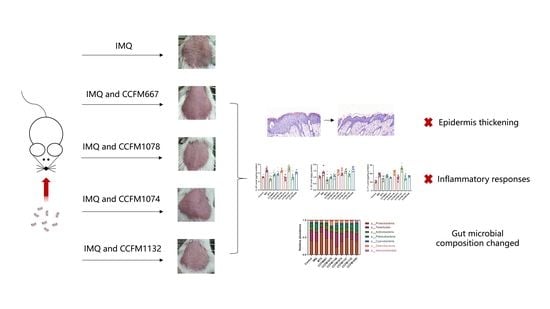
Potential Role of Probiotics in Ameliorating Psoriasis by Modulating Gut Microbiota in Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-Like Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains
2.2. Animal Experiments
2.3. Ear Thickness Determination and Dorsal Skin Score
2.4. Skin Histopathology
2.5. Skin Cytokine Analysis
2.6. SCFA Analysis
2.7. 16S rRNA Amplification Sequencing of Faecal Samples
2.8. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. CCFM667, CCFM1078, CCFM1074, and CCFM1132 Ameliorated Psoriasis-Like Pathological Characteristics
3.2. CCFM667, CCFM1078, CCFM1074, and CCFM1132 Suppressed the Psoriasis-Like Immune Response
3.3. Probiotics Exerted Different Effects on SCFA Metabolism
3.4. Probiotics Exerted Different Effects on Gut Microbial Composition
3.5. Key Differences between Effective and Ineffective Probiotics in Ameliorating Psoriasis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CCFM | Culture Collection of Food Microorganisms |
| EILISA | Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay |
| IL | Interleukin |
| IMQ | Imiquimod |
| LDA | Linear Discriminant Analysis |
| MRS | Man, Rogosa and Sharpe |
| MTX | Methotrexate |
| OD | Optical density |
| PASI | Psoriasis Area and Severity Index |
| PCA | Principal Components Analysis |
| PCR | Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| SCFAs | Short-Chain Fatty Acids |
| Th | Helper T cells |
| Tregs | Regulatory cells |
References
- Grayson, M. Psoriasis. Nature 2012, 492, S49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christophers, E. Psoriasis–Epidemiology and clinical spectrum. Clin. Exp. Derm. 2001, 26, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parisi, R.; Symmons, D.P.; Griffiths, C.E.; Ashcroft, D.M. Global epidemiology of psoriasis: A systematic review of incidence and prevalence. J. Investig. Derm. 2013, 133, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferreli, C.; Pinna, A.L.; Pilloni, L.; Tomasini, C.F.; Rongioletti, F. Histopathological aspects of psoriasis and its uncommon variants. G. Ital. Derm. Venereol. 2018, 153, 173–184. [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths, C.E.; Barker, J.N. Pathogenesis and clinical features of psoriasis. Lancet 2007, 370, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greb, J.E.; Goldminz, A.M.; Elder, J.T.; Lebwohl, M.G.; Gladman, D.D.; Wu, J.J.; Mehta, N.N.; Finlay, A.Y.; Gottlieb, A.B. Psoriasis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schn, M.P. Adaptive and innate immunity in psoriasis and other inflammatory disorders. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diani, M.; Altomare, G.; Reali, E. T helper cell subsets in clinical manifestations of psoriasis. J. Immunol. Res. 2016, 2016, 7692024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paust, H.J.; Turner, J.E.; Steinmetz, O.M.; Peters, A.; Heymann, F.; Holscher, C.; Wolf, G.; Kurts, C.; Mittrucker, H.W.; Stahl, R.A.; et al. The IL-23/Th17 axis contributes to renal injury in experimental glomerulonephritis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 969–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boehncke, W.H.; Schon, M.P. Psoriasis. Lancet 2015, 386, 983–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamata, M.; Tada, Y. Safety of biologics in psoriasis. J. Derm. 2018, 45, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thursby, E.; Juge, N. Introduction to the human gut microbiota. Biochem. J. 2017, 474, 1823–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Ivanova, N.; Kirton, E.; Allgaier, M.; Bergin, C.; Scheffrahn, R.H.; Kyrpides, N.C.; Warnecke, F.; Tringe, S.G.; Hugenholtz, P. Comparative metagenomic and metatranscriptomic analysis of hindgut paunch microbiota in wood- and dung-feeding higher termites. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez-Bello, M.G.; Godoy-Vitorino, F.; Knight, R.; Blaser, M.J. Role of the microbiome in human development. Gut 2019, 68, 1108–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyagi, A.M.; Yu, M.; Darby, T.M.; Vaccaro, C.; Li, J.Y.; Owens, J.A.; Hsu, E.; Adams, J.; Weitzmann, M.N.; Jones, R.M.; et al. The microbial metabolite butyrate stimulates bone formation via T regulatory cell-mediated regulation of WNT10B expression. Immunity 2018, 49, 1116–1131.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Sun, M.; Wu, W.; Yang, W.; Huang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Ma, C.; Xu, L.; Yao, S.; Liu, Z.; et al. Microbiota metabolite butyrate differentially regulates Th1 and Th17 cells’ differentiation and function in induction of colitis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2019, 25, 1450–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hidalgo-Cantabrana, C.; Gomez, J.; Delgado, S.; Requena-Lopez, S.; Queiro-Silva, R.; Margolles, A.; Coto, E.; Sanchez, B.; Coto-Segura, P. Gut microbiota dysbiosis in a cohort of patients with psoriasis. Br. J. Derm. 2019, 181, 1287–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scher, J.U.; Ubeda, C.; Artacho, A.; Attur, M.; Isaac, S.; Reddy, S.M.; Marmon, S.; Neimann, A.; Brusca, S.; Patel, T.; et al. Decreased bacterial diversity characterizes the altered gut microbiota in patients with psoriatic arthritis, resembling dysbiosis in inflammatory bowel disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.J.; Ho, H.J.; Tseng, C.H.; Lai, Z.L.; Shieh, J.J.; Wu, C.Y. Intestinal microbiota profiling and predicted metabolic dysregulation in psoriasis patients. Exp. Derm. 2018, 27, 1336–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doaa, M.; Dalia, M.; Ahmed, F.S. Gut bacterial microbiota in psoriasis: A case control study. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2016, 10, 1337–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Codoner, F.M.; Ramirez-Bosca, A.; Climent, E.; Carrion-Gutierrez, M.; Guerrero, M.; Perez-Orquin, J.M.; Horga de la Parte, J.; Genoves, S.; Ramon, D.; Navarro-Lopez, V.; et al. Gut microbial composition in patients with psoriasis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, L.; Zhao, S.; Zhu, W.; Wu, L.; Li, J.; Shen, M.; Lei, L.; Chen, X.; Peng, C. The Akkermansia muciniphila is a gut microbiota signature in psoriasis. Exp. Derm. 2018, 27, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolters, M. Diet and psoriasis: Experimental data and clinical evidence. Br. J. Derm. 2005, 153, 706–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrea, L.; Megna, M.; Cacciapuoti, S.; Frias-Toral, E.; Fabbrocini, G.; Savastano, S.; Colao, A.; Muscogiuri, G. Very low-calorie ketogenic diet (VLCKD) in patients with psoriasis and obesity: an update for dermatologists and nutritionists. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2020, 1, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosme-Silva, L.; Dal-Fabbro, R.; Cintra, L.T.A.; Ervolino, E.; Plazza, F.; Mogami Bomfim, S.; Duarte, P.C.T.; Junior, V.; Gomes-Filho, J.E. Reduced bone resorption and inflammation in apical periodontitis evoked by dietary supplementation with probiotics in rats. Int. Endod. J. 2020, 53, 1084–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hu, D.; Tian, Y.; Song, Y.; Hou, Y.; Sun, L.; Zhang, Y.; Man, C.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, Y. Protective effects of a novel Lactobacillus rhamnosus strain with probiotic characteristics against lipopolysaccharide-induced intestinal inflammation in vitro and in vivo. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 5799–5814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.H.; Wu, C.S.; Chao, Y.H.; Lin, C.C.; Tsai, H.Y.; Li, Y.R.; Chen, Y.Z.; Tsai, W.H.; Chen, Y.K. Lactobacillus pentosus GMNL-77 inhibits skin lesions in imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like mice. J. Food Drug Anal. 2017, 25, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rather, I.A.; Bajpai, V.K.; Huh, Y.S.; Han, Y.K.; Bhat, E.A.; Lim, J.; Paek, W.K.; Park, Y.H. Probiotic Lactobacillus sakei proBio-65 extract ameliorates the severity of imiquimod induced psoriasis-like skin inflammation in a mouse model. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Fang, Z.; Lee, Y.K.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Lu, W.; Chen, W. Prophylactic effects of oral administration of Lactobacillus casei on house dust mite-induced asthma in mice. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 9272–9284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Fits, L.; Mourits, S.; Voerman, J.S.; Kant, M.; Boon, L.; Laman, J.D.; Cornelissen, F.; Mus, A.M.; Florencia, E.; Prens, E.P.; et al. Imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin inflammation in mice is mediated via the IL-23/IL-17 axis. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 5836–5845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Di, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Liang, D.; Li, P. Paeoniflorin inhibits imiquimod-induced psoriasis in mice by regulating Th17 cell response and cytokine secretion. Eur. J. Pharm. 2016, 772, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baker, H.; Ryan, T.J. Methotrexate in psoriasis. Lancet 1968, 2, 1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, B.; Li, D.; Ai, C.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Lactulose differently modulates the composition of luminal and mucosal microbiota in C57BL/6J mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 6240–6247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, P.; Wang, G.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Bifidobacterium with the role of 5-hydroxytryptophan synthesis regulation alleviates the symptom of depression and related microbiota dysbiosis. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2019, 66, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, R.; Luo, Y.; Song, J.; Kuai, L.; Xing, M.; Hong, S.; Sun, X.; Ding, X.; et al. Role of keratinocytes and immune cells in the anti-inflammatory effects of Tripterygium wilfordii Hook. f. in a murine model of psoriasis. Phytomedicine 2020, 77, 153299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Lei, L.; Zeng, Q.; Yao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Li, Q.; Gao, L.; Du, H.; Xie, Y.; Huang, J.; et al. Ozone therapy attenuates NF-kappaB-mediated local inflammatory response and activation of Th17 cells in treatment for psoriasis. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 1833–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koh, A.; De Vadder, F.; Kovatcheva-Datchary, P.; Backhed, F. From dietary fiber to host physiology: Short-chain fatty acids as key bacterial metabolites. Cell 2016, 165, 1332–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foster, Z.S.; Sharpton, T.J.; Grunwald, N.J. Metacoder: An R package for visualization and manipulation of community taxonomic diversity data. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Di Cesare, A.; Di Meglio, P.; Nestle, F.O. The IL-23/Th17 axis in the immunopathogenesis of psoriasis. J. Investig. Derm. 2009, 129, 1339–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roberti, R.; Iannone, L.F.; Palleria, C.; De Sarro, C.; Spagnuolo, R.; Barbieri, M.A.; Vero, A.; Manti, A.; Pisana, V.; Fries, W.; et al. Safety profiles of biologic agents for inflammatory bowel diseases: a prospective pharmacovigilance study in Southern Italy. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2020, 36, 1457–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dattola, A.; Silvestri, M.; Tamburi, F.; Amoruso, G.F.; Bennardo, L.; Nistico, S.P. Emerging role of anti-IL23 in the treatment of psoriasis: When humanized is very promising. Dermatol. Ther. 2020, 33, e14504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarrati, M.; Salehi, E.; Mofid, V.; Hosseinzadeh-Attar, M.J.; Nourijelyani, K.; Bidad, K.; Shidfar, F. Relationship between probiotic consumption and IL-10 and IL-17 secreted by PBMCs in overweight and obese people. Iran. J. Allergy Asthm. 2013, 12, 404–406. [Google Scholar]
- Stehlikova, Z.; Kostovcikova, K.; Kverka, M.; Rossmann, P.; Dvorak, J.; Novosadova, I.; Kostovcik, M.; Coufal, S.; Srutkova, D.; Prochazkova, P.; et al. Crucial role of microbiota in experimental psoriasis revealed by a gnotobiotic mouse model. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leccese, G.; Bibi, A.; Mazza, S.; Facciotti, F.; Caprioli, F.; Landini, P.; Paroni, M. Probiotic Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains counteract adherent-invasive Escherichia coli (AIEC) virulence and hamper IL-23/Th17 axis in ulcerative colitis, but not in crohn’s disease. Cells 2020, 9, 1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zou, Y.; Peng, J.; Lu, F.; Yin, Y.; Li, F.; Yang, J. Lactobacillus acidophilus suppresses colitis-associated activation of the IL-23/Th17 axis. J. Immunol. Res. 2015, 2015, 909514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eppinga, H.; Sperna Weiland, C.J.; Thio, H.B.; van der Woude, C.J.; Nijsten, T.E.; Peppelenbosch, M.P.; Konstantinov, S.R. Similar depletion of protective Faecalibacterium prausnitzii in psoriasis and inflammatory bowel disease, but not in hidradenitis suppurativa. J. Crohn’s. Colitis 2016, 10, 1067–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khyshiktuev, B.S.; Karavaeva, T.M.; Fal’ko, E.V. Variability of quantitative changes in short-chain fatty acids in serum and epidermis in psoriasis. Klin. Lab. Diagn. 2008, 8, 22–24. [Google Scholar]
- Rinninella, E.; Raoul, P.; Cintoni, M.; Franceschi, F.; Miggiano, G.; Gasbarrini, A.; Mele, M. What is the healthy gut microbiota composition? A changing ecosystem across age, environment, diet, and diseases. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Myers, B.; Brownstone, N.; Reddy, V.; Chan, S.; Thibodeaux, Q.; Truong, A.; Bhutani, T.; Chang, H.W.; Liao, W. The gut microbiome in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2019, 33, 101494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Li, L.; Liu, X.; Lu, W.; Zhao, J. Strain-specific ameliorating effect of Bifidobacterium longum on atopic dermatitis in mice. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 60, 103426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, R.; Xue, X.; Zhang, L.; Yang, X.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, C. Strain-specific anti-inflammatory properties of two Akkermansia muciniphila strains on chronic colitis in mice. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, K.; Xiang, Q.; Chen, N.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, N.; Zhu, J.; He, Q. Antibiotic-induced disruption of gut microbiota alters local metabolomes and immune responses. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]










| Strain Number | Strain Original Number | Genus/Species | Origin |
|---|---|---|---|
| CCFM667 | CCFM667 | Bifidobacterium adolescentis | CCFM |
| CCFM1078 | JSWX17M1 | Bifidobacterium breve | |
| CCFM1148 | JSWX23M8 | Bifidobacterium animalis | |
| CCFM1074 | FJSWX1M3 | Lacticaseibacillus paracasei | |
| CCFM1147 | VCQQJ4174M3 | ||
| CCFM1032 | FZJTZ20M3 | Limosilactobacillus reuteri | |
| CCFM1040 | FYNDL13 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, W.; Deng, Y.; Fang, Z.; Zhai, Q.; Cui, S.; Zhao, J.; Chen, W.; Zhang, H. Potential Role of Probiotics in Ameliorating Psoriasis by Modulating Gut Microbiota in Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-Like Mice. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2010. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13062010
Lu W, Deng Y, Fang Z, Zhai Q, Cui S, Zhao J, Chen W, Zhang H. Potential Role of Probiotics in Ameliorating Psoriasis by Modulating Gut Microbiota in Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-Like Mice. Nutrients. 2021; 13(6):2010. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13062010
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Wenwei, Yadan Deng, Zhifeng Fang, Qixiao Zhai, Shumao Cui, Jianxin Zhao, Wei Chen, and Hao Zhang. 2021. "Potential Role of Probiotics in Ameliorating Psoriasis by Modulating Gut Microbiota in Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-Like Mice" Nutrients 13, no. 6: 2010. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13062010
APA StyleLu, W., Deng, Y., Fang, Z., Zhai, Q., Cui, S., Zhao, J., Chen, W., & Zhang, H. (2021). Potential Role of Probiotics in Ameliorating Psoriasis by Modulating Gut Microbiota in Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-Like Mice. Nutrients, 13(6), 2010. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13062010