The Effect of Ursodeoxycholic Acid on Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Patients with Functional Dyspepsia: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
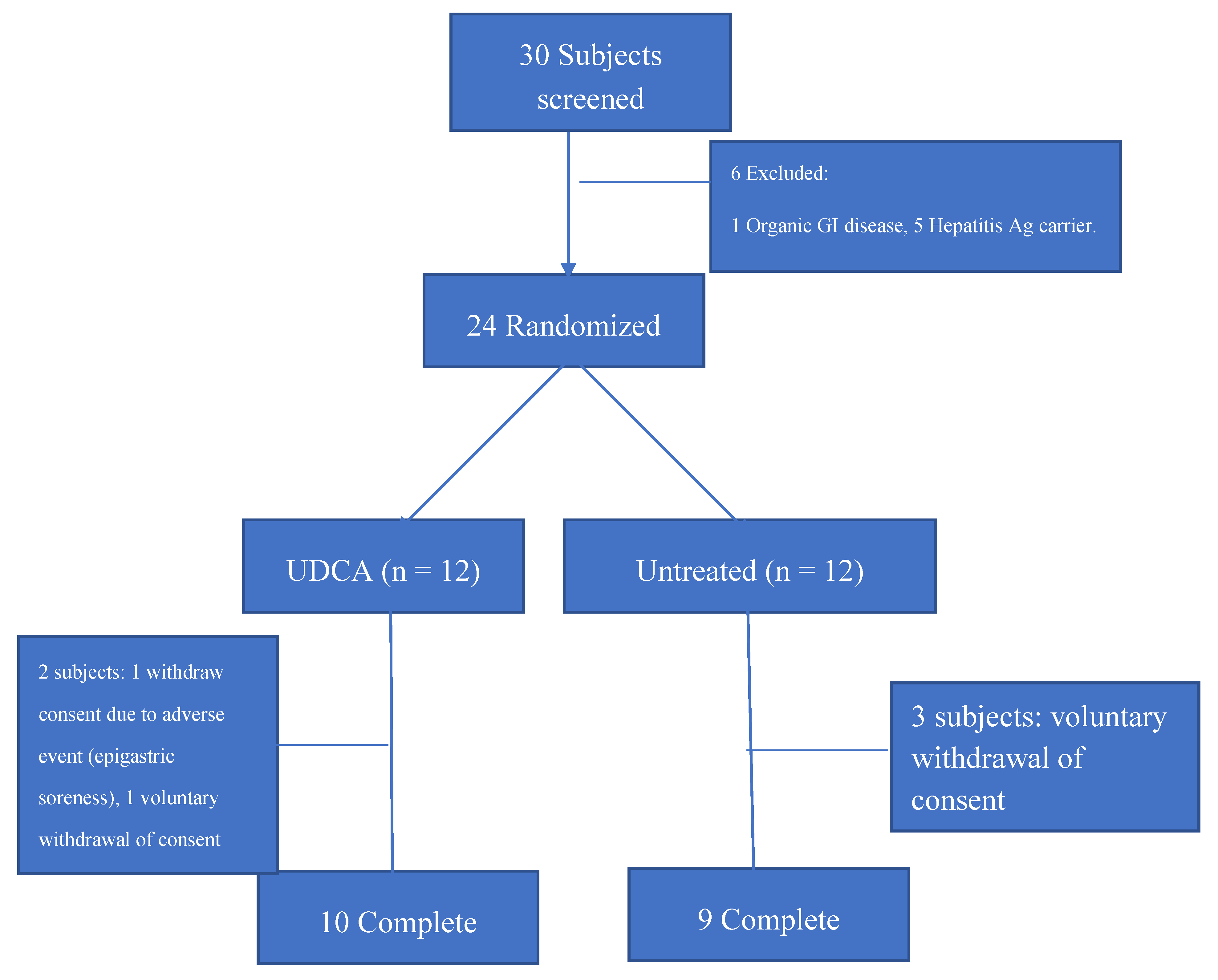
2.1. Study Populations and Design
2.2. Measurements
2.2.1. Gastrointestinal Symptoms
2.2.2. Lactulose Breath Test
2.3. Statistical Analysis
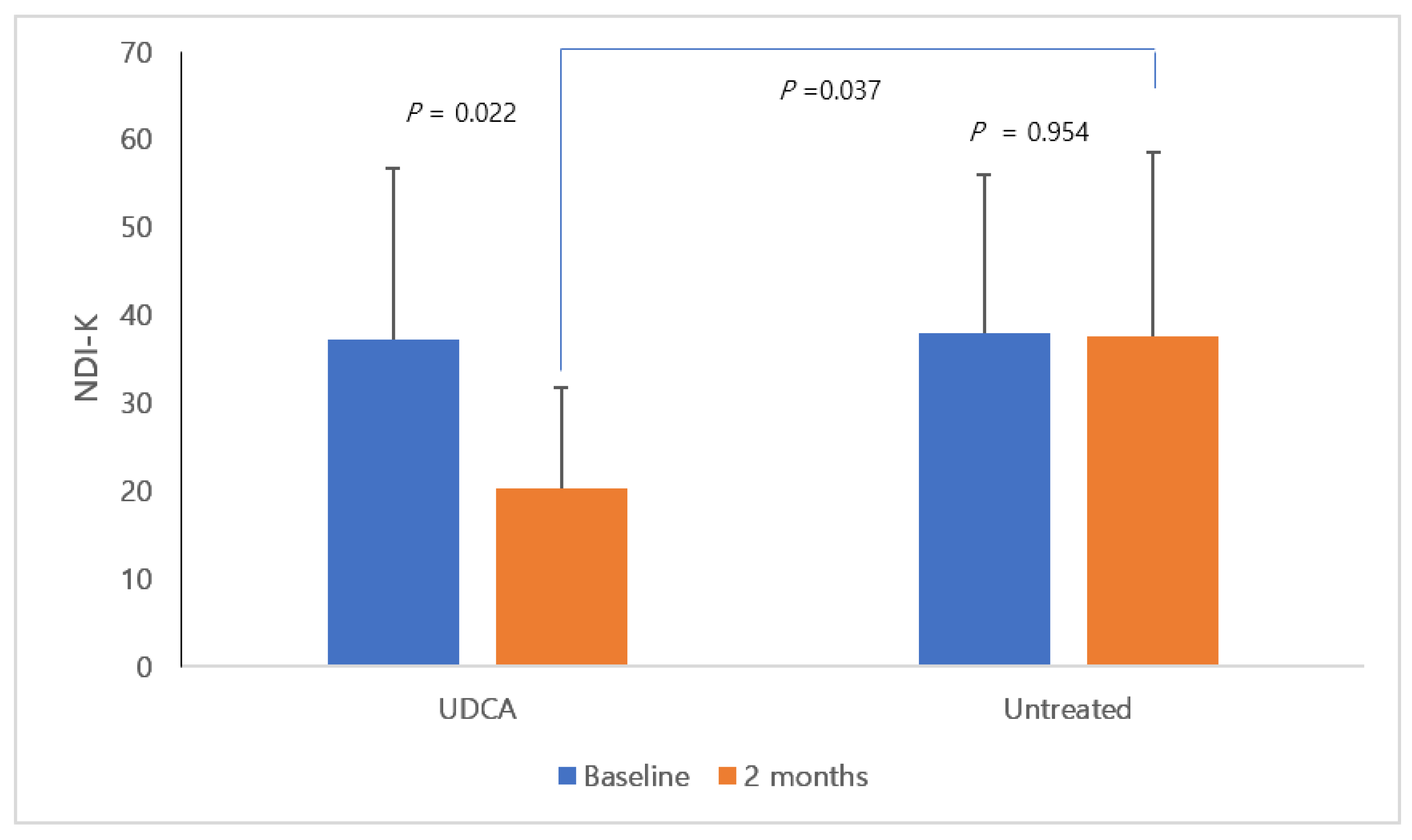
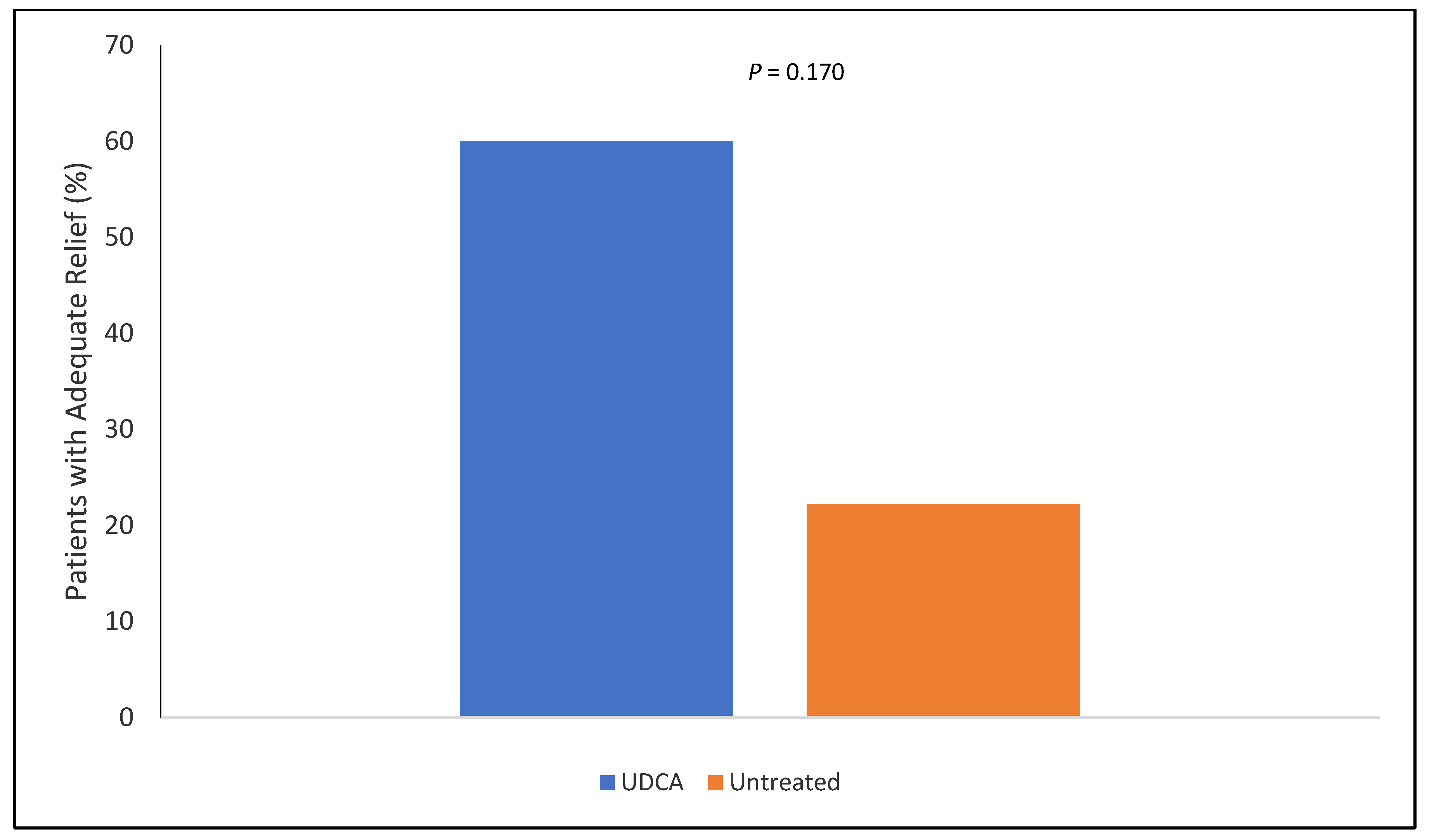
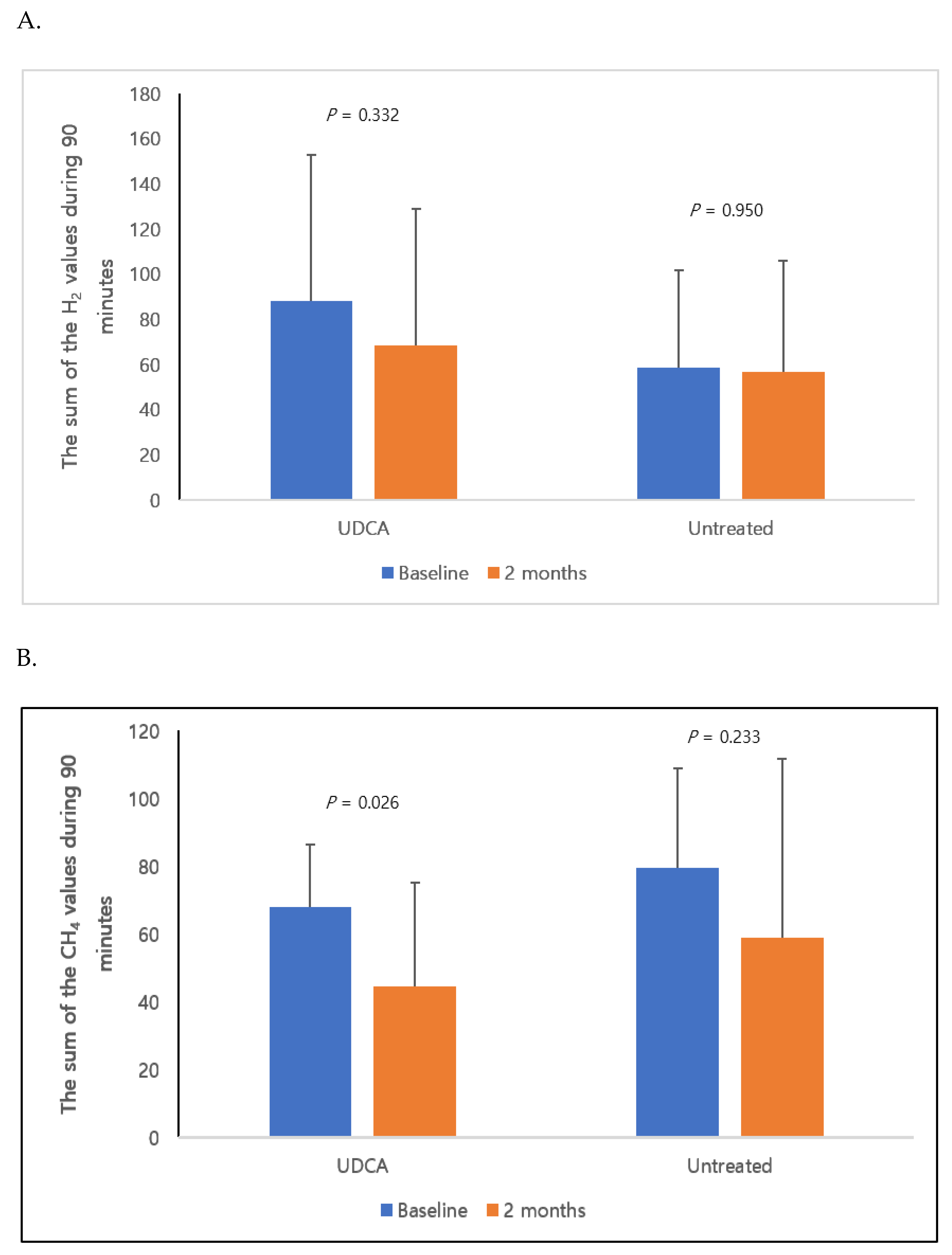
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Drossman, D.A. Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders: History, Pathophysiology, Clinical Features and Rome IV. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 1262–1279.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.J.; Chen, B.R.; Kim, J.J.; Kim, S.; Shen, J.H.; Dai, N. Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy for functional dyspepsia: Systematic review and meta-analysis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 3486–3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tack, J.; Caenepeel, P.; Fischler, B.; Piessevaux, H.; Janssens, J. Symptoms associated with hypersensitivity to gastric distention in functional dyspepsia. Gastroenterology 2001, 121, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarnelli, G.; Caenepeel, P.; Geypens, B.; Janssens, J.; Tack, J. Symptoms associated with impaired gastric emptying of solids and liquids in functional dyspepsia. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2003, 98, 783–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanghellini, V.; Tosetti, C.; Paternico, A.; Barbara, G.; Morselli-Labate, A.M.; Monetti, N.; Marengo, M.; Corinaldesi, R. Risk indicators of delayed gastric emptying of solids in patients with functional dyspepsia. Gastroenterology 1996, 110, 1036–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wauters, L.; Talley, N.J.; Walker, M.M.; Tack, J.; Vanuytsel, T. Novel concepts in the pathophysiology and treatment of functional dyspepsia. Gut 2020, 69, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.B.; Azeredo, I.L., Jr.; Marciano, R.D.; Caldeira, L.M.; Bafutto, M. Evaluation of small intestine bacterial overgrowth in patients with functional dyspepsia through H2 breath test. Arq. Gastroenterol. 2012, 49, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petzold, G.; Amanzada, A.; Gress, T.M.; Ellenrieder, V.; Neesse, A.; Kunsch, S. High Prevalence of Pathological Hydrogen Breath Tests in Patients with Functional Dyspepsia. Digestion 2019, 100, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, V.P.; Liu, K.S.; Lam, F.Y.; Hung, I.F.; Yuen, M.F.; Leung, W.K. Randomised clinical trial: Rifaximin versus placebo for the treatment of functional dyspepsia. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 45, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridlon, J.M.; Kang, D.J.; Hylemon, P.B. Bile salt biotransformations by human intestinal bacteria. J. Lipid Res. 2006, 47, 241–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Pérez, O.; Cruz-Ramón, V.; Chinchilla-López, P.; Méndez-Sánchez, N. The Role of the Gut Microbiota in Bile Acid Metabolism. Ann. Hepatol. 2017, 16 (Suppl. 1), S21–S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Bossche, L.; Hindryckx, P.; Devisscher, L.; Devriese, S.; Van Welden, S.; Holvoet, T.; Vilchez-Vargas, R.; Vital, M.; Pieper, D.H.; Vanden Bussche, J.; et al. Ursodeoxycholic Acid and Its Taurine- or Glycine-Conjugated Species Reduce Colitogenic Dysbiosis and Equally Suppress Experimental Colitis in Mice. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 17, 83. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Zhao, J.; Gui, W.; Sun, D.; Dai, H.; Xiao, L.; Chu, H.; Du, F.; Zhu, Q.; Schnabl, B.; et al. Tauroursodeoxycholic acid inhibits intestinal inflammation and barrier disruption in mice with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 469–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, T.; Caporaso, J.G.; Yellowhair, M.; Bokulich, N.A.; Padi, M.; Roe, D.J.; Wertheim, B.C.; Linhart, M.; Martinez, J.A.; Bilagody, C.; et al. Effects of ursodeoxycholic acid on the gut microbiome and colorectal adenoma development. Cancer. Med. 2019, 8, 617–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Wei, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, W.; Chen, H.; Wang, Q.; Yang, F.; Miao, Q.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, H.; et al. Gut microbial profile is altered in primary biliary cholangitis and partially restored after UDCA therapy. Gut 2018, 6, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staley, C.; Weingarden, A.R.; Khoruts, A.; Sadowsky, M.J. Interaction of gut microbiota with bile acid metabolism and its influence on disease states. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 47–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenfield, T.K. Ways of measuring drinking patterns and the difference they make: Experience with graduated frequencies. J. Subst. Abus. 2000, 12, 33–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Choi, S.C.; Cho, Y.K.; Choi, M.G. Validation of the Nepean Dyspepsia Index- Korean version. Korean J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2003, 15, 48. [Google Scholar]
- Rezaie, A.; Buresi, M.; Lembo, A.; Lin, H.; McCallum, R.; Rao, S.; Schmulson, M.; Valdovinos, M.; Zakko, S.; Pimentel, M. Hydrogen and Methane-Based Breath Testing in Gastrointestinal Disorders: The North American Consensus. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 112, 775–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tziatzios, G.; Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.J.; Papanikolaou, I.S.; Pimentel, M.; Dimitriadis, G.D.; Triantafyllou, K. Is small intestinal bacterial overgrowth involved in the pathogenesis of functional dyspepsia? Med. Hypotheses 2017, 106, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, D.; Ghoshal, U.; Mittal, R.D.; Ghoshal, U.C. Associations between IL-1RA polymorphisms and small intestinal bacterial overgrowth among patients with irritable bowel syndrome from India. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2014, 26, 1408–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, L.; Chen, B.; Kim, J.J.; Chen, X.; Dai, N. Micro-inflammation in functional dyspepsia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2018, 30, e13304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenman, L.K.; Holma, R.; Eggert, A.; Korpela, R. A novel mechanism for gut barrier dysfunction by dietary fat: Epithelial disruption by hydrophobic bile acids. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2013, 304, G227–G234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, A.; Wang, L.; Chen, X.; Guo, H.; Chu, S.; Zhang, X.; Peng, W. Ursodeoxycholic Acid Ameliorated Diabetic Nephropathy by Attenuating Hyperglycemia-Mediated Oxidative Stress. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2016, 39, 1300–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, J.; An, S.H.; Kang, S.W.; Kwon, K. Ursodeoxycholic Acid (UDCA) Exerts Anti-Atherogenic Effects by Inhibiting RAGE Signaling in Diabetic Atherosclerosis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Işık, S.; Karaman, M.; Micili, S.C.; Çağlayan-Sözmen, Ş.; Bağrıyanık, H.A.; Arıkan-Ayyıldız, Z.; Uzuner, N.; Karaman, Ö. Beneficial effects of ursodeoxycholic acid via inhibition of airway remodelling, apoptosis of airway epithelial cells, and Th2 immune response in murine model of chronic asthma. Allergol. Immunopathol. (Madr) 2017, 45, 339–349. [Google Scholar]
- Pimentel, M.; Lin, H.C.; Enayati, P.; van den Burg, B.; Lee, H.R.; Chen, J.H.; Park, S.; Kong, Y.; Conklin, J. Methane, a gasproduced by entericbacteria, slowsintestinaltransit and augments smallintestinal contractile activity. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2006, 290, G1089–G1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoshal, U.C.; Srivastava, D.; Verma, A.; Misra, A. Slow transit constipation associated with excess methane production and its improvement following rifaximin therapy: A case report. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2011, 17, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, S.V.; Sharma, S.; Kaur, J.; Sinha, S.K.; Singh, K. Comparison of lactulose and glucose breath test for diagnosis of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Digestion 2012, 85, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| UDCA (n = 10) | Untreated (n = 9) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 50.4 ± 9.7 | 48.3 ± 14.6 | 0.719 |
| Weight (kg) | 69.0 ± 12.7 | 68.7 ± 14.2 | 0.972 |
| Men (n,%) | 6, 60% | 5, 55% | 0.845 |
| Nepean dyspepsia index-K (score) | 37.2 ± 19.5 | 38.0 ± 18.0 | 0.927 |
| FD subtype | |||
| PDS (n,%) | 9, 90% | 6, 66% | 0.576 |
| EPS (n,%) | 1, 10% | 3, 33% | 0.672 |
| Helicobacter pylori infection prevalence (n,%) | 3, 30% | 2, 22% | 0.708 |
| Current smoker (n,%) | 0, 0% | 1, 11% | 0.541 |
| Weekly alcohol intake (g/week) | 93.5 ± 84.6 | 72.0 ± 56.8 | 0.608 |
| Diabetes (n,%) | 1, 10% | 2, 22% | 0.653 |
| Hypertension (n,%) | 0, 0 | 1, 11 | 0.541 |
| Dyslipidemia (n,%) | 1, 10 | 1, 11 | 0.452 |
| Positive Hydrogen Gas-Producing SIBO | Positive Methane Gas-Producing SIBO | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 2 Months | Baseline | 2 Months | |
| UDCA (n = 10) | 4 (40%) | 1 (10%) | 8 (80%) | 4 (40%) |
| Untreated (n = 9) | 2 (22%) | 2 (22%) | 9 (100%) | 4 (44%) |
| p | 0.874 | 0.784 | 0.510 | 0.845 |
| Baseline | 2 Months | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UDCA (n = 10) | Untreated (n = 9) | p | UDCA (n = 10) | Untreated (n = 9) | p | |
| White blood cells (x 103) | 5.7 ± 1.1 | 6.2 ± 1.7 | 0.456 | 6.6 ± 1.7 | 5.5 ± 0.7 | 0.109 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 14.2 ± 2.0 | 13.4 ± 1.8 | 0.408 | 14.4 ± 0.8 | 14.3 ± 1.6 | 0.912 |
| Alkaline phosphatase (IU/L) | 60.8 ± 12.7 | 64.4 ± 13.4 | 0.552 | 60.6 ± 10.9 | 66.6 ± 18.7 | 0.395 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 192.7 ± 27.6 | 203.3 ± 23.4 | 0.381 | 192.4 ± 41.2 | 198.3 ± 34.6 | 0.740 |
| Fasting glucose (mg/dL) | 100.3 ± 11.7 | 98.3 ± 14.0 | 0.743 | 99.4 ± 8.5 | 97.1 ± 15.2 | 0.698 |
| ALT (IU/L) | 28.6 ± 20.4 | 28.0 ± 19.0 | 0.948 | 29.3 ± 21.3 | 33.7 ± 29.0 | 0.705 |
| AST (IU/L) | 27.6 ± 11.4 | 26.4 ± 8.9 | 0.811 | 27.9 ± 10.4 | 27.7 ± 11.8 | 0.981 |
| GGT (IU/L) | 57.3 ± 15.3 | 56.0 ± 60.4 | 0.864 | 54.8 ± 12.1 | 55.0 ± 43.7 | 0.786 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, B.-T.; Kim, K.-M.; Kim, K.-N. The Effect of Ursodeoxycholic Acid on Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Patients with Functional Dyspepsia: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1410. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051410
Kim B-T, Kim K-M, Kim K-N. The Effect of Ursodeoxycholic Acid on Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Patients with Functional Dyspepsia: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients. 2020; 12(5):1410. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051410
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Bom-Taeck, Kwang-Min Kim, and Kyu-Nam Kim. 2020. "The Effect of Ursodeoxycholic Acid on Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Patients with Functional Dyspepsia: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial" Nutrients 12, no. 5: 1410. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051410
APA StyleKim, B.-T., Kim, K.-M., & Kim, K.-N. (2020). The Effect of Ursodeoxycholic Acid on Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Patients with Functional Dyspepsia: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients, 12(5), 1410. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051410





