What Are the Maternal Factors that Potentially Intervenes in the Nutritional Composition of Human Milk?
Abstract
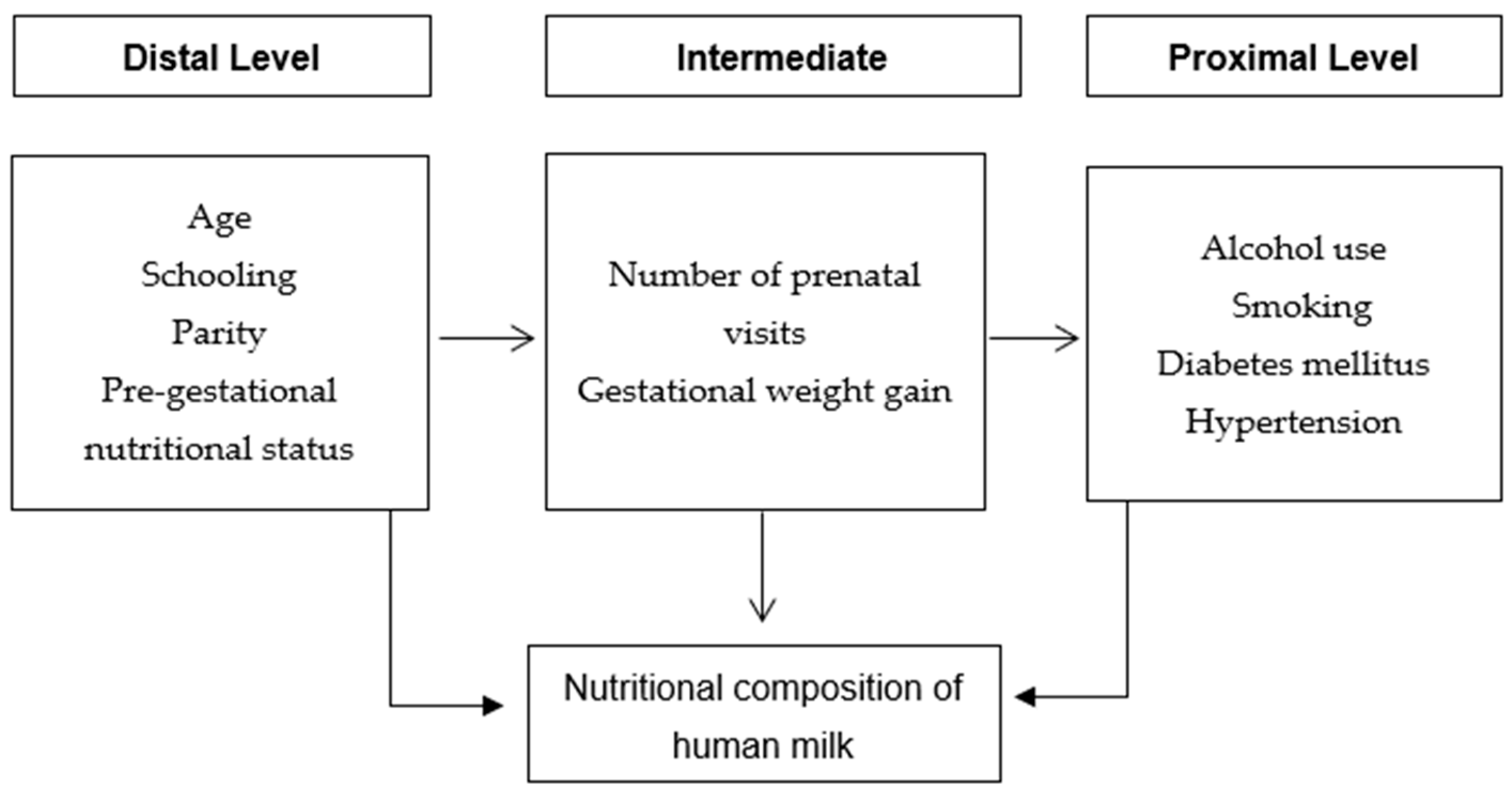
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andreas, N.J.; Kampmann, B.; Mehring Le-Doare, K. Human Breast Milk: A Review on Its Composition and Bioactivity. Early Hum. Dev. 2015, 91, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ares Segura, S.; Arena Ansótegui, J.; Díaz-Gómez, N.M. La importancia de la nutrición materna durante la lactancia, ¿necesitan las madres lactantes suplementos nutricionales? An. Pediatría 2016, 84, 347.e1–347.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization; UNICEF (Eds.) Protecting, Promoting, and Supporting Breast-Feeding: The Special Role of Maternity Services; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland; WHO Publications Center USA [Distributor]: Albany, NY, USA, 1989; ISBN 978-92-4-156130-3. [Google Scholar]
- Ballard, O.; Morrow, A.L. Human Milk Composition. Pediatric Clin. N. Am. 2013, 60, 49–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, J.; Gerss, J. Longitudinal Analysis of Macronutrients and Minerals in Human Milk Produced by Mothers of Preterm Infants. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 30, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, E.; Marano, D.; Amaral, Y.N.d.V.d.; Abranches, A.; Soares, F.V.M.; Moreira, M.E.L. O Excesso de Peso Modifica a Composição Nutricional Do Leite Materno? Uma Revisão Sistemática. Ciênc. Saúde Coletiva 2020, 25, 3969–3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, W.-H.; Jeong, T.; Park, S.; Song, S.; Kang, N.M. Content Fat and Calorie of Human Milk Is Affected by Interactions between Maternal Age and Body Mass Index. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2018, 31, 1385–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, A.G.V.; Sabarense, C.M. Modulação e Composição de Ácidos Graxos Do Leite Humano. Rev. Nutr. 2010, 23, 445–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Massmann, P.F.; França, E.L.; de Souza, E.G.; Souza, M.S.; Brune, M.F.S.S.; Honorio-França, A.C. Maternal Hypertension Induces Alterations in Immunological Factors of Colostrum and Human Milk. Front. Life Sci. 2013, 7, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dritsakou, K.; Liosis, G.; Valsami, G.; Polychronopoulos, E.; Skouroliakou, M. The Impact of Maternal- and Neonatal-Associated Factors on Human Milk’s Macronutrients and Energy. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2017, 30, 1302–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachour, P.; Yafawi, R.; Jaber, F.; Choueiri, E.; Abdel-Razzak, Z. Effects of Smoking, Mother’s Age, Body Mass Index, and Parity Number on Lipid, Protein, and Secretory Immunoglobulin A Concentrations of Human Milk. Breastfeed. Med. 2012, 7, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napierala, M.; Mazela, J.; Merritt, T.A.; Florek, E. Tobacco Smoking and Breastfeeding: Effect on the Lactation Process, Breast Milk Composition and Infant Development. A Critical Review. Environ. Res. 2016, 151, 321–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, Y.N.d.V.d.; Rocha, D.M.; Silva, L.M.L.; Soares, F.V.M.; Moreira, M.E.L. Morbidades Maternas Modificam a Composição Nutricional Do Leite Humano? Uma Revisão Sistemática. Ciênc. Saúde Coletiva 2019, 24, 2491–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakkar, S.K.; Giuffrida, F.; Cristina, C.-H.; De Castro, C.A.; Mukherjee, R.; Tran, L.-A.; Steenhout, P.; Lee, L.Y.; Destaillats, F. Dynamics of Human Milk Nutrient Composition of Women from Singapore with a Special Focus on Lipids: Dynamics of Human Milk Nutrients. Am. J. Hum. Biol. 2013, 25, 770–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Lara, N.R.; Escuder-Vieco, D.; García-Algar, O.; De la Cruz, J.; Lora, D.; Pallás-Alonso, C. Effect of Freezing Time on Macronutrients and Energy Content of Breastmilk. Breastfeed. Med. 2012, 7, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, C.; Fusch, G.; Rochow, N.; Fusch, C.; Kwan, C.; Fusch, G.; Rochow, N.; el-Helou, S.; Belfort, M.; Festival, J.; et al. Milk Analysis Using Milk Analyzers in a Standardized Setting (MAMAS) Study: A Multicentre Quality Initiative. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 2121–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute of Medicine (US) and National Research Council (US) Committee to Reexamine IOM Pregnancy Weight Guidelines. Weight Gain During Pregnancy: Reexamining the Guidelines; Rasmussen, K.M., Yaktine, A.L., Eds.; The National Academies Collection: Reports Funded by National Institutes of Health; National Academies Press (US): Washington, DC, USA, 2009; ISBN 978-0-309-13113-1. [Google Scholar]
- BRASIL. Resolução nº 466, de 12 de Dezembro de 2012. Dispõe Sobre Diretrizes e Normas Regulamentadoras de Pesquisas Envolvendo Seres Humanos. Diário Oficial [da] República Federativa do Brasil, Brasília, DF, 13 Jun. 2013. Available online: http://bit.ly/1mTMIS3 (accessed on 18 March 2021).
- Fujimori, M.; França, E.L.; Fiorin, V.; Morais, T.C.; Honorio-França, A.C.; de Abreu, L.C. Changes in the Biochemical and Immunological Components of Serum and Colostrum of Overweight and Obese Mothers. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2015, 15, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaral, Y.; Marano, D.; Abranches, A.; Silva, L.; Nehab, S.; Costa, A.C.; Moreira, M.E. Do Chronic Noncommunicable Diseases Modify the Macronutrient Composition of Human Milk? Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 72, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koletzko, B. Human Milk Lipids. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 69, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonakou, A.; Skenderi, K.P.; Chiou, A.; Anastasiou, C.A.; Bakoula, C.; Matalas, A.-L. Breast Milk Fat Concentration and Fatty Acid Pattern during the First Six Months in Exclusively Breastfeeding Greek Women. Eur. J. Nutr. 2013, 52, 963–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morceli, G.; França, E.; Magalhães, V.; Damasceno, D.; Calderon, I.; Honorio-França, A. Diabetes Induced Immunological and Biochemical Changes in Human Colostrum: Diabetes and Changes Human Colostrum. Acta Paediatr. 2011, 100, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peila, C.; Gazzolo, D.; Bertino, E.; Cresi, F.; Coscia, A. Influence of Diabetes during Pregnancy on Human Milk Composition. Nutrients 2020, 12, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keikha, M.; Bahreynian, M.; Saleki, M.; Kelishadi, R. Macro- and Micronutrients of Human Milk Composition: Are They Related to Maternal Diet? A Comprehensive Systematic Review. Breastfeed. Med. 2017, 12, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iranpour, R.; Kelishadi, R.; Babaie, S.; Khosravi-Darani, K.; Farajian, S. Comparison of Long Chain Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Content in Human Milk in Preterm and Term Deliveries and Its Correlation with Mothers’ Diet. J. Res. Med. Sci 2013, 18, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zuraini, A.; Mohd-Esa, N.; Azlan, A.; Chan, Y.M. The Trans Fatty Acid Content in Human Milk and Its Association with Maternal Diet among Lactating Mothers in Malaysia. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 22, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | n | % |
|---|---|---|
| Maternal age | ||
| Up to 18 years | 8 | 7.5 |
| 19–35 years | 75 | 70.1 |
| >35 years | 24 | 22.4 |
| Schooling (n = 106) | ||
| Primary education | 18 | 16.8 |
| Secondary education | 66 | 62.3 |
| College+ | 22 | 20.8 |
| Skin Color | ||
| White | 39 | 36.4 |
| Colored | 41 | 38.3 |
| Black | 22 | 20.6 |
| Others | 5 | 4.7 |
| Parity | ||
| Primipara | 40 | 37.4 |
| Multipara | 67 | 62.6 |
| Number of prenatal consultations (n = 102) | ||
| <6 | 5 | 4.9 |
| ≥6 | 97 | 95.1 |
| Alcohol consumption during pregnancy | ||
| No | 96 | 89.7 |
| Yes | 11 | 10.3 |
| Smoking during pregnancy | ||
| No | 103 | 96.3 |
| Yes | 4 | 3.7 |
| Drug consumption during pregnancy | ||
| No | 106 | 99.1 |
| Yes | 1 | 0.9 |
| Pregestational nutritional status (n = 106) | ||
| Low weight | 5 | 4.7 |
| Adequate weight | 52 | 49.1 |
| Overweight | 34 | 32.1 |
| Obese | 15 | 14.2 |
| Gestational weight gain 1 (n = 104) | ||
| Below recommended | 24 | 23.1 |
| Adequate | 41 | 38.3 |
| Above recommended | 39 | 37.5 |
| Diabetes mellitus | ||
| No | 87 | 81.3 |
| Yes | 20 | 18.7 |
| Hypertension (n = 106) | ||
| No | 73 | 68.9 |
| Yes | 33 | 31.1 |
| Human Milk Content | 2nd Month after Delivery |
|---|---|
| Energy (kcal/100 mL) | 55 (28–113) |
| Carbohydrates (g/100 mL) | 6.9 (3.2–8.9) |
| Lipids (g/100 mL) | 2.5 (0.5–8.6) |
| Protein (g/100 mL) | 0.9 (0.3–9.0) |
| 2nd Month after Delivery | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Energy | Carbohydrates | Lipids | Protein | |||||
| Level 1 (Distal) | Effect | p-Value | Effect | p-Value | Effect | p-Value | Effect | p-Value |
| Maternal Age in Years <19 | −1.58 | 0.80 | 0.17 | 0.59 | −0.11 | 0.87 | 1.06 | 0.03 |
| 19–34 | --- | --- | --- | --- | ||||
| >34 | 3.92 | 0.26 | −0.11 | 0.54 | 0.40 | 0.29 | −0.01 | 0.97 |
| Schooling | 0.36 | 0.63 | 0.02 | 0.68 | 0.04 | 0.62 | 0.08 | 0.20 |
| Parity | ||||||||
| Primipara | --- | --- | --- | --- | ||||
| Multipara | −3.89 | 0.20 | −0.10 | 0.50 | −0.39 | 0.24 | −0.37 | 0.13 |
| Nutritional status | ||||||||
| Low weight | −5.28 | 0.42 | −0.45 | 0.18 | −0.32 | 0.66 | 1.10 | 0.04 |
| Adequate weight | --- | --- | --- | --- | ||||
| Overweight | 6.76 | 0.04 | −0.18 | 0.28 | 0.73 | 0.04 | −0.01 | 0.96 |
| Obese | 6.58 | 0.16 | 0.04 | 0.88 | 0.76 | 0.14 | −0.18 | 0.64 |
| Level 2 (intermediate) | ||||||||
| Number of prenatal consultations | ||||||||
| < 6 | −4.56 | 0.55 | 0.20 | 0.59 | −0.58 | 0.48 | −0.19 | 0.76 |
| ≥ 6 | --- | --- | --- | --- | ||||
| Gestational weight gain | ||||||||
| Below recommended | −9.62 | 0.01 | 0.24 | 0.21 | −1.08 | 0.01 | −0.26 | 0.42 |
| Adequate | --- | --- | --- | --- | ||||
| Above recommended | −1.41 | 0.68 | −0.26 | 0.12 | −0.08 | 0.82 | 0.14 | 0.62 |
| Level 3 (proximal) | ||||||||
| Alcohol consumption | ||||||||
| Yes | 3.21 | 0.53 | −0.26 | 0.30 | 0.39 | 0.48 | −0.05 | 0.90 |
| No | --- | --- | --- | --- | ||||
| Smoking | ||||||||
| Yes | 26.30 | 0.01 | −0.65 | 0.20 | 2.99 | 0.01 | -0.12 | 0.88 |
| No | --- | --- | --- | --- | ||||
| Diabetes Mellitus | ||||||||
| Yes | −1.07 | 0.78 | 0.12 | 0.52 | -0.31 | 0.46 | 0.00 | .1.00 |
| No | --- | --- | --- | --- | ||||
| Hypertension | ||||||||
| Yes | 8.22 | 0.01 | −0.28 | 0.08 | 0.91 | 0.01 | -0.03 | 0.91 |
| No | --- | --- | --- | --- | ||||
| 2nd Month Post Delivery | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Energy | Lipids | |||
| Estimated | p-Value | Estimated | p-Value | |
| (CI 95%) | (CI 95%) | |||
| Block 1 (Distal) | ||||
| Pregestational nutritional status | ||||
| Low weight | −5.28 | 0.42 | −0.32 | 0.65 |
| (−18.32; 7.77) | (−1.75; 1.10) | |||
| Adequate | --- | --- | --- | --- |
| Overweight | 6.76 | 0.04 | 0.73 | 0.04 |
| (0.30; 13.22) | (0.03; 1.44) | |||
| Obese | 6.58 | 0.16 | 0.76 | 0.14 |
| (−2.70; 15.86) | (−0.26; 1.77) | |||
| Block 2 (Intermediate) | ||||
| Gestational weight gain | ||||
| Below recommendation | −8.47 | 0.03 | −1.00 | 0.02 |
| (−16.08; −0.87) | (−1.82; −0.17) | |||
| Adequate | --- | --- | --- | --- |
| Above recommendation | −2.33 | 0.49 | −0.19 | 0.61 |
| (−9.00; 4.34) | (−0.91; 0.54) | |||
| Block 3 (Proximal) | ||||
| Smoking | ||||
| Yes | 23.67 | 0.02 | 2.65 | 0.02 |
| (3.76; 43.58) | (0.49; 4.81) | |||
| No | --- | --- | --- | --- |
| Hypertension | ||||
| Yes | 8.22 | 0.01 | 0.91 | 0.01 |
| (2.10; 14.34) | (0.24;1.57) | |||
| No | --- | --- | --- | --- |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amaral, Y.; Silva, L.; Soares, F.; Marano, D.; Nehab, S.; Abranches, A.; Costa, A.C.; Moreira, M.E. What Are the Maternal Factors that Potentially Intervenes in the Nutritional Composition of Human Milk? Nutrients 2021, 13, 1587. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13051587
Amaral Y, Silva L, Soares F, Marano D, Nehab S, Abranches A, Costa AC, Moreira ME. What Are the Maternal Factors that Potentially Intervenes in the Nutritional Composition of Human Milk? Nutrients. 2021; 13(5):1587. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13051587
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmaral, Yasmin, Leila Silva, Fernanda Soares, Daniele Marano, Sylvia Nehab, Andrea Abranches, Ana Carolina Costa, and Maria Elisabeth Moreira. 2021. "What Are the Maternal Factors that Potentially Intervenes in the Nutritional Composition of Human Milk?" Nutrients 13, no. 5: 1587. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13051587
APA StyleAmaral, Y., Silva, L., Soares, F., Marano, D., Nehab, S., Abranches, A., Costa, A. C., & Moreira, M. E. (2021). What Are the Maternal Factors that Potentially Intervenes in the Nutritional Composition of Human Milk? Nutrients, 13(5), 1587. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13051587






