Vitamin D Status of Mice Deficient in Scavenger Receptor Class B Type 1, Cluster Determinant 36 and ATP-Binding Cassette Proteins G5/G8
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Feeding
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Analysis of Cholesterol and Triglycerides
2.4. Analysis of Transaminases
2.5. Analysis of 7-Dehydrocholesterol and Vitamin D Metabolites
2.6. Analysis of Relative mRNA Abundance
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Body Weight, Lipids and Serum Transaminases
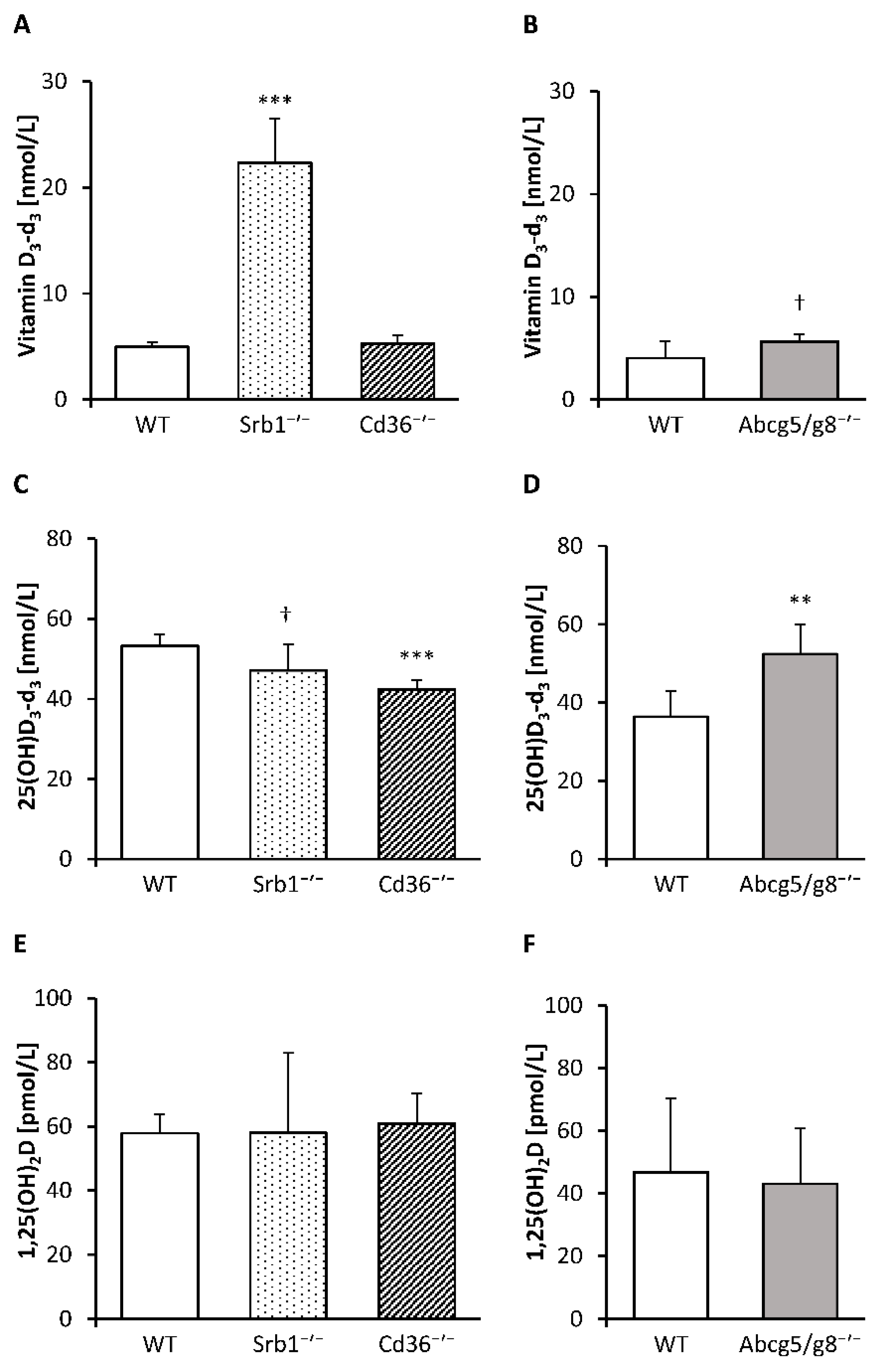
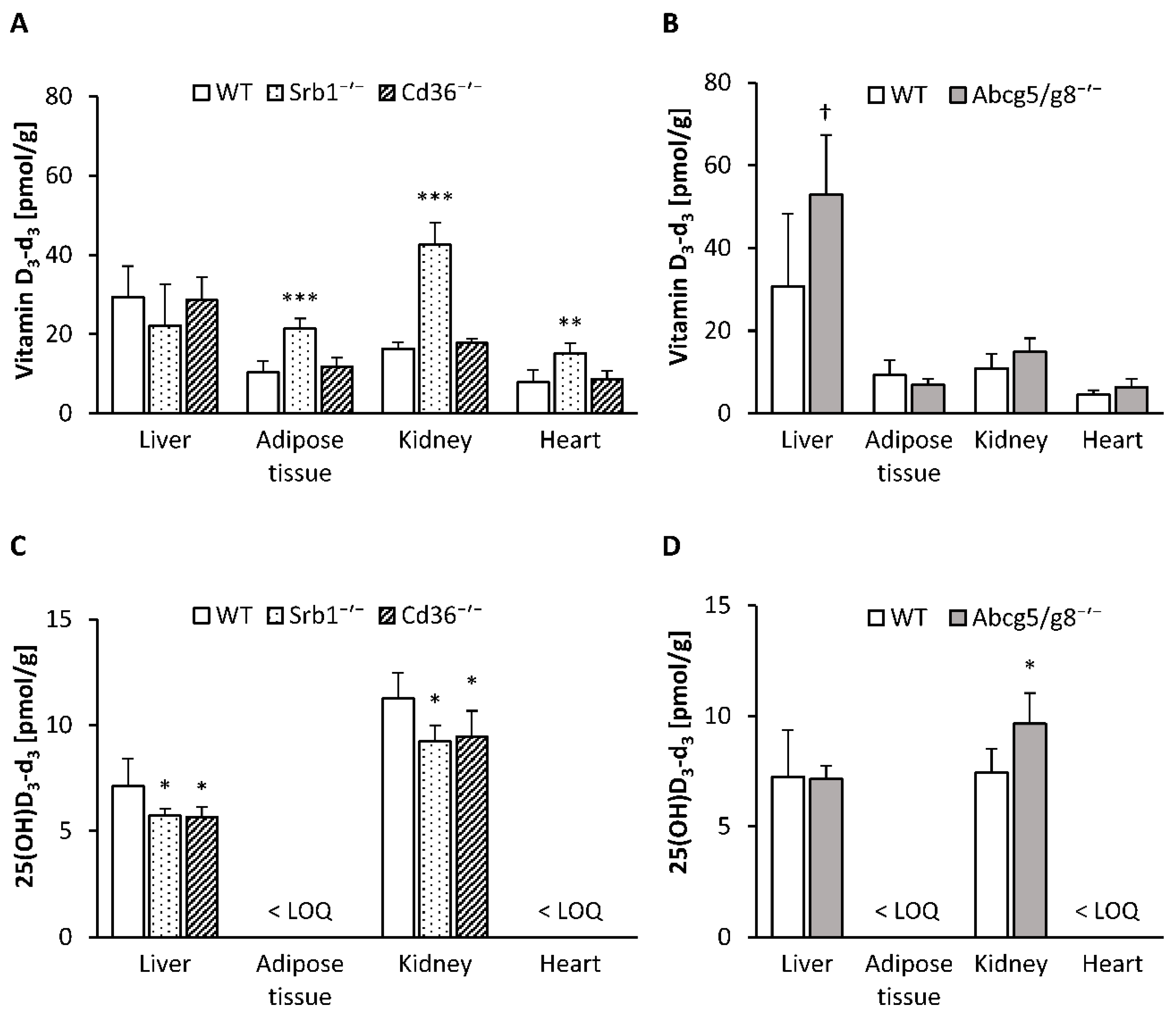
3.2. Concentrations of Deuterium-Labeled Vitamin D3 in Serum and Tissues
3.3. Serum and Tissue Levels of Hydroxylated Vitamin D3 Metabolites and mRNA Abundance of Hepatic and Renal Hydroxylases
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- European Food Safety Authority Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies. Scientific opinion on dietary reference values for vitamin D. EFSA J. 2016, 14, e04547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, A.C.; Manson, J.E.; Abrams, S.A.; Aloia, J.F.; Brannon, P.M.; Clinton, S.K.; Durazo-Arvizu, R.A.; Gallagher, J.C.; Gallo, R.L.; Jones, G.; et al. The 2011 report on dietary reference intakes for calcium and vitamin D from the Institute of Medicine: What clinicians need to know. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization/Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Vitamin and Mineral Requirements in Human Nutrition: Report of A Joint FAO/WHO Expert Consultation, Bangkok, Thailand, 21–30 September 1998, 2nd ed.; WHO/FAO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004; ISBN 92-4-154612-3. [Google Scholar]
- D-A-CH (Deutsche Gesellschaft für Ernährung (DGE); Österreichische Gesellschaft für Ernährung (ÖGE); Schweizerische Gesellschaft für Ernährung (SGE)). D-A-CH-Referenzwerte Für. Die. Nährstoffzufuhr, 2. Auflage, 4. Aktualisierte Ausgabe; DGE, ÖGE, SGE: Bonn, Germany, 2018; ISBN 978-3-88749-261-8. [Google Scholar]
- Nordic Council of Ministers. Nordic Nutrition Recommendations 2012. Integrating Nutrition and Physical Activity; Nordic Council of Ministers: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2014; ISBN 978-92-893-2670-4. [Google Scholar]
- Reboul, E.; Goncalves, A.; Comera, C.; Bott, R.; Nowicki, M.; Landrier, J.-F.; Jourdheuil-Rahmani, D.; Dufour, C.; Collet, X.; Borel, P. Vitamin D intestinal absorption is not a simple passive diffusion: Evidences for involvement of cholesterol transporters. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2011, 55, 691–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiourtzidis, M.; Kühn, J.; Schutkowski, A.; Baur, A.C.; Hirche, F.; Stangl, G.I. Inhibition of Niemann-Pick C1-like protein 1 by ezetimibe reduces uptake of deuterium-labeled vitamin D in mice. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2020, 197, 105504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.-J.; Azhar, S.; Kraemer, F.B. SR-B1: A unique multifunctional receptor for cholesterol influx and efflux. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2018, 80, 95–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reboul, E.; Klein, A.; Bietrix, F.; Gleize, B.; Malezet-Desmoulins, C.; Schneider, M.; Margotat, A.; Lagrost, L.; Collet, X.; Borel, P. Scavenger receptor class B type I (SR-BI) is involved in vitamin E transport across the enterocyte. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 4739–4745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- During, A.; Dawson, H.D.; Harrison, E.H. Carotenoid transport is decreased and expression of the lipid transporters SR-BI, NPC1L1, and ABCA1 is downregulated in Caco-2 cells treated with ezetimibe. J. Nutr. 2005, 135, 2305–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saddar, S.; Carriere, V.; Lee, W.-R.; Tanigaki, K.; Yuhanna, I.S.; Parathath, S.; Morel, E.; Warrier, M.; Sawyer, J.K.; Gerard, R.D.; et al. Scavenger receptor class B type I is a plasma membrane cholesterol sensor. Circ. Res. 2013, 112, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Yang, Y.; Braunstein, E.; Georgeson, K.E.; Harmon, C.M. Gut expression and regulation of FAT/CD36: Possible role in fatty acid transport in rat enterocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 281, E916–E923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habets, D.D.J.; Coumans, W.A.; Voshol, P.J.; den Boer, M.A.M.; Febbraio, M.; Bonen, A.; Glatz, J.F.C.; Luiken, J.J.F.P. AMPK-mediated increase in myocardial long-chain fatty acid uptake critically depends on sarcolemmal CD36. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 355, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abumrad, N.A.; Goldberg, I.J. CD36 actions in the heart: Lipids, calcium, inflammation, repair and more? Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1861, 1442–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klett, E.L.; Lee, M.-H.; Adams, D.B.; Chavin, K.D.; Patel, S.B. Localization of ABCG5 and ABCG8 proteins in human liver, gall bladder and intestine. BMC Gastroenterol. 2004, 4, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zein, A.A.; Kaur, R.; Hussein, T.O.K.; Graf, G.A.; Lee, J.-Y. ABCG5/G8: A structural view to pathophysiology of the hepatobiliary cholesterol secretion. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2019, 47, 1259–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, G.A.; Yu, L.; Li, W.-P.; Gerard, R.; Tuma, P.L.; Cohen, J.C.; Hobbs, H.H. ABCG5 and ABCG8 are obligate heterodimers for protein trafficking and biliary cholesterol excretion. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 48275–48282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Li-Hawkins, J.; Hammer, R.E.; Berge, K.E.; Horton, J.D.; Cohen, J.C.; Hobbs, H.H. Overexpression of ABCG5 and ABCG8 promotes biliary cholesterol secretion and reduces fractional absorption of dietary cholesterol. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 110, 671–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brufau, G.; Kuipers, F.; Lin, Y.; Trautwein, E.A.; Groen, A.K. A reappraisal of the mechanism by which plant sterols promote neutral sterol loss in mice. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, A.; Gleize, B.; Bott, R.; Nowicki, M.; Amiot, M.-J.; Lairon, D.; Borel, P.; Reboul, E. Phytosterols can impair vitamin D intestinal absorption in vitro and in mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2011, 55 (Suppl. S2), S303–S311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katan, M.B.; Grundy, S.M.; Jones, P.; Law, M.; Miettinen, T.; Paoletti, R. Efficacy and safety of plant stanols and sterols in the management of blood cholesterol levels. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2003, 78, 965–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acton, S.; Osgood, D.; Donoghue, M.; Corella, D.; Pocovi, M.; Cenarro, A.; Mozas, P.; Keilty, J.; Squazzo, S.; Woolf, E.A.; et al. Association of polymorphisms at the SR-BI gene locus with plasma lipid levels and body mass index in a white population. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1999, 19, 1734–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudkowska, I.; Jones, P.J.H. Polymorphisms in ABCG5/G8 transporters linked to hypercholesterolemia and gallstone disease. Nutr. Rev. 2008, 66, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morii, T.; Ohno, Y.; Kato, N.; Hirose, H.; Kawabe, H.; Hirao, K.; Eguchi, T.; Maruyama, T.; Hayashi, M.; Saito, I.; et al. CD36 single nucleotide polymorphism is associated with variation in low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol in young Japanese men. Biomarkers 2009, 14, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Research Council. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, 8th ed.; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; ISBN 0-309-15401-4. [Google Scholar]
- Rigotti, A.; Trigatti, B.L.; Penman, M.; Rayburn, H.; Herz, J.; Krieger, M. A targeted mutation in the murine gene encoding the high-density lipoprotein (HDL) receptor scavenger receptor class B type I reveals its key role in HDL metabolism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 12610–12615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Research Council. Nutrient Requirements of Laboratory Animals, 4th ed.; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1995; ISBN 0-309-05126-6. [Google Scholar]
- Hara, A.; Radin, N.S. Lipid extraction of tissues with a low-toxicity solvent. Anal. Biochem. 1978, 90, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutkowski, A.; Wege, N.; Stangl, G.I.; König, B. Tissue-specific expression of monocarboxylate transporters during fasting in mice. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfaffl, M.W. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varban, M.L.; Rinninger, F.; Wang, N.; Fairchild-Huntress, V.; Dunmore, J.H.; Fang, Q.; Gosselin, M.L.; Dixon, K.L.; Deeds, J.D.; Acton, S.L.; et al. Targeted mutation reveals a central role for SR-BI in hepatic selective uptake of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 4619–4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krieger, M. The “best” of cholesterols, the “worst” of cholesterols: A tale of two receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 4077–4080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, A.V.; Sharpe, L.J.; Brown, A.J. The sterol-based transcriptional control of human 7-dehydrocholesterol reductase (DHCR7): Evidence of a cooperative regulatory program in cholesterol synthesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1841, 1431–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpe, L.J.; Burns, V.; Brown, A.J. A lipidomic perspective on intermediates in cholesterol synthesis as indicators of disease status. J. Genet. Genomics 2014, 41, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Febbraio, M.; Silverstein, R.L. CD36: Implications in cardiovascular disease. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2007, 39, 2012–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazen, S.L. Oxidized phospholipids as endogenous pattern recognition ligands in innate immunity. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 15527–15531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajri, T.; Abumrad, N.A. Fatty acid transport across membranes: Relevance to nutrition and metabolic pathology. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2002, 22, 383–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brundert, M.; Heeren, J.; Merkel, M.; Carambia, A.; Herkel, J.; Groitl, P.; Dobner, T.; Ramakrishnan, R.; Moore, K.J.; Rinninger, F. Scavenger receptor CD36 mediates uptake of high-density lipoproteins in mice and by cultured cells. J. Lipid Res. 2011, 52, 745–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Cifarelli, V.; Pietka, T.; Newberry, E.P.; Kennedy, S.M.; Khalifeh-Soltani, A.; Clugston, R.; Atabai, K.; Abumrad, N.A.; Davidson, N.O. Cd36 knockout mice are protected against lithogenic diet-induced gallstones. J. Lipid Res. 2017, 58, 1692–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nauli, A.M.; Nassir, F.; Zheng, S.; Yang, Q.; Lo, C.-M.; Vonlehmden, S.B.; Lee, D.; Jandacek, R.J.; Abumrad, N.A.; Tso, P. CD36 is important for chylomicron formation and secretion and may mediate cholesterol uptake in the proximal intestine. Gastroenterology 2006, 131, 1197–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pepino, M.Y.; Kuda, O.; Samovski, D.; Abumrad, N.A. Structure-function of CD36 and importance of fatty acid signal transduction in fat metabolism. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2014, 34, 281–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassir, F.; Adewole, O.L.; Brunt, E.M.; Abumrad, N.A. CD36 deletion reduces VLDL secretion, modulates liver prostaglandins, and exacerbates hepatic steatosis in ob/ob mice. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 2988–2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speeckaert, M.M.; Taes, Y.E.; Buyzere, M.L.; de Christophe, A.B.; Kaufman, J.-M.; Delanghe, J.R. Investigation of the potential association of vitamin D binding protein with lipoproteins. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2010, 47, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Shen, Z.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, P.; Zeng, H.; Yu, M.; Chen, X.; Ning, L.; et al. Vitamin D receptor targets hepatocyte nuclear factor 4α and mediates protective effects of vitamin D in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 3891–3905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.E.; Basso, F.; Shamburek, R.D.; Amar, M.J.A.; Vaisman, B.; Szakacs, G.; Joyce, C.; Tansey, T.; Freeman, L.; Paigen, B.J.; et al. Hepatic ABCG5 and ABCG8 overexpression increases hepatobiliary sterol transport but does not alter aortic atherosclerosis in transgenic mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 22913–22925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.-C.; Shin, S.-J.; Kuo, K.-K.; Lin, K.-D.; Yu, M.-L.; Hsiao, P.-J. Significant association of ABCG8:D19H gene polymorphism with hypercholesterolemia and insulin resistance. J. Hum. Genet. 2008, 53, 757–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Acalovschi, M.; Ciocan, A.; Mostean, O.; Tirziu, S.; Chiorean, E.; Keppeler, H.; Schirin-Sokhan, R.; Lammert, F. Are plasma lipid levels related to ABCG5/ABCG8 polymorphisms? A preliminary study in siblings with gallstones. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2006, 17, 490–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDaniel, A.L.; Alger, H.M.; Sawyer, J.K.; Kelley, K.L.; Kock, N.D.; Brown, J.M.; Temel, R.E.; Rudel, L.L. Phytosterol feeding causes toxicity in ABCG5/G8 knockout mice. Am. J. Pathol. 2013, 182, 1131–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dikkers, A.; Freak de Boer, J.; Annema, W.; Groen, A.K.; Tietge, U.J.F. Scavenger receptor BI and ABCG5/G8 differentially impact biliary sterol secretion and reverse cholesterol transport in mice. Hepatology 2013, 58, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ståhlberg, N.; Rico-Bautista, E.; Fisher, R.M.; Wu, X.; Cheung, L.; Flores-Morales, A.; Tybring, G.; Norstedt, G.; Tollet-Egnell, P. Female-predominant expression of fatty acid translocase/CD36 in rat and human liver. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 1972–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| WT | Srb1-/- | Cd36-/- | WT vs. Srb1-/- p Value | WT vs. Cd36-/- p Value | WT | Abcg5/g8-/- | WT vs. Abcg5/g8-/- p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Food intake (g/d) | 2.4 ± 0.0 | 2.2 ± 0.2 | 2.4 ± 0.0 | 0.018 | 0.549 | 2.4 ± 0.0 | 2.4 ± 0.0 | 0.186 |
| Body weight gain (g) | 4.8 ± 1.5 | 3.1 ± 1.1 | 3.9 ± 0.9 | 0.073 | 0.264 | 3.2 ± 1.1 | 4.1 ± 1.3 | 0.287 |
| Final body weight (g) * | 26.6 ± 1.6 | 24.0 ± 1.9 | 26.8 ± 1.8 | 0.043 | 0.869 | 28.6 ± 2.6 | 28.3 ± 1.8 | 0.808 |
| Serum | ||||||||
| Triglycerides (mmol/L) | 0.92 ± 0.06 | 1.34 ± 0.25 | 0.73 ± 0.06 | 0.005 | 0.001 | 0.88 ± 0.30 | 2.20 ± 0.38 | <0.001 |
| Cholesterol (mmol/L) | 3.67 ± 0.51 | 10.73 ± 0.99 | 4.85 ± 0.46 | <0.001 | 0.004 | 3.37 ± 1.30 | 6.02 ± 0.58 | 0.001 |
| 7-DHC (nmol/L) | 136 ± 12 | 973 ± 250 | 180 ± 25 | <0.001 | 0.005 | 174 ± 54 | 236 ± 19 | 0.041 |
| ASAT (U/L) | 222 ± 41 | 232 ± 49 | 217 ± 77 | 0.734 | 0.900 | 283 ± 30 | 226 ± 99 | 0.222 |
| ALAT (U/L) | 28.7 ± 6.8 | 40.5 ± 14.1 | 35.6 ± 9.7 | 0.120 | 0.222 | 37.8 ± 14.6 | 46.0 ± 6.3 | 0.516 |
| Liver | ||||||||
| Absolute weight (g) | 0.91 ± 0.05 | 0.83 ± 0.08 | 1.04 ± 0.13 | 0.078 | 0.051 | 0.87 ± 0.18 | 1.23 ± 0.11 | 0.003 |
| Relative weight (g/100 g body weight) | 4.06 ± 0.41 | 3.85 ± 0.23 | 4.40 ± 0.39 | 0.339 | 0.210 | 3.16 ± 0.49 | 4.83 ± 0.46 | <0.001 |
| Triglycerides (mg/g) | 60.8 ± 12.1 | 65.2 ± 44.9 | 91.9 ± 36.7 | 0.837 | 0.102 | 140.4 ± 60.9 | 128.9 ± 41.1 | 0.730 |
| Cholesterol (mg/g) | 3.79 ± 0.54 | 3.63 ± 0.83 | 2.89 ± 0.47 | 0.737 | 0.027 | 4.76 ± 1.27 | 3.38 ± 0.85 | 0.067 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kiourtzidis, M.; Kühn, J.; Brandsch, C.; Stangl, G.I. Vitamin D Status of Mice Deficient in Scavenger Receptor Class B Type 1, Cluster Determinant 36 and ATP-Binding Cassette Proteins G5/G8. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2169. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12082169
Kiourtzidis M, Kühn J, Brandsch C, Stangl GI. Vitamin D Status of Mice Deficient in Scavenger Receptor Class B Type 1, Cluster Determinant 36 and ATP-Binding Cassette Proteins G5/G8. Nutrients. 2020; 12(8):2169. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12082169
Chicago/Turabian StyleKiourtzidis, Mikis, Julia Kühn, Corinna Brandsch, and Gabriele I. Stangl. 2020. "Vitamin D Status of Mice Deficient in Scavenger Receptor Class B Type 1, Cluster Determinant 36 and ATP-Binding Cassette Proteins G5/G8" Nutrients 12, no. 8: 2169. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12082169
APA StyleKiourtzidis, M., Kühn, J., Brandsch, C., & Stangl, G. I. (2020). Vitamin D Status of Mice Deficient in Scavenger Receptor Class B Type 1, Cluster Determinant 36 and ATP-Binding Cassette Proteins G5/G8. Nutrients, 12(8), 2169. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12082169





