Parental Feeding Practices in Relation to Maternal Education and Childhood Obesity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants and Data Collection
2.2. Anthropometric Measurements
2.3. Description of Factors in the Child Feeding Questionnaire (CFQ)
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sarrafzadegan, N.; Rabiei, K.; Nouri, F.; Mohammadifard, N.; Moattar, F.; Roohafza, H.; Haghjooy Javanmard, S.; Zarfeshani, S.; Pourmoghaddas, M. Parental perceptions of weight status of their children. ARYA Atheroscler. 2013, 9, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- CDC. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Obesity Prevalence USA: Childhood Obesity Facts, Prevalence of Childhood Obesity in the United States. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/obesity/data/childhood.html (accessed on 19 September 2019).
- CDC. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Obesity Prevalence USA: Division of Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Obesity, National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/obesity/data/prevalence-maps.html (accessed on 19 September 2019).
- Mattos, R.T.; Medeiros, N.I.; Menezes, C.A.; Fares, R.C.; Franco, E.P.; Dutra, W.O.; Rios-Santos, F.; Correa-Oliveira, R.; Gomes, J.A. Chronic Low-Grade Inflammation in Childhood Obesity Is Associated with Decreased IL-10 Expression by Monocyte Subsets. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0168610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahoo, K.; Sahoo, B.; Choudhury, A.K.; Sofi, N.Y.; Kumar, R.; Bhadoria, A.S. Childhood obesity: causes and consequences. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2015, 4, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Must, A.; McKeown, N.M. The Disease Burden Associated with Overweight and Obesity. In Endotext; Feingold, K.R., Anawalt, B., Boyce, A., Chrousos, G., Dungan, K., Grossman, A., Hershman, J.M., Kaltsas, G., Koch, C., Kopp, P., et al., Eds.; MDText.com, Inc.: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Antonino, B.; Caterina, M.; Marianna, B.; Felicia, F.; Antonio, P. Parental perception of childhood obesity in an inner-city area of Palermo, Italy. Ital. J. Pub. Health 2008, 5, 241–248. [Google Scholar]
- Owens, S.; Galloway, R. Childhood obesity and the metabolic syndrome. Curr. Atheroscler Rep. 2014, 16, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bridger, T. Childhood obesity and cardiovascular disease. Paediatr. Child Health 2009, 14, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Litwin, S.E. Childhood Obesity and Adulthood Cardiovascular Disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 64, 1588–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Umer, A.; Kelley, G.A.; Cottrell, L.E.; Giacobbi, P., Jr.; Innes, K.E.; Lilly, C.L. Childhood obesity and adult cardiovascular disease risk factors: a systematic review with meta-analysis. BMC Pub. Health 2017, 17, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, Y.; Hou, D.; Liang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Hu, Y.; Liu, J.; Cheng, H.; Yang, P.; Shan, X.; Xi, B.; et al. Tracking Body Mass Index From Childhood to Adulthood for Subclinical Cardiovascular Diseases at Adulthood. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 67, 1006–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Cheung, W.W.; Mak, R.H. Impact of obesity on kidney function and blood pressure in children. World J. Nephrol. 2015, 4, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savige, J.; Ratnaike, S.; Colville, D. Retinal abnormalities characteristic of inherited renal disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 1403–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kodhelaj, K.; Resuli, B.; Petrela, E.; Malaj, V.; Jaze, H. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in Albanian overweight children. Minerva Pediatr. 2014, 66, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mathur, P.; Das, M.K.; Arora, N.K. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and childhood obesity. Indian J. Pediatr. 2007, 74, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popkin, B.M. Contemporary nutritional transition: determinants of diet and its impact on body composition. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2011, 70, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ruggieri, D.G.; Bass, S.B. A comprehensive review of school-based body mass index screening programs and their implications for school health: do the controversies accurately reflect the research? J. Sch. Health 2015, 85, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulsifer, D.P.; Lakhtakia, A.; Narkhede, M.S. Education and Health: Evaluating Theories and Evidence. NBER Work. Pap. 2006, 10, 129–138. [Google Scholar]
- Wolfson, J.A.; Gollust, S.E.; Niederdeppe, J.; Barry, C.L. The role of parents in public views of strategies to address childhood obesity in the United States. Milbank Q 2015, 93, 73–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- de Lauzon-Guillain, B.; Oliveira, A.; Charles, M.A.; Grammatikaki, E.; Jones, L.; Rigal, N.; Lopes, C.; Manios, Y.; Moreira, P.; Emmett, P.; et al. A review of methods to assess parental feeding practices and preschool children’s eating behavior: the need for further development of tools. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2012, 112, 1578–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vaughn, A.E.; Tabak, R.G.; Bryant, M.J.; Ward, D.S. Measuring parent food practices: a systematic review of existing measures and examination of instruments. Int. J. Beh. Nutr. Physic. Activ. 2013, 10, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campbell, K.; Andrianopoulos, N.; Hesketh, K.; Ball, K.; Crawford, D.; Brennan, L.; Corsini, N.; Timperio, A. Parental use of restrictive feeding practices and child BMI z-score. A 3-year prospective cohort study. Appetite 2010, 55, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardel, M.; Willig, A.L.; Dulin-Keita, A.; Casazza, K.; Beasley, T.M.; Fernandez, J.R. Parental feeding practices and socioeconomic status are associated with child adiposity in a multi-ethnic sample of children. Appetite 2012, 58, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Webber, L.; Hill, C.; Cooke, L.; Carnell, S.; Wardle, J. Associations between child weight and maternal feeding styles are mediated by maternal perceptions and concerns. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 64, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Spruijt-Metz, D.; Li, C.; Cohen, E.; Birch, L.; Goran, M. Longitudinal influence of mother’s child-feeding practices on adiposity in children. J. Pediatr. 2006, 148, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowicka, P.; Sorjonen, K.; Pietrobelli, A.; Flodmark, C.E.; Faith, M.S. Parental feeding practices and associations with child weight status. Swedish validation of the Child Feeding Questionnaire finds parents of 4-year-olds less restrictive. Appetite 2014, 81, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blissett, J. Relationships between parenting style, feeding style and feeding practices and fruit and vegetable consumption in early childhood. Appetite 2011, 57, 826–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, C.; Duncanson, K.; Burrows, T. A systematic review investigating associations between parenting style and child feeding behaviours. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2014, 27, 557–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shloim, N.; Edelson, L.R.; Martin, N.; Hetherington, M.M. Parenting Styles, Feeding Styles, Feeding Practices, and Weight Status in 4-12 Year-Old Children: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Front. Psychol. 2015, 6, 1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mais, L.A.; Warkentin, S.; Latorre Mdo, R.; Carnell, S.; Taddei, J.A. Validation of the Comprehensive Feeding Practices Questionnaire among Brazilian Families of School-Aged Children. Front. Nutr. 2015, 2, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Venkatapoorna, C.M.K.; Ayine, P.; Selvaraju, V.; Parra, E.P.; Koenigs, T.; Babu, J.R.; Geetha, T. The relationship between obesity and sleep timing behavior, television exposure, and dinnertime among elementary school-age children. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2020, 16, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Onis, M.; Onyango, A.W.; Borghi, E.; Siyam, A.; Nishida, C.; Siekmann, J. Development of a WHO growth reference for school-aged children and adolescents. Bullet. World Health Org. 2007, 85, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birch, L.L.; Fisher, J.O.; Grimm-Thomas, K.; Markey, C.N.; Sawyer, R.; Johnson, S.L. Confirmatory factor analysis of the Child Feeding Questionnaire: a measure of parental attitudes, beliefs and practices about child feeding and obesity proneness. Appetite 2001, 36, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kheirollahpour, M.; Shohaimi, S. Dimensional model for estimating factors influencing childhood obesity: path analysis based modeling. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 512148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunnally, J.C., Jr. Introduction to psychological measurement.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Kline, R.B. Principles and Practice of Structural Equation Modeling; The Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson, K.N.; Reilly, J.J.; Basterfield, L.; Reilly, J.K.; Janssen, X.; Jones, A.R.; Cutler, L.R.; Le Couteur, A.; Adamson, A.J. Mothers’ perceptions of child weight status and the subsequent weight gain of their children: a population-based longitudinal study. Int. J. Obes. 2017, 41, 801–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Galloway, A.T.; Fiorito, L.M.; Francis, L.A.; Birch, L.L. ‘Finish your soup’: counterproductive effects of pressuring children to eat on intake and affect. Appetite 2006, 46, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matheson, D.M.; Robinson, T.N.; Varady, A.; Killen, J.D. Do Mexican-American mothers’food-related parenting practices influence their children’s weight and dietary intake? J. Am. Diet Assoc. 2006, 106, 1861–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, J.S.; Fisher, J.O.; Birch, L.L. Parental influence on eating behavior: conception to adolescence. J. Law. Med. Ethics 2007, 35, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doub, A.E.; Small, M.; Birch, L.L. A call for research exploring social media influences on mothers’ child feeding practices and childhood obesity risk. Appetite 2016, 99, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gemmill, A.W.; Worotniuk, T.; Holt, C.J.; Skouteris, H.; Milgrom, J. Maternal psychological factors and controlled child feeding practices in relation to child body mass index. Child Obes. 2013, 9, 326–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kral, T.V.; Moore, R.H.; Compher, C.W. Maternal concern about child weight in a study of weight-discordant siblings. Pub. Health Nurs. 2015, 32, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carnell, S.; Wardle, J. Associations between multiple measures of parental feeding and children’s adiposity in United Kingdom preschoolers. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2007, 15, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gregory, J.E.; Paxton, S.J.; Brozovic, A.M. Pressure to eat and restriction are associated with child eating behaviours and maternal concern about child weight, but not child body mass index, in 2- to 4-year-old children. Appetite 2010, 54, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogden, C.L.; Lamb, M.M.; Carroll, M.D.; Flegal, K.M. Obesity and socioeconomic status in children and adolescents: United States, 2005-2008. NCHS Data Brief 2010, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Shrewsbury, V.; Wardle, J. Socioeconomic status and adiposity in childhood: a systematic review of cross-sectional studies 1990-2005. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2008, 16, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxton, J.; Carnell, S.; van Jaarsveld, C.H.M.; Wardle, J. Maternal Education Is Associated with Feeding Style. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2009, 109, 894–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hennessy, E.; Hughes, S.O.; Goldberg, J.P.; Hyatt, R.R.; Economos, C.D. Parent behavior and child weight status among a diverse group of underserved rural families. Appetite 2010, 54, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulder, C.; Kain, J.; Uauy, R.; Seidell, J.C. Maternal attitudes and child-feeding practices: relationship with the BMI of Chilean children. Nutr. J. 2009, 8, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
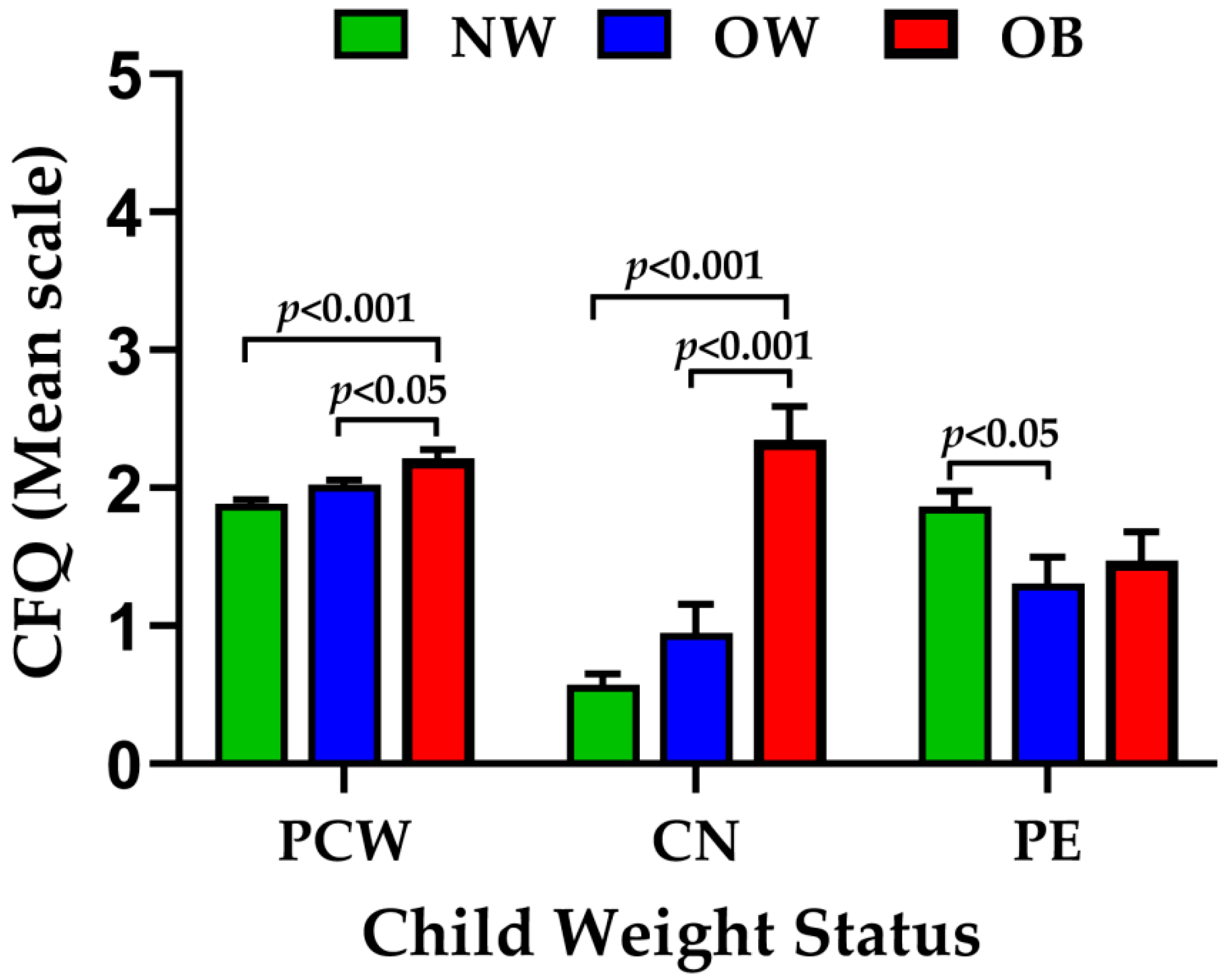

| NW | OW | OB | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All | 109 (64.5%) | 32 (18.9%) | 28 (16.6%) | |
| Age (y) | 8.37 ± 1.44 | 8.28 ± 1.29 | 8.77 ± 1.46 | 0.349 |
| Gender (%) | ||||
| Male | 50.46% | 50.0% | 42.86% | |
| Female | 49.54% | 50.0% | 57.14% | |
| Maternal Education (%) | ||||
| High School or less | 23.85% | 15.63% | 32.14% | |
| Associate Degree | 23.85% | 21.88% | 32.14% | |
| Bachelor’s Degree | 20.18% | 28.13% | 21.43% | |
| Graduate | 32.11% | 34.38% | 14.29% | |
| BMI z-score | −0.02 ± 0.82 | 1.56 ± 0.26 | 2.56 ± 0.37 | p < 0.001 |
| Factor | Mean ± SD | Cronbach Alpha |
|---|---|---|
| PR | 3.41 ± 0.70 | 0.89 |
| PPW | 2.23 ± 0.41 | 0.66 |
| PCW | 1.97 ± 0.31 | 0.75 |
| CN | 0.94 ± 1.19 | 0.87 |
| RST | 2.59 ± 0.97 | 0.83 |
| PE | 1.69 ± 1.18 | 0.80 |
| MN | 2.89 ± 1.12 | 0.94 |
| BMI z-Score | PR | PPW | PCW | CN | RST | PE | MN | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMI z-score | 1.000 | |||||||
| PR | −0.031 | 1.000 | ||||||
| PPW | 0.122 | 0.008 | 1.000 | |||||
| PCW | 0.399 ** | 0.218 ** | 0.062 | 1.000 | ||||
| CN | 0.399 ** | 0.115 | 0.154 * | 0.302 ** | 1.000 | |||
| RST | 0.052 | 0.238 ** | 0.068 | 0.171 * | 0.345 ** | 1.000 | ||
| PE | −0.177 * | 0.129 | −0.073 | −0.065 | 0.080 | 0.403 ** | 1.000 | |
| MN | 0.038 | 0.341 ** | −0.062 | 0.321 ** | 0.116 | 0.322 ** | 0.262 ** | 1.000 |
| CFQ Factor | B-Value | Change in R2 | β (95% CI min, max) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PR | −1.562 | 0.001 | −0.108 (−1.669, 1.453) | 0.130 |
| PPW | 1.105 | 0.016 | 0.050 (1.155, −1.055) | 0.454 |
| PCW | 7.644 | 0.165 | 0.312 (7.956, −7.332) | < 0.001 |
| CN | 1.691 | 0.069 | 0.320 (2.009, −1.369) | < 0.001 |
| RST | −0.531 | 0.014 | −0.063 (−0.595, 0.469) | 0.427 |
| PE | −1.342 | 0.034 | −0.224 (−1.564, 1.116) | 0.005 |
| MN | 0.164 | 0.000 | 0.023 (0.187, −0.141) | 0.767 |
| Maternal Education | PCW | CN | PE |
|---|---|---|---|
| High School or less | 1.94 (0.19) | 0.87 (1.03) | 2.56 (1.18) |
| Associate Degree | 1.94 (0.37) | 1.35 (1.38) | 1.88 (1.18) * |
| Bachelor’s Degree | 2.09 (0.36) | 0.74 (1.10) | 1.09 (0.96) ** |
| Graduate | 1.92 (0.30) | 0.79 (1.16) | 1.29 (0.88) ** |
| Parameters | Model | Variables | B | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Perceived Child Weight | Direct Relationship | Perceived Child Weight → BMI z-score | 7.11 | 0.008 |
| Indirect Relationship | PCW → Maternal Education → BMI z-score | −0.007 | 0.992 | |
| Total effect | Direct + Indirect | 7.10 | 0.008 | |
| Concern about Child Weight | Direct Relationship | CN → BMI z-score | 1.61 | 0.004 |
| Indirect Relationship | CN → Maternal Education → BMI z-score | 0.074 | 0.262 | |
| Total effect | Direct + Indirect | 1.69 | 0.004 | |
| Pressure to Eat | Direct Relationship | PE → BMI z-score | −1.53 | 0.004 |
| Indirect Relationship | PE → Maternal Education → BMI z-score | 0.49 | 0.002 | |
| Total effect | Direct + Indirect | −1.04 | 0.016 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ayine, P.; Selvaraju, V.; Venkatapoorna, C.M.K.; Geetha, T. Parental Feeding Practices in Relation to Maternal Education and Childhood Obesity. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1033. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12041033
Ayine P, Selvaraju V, Venkatapoorna CMK, Geetha T. Parental Feeding Practices in Relation to Maternal Education and Childhood Obesity. Nutrients. 2020; 12(4):1033. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12041033
Chicago/Turabian StyleAyine, Priscilla, Vaithinathan Selvaraju, Chandra M. K. Venkatapoorna, and Thangiah Geetha. 2020. "Parental Feeding Practices in Relation to Maternal Education and Childhood Obesity" Nutrients 12, no. 4: 1033. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12041033
APA StyleAyine, P., Selvaraju, V., Venkatapoorna, C. M. K., & Geetha, T. (2020). Parental Feeding Practices in Relation to Maternal Education and Childhood Obesity. Nutrients, 12(4), 1033. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12041033





