Interleukin-6 Gene Expression Changes after a 4-Week Intake of a Multispecies Probiotic in Major Depressive Disorder—Preliminary Results of the PROVIT Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Demographics and Scales of PROVIT
2.3. Probiotic Intervention
2.4. Gene Expression Methods
2.5. Statistics
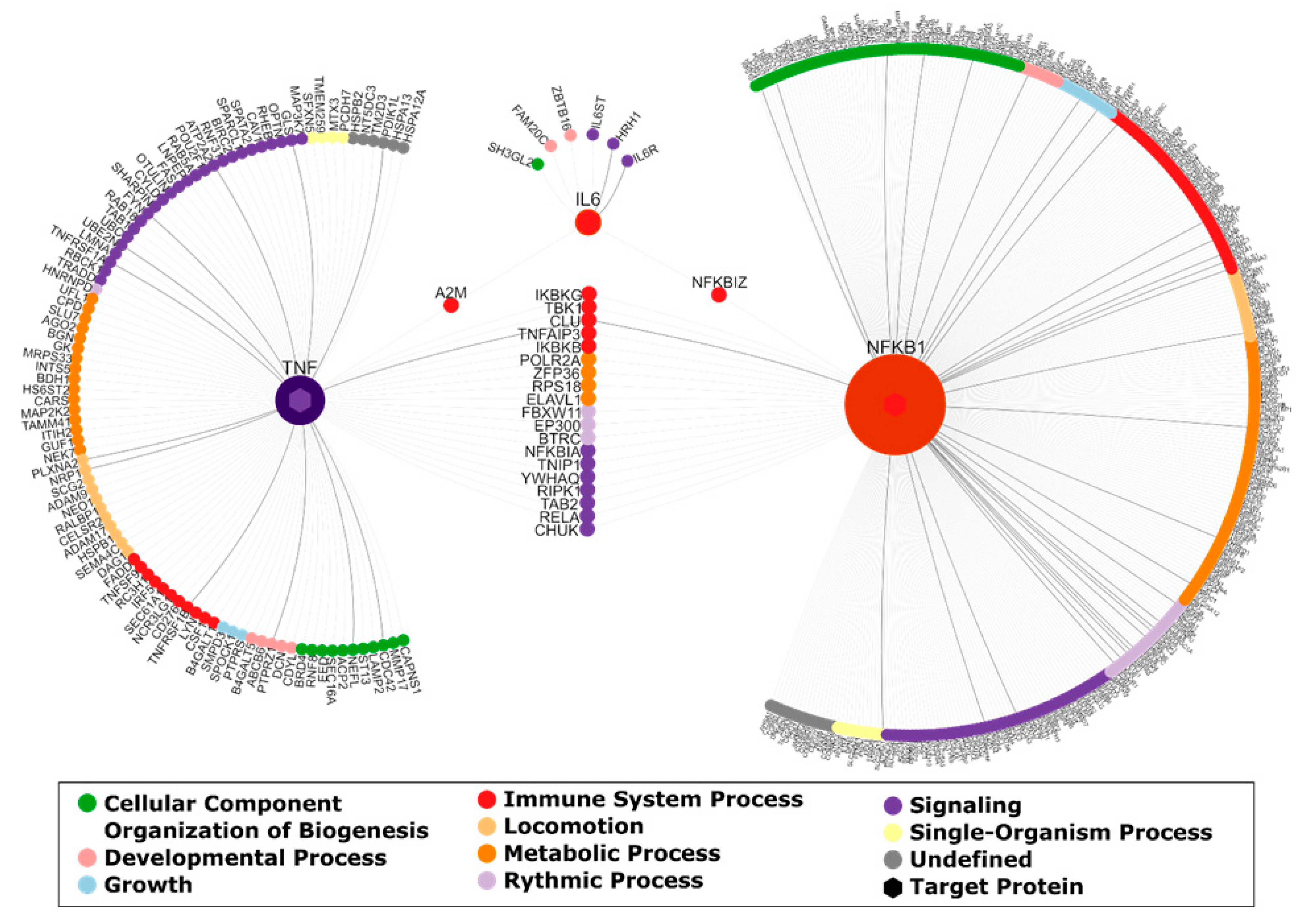
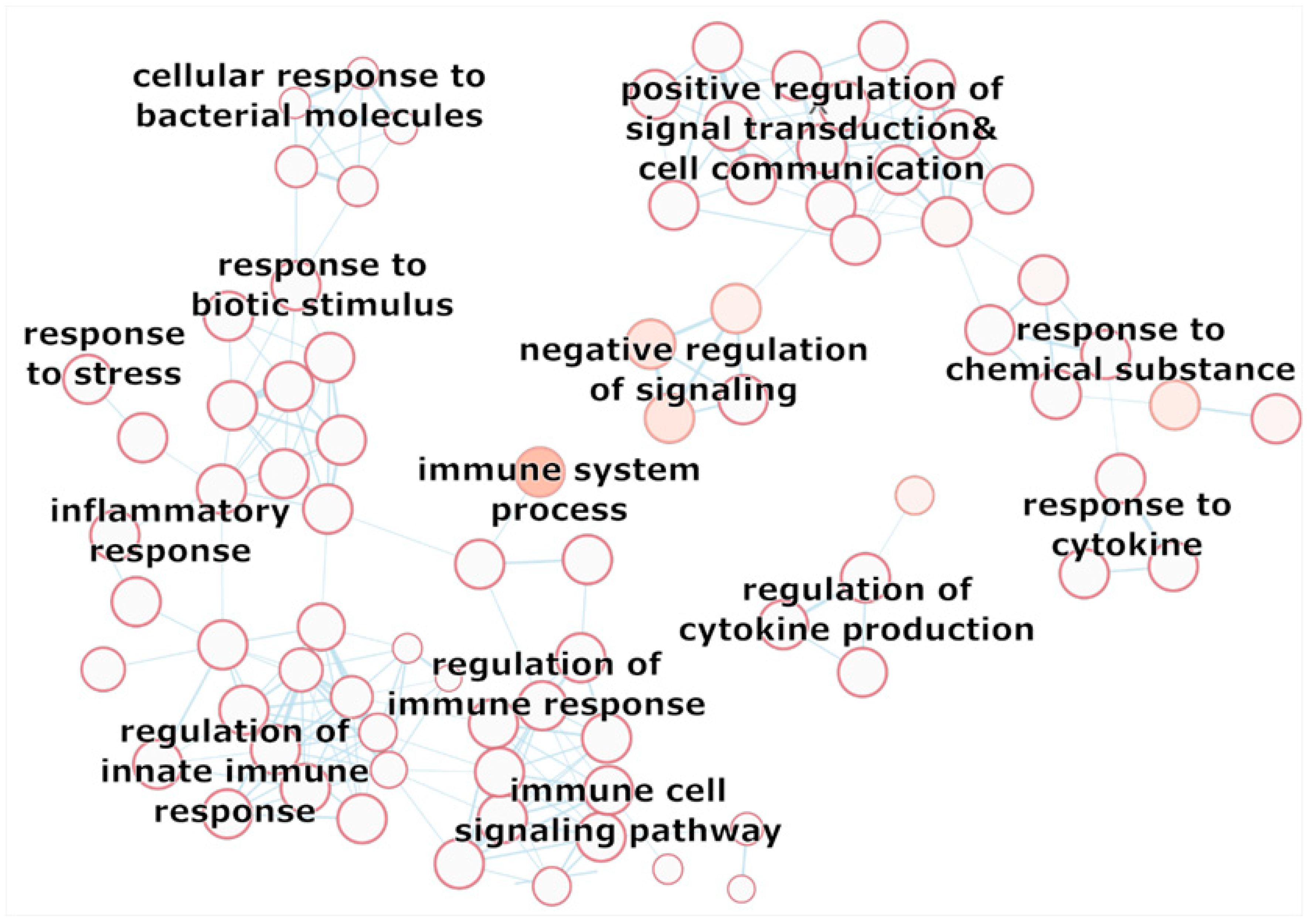
2.6. Network Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Statistics
3.2. Gene Expression
3.3. Network Analysis Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Harter, M.; Klesse, C.; Bermejo, I.; Schneider, F.; Berger, M. Unipolar Depression: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Recommendations from the Current S3/National Clinical Practice Guideline. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2010, 107, 700–708. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Depression and Other Common Mental Disorders: Global Health Estimates (No. WHO/MSD/MER/2017.2); World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kasper, S.; Bach, M.; Bartova, L.; Dold, M.; Frey, R.; Geretsegger, C.; Haring, C.; Hausmann, A.; Jelem, H.; Kapfhammer, H.-P.; et al. Therapieresistente Depression; ÖGPB: Wien, Austria, 2017; Konsensus-Statement—State of the Art 2017. CliniCum neuropsy, volume November 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kapusta, N. Available online: http://www.Suizidforschung.at/statistik_suizide_oesterreich.Pdf (accessed on 20 March 2020).
- DGPPN. S3-Leitlinie/Nationale VersorgungsLeitlinie Unipolare Depression Langfassung; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; Volume 2019, p. 264. [Google Scholar]
- Pantazatos, S.P.; Huang, Y.Y.; Rosoklija, G.B.; Dwork, A.J.; Arango, V.; Mann, J.J. Whole-Transcriptome Brain Expression and Exon-Usage Profiling in Major Depression and Suicide: Evidence for Altered Glial, Endothelial and ATPase Activity. Mol. Psychiatry 2017, 22, 760–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchida, S.; Yamagata, H.; Seki, T.; Watanabe, Y. Epigenetic Mechanisms of Major Depression: Targeting Neuronal Plasticity. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2018, 72, 212–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins-de-Souza, D. Proteomics, Metabolomics, and Protein Interactomics in the Characterization of the Molecular Features of Major Depressive Disorder. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2014, 16, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Wade, P.A. Crosstalk between the Microbiome and Epigenome: Messages from Bugs. J. Biochem. 2018, 163, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantzer, R.; O’Connor, J.C.; Freund, G.G.; Johnson, R.W.; Kelley, K.W. From Inflammation to Sickness and Depression: When the Immune System Subjugates the Brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2008, 9, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, C.N.; Bot, M.; Scheffer, P.G.; Cuijpers, P.; Penninx, B.W. Is Depression Associated with Increased Oxidative Stress? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2015, 51, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhong, S.; Liao, X.; Chen, J.; He, T.; Lai, S.; Jia, Y. A Meta-Analysis of Oxidative Stress Markers in Depression. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohler, C.A.; Freitas, T.H.; Maes, M.; de Andrade, N.Q.; Liu, C.S.; Fernandes, B.S.; Stubbs, B.; Solmi, M.; Veronese, N.; Herrmann, N.; et al. Peripheral Cytokine and Chemokine Alterations in Depression: A Meta-Analysis of 82 Studies. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2017, 135, 373–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangge, H.; Bengesser, S.; Dalkner, N.; Birner, A.; Fellendorf, F.; Platzer, M.; Queissner, R.; Pilz, R.; Maget, A.; Reininghaus, B.; et al. Weight Gain during Treatment of Bipolar Disorder (BD)-Facts and Therapeutic Options. Front. Nutr. 2019, 6, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soczynska, J.K.; Kennedy, S.H.; Woldeyohannes, H.O.; Liauw, S.S.; Alsuwaidan, M.; Yim, C.Y.; McIntyre, R.S. Mood Disorders and Obesity: Understanding Inflammation as a Pathophysiological Nexus. Neuromolecular Med. 2011, 13, 93–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Tanaka, T.; Narazaki, M.; Kishimoto, T. Targeting Interleukin-6 Signaling in Clinic. Immunity 2019, 50, 1007–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schett, G.; Elewaut, D.; McInnes, I.B.; Dayer, J.M.; Neurath, M.F. How Cytokine Networks Fuel Inflammation: Toward a Cytokine-Based Disease Taxonomy. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 822–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohleder, N.; Aringer, M.; Boentert, M. Role of Interleukin-6 in Stress, Sleep, and Fatigue. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2012, 1261, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, C.A.; Jones, S.A. IL-6 as a Keystone Cytokine in Health and Disease. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raison, C.L.; Capuron, L.; Miller, A.H. Cytokines Sing the Blues: Inflammation and the Pathogenesis of Depression. Trends Immunol. 2006, 27, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.M.; Stewart, R.; Kim, J.W.; Kang, H.J.; Bae, K.Y.; Kim, S.W.; Shin, I.S.; Yoon, J.S. Changes in Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Levels and Late-Life Depression: A Two Year Population Based Longitudinal Study. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2018, 90, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldsmith, D.R.; Rapaport, M.H.; Miller, B.J. A Meta-Analysis of Blood Cytokine Network Alterations in Psychiatric Patients: Comparisons between Schizophrenia, Bipolar Disorder and Depression. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 21, 1696–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passos, I.C.; Vasconcelos-Moreno, M.P.; Costa, L.G.; Kunz, M.; Brietzke, E.; Quevedo, J.; Salum, G.; Magalhaes, P.V.; Kapczinski, F.; Kauer-Sant’Anna, M. Inflammatory Markers in Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Meta-Regression. Lancet Psychiatry 2015, 2, 1002–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Xu, S.; Yuan, Z.; Shen, L. Weighted Gene Coexpression Network Analysis Identifies Specific Modules and Hub Genes Related to Major Depression. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2020, 16, 703–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbri, C.; Hosak, L.; Mossner, R.; Giegling, I.; Mandelli, L.; Bellivier, F.; Claes, S.; Collier, D.A.; Corrales, A.; Delisi, L.E.; et al. Consensus Paper of the WFSBP Task Force on Genetics: Genetics, Epigenetics and Gene Expression Markers of Major Depressive Disorder and Antidepressant Response. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2017, 18, 5–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, J.R. Intestinal Mucosal Barrier Function in Health and Disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 799–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasano, A.; Not, T.; Wang, W.; Uzzau, S.; Berti, I.; Tommasini, A.; Goldblum, S.E. Zonulin, a Newly Discovered Modulator of Intestinal Permeability, and its Expression in Coeliac Disease. Lancet 2000, 355, 1518–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturgeon, C.; Fasano, A. Zonulin, a Regulator of Epithelial and Endothelial Barrier Functions, and its Involvement in Chronic Inflammatory Diseases. Tissue Barriers 2016, 4, e1251384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohlsson, L.; Gustafsson, A.; Lavant, E.; Suneson, K.; Brundin, L.; Westrin, A.; Ljunggren, L.; Lindqvist, D. Leaky Gut Biomarkers in Depression and Suicidal Behavior. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2019, 139, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morkl, S.; Lackner, S.; Meinitzer, A.; Mangge, H.; Lehofer, M.; Halwachs, B.; Gorkiewicz, G.; Kashofer, K.; Painold, A.; Holl, A.K.; et al. Gut Microbiota, Dietary Intakes and Intestinal Permeability Reflected by Serum Zonulin in Women. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 57, 2985–2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, J.R.; Kennedy, P.J.; Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T.G.; Clarke, G.; Hyland, N.P. Breaking Down the Barriers: The Gut Microbiome, Intestinal Permeability and Stress-Related Psychiatric Disorders. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseribafrouei, A.; Hestad, K.; Avershina, E.; Sekelja, M.; Linlokken, A.; Wilson, R.; Rudi, K. Correlation between the Human Fecal Microbiota and Depression. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2014, 26, 1155–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Ling, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Mao, H.; Ma, Z.; Yin, Y.; Wang, W.; Tang, W.; Tan, Z.; Shi, J.; et al. Altered Fecal Microbiota Composition in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder. Brain Behav. Immun. 2015, 48, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, P.; Zeng, B.; Zhou, C.; Liu, M.; Fang, Z.; Xu, X.; Zeng, L.; Chen, J.; Fan, S.; Du, X.; et al. Gut Microbiome Remodeling Induces Depressive-Like Behaviors through a Pathway Mediated by the Host’s Metabolism. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 21, 786–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Ding, B.; Feng, C.; Yin, S.; Zhang, T.; Qi, X.; Lv, H.; Guo, X.; Dong, K.; Zhu, Y.; et al. Prevotella and Klebsiella Proportions in Fecal Microbial Communities are Potential Characteristic Parameters for Patients with Major Depressive Disorder. J. Affect. Disord. 2017, 207, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchesi, J.R.; Ravel, J. The Vocabulary of Microbiome Research: A Proposal. Microbiome 2015, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valles-Colomer, M.; Falony, G.; Darzi, Y.; Tigchelaar, E.F.; Wang, J.; Tito, R.Y.; Schiweck, C.; Kurilshikov, A.; Joossens, M.; Wijmenga, C.; et al. The Neuroactive Potential of the Human Gut Microbiota in Quality of Life and Depression. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAO/WHO Working Group. Guidelines for the Evaluation of Probiotics in Food; FAO/WHO: London, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Merenstein, D.J.; Pot, B.; Morelli, L.; Canani, R.B.; Flint, H.J.; Salminen, S.; et al. Expert Consensus Document: The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics Consensus Statement on the Scope and Appropriate use of the Term Probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, B.; Delgado, S.; Blanco-Miguez, A.; Lourenco, A.; Gueimonde, M.; Margolles, A. Probiotics, Gut Microbiota, and their Influence on Host Health and Disease. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borzabadi, S.; Oryan, S.; Eidi, A.; Aghadavod, E.; Daneshvar Kakhaki, R.; Tamtaji, O.R.; Taghizadeh, M.; Asemi, Z. The Effects of Probiotic Supplementation on Gene Expression Related to Inflammation, Insulin and Lipid in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease: A Randomized, Double-Blind, PlaceboControlled Trial. Arch. Iran. Med. 2018, 21, 289–295. [Google Scholar]
- Citar, M.; Hacin, B.; Tompa, G.; Stempelj, M.; Rogelj, I.; Dolinsek, J.; Narat, M.; Matijasic, B.B. Human Intestinal Mucosa-Associated Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium Strains with Probiotic Properties Modulate IL-10, IL-6 and IL-12 Gene Expression in THP-1 Cells. Benef. Microbes 2015, 6, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamtaji, O.R.; Kouchaki, E.; Salami, M.; Aghadavod, E.; Akbari, E.; Tajabadi-Ebrahimi, M.; Asemi, Z. The Effects of Probiotic Supplementation on Gene Expression Related to Inflammation, Insulin, and Lipids in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2017, 36, 660–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milajerdi, A.; Mousavi, S.M.; Sadeghi, A.; Salari-Moghaddam, A.; Parohan, M.; Larijani, B.; Esmaillzadeh, A. The Effect of Probiotics on Inflammatory Biomarkers: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. Eur. J. Nutr. 2020, 59, 633–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenbergen, L.; Sellaro, R.; van Hemert, S.; Bosch, J.A.; Colzato, L.S. A Randomized Controlled Trial to Test the Effect of Multispecies Probiotics on Cognitive Reactivity to Sad Mood. Brain Behav. Immun. 2015, 48, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messaoudi, M.; Violle, N.; Bisson, J.F.; Desor, D.; Javelot, H.; Rougeot, C. Beneficial Psychological Effects of a Probiotic Formulation (Lactobacillus Helveticus R0052 and Bifidobacterium Longum R0175) in Healthy Human Volunteers. Gut Microbes 2011, 2, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akkasheh, G.; Kashani-Poor, Z.; Tajabadi-Ebrahimi, M.; Jafari, P.; Akbari, H.; Taghizadeh, M.; Memarzadeh, M.R.; Asemi, Z.; Esmaillzadeh, A. Clinical and Metabolic Response to Probiotic Administration in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Nutrition 2016, 32, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rucklidge, J.J.; Eggleston, M.J.F.; Ealam, B.; Beaglehole, B.; Mulder, R.T. An Observational Preliminary Study on the Safety of Long-Term Consumption of Micronutrients for the Treatment of Psychiatric Symptoms. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2019, 25, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomasik, J.; Yolken, R.H.; Bahn, S.; Dickerson, F.B. Immunomodulatory Effects of Probiotic Supplementation in Schizophrenia Patients: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Biomark. Insights 2015, 10, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reininghaus, E.Z.; Wetzlmair, L.C.; Fellendorf, F.T.; Platzer, M.; Queissner, R.; Birner, A.; Pilz, R.; Hamm, C.; Maget, A.; Koidl, C.; et al. The Impact of Probiotic Supplements on Cognitive Parameters in Euthymic Individuals with Bipolar Disorder: A Pilot Study. Neuropsychobiology 2020, 79, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reininghaus, E.Z.; Wetzlmair, L.C.; Fellendorf, F.T.; Platzer, M.; Queissner, R.; Birner, A.; Pilz, R.; Hamm, C.; Maget, A.; Rieger, A.; et al. Probiotic Treatment in Individuals with Euthymic Bipolar Disorder: A Pilot-Study on Clinical Changes and Compliance. Neuropsychobiology 2020, 79, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reininghaus, E.; Platzer, M.; Kohlhammer-Dohr, A.; Hamm, C.; Mörkl, S.; Bengesser, S.; Fellendorf, F.; Lahousen, T.; Leitner-Afschar, B.; Schöggl, H.; et al. PROVIT: Supplementary Probiotic Treatment in Depression- a Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2020. in major revision. [Google Scholar]
- Moher, D.; Schulz, K.F.; Altman, D.G. The CONSORT Statement: Revised Recommendations for Improving the Quality of Reports of Parallel-Group Randomised Trials. Lancet 2001, 357, 1191–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheehan, D.V.; Lecrubier, Y.; Sheehan, K.H.; Amorim, P.; Janavs, J.; Weiller, E.; Hergueta, T.; Baker, R.; Dunbar, G.C. The Mini-International Neuropsychiatric Interview (M.I.N.I.): The Development and Validation of a Structured Diagnostic Psychiatric Interview for DSM-IV and ICD-10. J. Clin. Psychiatry 1998, 59 (Suppl. 20), 22–33; quiz 34–57. [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton, M. A Rating Scale for Depression. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry. 1960, 23, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhner, C.; Burger, C.; Keller, F.; Hautzinger, M. Reliability and Validity of the Revised Beck Depression Inventory (BDI-II). Results from German Samples. Nervenarzt 2007, 78, 651–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauschild, A.; Pastrello, C.; Kotlyar, M.; Jurisica, I. Protein–protein Interaction Data, their Quality, and Major Public Databases. In Analyzing Network Data in Biology and Medicine: An Interdisciplinary Textbook for Biological, Medical and Computational Scientists; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2019; p. 151. [Google Scholar]
- Kotlyar, M.; Pastrello, C.; Sheahan, N.; Jurisica, I. Integrated Interactions Database: Tissue-Specific View of the Human and Model Organism Interactomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D536–D541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, K.R.; Otasek, D.; Ali, M.; McGuffin, M.J.; Xie, W.; Devani, B.; Toch, I.L.; Jurisica, I. NAViGaTOR: Network Analysis, Visualization and Graphing Toronto. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 3327–3329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauschild, A.; Pastrello, C.; Rossos, A.; Jurisica, I. Visualization of Biomedical Networks. Anonymous 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimand, J.; Arak, T.; Vilo, J. G: Profiler—A Web Server for Functional Interpretation of Gene Lists (2011 Update). Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, W307–W315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimand, J.; Isserlin, R.; Voisin, V.; Kucera, M.; Tannus-Lopes, C.; Rostamianfar, A.; Wadi, L.; Meyer, M.; Wong, J.; Xu, C.; et al. Pathway Enrichment Analysis and Visualization of Omics Data using g:Profiler, GSEA, Cytoscape and EnrichmentMap. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 482–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A Software Environment for Integrated Models of Biomolecular Interaction Networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isserlin, R.; Merico, D.; Voisin, V.; Bader, G.D. Enrichment Map—A Cytoscape App to Visualize and Explore OMICs Pathway Enrichment Results. F1000Res 2014, 3, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadka, L.; Dziegiel, P.; Kulus, M.; Olajossy, M. Clinical Phenotype of Depression Affects Interleukin-6 Synthesis. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2017, 37, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamers, F.; Milaneschi, Y.; Smit, J.H.; Schoevers, R.A.; Wittenberg, G.; Penninx, B.W.J.H. Longitudinal Association between Depression and Inflammatory Markers: Results from the Netherlands Study of Depression and Anxiety. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 85, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabrizi, R.; Ostadmohammadi, V.; Lankarani, K.B.; Akbari, M.; Akbari, H.; Vakili, S.; Shokrpour, M.; Kolahdooz, F.; Rouhi, V.; Asemi, Z. The Effects of Probiotic and Synbiotic Supplementation on Inflammatory Markers among Patients with Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 852, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanada, K.; Nakajima, S.; Kurokawa, S.; Barcelo-Soler, A.; Ikuse, D.; Hirata, A.; Yoshizawa, A.; Tomizawa, Y.; Salas-Valero, M.; Noda, Y.; et al. Gut Microbiota and Major Depressive Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 266, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cussotto, S.; Clarke, G.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Psychotropics and the Microbiome: A Chamber of Secrets…. Psychopharmacology 2019, 236, 1411–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, Q.X.; Peters, C.; Ho, C.Y.X.; Lim, D.Y.; Yeo, W.S. A Meta-Analysis of the use of Probiotics to Alleviate Depressive Symptoms. J. Affect. Disord. 2018, 228, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.T.; Walsh, R.F.; Sheehan, A.E. Prebiotics and Probiotics for Depression and Anxiety: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Controlled Clinical Trials. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2019, 102, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagliabracci, V.S.; Engel, J.L.; Wen, J.; Wiley, S.E.; Worby, C.A.; Kinch, L.N.; Xiao, J.; Grishin, N.V.; Dixon, J.E. Secreted Kinase Phosphorylates Extracellular Proteins that Regulate Biomineralization. Science 2012, 336, 1150–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Tagliabracci, V.S.; Wen, J.; Kim, S.A.; Dixon, J.E. Crystal Structure of the Golgi Casein Kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 10574–10579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagliabracci, V.S.; Wiley, S.E.; Guo, X.; Kinch, L.N.; Durrant, E.; Wen, J.; Xiao, J.; Cui, J.; Nguyen, K.B.; Engel, J.L.; et al. A Single Kinase Generates the Majority of the Secreted Phosphoproteome. Cell 2015, 161, 1619–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.Y.; Huang, C.C.; Hsieh, Y.T.; Lin, H.C.; Pao, P.C.; Tsou, J.H.; Lai, C.Y.; Hung, L.Y.; Wang, J.M.; Chang, W.C.; et al. Analysis of the Interaction between Zinc Finger Protein 179 (Znf179) and Promyelocytic Leukemia Zinc Finger (Plzf). J. Biomed. Sci. 2013, 20, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, M.; He, Y.J.; Borchers, C.; Xiong, Y. Targeting of Protein Ubiquitination by BTB-Cullin 3-Roc1 Ubiquitin Ligases. Nat. Cell Biol. 2003, 5, 1001–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Intervention Group (N = 28) | Placebo Group (N = 33) | Statistics | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N (%) | N (%) | χ² | p | |
| Sex (female) | 20 (71.4 %) | 27 (81.8 %) | 0.925 | 0.336 |
| Smoking (yes) | 9 (32.1 %) | 19 (57.6%) | 3.946 | 0.047 |
| Dairy products before trial (yes) | 12 (48.0 %) | 10 (34.5 %) | 1.016 | 0.313 |
| Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | T | p | |
| Age (years) | 43.00 (14.31) | 40.11 (11.45) | −0.876 | 0.384 |
| Waist-to-hip ratio | 0.86 (0.07) | 0.84 (0.10) | −0.739 | 0.463 |
| Median (Mean rank) | Median (Mean rank) | U | p | |
| Education (years) | 9.00 (31.96) | 9.00 (30.18) | 435 | 0.665 |
| Illness duration (years) | 6.00 (27.92) | 10.00 (31.64) | 375 | 0.409 |
| BMI [kg/m²] | 23.96 (32.43) | 25.89 (29.79) | 422 | 0.563 |
| Intervention Group (N = 28) | Placebo Group (N = 33) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % | N | % | |
| Anticonvulsants | 3 | 10.7 | 3 | 9.1 |
| Atypical antipsychotics | 10 | 35.7 | 9 | 27.3 |
| Benzodiazepines and hypnotics | 5 | 17.9 | 7 | 21.2 |
| Glutamatergic antidepressants | 0 | 0.0 | 1 | 3.0 |
| Low potency antipsychotics | 1 | 3.6 | 7 | 21.2 |
| Melatonin-like antidepressants | 0 | 0.0 | 1 | 3.0 |
| Mixed preparation of antidepressant and antipsychotic | 1 | 3.6 | 0 | 0.0 |
| Noradrenergic and specific serotonergic antidepressants | 3 | 10.7 | 3 | 9.1 |
| Norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor (NDRI) | 1 | 3.6 | 5 | 15.2 |
| Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) | 16 | 57.1 | 25 | 75.8 |
| Serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) | 7 | 35.0 | 12 | 36.4 |
| Tri- and tetracyclic antidepressants (TZA) | 0 | 0.0 | 2 | 6.1 |
| Intervention Group (N = 28) | Placebo Group (N = 30) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |
| BDI-II t1 | 30.75 | 8.40 | 32.60 | 10.93 |
| BDI-II t2 | 15.11 | 7.91 | 18.20 | 11.53 |
| HAMD t1 | 15.07 | 6.32 | 14.43 | 4.41 |
| HAMD t2 | 9.11 | 5.16 | 8.13 | 6.16 |
| Intervention Group (N = 21) | Placebo Group (N = 25) | Time | Group | Interaction | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | F | p | F | p | F | p | |
| IL-6 t1 | 1.24 (0.49) | 1.04 (0.50) | 0.000 | 0.997 | 0.133 | 0.717 | 5.67 | 0.022 |
| IL-6 t2 | 1.09 (0.38) | 1.20 (0.60) | ||||||
| TNF t1 | 1.05 (0.27) | 1.04 (0.27) | 0.861 | 0.568 | 0.001 | 0.971 | 0.035 | 0.853 |
| TNF t2 | 1.08 (0.37) | 1.09 (0.29) | ||||||
| NFKB1 t1 | 1.02 (0.16) | 1.02 (0.17) | 0.331 | 0.359 | 0.062 | 0.804 | 0.674 | 0.416 |
| NFKB1 t2 | 0.99 (0.14) | 1.02 (0.21) | ||||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reiter, A.; Bengesser, S.A.; Hauschild, A.-C.; Birkl-Töglhofer, A.-M.; Fellendorf, F.T.; Platzer, M.; Färber, T.; Seidl, M.; Mendel, L.-M.; Unterweger, R.; et al. Interleukin-6 Gene Expression Changes after a 4-Week Intake of a Multispecies Probiotic in Major Depressive Disorder—Preliminary Results of the PROVIT Study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2575. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12092575
Reiter A, Bengesser SA, Hauschild A-C, Birkl-Töglhofer A-M, Fellendorf FT, Platzer M, Färber T, Seidl M, Mendel L-M, Unterweger R, et al. Interleukin-6 Gene Expression Changes after a 4-Week Intake of a Multispecies Probiotic in Major Depressive Disorder—Preliminary Results of the PROVIT Study. Nutrients. 2020; 12(9):2575. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12092575
Chicago/Turabian StyleReiter, Alexandra, Susanne A. Bengesser, Anne-Christin Hauschild, Anna-Maria Birkl-Töglhofer, Frederike T. Fellendorf, Martina Platzer, Tanja Färber, Matthias Seidl, Lilli-Marie Mendel, Renate Unterweger, and et al. 2020. "Interleukin-6 Gene Expression Changes after a 4-Week Intake of a Multispecies Probiotic in Major Depressive Disorder—Preliminary Results of the PROVIT Study" Nutrients 12, no. 9: 2575. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12092575
APA StyleReiter, A., Bengesser, S. A., Hauschild, A.-C., Birkl-Töglhofer, A.-M., Fellendorf, F. T., Platzer, M., Färber, T., Seidl, M., Mendel, L.-M., Unterweger, R., Lenger, M., Mörkl, S., Dalkner, N., Birner, A., Queissner, R., Hamm, C., Maget, A., Pilz, R., Kohlhammer-Dohr, A., ... Reininghaus, E. (2020). Interleukin-6 Gene Expression Changes after a 4-Week Intake of a Multispecies Probiotic in Major Depressive Disorder—Preliminary Results of the PROVIT Study. Nutrients, 12(9), 2575. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12092575






