Independent and Combined Association of Lifestyle Behaviours and Physical Fitness with Body Weight Status in Schoolchildren
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Calculation of the Sample Size
2.3. Procedures and Assessments
2.3.1. Anthropometric Measurements
2.3.2. Self-Reported Physical Fitness
2.3.3. Physical Activity and Screen Time
2.3.4. Eating Habits
2.3.5. Hours of Sleep
2.3.6. Lifestyle Behaviours
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Independent Associations of Lifestyle Behaviours
3.3. Independent Associations of Self-Reported Physical Fitness
3.4. Combined Associations of Lifestyle Behaviours and Self-Reported Physical Fitness
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Report of the Commission on Ending Childhood Obesity; WHO Document Production Services: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 1–30.
- Qi, S.-J. Childhood obesity and food intake. World J. Pediatr. 2015, 11, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Herrera, A.; Cruz-López, M. Childhood obesity: Current situation in Mexico. Nutr. Hosp. 2019, 36, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, M.; Fleming, T.; Robinson, M.; Thomson, B.; Graetz, N.; Margono, C.; Mullany, E.C.; Biryukov, S.; Abbafati, C.; Abera, S.F.; et al. Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during 1980-2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2014, 384, 766–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Kelly, A.S. Review of Childhood Obesity: From Epidemiology, Etiology, and Comorbidities to Clinical Assessment and Treatment. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2017, 92, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahrens, W.; Pigeot, I.; Pohlabeln, H.; De Henauw, S.; Lissner, L.; Molnár, D.; Moreno, L.A.; Tornaritis, M.; Veidebaum, T.; Siani, A.; et al. Prevalence of overweight and obesity in European children below the age of 10. Int. J. Obes. 2014, 38, S99–S107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadenas-Sanchez, C.; Nyström, C.; Sanchez-Delgado, G.; Martinez-Tellez, B.; Mora-Gonzalez, J.; Risinger, A.S.; Ruiz, J.R.; Ortega, F.B.; Löf, M. Prevalence of overweight/obesity and fitness level in preschool children from the north compared with the south of Europe: An exploration with two countries. Pediatr. Obes. 2016, 11, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauria, L.; Spinelli, A.; Buoncristiano, M.; Nardone, P. Decline of childhood overweight and obesity in Italy from 2008 to 2016: Results from 5 rounds of the population-based surveillance system. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassapidou, M.; Tzotzas, T.; Makri, E.; Pagkalos, I.; Kaklamanos, I.; Kapantais, E.; Abrahamian, A.; Polymeris, A.; Tziomalos, K. Prevalence and geographic variation of abdominal obesity in 7- and 9-year-old children in Greece; World Health Organization Childhood Obesity Surveillance Initiative 2010. BMC Public Health 2017, 17, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abarca-Gómez, L.; Abdeen, Z.A.; Hamid, Z.A.; Abu-Rmeileh, N.M.; Acosta-Cazares, B.; Acuin, C.; Adams, R.J.; Aekplakorn, W.; Afsana, K.; Aguilar-Salinas, C.A.; et al. Worldwide trends in body-mass index, underweight, overweight, and obesity from 1975 to 2016: A pooled analysis of 2416 population-based measurement studies in 128·9 million children, adolescents, and adults. Lancet 2017, 390, 2627–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agencia Española De Seguridad Alimentaria Y Nutrición. Aladino 2019. Informe Breve. Estudio Sobre La Alimentación, Actividad Física, Desarrollo Infantil Y obesidad En España 2019; Estrategia NAOS; Ministerio de Consumo: Madrid, Spain, 2020.
- Villagrán-Pérez, S.; Novalbos-Ruiz, J.P.; Rodríguez-Martín, A.; Martínez-Nieto, J.M.; Lechuga-Sancho, A.M. Implicaciones del nivel socioeconómico familiar sobre las conductas de riesgo en la obesidad infantojuvenil. Nutr. Hosp. 2013, 28, 1951–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappuccio, F.P.; Taggart, F.M.; Kandala, N.-B.; Currie, A.; Peile, E.; Stranges, S.; Miller, M.A. Meta-Analysis of Short Sleep Duration and Obesity in Children and Adults. Sleep 2008, 31, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Börnhorst, C.; Wijnhoven, T.M.; Kunešová, M.; Yngve, A.; Rito, A.I.; Lissner, L.; Duleva, V.; Petrauskiene, A.; Breda, J. WHO European Childhood Obesity Surveillance Initiative: Associations between sleep duration, screen time and food consumption frequencies. BMC Public Health 2015, 15, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega Anta, R.M.; López-Solaber, A.M.; Pérez-Farinós, N. Associated factors of obesity in Spanish representative samples. Nutr. Hosp. 2013, 28 (Suppl. 5), 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Rodríguez, E.; Palmeros-Exsome, C.; López-Sobaler, A.M.; Ortega, R.M. Research Group: 920030 Preliminary data on the association between waist circumference and insulin resistance in children without a previous diagnosis. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2011, 170, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, L.J.; Parsons, T.J.; Hill, A.J. Self-esteem and quality of life in obese children and adolescents: A systematic review. Int. J. Pediatr. Obes. 2010, 5, 282–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biro, F.M.; Wien, M. Childhood obesity and adult morbidities. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 91, 1499–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lorenzo, A.; Gratteri, S.; Gualtieri, P.; Cammarano, A.; Bertucci, P.; Di Renzo, L. Why primary obesity is a disease? J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kachur, S.; Lavie, C.J.; De Schutter, A.; Milani, R.V.; Ventura, H.O. Obesity and cardiovascular diseases. Minerva Med. 2017, 108, 212–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engin, A. The definition and prevalence of obesity and metabolic syndrome. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 960, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavie, C.J.; De Schutter, A.; Parto, P.; Jahangir, E.; Kokkinos, P.; Ortega, F.B.; Arena, R.; Milani, R.V. Obesity and Prevalence of Cardiovascular Diseases and Prognosis-The Obesity Paradox Updated. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2016, 58, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Country profiles on nutrition, physical activity and obesity in the 53 WHO European Region Member States: Methodology and summary. Reg. Off. Eur. 2013, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald, M.P.; Hennigan, K.; O’Gorman, C.S.; McCarron, L. Obesity, diet and lifestyle in 9-year-old children with parentally reported chronic diseases: Findings from the Growing Up in Ireland longitudinal child cohort study. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 188, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bischoff, S.C.; Boirie, Y.; Cederholm, T.; Chourdakis, M.; Cuerda, C.; Delzenne, N.M.; Deutz, N.E.; Fouque, D.; Genton, L.; Gil, C.; et al. Towards a multidisciplinary approach to understand and manage obesity and related diseases. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 917–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borges, C.A.; Slater, B.; Santaliestra-Pasías, A.M.; Mouratidou, T.; Huybrechts, I.; Widhalm, K.; Gottrand, F.; Manios, Y.; Jimenez-Pavón, D.; Valtueña, J.; et al. Dietary Patterns in European and Brazilian Adolescents: Comparisons and Associations with Socioeconomic Factors. Nutrients 2018, 10, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, Y.G.; Lim, H.; Kim, Y.; Ju, Y.S.; Lee, H.J.; Jang, H.B.; Park, K.H. The Effect of a Multidisciplinary Lifestyle Intervention on Obesity Status, Body Composition, Physical Fitness, and Cardiometabolic Risk Markers in Children and Adolescents with Obesity. Nutrients 2019, 11, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, I.; Schindler, C.; Adams, L.; Endes, K.; Gall, S.; Gerber, M.; Htun, N.; Nqweniso, S.; Joubert, N.; Probst-Hensch, N.; et al. Effect of a Multidimensional Physical Activity Intervention on Body Mass Index, Skinfolds and Fitness in South African Children: Results from a Cluster-Randomised Controlled Trial. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carson, V.; Tremblay, M.S.; Chaput, J.P.; Chastin, S. Associations between sleep duration, sedentary time, physical activity, and health indicators among Canadian children and youth using compositional analyses. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 41, S294–S302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustos, N.; Olivares, S.; Leyton, B.; Cano, M.; Albala, C. Impact of a school-based intervention on nutritional education and physical activity in primary public schools in Chile (KIND) programme study protocol: Cluster randomised controlled trial. BMC Public Health 2016, 16, 1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staiano, A.E.; Beyl, R.A.; Guan, W.; Hendrick, C.A.; Hsia, D.S.; Newton, R.L. Home-based exergaming among children with overweight and obesity: A randomized clinical trial. Pediatr. Obes. 2018, 13, 724–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, K.; Mu, M.; Liu, K.; He, Y. Screen time and childhood overweight/obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Child. Care Health Dev. 2019, 45, 744–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, T.N.; Banda, J.A.; Hale, L.; Lu, A.S.; Fleming-Milici, F.; Calvert, S.L.; Wartella, E. Screen Media Exposure and Obesity in Children and Adolescents. Pediatrics 2017, 140, S97–S101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sluggett, L.; Wagner, S.L.; Harris, R.L. Sleep Duration and Obesity in Children and Adolescents. Can. J. Diabetes. 2019, 43, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, E.A.; Evans, C.V.; Burda, B.U.; Walsh, E.S.; Eder, M.; Lozano, P. Screening for obesity and intervention forweight management in children and adolescents evidence report and systematic review for the us preventive services task force. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2017, 317, 2427–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega, F.B.; Sánchez-López, M.; Solera-Martínez, M.; Fernández-Sánchez, A.; Sjöström, M.; Martínez-Vizcaino, V. Self-reported and measured cardiorespiratory fitness similarly predict cardiovascular disease risk in young adults. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sport. 2013, 23, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez-Pavón, D.; Castillo, M.J.; Moreno, L.A.; Kafatos, A.; Manios, Y.; Kondaki, K.; Béghin, L.; Zaccaria, M.; de Henauw, S.; Widhalm, K.; et al. Fitness and fatness are independently associated with markers of insulin resistance in European adolescents; the HELENA study. Int. J. Pediatr. Obes. 2011, 6, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-López, M.; Martínez-Vizcaíno, V.; García-Hermoso, A.; Jiménez-Pavón, D.; Ortega, F.B. Construct validity and test-retest reliability of the International Fitness Scale (IFIS) in Spanish children aged 9-12 years. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sport. 2015, 25, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnelly, J.E.; Hillman, C.H.; Castelli, D.; Etnier, J.L.; Lee, S.; Tomporowski, P.; Lambourne, K.; Szabo-Reed, A.N. Physical Activity, Fitness, Cognitive Function, and Academic Achievement in Children: A Systematic Review. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2016, 48, 1197–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raistenskis, J.; Sidlauskiene, A.; Strukcinskiene, B.; Baysal, S.U.; Buckus, R. Physical activity and physical fitness in obese, overweight, and normal-weight children. Turkish J. Med. Sci. 2016, 46, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.J.; Eather, N.; Morgan, P.J.; Plotnikoff, R.C.; Faigenbaum, A.D.; Lubans, D.R. The health benefits of muscular fitness for children and adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sports Med. 2014, 44, 1209–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aragón-Martín, R.; Gómez-Sánchez, M.D.M.; Jiménez-Pavón, D.; Martínez-Nieto, J.M.; Schwarz-Rodríguez, M.; Segundo-Iglesias, C.; Novalbos-Ruiz, J.P.; Santi-Cano, M.J.; Castro-Piñero, J.; Lineros-González, C.; et al. A Multimodal Intervention for Prevention of Overweight and Obesity in Schoolchildren. A Protocol Study “PREVIENE-CÁDIZ.”. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marfell-Jones, M.J.; Stewart, A.D.; De Ridder, J.H. International Standards for Anthropometric Assessment; International Society for the Advancement of Kinanthropometry: Wellington, New Zealand, 2011; ISBN 0620362073. [Google Scholar]
- Cole, T.J.; Bellizzi, M.C.; Flegal, K.M.; Dietz, W.H. Establishing a standard definition for child overweight and obesity worldwide: International survey. Br. Med. J. 2000, 320, 1240–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lineros-González, C.; Marcos-Marcos, J.; Ariza, C.; Hernán-García, M. Importancia del proceso en la evaluación de la efectividad de una intervención sobre obesidad infantil. Gac. Sanit. 2017, 31, 238–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Martínez, F.; Torres Capcha, P.; Serral Cano, G.; Valmayor Safont, S.; Castell Abat, C.; Grupo de Evaluación del Proyecto POIBA. Factors Associated with Overweight and Obesity in Schoolchildren from 8 to 9 Years Old. Barcelona, Spain. Rev. Esp. Salud Publica 2016, 90, e1–e11. [Google Scholar]
- Tremblay, M.S.; Carson, V.; Chaput, J.P.; Connor Gorber, S.; Dinh, T.; Duggan, M.; Faulkner, G.; Gray, C.E.; Grube, R.; Janson, K.; et al. Canadian 24-hour movement guidelines for children and youth: An integration of physical activity, sedentary behaviour, and sleep. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 41, S311–S327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Sobaler, A.M.; Cuadrado-Soto, E.; Peral-Suárez, Á.; Aparicio, A.; Ortega, R.M. Importancia del desayuno en la mejora nutricional y sanitaria de la población. Nutr. Hosp. 2018, 35, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szajewska, H.; Ruszczyński, M. Systematic review demonstrating that breakfast consumption influences body weight outcomes in children and adolescents in Europe. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2010, 50, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monzani, A.; Ricotti, R.; Caputo, M.; Solito, A.; Archero, F.; Bellone, S.; Prodam, F. A systematic review of the association of skipping breakfast with weight and cardiometabolic risk factors in children and adolescents What should we better investigate in the future? Nutrients 2019, 11, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, L.F.; Lillegaard, I.T.L.; Øverby, N.; Klepp, K.I.; Lytle, L.; Johansson, L. Overweight and obesity among Norwegian schoolchildren: Changes from 1993 to 2000. Scand. J. Public Health 2005, 33, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; So, W.Y. Association between frequency of breakfast eating and obesity in Korean adolescents. Iran. J. Public Health 2012, 41, 50–57. [Google Scholar]
- Küpers, L.K.; De Pijper, J.J.; Sauer, P.J.J.; Stolk, R.P.; Corpeleijn, E. Skipping breakfast and overweight in 2-and 5-year-old Dutch children-the GECKO Drenthe cohort. Int. J. Obes. 2014, 38, 569–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardeshirlarijani, E.; Namazi, N.; Jabbari, M.; Zeinali, M.; Gerami, H.; Jalili, R.B.; Larijani, B.; Azadbakht, L. The link between breakfast skipping and overweigh/obesity in children and adolescents: A meta-analysis of observational studies. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2019, 18, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roos, R.; Mason, K.M.; Stefanogiannis, N.; Templeton, R.; Weerasekera, D. The Health of New Zealand Children 2011/12: Key findings of the New Zealand Health Survey; Ministry of Health: Wellington, New Zealand, 2012.
- Nelson, M.C.; Neumark-Stzainer, D.; Hannan, P.J.; Sirard, J.R.; Story, M. Longitudinal and secular trends in physical activity and sedentary behavior during adolescence. Pediatrics 2006, 118, e1627–e1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Beydoun, M.A.; Wang, Y. Is sleep duration associated with childhood obesity? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obesity 2008, 16, 265–274. [Google Scholar]
- Chaput, J.-P.; St-Onge, M.-P. Increased Food Intake by Insufficient Sleep in Humans: Are We Jumping the Gun on the Hormonal Explanation? Front. Endocrinol. 2014, 5, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, L.; Wardle, J.; Llewellyn, C.H.; Fisher, A. Nighttime sleep duration and hedonic eating in childhood. Int. J. Obes. 2015, 39, 1463–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Golley, R.K.; Maher, C.A.; Matricciani, L.; Olds, T.S. Sleep duration or bedtime? Exploring the association between sleep timing behaviour, diet and BMI in children and adolescents. Int. J. Obes. 2013, 37, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, A.; McDonald, L.; van Jaarsveld, C.H.M.; Llewellyn, C.; Fildes, A.; Schrempft, S.; Wardle, J. Sleep and energy intake in early childhood. Int. J. Obes. 2014, 38, 926–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, F.B.; Silventoinen, K.; Tynelius, P.; Rasmussen, F. Muscular strength in male adolescents and premature death: Cohort study of one million participants. BMJ 2012, 345, e7279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega, F.B.; Ruiz, J.R.; Castillo, M.J.; Sjöström, M. Physical fitness in childhood and adolescence: A powerful marker of health. Int. J. Obes. 2007, 32, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, J.R.; Castro-Piñero, J.; Artero, E.G.; Ortega, F.B.; Sjöström, M.; Suni, J.; Castillo, M.J. Predictive validity of health-related fitness in youth: A systematic review. Br. J. Sports Med. 2009, 43, 909–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Montero, P.J.; Chiva-Bartoll, O.; Baena-Extremera, A.; Hortigüela-Alcalá, D. Gender, Physical Self-Perception and Overall Physical Fitness in Secondary School Students: A Multiple Mediation Model. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swinburn, B.; Malakellis, M.; Moodie, M.; Waters, E.; Gibbs, L.; Millar, L.; Herbert, J.; Virgo-Milton, M.; Mavoa, H.; Kremer, P.; et al. Large reductions in child overweight and obesity in intervention and comparison communities 3 years after a community project. Pediatr. Obes. 2014, 9, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karppanen, A.-K.; Ahonen, S.-M.; Tammelin, T.; Vanhala, M.; Korpelainen, R. Physical activity and fitness in 8-year-old overweight and normal weight children and their parents. Int. J. Circumpolar Health 2012, 71, 17621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]





| Variable | Total Sample n = 864 | Male n = 452 | Female n = 412 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physical characteristics | Mean (SD) or Percentage | ||
| Age (years) | 8.42 ± 0.34 | 8.43 ± 0.35 | 8.42 ± 0.33 |
| Weight (kg) | 31.33 ± 7.62 | 31.92 ± 8.13 | 30.77 ± 7.07 |
| Height (cm) | 130.68 ± 5.99 | 131.53 ± 6.12 | 129.88 ± 5.75 ** |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 18.17 ± 3.44 | 18.27 ± 3.55 | 18.08 ± 3.44 |
| BMI Status (%) (UW/NW/OW/Ob) | 5/60/22/13 | 4/62/20/14 | 7/56/24/13 |
| Self-reported physical fitness | |||
| General physical fitness (%) (B/A/G/VG) | 2/15/37/46 | 2/16/33/49 | 2/14/41/43 |
| Cardiorespiratory fitness (%) (B/A/G/VG) | 7/21/33/39 | 6/20/30/44 | 7/22/37/34 * |
| Muscular strength (%) (B/A/G/VG) | 3/19/33/45 | 4/20/25/51 | 3/17/41/39 † |
| Speed/Agility (%) (B/A/G/VG) | 4/15/30/51 | 3/12/31/54 | 5/18/29/48 |
| Flexibility (%) (B/A/G/VG) | 14/24/25/37 | 20/28/25/27 | 7/20/25/48 † |
| Feeding (children reported) | |||
| Breakfast (%) (Yes/No) | 91/9 | 89/11 | 92/8 |
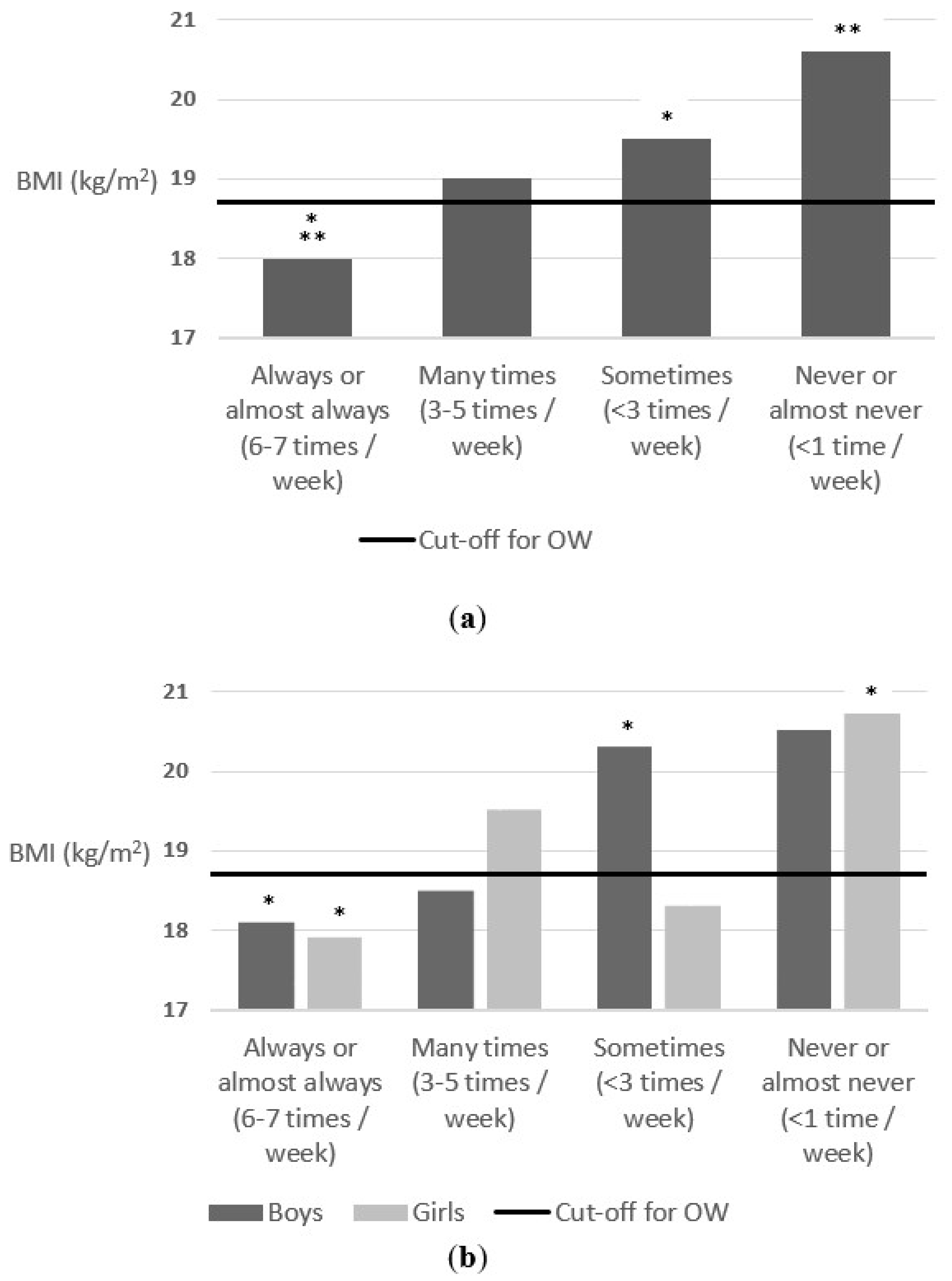
| To eat in a restaurant (%) (Al/MT/S/N) | 2/28/64/6 | 3/30/61/6 | 2/25/67/6 |
| Feeding (parents reported) | |||
| Breakfast (%) (Al/MT/S/N) | 86/6/5/3 | 87/6/5/2 | 85/6/6/3 |
| To eat in a restaurant (%) (N/S/MT/Al) | 30/67/2/1 | 29/69/2/0 | 30/67/2/1 |
| Screen time (children reported) | |||
| TV and VG weekdays (%) (<2 h/2–4 h/>4 h) | 61/23/16 | 55/25/20 | 67/21/12 ** |
| TV and VG weekends (%) (<2 h/2–4 h/>4 h) | 46/28/26 | 38/30/32 | 54/26/20 † |
| PC and MP weekdays (%) (<2 h/2–4 h/>4 h) | 72/17/11 | 68/18/14 | 76/17/7 ** |
| PC and MP weekends (%) (<2 h/2–4 h/>4 h) | 60/21/19 | 54/23/23 | 67/19/14 † |
| Screen time (parents reported) | |||
| TV weekdays (%) (<2 h/2–4 h/>4 h) | 89/10/1 | 87/11/2 | 91/8/1 |
| TV weekends (%) (<2 h/2–4 h/>4 h) | 64/33/3 | 63/34/3 | 64/33/3 |
| VG weekdays (%) (<2 h/2–4 h/>4 h) | 97/2/1 | 95/4/1 | 98/1/1 ** |
| VG weekends (%) (<2 h/2–4 h/>4 h) | 85/13/2 | 78/17/5 | 90/8/2 † |
| PC and MP weekdays (%) (<2 h/2–4 h/>4 h) | 97/2/1 | 98/1/1 | 96/3/1 |
| PC and MP weekends (%) (<2 h/2–4 h/>4 h) | 86/12/2 | 85/13/2 | 87/11/2 |
| Hours of sleep | |||
| Weekdays (h/day) | 10.00 ± 0.55 | 10.05 ± 0.52 | 9.96 ± 0.58 * |
| Weekends (h/day) | 10.38 ± 0.89 | 10.33 ± 0.95 | 10.43 ± 0.83 |
| Weekdays (%) (<9 h/9–12 h/>12 h) | 2/98/0 | 1/99/0 | 2/98/0 |
| Weekends (%) (<9 h/9–12 h/>12 h) | 2/96/2 | 2/96/2 | 2/96/2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aragón-Martín, R.; Gómez-Sánchez, M.d.M.; Martínez-Nieto, J.M.; Novalbos-Ruiz, J.P.; Segundo-Iglesias, C.; Santi-Cano, M.J.; Castro-Piñero, J.; Lineros-González, C.; Hernán-García, M.; Schwarz-Rodríguez, M.; et al. Independent and Combined Association of Lifestyle Behaviours and Physical Fitness with Body Weight Status in Schoolchildren. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1208. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14061208
Aragón-Martín R, Gómez-Sánchez MdM, Martínez-Nieto JM, Novalbos-Ruiz JP, Segundo-Iglesias C, Santi-Cano MJ, Castro-Piñero J, Lineros-González C, Hernán-García M, Schwarz-Rodríguez M, et al. Independent and Combined Association of Lifestyle Behaviours and Physical Fitness with Body Weight Status in Schoolchildren. Nutrients. 2022; 14(6):1208. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14061208
Chicago/Turabian StyleAragón-Martín, Rubén, María del Mar Gómez-Sánchez, José Manuel Martínez-Nieto, José Pedro Novalbos-Ruiz, Carmen Segundo-Iglesias, María José Santi-Cano, José Castro-Piñero, Carmen Lineros-González, Mariano Hernán-García, Mónica Schwarz-Rodríguez, and et al. 2022. "Independent and Combined Association of Lifestyle Behaviours and Physical Fitness with Body Weight Status in Schoolchildren" Nutrients 14, no. 6: 1208. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14061208
APA StyleAragón-Martín, R., Gómez-Sánchez, M. d. M., Martínez-Nieto, J. M., Novalbos-Ruiz, J. P., Segundo-Iglesias, C., Santi-Cano, M. J., Castro-Piñero, J., Lineros-González, C., Hernán-García, M., Schwarz-Rodríguez, M., Jiménez-Pavón, D., & Rodríguez-Martín, A. (2022). Independent and Combined Association of Lifestyle Behaviours and Physical Fitness with Body Weight Status in Schoolchildren. Nutrients, 14(6), 1208. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14061208












