The Association between Vitamin D and Zinc Status and the Progression of Clinical Symptoms among Outpatients Infected with SARS-CoV-2 and Potentially Non-Infected Participants: A Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Setting
2.3. Study Population and Sample
2.4. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.5. Variables
2.6. Data Sources and Measurements
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participants’ Characteristics
3.2. Vitamin D Status and Sunlight Exposure of Infected Patients and Potentially Non-Infected Participants
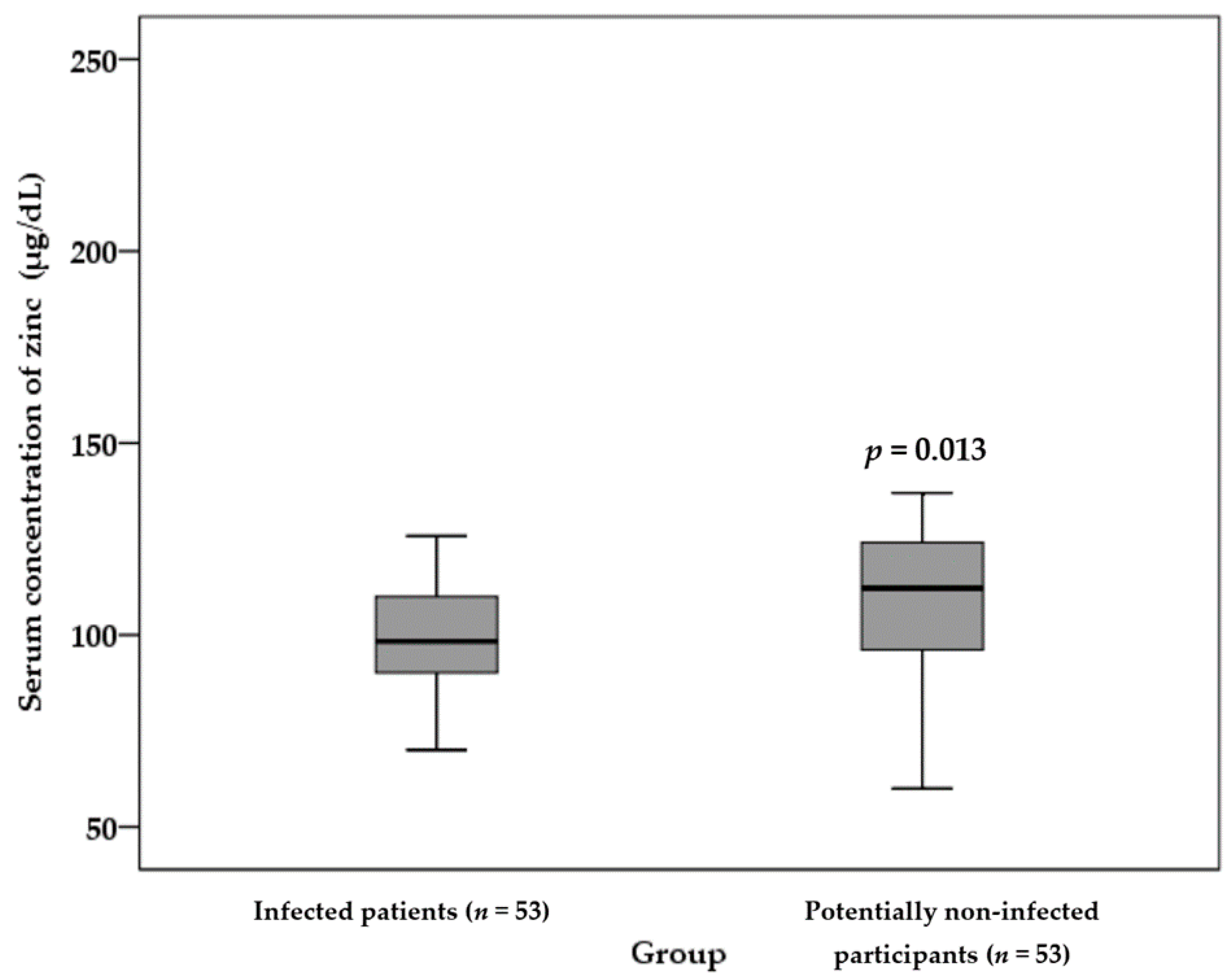
3.3. Zinc Status of the Infected Patients and Potentially Non-Infected Participants
3.4. Symptom Follow-Up, Outcomes, and Associations with Demographic, BMI and Laboratory Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raoofi, A.; Takian, A.; Sari, A.A.; Olyaeemanesh, A.; Haghighi, H.; Aarabi, M. COVID-19 Pandemic and Comparative Health Policy Learning in Iran. Arch. Iran. Med. 2020, 23, 220–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guan, W.-J.; Liang, W.-H.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, H.-R.; Chen, Z.-S.; Li, Y.-M.; Liu, X.-Q.; Chen, R.-C.; Tang, C.-L.; Wang, T.; et al. Comorbidity and its impact on 1590 patients with COVID-19 in China: A nationwide analysis. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 2000547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ugbolue, U.; Duclos, M.; Urzeala, C.; Berthon, M.; Kulik, K.; Bota, A.; Thivel, D.; Bagheri, R.; Gu, Y.; Baker, J.; et al. An Assessment of the Novel COVISTRESS Questionnaire: COVID-19 Impact on Physical Activity, Sedentary Action and Psychological Emotion. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wessels, I.; Rolles, B.; Slusarenko, A.J.; Rink, L. Zinc deficiency as a possible risk factor for increased susceptibility and severe progression of Corona Virus Disease 19. Br. J. Nutr. 2021, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Im, J.H.; Je, Y.S.; Baek, J.; Chung, M.-H.; Kwon, H.Y.; Lee, J.-S. Nutritional status of patients with COVID-19. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 100, 390–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashtary-Larky, D.; Kheirollah, A.; Bagheri, R.; Ghaffari, M.A.; Mard, S.A.; Hashemi, S.J.; Mir, I.; Wong, A. A single injection of vitamin D3 improves insulin sensitivity and β-cell function but not muscle damage or the inflammatory and cardiovascular responses to an acute bout of resistance exercise in vitamin D-deficient resistance-trained males. Br. J. Nutr. 2019, 123, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabrizi, R.; Moosazadeh, M.; Akbari, M.; Dabbaghmanesh, M.H.; Mohamadkhani, M.; Asemi, Z.; Heydari, S.T.; Akbari, M.; Lankarani, K.B. High Prevalence of Vitamin D Deficiency among Iranian Population: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Iran. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 43, 125–139. [Google Scholar]
- Aranow, C. Vitamin D and the Immune System. J. Investig. Med. 2011, 59, 881–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ginde, A.A.; Mansbach, J.M.; Camargo, C.A. Association Between Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Level and Upper Respiratory Tract Infection in the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Arch. Intern. Med. 2009, 169, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cannell, J.J.; Vieth, R.; Umhau, J.C.; Holick, M.F.; Grant, W.B.; Madronich, S.; Garland, C.F.; Giovannucci, E. Epidemic influenza and vitamin D. Epidemiol. Infect. 2006, 134, 1129–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilie, P.C.; Stefanescu, S.; Smith, L. The role of vitamin D in the prevention of coronavirus disease 2019 infection and mortality. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2020, 32, 1195–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebadi, M.; Montano-Loza, A.J. Perspective: Improving vitamin D status in the management of COVID-19. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 74, 856–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, A.S. Discovery of Zinc for Human Health and Biomarkers of Zinc deficiency. In Molecular, Genetic, and Nutritional Aspects of Major and Trace Minerals; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 241–260. [Google Scholar]
- Wessels, I.; Maywald, M.; Rink, L. Zinc as a Gatekeeper of Immune Function. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maywald, M.; Wessels, I.; Rink, L. Zinc Signals and Immunity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haase, H.; Rink, L. Multiple impacts of zinc on immune function. Metallomics 2014, 6, 1175–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, C.L.F.; Rudan, I.; Liu, L.; Nair, H.; Theodoratou, E.; Bhutta, Z.; O’Brien, K.; Campbell, H.; Black, R. Global burden of childhood pneumonia and diarrhoea. Lancet 2013, 381, 1405–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aftanas, L.; Eyu, B.; Varenik, V.; Grabeklis, A.; Kiselev, M.; Lakarova, E.; Nechiporenko, S.P.; Nikolaev, V.A.; Skalny, A.V.; Skalnaya, M.G. Element status of population of Central Federal Region. In Element Status of Population of Russia. Part II.; Skalny, A.V., Kiselev, M.F., Eds.; ELBI-SPb: Saint Petersburg, Russia, 2011; p. 430. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, Y. Potential interventions for novel coronavirus in China: A systematic review. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alexander, J.; Tinkov, A.; Strand, T.A.; Alehagen, U.; Skalny, A.; Aaseth, J. Early Nutritional Interventions with Zinc, Selenium and Vitamin D for Raising Anti-Viral Resistance Against Progressive COVID-19. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galmés, S.; Serra, F.; Palou, A. Current State of Evidence: Influence of Nutritional and Nutrigenetic Factors on Immunity in the COVID-19 Pandemic Framework. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gay, J.D.L.; Grimes, J.D. Idiopathic hypoparathyroidism with impaired vitamin B12 absorption and neuropathy. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 1972, 107, 54–58. [Google Scholar]
- CDC Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/need-extra-precautions/people-with-medical-conditions.html (accessed on 18 September 2020).
- COVID-19: Clinical Features. Available online: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/covid-19-clinical-features#H2858229650 (accessed on 10 June 2021).
- McCarty, C. Sunlight exposure assessment: Can we accurately assess vitamin D exposure from sunlight questionnaires? Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 87, 1097S–1101S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ross, A.C.; Taylor, C.L.; Yaktine, A.L.; Del Valle, H.B. Institute of Medicine (US) Committee to Review Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin D and Calcium Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium and Vitamin D; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Mehra, P.; Wolford, L.M. Serum nutrient deficiencies in the patient with complex temporomandibular joint problems. Bayl. Univ. Med. Cent. Proc. 2008, 21, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munshi, R.; Hussein, M.H.; Toraih, E.A.; Elshazli, R.M.; Jardak, C.; Sultana, N.; Youssef, M.R.; Omar, M.; Attia, A.S.; Fawzy, M.S.; et al. Vitamin D insufficiency as a potential culprit in critical COVID-19 patients. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 93, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiri, M.; Khodadadi, J.; Molaei, S. Does vitamin D serum level affect prognosis of COVID-19 patients? Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 107, 264–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Penninger, J.M.; Li, Y.; Zhong, N.; Slutsky, A.S. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) as a SARS-CoV-2 receptor: Molecular mechanisms and potential therapeutic target. Intensive Care. Med. 2020, 46, 586–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sulli, A.; Gotelli, E.; Casabella, A.; Paolino, S.; Pizzorni, C.; Alessandri, E.; Grosso, M.; Ferone, D.; Smith, V.; Cutolo, M. Vitamin D and Lung Outcomes in Elderly COVID-19 Patients. Nutrients 2021, 13, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, M.R.; Wibowo, A.; Pranata, R.; Setiabudiawan, B. Low Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (Vitamin D) Level Is Associated with Susceptibility to COVID-19, Severity, and Mortality: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, J.; Giménez, V.M.M.; Bergam, I.; Tajer, C.; Antonietti, L.; Inserra, F.; Ferder, L.; Manucha, W. Association Between Vitamin D Deficiency and COVID-19 Incidence, Complications, and Mortality in 46 Countries: An Ecological Study. Health Secur. 2021, 19, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, C.E.; Mackay, D.F.; Ho, F.; Celis-Morales, C.A.; Katikireddi, S.V.; Niedzwiedz, C.L.; Jani, B.D.; Welsh, P.; Mair, F.S.; Gray, S.R.; et al. Vitamin D concentrations and COVID-19 infection in UK Biobank. Diabetes. Metab. Syndr. 2020, 14, 561–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.T.; Nestel, F.P.; Bourdeau, V.; Nagai, Y.; Wang, Q.; Liao, J.; Tavera-Mendoza, L.; Lin, R.; Hanrahan, J.W.; Mader, S.; et al. Cutting edge: 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 is a direct inducer of antimicrobial peptide gene expression. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 2909–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, P.T.; Stenger, S.; Li, H.; Wenzel, L.; Tan, B.H.; Krutzik, S.R.; Ochoa, M.T.; Schauber, J.; Wu, K.; Meinken, C.; et al. Toll-Like Receptor Triggering of a Vitamin D-Mediated Human Antimicrobial Response. Science 2006, 311, 1770–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuti, F.A.C.; Guimaraes, F.D.S.F.; Guimaraes, P.D.S.F. Applications of vitamin D in sepsis prevention. Discov. Med. 2018, 25, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gombart, A.F.; Borregaard, N.; Koeffler, H.P. Human cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide (CAMP) gene is a direct target of the vitamin D receptor and is strongly up-regulated in myeloid cells by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 1067–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.; Ran, Z.; Jiang, Q.; Hu, N.; Yu, B.; Zhu, L.; Shen, L.; Zhang, S.; Chen, L.; Chen, H.; et al. Vitamin D Alleviates Rotavirus Infection through a Microrna-155-5p Mediated Regulation of the TBK1/IRF3 Signaling Pathway In Vivo and In Vitro. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sharifi, A.; Vahedi, H.; Nedjat, S.; Rafiei, H.; Hosseinzadeh-Attar, M.J. Effect of single-dose injection of vitamin D on immune cytokines in ulcerative colitis patients: A randomized placebo-controlled trial. APMIS 2019, 127, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gombart, A.F.; Pierre, A.; Maggini, S. A Review of Micronutrients and the Immune System–Working in Harmony to Reduce the Risk of Infection. Nutrients 2020, 12, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cereda, E.; Bogliolo, L.; Lobascio, F.; Barichella, M.; Zecchinelli, A.L.; Pezzoli, G.; Caccialanza, R. Vitamin D supplementation and outcomes in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients from the outbreak area of Lombardy, Italy. Nutrition 2020, 82, 111055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vankadari, N.; Wilce, J.A. Emerging WuHan (COVID-19) coronavirus: Glycan shield and structure prediction of spike glycoprotein and its interaction with human CD26. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 601–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komolmit, P.; Charoensuk, K.; Thanapirom, K.; Suksawatamnuay, S.; Thaimai, P.; Chirathaworn, C.; Poovorawan, Y. Correction of vitamin D deficiency facilitated suppression of IP-10 and DPP IV levels in patients with chronic hepatitis C: A randomised double-blinded, placebo-control trial. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fabri, M.; Realegeno, S.E.; Jo, E.-K.; Modlin, R.L. Role of autophagy in the host response to microbial infection and potential for therapy. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2011, 23, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campbell, G.R.; Spector, S.A. Toll-like receptor 8 ligands activate a vitamin D mediated autophagic response that inhibits human immunodeficiency virus type 1. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1003017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jothimani, D.; Kailasam, E.; Danielraj, S.; Nallathambi, B.; Ramachandran, H.; Sekar, P.; Manoharan, S.; Ramani, V.; Narasimhan, G.; Kaliamoorthy, I.; et al. COVID-19: Poor outcomes in patients with zinc deficiency. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 100, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anuk, A.T.; Polat, N.; Akdas, S.; Erol, S.A.; Tanacan, A.; Biriken, D.; Keskin, H.L.; Tekin, O.M.; Yazihan, N.; Sahin, D. The Relation Between Trace Element Status (Zinc, Copper, Magnesium) and Clinical Outcomes in COVID-19 Infection During Pregnancy. Biol. Trace Element Res. 2020, 199, 3608–3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeri, H.; Azimian, A.; Ghasemzadeh-Moghaddam, H.; Safdari, M.; Haresabadi, M.; Daneshmand, T.; Ahmadabad, H.N. Evaluation of the relationship between serum levels of zinc, vitamin B12, vitamin D, and clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19. J. Med. Virol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joachimiak, M.P. Zinc against COVID-19? Symptom surveillance and deficiency risk groups. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0008895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Read, S.; Obeid, S.; Ahlenstiel, C.; Ahlenstiel, G. The Role of Zinc in Antiviral Immunity. Adv. Nutr. 2019, 10, 696–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aggarwal, R.; Sentz, J.; Miller, M.A. Role of Zinc Administration in Prevention of Childhood Diarrhea and Respiratory Illnesses: A Meta-analysis. Pediatrics 2007, 119, 1120–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Finzi, E.; Harrington, A. Zinc treatment of outpatient COVID-19: A retrospective review of 28 consecutive patients. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 2588–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finzi, E. Treatment of SARS-CoV-2 with high dose oral zinc salts: A report on four patients. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 99, 307–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skalny, A.V.; Rink, L.; Ajsuvakova, O.P.; Aschner, M.; Gritsenko, V.A.; Alekseenko, S.I.; Svistunov, A.A.; Petrakis, D.; Spandidos, D.A.; Aaseth, J.; et al. Zinc and respiratory tract infections: Perspectives for COVID-19. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 46, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Asl, S.H.; Nikfarjam, S.; Majidi Zolbanin, N.; Nassiri, R.; Jafari, R. Immunopharmacological perspective on zinc in SARS-CoV-2 infection. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 96, 107630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velthuis, A.T.; Worm, S.H.E.V.D.; Sims, A.C.; Baric, R.S.; Snijder, E.J.; Van Hemert, M.J. Zn2+ Inhibits Coronavirus and Arterivirus RNA Polymerase Activity In Vitro and Zinc Ionophores Block the Replication of These Viruses in Cell Culture. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlucci, P.M.; Ahuja, T.; Petrilli, C.; Rajagopalan, H.; Jones, S.; Rahimian, J. Zinc sulfate in combination with a zinc ionophore may improve outcomes in hospitalized COVID-19 patients. J. Med. Microbiol. 2020, 69, 1228–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandstead, H.H.; Prasad, A.S. Zinc intake and resistance to H1N1 influenza. Am. J. Public Health 2010, 100, 970–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Tong, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Lin, B.-L. Targeted oxidation strategy (TOS) for potential inhibition of coronaviruses by disulfiram—A 70-year old anti-alcoholism drug. ChemRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korant, B.D.; Kauer, J.C.; Butterworth, B.E. Zinc ions inhibit replication of rhinoviruses. Nature 1974, 248, 588–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakman, I.; Kirchner, H.; Rink, L. Zinc Supplementation Reconstitutes the Production of Interferon-α by Leukocytes from Elderly Persons. J. Interf. Cytokine Res. 1997, 17, 469–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyagbemi, A.A.; Ajibade, T.O.; Aboua, Y.G.; Gbadamosi, I.T.; Adedapo, A.D.A.; Aro, A.O.; Adejumobi, O.A.; Thamahane-Katengua, E.; Omobowale, T.O.; Falayi, O.O.; et al. Potential health benefits of zinc supplementation for the management of COVID-19 pandemic. J. Food Biochem. 2021, 45, e13604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, C.J.; Hansen, M.; Roscioli, E.; Jones, J.; Murgia, C.; Ackland, M.L.; Zalewski, P.; Anderson, G.; Ruffin, R. Dietary zinc mediates inflammation and protects against wasting and metabolic derangement caused by sustained cigarette smoke exposure in mice. BioMetals 2010, 24, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessels, I.; Haase, H.; Engelhardt, G.; Rink, L.; Uciechowski, P. Zinc deficiency induces production of the proinflammatory cytokines IL-1β and TNFα in promyeloid cells via epigenetic and redox-dependent mechanisms. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2013, 24, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khera, D.; Singh, S.; Purohit, P.; Sharma, P.; Singh, K. Prevalence of Zinc deficiency and effect of Zinc supplementation on prevention of acute respiratory infections: A non-randomized open label study. Turk. Thorac. J. 2020, 21, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zabetakis, I.; Lordan, R.; Norton, C.; Tsoupras, A. COVID-19: The Inflammation Link and the Role of Nutrition in Potential Mitigation. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakochuk, C.D.; Barr, S.; Boy, E.; Bahizire, E.; Tugirimana, P.L.; Akilimali, P.Z.; Houghton, L.; Green, T.J. The effect of inflammation on serum zinc concentrations and the prevalence estimates of population-level zinc status among Congolese children aged 6–59 months. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 71, 1467–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacDonell, S.; Miller, J.C.; Harper, M.J.; Reid, M.R.; Haszard, J.J.; Gibson, R.S.; Houghton, L. A comparison of methods for adjusting biomarkers of iron, zinc, and selenium status for the effect of inflammation in an older population: A case for interleukin 6. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 107, 932–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Characteristics | Infected Patients (n = 53) | Potentially Non-Infected Participants (n = 53) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year) | 41 ± 13 | 40 ± 14 | 0.609 |
| Sex | |||
| Male, n (%) | 36 (68) | 38 (72) | 0.672 |
| Married status, n (%) | |||
| Single | 12 (23) | 12 (23) | 0.592 |
| Married | 41 (77) | 41 (77) | |
| Education levels, n (%) | |||
| Illiterate | 2 (4) | 1 (2) | 0.754 |
| Under diploma | 15 (29) | 19 (37) | |
| Diploma | 13 (25) | 10 (19) | |
| College education | 22 (42) | 22 (42) | |
| Cigarette smoking, n (%) | |||
| No | 40 (76) | 45 (85) | 0.223 |
| Yes | 13 (25) | 8 (15) | |
| RR (number/min) | 14 ± 0.2 | 13 ± 0.3 | 0.001 |
| PR (number/min) | 91 ± 3 | 87 ± 2 | 0.271 |
| SpO2 (%) | 97 ± 1.4 | 97 ± 1.2 | 0.032 |
| Duration of disease (day) 2 | 7 ± 2 | - | |
| Comorbidities, n (%) | |||
| Chronic pulmonary diseases | 2 (4) | 0 (0) | 0.153 |
| Hypertension | 10 (19) | 5 (9) | 0.164 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 6 (11) | 4 (8) | 0.506 |
| Obesity | 13 (25) | 21 (40) | 0.096 |
| Malnutrition | 1 (2) | 0 (0) | 0.315 |
| Cancer | 2 (4) | 0 (0) | 0.153 |
| Liver disease | 5 (9) | 3 (6) | 0.462 |
| Chronic neurological diseases | 2 (4) | 1 (2) | 0.547 |
| Chronic hematologic diseases | 2 (4) | 0 (0) | 0.157 |
| Renal diseases | 3 (6) | 4 (8) | 0.696 |
| Chronic heart disease | 4 (8) | 2 (4) | 0.414 |
| HIV | 2 (4) | 0 (0) | 0.153 |
| Asthma and allergy | 6 (11) | 5 (9) | 0.750 |
| Others 3 | 8 (15) | 16 (30) | 0.063 |
| BMI (Kg/m2) | 27 ± 5 | 28 ± 4 | 0.663 |
| Components of Individual UV Exposure and Modifying Factors | Infected Patients (n = 53) | Potentially Non-Infected Participants (n = 53) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25(OH)D (ng/mL) | 26 ± 17 | 29 ± 16. | 0.424 |
| 25(OH)D status, n (%) | |||
| Vitamin D deficiency | 10 (19) | 3 (6) | 0.086 |
| Vitamin D insufficiency | 9 (17) | 14 (26) | |
| Normal vitamin D | 34 (64) | 36 (68) | |
| Daily sun exposure (minute) | 78 ± 104 | 87 ± 60 | 0.585 |
| How much time did you spend outdoors between the hours of 9 and 11 a.m.? (hour) | 1.3 ±0.9 | 1.3 ±0.9 | 0.855 |
| How much time did you spend outdoors between the hours of 11 a.m. and 1 p.m.? (hour) | 1.2 ± 0.9 | 1.1 ± 1 | 0.810 |
| How much time did you spend outdoors between the hours of 7 and 9 a.m.? (hour) | 1.1 ± 1 | 1.1 ± 1 | 0.888 |
| How much time did you spend outdoors between the hours of 1 and 3 p.m.? (hour) | 0.8 ± 0.9 | 0.7 ± 0.9 | 0.594 |
| How much time did you spend outdoors between the hours of 3 and 5 p.m.? (hour) | 0.7 ± 0.9 | 0.6 ± 0.9 | 0.676 |
| How much time did you spend outdoors between the hours of 5 and 7 p.m.? (hour) | 0.8 ± 0.9 | 1 ± 0.9 | 0.328 |
| What percent of this time did you spend under shade (e.g., tree or beach shade)? (%) | 78 ± 22 | 63 ± 32 | 0.006 |
| What percent of time did you wear a brimmed hat? (%) | 18 ± 37 | 11 ± 31 | 0.330 |
| What percent of time did you wear long sleeves? Long pants? (%) | 84 ± 34 | 76 ± 39 | 0.264 |
| What percent of time did you wear sunscreen? (%) | 9 ± 26 | 2 ± 10 | 0.090 |
| Days of Follow-Up | Day 1 | Day 7 | Day 14 | Day 21 | Day 28 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Symptoms | ||||||
| General | ||||||
| Fatigue | 32 (60) | 16 (30) | 11 (21) | 7 (13) | 4 (8) | |
| Fever | 12 (23) | 3 (6) | 1 (2) | 1 (2) | 0(0) | |
| Night sweats | 25 (47) | 10 (19) | 8 (15) | 2 (4) | 0 (0) | |
| Flushing | 1 (2) | 1 (2) | 1 (2) | 1 (2) | 1 (2) | |
| Chills | 5 (9) | 6 (11) | 3 (6) | 1 (2) | 1 (2) | |
| Hypothermia | 0(0) | 2 (4) | 2 (4) | 0 (0) | 1 (2) | |
| Runny nose | 4 (8) | 2 (4) | 2 (4) | 2 (4) | 1 (2) | |
| Sore throat | 14 (26) | 7 (13) | 4 (8) | 1 (2) | 4 (8) | |
| Pulmonary | ||||||
| Chest pain | 5 (9) | 8 (15) | 4 (8) | 4 (8) | 4 (8) | |
| Shortness of breath | 14 (26) | 8 (15) | 6 (11) | 4 (8) | 1 (2) | |
| Cough | 23 (43) | 18 (34) | 15 (28) | 9 (17) | 5 (10) | |
| Gastrointestinal | ||||||
| Anorexia | 24 (45) | 12 (23) | 3 (6) | 2 (4) | 4 (8) | |
| Abdominal cramps | 10 (19) | 9 (17) | 4 (8) | 3 (6) | 1 (2) | |
| Diarrhea | 19 (36) | 8 (15) | (0) | 5 (9) | 1 (2) | |
| Vomiting | 3 (6) | 1 (2) | 1 (2) | 1 (2) | 1 (2) | |
| Nausea | 11 (21) | 3 (6) | 2 (4) | 1 (2) | 1 (2) | |
| Constipation | 5 (9) | 4 (8) | 3 (6) | 2 (4) | 6 (11) | |
| Bloating | 8 (15) | 7 (13) | 6 (11) | 3 (6) | 1 (2) | |
| Neurologic | ||||||
| Headache | 18 (34) | 9 (17) | 4 (8) | 3 (6) | 1 (2) | |
| Muscle pain | 11 (21) | 7 (13) | 6 (11) | 3 (6) | 5 (10) | |
| Joint pain | 13 (25) | 4 (8) | 4 (8) | 2 (4) | 1 (2) | |
| Ear pain | 5 (9) | 5 (9) | 3 (6) | 1 (2) | 2 (4) | |
| Smell disorders | 33 (62) | 15 (28) | 9 (17) | 8 (15) | 5 (9) | |
| Taste disorder | 26 (49) | 11 (21) | 5 (9) | 2 (4) | 3 (6) | |
| Symptom Categories | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | General | Pulmonary | Gastrointestinal | Neurologic |
| Age (year) | 1.02 (0.99–1.05) | 1.05 (1.00–1.11) | 0.97 (0.92–1.02) | 0.97 (0.93–1.02) |
| Sex | ||||
| Female | 1 (ref) | 1 (ref) | 1 (ref) | 1 (ref) |
| Male | 3.06 (1.13–8.33) 2 | 1.11 (0.33–3.68) | 1.71 (0.62–4.75) | 0.41 (0.17–0.98) 2 |
| Married status | ||||
| Single | 1 (ref) | 1 (ref) | 1 (ref) | 1 (ref) |
| Married | 0.91 (0.23–3.54) | 1.32 (0.39–4.42) | 2.56 (0.87–7.32) | 1.97 (0.60–6.69) |
| Education levels | ||||
| Illiterate | 1 (ref) | 1 (ref) | 1 (ref) | 1 (ref) |
| Under diploma | 0.70 (0.08–5.96) | 18.45 (0.73–463.77) | 0.28 (0.03–3.08) | 0.10 (0.01–1.38) |
| Diploma | 0.54 (0.06–5.10) | 7.45 (0.21–212.65) | 0.29 (0.02–4.12) | 0.26 (0.02–3.35) |
| College education | 1.24 (0.17–9.09) | 12.80 (0.46–354.25) | 0.64 (0.06–7.05) | 0.38 (0.03–4.69) |
| Category of vitamin D status | ||||
| Deficiency | 1 (ref) | 1 (ref) | 1 (ref) | 1 (ref) |
| Insufficiency | 0.19 (0.06–0.65) 4 | 0.63 (0.10–3.87) | 0.52 (0.10–2.81) | 1.09 (0.32–3.72) |
| Normal | 0.10 (0.04–0.24) 3 | 0.27 (0.07–0.99) 2 | 0.39 (0.12–1.21) | 0.50 (0.21–1.19) |
| Serum concentration of zinc (µg/dL) | 0.98 (0.96–1.01) | 1.00 (0.98–1.02) | 0.99 (0.97–1.01) | 1.02 (0.99–1.05) |
| BMI (Kg/m2) | 1.06 (0.97–1.17) | 0.98 (0.90–1.07) | 1.04 (0.95–1.15) | 1.08 (0.97–1.19) |
| Time (Day) | 0.88 (0.84–0.93) 4 | 0.91 (0.88–0.95) 4 | 0.91 (0.87–0.94) 4 | 0.89 (0.86–0.93) 4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Golabi, S.; Adelipour, M.; Mobarak, S.; Piri, M.; Seyedtabib, M.; Bagheri, R.; Suzuki, K.; Ashtary-Larky, D.; Maghsoudi, F.; Naghashpour, M. The Association between Vitamin D and Zinc Status and the Progression of Clinical Symptoms among Outpatients Infected with SARS-CoV-2 and Potentially Non-Infected Participants: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3368. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13103368
Golabi S, Adelipour M, Mobarak S, Piri M, Seyedtabib M, Bagheri R, Suzuki K, Ashtary-Larky D, Maghsoudi F, Naghashpour M. The Association between Vitamin D and Zinc Status and the Progression of Clinical Symptoms among Outpatients Infected with SARS-CoV-2 and Potentially Non-Infected Participants: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients. 2021; 13(10):3368. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13103368
Chicago/Turabian StyleGolabi, Sahar, Maryam Adelipour, Sara Mobarak, Maghsud Piri, Maryam Seyedtabib, Reza Bagheri, Katsuhiko Suzuki, Damoon Ashtary-Larky, Fatemeh Maghsoudi, and Mahshid Naghashpour. 2021. "The Association between Vitamin D and Zinc Status and the Progression of Clinical Symptoms among Outpatients Infected with SARS-CoV-2 and Potentially Non-Infected Participants: A Cross-Sectional Study" Nutrients 13, no. 10: 3368. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13103368
APA StyleGolabi, S., Adelipour, M., Mobarak, S., Piri, M., Seyedtabib, M., Bagheri, R., Suzuki, K., Ashtary-Larky, D., Maghsoudi, F., & Naghashpour, M. (2021). The Association between Vitamin D and Zinc Status and the Progression of Clinical Symptoms among Outpatients Infected with SARS-CoV-2 and Potentially Non-Infected Participants: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients, 13(10), 3368. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13103368








