Novel Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptides Identified from Walnut Glutelin-1 Hydrolysates: Molecular Interaction, Stability, and Antihypertensive Effects
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Glutelin-1 in Degreased Walnut Meal
2.3. Preparation of Glutelin-1 Hydrolysate
2.4. Separation and Purification of the ACE-Inhibitory Peptides from Glutelin-1 Hydrolysate
2.5. Amino Acid Sequence Analysis of the Purified Peptides
2.6. Commercially Synthesis of the Identified Peptides
2.7. Determination of ACE Inhibitory Activity
2.8. Molecular Docking
2.9. Antihypertensive Effect in SHR
2.9.1. BP Measurement
2.9.2. Assay for Serum ET-1, NO, ACE, Ang II, AGT, and ALD in SHR Rats
2.10. Stability of the Synthetic Peptides
2.10.1. GI Digestion Stability Analysis of the Synthesized Peptides
2.10.2. Temperature, pH, Metal Ion, Sugar, and Salt Treatments Stabilities of the Synthesized Peptides
2.11. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
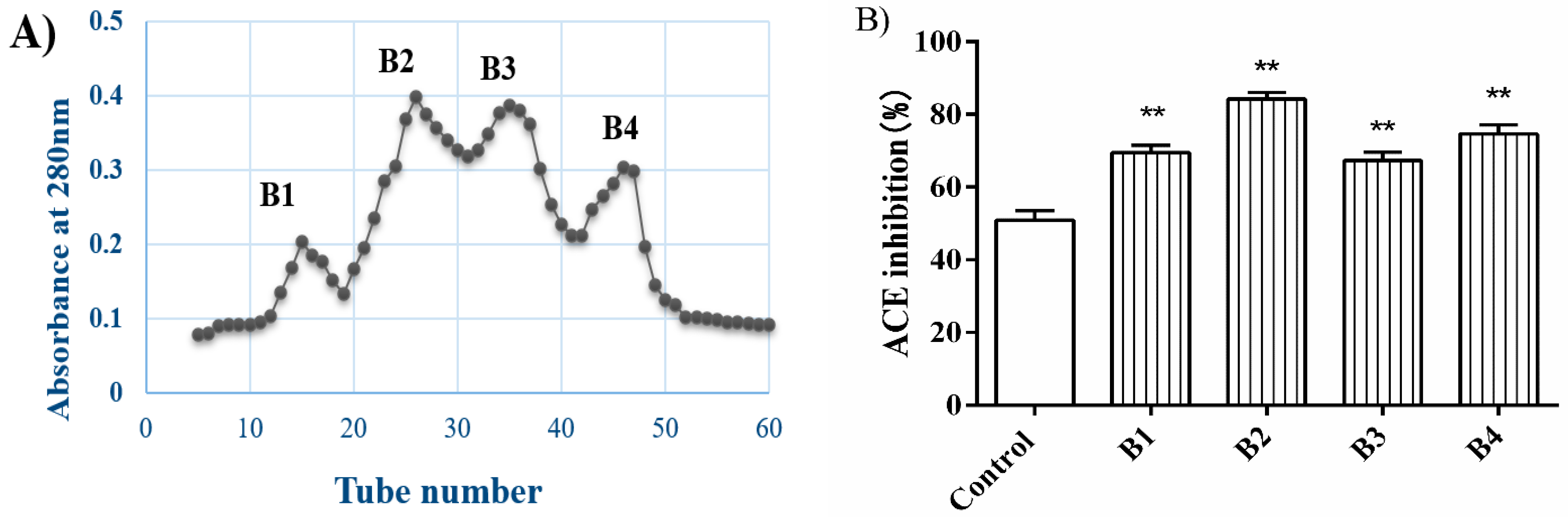
3.1. Isolation and Purification of ACE Inhibitory Peptides of Glutelin-1 Hydrolysate
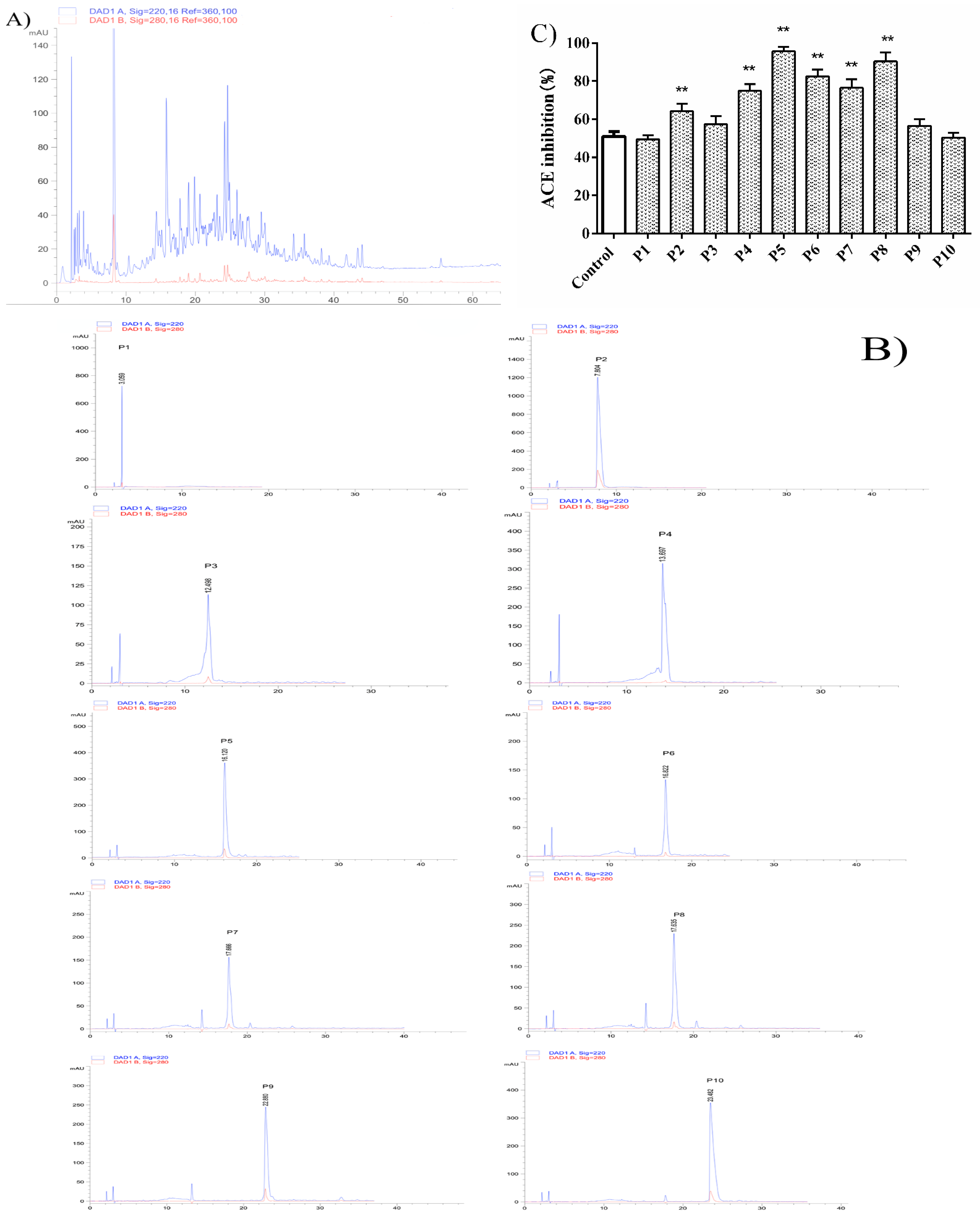
3.2. Peptide Identification and Synthesis
3.3. Molecular Docking Simulation
3.4. Antihypertensive Effect in SHR
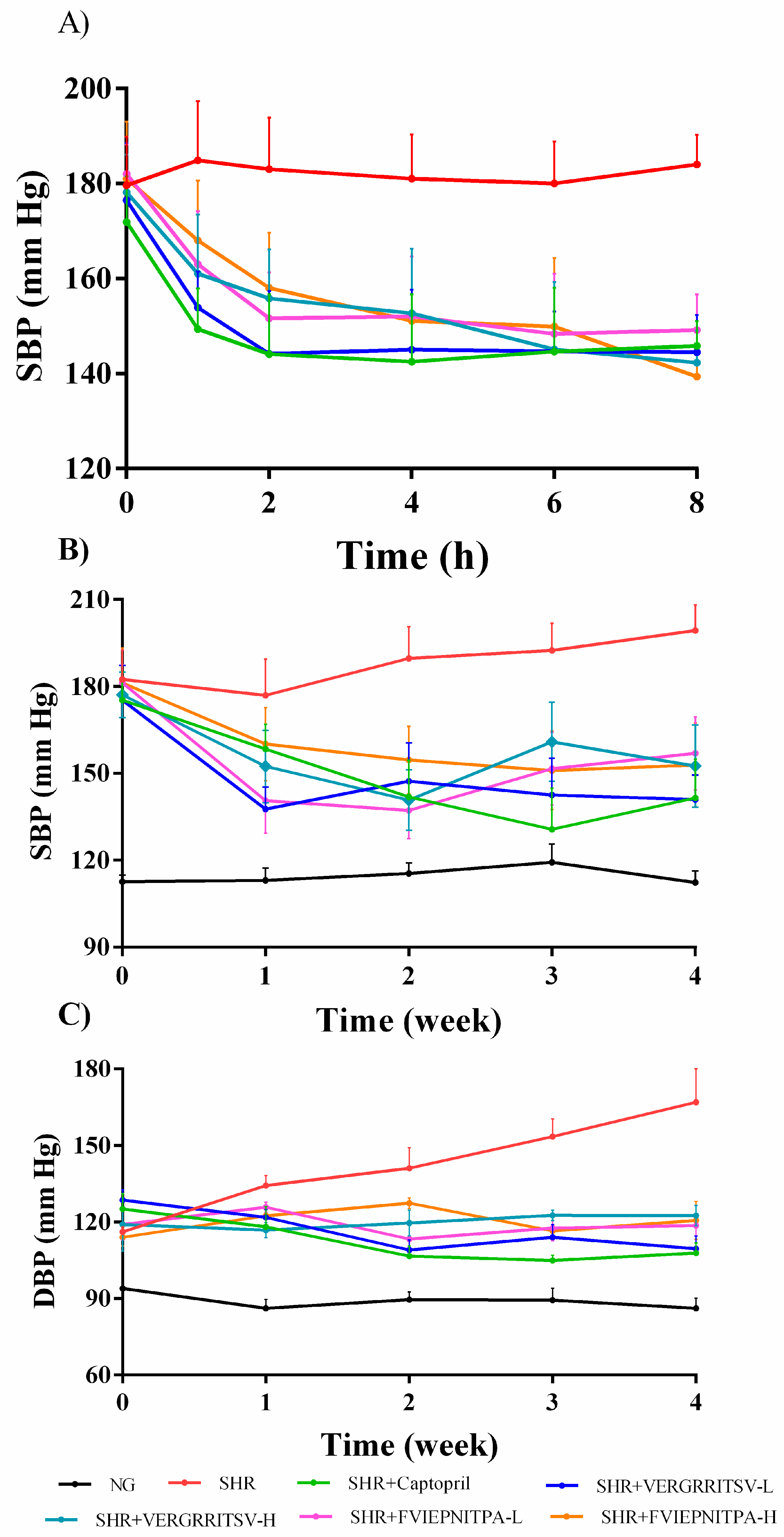
3.4.1. Effect of Oral Administration of Glutelin-1 ACE Inhibitory Peptide on SBP and DBP in SHR
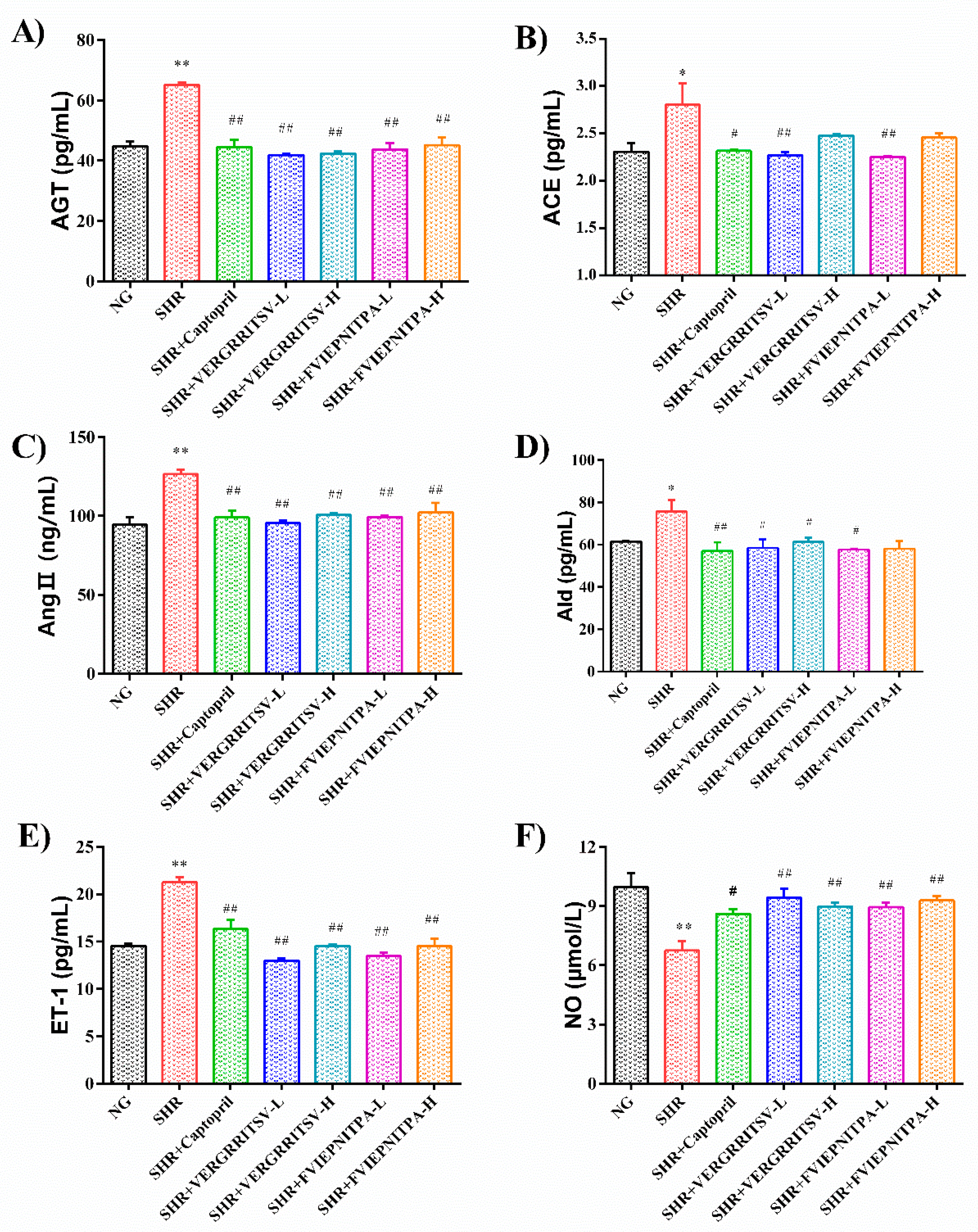
3.4.2. Effects of Glutelin-1 ACE Inhibitory Peptide on Serum ACE, AngII, AGT, and ALD Levels in SHR
3.4.3. Effects of the ACE Inhibitory Peptide of Walnut Glutelin-1 on Serum ET-1 and NO Levels in SHR
3.5. Stability of Synthetic Peptides
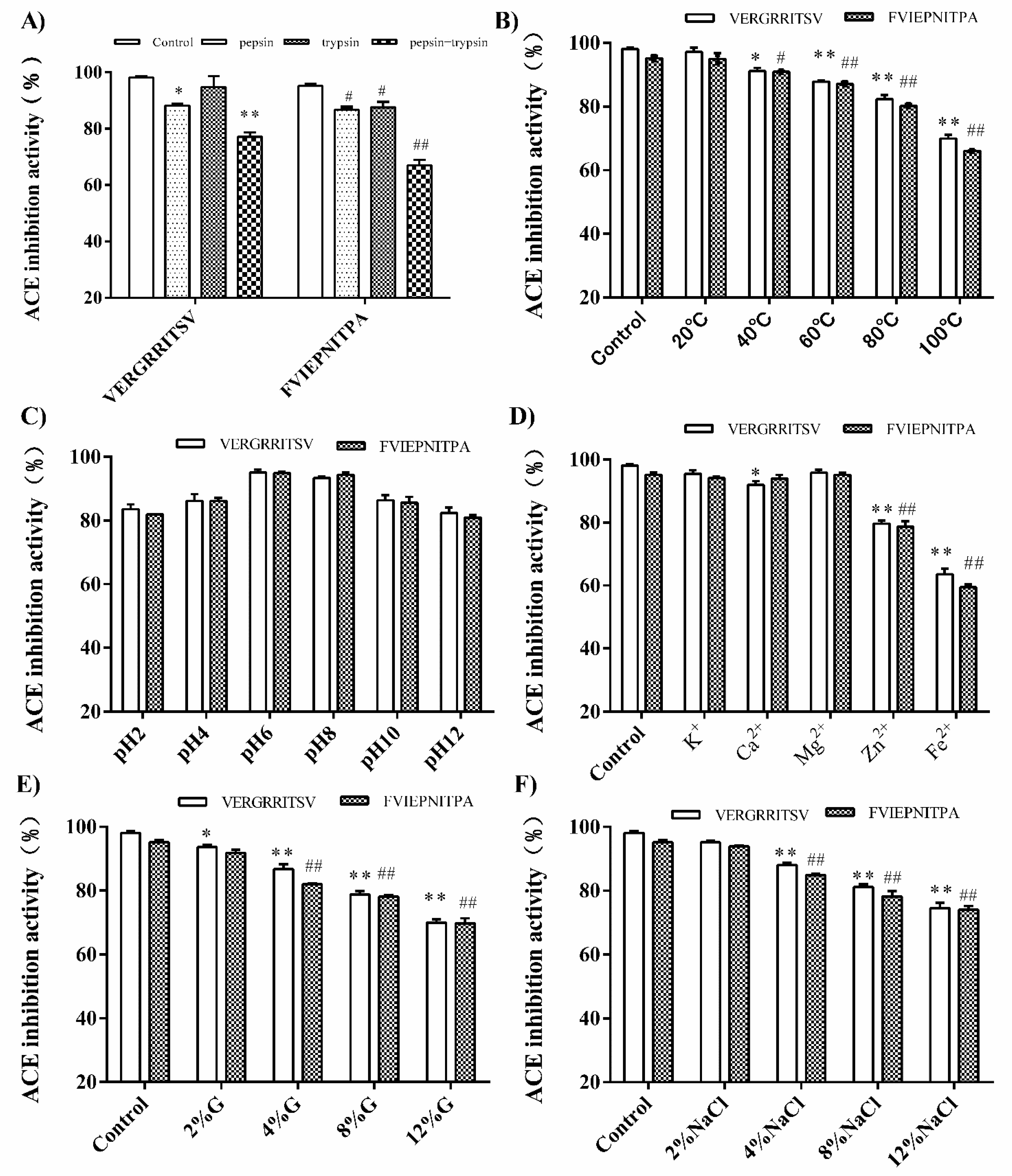
3.5.1. Effect of In Vitro GI Digestion
3.5.2. Effect of Temperature, pH, Metal Ion, Sugar, and Salt Treatments
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sze-Tao, K.W.C.; Sathe, S.K. Walnuts (Juglans regia L): Proximate composition, protein solubility, protein amino acid composition and protein in vitro digestibility. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2000, 80, 1393–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, D.; Zhang, F.; Lin, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, S.; Chen, C.; Wang, X.; Liu, J. Preventive effect of pressed degreased walnut meal extracts on T2DM rats by regulating glucolipid metabolism and modulating gut bacteria flora. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 64, 103694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, K.; Wu, J. Molecular Targets of Antihypertensive Peptides: Understanding the Mechanisms of Action Based on the Pathophysiology of Hypertension. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 16, 256–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, M.; Mirdamadi, S.; Safavi, M. Structural analysis of ACE-inhibitory peptide (VL-9) derived from Kluyveromyces marxianus protein hydrolysate. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1213, 128199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khueychai, S.; Jangpromma, N.; Choowongkomon, K.; Joompang, A.; Daduang, S.; Vesaratchavest, M.; Payoungkiattikun, W.; Tachibana, S.; Klaynongsruang, S. A novel ACE inhibitory peptide derived from alkaline hydrolysis of ostrich (Struthio camelus) egg white ovalbumin. Process Biochem. 2018, 73, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natesh, R.; Schwager, S.; Sturrock, E.; Acharya, K.R. Crystal structure of the human ace-lisinopril complex. Nature 2003, 421, 551–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDowell, S.; Coleman, J.; Ferner, R. Systematic review and meta-analysis of ethnic differences in risks of adverse drug reactions to drugs used in cardiovascular MEDICINE. BMJ 2006, 332, 1177–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asoodeh, A.; Homayouni-Tabrizi, M.; Shabestarian, H.; Emtenani, S.; Emtenani, S. Biochemical characterization of a novel antioxidant and angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptide from Struthio camelus egg white protein hydrolysis. J. Food Drug Anal. 2016, 24, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleh, A.; Zhang, Q.; Shen, Q. Recent Research in Antihypertensive Activity of Food Protein-derived Hydrolyzates and Peptides. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 56, 760–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonklin, C.; Alashi, M.A.; Laohakunjit, N.; Kerdchoechuen, O.; Aluko, R.E. Identification of antihypertensive peptides from mung bean protein hydrolysate and their effects in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 64, 103635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Chen, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Huang, W.; Yuan, Y.; Fang, M.; Xie, J.; Wei, D. Angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from Sipuncula (Phascolosoma esculenta): Purification, identification, molecular docking and antihypertensive effects on spontaneously hypertensive rats. Process Biochem. 2017, 63, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Chang, C.; Liu, H.; Li, B.; Yan, Q.; Jiang, Z. Identification of novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from wheat gluten hydrolysate by the protease of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 65, 103751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Wu, Q.; Yan, H.; Gui, Z. Purification and molecular docking study of a novel angiotensin-I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptide from alcalase hydrolysate of ultrasonic-pretreated silkworm pupa (Bombyx mori) protein. Process Biochem. 2015, 50, 876–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, M.; Wang, C.; Chen, C.; Zhang, R.; Liu, H.; Lu, W.; Jiang, L.; Du, M. Identification of a novel ACE-inhibitory peptide from casein and evaluation of the inhibitory mechanisms. Food Chem. 2018, 256, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Hur, S.J. Antihypertensive peptides from animal products, marine organisms, and plants. Food Chem. 2017, 228, 506–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-hamid, M.; Otte, J.; De Gobba, C.; Osman, A. Angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory activity and antioxidant capacity of bioactive peptides derived from enzymatic hydrolysis of buffalo milk proteins. Int. Dairy J. 2017, 66, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, L. Microfluidic paper-based chips in rapid detection: Current status, challenges, and perspectives. TrAC -Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 143, 116371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.J.; Yin, X.Y.; Regenstein, J.M.; Wang, J.Z. Separation and purification of angiotensin-I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from walnuts (Juglans regia L.) meal. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2016, 242, 911–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Song, W.; Jiang, L.; Du, M. Purification and identification of an ACE-inhibitory peptide from walnut protein hydrolysate. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2014, 239, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, G.; Chen, N.; An, F.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Rahman, M.U.; Zhang, Y. Characterization of structural, functional and antioxidant properties and amino acid composition of pepsin-derived glutelin-1 hydrolysate from walnut processing by-products. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 19158–19168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ruan, X.; Zhang, R. Purification, characterization, synthesis, in vitro ACE inhibition and in vivo antihypertensive activity of bioactive peptides derived from oil palm kernel glutelin-2 hydrolysates. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 28, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sadiq, F.A.; Fu, L.; Zhu, H.; Zhong, M.; Sohail, M. Identification of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides derived from enzymatic hydrolysates of razor clam Sinonovacula constricta. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhedi, O.; Nasri, R.; Mora, L.; Jridi, M.; Toldrá, F.; Nasri, M. In silico analysis and molecular docking study of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from smooth-hound viscera protein hydrolysates fractionated by ultrafiltration. Food Chem. 2018, 239, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Ledesma, B.; Contreras, M.d.M.; Recio, I. Antihypertensive peptides: Production, bioavailability and incorporation into foods. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 165, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Moreno, P.; Espejo-Carpio, F.J.; Guadix, A.; Guadix, E. Production and identification of angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from Mediterranean fish discards. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 18, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Wang, S.; Jing, L.; Yao, D. Purification and characterisation of a novel angiotensin-I converting enzyme (ACE)-inhibitory peptide derived from the enzymatic hydrolysate of Enteromorpha clathrata protein. Food Chem. 2016, 211, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Fang, L.; Min, W.; Liu, J.; Li, H. Exploration of the molecular interactions between angiotensin-I-converting enzyme (ACE) and the inhibitory peptides derived from hazelnut (Corylus heterophylla Fisch.). Food Chem. 2018, 245, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngo, D.H.; Vo, T.S.; Ryu, B.M.; Kim, S.K. Angiotensin-I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from Pacific cod skin gelatin using ultrafiltration membranes. Process Biochem. 2016, 51, 1622–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Alashi, A.; Young, J.; Therkildsen, M.; Aluko, R. Enzyme inhibition kinetics and molecular interactions of patatin peptides with angiotensin I-converting enzyme and renin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 101, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chougule, R.; Kamanna, S. A variant peptide of buffalo colostrum β-lactoglobulin inhibits angiotensin I-converting enzyme activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 53, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhedi, O.; Nasri, R.; Jridi, M.; Mora, L.; Oseguera-Toledo, M.E.; Aristoy, M.C.; Ben Amara, I.; Toldrá, F.; Nasri, M. In silico analysis and antihypertensive effect of ACE-inhibitory peptides from smooth-hound viscera protein hydrolysate: Enzyme-peptide interaction study using molecular docking simulation. Process Biochem. 2017, 58, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.K.; Jeon, J.K.; Byun, H.G. Antihypertensive effect of novel angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitory peptide from chum salmon (Oncorhynchus keta) skin in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J. Funct. Foods 2014, 7, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Je, J.Y.; Kang, N.; Han, E.J.; Um, J.H.; Jeon, Y.J.; Ahn, G.; Ahn, C.B. Antihypertensive effects of Ile–Pro–Ile–Lys from krill (Euphausia superba) protein hydrolysates: Purification, identification and in vivo evaluation in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2017, 243, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aluko, R. Food protein-derived renin-inhibitory peptides: In vitro and in vivo properties. J. Food Biochem. 2018, 43, e12648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffrin, E. Vascular endothelin in hypertension. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2005, 43, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, B.-H.; Kim, S.; Kim, J.-D.; Lee, J.; Baek, Y.-Y.; Jeoung, D.; Lee, H.; Choe, J.; Ha, K.-S.; Won, M.-H.; et al. Syringaresinol causes vasorelaxation by elevating nitric oxide production through the phosphorylation and dimerization of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Exp. Mol. Med. 2011, 44, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.-C.; Long, H.-B.; Luo, K.-Q. Tert-butylhydroquinone lowers blood pressure in AngII-induced hypertension in mice via proteasome-PTEN-Akt-eNOS pathway. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akillioǧlu, H.G.; Karakaya, S. Effects of heat treatment and in vitro digestion on the angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitory activity of some legume species. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2009, 229, 915–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Ding, X. Characterization of inhibition and stability of soy-protein-derived angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides. Food Res. Int. 2002, 35, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskar, B.; Ananthanarayan, L.; Jamdar, S. Purification, identification, and characterization of novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from alcalase digested horse gram flour. LWT 2019, 103, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Wang, X.; Hu, Z.; Wu, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Yang, M. Peptides Identi fi cation and characterization of an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitory peptide derived from bovine casein. Peptides 2018, 99, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toopcham, T.; Roytrakul, S.; Yongsawatdigul, J. Characterization and identification of angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides derived from tilapia using Virgibacillus halodenitrificans SK1-3-7 proteinases. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 14, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Xia, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X. LWT—Food Science and Technology Optimization of ACE inhibitory peptides from black soybean by microwave- assisted enzymatic method and study on its stability. LWT -Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 98, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chi, Y.J.; Zhao, M.Y.; Xu, W. Influence of degree of hydrolysis on functional properties, antioxidant and ACE inhibitory activities of egg white protein hydrolysate. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2012, 21, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasri, R.; Younes, I.; Jridi, M.; Trigui, M.; Bougatef, A.; Nedjar-Arroume, N.; Dhulster, P.; Karra Chaabouni, M. ACE inhibitory and antioxidative activities of Goby (Zosterissessor ophiocephalus) fish protein hydrolysates: Effect on meat lipid oxidation. Food Res. Int. 2013, 54, 552–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, N.; Yang, Z.; Gao, M.; Yang, X.; Cui, L. High-dose glucose-insulin-potassium has hemodynamic benefits and can improve cardiac remodeling in acute myocardial infarction treated with primary Percutaneous coronary intervention: From a randomized controlled study. J. Cardiovasc. Dis. Res. 2010, 1, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lai, X.; Pan, S.; Zhang, W.; Sun, L.; Li, Q.; Chen, R.; Sun, S. Properties of ACE inhibitory peptide prepared from protein in green tea residue and evaluation of its anti-hypertensive activity. Process Biochem. 2020, 92, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, I.G.; Kim, H.Y.; Woo, K.S.; Lee, J.; Jeong, H.S. Biological activities of Maillard reaction products (MRPs) in a sugar-amino acid model system. Food Chem. 2011, 126, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Yin, L.; Li, L. Effect of the Maillard Reaction on Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme (ACE)-Inhibitory Activity of Douchi During Fermentation. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2013, 6, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, M.; Mirdamadi, S.; Safavi, M.; Hadizadeh, M. In vitro and in silico studies of novel synthetic ACE-inhibitory peptides derived from Saccharomyces cerevisiae protein hydrolysate. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 87, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Fraction | Retention Time (Min) | Amino Acid Sequence | Mass (Da) | IC50 (μM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P5 | 16.120 | Val-Glu-Arg-Gly-Arg-Arg-Ile-Thr-Ser-Val (VERGRRITSV) | 1172.35 | 6.82 |
| P8 | 17.635 | Phe-Val-Ile-Glu-Pro-Asn-Ile-Thr-Pro-Ala (FVIEPNITPA) | 1100.28 | 6.36 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Y. Novel Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptides Identified from Walnut Glutelin-1 Hydrolysates: Molecular Interaction, Stability, and Antihypertensive Effects. Nutrients 2022, 14, 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14010151
Wang J, Wang G, Zhang Y, Zhang R, Zhang Y. Novel Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptides Identified from Walnut Glutelin-1 Hydrolysates: Molecular Interaction, Stability, and Antihypertensive Effects. Nutrients. 2022; 14(1):151. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14010151
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jing, Guoliang Wang, Yufeng Zhang, Runguang Zhang, and Youlin Zhang. 2022. "Novel Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptides Identified from Walnut Glutelin-1 Hydrolysates: Molecular Interaction, Stability, and Antihypertensive Effects" Nutrients 14, no. 1: 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14010151
APA StyleWang, J., Wang, G., Zhang, Y., Zhang, R., & Zhang, Y. (2022). Novel Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptides Identified from Walnut Glutelin-1 Hydrolysates: Molecular Interaction, Stability, and Antihypertensive Effects. Nutrients, 14(1), 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14010151