Individual Behavioral Reactions in the Context of Food Sensitivities in Children with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder before and after an Oligoantigenic Diet
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Measures
2.4. Anamnesis Concerning Food Sensitivity and Allergies in the Beginning
2.5. Conners’ Rating Scale
2.6. Nutrition and Behavior Diary
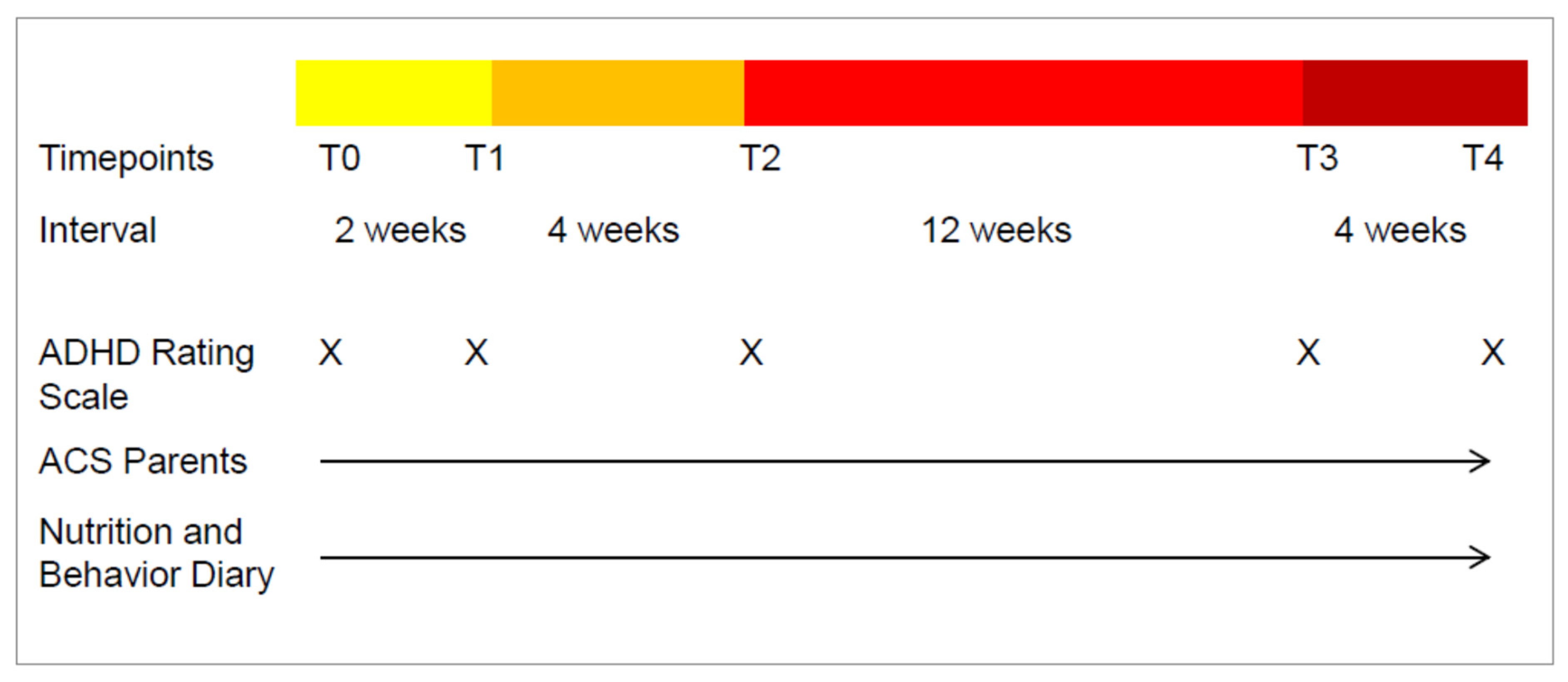
2.7. Procedure
2.8. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Participants
3.2. ADHD Symptoms According to ARS
3.3. Identified Food Sensitivity
3.4. Reactions to Intolerant Food after the OD
3.4.1. Example 1: Milk Products
3.4.2. Example 2: Corn
3.4.3. Example 3: Grain
3.5. Behavioral Reactions to Intolerant Foods before Starting the OD
3.6. Anamnestic Intolerance Prior to OD and Observed Sensitivity during Food Reintroduction
4. Discussion
Limitations and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Polanczyk, G.; de Lima, M.S.; Horta, B.L.; Biederman, J.; Rohde, L.A. The Worldwide Prevalence of ADHD: A Systematic Re-view and Metaregression Analysis. Am. J. Psychiatry 2007, 164, 942–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayal, K.; Prasad, V.; Daley, D.; Ford, T.; Coghill, D. ADHD in Children and Young People: Prevalence, Care Pathways, and Service Provision. Lancet Psychiatry 2018, 5, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, E.; Sergeant, J.; Asherson, P.; Banaschewski, T.; Buitelaar, J.; Coghill, D.; Danckaerts, M.; Rothenberger, A.; Sonuga-Barke, E.; Steinhausen, H.-C.; et al. European Clinical Guidelines for Hyperkinetic Disorder ? First Upgrade. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2004, 13, i7–i30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraone, S.V.; Perlis, R.H.; Doyle, A.E.; Smoller, J.W.; Goralnick, J.J.; Holmgren, M.A.; Sklar, P. Molecular Genetics of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 2005, 57, 1313–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khan, S.A.; Faraone, S.V. The Genetics of ADHD: A Literature Review of 2005. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2006, 8, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillis, J.J.; Gilger, J.W.; Pennington, B.F.; DeFries, J.C. Attention Deficit Disorder in Reading-Disabled Twins: Evidence for Ge-netic Etiology. J. Abnorm. Child Psychol. 1992, 20, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonuga-Barke, E.J.; Brandeis, D.; Cortese, S.; Daley, D.; Ferrin, M.; Holtmann, M.; Stevenson, J.; Danckaerts, M.; Van Der Oord, S.; Döpfner, M.; et al. Nonpharmacological Interventions for ADHD: Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses of Randomized Controlled Trials of Dietary and Psychological Treatments. Am. J. Psychiatry 2013, 170, 275–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Academy of Pediatrics. Wolraich ML, Hagan JF, Allan C, et al; Subcommittee on Children and Adolescents with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactive Disorder. Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis, Evaluation, and Treatment of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder in Children and Adolescents. Pediatrics 2020, 145, e20193997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, A.; Couture, J. A Review of the Pathophysiology, Etiology, and Treatment of Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). Ann. Pharmacother. 2014, 48, 209–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, W.R. Neuropathic Manifestations in Infants and Children as a Result of Anaphylactic Reaction to Foods Contained in Their Dietary. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 1922, 24, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Egger, J.; Graham, P.; Carter, C.; Gumley, D.; Soothill, J. Controlled Trial of Oligoantigenic Treatment in the HYPERKINETIC SYNDROME. Lancet 1985, 325, 540–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelsser, L.; Frankena, K.; Toorman, J.; Savelkoul, H.F.J.; Pereira, R.R.; Buitelaar, J.K. A Randomised Controlled Trial into the Effects of Food on ADHD. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2008, 18, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelsser, L.M.; Frankena, K.; Buitelaar, J.K.; Rommelse, N.N. Effects of Food on Physical and Sleep Complaints in Children with ADHD: A Randomised Controlled Pilot Study. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2010, 169, 1129–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pelsser, L.; Frankena, K.; Toorman, J.; Savelkoul, H.F.; Dubois, E.A.; Pereira, R.R.; Haagen, A.T.; Rommelse, N.N.; Buitelaar, J.K. Effects of a Restricted Elimination Diet on the Behaviour of Children with Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (INCA study): A Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet 2011, 377, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, B.J.; McNicol, J.; Conte, A.R.; Moghadam, H.K. Dietary replacement in preschool-aged hyperactive boys. Pediatrics 1989, 83, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carter, C.M.; Urbanowicz, M.; Hemsley, R.; Mantilla, L.; Strobel, S.; Graham, P.J.; Taylor, E. Effects of a Few Food Diet in Attention Deficit Disorder. Arch. Dis. Child. 1993, 69, 564–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCann, D.; Barrett, A.; Cooper, A.; Crumpler, D.; Dalen, L.; Grimshaw, K.; Kitchin, E.; Lok, K.Y.-W.; Porteous, L.; Prince, E.; et al. Food Additives and Hyperactive Behaviour in 3-Year-Old and 8/9-Year-Old Children in the Community: A Randomised, Double-Blinded, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Lancet 2007, 370, 1560–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boris, M.; Mandel, F.S. Foods and Additives are Common Causes of the Attention Deficit Hyperactive Disorder in Children. Ann. Allergy 1994, 72, 462–468. [Google Scholar]
- Rytter, M.J.H.; Andersen, L.B.B.; Houmann, T.; Bilenberg, N.; Hvolby, A.; Mølgaard, C.; Michaelsen, K.F.; Lauritzen, L. Diet in the Treatment of ADHD in Children—A Systematic Review of the Literature. Nord. J. Psychiatry 2014, 69, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hill, P. Current Topic: An Auditable Protocol for Treating Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. Arch. Dis. Child. 2001, 84, 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pelsser, L.; Frankena, K.; Toorman, J.; Pereira, R.R. Diet and ADHD, Reviewing the Evidence: A Systematic Review of Meta-Analyses of Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Trials Evaluating the Efficacy of Diet Interventions on the Behavior of Children with ADHD. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dölp, A.; Schneider-Momm, K.; Heiser, P.; Clement, C.; Rauh, R.; Clement, H.-W.; Schulz, E.; Fleischhaker, C. Oligoantigenic Diet Improves Children’s ADHD Rating Scale Scores Reliably in Added Video-Rating. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, W.J.; Puig-Antich, J.; Hirsch, M.; Paez, P.; Ambrosini, P.J.; Tabrizi, M.A.; Davies, M. The Assessment of Affective Dis-Orders in Children and Adolescents by Semistructured Interview. Test-Retest Reliability of the Schedule for Affective Disorders and Schizophrenia for School-Age Children, Present Episode Version. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1985, 42, 696–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupaul, G.J. Parent and Teacher Ratings of ADHD Symptoms: Psychometric Properties in a Community-Based Sample. J. Clin. Child Psychol. 1991, 20, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupaul, G.J.; Reid, R.; Anastopoulos, A.D.; Lambert, M.C.; Watkins, M.W.; Power, T.J. Parent and Teacher Ratings of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder Symptoms: Factor Structure and Normative Data. Psychol. Assess. 2016, 28, 214–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anastopoulos, A.D.; Beal, K.K.; Reid, R.J.; Reid, R.; Power, T.J.; Dupaul, G.J. Impact of Child and Informant Gender on Parent and Teacher Ratings of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. Psychol. Assess. 2018, 30, 1390–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storebø, O.J.; Ramstad, E.; Krogh, H.B.; Nilausen, T.D.; Skoog, M.; Holmskov, M.; Rosendal, S.; Groth, C.; Magnusson, F.L.; Moreira-Maia, C.R.; et al. Methylphenidate for Children and Adolescents with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, CD009885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mercier, C.; Roche, S.; Gaillard, S.; Kassai, B.; Arzimanoglou, A.; Herbillon, V.; Roy, P.; Rheims, S. Partial Validation of a French Version of the ADHD-Rating Scale IV on a French Population of Children with ADHD and Epilepsy. Factorial Structure, Reliability, and Responsiveness. Epilepsy Behav. 2016, 58, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Faries, D.; Vowles, M.; Michelson, D. ADHD Rating Scale IV: Psychometric Properties from a Multinational Study as Clinician-Administered Instrument. Int. J. Methods Psychiatr. Res. 2005, 14, 186–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandre, J.L.; Lange, A.-M.; Bilenberg, N.; Gorrissen, A.M.; Søbye, N.; Lambek, R. The ADHD Rating Scale-IV Preschool Version: Factor Structure, Reliability, Validity, and Standardisation in a Danish Community Sample. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2018, 78, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richarte, V.; Corrales, M.; Pozuelo, M.; Serra-Pla, J.; Ibáñez, P.; Calvo, E.; Corominas, M.; Bosch, R.; Casas, M.; Ramos-Quiroga, J.A. Spanish Validation of the Adult Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder Rating Scale (ADHD-RS): Relevance of clinical subtypes. Rev. Psiquiatr. Salud Ment. 2017, 10, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittchen, H.-U.; Zaudig, M.; Fydrich, T. SKID Strukturiertes Klinisches Interview für DSM-IV. Achse I und II. Göttingen: Hogrefe. Zeitschrift für klinische Psychologie und Psychotherapie. 1999. Available online: https://econtent.hogrefe.com/doi/10.1026//0084-5345.28.1.68 (accessed on 27 July 2021).
- DuPaul, G.J.; Power, T.J.; Anastopoulos, A.D.; Reid, R. ADHD Rating Scale—IV: Checklists, Norms, and Clinical Interpretation; Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 1998; pp. 1–80. [Google Scholar]
- Conners, C.K.; Goyette, C.H.; Southwick, D.A.; Lees, J.M.; Andrulonis, P.A. Food additives and hyperkinesis: A controlled double-blind experiment. Pediatrics 1976, 58, 154–166. [Google Scholar]
- Koerner, U.; Schareina, A. Nahrungsmittelallergien und -Unverträglichkeiten. In Diagnostik, Therapie und Beratung; Haug: Stuttgart, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Lidzba, K.; Christiansen, H.; Drechsler, R. Conners 3: Conners Skalen zur Aufmerksamkeit und Verhalten-3: Deutschsprachige Adaptation der Conners 3rd Edition (Conners 3) von C. Keith Conners: Manual (K. Conners, Hrsg.); Hans Huber: Bern, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Pelsser, L.M.; Van Steijn, D.J.; Frankena, K.; Toorman, J.; Buitelaar, J.K.; Rommelse, N.N. A Randomized Controlled Pilot Study into the Effects of a Restricted Elimination Diet on Family Structure in Families with ADHD and ODD. Child. Adolesc. Ment. Health 2012, 18, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiedl, S. Duodenale VIP-Rezeptoren in der Dünndarmmukosa bei Kindern mit Nahrungsmittelinduziertem Hyperkinetischen Syndrom. Zur Erlangung des Medizinischen Doktorgrades; Ludwig-Maximillians-Universität München: München, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Endreffy, I.; Bjørklund, G.; Urbina, M.A.; Chirumbolo, S.; Doşa, M.D.; Dicső, F. High Levels of Glycosaminoglycans in the Urines of Children with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). J. Mol. Neurosci. 2020, 70, 1018–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alabaf, S.; Gillberg, C.; Lundström, S.; Lichtenstein, P.; Kerekes, N.; Rastam, M.; Anckarsäter, H. Physical Health in Children with Neurodevelopmental Disorders. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2019, 49, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niederhofer, H. Association of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder and Celiac Disease: A Brief Report. Prim. Care Companion CNS Disord. 2011, 13, e1–e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aarts, E.; Ederveen, T.; Naaijen, J.; Zwiers, M.P.; Boekhorst, J.; Timmerman, H.M.; Smeekens, S.P.; Netea, M.G.; Buitelaar, J.K.; Franke, B.; et al. Gut Microbiome in ADHD and Its Relation to Neural Reward Anticipation. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiergeist, A.; Gessner, J.; Gessner, A. Current Limitations for the Assessment of the Role of the Gut Microbiome for Attention Deficit Hyperactivitiy Disorder (ADHD). Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schink, M.; Konturek, P.C.; Tietz, E.; Dieterich, W.; Pinzer, T.C.; Wirtz, S.; Neurath, M.F.; Zopf, Y. Microbial Patterns in Patients with Histamine Intolerance. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2018, 69, 579–593. [Google Scholar]
- Barko, P.; McMichael, M.; Swanson, K.; Williams, D. The Gastrointestinal Microbiome: A Review. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2017, 32, 9–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumperscak, H.G.; Gricar, A.; Ülen, I.; Micetic-Turk, D. A Pilot Randomized Control Trial with the Probiotic Strain Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG) in ADHD: Children and Adolescents Report Better Health-Related Quality of Life. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.-W.; Liong, M.T.; Chung, Y.-C.E.; Huang, H.-Y.; Peng, W.-S.; Cheng, Y.-F.; Lin, Y.-S.; Wu, Y.-Y.; Tsai, Y.-C. Effects of Lactobacillus Plantarum PS128 on Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder in Taiwan: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2019, 11, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dieterich, W.; Tietz, E.; Kohl, M.; Konturek, P.C.; Rath, T.; Neurath, M.F.; Zopf, Y. Food Intolerance of Unknown Origin: Caused by Mucosal Inflammation? A Pilot Study. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2021, 12, e00312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farin, H.F.; Karthaus, W.R.; Kujala, P.; Rakhshandehroo, M.; Schwank, G.; Vries, R.G.; Kalkhoven, E.; Nieuwenhuis, E.E.; Clevers, H. Paneth Cell Extrusion and Release of Antimicrobial Products is Directly Controlled by Immune Cell–Derived IFN-γ. J. Exp. Med. 2014, 211, 1393–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevenson, J.; Buitelaar, J.; Cortese, S.; Ferrin, M.; Konofal, Éric; Lecendreux, M.; Simonoff, E.; Wong, I.C.K.; Sonuga-Barke, E.; The European ADHD Guidelines Group. Research Review: The Role of Diet in the Treatment of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder-An Appraisal of the Evidence on Efficacy and Recommendations on the Design of Future Studies. J. Child. Psychol. Psychiatry 2014, 55, 416–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Included (n) | 16 out of 28 |
| Age (means ± SD (range)) | 9.25 ± 1.73 (7–13) |
| Gender (m/f) | 13/3 |
| Subtypes c/hi/i (n = 28) Responder (n = 16) | 16/10/2 9//6/1 |
| Comorbidity | Dyslexia (F81.0, n = 6) Dyscalculia (F81.2, n = 2) Oppositional Defiant Disorder (F91.3, F91.8, n = 2) Autism (F84.0, n = 2) diagnosed in the course of the study Encopresis (F98.1, n = 1) |
| Dropped out (n) | 12 out of 28 |
| Age (means ± SD (range)) | 10.5 ± 1.86 (8–14) |
| Gender (m/f) | 9/3 |
| Day | M | SD | t(4) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| dE | −3.40 | 0.89 | −8.50 | 0.001 |
| dE + 1 | 1.40 | 2.30 | 1.36 | 0.246 |
| dE + 2 | 3.60 | 4.83 | 1.67 | 0.171 |
| dE + 3 | 2.00 | 6.16 | 0.73 | 0.508 |
| Day | M | SD | t(5) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| dE | 8.17 | 4.36 | 4.59 | 0.006 |
| dE + 1 | 5.83 | 2.32 | 6.17 | 0.002 |
| dE + 2 | 4.17 | 5.74 | 1.78 | 0.136 |
| dE + 3 | 7.67 | 7.34 | 2.56 | 0.051 |
| Day | M | SD |
|---|---|---|
| dE | −2.0 | 0 |
| dE + 1 | 11.0 | 5.66 |
| dE + 2 | 5.5 | 6.36 |
| dE + 3 | 0 | 2.83 |
| Day | M | SD | t(4) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| dE | 4.40 | 4.83 | 2.04 | 0.111 |
| dE + 1 | 7.80 | 3.42 | 5.10 | 0.007 |
| dE + 2 | 6.80 | 5.40 | 2.81 | 0.048 |
| dE + 3 | 7.40 | 8.68 | 1.91 | 0.129 |
| Day | M | SD | t(5) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| dE | 4.83 | 4.67 | 2.54 | 0.052 |
| dE + 1 | 3.17 | 2.14 | 3.63 | 0.015 |
| dE + 2 | 2.33 | 1.63 | 3.50 | 0.017 |
| dE + 3 | 1.00 | 2.10 | 1.17 | 0.296 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yorgidis, E.; Beiner, L.; Blazynski, N.; Schneider-Momm, K.; Clement, H.-W.; Rauh, R.; Schulz, E.; Clement, C.; Fleischhaker, C. Individual Behavioral Reactions in the Context of Food Sensitivities in Children with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder before and after an Oligoantigenic Diet. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2598. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13082598
Yorgidis E, Beiner L, Blazynski N, Schneider-Momm K, Clement H-W, Rauh R, Schulz E, Clement C, Fleischhaker C. Individual Behavioral Reactions in the Context of Food Sensitivities in Children with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder before and after an Oligoantigenic Diet. Nutrients. 2021; 13(8):2598. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13082598
Chicago/Turabian StyleYorgidis, Elena, Lisa Beiner, Nicola Blazynski, Katja Schneider-Momm, Hans-Willi Clement, Reinhold Rauh, Eberhard Schulz, Christina Clement, and Christian Fleischhaker. 2021. "Individual Behavioral Reactions in the Context of Food Sensitivities in Children with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder before and after an Oligoantigenic Diet" Nutrients 13, no. 8: 2598. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13082598
APA StyleYorgidis, E., Beiner, L., Blazynski, N., Schneider-Momm, K., Clement, H.-W., Rauh, R., Schulz, E., Clement, C., & Fleischhaker, C. (2021). Individual Behavioral Reactions in the Context of Food Sensitivities in Children with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder before and after an Oligoantigenic Diet. Nutrients, 13(8), 2598. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13082598






