Expression of Jejunal Taste Receptors in Women with Morbid Obesity
Abstract
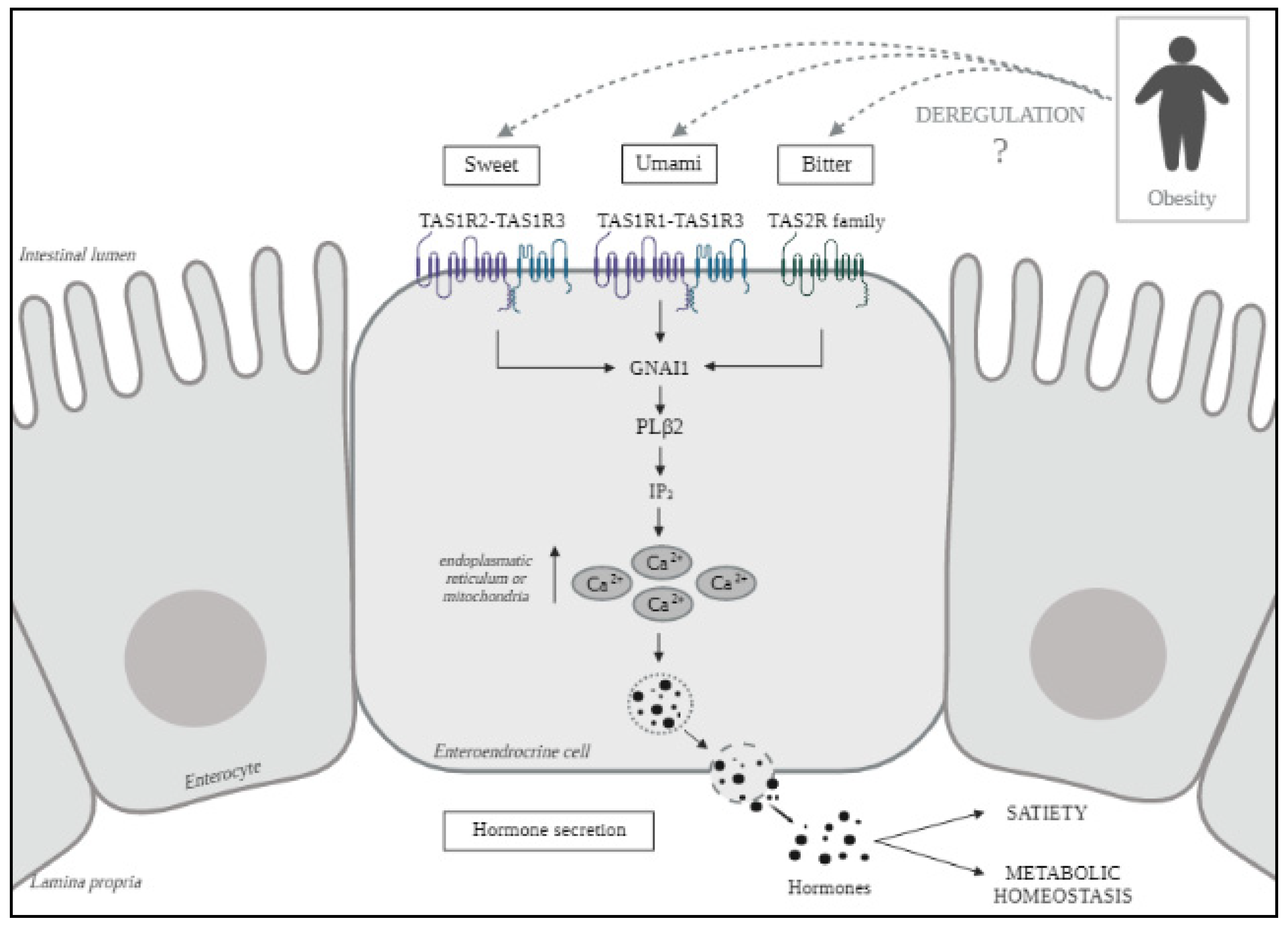
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Baseline Characteristics of Subjects
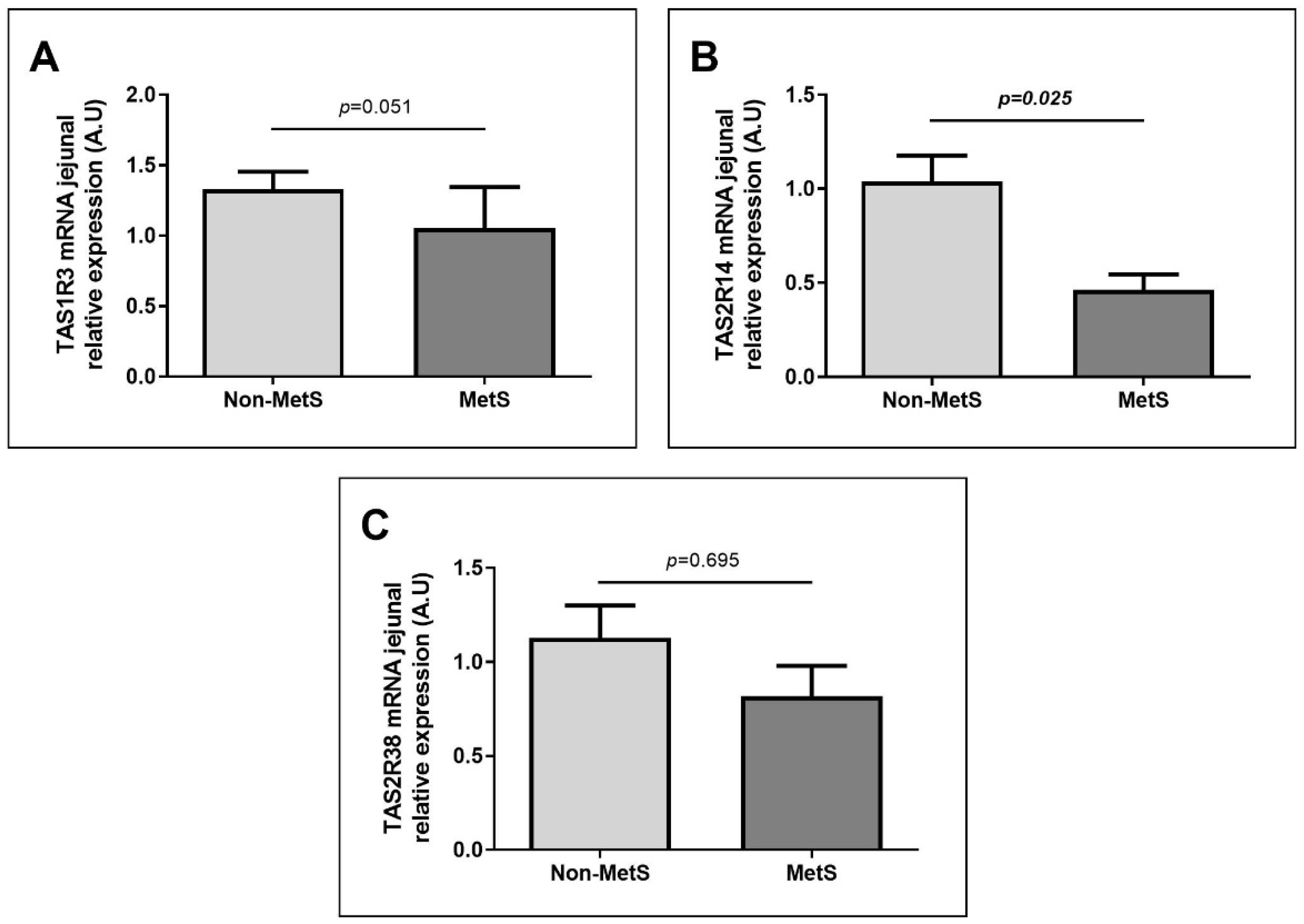
2.2. Nutrient Taste Receptors Expression in Jejunum According to Metabolic Diseases
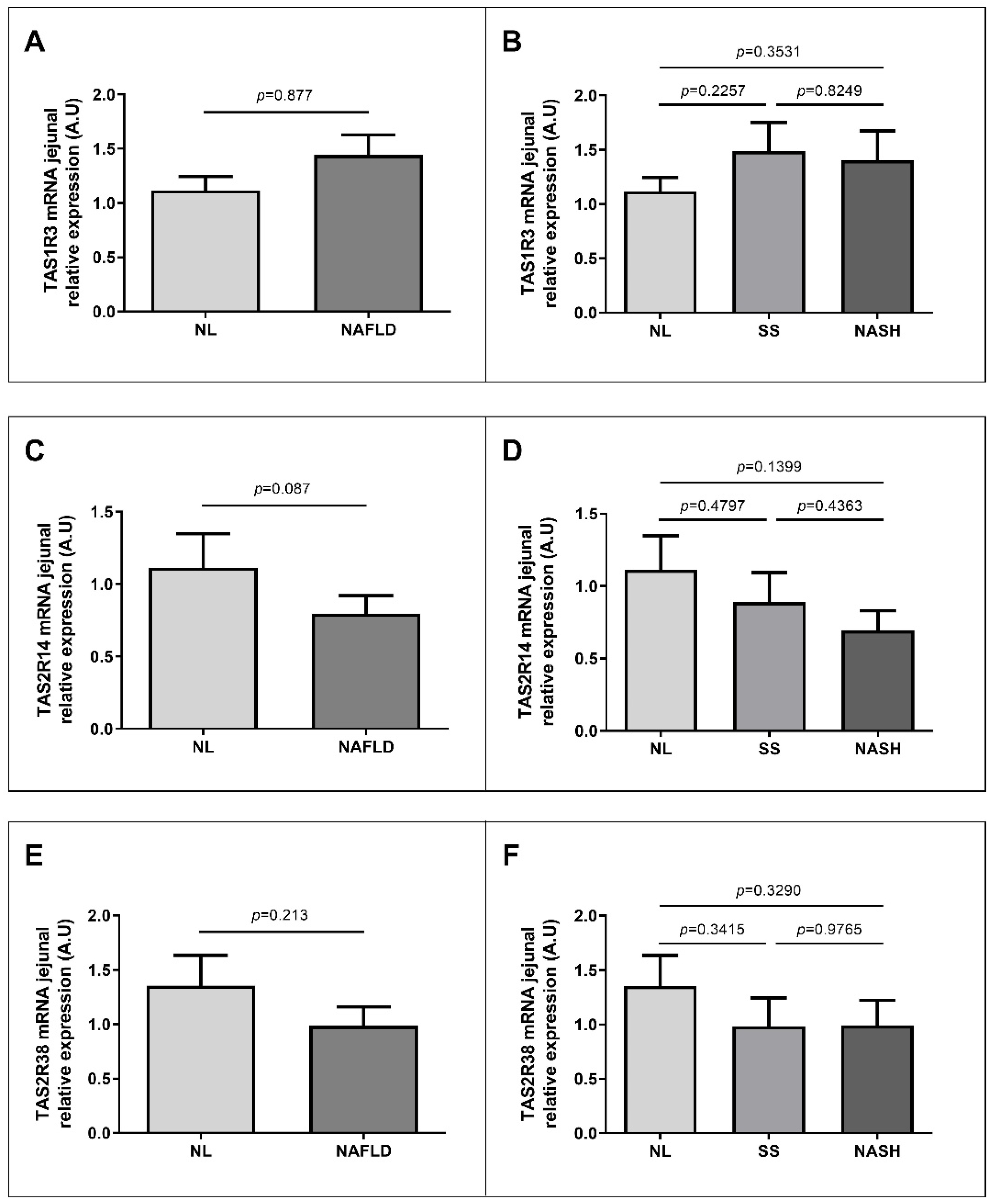
2.3. Nutrient Taste Receptors Expression in Jejunum According to NAFLD Classification
2.4. Correlations between TAS Jejunal Expressions and Other Biochemical Parameters and Genes Related to Lipid Metabolism
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Subjects
4.2. Sample Size
4.3. Biochemical Analyses
4.4. Jejunal Gene Expression
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saklayen, M.G. The Global Epidemic of the Metabolic Syndrome. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2018, 20, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pérez-Martínez, P.; Mikhailidis, D.P.; Athyros, V.G.; Bullo, M.; Couture, P.; Covas, M.I.; de Koning, L.; Delgado-Lista, J.; Díaz-López, A.; Drevon, C.A.; et al. Lifestyle Recommendations for the Prevention and Management of Metabolic Syndrome: An International Panel Recommendation. Nutr. Rev. 2017, 75, 307–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yubero-Serrano, E.M.; Delgado-Lista, J.; Peña-Orihuela, P.; Perez-Martinez, P.; Fuentes, F.; Marin, C.; Tunez, I.; Jose Tinahones, F.; Perez-Jimenez, F.; Roche, H.M.; et al. Oxidative Stress Is Associated with the Number of Components of Metabolic Syndrome: LIPGENE Study. Exp. Mol. Med. 2013, 45, e28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Furukawa, S.; Fujita, T.; Shimabukuro, M.; Iwaki, M.; Yamada, Y.; Nakajima, Y.; Nakayama, O.; Makishima, M.; Matsuda, M.; Shimomura, I. Increased Oxidative Stress in Obesity and Its Impact on Metabolic Syndrome. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 114, 1752–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grundy, S.M.; Brewer, H.B.; Cleeman, J.I.; Smith, S.C.; Lenfant, C. Definition of Metabolic Syndrome: Report of the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute/American Heart Association Conference on Scientific Issues Related to Definition. Circulation 2004, 109, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hrncir, T.; Hrncirova, L.; Kverka, M.; Hromadka, R.; Machova, V.; Trckova, E.; Kostovcikova, K.; Kralickova, P.; Krejsek, J.; Tlaskalova-Hogenova, H. Gut Microbiota and NAFLD: Pathogenetic Mechanisms, Microbiota Signatures, and Therapeutic Interventions. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manne, V.; Handa, P.; Kowdley, K.V. Pathophysiology of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease/Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Clin. Liver Dis. 2018, 22, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, A.R.; Rosso, N.; Bedogni, G.; Tiribelli, C.; Bellentani, S. Global Epidemiology of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease/Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis: What We Need in the Future. Liver Int. 2018, 38, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chalasani, N.; Younossi, Z.; Lavine, J.E.; Charlton, M.; Cusi, K.; Rinella, M.; Harrison, S.A.; Brunt, E.M.; Sanyal, A.J. The Diagnosis and Management of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Practice Guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2018, 67, 328–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blachier, M.; Leleu, H.; Peck-Radosavljevic, M.; Valla, D.-C.; Roudot-Thoraval, F. The Burden of Liver Disease in Europe: A Review of Available Epidemiological Data. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 593–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohen, J.C.; Horton, J.D.; Hobbs, H.H. Human Fatty Liver Disease: Old Questions and New Insights. Science 2011, 332, 1519–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Duseja, A.; Dhiman, R.K.; Premkumar, M. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Lessons Learnt in the Last Five Years. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2021, 11, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Ding, Z.; Ishaq, M.; Bacha, A.S.; Khan, I.; Hanif, A.; Li, W.; Guo, X. Understanding the Effects of Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and the Possible Probiotics Role: Recent Updates. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 818–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croci, S.; D’Apolito, L.I.; Gasperi, V.; Catani, M.V.; Savini, I. Dietary Strategies for Management of Metabolic Syndrome: Role of Gut Microbiota Metabolites. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minihane, A.M.; Vinoy, S.; Russell, W.R.; Baka, A.; Roche, H.M.; Tuohy, K.M.; Teeling, J.L.; Blaak, E.E.; Fenech, M.; Vauzour, D.; et al. Low-Grade Inflammation, Diet Composition and Health: Current Research Evidence and Its Translation. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 114, 999–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delli Bovi, A.P.; Marciano, F.; Mandato, C.; Siano, M.A.; Savoia, M.; Vajro, P. Oxidative Stress in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. An Updated Mini Review. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 595371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezzaidi, N.; Zhang, X.; Coker, O.O.; Yu, J. New Insights and Therapeutic Implication of Gut Microbiota in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Its Associated Liver Cancer. Cancer Lett. 2019, 459, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohórquez, D.V.; Liddle, R.A. The Gut Connectome: Making Sense of What You Eat. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 888–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeruzal-Świątecka, J.; Fendler, W.; Pietruszewska, W. Clinical Role of Extraoral Bitter Taste Receptors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaggupilli, A.; Singh, N.; Upadhyaya, J.; Sikarwar, A.S.; Arakawa, M.; Dakshinamurti, S.; Bhullar, R.P.; Duan, K.; Chelikani, P. Analysis of the Expression of Human Bitter Taste Receptors in Extraoral Tissues. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2017, 426, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesta, D.H.; Samuel, V.T. A High-Protein Diet for Reducing Body Fat: Mechanisms and Possible Caveats. Nutr. Metab. 2014, 11, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Turner, A.; Veysey, M.; Keely, S.; Scarlett, C.J.; Lucock, M.; Beckett, E.L. Intense Sweeteners, Taste Receptors and the Gut Microbiome: A Metabolic Health Perspective. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, R.L.; Sutherland, K.; Pezos, N.; Brierley, S.M.; Horowitz, M.; Rayner, C.K.; Blackshaw, L.A. Expression of Taste Molecules in the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract in Humans with and without Type 2 Diabetes. Gut 2009, 58, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raka, F.; Farr, S.; Kelly, J.; Stoianov, A.; Adeli, K. Metabolic Control via Nutrient-Sensing Mechanisms: Role of Taste Receptors and the Gut-Brain Neuroendocrine Axis. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 317, E559–E572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, S.; Depoortere, I. Nutrient Sensing in the Gut: New Roads to Therapeutics? Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 24, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirazi-Beechey, S.P.; Daly, K.; Al-Rammahi, M.; Moran, A.W.; Bravo, D. Role of Nutrient-Sensing Taste 1 Receptor (T1R) Family Members in Gastrointestinal Chemosensing. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 111, S8–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meyerhof, W.; Batram, C.; Kuhn, C.; Brockhoff, A.; Chudoba, E.; Bufe, B.; Appendino, G.; Behrens, M. The Molecular Receptive Ranges of Human TAS2R Bitter Taste Receptors. Chem. Senses 2010, 35, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Wang, X.; Young, R.L.; Horowitz, M.; Rayner, C.K.; Wu, T. Role of Intestinal Bitter Sensing in Enteroendocrine Hormone Secretion and Metabolic Control. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, H.; Hui, H.; Morvaridi, S.; Cai, J.; Zhang, S.; Tan, J.; Wu, V.; Levin, N.; Knudsen, B.; Goddard, W.A.; et al. A Bitter Pill for Type 2 Diabetes? The Activation of Bitter Taste Receptor TAS2R38 Can Stimulate GLP-1 Release from Enteroendocrine L-Cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 475, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le Nevé, B.; Foltz, M.; Daniel, H.; Gouka, R. The Steroid Glycoside H.g.-12 from Hoodia Gordonii Activates the Human Bitter Receptor TAS2R14 and Induces CCK Release from HuTu-80 Cells. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2010, 299, G1368–G1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, K.G.M.M.; Eckel, R.H.; Grundy, S.M.; Zimmet, P.Z.; Cleeman, J.I.; Donato, K.A.; Fruchart, J.-C.; James, W.P.T.; Loria, C.M.; Smith, S.C. Harmonizing the Metabolic Syndrome: A Joint Interim Statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; and International Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation 2009, 120, 1640–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nelson, G.; Hoon, M.A.; Chandrashekar, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ryba, N.J.P.; Zuker, C.S. Mammalian Sweet Taste Receptors. Cell 2001, 106, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Depoortere, I. Taste Receptors of the Gut: Emerging Roles in Health and Disease. Gut 2014, 63, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Liszt, K.I.; Depoortere, I. Extra-Oral Bitter Taste Receptors: New Targets against Obesity? Peptides 2020, 127, 170284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezencon, C.; le Coutre, J.; Damak, S. Taste-Signaling Proteins Are Coexpressed in Solitary Intestinal Epithelial Cells. Chem. Senses 2007, 32, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Janssen, S.; Laermans, J.; Verhulst, P.-J.; Thijs, T.; Tack, J.; Depoortere, I. Bitter Taste Receptors and α-Gustducin Regulate the Secretion of Ghrelin with Functional Effects on Food Intake and Gastric Emptying. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 2094–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kok, B.P.; Galmozzi, A.; Littlejohn, N.K.; Albert, V.; Godio, C.; Kim, W.; Kim, S.M.; Bland, J.S.; Grayson, N.; Fang, M.; et al. Intestinal Bitter Taste Receptor Activation Alters Hormone Secretion and Imparts Metabolic Benefits. Mol. Metab. 2018, 16, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widmayer, P.; Küper, M.; Kramer, M.; Königsrainer, A.; Breer, H. Altered Expression of Gustatory-Signaling Elements in Gastric Tissue of Morbidly Obese Patients. Int. J. Obes. 2012, 36, 1353–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Esser, N.; Legrand-Poels, S.; Piette, J.; Scheen, A.J.; Paquot, N. Inflammation as a Link between Obesity, Metabolic Syndrome and Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2014, 105, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Engin, A. The Pathogenesis of Obesity-Associated Adipose Tissue Inflammation. Obes. Lipotoxicity 2017, 960, 221–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschöp, M.; Smiley, D.L.; Heiman, M.L. Ghrelin Induces Adiposity in Rodents. Nature 2000, 407, 908–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, J.; Oliver, P.; Palou, A.; Picó, C. The Inhibition of Gastric Ghrelin Production by Food Intake in Rats Is Dependent on the Type of Macronutrient. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 5049–5055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yajima, H.; Ikeshima, E.; Shiraki, M.; Kanaya, T.; Fujiwara, D.; Odai, H.; Tsuboyama-Kasaoka, N.; Ezaki, O.; Oikawa, S.; Kondo, K. Isohumulones, Bitter Acids Derived from Hops, Activate Both Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor α and γ and Reduce Insulin Resistance. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 33456–33462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Compare, D.; Coccoli, P.; Rocco, A.; Nardone, O.M.; De Maria, S.; Cartenì, M.; Nardone, G. Gut–Liver Axis: The Impact of Gut Microbiota on Non Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2012, 22, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragonès, G.; Colom-Pellicer, M.; Aguilar, C.; Guiu-Jurado, E.; Martínez, S.; Sabench, F.; Antonio Porras, J.; Riesco, D.; Del Castillo, D.; Richart, C.; et al. Circulating Microbiota-Derived Metabolites: A “liquid Biopsy”? Int. J. Obes. 2020, 44, 875–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miura, K. Role of Gut Microbiota and Toll-like Receptors in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 7381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunt, E.M.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A. Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: A Proposal for Grading and Staging the Histological Lesions. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1999, 94, 2467–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variables | Non-MetS | MetS |
|---|---|---|
| (n = 45) | (n = 24) | |
| Weight (kg) | 117.00 (108.00–128.50) | 112.00 (105.48–125.50) |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 44.14 (41.34–46.63) | 42.64 (40.67–46.24) |
| SBP (mmHg) | 114.39 ± 13.86 | 124.00 ± 16.55 * |
| DBP (mmHg) | 62.50 (59.00–71.25) | 63.50 (56.50–74.75) |
| HOMA2-IR | 1.10 (0.79–1.66) | 1.35(0.77–3.57) |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 85.00 (76.00–93.00) | 100.50 (89.75–109.00) * |
| Insulin (mUI/L) | 8.49 (6.00–13.25) | 10.22 (5.68–32.41) |
| TG (mg/dL) | 106.00 (77.50–132.00) | 168.50 (124.00–232.25) * |
| Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 168.72 ± 33.02 | 186.58 ± 41.65 |
| LDL-C (mg/dL) | 102.37 ± 25.79 | 110.68 ± 33.98 |
| HDL-C (mg/dL) | 43.44 ± 11.93 | 37.77 ± 7.26 |
| AST (UI/L) | 19.50 (15.25–30.75) | 33.00 (20.75–45.75) * |
| ALT (UI/L) | 23.00 (17.00–34.50) | 34.00 (23.00–43.00) |
| GGT (UI/L) | 20.00 (14.50–27.00) | 22.00 (16.00–29.50) |
| ALP (Ul/L) | 66.48 ± 15.10 | 67.57 ± 12.07 |
| Variables | NL | NAFLD | SS | NASH |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (N = 28) | (N = 41) | (N = 24) | (N = 17) | |
| Weight (kg) | 116.50 (107.25–130.50) | 112.40 (106.00–128.00) | 113.20 (108.33–128.00) | 112.00 (104.65–125.00) |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 43.30 (40.94–46.47) | 44.46 (40.84–46.60) | 44.35 (40.82–46.83) | 44.46 (40.76–46.03) |
| SBP (mmHg) | 119.00 ± 18.26 | 117.29 ± 13.86 | 120.09 ± 13.41 | 113.44 ± 13.96 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 63.00 (57.75–75.75) | 62.00 (59.00–71.25) | 62.00 (59.00–72.50) | 65.50 (56.75–70.75) |
| HOMA2-IR | 1.23 (0.75–2.05) | 1.25 (0.79–2.18) | 1.49 (0.95–2.18) | 0.86 (0.61–3.00) |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 85.50 (76.25–93.00) | 93.00 (84.00–105.00) * | 93.50 (85.75–107.00) # | 91.00 (82.50–101.20) |
| Insulin (mUI/L) | 9.43 (5.59–16.21) | 9.63 (5.88–14.52) | 11.27 (7.81–14.51) | 6.57 (5.09–23.04) |
| TG (mg/dL) | 106.00 (89.00–136.00) | 132.00 (91.00–189.00) | 129.50 (85.75- 175.50) | 140.00 (106.00–247.00) |
| Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 171.88 ± 36.20 | 179.07 ± 38.80 | 174.42 ± 35.41 | 185.28 ± 43.39 |
| LDL-C (mg/dL) | 108.16 ± 27.94 | 104.48 ± 30.86 | 104.39 ± 31.21 | 104.62 ± 31.58 |
| HDL-C (mg/dL) | 40.84 ± 9.89 | 41.04 ± 10.95 | 42.56 ± 12.38 | 38.89 ± 8.47 |
| AST (UI/L) | 20.50 (15.75–36.25) | 23.50 (17.00–41.75) | 23.00 (17.00–35.00) | 24.00 (17.00–43.00) |
| ALT (UI/L) | 22.00 (16.00–27.00) | 31.00 (21.00–37.00) | 31.00 (23.00–35.75) # | 30.00 (15.50–40.00) |
| GGT (UI/L) | 18.00 (16.00–27.00) | 22.00 (16.00–27.00) | 21.00 (16.25–30.50) | 25.00 (15.00–27.00) |
| ALP (Ul/L) | 60.42 ± 13.09 | 70.67 ± 13.01 * | 75.80 ± 11.66 # | 62.77 ± 11.16 & |
| Variables | TAS1R3 JRE | TAS2R14 JRE | TAS2R38 JRE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glucose (mg/dL) | −0.414 * | ns | ns |
| TG (mg/dL) | −0.608 ** | ns | ns |
| JRE TLR4 | ns | 0.472 ** | ns |
| JRE TLR9 | ns | ns | −0.481 * |
| JRE PPAR-γ | ns | 0.364 * | ns |
| IL-6 (pg/mL) | ns | ns | −0.434 * |
| TLR4 (ng/mL) | ns | ns | 0.410 * |
| Ghrelin (ng/mL) | ns | −0.900 * | ns |
| IL-10 (pg/mL) | ns | 0.481 ** | ns |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bertran, L.; Portillo-Carrasquer, M.; Martínez, S.; Aguilar, C.; Lopez-Dupla, M.; Riesco, D.; Binetti, J.; Vives, M.; Sabench, F.; Del Castillo, D.; et al. Expression of Jejunal Taste Receptors in Women with Morbid Obesity. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2437. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13072437
Bertran L, Portillo-Carrasquer M, Martínez S, Aguilar C, Lopez-Dupla M, Riesco D, Binetti J, Vives M, Sabench F, Del Castillo D, et al. Expression of Jejunal Taste Receptors in Women with Morbid Obesity. Nutrients. 2021; 13(7):2437. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13072437
Chicago/Turabian StyleBertran, Laia, Marta Portillo-Carrasquer, Salomé Martínez, Carmen Aguilar, Miguel Lopez-Dupla, David Riesco, Jessica Binetti, Margarita Vives, Fàtima Sabench, Daniel Del Castillo, and et al. 2021. "Expression of Jejunal Taste Receptors in Women with Morbid Obesity" Nutrients 13, no. 7: 2437. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13072437
APA StyleBertran, L., Portillo-Carrasquer, M., Martínez, S., Aguilar, C., Lopez-Dupla, M., Riesco, D., Binetti, J., Vives, M., Sabench, F., Del Castillo, D., Richart, C., & Auguet, T. (2021). Expression of Jejunal Taste Receptors in Women with Morbid Obesity. Nutrients, 13(7), 2437. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13072437







