N.; Blair, C.K.; Prizment, A.E.; Jacobs, D.R.; Hébert, J.R. Dietary inflammatory index and risk of renal cancer in the Iowa Women’s Health Study. Eur. J. Nutr. 2017, 57, 1207–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivappa, N.; Hébert, J.R.; Rosato, V.; Rossi, M.; Montella, M.; Serraino, D.; La Vecchia, C. Dietary Inflammatory Index and Renal Cell Carcinoma Risk in an Italian Case-Control Study. Nutr. Cancer 2017, 69, 833–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivappa, N.; Bosetti, C.; Zucchetto, A.; Serraino, D.; La Vecchia, C.; Hebert, J.R. Dietary inflammatory index and risk of pancreatic cancer in an Italian case-control study. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 113, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antwi, S.O.; Oberg, A.L.; Shivappa, N.; Bamlet, W.R.; Chaffee, K.G.; Steck, S.E.; Hebert, J.R.; Petersen, G.M. Pancreatic cancer: Associations of inflammatory potential of diet, cigarette smoking and long-standing diabetes. Carcinogenesis 2016, 37, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antwi, S.O.; Bamlet, W.R.; Pedersen, K.S.; Chaffee, K.G.; Risch, H.A.; Shivappa, N.; Steck, S.E.; Anderson, K.E.; Bracci, P.M.; Polesel, J.; et al. Pancreatic Cancer Risk is Modulated by Inflammatory Potential of Diet and ABO Genotype: A Consortia-based Evaluation and Replication Study. Carcinogenesis 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Merchant, A.T.; Wirth, M.D.; Zhang, J.; Antwi, S.O.; Shoaibi, A.; Shivappa, N.; Stolzenberg-Solomon, R.Z.; Hebert, J.R.; Steck, S.E. Inflammatory potential of diet and risk of pancreatic cancer in the Prostate, Lung, Colorectal and Ovarian (PLCO) Cancer Screening Trial. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 142, 2461–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Wirth, M.D.; Merchant, A.T.; Zhang, J.; Shivappa, N.; Stolzenberg-Solomon, R.Z.; Hebert, J.R.; Steck, S.E. Inflammatory potential of diet, inflammation-related lifestyle factors and risk of pancreatic cancer: Results from the NIH-AARP Diet and Health Study. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivappa, N.; Hebert, J.R.; Polesel, J.; Zucchetto, A.; Crispo, A.; Montella, M.; Franceschi, S.; Rossi, M.; La Vecchia, C.; Serraino, D. Inflammatory potential of diet and risk for hepatocellular cancer in a case-control study from Italy. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 115, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-Y.; Fang, A.-P.; Chen, P.-Y.; Liao, G.-C.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Shivappa, N.; Hébert, J.R.; Chen, Y.-M.; Zhu, H.-L. High dietary inflammatory index scores are associated with an elevated risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in a case–control study. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 5832–5842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivappa, N.; Hébert, J.R.; Ferraroni, M.; La Vecchia, C.; Rossi, M. Association between dietary inflammatory index and gastric cancer risk in an Italian case-control study. Nutr. Cancer 2016, 68, 1262–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graffouillère, L.; Deschasaux, M.; Mariotti, F.; Neufcourt, L.; Shivappa, N.; Hébert, J.R.; Wirth, M.D.; Latino-Martel, P.; Hercberg, S.; Galan, P.; et al. The Dietary Inflammatory Index Is Associated with Prostate Cancer Risk in French Middle-Aged Adults in a Prospective Study. J. Nutr. 2016, 146, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, D.V.; Shivappa, N.; Pham, N.M.; Hebert, J.R.; Binns, C.W.; Lee, A.H. Dietary inflammatory index is associated with increased risk for prostate cancer among Vietnamese men. Nutrition 2019, 62, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, D.M.; Burch, J.B.; Hebert, J.R.; Hardin, J.W.; Zhang, J.; Wirth, M.D.; Youngstedt, S.D.; Shivappa, N.; Jacobsen, S.J.; Caan, B.; et al. Diet-related inflammation and risk of prostate cancer in the California Men’s Health Study. Ann. Epidemiol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivappa, N.; Bosetti, C.; Zucchetto, A.; Montella, M.; Serraino, D.; La Vecchia, C.; Hebert, J.R. Association between dietary inflammatory index and prostate cancer among Italian men. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 113, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivappa, N.; Jackson, M.D.; Bennett, F.; Hebert, J.R. Increased Dietary Inflammatory Index (DII) Is Associated With Increased Risk of Prostate Cancer in Jamaican Men. Nutr. Cancer 2015, 67, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivappa, N.; Hebert, J.R.; Askari, F.; Kardoust Parizi, M.; Rashidkhani, B. Increased Inflammatory Potential of Diet is Associated with Increased Risk of Prostate Cancer in Iranian Men. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. Int. Z. Vitam. 2017, 86, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivappa, N.; Miao, Q.; Walker, M.; Hébert, J.R.; Aronson, K.J. Association Between a Dietary Inflammatory Index and Prostate Cancer Risk in Ontario, Canada. Nutr. Cancer 2017, 69, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivappa, N.; Niclis, C.; Coquet, J.B.; Román, M.D.; Hébert, J.R.; Diaz, M.D.P. Increased inflammatory potential of diet is associated with increased odds of prostate cancer in Argentinian men. Cancer Causes Control 2018, 29, 803–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Salas, R.A.; Shivappa, N.; Galván-Portillo, M.; López-Carrillo, L.; Hébert, J.R.; Torres-Sánchez, L. Dietary inflammatory index and prostate cancer risk in a case–control study in Mexico. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 116, 1945–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, A.C.; Oyekunle, T.; Howard, L.E.; Shivappa, N.; De Hoedt, A.; Figueiredo, J.C.; Taioli, E.; Fowke, J.H.; Lin, P.H.; Hebert, J.R.; et al. Dietary inflammatory index (DII) and risk of prostate cancer in a case-control study among Black and White US Veteran men. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucchetto, A.; Gini, A.; Shivappa, N.; Hebert, J.R.; Stocco, C.; Maso, L.D.; Birri, S.; Serraino, D.; Polesel, J. Dietary inflammatory index and prostate cancer survival. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 139, 2398–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivappa, N.; Sandin, S.; Löf, M.; Hébert, J.R.; Adami, H.-O.; Weiderpass, E. Prospective study of dietary inflammatory index and risk of breast cancer in Swedish women. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 113, 1099–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, W.-Q.; Mo, X.-F.; Ye, Y.-B.; Shivappa, N.; Lin, F.-Y.; Huang, J.; Hébert, J.R.; Yan, B.; Zhang, C.-X. A higher Dietary Inflammatory Index score is associated with a higher risk of breast cancer among Chinese women: A case-control study. Br. J. Nutr. 2017, 117, 1358–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivappa, N.; Blair, C.K.; Prizment, A.E.; Jacobs, D.R.; Hébert, J.R. Prospective study of the dietary inflammatory index and risk of breast cancer in postmenopausal women. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivappa, N.; Hebert, J.R.; Rosato, V.; Montella, M.; Serraino, D.; La Vecchia, C. Association between the dietary inflammatory index and breast cancer in a large Italian case-control study. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalali, S.; Shivappa, N.; Hébert, J.R.; Heidari, Z.; Hekmatdoost, A.; Rashidkhani, B. Dietary Inflammatory Index and Odds of Breast Cancer in a Case-Control Study from Iran. Nutr. Cancer 2018, 70, 1034–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardeazabal, I.; Ruiz-Canela, M.; Sánchez-Bayona, R.; Romanos-Nanclares, A.; Aramendía-Beitia, J.; Shivappa, N.; Hébert, J.; Martínez-González, M.; Toledo, E. Dietary inflammatory index and incidence of breast cancer in the SUN project. Clin. Nutr. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, I.; Rudolph, A.; Shivappa, N.; Flesch-Janys, D.; Hebert, J.R.; Chang-Claude, J. Dietary inflammation potential and postmenopausal breast cancer risk in a German case-control study. Breast 2015, 24, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Tabung, F.K.; Zhang, J.; Liese, A.D.; Shivappa, N.; Ockene, J.K.; Caan, B.; Kroenke, C.H.; Hebert, J.R.; Steck, S.E. Association between Post-Cancer Diagnosis Dietary Inflammatory Potential and Mortality among Invasive Breast Cancer Survivors in the Women’s Health Initiative. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2018, 27, 454–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabung, F.K.; Steck, S.E.; Liese, A.D.; Zhang, J.; Ma, Y.; Caan, B.; Chlebowski, R.T.; Freudenheim, J.L.; Hou, L.; Mossavar-Rahmani, Y.; et al. Association between dietary inflammatory potential and breast cancer incidence and death: Results from the Women’s Health Initiative. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 114, 1277–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucchetto, A.; Serraino, D.; Shivappa, N.; Hébert, J.R.; Stocco, C.; Puppo, A.; Falcini, F.; Panato, C.; Maso, L.D.; Polesel, J. Dietary inflammatory index before diagnosis and survival in an Italian cohort of women with breast cancer. Br. J. Nutr. 2017, 117, 1456–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shivappa, N.; Hebert, J.R.; Rosato, V.; Rossi, M.; Montella, M.; Serraino, D.; La Vecchia, C. Dietary Inflammatory Index and ovarian cancer risk in a large Italian case-control study. Cancer Causes Control 2016, 27, 897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagle, C.M.; Ibiebele, T.; Shivappa, N.; Hébert, J.R.; DeFazio, A.; Webb, P.M.; Australian Ovarian Cancer Study. The association between the inflammatory potential of diet and risk of developing, and survival following, a diagnosis of ovarian cancer. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 58, 1747–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivappa, N.; Hebert, J.R.; Paddock, L.E.; Rodriguez-Rodriguez, L.; Olson, S.H.; Bandera, E.V. Dietary inflammatory index and ovarian cancer risk in a New Jersey case-control study. Nutrition 2018, 46, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peres, L.C.; Bandera, E.V.; Qin, B.; Guertin, K.A.; Shivappa, N.; Hebert, J.R.; Abbott, S.E.; Alberg, A.J.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.; Bondy, M.; et al. Dietary inflammatory index and risk of epithelial ovarian cancer in African American women. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 140, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivappa, N.; Hebert, J.R.; Zucchetto, A.; Montella, M.; Serraino, D.; La Vecchia, C.; Rossi, M. Dietary inflammatory index and endometrial cancer risk in an Italian case-control study. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 115, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivappa, N.; Hébert, J.R.; Taborelli, M.; Montella, M.; Libra, M.; Zucchetto, A.; Crispo, A.; Grimaldi, M.; La Vecchia, C.; Serraino, D.; et al. Dietary Inflammatory Index and Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma risk in an Italian case-control study. Cancer Causes Control 2017, 28, 791–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivappa, N.; Hebert, J.R.; Taborelli, M.; Zucchetto, A.; Montella, M.; Libra, M.; La Vecchia, C.; Serraino, D.; Polesel, J. Association between dietary inflammatory index and Hodgkin’s lymphoma in an Italian case-control study. Nutrition 2018, 53, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Moellering, D.R.; Garvey, W.T. The progression of cardiometabolic disease: Validation of a new cardiometabolic disease staging system applicable to obesity. Obesity 2014, 22, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, G.E.; Jay, S.M.; Sargent, C.; Vandelanotte, C.; Ridgers, N.D.; Ferguson, S.A. Improving Cardiometabolic Health with Diet, Physical Activity, and Breaking Up Sitting: What about Sleep? Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, C.M.; Perry, I.J. Does Inflammation Determine Metabolic Health Status in Obese and Nonobese Adults? J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, E1610–E1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Se-Young, O.; Lee, D.; Tak, S.; Hong, M.; Park, S.M.; Cho, B.; Park, M. Characteristics of diet patterns in metabolically obese, normal weight adults (Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey III, 2005). Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2012, 22, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, A.; Bhardwaj, S. Obesity and the metabolic syndrome in developing countries: Focus on South Asians. Nestle Nutr. Inst. Workshop Ser. 2014, 78, 133–140. [Google Scholar]
- Kelishadi, R.; Hashemipour, M.; Sarrafzadegan, N.; Mohammadifard, N.; Alikhasy, H.; Beizaei, M.; Sajjadi, F.; Poursafa, P.; Amin, Z.; Ghatreh-Samani, S.; et al. Effects of a lifestyle modification trial among phenotypically obese metabolically normal and phenotypically obese metabolically abnormal adolescents in comparison with phenotypically normal metabolically obese adolescents. Matern. Child Nutr. 2010, 6, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, J.R.; Wirth, M.; Davis, L.; Davis, B.; Harmon, B.E.; Hurley, T.G.; Drayton, R.; Angela Murphy, E.; Shivappa, N.; Wilcox, S.; et al. C-reactive protein levels in African Americans: A diet and lifestyle randomized community trial. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2013, 45, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO (World Health Organization). Global Health Estimates 2016: Disease Burden by Cause, Age, Sex, by Country and by Region, 2000–2016; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switherland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Emerging Risk Factors, C.; Kaptoge, S.; Di Angelantonio, E.; Lowe, G.; Pepys, M.B.; Thompson, S.G.; Collins, R.; Danesh, J. C-reactive protein concentration and risk of coronary heart disease, stroke, and mortality: An individual participant meta-analysis. Lancet 2010, 375, 132–140. [Google Scholar]
- Ridker, P.M.; Tracy, R.P.; Hennekens, C.H.; Cushman, M.; Stampfer, M.J. Inflammation, Aspirin, and the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease in Apparently Healthy Men. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997, 336, 973–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spranger, J.; Kroke, A.; Möhlig, M.; Hoffmann, K.; Bergmann, M.M.; Ristow, M.; Boeing, H.; Pfeiffer, A.F.H. Inflammatory Cytokines and the Risk to Develop Type 2 Diabetes: Results of the Prospective Population-Based European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC)-Potsdam Study. Diabetes 2003, 52, 812–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, A.D.; Manson, J.E.; Rifai, N.; Buring, J.E.; Ridker, P.M. C-Reactive Protein, Interleukin 6, and Risk of Developing Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. JAMA 2001, 286, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Festa, A.; D’Agostino, R.; Tracy, R.P.; Haffner, S.M. Elevated Levels of Acute-Phase Proteins and Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 Predict the Development of Type 2 Diabetes: The Insulin Resistance Atherosclerosis Study. Diabetes 2002, 51, 1131–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kord Varkaneh, H.; Fatahi, S.; Tajik, S.; Rahmani, J.; Zarezadeh, M.; Shab-Bidar, S. Dietary inflammatory index in relation to obesity and body mass index: A meta-analysis. Nutr. Food Sci. 2018, 48, 702–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namazi, N.; Larijani, B.; Azadbakht, L. Dietary Inflammatory Index and its Association with the Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases, Metabolic Syndrome, and Mortality: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Horm. Metab. Res. 2018, 50, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Canela, M.; Bes-Rastrollo, M.; Martinez-Gonzalez, M.A. The Role of Dietary Inflammatory Index in Cardiovascular Disease, Metabolic Syndrome and Mortality. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, D.; White, G.E.; Sekikawa, A.; Gianaros, P. Higher dietary inflammation is associated with increased odds of depression independent of Framingham Risk Score in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Nutr. Res. 2018, 54, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, E.; Shirakawa, T.; Shivappa, N.; Wakai, K.; Suzuki, K.; Date, C.; Iso, H.; Hébert, J.R.; Tamakoshi, A. Dietary Inflammatory Index Is Associated with Risk of All-Cause and Cardiovascular Disease Mortality but Not with Cancer Mortality in Middle-Aged and Older Japanese Adults. J. Nutr. 2019, 149, 1451–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramallal, R.; Toledo, E.; Martinez-Gonzalez, M.A.; Hernández-Hernández, A.; García-Arellano, A.; Shivappa, N.; Hebert, J.R.; Ruíz-Canela, M. Dietary Inflammatory Index and Incidence of Cardiovascular Disease in the SUN Cohort. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivappa, N.; Steck, S.E.; Hussey, J.R.; Ma, Y.; Hebert, J.R. Inflammatory potential of diet and all-cause, cardiovascular, and cancer mortality in National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey III Study. Eur. J. Nutr. 2017, 56, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willerson, J.T.; Ridker, P.M. Inflammation as a Cardiovascular Risk Factor. Circulation 2004, 109, II-2–II-10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sokol, A.; Wirth, M.D.; Manczuk, M.; Shivappa, N.; Zatonska, K.; Hurley, T.G.; Hébert, J.R. Association between the dietary inflammatory index, waist-to-hip ratio and metabolic syndrome. Nutr. Res. 2016, 36, 1298–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carvalho, C.A.; Silva, A.A.M.; Assunção, M.C.F.; Fonseca, P.C.A.; Barbieri, M.A.; Bettiol, H.; Shivappa, N.; Hébert, J.R. The dietary inflammatory index and insulin resistance or metabolic syndrome in young adults. Nutrition 2019, 58, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-Y.; Lee, J.; Kim, J. Association between Dietary Inflammatory Index and Metabolic Syndrome in the General Korean Population. Nutrients 2018, 10, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Zhao, A.; Wang, Y.; Meng, L.; Szeto, I.M.-Y.; Li, T.; Gong, H.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, P. Association between Dietary Inflammatory Index, C-Reactive Protein and Metabolic Syndrome: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients 2018, 10, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, P.; Polisecki, E.; Robertson, M.; Jahn, S.; Buckley, B.M.; de Craen, A.J.; Ford, I.; Jukema, J.W.; Macfarlane, P.W.; Packard, C.J.; et al. Unraveling the directional link between adiposity and inflammation: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization approach. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Zuydam, N.; Wielscher, M.; McCarthy, M.; Järvelin, M.-R. Increased Obesity Is Causal for Increased Inflammation—A Mendelian Randomisation Study. Diabetes 2018, 67, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, I.; Shivappa, N.; Hebert, J.R.; Pawelec, G.; Larbi, A. Relationships between the inflammatory potential of the diet, aging and anthropometric measurements in a cross-sectional study in Pakistan. Nutr. Health Aging 2018, 4, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslani, Z.; Qorbani, M.; Hebert, J.R.; Shivappa, N.; Motlagh, M.E.; Asayesh, H.; Mahdavi-Gorabi, A.; Kelishadi, R. Association of Dietary Inflammatory Index with anthropometric indices in children and adolescents: The weight disorder survey of the Childhood and Adolescence Surveillance and Prevention of Adult Non-communicable Disease (CASPIAN)-IV study. Br. J. Nutr. 2019, 121, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, P.A.; Hermsdorff, H.H.M.; Leite, J.I.A.; Shivappa, N.; Hebert, J.R.; Henriques, H.K.F.; de Oliveira Barbosa Rosa, C. Baseline Pro-inflammatory Diet Is Inversely Associated with Change in Weight and Body Fat 6 Months Following-up to Bariatric Surgery. Obes. Surg. 2019, 29, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denova-Gutiérrez, E.; Muñoz-Aguirre, P.; Shivappa, N.; Hébert, J.R.; Tolentino-Mayo, L.; Batis, C.; Barquera, S. Dietary Inflammatory Index and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Adults: The Diabetes Mellitus Survey of Mexico City. Nutrients 2018, 10, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivappa, N.; Hébert, J.R.; Akhoundan, M.; Mirmiran, P.; Rashidkhani, B. Association between inflammatory potential of diet and odds of gestational diabetes mellitus among Iranian women. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2018, 32, 3552–3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahid, F.; Shivappa, N.; Karamati, M.; Jafari Naeini, A.; Hebert, J.R.; Davoodi, S.H. Association between Dietary Inflammatory Index (DII) and Risk of Pre-Diabetes: A Case-Control Study. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 42, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckhaus, A.A.; Garcia-Marcos, L.; Forno, E.; Pacheco-Gonzalez, R.M.; Celedón, J.C.; Castro-Rodriguez, J.A.; Garcia-Marcos, L.; Pacheco-Gonzalez, R.M.; Castro-Rodriguez, J.A. Maternal nutrition during pregnancy and risk of asthma, wheeze and atopic diseases during childhood: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Allergy 2015, 70, 1588–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilleminault, L.; Williams, E.J.; Scott, H.A.; Berthon, B.S.; Jensen, M.; Wood, L.G. Diet and Asthma: Is It Time to Adapt Our Message? Nutrients 2017, 9, 1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthon, B.S.; MacDonald-Wicks, L.K.; Gibson, P.G.; Wood, L.G. Investigation of the association between dietary intake, disease severity and airway inflammation in asthma. Respirology 2013, 18, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, L.G.; Gibson, P.G. Dietary factors lead to innate immune activation in asthma. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 123, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devereux, G. The increase in the prevalence of asthma and allergy: Food for thought. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 6, 869–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, B.; Berthon, B.S.; Wark, P.; Wood, L.G. Effects of Fruit and Vegetable Consumption on Risk of Asthma, Wheezing and Immune Responses: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2017, 9, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, L.G.; Shivappa, N.; Berthon, B.S.; Gibson, P.G.; Hebert, J.R. Dietary inflammatory index is related to asthma risk, lung function and systemic inflammation in asthma. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2015, 45, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.-Y.; Forno, E.; Shivappa, N.; Wirth, M.D.; Hébert, J.R.; Celedón, J.C. The Dietary Inflammatory Index and Current Wheeze Among Children and Adults in the United States. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2018, 6, 834–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duijts, L.; Reiss, I.K.; Brusselle, G.; De Jongste, J.C. Early origins of chronic obstructive lung diseases across the life course. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2014, 29, 871–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, S.O.; Northstone, K.; Newson, R.B.; Emmett, P.; Sherriff, A.; Henderson, A.J. Dietary patterns in pregnancy and respiratory and atopic outcomes in childhood. Thorax 2009, 64, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lange, N.E.; Rifas-Shiman, S.L.; Camargo, C.A.; Gold, D.R.; Gillman, M.W.; Litonjua, A.A. Maternal dietary pattern during pregnancy is not associated with recurrent wheeze in children. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 126, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, Y.; Sasaki, S.; Tanaka, K.; Ohfuji, S.; Hirota, Y. Maternal fat consumption during pregnancy and risk of wheeze and eczema in Japanese infants aged 16-24 months: The Osaka Maternal and Child Health Study. Thorax 2009, 64, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, Y.; Okubo, H.; Sasaki, S.; Tanaka, K.; Hirota, Y. Maternal dietary patterns during pregnancy and risk of wheeze and eczema in Japanese infants aged 16–24 months: The Osaka Maternal and Child Health Study. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2011, 22, 734–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willers, S.M.; Devereux, G.; Craig, L.C.A.; McNeill, G.; Wijga, A.H.; El-Magd, W.A.; Turner, S.W.; Helms, P.J.; Seaton, A. Maternal food consumption during pregnancy and asthma, respiratory and atopic symptoms in 5-year-old children. Thorax 2007, 62, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miyake, Y.; Sasaki, S.; Tanaka, K.; Hirota, Y. Consumption of vegetables, fruit, and antioxidants during pregnancy and wheeze and eczema in infants. Allergy 2010, 65, 758–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorsen, J.; Bisgaard, H.; Chawes, B.L.; Vissing, N.H.; Schoos, A.-M.M.; Wolsk, H.M.; Pedersen, T.M.; Vinding, R.K.; Følsgaard, N.V.; Fink, N.R.; et al. Fish Oil–Derived Fatty Acids in Pregnancy and Wheeze and Asthma in Offspring. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 2530–2539. [Google Scholar]
- Sen, S.; Rifas-Shiman, S.L.; Shivappa, N.; Wirth, M.D.; Hébert, J.R.; Gold, D.R.; Gillman, M.W.; Oken, E. Dietary Inflammatory Potential during Pregnancy Is Associated with Lower Fetal Growth and Breastfeeding Failure: Results from Project Viva. J. Nutrients 2016, 146, 728–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnenschein-van der Voort, A.M.; Jaddoe, V.W.; Moll, H.A.; Hofman, A.; van der Valk, R.J.; de Jongste, J.C.; Duijts, L. Influence of maternal and cord blood C-reactive protein on childhood respiratory symptoms and eczema. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2013, 24, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, E.L.; Dewey, K.G. Nutrition and brain development in early life. Nutr. Rev. 2014, 72, 267–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borge, T.C.; Aase, H.; Brantsæter, A.L.; Biele, G. The importance of maternal diet quality during pregnancy on cognitive and behavioural outcomes in children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e016777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, H.F.; Visentin, S. Micronutrients and neurodevelopment: An update. Arch. Argent. Pediatr. 2016, 114, 570–575. [Google Scholar]
- Iglesias, L.; Canals, J.; Arija, V. Effects of prenatal iron status on child neurodevelopment and behavior: A systematic review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 1604–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorós, R.; Murcia, M.; González, L.; Rebagliato, M.; Iniguez, C.; Lopez-Espinosa, M.-J.; Vioque, J.; Broberg, K.; Ballester, F.; Llop, S. Maternal selenium status and neuropsychological development in Spanish preschool children. Environ. Res. 2018, 166, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barker, E.D.; Kirkham, N.; Ng, J.; Jensen, S.K.G. Prenatal maternal depression symptoms and nutrition, and child cognitive function. Br. J. Psychiatry 2013, 203, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daniels, J.L.; Longnecker, M.P.; Rowland, A.S.; Golding, J. Fish Intake During Pregnancy and Early Cognitive Development of Offspring. Epidemiology 2004, 15, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, P.W.; Strain, J.; Myers, G.J.; Thurston, S.W.; Bonham, M.P.; Shamlaye, C.F.; Stokes-Riner, A.; Wallace, J.M.; Robson, P.J.; Duffy, E.M.; et al. Neurodevelopmental Effects of Maternal Nutritional Status and Exposure to Methylmercury from Eating Fish during Pregnancy. NeuroToxicology 2008, 29, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gale, C.R.; Robinson, S.M.; Godfrey, K.M.; Law, C.M.; Schlotz, W.; O’Callaghan, F.J. Oily fish intake during pregnancy—Association with lower hyperactivity but not with higher full-scale IQ in offspring. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2008, 49, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibbeln, J.R.; Davis, J.M.; Steer, C.; Emmett, P.; Rogers, I.; Williams, C.; Golding, J. Maternal seafood consumption in pregnancy and neurodevelopmental outcomes in childhood (ALSPAC study): An observational cohort study. Lancet 2007, 369, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacka, F.N.; Ystrom, E.; Brantsaeter, A.L.; Karevold, E.; Roth, C.; Haugen, M.; Meltzer, H.M.; Schjolberg, S.; Berk, M. Maternal and Early Postnatal Nutrition and Mental Health of Offspring by Age 5 Years: A Prospective Cohort Study. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2013, 52, 1038–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez, M.A.; Torrent, M.; Julvez, J.; Ribas-Fitó, N.; Kogevinas, M.; Sunyer, J. Maternal fish and other seafood intakes during pregnancy and child neurodevelopment at age 4 years. Public Health Nutr. 2009, 12, 1702–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oken, E.; Radesky, J.S.; Wright, R.O.; Bellinger, D.C.; Amarasiriwardena, C.J.; Kleinman, K.P.; Hu, H.; Gillman, M.W. Maternal Fish Intake During Pregnancy, Blood Mercury Levels, and Child Cognition at Age 3 Years in a US Cohort. Obstet. Gynecol. Surv. 2008, 63, 557–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oken, E.; Østerdal, M.L.; Gillman, M.W.; Knudsen, V.K.; Halldorsson, T.I.; Strøm, M.; Bellinger, D.C.; Hadders-Algra, M.; Michaelsen, K.F.; Olsen, S.F. Associations of maternal fish intake during pregnancy and breastfeeding duration with attainment of developmental milestones in early childhood: A study from the Danish National Birth Cohort. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 88, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pina-Camacho, L.; Jensen, S.K.; Gaysina, D.; Barker, E.D. Maternal depression symptoms, unhealthy diet and child emotional-behavioural dysregulation. Psychol. Med. 2015, 45, 1851–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenweg-de Graaff, J.; Tiemeier, H.; Steegers-Theunissen, R.P.; Hofman, A.; Jaddoe, V.W.; Verhulst, F.C.; Roza, S.J. Maternal dietary patterns during pregnancy and child internalising and externalising problems. The Generation R Study. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 33, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valent, F.; Mariuz, M.; Bin, M.; Little, D.; Mazej, D.; Tognin, V.; Tratnik, J.; McAfee, A.J.; Mulhern, M.S.; Parpinel, M.; et al. Associations of Prenatal Mercury Exposure From Maternal Fish Consumption and Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids With Child Neurodevelopment: A Prospective Cohort Study in Italy. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 23, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sagiv, S.K.; Thurston, S.W.; Bellinger, D.C.; Amarasiriwardena, C.; Korrick, S.A. Prenatal exposure to mercury and fish consumption during pregnancy and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder-related behavior in children. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 2012, 166, 1123–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The EDEN Mother-Child Cohort Study Group; Bernard, J.Y.; De Agostini, M.; Forhan, A.; De Lauzon-Guillain, B.; Charles, M.-A.; Heude, B. The Dietary n6, n3 Fatty Acid Ratio during Pregnancy Is Inversely Associated with Child Neurodevelopment in the EDEN Mother-Child Cohort. J. Nutr. 2013, 143, 1481–1488. [Google Scholar]
- Bolduc, F.V.; Lau, A.; Rosenfelt, C.S.; Langer, S.; Wang, N.; Smithson, L.; Lefebvre, D.; Alexander, R.T.; Dickson, C.T.; Li, L.; et al. Cognitive Enhancement in Infants Associated with Increased Maternal Fruit Intake During Pregnancy: Results from a Birth Cohort Study with Validation in an Animal Model. EBioMedicine 2016, 8, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gustafsson, H.C.; Kuzava, S.E.; Werner, E.A.; Monk, C. Maternal dietary fat intake during pregnancy is associated with infant temperament. Dev. Psychobiol. 2016, 58, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julvez, J.; Mendez, M.; Fernández-Barrés, S.; Romaguera, D.; Vioque, J.; Llop, S.; Ibarluzea, J.; Guxens, M.; Avella-Garcia, C.; Tardón, A.; et al. Maternal Consumption of Seafood in Pregnancy and Child Neuropsychological Development: A Longitudinal Study Based on a Population With High Consumption Levels. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 183, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oken, E.; Rifas-Shiman, S.L.; Amarasiriwardena, C.; Jayawardene, I.; Bellinger, D.C.; Hibbeln, J.R.; Wright, R.O.; Gillman, M.W. Maternal prenatal fish consumption and cognition in mid childhood: Mercury, fatty acids, and selenium. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2016, 57, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malin, A.J.; Busgang, S.A.; Cantoral, A.J.; Svensson, K.; Orjuela, M.A.; Pantic, I.; Schnaas, L.; Oken, E.; Baccarelli, A.A.; Téllez-Rojo, M.M.; et al. Quality of Prenatal and Childhood Diet Predicts Neurodevelopmental Outcomes among Children in Mexico City. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.M.; Cowan, M.; Moonah, S.N.; Petri, W.A. The Impact of Systemic Inflammation on Neurodevelopment. Trends Mol. Med. 2018, 24, 794–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deverman, B.E.; Patterson, P.H. Cytokines and CNS development. Neuron 2009, 64, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuban, K.C.; O’Shea, T.M.; Allred, E.N.; Fichorova, R.N.; Heeren, T.; Paneth, N.; Hirtz, D.; Dammann, O.; Leviton, A.; ELGAN Study Investigators. The breadth and type of systemic inflammation and the risk of adverse neurological outcomes in extremely low gestation newborns. Pediatr. Neurol. 2015, 52, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goeden, N.; Velasquez, J.; Arnold, K.A.; Chan, Y.; Lund, B.T.; Anderson, G.M.; Bonnin, A. Maternal Inflammation Disrupts Fetal Neurodevelopment via Increased Placental Output of Serotonin to the Fetal Brain. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 6041–6049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Shea, T.M.; Joseph, R.M.; Kuban, K.C.; Allred, E.N.; Ware, J.; Coster, T.; Fichorova, R.N.; Dammann, O.; Leviton, A.; ELGAN Study Investigators. Elevated blood levels of inflammation-related proteins are associated with an attention problem at age 24 mo in extremely preterm infants. Pediatr. Res. 2014, 75, 781–787. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, N.M.; Tofail, F.; Moonah, S.N.; Scharf, R.J.; Taniuchi, M.; Ma, J.Z.; Hamadani, J.D.; Gurley, E.S.; Houpt, E.R.; Azziz-Baumgartner, E.; et al. Febrile illness and pro-inflammatory cytokines are associated with lower neurodevelopmental scores in Bangladeshi infants living in poverty. BMC Pediatr. 2014, 14, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheller, J.; Chalaris, A.; Schmidt-Arras, D.; Rose-John, S. The pro- and anti-inflammatory properties of the cytokine interleukin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Bioenerg. 2011, 1813, 878–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, K.M.; Beavers, D.P.; Steck, S.E.; Hebert, J.R.; Tabung, F.K.; Shivappa, N.; Casanova, R.; Manson, J.E.; Padula, C.B.; Salmoirago-Blotcher, E.; et al. The association between an inflammatory diet and global cognitive function and incident dementia in older women: The Women’s Health Initiative Memory Study. Alzheimers Dement. 2017, 13, 1187–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesse-Guyot, E.; Assmann, K.E.; Andreeva, V.A.; Touvier, M.; Neufcourt, L.; Shivappa, N.; Hébert, J.R.; Wirth, M.D.; Hercberg, S.; Galan, P.; et al. Long-term association between the dietary inflammatory index and cognitive functioning: Findings from the SU.VI.MAX study. Eur. J. Nutr. 2017, 56, 1647–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assmann, K.E.; Hébert, J.R.; Wirth, M.D.; Hercberg, S.; Adjibade, M.; Shivappa, N.; Touvier, M.; Akbaraly, T.; Galan, P.; Julia, C.; et al. The Inflammatory Potential of the Diet at Midlife Is Associated with Later Healthy Aging in French Adults. J. Nutr. 2018, 148, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frith, E.; Shivappa, N.; Mann, J.R.; Hebert, J.R.; Wirth, M.D.; Loprinzi, P.D. Dietary inflammatory index and memory function: Population-based national sample of elderly Americans. Br. J. Nutr. 2018, 119, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frith, E.; Shivappa, N.; Mann, J.R.; Hebert, J.R.; Wirth, M.D.; Loprinzi, P.D. Letter to Editor in response to: Potential confounding in a study of dietary inflammatory index and cognitive function. Br. J. Nutr. 2018, 120, 1078–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shin, D.; Kwon, S.C.; Kim, M.H.; Lee, K.W.; Choi, S.Y.; Shivappa, N.; Hébert, J.R.; Chung, H.K. Inflammatory potential of diet is associated with cognitive function in an older adult Korean population. Nutrition 2018, 55–56, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteford, H.; Ferrari, A.; Degenhardt, L. Global Burden Of Disease Studies: Implications For Mental And Substance Use Disorders. Health Aff. 2016, 35, 1114–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organisation. Depression and Other Common Mental Disorders: Global Health Estimates; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switherland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Risks to Mental Health: An Overview of Vulnerabilities and Risk Factors; Background Paper by WHO Secretariat for the Development of a Comprehensive Mental Health Action Plan; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switherland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Akbaraly, T.N.; Brunner, E.J.; Ferrie, J.E.; Marmot, M.G.; Kivimäki, M.; Singh-Manoux, A. Dietary pattern and depressive symptoms in middle age. Br. J. Psychiatry 2009, 195, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanchez-Villegas, A.; Toledo, E.; de Irala, J.; Ruiz-Canela, M.; Pla-Vidal, J.; Martinez-Gonzalez, M.A. Fast-food and commercial baked goods consumption and the risk of depression. Public Health Nutr. 2012, 15, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.S.; Hiles, S.; Bisquera, A.; Hure, A.J.; McEvoy, M.; Attia, J. A systematic review and meta-analysis of dietary patterns and depression in community-dwelling adults. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 99, 181–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quirk, S.E.; Williams, L.J.; O’Neil, A.; Pasco, J.A.; Jacka, F.N.; Housden, S.; Berk, M.; Brennan, S.L. The association between diet quality, dietary patterns and depression in adults: A systematic review. BMC Psychiatry 2013, 13, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivimaki, M.; Shipley, M.J.; Batty, G.D.; Hamer, M.; Akbaraly, T.N.; Kumari, M.; Jokela, M.; Virtanen, M.; Lowe, G.D.; Ebmeier, K.P.; et al. Long-term inflammation increases risk of common mental disorder: A cohort study. Mol. Psychiatry 2014, 19, 149–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, C.A.; Freitas, T.H.; Maes, M.; De Andrade, N.Q.; Liu, C.S.; Fernandes, B.S.; Stubbs, B.; Solmi, M.; Veronese, N.; Herrmann, N.; et al. Peripheral cytokine and chemokine alterations in depression: A meta-analysis of 82 studies. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2017, 135, 373–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassale, C.; Batty, G.D.; Baghdadli, A.; Jacka, F.; Sánchez-Villegas, A.; Kivimäki, M.; Akbaraly, T. Correction: Healthy dietary indices and risk of depressive outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Mol. Psychiatry 2018, 24, 1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molendijk, M.; Molero, P.; Sánchez-Pedreño, F.O.; Van Der Does, W.; Martínez-González, M.A. Diet quality and depression risk: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of prospective studies. J. Affect. Disord. 2018, 226, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tolkien, K.; Bradburn, S.; Murgatroyd, C. An anti-inflammatory diet as a potential intervention for depressive disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 20, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheirouri, S.; Alizadeh, M. Dietary Inflammatory Potential and the Risk of Incident Depression in Adults: A Systematic Review. Adv. Nutr. 2019, 10, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, K.; Jing, Y.; He, J.; Sun, H.; Hu, X. Dietary inflammatory index and depression: A meta-analysis. Public Health Nutr. 2018, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firth, J.; Stubbs, B.; Teasdale, S.B.; Ward, P.B.; Veronese, N.; Shivappa, N.; Hebert, J.R.; Berk, M.; Yung, A.R.; Sarris, J. Diet as a hot topic in psychiatry: A population-scale study of nutritional intake and inflammatory potential in severe mental illness. World Psychiatry 2018, 17, 365–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivappa, N.; Hebert, J.R.; Tehrani, A.N.; Bayzai, B.; Naja, F.; Rashidkhani, B. A Pro-Inflammatory Diet Is Associated With an Increased Odds of Depression Symptoms Among Iranian Female Adolescents: A Cross-Sectional Study. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivappa, N.; Schoenaker, D.A.J.M.; Hebert, J.R.; Mishra, G.D. Association between inflammatory potential of diet and risk of depression in middle-aged women: The Australian Longitudinal Study on Women’s Health. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 116, 1077–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjibade, M.; Andreeva, V.A.; Lemogne, C.; Touvier, M.; Shivappa, N.; Hébert, J.R.; Wirth, M.D.; Hercberg, S.; Galan, P.; Julia, C.; et al. The Inflammatory Potential of the Diet Is Associated with Depressive Symptoms in Different Subgroups of the General Population. J. Nutr. 2017, 147, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, C.M.; Shivappa, N.; Hébert, J.R.; Perry, I.J. Dietary inflammatory index and mental health: A cross-sectional analysis of the relationship with depressive symptoms, anxiety and well-being in adults. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 1485–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbaraly, T.N.; Kerlau, C.; Wyart, M.; Chevallier, N.; Ndiaye, L.; Shivappa, N.; Hébert, J.R.; Kivimäki, M. Dietary inflammatory index and recurrence of depressive symptoms: Results from the Whitehall II Study. Clin. Psychol. Sci. 2016, 4, 1125–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Villegas, A.; Ruíz-Canela, M.; De La Fuente-Arrillaga, C.; Gea, A.; Shivappa, N.; Hébert, J.R.; Martínez-González, M.A. Dietary inflammatory index, cardiometabolic conditions and depression in the Seguimiento Universidad de Navarra cohort study. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 114, 1471–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shivappa, N.; Hebert, J.R.; Veronese, N.; Caruso, M.G.; Notarnicola, M.; Maggi, S.; Stubbs, B.; Firth, J.; Fornaro, M.; Solmi, M. The relationship between the dietary inflammatory index (DII((R))) and incident depressive symptoms: A longitudinal cohort study. J. Affect. Disord. 2018, 235, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauenstein, E.J. Young women and depression. Origin, outcome, and nursing care. Nurs. Clin. N. Am. 1991, 26, 601–612. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. WHO Fact Sheets; Depression; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Knott, L.; Avery, N.; Hollander, A.; Tarlton, J. Regulation of osteoarthritis by omega-3 (n-3) polyunsaturated fatty acids in a naturally occurring model of disease. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2011, 19, 1150–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mabey, T.; Honsawek, S. Role of Vitamin D in Osteoarthritis: Molecular, Cellular, and Clinical Perspectives. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 2015, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, C.-L.; Smith, B.J.; Lo, D.-F.; Chyu, M.-C.; Dunn, D.M.; Chen, C.-H.; Kwun, I.-S. Dietary polyphenols and mechanisms of osteoarthritis. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2012, 23, 1367–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veronese, N.; Stubbs, B.; Noale, M.; Solmi, M.; Luchini, C.; Smith, T.O.; Cooper, C.; Guglielmi, G.; Reginster, J.Y.; Rizzoli, R.; et al. Adherence to a Mediterranean diet is associated with lower prevalence of osteoarthritis: Data from the osteoarthritis initiative. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 1609–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbour, K.E.; Boudreau, R.; Danielson, M.E.; Youk, A.O.; Wactawski-Wende, J.; Greep, N.C.; Lacroix, A.Z.; Jackson, R.D.; Wallace, R.B.; Bauer, D.C.; et al. Inflammatory Markers and the Risk of Hip Fracture: The Women’s Health Initiative. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2012, 27, 1167–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cauley, J.A.; Danielson, M.E.; Boudreau, R.M.; Forrest, K.Y.Z.; Zmuda, J.M.; Pahor, M.; Tylavsky, F.A.; Cummings, S.R.; Harris, T.B.; Newman, A.B. Inflammatory Markers and Incident Fracture Risk in Older Men and Women: The Health Aging and Body Composition Study. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2007, 22, 1088–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolove, J.; Lepus, C.M. Role of inflammation in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis: Latest findings and interpretations. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2013, 5, 77–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orchard, T.; Yildiz, V.; Steck, S.E.; Hébert, J.R.; Ma, Y.; Cauley, J.A.; Li, W.; Mossavar-Rahmani, Y.; Johnson, K.C.; Sattari, M.; et al. Dietary Inflammatory Index, Bone Mineral Density, and Risk of Fracture in Postmenopausal Women: Results From the Women’s Health Initiative. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2017, 32, 1136–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, W.; Park, S.; Shivappa, N.; Hebert, J.R.; Kim, M.K.; Sohn, C. Association between Inflammatory Potential of Diet and Bone-Mineral Density in Korean Postmenopausal Women: Data from Fourth and Fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys. Nutrients 2019, 11, 885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivappa, N.; Hebert, J.R.; Karamati, M.; Shariati-Bafghi, S.E.; Rashidkhani, B. Increased inflammatory potential of diet is associated with bone mineral density among postmenopausal women in Iran. Eur. J. Nutr. 2016, 55, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazidi, M.; Shivappa, N.; Wirth, M.D.; Hebert, J.R.; Vatanparast, H.; Kengne, A.P. The association between dietary inflammatory properties and bone mineral density and risk of fracture in US adults. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 71, 1273–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veronese, N.; Shivappa, N.; Stubbs, B.; Smith, T.; Hébert, J.R.; Cooper, C.; Guglielmi, G.; Reginster, J.-Y.; Rizzoli, R.; Maggi, S. The relationship between the dietary inflammatory index and prevalence of radiographic symptomatic osteoarthritis: Data from the Osteoarthritis Initiative. Eur. J. Nutr. 2017, 58, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veronese, N.; Stubbs, B.; Koyanagi, A.; Hebert, J.R.; Cooper, C.; Caruso, M.G.; Guglielmi, G.; Reginster, J.Y.; Rizzoli, R.; Maggi, S.; et al. Pro-inflammatory dietary pattern is associated with fractures in women: An eight-year longitudinal cohort study. Osteoporos. Int. 2018, 29, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-Q.; Cao, W.-T.; Shivappa, N.; Hebert, J.R.; Li, B.-L.; He, J.; Tang, X.-Y.; Liang, Y.-Y.; Chen, Y.-M. Association between Diet Inflammatory Index and Osteoporotic Hip Fracture in Elderly Chinese Population. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2017, 18, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervo, M.M.; Shivappa, N.; Hebert, J.R.; Oddy, W.H.; Winzenberg, T.; Balogun, S.; Wu, F.; Ebeling, P.; Aitken, D.; Jones, G.; et al. Longitudinal associations between dietary inflammatory index and musculoskeletal health in community-dwelling older adults. Clin. Nutr. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, M.; Shivappa, N.; Genaro, P.D.S.; Martini, L.A.; Schuch, N.J.; Hebert, J.R.; Pinheiro, M.M. Lack of association between dietary inflammatory index and low impact fractures in the Brazilian population: The Brazilian Osteoporosis Study (BRAZOS). Adv. Rheumatol. 2019, 59, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amakye, W.K.; Zhang, Z.; Wei, Y.; Shivappa, N.; Hebert, J.R.; Wang, J.; Su, Y.; Mao, L. The relationship between dietary inflammatory index (DII) and muscle mass and strength in Chinese children aged 6–9 years. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 27, 1315–1324. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, C.H.; Mears, D.C.; McKnight, J.L. A preliminary ferrographic survey of the wear particles in human synovial fluid. Arthritis Rheum. 1981, 24, 912–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginaldi, L.; Di Benedetto, M.C.; De Martinis, M. Osteoporosis, inflammation and ageing. Immun. Ageing 2005, 2, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homandberg, G.A.; Hui, F. Association of Proteoglycan Degradation with Catabolic Cytokine and Stromelysin Release from Cartilage Cultured with Fibronectin Fragments. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1996, 334, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takayanagi, H. Osteoimmunology: Shared mechanisms and crosstalk between the immune and bone systems. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 7, 292–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.; Harvey, N.C.; Crozier, S.R.; Poole, J.R.; Javaid, M.K.; Dennison, E.M.; Inskip, H.M.; Hanson, M.; Godfrey, K.M.; Cooper, C.; et al. Placental calcium transporter (PMCA3) gene expression predicts intrauterine bone mineral accrual. Bone 2007, 40, 1203–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, E.M.; Krstic, N.; Cook, E.; D’Angelo, S.; Crozier, S.R.; Moon, R.J.; Murray, R.; Garratt, E.; Costello, P.; Cleal, J.; et al. Gestational Vitamin D Supplementation Leads to Reduced Perinatal RXRA DNA Methylation: Results From the MAVIDOS Trial. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2019, 34, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cooper, C.; Harvey, N.C.; Bishop, N.J.; Kennedy, S.; Papageorghiou, A.T.; Schoenmakers, I.; Fraser, R.; Gandhi, S.V.; Carr, A.; D’Angelo, S.; et al. Maternal gestational vitamin D supplementation and offspring bone health (MAVIDOS): A multicentre, double-blind, randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2016, 4, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, D.P.; Klein, S.L. Pregnancy and pregnancy-associated hormones alter immune responses and disease pathogenesis. Horm. Behav. 2012, 62, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ingvorsen, C.; Brix, S.; Ozanne, S.E.; Hellgren, L.I. The effect of maternal Inflammation on foetal programming of metabolic disease. Acta Physiol. 2015, 214, 440–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, S.; Tremblay, L.; Lepage, M.; Sébire, G. IL-1 Receptor Antagonist Protects against Placental and Neurodevelopmental Defects Induced by Maternal Inflammation. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 3997–4005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sureshchandra, S.; Marshall, N.E.; Wilson, R.M.; Barr, T.; Rais, M.; Purnell, J.Q.; Thornburg, K.L.; Messaoudi, I. Inflammatory Determinants of Pregravid Obesity in Placenta and Peripheral Blood. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segovia, S.A.; Vickers, M.H.; Gray, C.; Reynolds, C.M. Maternal Obesity, Inflammation, and Developmental Programming. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaenisch, R.; Bird, A. Epigenetic regulation of gene expression: How the genome integrates intrinsic and environmental signals. Nat. Genet. 2003, 33, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, D.; Osmond, C. Infant mortality, childhood nutrition, and ischaemic heart disease in england and wales. Lancet 1986, 327, 1077–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vansant, G.W.S.; Godderis, L. Effect of maternal and paternal nutrition on DNA methylation in the offspring: A systematic review of human and animal studies. Adv. Obes. Weight Manag. Control 2016, 4, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakyan, V.K.; Blewitt, M.E.; Druker, R.; Preis, J.I.; Whitelaw, E. Metastable epialleles in mammals. Trends Genet. 2002, 18, 348–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, P.T.; Dominguez-Salas, P.; Hennig, B.J.; Moore, S.E.; Prentice, A.M.; Silver, M.J. Maternal One-Carbon Metabolism and Infant DNA Methylation between Contrasting Seasonal Environments: A Case Study from The Gambia. Curr. Dev. Nutr. 2019, 3, nzy082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, S.; Rifas-Shiman, S.L.; Shivappa, N.; Wirth, M.D.; Hebert, J.R.; Gold, D.R.; Gillman, M.W.; Oken, E. Associations of prenatal and early life dietary inflammatory potential with childhood adiposity and cardiometabolic risk in Project Viva. Pediatr. Obes. 2018, 13, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, B.F.; Sauder, K.A.; Starling, A.P.; Hebert, J.R.; Shivappa, N.; Ringham, B.M.; Glueck, D.H.; Dabelea, D. Proinflammatory Diets during Pregnancy and Neonatal Adiposity in the Healthy Start Study. J. Pediatr. 2018, 195, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCullough, L.E.; Miller, E.E.; Calderwood, L.E.; Shivappa, N.; Steck, S.E.; Forman, M.R.; Mendez, M.A.; Maguire, R.; Fuemmeler, B.F.; Kollins, S.H.; et al. Maternal inflammatory diet and adverse pregnancy outcomes: Circulating cytokines and genomic imprinting as potential regulators? Epigenetics 2017, 12, 688–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, A.B. Observation and Experiment. N. Engl. J. Med. 1953, 248, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, A.B. The Environment and Disease: Association or Causation? Proc. R. Soc. Med. 1965, 58, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hebert, J.R.; Frongillo, E.A.; Adams, S.A.; Turner-McGrievy, G.M.; Hurley, T.G.; Miller, D.R.; Ockene, I.S. Perspective: Randomized Controlled Trials Are Not a Panacea for Diet-Related Research. Adv. Nutr. 2016, 7, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hebert, J.R.; Hurley, T.G.; Steck, S.E.; Miller, D.R.; Tabung, F.K.; Peterson, K.E.; Kushi, L.H.; Frongillo, E.A. Considering the value of dietary assessment data in informing nutrition-related health policy. Adv. Nutr. 2014, 5, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, A.; Macdonald-Wallis, C.; Tilling, K.; Boyd, A.; Golding, J.; Davey Smith, G.; Henderson, J.; Macleod, J.; Molloy, L.; Ness, A.; et al. Cohort Profile: The Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children: ALSPAC mothers cohort. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 42, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heude, B.; Forhan, A.; Slama, R.; Douhaud, L.; Bedel, S.; Saurel-Cubizolles, M.J.; Hankard, R.; Thiebaugeorges, O.; De Agostini, M.; Annesi-Maesano, I.; et al. Cohort Profile: The EDEN mother-child cohort on the prenatal and early postnatal determinants of child health and development. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 45, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inskip, H.M.; Godfrey, K.M.; Robinson, S.M.; Law, C.M.; Barker, D.J.; Cooper, C.; SWS Study Group. Cohort profile: The Southampton Women’s Survey. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2006, 35, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelleher, C.C.; Viljoen, K.; Khalil, H.; Somerville, R.; O’Brien, J.; Shrivastava, A.; Murrin, C.; Lifeways Cross-Generation Cohort Study Steering Group. Longitudinal follow-up of the relationship between dietary intake and growth and development in the Lifeways cross-generation cohort study 2001–2003. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2014, 73, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooijman, M.N.; Kruithof, C.J.; van Duijn, C.M.; Duijts, L.; Franco, O.H.; van IJzendoorn, M.H.; de Jongste, J.C.; Klaver, C.C.W.; van der Lugt, A.; Mackenbach, J.P.; et al. The Generation R Study: Design and cohort update 2017. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 31, 1243–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polańska, K.; Hanke, W.; Król, A.; Potocka, A.; Waszkowska, M.; Jacukowicz, A.; Jerzyńska, J.; Stelmach, W.; Stelmach, I.; Gromadzińska, J.; et al. Polish mother and child cohort study (REPRO_PL)—Methodology of the follow-up of the children at the age of 7. Int. J. Occup. Med. Environ. Health 2016, 29, 883–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, J.M.; McGowan, C.A.; Mahony, R.; Foley, M.E.; McAuliffe, F.M. Low glycaemic index diet in pregnancy to prevent macrosomia (ROLO study): Randomised control trial. BMJ 2012, 345, e5605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
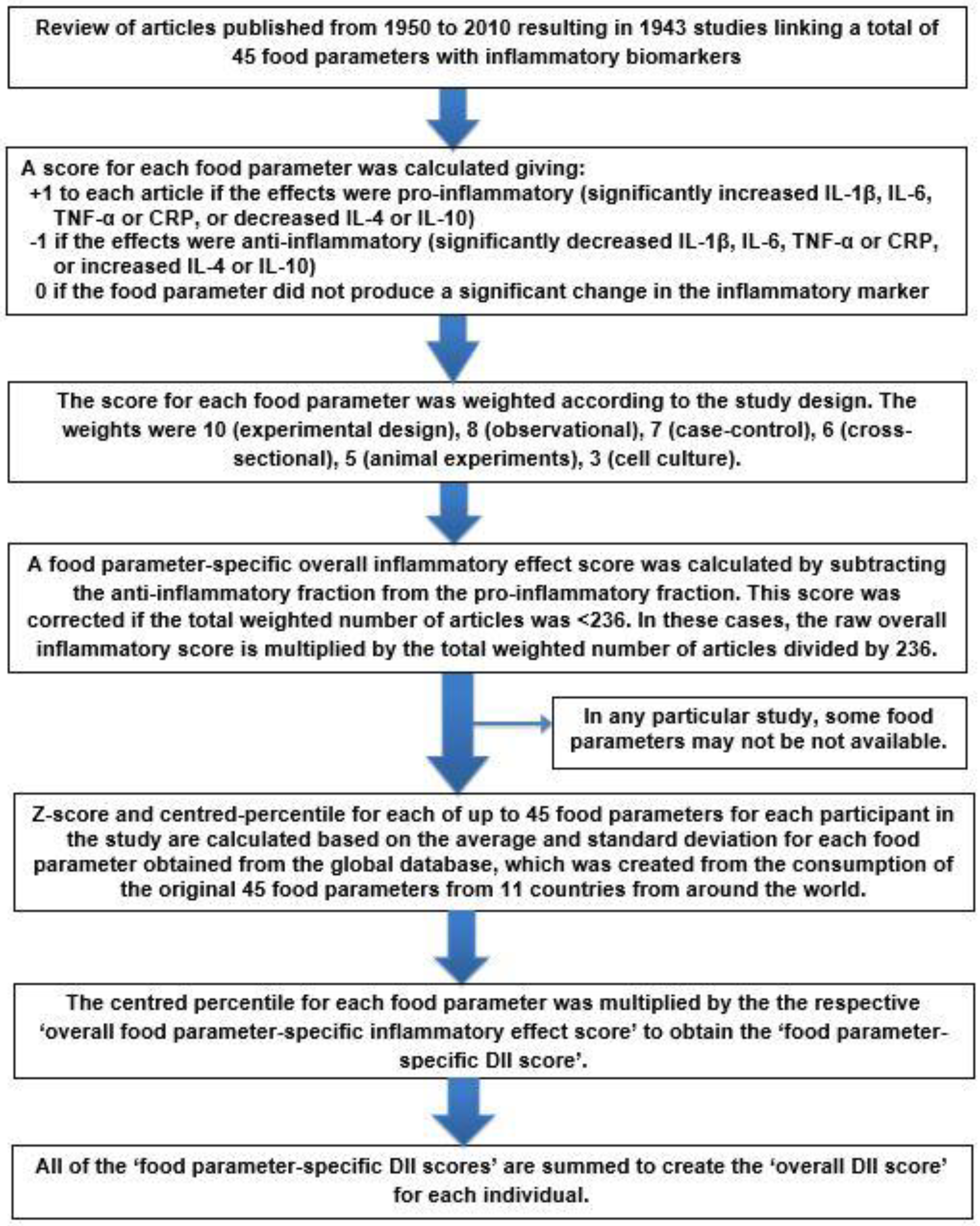
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Phillips, C.M.; Chen, L.-W.; Heude, B.; Bernard, J.Y.; Harvey, N.C.; Duijts, L.; Mensink-Bout, S.M.; Polanska, K.; Mancano, G.; Suderman, M.; et al. Dietary Inflammatory Index and Non-Communicable Disease Risk: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1873. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081873
Phillips CM, Chen L-W, Heude B, Bernard JY, Harvey NC, Duijts L, Mensink-Bout SM, Polanska K, Mancano G, Suderman M, et al. Dietary Inflammatory Index and Non-Communicable Disease Risk: A Narrative Review. Nutrients. 2019; 11(8):1873. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081873
Chicago/Turabian StylePhillips, Catherine M., Ling-Wei Chen, Barbara Heude, Jonathan Y. Bernard, Nicholas C. Harvey, Liesbeth Duijts, Sara M. Mensink-Bout, Kinga Polanska, Giulia Mancano, Matthew Suderman, and et al. 2019. "Dietary Inflammatory Index and Non-Communicable Disease Risk: A Narrative Review" Nutrients 11, no. 8: 1873. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081873
APA StylePhillips, C. M., Chen, L.-W., Heude, B., Bernard, J. Y., Harvey, N. C., Duijts, L., Mensink-Bout, S. M., Polanska, K., Mancano, G., Suderman, M., Shivappa, N., & Hébert, J. R. (2019). Dietary Inflammatory Index and Non-Communicable Disease Risk: A Narrative Review. Nutrients, 11(8), 1873. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081873






