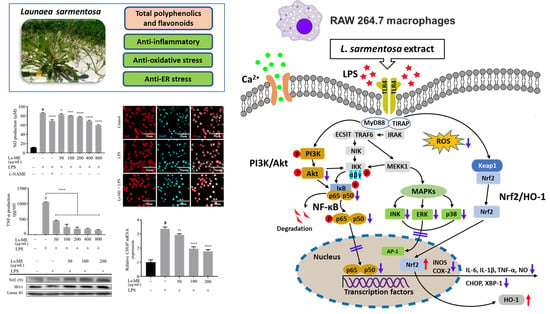
Effects of Launaea sarmentosa Extract on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation via Suppression of NF-κB/MAPK Signaling and Nrf2 Activation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Ls-ME Preparation
2.3. Radical Scavenging Activity
2.4. Total Polyphenolic, Flavonoid and Polysaccharide Content
2.5. Cell Culture and Cell Viability Assay
2.6. Cell Cytotoxicity Assay
2.7. Nitric Oxide and Reactive Oxygen Species Production Assay
2.8. TNF-a Production
2.9. Reverse Transcription–Quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR)
2.10. Western Blotting
2.11. Immunofluorescence Staining
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Antioxidant Activity of Ls-ME
3.2. Effects of Ls-ME on the Viability of LPS-Stimulated RAW 264.7 Macrophages
3.3. Ls-ME Reduces NO, ROS, and TNF-α Production
3.4. Ls-ME Suppressed the Expression of Pro-Inflammatory Genes
3.5. Ls-ME Attenuates the Activation of NF-ĸB/PI3K/Akt Pathways
3.6. Ls-ME Suppresses the Activation of MAPKs Signaling Pathway
3.7. Ls-ME Suppresses ER-Stress
3.8. Ls-ME Promotes the Nrf2/HO-1 Activation
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| PS | Penicillin-streptomycin |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| IκBα | Nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells inhibitor, alpha |
| PI3K | Phosphoinositide-3-kinase/protein kinase B |
| RIPA | Radioimmunoprecipitation |
References
- Fürst, R.; Zündorf, I. Plant-derived anti-inflammatory compounds: Hopes and disappointments regarding the translation of preclinical knowledge into clinical progress. Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 146832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scrivo, R.; Vasile, M.; Bartosiewicz, I.; Valesini, G. Inflammation as “common soil” of the multifactorial diseases. Autoimmun. Rev. 2011, 10, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminoshariae, A.; Kulild, J.C.; Donaldson, M. Short-term use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and adverse effects: An updated systematic review. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2016, 147, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghasemian, M.; Owlia, S.; Owlia, M.B. Review of Anti-Inflammatory Herbal Medicines. Adv. Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 2016, 9130979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Them, L.T.; Tuong Nguyen Dung, P.; Thi Nhat Trinh, P.; Tong Hung, Q.; Tuong, L.N.; Trong Tuan, N.; Duc Lam, T.; Thuy Nguyen, V.; Dung, L.T. Saponin, Polyphenol, Flavonoid content and α-glucosidase Inhibitory Activity, Antioxidant Potential of Launaea sarmentosa Leaves grown in Ben Tre province, Vietnam. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 542, 012036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makwana, H.T.; Pandya, D.J. Launaea pinnatifida Cass. A Species of the Controversial Drug Gojihva: Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. Res. 2019, 11, 240–243. [Google Scholar]
- Raju, G.S.; Moghal, M.M.R.; Hossain, M.S.; Hassan, M.M.; Billah, M.M.; Ahamed, S.K.; Rana, S.M.M. Assessment of pharmacological activities of two medicinal plant of Bangladesh: Launaea sarmentosa and Aegialitis rotundifolia roxb in the management of pain, pyrexia and inflammation. Biol. Res. 2014, 47, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, K.Y.; Kim, K.M.; Kim, Y.H.; Im, A.R.; Lee, J.Y.; Park, B.; Na, M.K.; Chae, S. The enhancing immune response and anti-inflammatory effects of Anemarrhena asphodeloides extract in RAW 264.7 cells. Phytomedicine 2019, 59, 152789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.H.; Kim, G.Y.; Lee, H.H. Anti-inflammatory effects of cordycepin in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages through Toll-like receptor 4-mediated suppression of mitogen-activated protein kinases and NF-κB signaling pathways. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2014, 8, 1941–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, D.H.; Cha, H.J.; Choi, E.O.; Leem, S.H.; Kim, G.Y.; Moon, S.K.; Chang, Y.C.; Yun, S.J.; Hwang, H.J.; Kim, B.W.; et al. Schisandrin A suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation and oxidative stress in RAW 264.7 macrophages by suppressing the NF-κB, MAPKs and PI3K/Akt pathways and activating Nrf2/HO-1 signaling. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Li, W.; Su, Z.Y.; Kong, A.N.T. The complexity of the Nrf2 pathway: Beyond the antioxidant response. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2015, 26, 1401–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loboda, A.; Damulewicz, M.; Pyza, E.; Jozkowicz, A.; Dulak, J. Role of Nrf2/HO-1 system in development, oxidative stress response and diseases: An evolutionarily conserved mechanism. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 3221–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, K.A.; Hyun, J.W. Oxidative stress, Nrf2, and epigenetic modification contribute to anticancer drug resistance. Toxicol. Res. 2017, 33, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tailor Chandra Shekhar, G.A. Antioxidant Activity by DPPH Radical Scavenging Method of Ageratum conyzoides. Am. J. Ethnomed. 2014, 1, 244–249. [Google Scholar]
- Singleton, V.; Othofer, R.; Lamuela-Raventos, R.M. Analysis of Total Phenols and Other Oxidation Substrates and Antioxidants by Means of Folin-Ciocalteu Reagent. Methods Enzymol. 1999, 299, 152–178. [Google Scholar]
- Aryal, S.; Baniya, M.K.; Danekhu, K.; Kunwar, P.; Gurung, R.; Koirala, N. Total Phenolic content, Flavonoid content and antioxidant potential of wild vegetables from western Nepal. Plants 2019, 8, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Chen, L.; Chu, B.; Zhang, C. Determination of total polysaccharides and total flavonoids in chrysanthemum morifolium using near-infrared hyperspectral imaging and multivariate analysis. Molecules 2018, 23, 2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Zhang, H.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Fan, S. Extraction of water-soluble polysaccharide and the antioxidant activity from Ginkgo biloba leaves. Med. Chem. Res. 2010, 19, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.Q.; Duy Binh, T.; Pham, T.L.; Nguyen, Y.D.; Dai Trang, T.X.; Nguyen, T.T.; Kanaori, K.; Kamei, K. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Lasia spinosa Leaf Extract in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced RAW 264.7 Macrophages. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmölz, L.; Wallert, M.; Lorkowski, S. Optimized incubation regime for nitric oxide measurements in murine macrophages using the Griess assay. J. Immunol. Methods 2017, 449, 68–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R. Immunoflurescence (Indirect Staining) Protocol for Adherent Cells. Bio-Protocol 2012, 2, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, B.; Wei, D.; Zheng, N.N.; Chi, Z.H.; Xin, N.; Ma, T.X.; Zheng, L.Y.; Sumi, R.; Sun, L. Coccomyxa gloeobotrydiformis polysaccharide inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 51, 2523–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Liu, L.; Chen, B.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, F.; Li, Q.; Lv, C.; Sun, H.; Li, J.; Rubby, S.; et al. Involvement of the PI3K/Akt/NF-κB Signaling Pathway in the Attenuation of Severe Acute Pancreatitis-Associated Acute Lung Injury by Sedum sarmentosum Bunge Extract. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 9698410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, Y.E.; Lee, M.Y. Anti-inflammatory activity of populus deltoides leaf extract via modulating NF-κB and p38/JNK pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Kaufman, R.J. From endoplasmic-reticulum stress to the inflammatory response. Nature 2008, 454, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargalovic, P.S.; Gharavi, N.M.; Clark, M.J.; Pagnon, J.; Yang, W.P.; He, A.; Truong, A.; Baruch-Oren, T.; Berliner, J.A.; Kirchgessner, T.G.; et al. The unfolded protein response is an important regulator of inflammatory genes in endothelial cells. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2006, 26, 2490–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, E.H.; Suzuki, T.; Funayama, R.; Nagashima, T.; Hayashi, M.; Sekine, H.; Tanaka, N.; Moriguchi, T.; Motohashi, H.; Nakayama, K.; et al. Nrf2 suppresses macrophage inflammatory response by blocking proinflammatory cytokine transcription. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Ma, Q.; Ye, L.; Piao, G. The traditional medicine and modern medicine from natural products. Molecules 2016, 21, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beg, S.; Swain, S.; Hasan, H.; Barkat, M.A.; Hussain, M.S. Systematic review of herbals as potential anti-inflammatory agents: Recent advances, current clinical status and future perspectives. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2011, 5, 120–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzoyem, J.P.; Eloff, J.N. Anti-inflammatory, anticholinesterase and antioxidant activity of leaf extracts of twelve plants used traditionally to alleviate pain and inflammation in South Africa. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 160, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hu, S.; Nie, S.; Yu, Q.; Xie, M. Reviews on Mechanisms of in Vitro Antioxidant Activity of Polysaccharides. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 5692852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, S.; Ansari, P.; Rashid, M.M.U.; Alam, M.N.; Ahmed, I.H.; Ibarahim, M.Y.; Shafi, S.M.; Rahman, S.; Hossen, A. In vitro anti-oxidant and in vivo anti-inflammatory activity determination of the methanolic leaves extract of Millettiapachycarpa. Biomed. Res. Ther. 2015, 2, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouriche, H.; Kherbache, A.; Kada, S.; Senator, A.; Demirtas, I. Phenolic content, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities of Anacyclus clavatus extracts. Environ. Exp. Biol. 2016, 14, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Xiao, M.; Zhao, J.; Li, Z.; Xing, B.; Li, X.; Kong, M.; Li, L.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; et al. An overview of plant phenolic compounds and their importance in human nutrition and management of type 2 diabetes. Molecules 2016, 21, 1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, F.; Chen, J.; Duan, L.; Zhang, T.; Wang, J.; Zhang, F. Breaking the vicious loop between inflammation, oxidative stress and coagulation, a novel anti-thrombus insight of nattokinase by inhibiting LPS-induced inflammation and oxidative stress. Redox Biol. 2020, 32, 101500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogdan, C.; Röllinghoff, M.; Diefenbach, A. Reactive oxygen and reactive nitrogen intermediates in innate and specific immunity. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2000, 12, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, P.C.; Nunes, C.; Jamal, S.K.; Cuccovia, I.M.; Salette, R. Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Therapy: A Journey Toward Safety. Med. Res. Rev. 2017, 37, 802–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; Narazaki, M.; Kishimoto, T. IL-6 in Inflammation, Immunity, and Disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a016295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, K.J.; Houston, A.; Brint, E. IL-1 family members in cancer; two sides to every story. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Shen, P. NF-κB and Its Regulation on the Immune System. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2004, 1, 343–350. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, L.; Joo, D.; Sun, S.C. NF-κB signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2017, 2, 17023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tak, P.P.; Firestein, G.S. NF-κB: A key role in inflammatory diseases. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 107, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingappan, K. NF-κB in Oxidative Stress. Curr Opin. Toxicol. 2018, 7, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akanda, M.R.; Kim, I.S.; Ahn, D.; Tae, H.J.; Nam, H.H.; Choo, B.K.; Kim, K.; Park, B.Y. Anti-inflammatory and gastroprotective roles of rabdosia inflexa through downregulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines and MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saponaro, C.; Cianciulli, A.; Calvello, R.; Dragone, T.; Iacobazzi, F.; Panaro, M.A. The PI3K/Akt pathway is required for LPS activation of microglial cells. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2012, 34, 858–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.M.; Lee, E.K.; Gong, S.Y.; Sohng, J.K.; Kang, Y.J.; Jung, H.J. Sparassis crispa exerts anti-inflammatory activity via suppression of TLR-mediated NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways in LPS-induced RAW264.7 macrophage cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 231, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantley, L.C. The phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway. Science 2002, 296, 1655–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, D.M.; Correia-da-Silva, G.; Valentão, P.; Teixeira, N.; Andrade, P.B. Anti-inflammatory effect of unsaturated fatty acids and ergosta-7,22-dien-3-ol from Marthasterias glacialis: Prevention of CHOP-mediated ER-stress and NF-κB activation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endo, M.; Mori, M.; Akira, S.; Gotoh, T. C/EBP Homologous Protein (CHOP) is Crucial for the Induction of Caspase-11 and the Pathogenesis of lipopolysacchride-induced inflammation. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 6245–6253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, Y.; Endo, M.; Tsukano, H.; Mori, M.; Oike, Y.; Gotoh, T. Molecular mechanisms of the LPS-induced non-apoptotic ER stress-CHOP pathway. J. Biochem. 2010, 147, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Z.; Ron, D. Stress-induced phosphorylation and activation of the transcription factor CHOP (GADD153) by p38 MAP kinase. Science 1996, 272, 1347–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, L.; Prather, E.R.; Stetskiv, M.; Garrison, D.E.; Meade, J.R.; Peace, T.I.; Zhou, T. Inflammaging and oxidative stress in human diseases: From molecular mechanisms to novel treatments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhai, J.; Chen, G.; Hu, K. Gambogic acid induces heme oxygenase-1 through Nrf2 signaling pathway and inhibits NF-κB and MAPK activation to reduce inflammation in LPS-activated RAW264.7 cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 109, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.Y.; Park, D.J.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, S.G.; Shon, K.J.; Choi, Y.W.; Lee, S.J. Upregulation of heme oxygenase-1 via PI3K/Akt and Nrf-2 signaling pathways mediates the anti-inflammatory activity of Schisandrin in Porphyromonas gingivalis LPS-stimulated macrophages. Immunol. Lett. 2011, 139, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yahfoufi, N.; Alsadi, N.; Jambi, M.; Matar, C. The immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory role of polyphenols. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyva-López, N.; Gutierrez-Grijalva, E.P.; Ambriz-Perez, D.L.; Basilio Heredia, J. Flavonoids as cytokine modulators: A possible therapy for inflammation-related diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.; Chen, L.; Yang, L.; Ji, X. An insight into anti-inflammatory effects of natural polysaccharides. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 153, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Burgos, E.; Gomez-Serranillos, M.P. Terpene Compounds in Nature: A Review of Their Potential Antioxidant Activity. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 5319–5341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, T.Q.C.; Binh, T.D.; Kusunoki, R.; Pham, T.L.A.; Nguyen, Y.D.H.; Nguyen, T.T.; Kanaori, K.; Kamei, K. Effects of Launaea sarmentosa Extract on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation via Suppression of NF-κB/MAPK Signaling and Nrf2 Activation. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2586. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12092586
Nguyen TQC, Binh TD, Kusunoki R, Pham TLA, Nguyen YDH, Nguyen TT, Kanaori K, Kamei K. Effects of Launaea sarmentosa Extract on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation via Suppression of NF-κB/MAPK Signaling and Nrf2 Activation. Nutrients. 2020; 12(9):2586. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12092586
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Thanh Q. C., Tran Duy Binh, Ryo Kusunoki, Tuan L. A. Pham, Yen D. H. Nguyen, Trong Tuan Nguyen, Kenji Kanaori, and Kaeko Kamei. 2020. "Effects of Launaea sarmentosa Extract on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation via Suppression of NF-κB/MAPK Signaling and Nrf2 Activation" Nutrients 12, no. 9: 2586. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12092586
APA StyleNguyen, T. Q. C., Binh, T. D., Kusunoki, R., Pham, T. L. A., Nguyen, Y. D. H., Nguyen, T. T., Kanaori, K., & Kamei, K. (2020). Effects of Launaea sarmentosa Extract on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation via Suppression of NF-κB/MAPK Signaling and Nrf2 Activation. Nutrients, 12(9), 2586. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12092586