Reactive Dicarbonyl Scavenging Effectively Reduces MPO-Mediated Oxidation of HDL and Restores PON1 Activity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
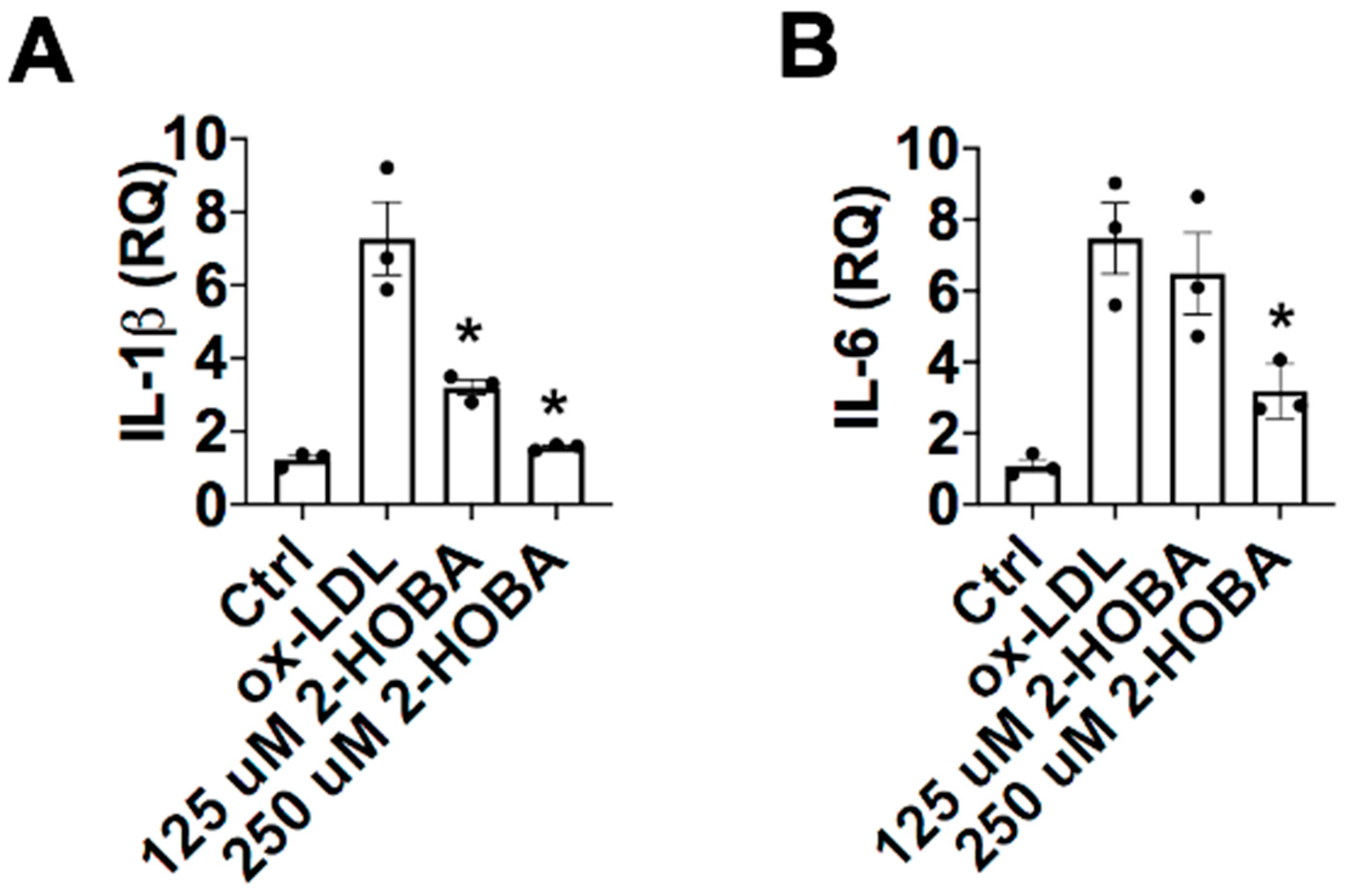
3. Results
3.1. Effects of PON1 on MPO Activity, apoAI Crosslinking, MDA-HDL Adducts, and HDL Cholesterol Efflux Capacity
3.2. Effects of MDA Modification of apoAI or HDL on apoAI Crosslinking, Cholesterol Efflux Capacity, and HDL-apoAI Exchangeability
3.3. Effects of Reactive Dicarbonyl Scavenging on HDL-apoAI Crosslinking and Cholesterol Efflux Capacity during MDA Modification and MPO-Mediated Oxidation
3.4. Effects of HDL MDA Modification and Dicarbonyl Scavenging on PON1 Activity
3.5. FH Patients Have Decreased PON1 Activity, Increased MDA-apoAI Adducts, Defective HDL Cholesterol Efflux Capacity and Impaired HDL Anti-Inflammatory Function
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FH | familial hypercholesterolemia |
| MPO | myeloperoxidase |
| PON1 | paraoxonase 1 |
| HOCl | hypochlorous acid |
| H2O2 | hydrogen peroxide |
| MDA | malondialdehyde |
| HDL | high-density lipoprotein |
| ApoAI | apolipoproteinA-I |
| ABCA1 | the ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| SAA | serum amyloid A |
References
- Linton, M.F.; Yancey, P.G.; Davies, S.S.; Jerome, W.G.J.; Linton, E.F.; Vickers, K.C. The Role of Lipids and Lipoproteins in Atherosclerosis. In Endotext; De Groot, L.J., Chrousos, G., Dungan, K., Feingold, K.R., Grossman, A., Hershman, J.M., Koch, C., Korbonits, M., Mclachlan, R., New, M., et al., Eds.; MDText.com, Inc.: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, E.A.; Feig, J.E.; Hewing, B.; Hazen, S.L.; Smith, J.D. High-Density Lipoprotein Function, Dysfunction, and Reverse Cholesterol Transport. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2012, 32, 2813–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khera, A.V.; Cuchel, M.; De La Llera-Moya, M.; Rodrigues, A.; Burke, M.F.; Jafri, K.; French, B.C.; Phillips, J.A.; Mucksavage, M.L.; Wilensky, R.L.; et al. Cholesterol Efflux Capacity, High-Density Lipoprotein Function, and Atherosclerosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohatgi, A.; Khera, A.; Berry, J.D.; Givens, E.G.; Ayers, C.R.; Wedin, K.E.; Neeland, I.J.; Yuhanna, I.S.; Rader, D.R.; De Lemos, J.A.; et al. Hdl Cholesterol Efflux Capacity and Incident Cardiovascular Events. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 2383–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenson, R.S.; Brewer, H.B., Jr.; Ansell, B.J.; Barter, P.; Chapman, M.J.; Heinecke, J.W.; Kontush, A.; Tall, A.R.; Webb, N.R. Dysfunctional Hdl And Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2016, 13, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleheen, D.; Scott, R.; Javad, S.; Zhao, W.; Rodrigues, A.; Picataggi, A.; Lukmanova, D.; Mucksavage, M.L.; Luben, R.; Billheimer, J.; et al. Association of Hdl Cholesterol Efflux Capacity with Incident Coronary Heart Disease Events: A Prospective Case-Control Study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015, 3, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergt, C.; Pennathur, S.; Fu, X.; Byun, J.; O’brien, K.; Mcdonald, T.O.; Singh, P.; Anantharamaiah, G.M.; Chait, A.; Brunzell, J.; et al. The Myeloperoxidase Product Hypochlorous Acid Oxidizes Hdl in The Human Artery Wall and Impairs Abca1-Dependent Cholesterol Transport. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 13032–13037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, B.; Oda, M.N.; Bergt, C.; Fu, X.; Green, P.S.; Brot, N.; Oram, J.F.; Heinecke, J.W. Myeloperoxidase Impairs Abca1-Dependent Cholesterol Efflux through Methionine Oxidation and Site-Specific Tyrosine Chlorination of Apolipoprotein A-I. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 9001–9004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, B.H.; Tang, C.R.; Sinha, A.; Mayer, P.S.; Davenport, G.D.; Brot, N.; Oda, M.N.; Zhao, X.Q.; Heinecke, J.W. Humans with Atherosclerosis Have Impaired Abca1 Cholesterol Efflux and Enhanced High-Density Lipoprotein Oxidation by Myeloperoxidase. Circ. Res. 2014, 114, 1733–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, B.; Cavigiolio, G.; Brot, N.; Oda, M.N.; Heinecke, J.W. Methionine Oxidation Impairs Reverse Cholesterol Transport by Apolipoprotein A-I. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 12224–12229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Undurti, A.; Huang, Y.; Lupica, J.A.; Smith, J.D.; Didonato, J.A.; Hazen, S.L. Modification of High Density Lipoprotein by Myeloperoxidase Generates A Pro-Inflammatory Particle. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 30825–30835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Didonato, J.A.; Levison, B.S.; Schmitt, D.; Li, L.; Wu, Y.; Buffa, J.; Kim, T.; Gerstenecker, G.S.; Gu, X.; et al. An Abundant Dysfunctional Apolipoprotein A1 in Human Atheroma. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, B.; Pennathur, S.; Pagani, I.; Oda, M.N.; Witztum, J.L.; Oram, J.F.; Heinecke, J.W. Modifying Apolipoprotein A-I by Malondialdehyde, But Not by An Array of Other Reactive Carbonyls, Blocks Cholesterol Efflux by The Abca1 Pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 18473–18484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May-Zhang, L.S.; Yermalitsky, V.; Huang, J.; Pleasent, T.; Borja, M.S.; Oda, M.N.; Jerome, W.G.; Yancey, P.G.; Linton, M.F.; Davies, S.S. Modification by Isolevuglandins, Highly Reactive Gamma-Ketoaldehydes, Deleteriously Alters High-Density Lipoprotein Structure and Function. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 9176–9187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domagala, T.B.; Lacinski, M.; Trzeciak, W.H.; Mackness, B.; Mackness, M.I.; Jakubowski, H. The Correlation of Homocysteine-Thiolactonase Activity of the Paraoxonase (Pon1) Protein with Coronary Heart Disease Status. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2006, 52, 4–10. [Google Scholar]
- Van Himbergen, T.M.; Roest, M.; de Graaf, J.; Jansen, E.H.; Hattori, H.; Kastelein, J.J.; Voorbij, H.A.; Stalenhoef, A.F.; van Tits, L.J. Indications That Paraoxonase-1 Contributes to Plasma High Density Lipoprotein Levels in Familial Hypercholesterolemia. J. Lipid Res. 2005, 46, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riwanto, M.; Landmesser, U. Thematic Review Series: High Density Lipoprotein Structure, Function, and Metabolism High Density Lipoproteins and Endothelial Functions: Mechanistic Insights and Alterations in Cardiovascular Disease. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 3227–3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perla-Kajan, J.; Jakubowski, H. Paraoxonase 1 Protects Against Protein N-Homocysteinylation in Humans. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 931–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, A.D.; Berliner, J.A.; Hama, S.Y.; La Du, B.N.; Faull, K.F.; Fogelman, A.M.; Navab, M. Protective Effect of High Density Lipoprotein Associated Paraoxonase. Inhibition of the Biological Activity of Minimally Oxidized Low Density Lipoprotein. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 96, 2882–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Riwanto, M.; Gao, S.; Levison, B.S.; Gu, X.; Fu, X.; Wagner, M.A.; Besler, C.; Gerstenecker, G.; et al. Myeloperoxidase, Paraoxonase-1, And Hdl Form A Functional Ternary Complex. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 3815–3828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Smith, F.; Panizzi, P. Ordered Cleavage of Myeloperoxidase Ester Bonds Releases Active Site Heme Leading to Inactivation of Myeloperoxidase by Benzoic Acid Hydrazide Analogs. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2014, 548, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Milton, A.; Arnold, R.D.; Huang, H.; Smith, F.; Panizzi, J.R.; Panizzi, P. Methods for Measuring Myeloperoxidase Activity toward Assessing Inhibitor Efficacy in Living Systems. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2016, 99, 541–548, Epub 2016/02/18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goiffon, R.J.; Martinez, S.C.; Piwnica-Worms, D. A Rapid Bioluminescence Assay for Measuring Myeloperoxidase Activity in Human Plasma. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, W.S.; Heink, A.; Sexmith, H.; Melchior, J.T.; Gordon, S.M.; Kuklenyik, Z.; Woollett, L.; Barr, J.R.; Jones, J.I.; Toth, C.A.; et al. The Effects of Apolipoprotein B Depletion on Hdl Subspecies Composition and Function. J. Lipid Res. 2016, 57, 674–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, B.H.; Tang, C.R.; Heinecke, J.W.; Oram, J.F. Oxidation of Apolipoprotein A-I by Myeloperoxidase Impairs the Initial Interactions with Abca1 Required for Signaling and Cholesterol Export. J. Lipid Res. 2010, 51, 1849–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Smith, F.; Panizzi, J.R.; Goodwin, D.C.; Panizzi, P. Inactivation of Myeloperoxidase by Benzoic Acid Hydrazide. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2015, 570, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yancey, P.G.; De La Llera-Moya, M.; Swarnakar, S.; Monzo, P.; Klein, S.M.; Connelly, M.A.; Johnson, W.J.; Williams, D.L.; Rothblat, G.H. High Density Lipoprotein Phospholipid Composition Is A Major Determinant of the Bi-Directional Flux and Net Movement of Cellular Free Cholesterol Mediated by Scavenger Receptor Bi. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 36596–36604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yancey, P.G.; Yu, H.; Linton, M.F.; Fazio, S. A Pathway-Dependent on Apoe, Apoai, and Abca1 Determines Formation of Buoyant High-Density Lipoprotein by Macrophage Foam Cells. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2007, 27, 1123–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borja, M.S.; Zhao, L.; Hammerson, B.; Tang, C.; Yang, R.; Carson, N.; Fernando, G.; Liu, X.; Budamagunta, M.S.; Genest, J.; et al. Hdl-Apoa-I Exchange: Rapid Detection and Association with Atherosclerosis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, E71541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borja, M.S.; Ng, K.F.; Irwin, A.; Hong, J.; Wu, X.; Isquith, D.; Zhao, X.Q.; Prazen, B.; Gildengorin, V.; Oda, M.N.; et al. Hdl-Apolipoprotein A-I Exchange Is Independently Associated with Cholesterol Efflux Capacity. J. Lipid Res. 2015, 56, 2002–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.Q.; Brubaker, G.; Wu, Z.; Zheng, L.; Willard, B.; Kinter, M.; Hazen, S.L.; Smith, J.D. Apolipoprotein A-I Tryptophan Substitution Leads to Resistance to Myeloperoxidase-Mediated Loss of Function. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2008, 28, 2063–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.Q.; Wu, Z.; Brubaker, G.; Zheng, L.; Settle, M.; Gross, E.; Kinter, M.; Hazen, S.L.; Smith, J.D. Tyrosine Modification Is Not Required for Myeloperoxidase-Induced Loss of Apolipoprotein A-I Functional Activities. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 33775–33784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.J.; Yin, K.; Fu, Y.C.; Tang, C.K. The Interaction of Apoa-I and Abca1 Triggers Signal Transduction Pathways to Mediate Efflux of Cellular Lipids. Mol. Med. 2012, 18, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, X.; Huang, Y.; Levison, B.S.; Gerstenecker, G.; Didonato, A.J.; Hazen, L.B.; Lee, J.; Gogonea, V.; Didonato, J.A.; Hazen, S.L. Identification of Critical Paraoxonase 1 Residues Involved in High Density Lipoprotein Interaction. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 1890–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedrick, C.C.; Hassan, K.; Hough, G.P.; Yoo, J.H.; Simzar, S.; Quinto, C.R.; Kim, S.M.; Dooley, A.; Langi, S.; Hama, S.Y.; et al. Short-Term Feeding of Atherogenic Diet to Mice Results in Reduction of Hdl and Paraoxonase That May Be Mediated by An Immune Mechanism. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2000, 20, 1946–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, Y.S.; Lee, J.H.; Choi, S.H.; Kim, S.; Almazan, F.; Witztum, J.L.; Miller, Y.I. Macrophages Generate Reactive Oxygen Species in Response to Minimally Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein: Toll-Like Receptor 4- and Spleen Tyrosine Kinase-Dependent Activation of Nadph Oxidase 2. Circ. Res. 2009, 104, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lara-Guzman, O.J.; Gil-Izquierdo, A.; Medina, S.; Osorio, E.; Alvarez-Quintero, R.; Zuluaga, N.; Oger, C.; Galano, J.M.; Durand, T.; Munoz-Durango, K. Oxidized Ldl Triggers Changes in Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Biomarkers in Human Macrophages. Redox Biol. 2018, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Brennan, M.L.; Fu, X.; Aviles, R.J.; Pearce, G.L.; Penn, M.S.; Topol, E.J.; Sprecher, D.L.; Hazen, S.L. Association between Myeloperoxidase Levels and Risk of Coronary Artery Disease. JAMA 2001, 286, 2136–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholls, S.J.; Hazen, S.L. Myeloperoxidase, Modified Lipoproteins, and Atherogenesis. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, S346–S351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daugherty, A.; Dunn, J.L.; Rateri, D.L.; Heinecke, J.W. Myeloperoxidase, A Catalyst for Lipoprotein Oxidation, is Expressed in Human Atherosclerotic Lesions. J. Clin. Investig. 1994, 94, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsche, G.; Furtmuller, P.G.; Obinger, C.; Sattler, W.; Malle, E. Hypochlorite-Modified High-Density Lipoprotein Acts as a Sink for Myeloperoxidase In Vitro. Cardiovasc. Res. 2008, 79, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zeng, L.; Mathew, A.V.; Byun, J.; Atkins, K.B.; Brosius, F.C., 3rd; Pennathur, S. Myeloperoxidase-Derived Oxidants Damage Artery Wall Proteins in An Animal Model of Chronic Kidney Disease-Accelerated Atherosclerosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 7238–7249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, G.A.; Knopp, R.H.; Oram, J.F. Defective Removal of Cellular Cholesterol and Phospholipids by Apolipoprotein A-I in Tangier Disease. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 96, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuhira, K.; Tsujita, M.; Yamauchi, Y.; Abe-Dohmae, S.; Kato, K.; Handa, T.; Yokoyama, S. Potential Involvement of Dissociated Apoa-I in the Abca1-Dependent Cellular Lipid Release by Hdl. J. Lipid Res. 2004, 45, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Settle, M.; Brubaker, G.; Schmitt, D.; Hazen, S.L.; Smith, J.D.; Kinter, M. Localization of Nitration And Chlorination Sites on Apolipoprotein A-I Catalyzed by Myeloperoxidase in Human Atheroma and Associated Oxidative Impairment in Abca1-Dependent Cholesterol Efflux from Macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.; Liu, Y.; Kessler, P.S.; Vaughan, A.M.; Oram, J.F. The Macrophage Cholesterol Exporter Abca1 Functions as an Anti-Inflammatory Receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 32336–32343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, A.M.; Tsuchida, Y.; Nowak, K.L.; Sarkar, S.; Chonchol, M.; Whitfield, V.; Salas, N.; Dikalova, A.; Yancey, P.G.; Huang, J.; et al. Il-1 Inhibition And Function of the Hdl-Containing Fraction of Plasma in Patients with Stages 3 to 5 Ckd. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2019, 14, 702–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganjali, S.; Momtazi, A.A.; Banach, M.; Kovanen, P.T.; Stein, E.A.; Sahebkar, A. Hdl Abnormalities in Familial Hypercholesterolemia: Focus on Biological Functions. Prog. Lipid Res. 2017, 67, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wang, D.; Huang, L.H.; Huang, H. Roles of Reconstituted High-Density Lipoprotein Nanoparticles in Cardiovascular Disease: A New Paradigm for Drug Discovery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Huang, J.; Gui, T.; Yang, Y.; Feng, T.; Tzvetkov, N.T.; Xu, T.; Gai, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, J.; et al. Sr-Bi as A Target of Natural Products and Its Significance in Cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madu, H.; Avance, J.; Chetyrkin, S.; Darris, C.; Rose Kl Sanchez, O.A.; Hudson, B.; Voziyan, P. Pyridoxamine Protects Proteins from Damage by Hypohalous Acids In Vitro and In Vivo. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 89, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoff, H.F.; O’neil, J. Structural and Functional Changes in Ldl after Modification with Both 4-Hydroxynonenal and Malondialdehyde. J. Lipid Res. 1993, 34, 1209–1217. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hoppe, G.; Subbanagounder, G.; O’neil, J.; Salomon, R.G.; Hoff, H.F. Macrophage Recognition of Ldl Modified by Levuglandin E2, An Oxidation Product of Arachidonic Acid. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1997, 1344, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, J.; Yancey, P.G.; Tao, H.; Borja, M.S.; Smith, L.E.; Kon, V.; Davies, S.S.; Linton, M.F. Reactive Dicarbonyl Scavenging Effectively Reduces MPO-Mediated Oxidation of HDL and Restores PON1 Activity. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1937. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12071937
Huang J, Yancey PG, Tao H, Borja MS, Smith LE, Kon V, Davies SS, Linton MF. Reactive Dicarbonyl Scavenging Effectively Reduces MPO-Mediated Oxidation of HDL and Restores PON1 Activity. Nutrients. 2020; 12(7):1937. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12071937
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Jiansheng, Patricia G. Yancey, Huan Tao, Mark S. Borja, Loren E. Smith, Valentina Kon, Sean S. Davies, and MacRae F. Linton. 2020. "Reactive Dicarbonyl Scavenging Effectively Reduces MPO-Mediated Oxidation of HDL and Restores PON1 Activity" Nutrients 12, no. 7: 1937. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12071937
APA StyleHuang, J., Yancey, P. G., Tao, H., Borja, M. S., Smith, L. E., Kon, V., Davies, S. S., & Linton, M. F. (2020). Reactive Dicarbonyl Scavenging Effectively Reduces MPO-Mediated Oxidation of HDL and Restores PON1 Activity. Nutrients, 12(7), 1937. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12071937





