Dietary Emulsifiers Exacerbate Food Allergy and Colonic Type 2 Immune Response through Microbiota Modulation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mice
2.2. Emulsifier Agent Treatment
2.3. Food Allergy Induction
2.4. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.5. ELISA
2.6. 16S rRNA Sequencing
2.7. Isolation of Colonic Lamina Propria (LP) Cells
2.8. RNA-seq
2.9. Histology
2.10. Statistics
3. Results
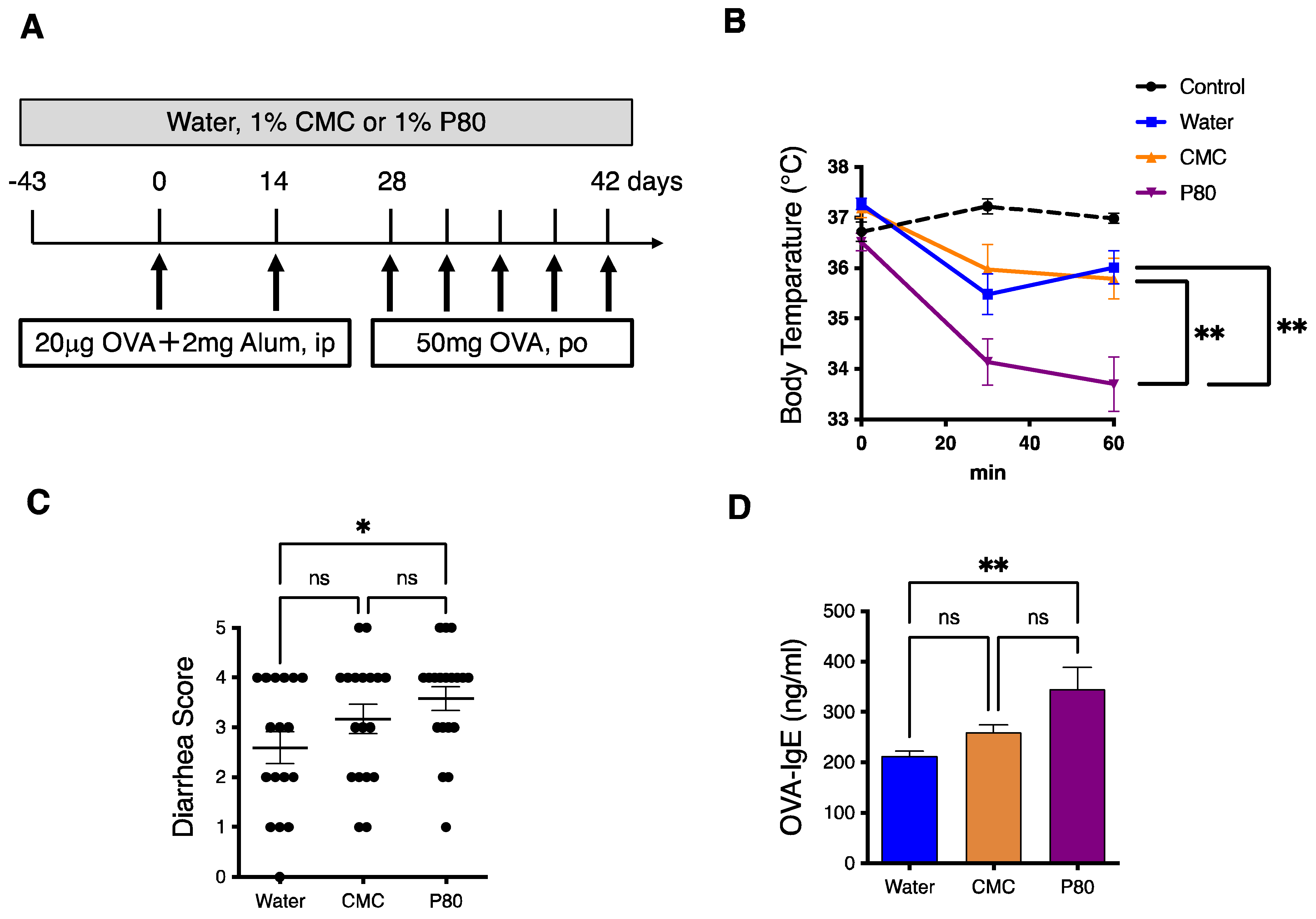
3.1. Dietary Emulsifier-Treated Mice Showed Symptoms of Severe Food Allergy
3.2. Colonic Type 2 Immune Response Is Exacerbated by Dietary Emulsifier Consumption
3.3. Periodic Acid-Schiff Staining of GI Tissue
3.4. Dietary Emulsifiers Facilitate Mast Cell Activation and Type 2 Immune Responses in Colonic Immune Cells
3.5. Alteration of the Microbiota in Dietary Emulsifiers Treated Mice with Food Allergy
3.6. Elimination of Microbiota Reversed Dietary Emulsifier-Mediated Exacerbated Susceptibility to Food Allergy
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sicherer, S.H. Food Allergy. Lancet 2002, 360, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampath, V.; Abrams, E.M.; Adlou, B.; Akdis, C.; Akdis, M.; Brough, H.A.; Chan, S.; Chatchatee, P.; Chinthrajah, R.S.; Cocco, R.R.; et al. Food Allergy across the Globe. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 148, 1347–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melén, E.; Koppelman, G.H.; Vicedo-Cabrera, A.M.; Andersen, Z.J.; Bunyavanich, S. Allergies to Food and Airborne Allergens in Children and Adolescents: Role of Epigenetics in a Changing Environment. Lancet Child Adolesc. Health 2022, 6, 810–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantzer, J.A.; Kim, E.H.; Chinthrajah, R.S.; Wood, R.A. Treatment for Food Allergy: Current Status and Unmet Needs. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du Toit, G.; Tsakok, T.; Lack, S.; Lack, G. Prevention of Food Allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 137, 998–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Renz, H.; Allen, K.J.; Sicherer, S.H.; Sampson, H.A.; Lack, G.; Beyer, K.; Oettgen, H.C. Food Allergy. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2018, 4, 17098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giugliano, D.; Ceriello, A.; Esposito, K. The Effects of Diet on Inflammation: Emphasis on the Metabolic Syndrome. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006, 48, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chassaing, B.; Koren, O.; Goodrich, J.K.; Poole, A.C.; Srinivasan, S.; Ley, R.E.; Gewirtz, A.T. Dietary Emulsifiers Impact the Mouse Gut Microbiota Promoting Colitis and Metabolic Syndrome. Nature 2015, 519, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cox, S.; Sandall, A.; Smith, L.; Rossi, M.; Whelan, K. Food Additive Emulsifiers: A Review of Their Role in Foods, Legislation and Classifications, Presence in Food Supply, Dietary Exposure, and Safety Assessment. Nutr. Rev. 2021, 79, 726–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, C.A.; Moubarac, J.C.; Cannon, G.; Ng, S.W.; Popkin, B. Ultra-Processed Products Are Becoming Dominant in the Global Food System. Obes. Rev. 2013, 14 (Suppl. S2), 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinninella, E.; Cintoni, M.; Raoul, P.; Lopetuso, L.R.; Scaldaferri, F.; Pulcini, G.; Miggiano, G.A.D.; Gasbarrini, A.; Mele, M.C. Food Components and Dietary Habits: Keys for a Healthy Gut Microbiota Composition. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Camilleri, M. Leaky Gut: Mechanisms, Measurement and Clinical Implications in Humans. Gut 2019, 68, 1516–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, C.L.; Rushworth, S.L.; Richman, E.; Rhodes, J.M. Hypothesis: Increased Consumption of Emulsifiers as an Explanation for the Rising Incidence of Crohn’s Disease. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2013, 7, 338–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Viennois, E.; Merlin, D.; Gewirtz, A.T.; Chassaing, B. Dietary Emulsifier-Induced Low-Grade Inflammation Promotes Colon Carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Viennois, E.; Bretin, A.; Dubé, P.E.; Maue, A.C.; Dauriat, C.J.G.; Barnich, N.; Gewirtz, A.T.; Chassaing, B. Dietary Emulsifiers Directly Impact Adherent-Invasive E. Coli Gene Expression to Drive Chronic Intestinal Inflammation. Cell Rep. 2020, 33, 108229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Chun, Y.; Ho, H.-E.; Arditi, Z.; Lo, T.; Sajja, S.; Rose, R.; Jones, D.; Wang, J.; Sicherer, S.; et al. Multiscale Study of the Oral and Gut Environments in Children with High- and Low-Threshold Peanut Allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 150, 714–720.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey-Mariño, A.; Francino, M.P. Nutrition, Gut Microbiota, and Allergy Development in Infants. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harusato, A.; Geem, D.; Denning, T.L. Macrophage Isolation from the Mouse Small and Large Intestine. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1422, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fallon, P.G.; Ballantyne, S.J.; Mangan, N.E.; Barlow, J.L.; Dasvarma, A.; Hewett, D.R.; McIlgorm, A.; Jolin, H.E.; McKenzie, A.N.J. Identification of an Interleukin (IL)-25–Dependent Cell Population That Provides IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 at the Onset of Helminth Expulsion. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 1105–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chassaing, B.; Van De Wiele, T.; De Bodt, J.; Marzorati, M.; Gewirtz, A.T. Dietary Emulsifiers Directly Alter Human Microbiota Composition and Gene Expression Ex Vivo Potentiating Intestinal Inflammation. Gut 2017, 66, 1414–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Siena, M.; Raoul, P.; Costantini, L.; Scarpellini, E.; Cintoni, M.; Gasbarrini, A.; Rinninella, E.; Mele, M.C. Food Emulsifiers and Metabolic Syndrome: The Role of the Gut Microbiota. Foods 2022, 11, 2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.B.; Chen, C.Y.; Liu, B.; Mugge, L.; Angkasekwinai, P.; Facchinetti, V.; Dong, C.; Liu, Y.J.; Rothenberg, M.E.; Hogan, S.P.; et al. IL-25 and CD4+ TH2 Cells Enhance Type 2 Innate Lymphoid Cell-Derived IL-13 Production, Which Promotes IgE-Mediated Experimental Food Allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 137, 1216–1225.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harusato, A.; Abo, H.; Ngo, V.L.; Yi, S.W.; Mitsutake, K.; Osuka, S.; Kohlmeier, J.E.; Li, J.D.; Gewirtz, A.T.; Nusrat, A.; et al. IL-36γ Signaling Controls the Induced Regulatory T Cell-Th9 Cell Balance via NFκB Activation and STAT Transcription Factors. Mucosal Immunol. 2017, 10, 1455–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hovhannisyan, Z.; Liu, N.; Khalil-Aguero, S.; Panea, C.; VanValkenburgh, J.; Zhang, R.; Lim, W.K.; Bai, Y.; Fury, W.; Huang, T.; et al. Enhanced IL-36R Signaling Promotes Barrier Impairment and Inflammation in Skin and Intestine. Sci. Immunol. 2020, 5, eaax1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chassaing, B.; Compher, C.; Bonhomme, B.; Liu, Q.; Tian, Y.; Walters, W.; Nessel, L.; Delaroque, C.; Hao, F.; Gershuni, V.; et al. Randomized Controlled-Feeding Study of Dietary Emulsifier Carboxymethylcellulose Reveals Detrimental Impacts on the Gut Microbiota and Metabolome. Gastroenterology 2022, 162, 743–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.H.; Kim, K.W.; Lee, S.Y.; Koo, K.O.; Kwon, S.O.; Seo, J.H.; Suh, D.I.; Shin, Y.H.; Ahn, K.; Oh, S.Y.; et al. Maternal Perinatal Dietary Patterns Affect Food Allergy Development in Susceptible Infants. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2019, 7, 2337–2347.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matsui, T.; Tanaka, K.; Yamashita, H.; Saneyasu, K.; Tanaka, H.; Takasato, Y.; Sugiura, S.; Inagaki, N.; Ito, K. Food Allergy Is Linked to Season of Birth, Sun Exposure, and Vitamin D Deficiency. Allergol. Int. 2019, 68, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berin, M.C.; Berin, C. Pathogenesis of IgE-Mediated Food Allergy. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2015, 45, 1483–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, M.; Koplin, J.J.; Dharmage, S.C.; Field, M.J.; Sawyer, S.M.; McWilliam, V.; Peters, R.L.; Gurrin, L.C.; Vuillermin, P.J.; Douglass, J.; et al. Prevalence of Clinic-Defined Food Allergy in Early Adolescence: The SchoolNuts Study. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 391–398.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thio, C.L.P.; Chi, P.Y.; Lai, A.C.Y.; Chang, Y.J. Regulation of Type 2 Innate Lymphoid Cell-Dependent Airway Hyperreactivity by Butyrate. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 142, 1867–1883.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura-Alves, P.; Faé, K.; Houthuys, E.; Dorhoi, A.; Kreuchwig, A.; Furkert, J.; Barison, N.; Diehl, A.; Munder, A.; Constant, P.; et al. AhR Sensing of Bacterial Pigments Regulates Antibacterial Defence. Nature 2014, 512, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agus, A.; Planchais, J.; Sokol, H. Gut Microbiota Regulation of Tryptophan Metabolism in Health and Disease. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 23, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Harusato, A.; Chassaing, B.; Dauriat, C.J.G.; Ushiroda, C.; Seo, W.; Itoh, Y. Dietary Emulsifiers Exacerbate Food Allergy and Colonic Type 2 Immune Response through Microbiota Modulation. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4983. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14234983
Harusato A, Chassaing B, Dauriat CJG, Ushiroda C, Seo W, Itoh Y. Dietary Emulsifiers Exacerbate Food Allergy and Colonic Type 2 Immune Response through Microbiota Modulation. Nutrients. 2022; 14(23):4983. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14234983
Chicago/Turabian StyleHarusato, Akihito, Benoit Chassaing, Charlène J. G. Dauriat, Chihiro Ushiroda, Wooseok Seo, and Yoshito Itoh. 2022. "Dietary Emulsifiers Exacerbate Food Allergy and Colonic Type 2 Immune Response through Microbiota Modulation" Nutrients 14, no. 23: 4983. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14234983
APA StyleHarusato, A., Chassaing, B., Dauriat, C. J. G., Ushiroda, C., Seo, W., & Itoh, Y. (2022). Dietary Emulsifiers Exacerbate Food Allergy and Colonic Type 2 Immune Response through Microbiota Modulation. Nutrients, 14(23), 4983. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14234983







