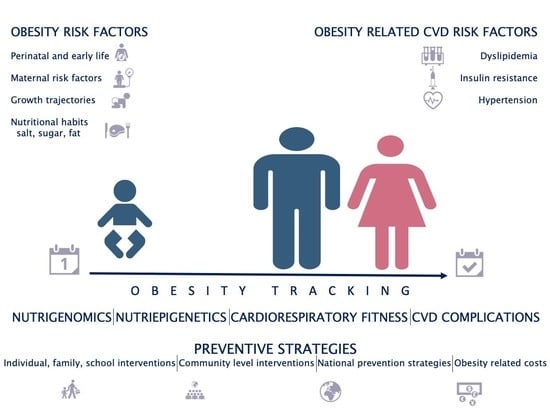
Obesity and Cardiometabolic Risk Factors: From Childhood to Adulthood
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Cardiometabolic Risk Factors
2.1. Perinatal and Early Life Risk Factors
2.1.1. Maternal Risk Factors
2.1.2. Early Childhood Risk Factors
2.1.3. Molecular Techniques and Their Contribution to Understanding Programming
2.2. Diet as a Risk Factor for Obesity and Cardiovascular Complications
2.3. Nutrigenomics and Nutri-Epigenetics
2.4. Dyslipidemia, Insulin Resistance, Hypertension and Cluster of CV Risk Factors
2.5. Obesity or Cardiorespiratory Fitness—What Does Really Matter?
2.6. The Role of Tracking in Increased CV Risk in Adulthood
2.7. The Economic Impact of Childhood Obesity
2.8. Preventive Strategies for Hypertension in Children
3. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
 .
.Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Obesity and Overweight. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 12 October 2021).
- Falkner, B.; Lurbe, E. Primordial Prevention of High Blood Pressure in Childhood an Opportunity Not to Be Missed. Hypertension 2020, 75, 1142–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, K.A.; Luo, S.; Wang, X.; Chow, T.; Alves, J.; Buchanan, T.A.; Xiang, A.H. Children Exposed to Maternal Obesity or Gestational Diabetes Mellitus during Early Fetal Development Have Hypothalamic Alterations That Predict Future Weight Gain. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 1473–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godfrey, K.M.; Reynolds, R.M.; Prescott, S.L.; Nyirenda, M.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Eriksson, J.G.; Broekman, B.F.P. Influence of Maternal Obesity on the Long-Term Health of Offspring. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017, 5, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holland, S.L.; Reader, T.; Dyer, P.S.; Avery, S.V. Phenotypic heterogeneity is a selected trait in natural yeast populations subject to environmental stress. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 1729–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gingras, V.; Hivert, M.F.; Oken, E. Early-Life Exposures and Risk of Diabetes Mellitus and Obesity. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2018, 18, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitaker, K.L.; Jarvis, M.J.; Beeken, R.J.; Boniface, D.; Wardle, J. Comparing Maternal and Paternal Intergenerational Transmission of Obesity Risk in a Large Population-Based Sample. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 91, 1560–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oken, E.; Levitan, E.B.; Gillman, M.W. Maternal Smoking during Pregnancy and Child Overweight: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lurbe, E.; Ingelfinger, J. Developmental and Early Life Origins of Cardiometabolic Risk Factors: Novel Findings and Implications. Hypertension 2021, 77, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Heilbronn, L.K. The Health Outcomes of Human Offspring Conceived by Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART). J. Dev. Orig. Health Dis. 2017, 8, 388–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceelen, M.; Van Weissenbruch, M.M.; Roos, J.C.; Vermeiden, J.P.W.; Van Leeuwen, F.E.; Delemarre-van De Waal, H.A. Body Composition in Children and Adolescents Born after in Vitro Fertilization or Spontaneous Conception. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 3417–3423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kelishadi, R.; Haghdoost, A.A.; Jamshidi, F.; Aliramezany, M.; Moosazadeh, M. Low Birthweight or Rapid Catch-up Growth: Which Is More Associated with Cardiovascular Disease and Its Risk Factors in Later Life? A Systematic Review and Cryptanalysis. Paediatr. Int. Child Health 2015, 35, 110–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, M.; Lamb, K.E.; Grimes, C.; Laws, R.; Bolton, K.; Ong, K.K.; Campbell, K. Rapid Weight Gain during Infancy and Subsequent Adiposity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Evidence. Obes. Rev. 2018, 19, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oken, E.; Fields, D.A.; Lovelady, C.A.; Redman, L.M. TOS Scientific Position Statement: Breastfeeding and Obesity. Obesity 2017, 25, 1864–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bianco-Miotto, T.; Craig, J.M.; Gasser, Y.P.; Van Dijk, S.J.; Ozanne, S.E. Epigenetics and DOHaD: From Basics to Birth and Beyond. J. Dev. Orig. Health Dis. 2017, 8, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiemsma, L.T.; Michels, K.B. The Role of the Microbiome in the Developmental Origins of Health and Disease. Pediatrics 2018, 141, e20172437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Gregg, E.W.; Flanders, W.D.; Merritt, R.; Hu, F.B. Added Sugar Intake and Cardiovascular Diseases Mortality among Us Adults. JAMA Intern. Med. 2014, 174, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Genovesi, S.; Giussani, M.; Orlando, A.; Orgiu, F.; Parati, G. Salt and Sugar: Two Enemies of Healthy Blood Pressure in Children. Nutrients 2021, 13, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaagib, N.; Sukkar, M.; Kardash, M. The Effects of Salt and Glucose Intake on Angiotensin II and Aldosterone in Obese and Nonobese Patients with Essential Hypertension. Int. J. Hypertens. 2020, 2020, 6017105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turck, D.; Castenmiller, J.; de Henauw, S.; Hirsch-Ernst, K.; Kearney, J.; Knutsen, H.K.; Maciuk, A.; Mangelsdorf, I.; McArdle, H.J.; Pelaez, C.; et al. Dietary Reference Values for Sodium. EFSA J. 2019, 17, e05778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ambard, L.; Beaujard, E. Causes de l’hypertension Artérielle. Arch. Gén. Méd. 1904, 81, 520–533. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, J.E. The Kidney, Hypertension, and Obesity. Hypertension 2003, 41, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Guideline: Sodium Intake for Adults and Children; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Stolarz-Skrzypek, K.; Staessen, J.A. Reducing Salt Intake for Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease-Times Are Changing. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2015, 22, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mente, A.; O’Donnell, M.; Rangarajan, S.; Dagenais, G.; Lear, S.; McQueen, M.; Diaz, R.; Avezum, A.; Lopez-Jaramillo, P.; Lanas, F.; et al. Associations of Urinary Sodium Excretion with Cardiovascular Events in Individuals with and without Hypertension: A Pooled Analysis of Data from Four Studies. Lancet 2016, 388, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umesawa, M.; Iso, H.; Date, C.; Yamamoto, A.; Toyoshima, H.; Watanabe, Y.; Kikuchi, S.; Koizumi, A.; Kondo, T.; Inaba, Y.; et al. Relations between Dietary Sodium and Potassium Intakes and Mortality from Cardiovascular Disease: The Japan Collaborative Cohort Study for Evaluation of Cancer Risks. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 88, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stein, P.P.; Black, H.R. The Role of Diet in the Genesis and Treatment of Hypertension. Med. Clin. N. Am. 1993, 77, 831–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardin, T.; Richette, P. Definition of Hyperuricemia and Gouty Conditions. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2014, 26, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reginato, A.M.; Mount, D.B.; Yang, I.; Choi, H.K. The Genetics of Hyperuricaemia and Gout. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2012, 8, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndrepepa, G. Uric Acid and Cardiovascular Disease. Clin. Chim. Acta 2018, 484, 150–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghi, C.; Agabiti-Rosei, E.; Johnson, R.J.; Kielstein, J.T.; Lurbe, E.; Mancia, G.; Redon, J.; Stack, A.G.; Tsioufis, K.P. Hyperuricaemia and Gout in Cardiovascular, Metabolic and Kidney Disease. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2020, 80, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lurbe, E.; Torro, M.I.; Alvarez-Pitti, J.; Redon, J.; Borghi, C.; Redon, P. Uric Acid Is Linked to Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Overweight and Obese Youths. J. Hypertens. 2018, 36, 1840–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caliceti, C.; Calabria, D.; Roda, A.; Cicero, A.F.G. Fructose Intake, Serum Uric Acid, and Cardiometabolic Disorders: A Critical Review. Nutrients 2017, 9, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alper, A.B.; Chen, W.; Yau, L.; Srinivasan, S.R.; Berenson, G.S.; Hamm, L.L. Childhood Uric Acid Predicts Adult Blood Pressure: The Bogalusa Heart Study. Hypertension 2005, 45, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Borghi, C.; Piani, F. Uric Acid and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease. A Question of Start and Finish. Hypertension 2021, 78, 1219–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khot, V.; Chavan-Gautam, P.; Joshi, S. Proposing Interactions between Maternal Phospholipids and the One Carbon Cycle: A Novel Mechanism Influencing the Risk for Cardiovascular Diseases in the Offspring in Later Life. Life Sci. 2015, 129, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobi, E.W.; Lumey, L.H.; Talens, R.P.; Kremer, D.; Putter, H.; Stein, A.D.; Slagboom, P.E.; Heijmans, B.T. DNA Methylation Differences after Exposure to Prenatal Famine Are Common and Timing- and Sex-Specific. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2009, 18, 4046–4053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordoni, L.; Gabbianelli, R. Primers on Nutrigenetics and Nutri(Epi)Genomics: Origins and Development of Precision Nutrition. Biochimie 2019, 160, 156–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordoni, L.; Nasuti, C.; Mirto, M.; Caradonna, F.; Gabbianelli, R. Intergenerational Effect of Early Life Exposure to Permethrin: Changes in Global DNA Methylation and in Nurr1 Gene Expression. Toxics 2015, 3, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barabási, A.L.; Menichetti, G.; Loscalzo, J. The Unmapped Chemical Complexity of Our Diet. Nat. Food 2020, 1, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bordoni, L.; Petracci, I.; Zhao, F.; Min, W.; Pierella, E.; Assmann, T.S.; Martinez, J.A.; Gabbianelli, R. Nutrigenomics of Dietary Lipids. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lottenberg, A.M.; da S. Afonso, M.; Lavrador, M.S.F.; Machado, R.M.; Nakandakare, E.R. The Role of Dietary Fatty Acids in the Pathology of Metabolic Syndrome. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2012, 23, 1027–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finucane, O.M.; Lyons, C.L.; Murphy, A.M.; Reynolds, C.M.; Klinger, R.; Healy, N.P.; Cooke, A.A.; Coll, R.C.; Mcallan, L.; Nilaweera, K.N.; et al. Monounsaturated Fatty Acid-Enriched High-Fat Diets Impede Adipose NLRP3 Inflammasome-Mediated IL-1β Secretion and Insulin Resistance despite Obesity. Diabetes 2015, 64, 2116–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hall, K.D.; Ayuketah, A.; Brychta, R.; Cai, H.; Cassimatis, T.; Chen, K.Y.; Chung, S.T.; Costa, E.; Courville, A.; Darcey, V.; et al. Ultra-Processed Diets Cause Excess Calorie Intake and Weight Gain: An Inpatient Randomized Controlled Trial of Ad Libitum Food Intake. Cell Metab. 2019, 30, 67–77.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bonaccio, M.; Di Castelnuovo, A.; Costanzo, S.; De Curtis, A.; Persichillo, M.; Sofi, F.; Cerletti, C.; Donati, M.B.; de Gaetano, G.; Iacoviello, L. Ultra-Processed Food Consumption Is Associated with Increased Risk of All-Cause and Cardiovascular Mortality in the Moli-Sani Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 113, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittendorfer, B.; Klein, S.; Fontana, L. A Word of Caution against Excessive Protein Intake. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2020, 16, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Guasch-Ferré, M.; Chung, W.; Ruiz-Canela, M.; Toledo, E.; Corella, D.; Bhupathiraju, S.N.; Tobias, D.K.; Tabung, F.K.; Hu, J.; et al. The Mediterranean Diet, Plasma Metabolome, and Cardiovascular Disease Risk. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 2645–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordoni, L.; Petracci, I.; Pelikant-Malecka, I.; Radulska, A.; Piangerelli, M.; Samulak, J.J.; Lewicki, L.; Kalinowski, L.; Gabbianelli, R.; Olek, R.A. Mitochondrial DNA Copy Number and Trimethylamine Levels in the Blood: New Insights on Cardiovascular Disease Biomarkers. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, J.; Gaskin, E.; Ji, C.; Miller, M.A.; Cappuccio, F.P. The Effect of Plant-Based Dietary Patterns on Blood Pressure: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Controlled Intervention Trials. J. Hypertens. 2021, 39, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Liao, L.M.; Weinstein, S.J.; Sinha, R.; Graubard, B.I.; Albanes, D. Association Between Plant and Animal Protein Intake and Overall and Cause-Specific Mortality. JAMA Intern. Med. 2020, 180, 1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, G.-Y.; Meng, X.; Li, Y.; Zhao, C.-N.; Liu, Q.; Li, H.-B. Effects of Vegetables on Cardiovascular Diseases and Related Mechanisms. Nutrients 2017, 9, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Jesus, J.M. Expert Panel on Integrated Guidelines for Cardiovascular Health and Risk Reduction in Children and Adolescents: Summary Report. Pediatrics 2011, 128, S213. [Google Scholar]
- Jolliffe, C.J.; Janssen, I. Distribution of Lipoproteins by Age and Gender in Adolescents. Circulation 2006, 114, 1056–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, S.; Yang, Q.; Yuan, K.; Loustalot, F.; Fang, J.; Daniels, S.R.; Hong, Y. Non-High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol: Distribution and Prevalence of High Serum Levels in Children and Adolescents: United States National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys, 2005–2010. J. Pediatr. 2014, 164, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kit, B.K.; Carroll, M.D.; Lacher, D.A.; Sorlie, P.D.; DeJesus, J.M.; Ogden, C.L. Trends in Serum Lipids among US Youths Aged 6 to 19 Years, 1988–2010. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2012, 308, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perak, A.M.; Ning, H.; Kit, B.K.; De Ferranti, S.D.; Van Horn, L.V.; Wilkins, J.T.; Lloyd-Jones, D.M. Trends in Levels of Lipids and Apolipoprotein B in US Youths Aged 6 to 19 Years, 1999–2016. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2019, 321, 1895–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stewart, J.; McCallin, T.; Martinez, J.; Chacko, S.; Yusuf, S. Hyperlipidemia. Pediatr. Rev. 2020, 41, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, L. Overview of Dyslipidemia in Childhood and Adolescence: Why Does It Matter and What Do We Do about It? Pediatr. Ann. 2021, 50, e4–e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caprio, S.; Hyman, L.D.; McCarthy, S.; Lange, R.; Bronson, M.; Tamborlane, W.V. Fat Distribution and Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Obese Adolescent Girls: Importance of the Intraabdominal Fat Depot. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1996, 64, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caprio, S.; Perry, R.; Kursawe, R. Adolescent Obesity and Insulin Resistance: Roles of Ectopic Fat Accumulation and Adipose Inflammation. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 1638–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berenson, G.S.; Srinivasan, S.R.; Bao, W.; Newman, W.P.; Tracy, R.E.; Wattigney, W.A. Association between Multiple Cardiovascular Risk Factors and Atherosclerosis in Children and Young Adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 338, 1650–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webber, B.J.; Seguin, P.G.; Burnett, D.G.; Clark, L.L.; Otto, J.L. Prevalence of and Risk Factors for Autopsy-Determined Atherosclerosis among US Service Members, 2001–2011. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2012, 308, 2577–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McGill, H.C.; McMahan, C.A.; Zieske, A.W.; Sloop, G.D.; Walcott, J.V.; Troxclair, D.A.; Malcom, G.T.; Tracy, R.E.; Oalmann, M.C.; Strong, J.P.; et al. Associations of Coronary Heart Disease Risk Factors With the Intermediate Lesion of Atherosclerosis in Youth. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2000, 20, 1998–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McMahan, C.A.; Gidding, S.S.; Malcom, G.T.; Schreiner, P.J.; Strong, J.P.; Tracy, R.E.; Williams, O.D.; McGill, H.C.; Pathobiological Determinants of Atherosclerosis in Youth (PDAY) Research Group. Comparison of Coronary Heart Disease Risk Factors in Autopsied Young Adults from the PDAY Study with Living Young Adults from the CARDIA Study. Cardiovasc. Pathol. 2007, 16, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahoney, L.T.; Burns, T.L.; Stanford, W.; Thompson, B.H.; Witt, J.D.; Rost, C.A.; Lauer, R.M. Coronary Risk Factors Measured in Childhood and Young Adult Life Are Associated with Coronary Artery Calcification in Young Adults: The Muscatine Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1996, 27, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davis, P.H.; Dawson, J.D.; Riley, W.A.; Lauer, R.M. Carotid Intimal-Medial Thickness Is Related to Cardiovascular Risk Factors Measured from Childhood through Middle Age the Muscatine Study. Circulation 2001, 104, 2815–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koskinen, J.S.; Kytö, V.; Juonala, M.; Viikari, J.S.A.; Nevalainen, J.; Kähönen, M.; Lehtimäki, T.; Hutri-Kähönen, N.; Laitinen, T.; Tossavainen, P.; et al. Childhood Risk Factors and Carotid Atherosclerotic Plaque in Adulthood: The Cardiovascular Risk in Young Finns Study. Atherosclerosis 2020, 293, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pletcher, M.J.; Bibbins-Domingo, K.; Liu, K.; Sidney, S.; Lin, F.; Vittinghoff, E.; Hulley, S.B. Nonoptimal Lipids Commonly Present in Young Adults and Coronary Calcium Later in Life: The CARDIA (Coronary Artery Risk Development in Young Adults) Study. Ann. Intern. Med. 2010, 153, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koskinen, J.; Juonala, M.; Dwyer, T.; Venn, A.; Thomson, R.; Bazzano, L.; Berenson, G.S.; Sabin, M.A.; Burns, T.L.; Viikari, J.S.A.; et al. Impact of Lipid Measurements in Youth in Addition to Conventional Clinic-Based Risk Factors on Predicting Preclinical Atherosclerosis in Adulthood International Childhood Cardiovascular Cohort Consortium. Circulation 2018, 137, 1246–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haney, E.M.; Huffman, L.H.; Bougatsos, C.; Freeman, M.; Steiner, R.D.; Nelson, H.D. Screening and Treatment for Lipid Disorders in Children and Adolescents: Systematic Evidence Review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. Pediatrics 2007, 120, e189–e214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ferranti, S.D.; Steinberger, J.; Ameduri, R.; Baker, A.; Gooding, H.; Kelly, A.S.; Mietus-Snyder, M.; Mitsnefes, M.M.; Peterson, A.L.; St-Pierre, J.; et al. Cardiovascular Risk Reduction in High-Risk Pediatric Patients: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2019, 139, E603–E634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vague, J. The Degree of Masculine Differentiation of Obesities: A Factor Determining Predisposition to Diabetes, Atherosclerosis, Gout, and Uric Calculous Disease. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1956, 4, 20–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muntner, P.; He, J.; Cutler, J.A.; Wildman, R.P.; Whelton, P.K. Trends in Blood Pressure among Children and Adolescents. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2004, 291, 2107–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheung, E.L.; Bell, C.S.; Samuel, J.P.; Poffenbarger, T.; Redwine, K.M.; Samuels, J.A. Race and Obesity in Adolescent Hypertension. Pediatrics 2017, 139, e20161433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koebnick, C.; Black, M.H.; Wu, J.; Martinez, M.P.; Smith, N.; Kuizon, B.; Cuan, D.; Young, D.R.; Lawrence, J.M.; Jacobsen, S.J. High Blood Pressure in Overweight and Obese Youth: Implications for Screening. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2013, 15, 793–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdés Pizarro, J.; Royo-Bordonada, M.A. Prevalence of Childhood Obesity in Spain: National Health Survey 2006–2007. Nutr. Hosp. 2012, 27, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kollias, A.; Skliros, E.; Stergiou, G.S.; Leotsakos, N.; Saridi, M.; Garifallos, D. Obesity and Associated Cardiovascular Risk Factors among Schoolchildren in Greece: A Cross-Sectional Study and Review of the Literature. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 24, 929–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorof, J.M.; Lai, D.; Turner, J.; Poffenbarger, T.; Portman, R.J. Overweight, Ethnicity, and the Prevalence of Hypertension in School-Aged Children. Pediatrics 2004, 113, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, J. The Changing Face of Pediatric Hypertension in the Era of the Childhood Obesity Epidemic. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2013, 28, 1059–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrison, R.J.; Kannel, W.B.; Stokes, J.; Castelli, W.P. Incidence and Precursors of Hypertension in Young Adults: The Framingham Offspring Study. Prev. Med. 1987, 16, 235–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, V.T.; Shulman, G.I. Mechanisms for Insulin Resistance: Common Threads and Missing Links. Cell 2012, 148, 852–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kotsis, V.; Stabouli, S.; Papakatsika, S.; Rizos, Z.; Parati, G. Mechanisms of Obesity-Induced Hypertension. Hypertens. Res. 2010, 33, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grøntved, A.; Steene-Johannessen, J.; Kynde, I.; Franks, P.W.; Helge, J.W.; Froberg, K.; Anderssen, S.A.; Andersen, L.B. Association between Plasma Leptin and Blood Pressure in Two Population-Based Samples of Children and Adolescents. J. Hypertens. 2011, 29, 1093–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, S.; Shimosawa, T.; Ogura, S.; Wang, H.; Uetake, Y.; Kawakami-Mori, F.; Marumo, T.; Yatomi, Y.; Geller, D.S.; Tanaka, H.; et al. Epigenetic Modulation of the Renal β-Adrenergic–WNK4 Pathway in Salt-Sensitive Hypertension. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.E.; do Carmo, J.M.; da Silva, A.A.; Wang, Z.; Hall, M.E. Obesity, Kidney Dysfunction and Hypertension: Mechanistic Links. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2019, 15, 367–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shatat, I.F.; Flynn, J.T. Relationships between Renin, Aldosterone, and 24-Hour Ambulatory Blood Pressure in Obese Adolescents. Pediatr. Res. 2011, 69, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goodfriend, T.L.; Kelley, D.E.; Goodpaster, B.H.; Winters, S.J. Visceral Obesity and Insulin Resistance Are Associated with Plasma Aldosterone Levels in Women. Obes. Res. 1999, 7, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawarazaki, W.; Fujita, T. The Role of Aldosterone in Obesity-Related Hypertension. Am. J. Hypertens. 2016, 29, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Briones, A.M.; Cat, A.N.D.; Callera, G.E.; Yogi, A.; Burger, D.; He, Y.; Corrêa, J.W.; Gagnon, A.M.; Gomez-Sanchez, C.E.; Gomez-Sanchez, E.P.; et al. Adipocytes Produce Aldosterone through Calcineurin-Dependent Signaling Pathways: Implications in Diabetes Mellitus-Associated Obesity and Vascular Dysfunction. Hypertension 2012, 59, 1069–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Blasio, A.M.; Van Rossum, E.F.C.; Maestrini, S.; Berselli, M.E.; Tagliaferri, M.; Podestà, F.; Koper, J.W.; Liuzzi, A.; Lamberts, S.W.J. The Relation between Two Polymorphisms in the Glucocorticoid Receptor Gene and Body Mass Index, Blood Pressure and Cholesterol in Obese Patients. Clin. Endocrinol. 2003, 59, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellili, N.M.; Foucan, L.; Fumeron, F.; Mohammedi, K.; Travert, F.; Roussel, R.; Balkau, B.; Tichet, J.; Marre, M. Associations of the 344 T>C and the 3097 G>A Polymorphisms of CYP11B2 Gene with Hypertension, Type 2 Diabetes, and Metabolic Syndrome in a French Population. Am. J. Hypertens. 2010, 23, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lang, F.; Stournaras, C. Serum and Glucocorticoid Inducible Kinase, Metabolic Syndrome, Inflammation, and Tumor Growth. Hormones 2013, 12, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cat, A.N.D.; Friederich-Persson, M.; White, A.; Touyz, R.M. Adipocytes, Aldosterone and Obesity-Related Hypertension. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2016, 57, F7–F21. [Google Scholar]
- Castrop, H.; Höcherl, K.; Kurtz, A.; Schweda, F.; Todorov, V.; Wagner, C. Physiology of Kidney Renin. Physiol. Rev. 2010, 90, 607–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinehr, T.; Andler, W. Cortisol and Its Relation to Insulin Resistance before and after Weight Loss in Obese Children. Horm. Res. 2004, 62, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanaspa, M.A.; Kuwabara, M.; Andres-Hernando, A.; Li, N.; Cicerchi, C.; Jensen, T.; Orlicky, D.J.; Roncal-Jimenez, C.A.; Ishimoto, T.; Nakagawa, T.; et al. High Salt Intake Causes Leptin Resistance and Obesity in Mice by Stimulating Endogenous Fructose Production and Metabolism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 3138–3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shibata, S.; Nagase, M.; Yoshida, S.; Kawachi, H.; Fujita, T. Podocyte as the Target for Aldosterone: Roles of Oxidative Stress and Sgk1. Hypertension 2007, 49, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nishiyama, A.; Yao, L.; Nagai, Y.; Miyata, K.; Yoshizumi, M.; Kagami, S.; Kondo, S.; Kiyomoto, H.; Shokoji, T.; Kimura, S.; et al. Possible Contributions of Reactive Oxygen Species and Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase to Renal Injury in Aldosterone/Salt-Induced Hypertensive Rats. Hypertension 2004, 43, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whaley-Connell, A.; Sowers, J.R. Insulin Resistance in Kidney Disease: Is There a Distinct Role Separate from That of Diabetes or Obesity. CardioRenal Med. 2017, 8, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman, D.S.; Williamson, D.F.; Gunter, E.W.; Byers, T. Relation of Serum Uric Acid to Mortality and Ischemic Heart Disease. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1995, 141, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lurbe, E.; Agabiti-Rosei, E.; Cruickshank, J.K.; Dominiczak, A.; Erdine, S.; Hirth, A.; Invitti, C.; Litwin, M.; Mancia, G.; Pall, D.; et al. 2016 European Society OfHypertension Guidelines for Themanagement of High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents. J. Hypertens. 2016, 34, 1887–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wühl, E. Hypertension in Childhood Obesity. Acta Paediatr. Int. J. Paediatr. 2019, 108, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bełtowski, J. Salt Intake, Aldosterone Secretion, and Obesity: Role in the Pathogenesis of Resistant Hypertension. Am. J. Hypertens. 2021, 34, 588–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, R.; Kneen, L.; Williams, G.H.; Adler, G.K. Effect of Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonist on Insulin Resistance and Endothelial Function in Obese Subjects. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2014, 16, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ross, R.; Blair, S.N.; Arena, R.; Church, T.S.; Després, J.P.; Franklin, B.A.; Haskell, W.L.; Kaminsky, L.A.; Levine, B.D.; Lavie, C.J.; et al. Importance of Assessing Cardiorespiratory Fitness in Clinical Practice: A Case for Fitness as a Clinical Vital Sign: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2016, 134, e653–e699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caspersen, C.J.; Christenson, G.M. Physical Activity, Exercise, and Physical Fitness: Definitions and Distinctions for Health-Related Research. Public Health Rep. 1985, 100, 126–131. [Google Scholar]
- Lang, J.J.; Belanger, K.; Poitras, V.; Janssen, I.; Tomkinson, G.R.; Tremblay, M.S. Systematic Review of the Relationship between 20 m Shuttle Run Performance and Health Indicators among Children and Youth. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2018, 21, 383–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ortega, F.B.; Ruiz, J.R.; Castillo, M.J.; Sjöström, M. Physical Fitness in Childhood and Adolescence: A Powerful Marker of Health. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Högström, G.; Nordström, A.; Nordström, P. High Aerobic Fitness in Late Adolescence Is Associated with a Reduced Risk of Myocardial Infarction Later in Life: A Nationwide Cohort Study in Men. Eur. Heart J. 2014, 35, 3133–3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santana, C.C.A.; Azevedo, L.B.; Cattuzzo, M.T.; Hill, J.O.; Andrade, L.P.; Prado, W.L. Physical Fitness and Academic Performance in Youth: A Systematic Review. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2017, 27, 579–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lubans, D.; Richards, J.; Hillman, C.; Faulkner, G.; Beauchamp, M.; Nilsson, M.; Kelly, P.; Smith, J.; Raine, L.; Biddle, S. Physical Activity for Cognitive and Mental Health in Youth: A Systematic Review of Mechanisms. Pediatrics 2016, 138, e20161642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Redón, P.; Grassi, G.; Redon, J.; Álvarez-Pitti, J.; Lurbe, E. Sympathetic Neural Activity, Metabolic Parameters and Cardiorespiratory Fitness in Obese Youths. J. Hypertens. 2017, 35, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Oliveira, R.G.; Guedes, D.P. Physical Activity, Sedentary Behavior, Cardiorespiratory Fitness and Metabolic Syndrome in Adolescents: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Evidence. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0168503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olds, T.S.; Tomkinson, G.R.; Ferrar, K.E.; Maher, C. A Trends in the Prevalence of Childhood Overweight and Obesity in Australia between 1985 and 2008. Int. J. Obes. 2010, 34, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ortega, F.B.; Ruiz, J.R.; España-Romero, V.; Vicente-Rodriguez, G.; Martínez-Gómez, D.; Manios, Y.; Béghin, L.; Molnar, D.; Widhalm, K.; Moreno, L.; et al. The International Fitness Scale (IFIS): Usefulness of Self-Reported Fitness in Youth. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 40, 701–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruiz, J.R.; Silva, G.; Oliveira, N.; Ribeiro, J.C.; Oliveira, J.F.; Mota, J. Criterion-Related Validity of the 20-m Shuttle Run Test in Youths Aged 13-19 Years. J. Sports Sci. 2009, 27, 899–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artero, E.G.; España-Romero, V.; Castro-Piñero, J.; Ruiz, J.R.; Jiménez-Pavón, D.; Aparicio, V.A.; Gatto-Cardia, M.C.; Baena, P.A.; Vicente-Rodríguez, G.; Castillo, M.J.; et al. Criterion-Related Validity of Field-Based Muscular Fitness Tests in Youth. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fitness 2012, 52, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, R.M.; Maldonado, D.; Gossett, T.; Shepherd, T.; Mehta, S.P.; Flesher, S.L. Developing and Validating a Step Test of Aerobic Fitness among Elementary School Children. Physiother. Can. 2019, 71, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pate, R.R.; Wang, C.Y.; Dowda, M.; Farrell, S.W.; O’Neill, J.R. Cardiorespiratory Fitness Levels among US Youth 12 to 19 Years of Age: Findings from the 1999-2002 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 2006, 160, 1005–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- García-Artero, E.; Ortega, F.B.; Ruiz, J.R.; Mesa, J.L.; Delgado, M.; González-Gross, M.; García-Fuentes, M.; Vicente-Rodríguez, G.; Gutiérrez, Á.; Castillo, M.J. Lipid and Metabolic Profiles in Adolescents Are Affected More by Physical Fitness than Physical Activity (AVENA Study). Rev. Esp. Cardiol. 2007, 60, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Garzón, M.; Ruiz, J.; Ortega, F.; Gutierrez-Sainz, A. A Mediterranean Diet Is Not Enough for Health: Physical Fitness Is an Important Additional Contributor to Health for the Adults of Tomorrow. World Rev. Nutr. Diet. 2007, 97, 114–138. [Google Scholar]
- Gahche, J.; Fakhouri, T.; Carroll, D.D.; Burt, V.L.; Wang, C.-Y.; Fulton, J.E. Cardiorespiratory Fitness Levels among U.S. Youth Aged 12–15 Years: United States, 1999–2004 and 2012; NCHS Data Brief; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2014; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Costigan, S.A.; Eather, N.; Plotnikoff, R.C.; Taaffe, D.R.; Lubans, D.R. High-Intensity Interval Training for Improving Health-Related Fitness in Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Br. J. Sports Med. 2015, 49, 1253–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhu, L.; Su, Y. Comparative Effectiveness of High-Intensity Interval Training and Moderate-Intensity Continuous Training for Cardiometabolic Risk Factors and Cardiorespiratory Fitness in Childhood Obesity: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghuveer, G.; Hartz, J.; Lubans, D.R.; Takken, T.; Wiltz, J.L.; Mietus-Snyder, M.; Perak, A.M.; Baker-Smith, C.; Pietris, N.; Edwards, N.M. Cardiorespiratory Fitness in Youth: An Important Marker of Health: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2020, 142, E101–E118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freedman, D.S.; Khan, L.K.; Dietz, W.H.; Srinivasan, S.R.; Berenson, G.S. Relationship of Childhood Obesity to Coronary Heart Disease Risk Factors in Adulthood: The Bogalusa Heart Study. Pediatrics 2001, 108, 712–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmonds, M.; Llewellyn, A.; Owen, C.G.; Woolacott, N. Predicting Adult Obesity from Childhood Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Obes. Rev. 2016, 17, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Cesare, M.; Sorić, M.; Bovet, P.; Miranda, J.J.; Bhutta, Z.; Stevens, G.A.; Laxmaiah, A.; Kengne, A.P.; Bentham, J. The Epidemiological Burden of Obesity in Childhood: A Worldwide Epidemic Requiring Urgent Action. BMC Med. 2019, 17, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Kelly, A.S. Review of Childhood Obesity: From Epidemiology, Etiology, and Comorbidities to Clinical Assessment and Treatment. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2017, 92, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rodrigues, A.N.; Abreu, G.R.; Resende, R.S.; Goncalves, W.L.S.; Gouvea, A.S. Cardiovascular Risk Factor Investigation: A Pediatric Issue. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2013, 6, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McPhee, P.G.; Singh, S.; Morrison, K.M. Childhood Obesity and Cardiovascular Disease Risk: Working Toward Solutions. Can. J. Cardiol. 2020, 36, 1352–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llewellyn, A.; Simmonds, M.; Owen, C.G.; Woolacott, N. Childhood Obesity as a Predictor of Morbidity in Adulthood: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Obes. Rev. 2016, 17, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.S.; Mulder, C.; Twisk, J.W.R.; Van Mechelen, W.; Chinapaw, M.J.M. Tracking of Childhood Overweight into Adulthood: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Obes. Rev. 2008, 9, 474–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reilly, J.J.; Kelly, J. Long-Term Impact of Overweight and Obesity in Childhood and Adolescence on Morbidity and Premature Mortality in Adulthood: Systematic Review. Int. J. Obes. 2011, 35, 891–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, M.H.; Falconer, C.; Viner, R.M.; Kinra, S. The Impact of Childhood Obesity on Morbidity and Mortality in Adulthood: A Systematic Review. Obes. Rev. 2012, 13, 985–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berenson, G.S.; Wattigney, W.A.; Tracy, R.E.; Newman, W.P.; Srinivasan, S.R.; Webber, L.S.; Dalferes, E.R.; Strong, J.P. Atherosclerosis of the Aorta and Coronary Arteries and Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Persons Aged 6 to 30 Years and Studied at Necropsy (the Bogalusa Heart Study). Am. J. Cardiol. 1992, 70, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, S.R. Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors and Atherosclerosis in Children and Adolescents. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2001, 3, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, S.; Kavey, R.E.W. Dyslipidemia and Pediatric Obesity. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 2011, 58, 1363–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smoak, C.G.; Burke, G.L.; Webber, L.S.; Harsha, D.W.; Srinivasan, S.R.; Berenson, G.S. Relation of Obesity to Clustering of Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors in Children and Young Adults: The Bogalusa Heart Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1987, 125, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, J.A.; Friedman, L.A.; Gray-McGuire, C. Metabolic Syndrome in Childhood Predicts Adult Cardiovascular Disease 25 Years Later: The Princeton Lipid Research Clinics Follow-up Study. Pediatrics 2007, 120, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, J.L.; Olsen, L.W.; Sørensen, T.I.A. Childhood Body-Mass Index and the Risk of Coronary Heart Disease in Adulthood. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 2329–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirosh, A.; Shai, I.; Afek, A.; Dubnov-Raz, G.; Ayalon, N.; Gordon, B.; Derazne, E.; Tzur, D.; Shamis, A.; Vinker, S.; et al. Adolescent BMI Trajectory and Risk of Diabetes versus Coronary Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1315–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Juonala, M.; Magnussen, C.G.; Berenson, G.S.; Venn, A.; Burns, T.L.; Sabin, M.A.; Srinivasan, S.R.; Daniels, S.R.; Davis, P.H.; Chen, W.; et al. Childhood Adiposity, Adult Adiposity, and Cardiovascular Risk Factors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 1876–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Serra-Paya, N.; Ensenyat, A.; Real, J.; Castro-Viñuales, I.; Zapata, A.; Galindo, G.; Solé-Mir, E.; Bosch-Muñoz, J.; Mur, J.M.; Teixidó, C. Evaluation of a Family Intervention Programme for the Treatment of Overweight and Obese Children (Nereu Programme): A Randomized Clinical Trial Study Protocol. BMC Public Health 2013, 13, 1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lier, L.M.; Breuer, C.; Ferrari, N.; Friesen, D.; Maisonave, F.; Schmidt, N.; Graf, C. Cost-Effectiveness of a Family-Based Multicomponent Outpatient Intervention Program for Children with Obesity in Germany. Public Health 2020, 186, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemes, S.A.; Bingham, D.D.; Pearson, N.; Chen, Y.L.; Edwardson, C.; McEachan, R.; Tolfrey, K.; Cale, L.; Richardson, G.; Fray, M.; et al. Stand out in Class: Restructuring the Classroom Environment to Reduce Sedentary Behaviour in 9–10-Yearolds—Study Protocol for a Pilot Cluster Randomised Controlled Trial. Pilot Feasibility Stud. 2018, 4, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jan, S.; Yan, L.L.; Hayes, A.; Chu, Y.; Wang, H.; Feng, X.; Niu, W.; He, F.J.; Ma, J.; et al. Cost and Cost-Effectiveness of a School-Based Education Program to Reduce Salt Intake in Children and Their Families in China. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.C.; Cheung, A.M.; Bibbins-Domingo, K.; Prosser, L.A.; Cook, N.R.; Goldman, L.; Gillman, M.W. Effectiveness and Cost-Effectiveness of Blood Pressure Screening in Adolescents in the United States. J. Pediatr. 2011, 158, 257–264.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swartz, S.J.; Srivaths, P.R.; Croix, B.; Feig, D.I. Cost-Effectiveness of Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring in the Initial Evaluation of Hypertension in Children. Pediatrics 2008, 122, 1177–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, J.T.; Kaelber, D.C.; Baker-Smith, C.M.; Blowey, D.; Carroll, A.E.; Daniels, S.R.; de Ferranti, S.D.; Dionne, J.M.; Falkner, B.; Flinn, S.K.; et al. Clinical Practice Guideline for Screening and Management of High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents. Pediatrics 2017, 140, e20171904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Falkner, B.; Gidding, S.S.; Ramirez-Garnica, G.; Wiltrout, S.A.; West, D.; Rappaport, E.B. The Relationship of Body Mass Index and Blood Pressure in Primary Care Pediatric Patients. J. Pediatr. 2006, 148, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkner, B.; Lurbe, E.; Schaefer, F. High Blood Pressure in Children: Clinical and Health Policy Implications. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2010, 12, 261–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, P.E.; West, C. A Balanced Intervention Ladder: Promoting Autonomy through Public Health Action. Public Health 2015, 129, 1092–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamage, D.G.; Riddell, M.A.; Joshi, R.; Thankappan, K.R.; Chow, C.K.; Oldenburg, B.; Evans, R.G.; Mahal, A.S.; Kalyanram, K.; Kartik, K.; et al. Effectiveness of a Scalable Group-Based Education and Monitoring Program, Delivered by Health Workers, to Improve Control of Hypertension in Rural India: A Cluster Randomised Controlled Trial. PLoS Med. 2020, 17, e1002997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farpour-Lambert, N.J.; Aggoun, Y.; Marchand, L.M.; Martin, X.E.; Herrmann, F.R.; Beghetti, M. Physical Activity Reduces Systemic Blood Pressure and Improves Early Markers of Atherosclerosis in Pre-Pubertal Obese Children. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 54, 2396–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Li, Y.; Shang, X.; Du, S.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, A.; Ma, G. Effect of Comprehensive Interventions Including Nutrition Education and Physical Activity on High Blood Pressure among Children: Evidence from School-Based Cluster Randomized Control Trial in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketelhut, S.; Ketelhut, S.R.; Ketelhut, K. School-Based Exercise Intervention Improves Blood Pressure and Parameters of Arterial Stiffness in Children: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Pediatr. Exerc. Sci. 2021, 33, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelopoulos, P.D.; Milionis, H.J.; Grammatikaki, E.; Moschonis, G.; Manios, Y. Changes in BMI and Blood Pressure after a School Based Intervention: The CHILDREN Study. Eur. J. Public Health 2009, 19, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Straub, N.; Grunert, P.; Von Kries, R.; Koletzko, B. Health Economic Potential of Early Nutrition Programming: A Model Calculation of Long-Term Reduction in Blood Pressure and Related Morbidity Costs by Use of Long-Chain Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid-Supplemented Formula. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 94, 2030S–2035S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelius, P.; Messing, S.; Goodwin, L.; Schow, D.; Abu-Omar, K. What Are Effective Policies for Promoting Physical Activity? A Systematic Review of Reviews. Prev. Med. Rep. 2020, 18, 101095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute of Medicine (US); National Research Council (US) Committee on Childhood Obesity Prevention Actions for Local Governments; Parker, L.; Burns, A.C.; Sanchez, E. Actions for Increasing Physical Activity; National Academies Press (US): Washington, DC, USA, 2009.
- WHO. Physical Activity Strategy for the WHO European Region 2016–2025; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Hannan, P.; French, S.A.; Story, M.; Fulkerson, J.A. A Pricing Strategy to Promote Sales of Lower Fat Foods in High School Cafeterias: Acceptability and Sensitivity Analysis. Am. J. Health Promot. 2002, 17, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, S.A. Pricing Effects on Food Choices. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 841S–843S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, R.S.; Siqueira, J.H.; Cunha, D.B.; del C.B. Molina, M. Impact of a Randomized School-Based Intervention Program on Blood Pressure Levels. Rev. Bras. Saude Matern. Infant. 2020, 20, 965–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimuli, J.; Sundborn, G.; Rush, E.; Oliver, M.; Savila, F. Parental Perceptions of Their Child’s Weight and Future Concern: The Pacific Islands Families Study. Pac. Health Dialog 2011, 17, 33–49. [Google Scholar]
- Bricarello, L.P.; Poltronieri, F.; Fernandes, R.; Retondario, A.; de Moraes Trindade, E.B.; de Vasconcelos, F.D. Effects of the Dietary Approach to Stop Hypertension (DASH) Diet on Blood Pressure, Overweight and Obesity in Adolescents: A Systematic Review. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2018, 28, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, V.S.; Hu, F.B. Sugar-Sweetened Beverages and Cardiometabolic Health: An Update of the Evidence. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Popkin, B.M.; Ng, S.W. Sugar-Sweetened Beverage Taxes: Lessons to Date and the Future of Taxation. PLoS Med. 2021, 18, e1003412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appel, L.J.; Lichtenstein, A.H.; Callahan, E.A.; Sinaiko, A.; Van Horn, L.; Whitsel, L. Reducing Sodium Intake in Children: A Public Health Investment. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2015, 17, 657–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hyseni, L.; Guzman-Castillo, M.; Kypridemos, C.; Collins, B.; Schwaller, E.; Capewell, S.; Boland, A.; Dickson, R.; O’Flaherty, M.; Gallacher, K.; et al. Engaging with Stakeholders to Inform the Development of a Decision-Support Tool for the NHS Health Check Programme: Qualitative Study. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2020, 20, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfenden, L.; Jones, J.; Williams, C.M.; Finch, M.; Wyse, R.J.; Kingsland, M.; Tzelepis, F.; Wiggers, J.; Williams, A.J.; Seward, K.; et al. Strategies to Improve the Implementation of Healthy Eating, Physical Activity and Obesity Prevention Policies, Practices or Programmes within Childcare Services. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 2016, CD011779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmer, T.P.; O’Connor, P.J.; Sinaiko, A.R.; Kharbanda, E.O.; Magid, D.J.; Sherwood, N.E.; Adams, K.F.; Parker, E.D.; Margolis, K.L. Impact of Hypertension on Healthcare Costs among Children. Am. J. Manag. Care 2014, 20, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Drozdz, D.; Alvarez-Pitti, J.; Wójcik, M.; Borghi, C.; Gabbianelli, R.; Mazur, A.; Herceg-Čavrak, V.; Lopez-Valcarcel, B.G.; Brzeziński, M.; Lurbe, E.; et al. Obesity and Cardiometabolic Risk Factors: From Childhood to Adulthood. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4176. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13114176
Drozdz D, Alvarez-Pitti J, Wójcik M, Borghi C, Gabbianelli R, Mazur A, Herceg-Čavrak V, Lopez-Valcarcel BG, Brzeziński M, Lurbe E, et al. Obesity and Cardiometabolic Risk Factors: From Childhood to Adulthood. Nutrients. 2021; 13(11):4176. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13114176
Chicago/Turabian StyleDrozdz, Dorota, Julio Alvarez-Pitti, Małgorzata Wójcik, Claudio Borghi, Rosita Gabbianelli, Artur Mazur, Vesna Herceg-Čavrak, Beatriz Gonzalez Lopez-Valcarcel, Michał Brzeziński, Empar Lurbe, and et al. 2021. "Obesity and Cardiometabolic Risk Factors: From Childhood to Adulthood" Nutrients 13, no. 11: 4176. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13114176
APA StyleDrozdz, D., Alvarez-Pitti, J., Wójcik, M., Borghi, C., Gabbianelli, R., Mazur, A., Herceg-Čavrak, V., Lopez-Valcarcel, B. G., Brzeziński, M., Lurbe, E., & Wühl, E. (2021). Obesity and Cardiometabolic Risk Factors: From Childhood to Adulthood. Nutrients, 13(11), 4176. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13114176