Association of Serum Magnesium with Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes among Adults in China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Subjects and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Exposure and Outcome Assessment
2.3. Covariate Assessment
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Association of Serum Magnesium with Insulin Resistance
3.3. Association of Serum Magnesium with Type 2 Diabetes
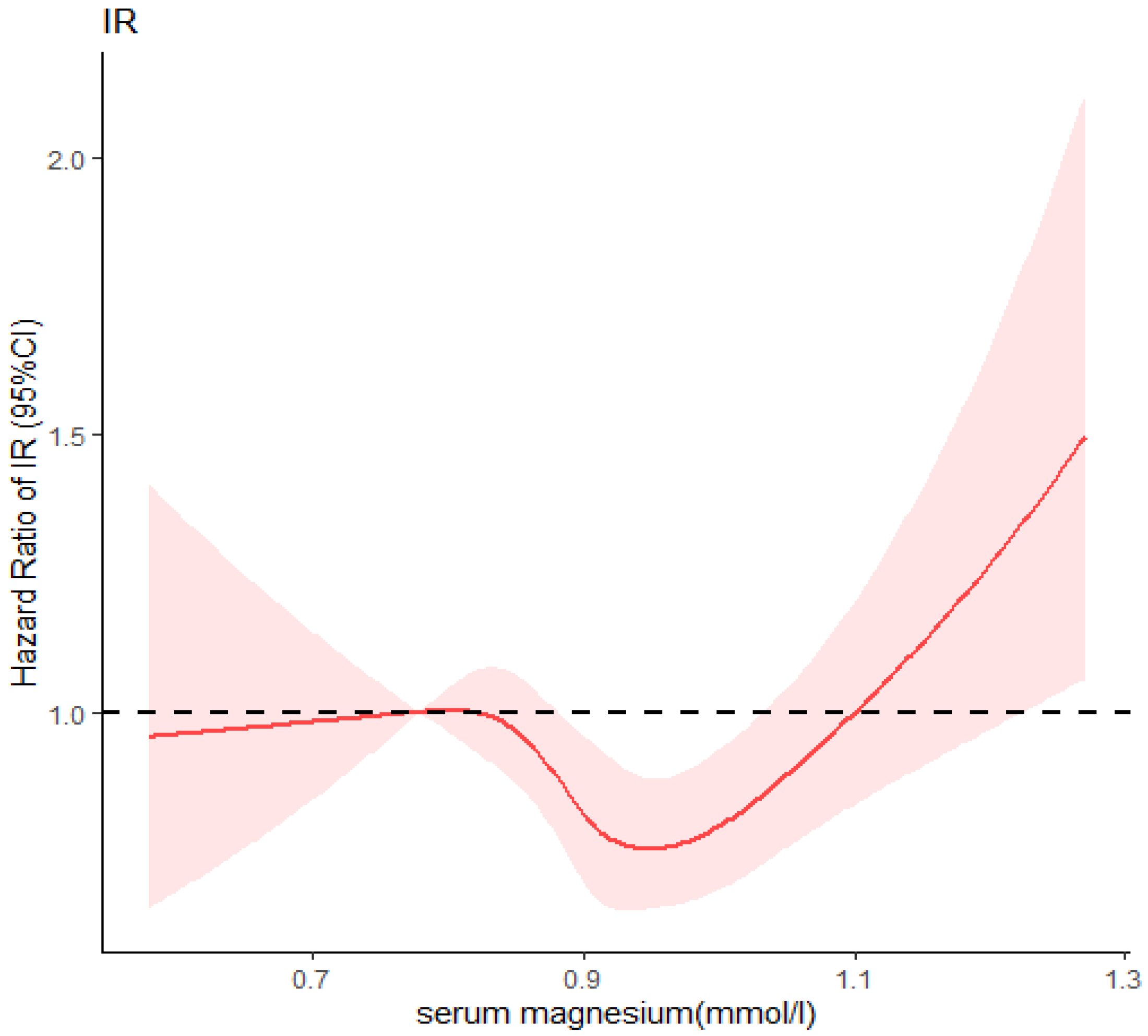
3.4. Dose–Response Relationship between Serum Magnesium and Insulin Resistance, and Type 2 Diabetes
3.5. Sensitivity Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khan, M.A.B.; Hashim, M.J.; King, J.K.; Govender, R.D.; Mustafa, H.; Al Kaabi, J. Epidemiology of Type 2 Diabetes—Global Burden of Disease and Forecasted Trends. J. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2020, 10, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Peng, W.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, M.; Shi, Z.; Song, Z.; Zhang, X.; Li, C.; Huang, Z.; Sun, X.; et al. Prevalence and Treatment of Diabetes in China, 2013–2018. JAMA 2021, 326, 2498–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batista, T.M.; Haider, N.; Kahn, C.R. Defining the underlying defect in insulin action in type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2021, 64, 994–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachdaoui, N. Insulin: The Friend and the Foe in the Development of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piuri, G.; Zocchi, M.; Della Porta, M.; Ficara, V.; Manoni, M.; Zuccotti, G.V.; Pinotti, L.; Maier, J.A.; Cazzola, R. Magnesium in Obesity, Metabolic Syndrome, and Type 2 Diabetes. Nutrients 2021, 13, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vormann, J. Magnesium: Nutrition and Homoeostasis. AIMS Public Health 2016, 3, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caspi, R.; Billington, R.; Keseler, I.M.; Kothari, A.; Krummenacker, M.; Midford, P.E.; Ong, W.K.; Paley, S.; Subhraveti, P.; Karp, P.D. The MetaCyc database of metabolic pathways and enzymes—A 2019 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D445–D453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sohrabipour, S.; Sharifi, M.R.; Sharifi, M.; Talebi, A.; Soltani, N. Effect of magnesium sulfate administration to improve insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes animal model: Using the hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp technique. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 32, 603–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorentini, D.; Cappadone, C.; Farruggia, G.; Prata, C. Magnesium: Biochemistry, Nutrition, Detection, and Social Impact of Diseases Linked to Its Deficiency. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Li, N.; Jin, M.; Miao, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhong, W. Magnesium supplementation enhances insulin sensitivity and decreases insulin resistance in diabetic rats. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2020, 23, 990–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbagallo, M.; Veronese, N.; Dominguez, L.J. Magnesium in Aging, Health and Diseases. Nutrients 2021, 13, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertinato, J.; Wang, K.C.; Hayward, S. Serum Magnesium Concentrations in the Canadian Population and Associations with Diabetes, Glycemic Regulation, and Insulin Resistance. Nutrients 2017, 9, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Zhai, F.Y.; Du, S.F.; Popkin, B.M. The China Health and Nutrition Survey, 1989-2011. Obes. Rev. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Obes. 2014, 15 (Suppl. S1), 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Siega-Riz, A.M.; Gordon-Larsen, P.; Cai, J.; Adair, L.S.; Zhang, B.; Popkin, B.M. Diet quality and its association with type 2 diabetes and major cardiometabolic risk factors among adults in China. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. NMCD 2018, 28, 987–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Wang, H.; Su, C.; Wang, Z.; Huang, F.; Zhang, J.; Du, W.; Jia, X.; Jiang, H.; Ouyang, Y.; et al. Association of Time-of-Day Energy Intake Patterns with Nutrient Intakes, Diet Quality, and Insulin Resistance. Nutrients 2021, 13, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Society, C.D. Guideline for the prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus in China (2020 edition). Chin. J. Diabetes Mellit. 2021, 13, 315–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, T.M.; Levy, J.C.; Matthews, D.R. Use and abuse of HOMA modeling. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 1487–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamada, C.; Mitsuhashi, T.; Hiratsuka, N.; Inabe, F.; Araida, N.; Takahashi, E. Optimal reference interval for homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance in a Japanese population. J. Diabetes Investig. 2011, 2, 373–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ainsworth, B.E.; Haskell, W.L.; Whitt, M.C.; Irwin, M.L.; Swartz, A.M.; Strath, S.J.; O’Brien, W.L.; Bassett, D.R., Jr.; Schmitz, K.H.; Emplaincourt, P.O.; et al. Compendium of physical activities: An update of activity codes and MET intensities. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2000, 32, S498–S504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wei, Y.; Zhou, J.H.; Zhang, Z.W.; Tan, Q.Y.; Lyu, Y.B. Application of restricted cube spline in cox regression model. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi [Chin. J. Prev. Med.] 2020, 40, E001. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.H.; Shih, A.Z.; Woo, Y.C.; Fong, C.H.; Leung, O.Y.; Janus, E.; Cheung, B.M.; Lam, K.S. Optimal Cut-Offs of Homeostasis Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance (HOMA-IR) to Identify Dysglycemia and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A 15-Year Prospective Study in Chinese. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Elin, R.J. Assessment of magnesium status for diagnosis and therapy. Magnes. Res. 2010, 23, S194–S198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, B. Association between Toenail Magnesium and Type 2 Diabetes in Chinese Adults. Nutrients 2017, 9, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luo, X.; Cai, W.Y.; Ma, H.L.; Cong, J.; Chang, H.; Gao, J.S.; Shen, W.J.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X.M.; Wu, X.K. Associations of Serum Magnesium With Insulin Resistance and Testosterone in Women With Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 683040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamnani, G.; Bhartiy, S.S.; Jiwane, R.; Gupta, V.; Verma, N.; Verma, D. Correlation of Serum Magnesium with Insulin Resistance in North Indian Adult Population. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2020, 16, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieboom, B.C.T.; Ligthart, S.; Dehghan, A.; Kurstjens, S.; de Baaij, J.H.F.; Franco, O.H.; Hofman, A.; Zietse, R.; Stricker, B.H.; Hoorn, E.J. Serum magnesium and the risk of prediabetes: A population-based cohort study. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Akter, S.; Eguchi, M.; Nanri, A.; Kochi, T.; Kashino, I.; Kuwahara, K.; Hu, H.; Miki, T.; Kabe, I.; Mizoue, T. Association of dietary and serum magnesium with glucose metabolism markers: The Furukawa Nutrition and Health Study. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2018, 24, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naser, W.; Adam, I.; Rayis, D.A.; Ahmed, M.A.; Hamdan, H.Z. Serum magnesium and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein as a predictor for gestational diabetes mellitus in Sudanese pregnant women. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2019, 19, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Xu, W.; Yao, H.; Sun, W.; Zhou, Q.; Cai, L. Associations of serum and urinary magnesium with the pre-diabetes, diabetes and diabetic complications in the Chinese Northeast population. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopping, B.N.; Erber, E.; Grandinetti, A.; Verheus, M.; Kolonel, L.N.; Maskarinec, G. Grandinetti. Dietary fiber, magnesium, and glycemic load alter risk of type 2 diabetes in a multiethnic cohort in Hawaii. J. Nutr. Off. Organ Am. Inst. Nutr. 2010, 140, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chambers, E.C.; Heshka, S.; Gallagher, D.; Wang, J.; Pi-Sunyer, F.X.; Pierson, R.N., Jr. Serum magnesium and type-2 diabetes in African Americans and Hispanics: A New York cohort. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2006, 25, 509–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lecube, A.; Baena-Fustegueras, J.A.; Fort, J.M.; Pelegrí, D.; Hernández, C.; Simó, R. Diabetes is the main factor accounting for hypomagnesemia in obese subjects. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, S.J.; Hwang, S.Y.; Baik, S.H.; Lee, K.W.; Nam, M.S.; Park, Y.S.; Woo, J.T.; Kim, Y.S.; Park, S.; Park, S.Y.; et al. Serum magnesium level is associated with type 2 diabetes in women with a history of gestational diabetes mellitus: The Korea National Diabetes Program study. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2014, 29, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiga, R.; Mannino, G.C.; Mancuso, E.; Averta, C.; Paone, C.; Rubino, M.; Sciacqua, A.; Succurro, E.; Perticone, F.; Andreozzi, F.; et al. Are Circulating Mg(2+) Levels Associated with Glucose Tolerance Profiles and Incident Type 2 Diabetes? Nutrients 2019, 11, 2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salhi, H.; El Ouahabi, H. Magnesium status in patients with Type 2 diabetes (about 170 cases). Ann. Afr. Med. 2021, 20, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joy, S.S.; George, T.P.; Siddiqui, K. Low magnesium level as an indicator of poor glycemic control in type 2 diabetic patients with complications. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2019, 13, 1303–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musavi, H.; Mohammadi Tahroodi, F.; Fesahat, F.; Bouzari, Z.; Esmaeilzadeh, S.; Elmi, F.; Yazdani, S.; Moazezi, Z. Investigating the Relationship between Magnesium levels and Diabetes Mellitus in Pregnant Women. Int. J. Mol. Cell. Med. 2019, 8, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winzer, E.; Grabovac, I.; Ludvik, B.; Kruschitz, R.; Schindler, K.; Prager, G.; Klammer, C.; Smith, L.; Hoppichler, F.; Marculescu, R.; et al. Differences in Serum Magnesium Levels in Diabetic and Non-Diabetic Patients Following One-Anastomosis Gastric Bypass. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ebrahimi Mousavi, S.; Ghoreishy, S.M.; Hemmati, A.; Mohammadi, H. Association between magnesium concentrations and prediabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 24388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Zeng, C.; Li, X.X.; Gong, Q.Y.; Lei, G.H.; Yang, T.B. Association among dietary magnesium, serum magnesium, and diabetes: A cross-sectional study in middle-aged and older adults. J. Health Popul. Nutr. 2016, 35, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chowdhury, J.A.; Nessa, A. Study on Serum Magnesium, Fasting Serum Glucose, Serum Glucose 2 Hours after Meal in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients. Mymensingh Med. J. MMJ 2019, 28, 773–778. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Costello, R.B.; Elin, R.J.; Rosanoff, A.; Wallace, T.C.; Guerrero-Romero, F.; Hruby, A.; Lutsey, P.L.; Nielsen, F.H.; Rodriguez-Moran, M.; Song, Y.; et al. Perspective: The Case for an Evidence-Based Reference Interval for Serum Magnesium: The Time Has Come. Adv. Nutr. 2016, 7, 977–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viering, D.; de Baaij, J.H.F.; Walsh, S.B.; Kleta, R.; Bockenhauer, D. Genetic causes of hypomagnesemia, a clinical overview. Pediatric Nephrol. 2017, 32, 1123–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Petroni, M.L.; Brodosi, L.; Marchignoli, F.; Sasdelli, A.S.; Caraceni, P.; Marchesini, G.; Ravaioli, F. Nutrition in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Present Knowledge and Remaining Challenges. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamedifard, Z.; Farrokhian, A.; Reiner, Ž.; Bahmani, F.; Asemi, Z.; Ghotbi, M.; Taghizadeh, M. The effects of combined magnesium and zinc supplementation on metabolic status in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and coronary heart disease. Lipids Health Dis. 2020, 19, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Wang, H.; Jing, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, W. Relationships of the Trace Elements Zinc and Magnesium With Diabetic Nephropathy-Associated Renal Functional Damage in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 626909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.A.; Rajendiran, K.S.; Mohan, M.; Munisammy, L.; Cassinadane, A.V. Serum Zinc and Magnesium Levels in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients on Metformin Therapy. Eur. J. Mol. Clin. Med. 2020, 7, 609–616. [Google Scholar]
- Jafarnejad, S.; Mahboobi, S.; McFarland, L.V.; Taghizadeh, M.; Rahimi, F. Meta-Analysis: Effects of Zinc Supplementation Alone or with Multi-Nutrients, on Glucose Control and Lipid Levels in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2019, 24, 8–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wu, W.; Zheng, W.; Fang, X.; Chen, L.; Rink, L.; Min, J.; Wang, F. Zinc supplementation improves glycemic control for diabetes prevention and management: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 110, 76–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Characteristic | Quintile of Serum Magnesium (mmol/L) | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q1 (<0.85) | Q2 (0.85–0.89) | Q3 (0.89–0.93) | Q4 (0.93–0.98) | Q5 (≥0.98) | ||
| No. of subjects | 948 | 1110 | 906 | 1082 | 1008 | |
| Age at baseline (mean ± SD) a | 49.7 ± 13.2 | 51.5 ± 13.6 | 52.0 ± 13.3 | 52.4 ± 13.0 | 53.1 ± 13.0 | <0.001 |
| Age (n, %) b | ||||||
| 18–49 | 486 (51.27) | 506 (46.00) | 387 (42.72) | 444 (41.04) | 378 (37.50) | <0.001 |
| 50–64 | 343 (36.18) | 410 (37.27) | 364 (40.18) | 460 (42.51) | 455 (45.14) | |
| 65+ | 119 (12.55) | 184 (16.73) | 155 (17.11) | 178 (16.45) | 175 (17.36) | |
| Female (n, %) b | 577 (60.86) | 623 (56.64) | 523 (57.73) | 567 (52.40) | 471 (46.73) | <0.001 |
| Education (n, %) b | ||||||
| low | 362 (38.19) | 389 (35.36) | 364 (40.18) | 401 (37.06) | 356 (35.32) | 0.323 |
| Medium | 436 (45.99) | 521 (47.36) | 408 (45.03) | 506 (46.77) | 468 (46.43) | |
| high | 150 (15.82) | 190 (17.27) | 134 (14.79) | 175 (16.17) | 184 (18.25) | |
| Urban (n, %) b | 310 (32.70) | 410 (37.27) | 316 (34.88) | 350 (32.35) | 328 (32.54) | 0.073 |
| Household income (n, %) b | ||||||
| Low | 318 (33.54) | 369 (33.55) | 331 (36.53) | 370 (34.20) | 293 (29.07) | <0.001 |
| Medium | 345 (36.39) | 359 (32.64) | 311 (34.33) | 352 (32.53) | 314 (31.15) | |
| High | 285 (30.06) | 372 (33.82) | 264 (29.14) | 360 (33.27) | 401 (39.78) | |
| Never smoked (n, %) b | 239 (25.21) | 288 (26.18) | 261 (28.81) | 339 (31.33) | 333 (33.04) | <0.001 |
| Never drank alcohol (n, %) b | 262 (27.64) | 340 (30.91) | 278 (30.68) | 357 (32.99) | 357 (35.42) | 0.004 |
| Physical activity (n, %) b | ||||||
| Low | 282 (29.75) | 373 (33.91) | 285 (31.46) | 370 (34.20) | 371 (36.81) | 0.019 |
| Medium | 343 (36.18) | 372 (33.82) | 299 (33.00) | 334 (30.87) | 330 (32.74) | |
| High | 323 (34.07) | 355 (32.27) | 322 (35.54) | 378 (34.94) | 307 (30.46) | |
| BMI (kg/m2) (n, %) b | ||||||
| <18.5 | 48 (5.06) | 64 (5.82) | 56 (6.18) | 64 (5.91) | 52 (5.16) | 0.159 |
| 18.5–23.9 | 540 (56.96) | 593 (53.91) | 501 (55.30) | 556 (51.39) | 518 (51.39) | |
| ≥24.0 | 360 (37.97) | 443 (40.27) | 349 (38.52) | 462 (42.70) | 438 (43.45) | |
| Fasting blood glucose (mmol/L) a | 4.89 (4.55, 5.28) | 4.99 (4.62, 5.35) | 4.97 (4.63, 5.36) | 5.00 (4.60, 5.39) | 5.04 (4.62, 5.46) | <0.001 |
| Fasting insulin (µU/mL) a | 6.85 (4.97, 8.79) | 7.74 (5.77, 9.33) | 7.55 (5.79, 9.21) | 7.88 (6.26, 9.35) | 7.41 (5.72, 9.08) | <0.001 |
| HOMA-IR a | 1.47 (1.02, 1.95) | 1.73 (1.25, 2.05) | 1.67 (1.25, 2.05) | 1.71 (1.33, 2.08) | 1.65 (1.22, 2.01) | <0.001 |
| Quintile of Serum Magnesium | p-Trend | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q1 (<0.85) | Q2 (0.85–0.89) | Q3 (0.89–0.93) | Q4 (0.93–0.98) | Q5 (≥0.98) | ||
| Serum magnesium (mmol/L) medium (p25, p75) | 0.81 (0.78, 0.83) | 0.87 (0.86, 0.89) | 0.91 (0.90, 0.92) | 0.95 (0.94, 0.96) | 1.02 (1.00, 1.05) | |
| Model 1 | 1.00 | 0.93 (0.78, 1.11) | 0.73 (0.61, 0.88) * | 0.84 (0.71, 1.00) | 0.97 (0.82, 1.16) | 0.41 |
| Model 2 | 1.00 | 0.92 (0.77, 1.09) | 0.72 (0.60, 0.87) * | 0.83 (0.69, 0.99) * | 0.96 (0.80, 1.14) | 0.34 |
| Model 3 | 1.00 | 0.90 (0.75, 1.08) | 0.71 (0.58, 0.86) * | 0.76 (0.63, 0.91) * | 0.92 (0.77, 1.11) | 0.19 |
| Quintile of Serum Magnesium | p-Trend | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q1 (<0.85) | Q2 (0.85–0.89) | Q3 (0.89–0.93) | Q4 (0.93–0.98) | Q5 (≥0.98) | ||
| Serum magnesium (mmol/L) medium (p25, p75) | 0.81 (0.78, 0.83) | 0.87 (0.86, 0.89) | 0.91 (0.90, 0.92) | 0.95 (0.94, 0.96) | 1.02 (1.00, 1.05) | |
| Model 1 | 1.00 | 0.76 (0.56, 1.05) | 0.68 (0.49, 0.95) * | 0.75 (0.55, 1.02) | 0.84 (0.62, 1.15) | 0.82 |
| Model 2 | 1.00 | 0.81 (0.59, 1.12) | 0.69 (0.50, 0.97) * | 0.75 (0.55, 1.03) | 0.88 (0.63, 1.22) | 0.82 |
| Model 3 | 1.00 | 0.78 (0.56, 1.08) | 0.68 (0.49, 0.96) * | 0.69 (0.50, 0.95) * | 0.87 (0.63, 1.20) | 0.50 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, W.; Jiao, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Hao, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhang, B.; Ding, G.; Jiang, H. Association of Serum Magnesium with Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes among Adults in China. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1799. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091799
Li W, Jiao Y, Wang L, Wang S, Hao L, Wang Z, Wang H, Zhang B, Ding G, Jiang H. Association of Serum Magnesium with Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes among Adults in China. Nutrients. 2022; 14(9):1799. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091799
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Weiyi, Yingying Jiao, Liusen Wang, Shaoshunzi Wang, Lixin Hao, Zhihong Wang, Huijun Wang, Bing Zhang, Gangqiang Ding, and Hongru Jiang. 2022. "Association of Serum Magnesium with Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes among Adults in China" Nutrients 14, no. 9: 1799. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091799
APA StyleLi, W., Jiao, Y., Wang, L., Wang, S., Hao, L., Wang, Z., Wang, H., Zhang, B., Ding, G., & Jiang, H. (2022). Association of Serum Magnesium with Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes among Adults in China. Nutrients, 14(9), 1799. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091799







