Changes in Serum Levels of Ketone Bodies and Human Chorionic Gonadotropin during Pregnancy in Relation to the Neonatal Body Shape: A Retrospective Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
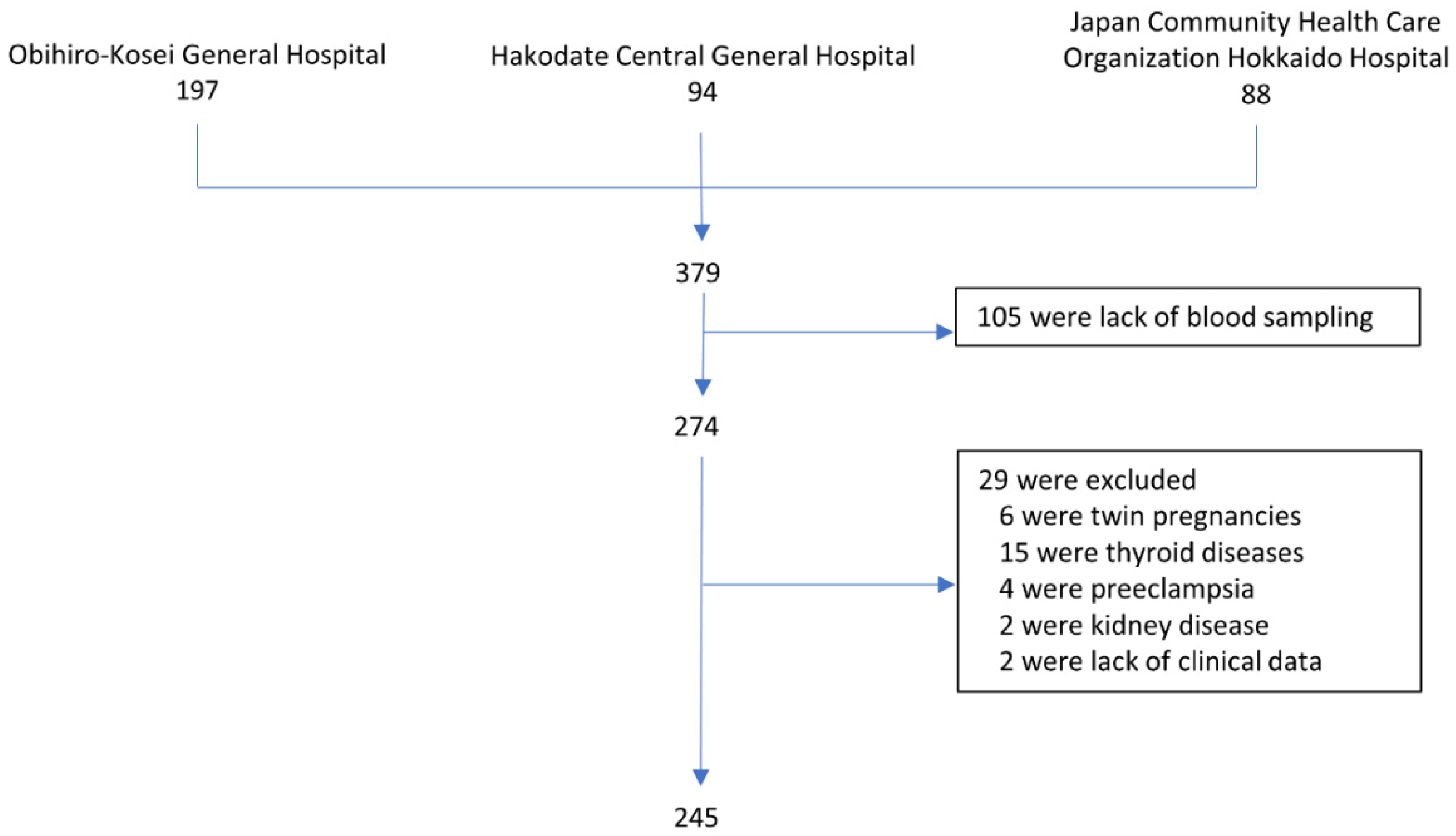
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Biochemical Procedures
2.2. Statistical Methods
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Characteristics
3.2. Hematological Parameters during Pregnancy
3.3. Effect of Glucose Challenge Test on Ketone Body Concentrations
3.4. Changes in HCG during Pregnancy
3.5. Relationship between Ketone Body and HCG in Early Pregnancy and the Neonatal Body Shape
3.6. Relationship between Placental Weight and Other Factors
3.7. Gestational Characteristics of the Weight-Loss and Non-Weight-Loss Groups
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Quinla, J.D.; Hill, D.A. Nausea and vomiting of pregnancy. Am. Fam. Phys. 2003, 68, 121–128. [Google Scholar]
- Bailit, J.L. Hyperemesis gravidarium: Epidemiologic findings from a large cohort. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2005, 193, 811–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fell, D.B.; Dodds, L.; Joseph, K.S.; Allen, V.M.; Butler, B. Risk factors for hyperemesis gravidarum requiring hospital admission during pregnancy. Obstet. Gynecol. 2006, 107, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuo, K.; Ushioda, N.; Nagamatsu, M.; Kimura, T. Hyperemesis gravidarum in eastern Asian population. Gynecol. Obstet. Investig. 2007, 64, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verberg, M.F.G.; Gillott, D.J.; Al-Fardan, N.; Grudzinskas, J.G. Hyperemesis gravidarum, a literature review. Hum. Reprod. Update 2005, 11, 527–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Haas, S.; Ghossein-Doha, C.; Van Kuijk, S.M.J.; Van Drongelen, J.; Spaanderman, M.E.A. Physiological adaption of maternal plasma volume during pregnancy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2017, 49, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robertson, A.F.; Karp, W.B. Placental transport of nutrients. South. Med. J. 1976, 69, 1358–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sussman, D.; Germann, J.; Henkelman, M. Gestational ketogenic diet programs brain structure and susceptibility to depression & anxiety in the adult mouse offspring. Brain Behav. 2015, 5, e00300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Auwera, I.; Wera, S.; Van Leuven, F.; Henderson, S.T. A ketogenic diet reduces amyloid beta 40 and 42 in a mouse model of alzheimer’s disease. Nutr. Metab. 2005, 2, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Youm, Y.H.; Nguyen, K.Y.; Grant, R.W.; Goldberg, E.L.; Bodogai, M.; Kim, D.; D’agostino, D.; Planavsky, N.; Lupfer, C.; Kanneganti, T.D.; et al. Ketone body β-hydroxybutyrate blocks the NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated inflammatory disease. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bronisz, A.; Ozorowski, M.; Hagner-Derengowska, M. Pregnancy ketonemia and development of the fetal central nervous system. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 2018, 1232901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morita, H.; Kajiura-Kobayashi, H.; Takagi, C.; Yamamoto, T.S.; Nonaka, S.; Ueno, N. Cell movements of the deep layer of non-neural ectoderm underlie complete neural tube closure in xenopus. Development 2012, 139, 1417–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tamay, A.G.; Kuşçu, N.K. Hyperemesis gravidarum: Current aspect. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2011, 31, 708–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dypvik, J.; Pereira, A.L.; Tanbo, T.G.; Eskild, A. Maternal human chorionic gonadotrophin concentrations in very early pregnancy and risk of hyperemesis gravidarum: A retrospective cohort study of 4372 pregnancies after in vitro fertilization. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2018, 221, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.Y.; Davis, L.M.; Sullivan, P.G.; Maalouf, M.; Simeone, T.A.; van Brederode, J.; Rho, J.M. Ketone bodies are protective against oxidative stress in neocortical neurons. J. Neurochem. 2007, 101, 1316–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Louw, E.J.; Williams, T.J.; Henry-Barron, B.J.; Olieman, J.F.; Duvekot, J.J.; Vermeulen, M.J.; Bannink, N.; Williams, M.; Neuteboom, R.F.; Kossoff, E.H.; et al. Ketogenic diet therapy for epilepsy furing pregnancy: A case series. Seizure 2017, 45, 198–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simeone, T.A.; Simeone, K.A.; Stafstrom, C.E.; Rho, J.M. Do ketone bodies mediate the anti-seizure effects of the ketogenic diet? Neuropharmacology 2018, 133, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, T.; Metzger, B.E.; Burns, W.J.; Burns, K. Correlation between antepartum maternal metabolism and intelligence of offspring. N. Engl. J. Med. 1991, 325, 911–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, L.A. Biological functions of hCG and hCG-related molecules. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2010, 8, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nascente, L.M.D.P.; Grandi, C.; Aragon, D.C.; Cardoso, V.C. Plcental measurements and their association with birth weight in a brazilian cohort. Rev. Bras. Epidemiol. 2020, 23, e200004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salafia, C.M.; Zhang, J.; Charles, A.K.; Bresnahan, M.; Shrout, P.; Sun, W.; Maas, E.M. Placental characteristics and birthweight. Paediatr. Perinat. Epidemiol. 2008, 22, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korevaar, T.I.M.; Steegers, E.A.; de Rijke, Y.B.; Schalekamp-Timmermans, S.; Visser, W.E.; Hofman, A.; Jaddoe, V.W.; Tiemeier, H.; Visser, T.J.; Medici, M.; et al. Reference ranges and determinants of total hCG levels furing pregnancy: The generation R study. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 30, 1057–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nurmi, M.; Rautava, P.; Gissler, M.; Vahlberg, T.; Polo-Kantola, P. Incidence and risk factors of hyperemesis gravidarum: A national register-based study in Finland, 2005–2017. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2020, 99, 1003–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouvier, D.; Forest, J.C.; Dion-Buteau, E.; Bernard, N.; Bujold, E.; Pereira, B.; Giguère, Y. Association of maternal weight and gestational weight gain with maternal and neonate outcomes: A prospective cohort study. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dude, A.M.; Kominiarek, M.A.; Haas, D.M.; Iams, J.; Mercer, B.M.; Parry, S.; Reddy, U.M.; Saade, G.; Silver, R.M.; Simhan, H.; et al. Weight gain in early, mid, and late pregnancy and hypertensive disorder of pregnancy. Pregnancy Hypertens. 2020, 20, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, R.F.; Abell, S.K.; Ranasinha, S.; Misso, M.; Boyle, J.A.; Black, M.H.; Li, N.; Hu, G.; Corrado, F.; Rode, L.; et al. Association of gestational weight gain with maternal and infant outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 2017, 317, 2207–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, T.-H.; Hsieh, T.T. Pregestational body mass index, gestational weight gain, and risks for adverse pregnancy outcomes among taiwanese women: A retrospective cohort study. Taiwan J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2016, 55, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Nulliparous women | 85, 35% |
| Age, years | 31.9 (5.0) |
| Height, m | 1.58 (0.05) |
| Pre-pregnancy weight, kg | 53.1 (10.3) |
| Pre-pregnancy body mass index, kg/m2 | 21.3 (3.5) |
| Weight gain in pregnancy, kg | 11.2 (3.5) |
| Gestational week at delivery, week | 39.1 (1.2) |
| Preterm delivery at 36 gestational weeks | 13 (5.3%) |
| Vaginal delivery | 191 (78%) |
| Cesarean delivery | 54 (22%) |
| Infant sex | |
| Male | 125, 51% |
| Birth weight, kg | 3.1 (0.4) |
| Birth length, cm | 49.4 (1.8) |
| Birth head circumference, cm | 33.4 (1.3) |
| Birth chest circumference, cm | 32.2 (1.6) |
| Timing of the tests | |
| First trimester, week | 10.2 (1.5) |
| Second trimester, week | 25.8 (1.3) |
| Third trimester, week | 36.2 (0.9) |
| 1st Trimester | 2nd Trimester | 3rd Trimester | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical data | ||||
| Maternal body weight, kg | 53.8 (10.4) | 48.6 (9.8) | 62.6 (10.1) | <0.001 |
| Weight gain during pregnancy, kg | 0.7 (2.4) | 5.6 (3.2) | 9.5 (3.9) | <0.001 |
| Weight gain, % | 1.4 (4.5) | 11.1 (6.6) | 18.8 (8.4) | <0.001 |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 21.6 (3.6) | 23.5 (3.3) | 25.0 (3.4) | <0.001 |
| Gestational age, week | 10.2 (1.5) | 25.8 (1.3) | 36.2 (0.9) | <0.001 |
| Hematological data | ||||
| Total ketones, µmol/L | 39.3 (5.0–934) | 32.8 (5.0–812) | 58.8 (5.0–1460) | <0.001 |
| 3-hydroxybutyric acid, µmol/L | 27.8 (5.0–821) | 21.2 (5.0–690) | 42.2 (5.0–1420) | <0.001 |
| Acetoacetic acid, µmol/L | 18.6 (5.0–140) | 19.9 (5.0–146) | 24.1 (5.0–161) | 0.083 |
| Human chorionic gonadotropin, IU/L | 132,000 (2620–341,000) | 16,400 (166–216,000) | 22,300 (31.9–113,000) | <0.001 |
| without GCT | with GCT | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Data | |||
| Number of women | 105 | 140 | |
| Age, years | 31.8 (4.7) | 32.2 (5.2) | 0.196 |
| Height, m | 157.2 (0.5) | 158.3 (0.5) | 0.115 |
| Pre-pregnancy weight, kg | 52.3 (9.8) | 53.7 (10.8) | 0.277 |
| Body weight in the second trimester, kg | 58.5 (9.5) | 58.9 (10.2) | 0.732 |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 23.6 (3.1) | 23.5 (3.5) | 0.758 |
| Weight gain in the second trimester, kg | 6.1 (3.2) | 5.1 (3.1) | 0.014 |
| Weight gain, % | 12.3 (6.9) | 10.2 (6.3) | 0.012 |
| Gestational age, weeks | 26.8 (0.6) | 25.0 (1.1) | <0.001 |
| Hematological data | |||
| Total ketones, µmol/L | 46.7 (12.3–812) | 18.9 (5–296) | <0.001 |
| 3-hydroxybutyric acid, µmol/L | 26.0 (5–690) | 16.3 (5–271) | <0.001 |
| Acetoacetic acid, µmol/L | 19.3 (5–146) | 5.0 (5–25.3) | <0.001 |
| Human chorionic gonadotropin, IU/L | 16,300 (1890–92,900) | 16,550 (166–216,000) | 0.191 |
| Weight Loss during Pregnancy | Non-Weight Loss | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical data | |||
| Number of women | 88 | 157 | |
| Height, m | 1.58 (0.05) | 1.58 (0.06) | 0.345 |
| Pre-pregnancy body weight, kg | 54.8 (11.8) | 52.2 (9.3) | 0.058 |
| Pre-pregnancy body mass index, kg/m2 | 22.0 (4.2) | 20.9 (3.1) | 0.025 |
| Minimum body weight, kg | 53.0 (11.4) | 52.2 (9.3) | 0.537 |
| Weight loss, kg | 1.78 (2.0) | not available. | |
| Weight gain during pregnancy, % | 9.8 (2.9) | 12.1 (3.6) | <0.001 |
| Body weight at delivery, kg | 62.8 (11.1) | 64.3 (9.8) | 0.274 |
| Body mass index at delivery, kg/m2 | 25.2 (3.8) | 25.8 (3.2) | 0.193 |
| Gestational age at delivery, week | 39.2 (1.1) | 39.0 (1.2) | 0.362 |
| Birth length, cm | 49.7 (1.6) | 49.3 (1.9) | 0.091 |
| Birth weight, kg | 3.08 (0.35) | 3.08 (0.41) | 0.981 |
| Birth head circumstance, cm | 33.6 (1.3) | 33.3 (1.3) | 0.114 |
| Birth chest circumstance, cm | 32.3 (1.5) | 32.2 (1.7) | 0.397 |
| Hematological data at first trimester | |||
| Total ketones, µmol/L | 46.0 (5–934) | 34.0 (5–541) | <0.001 |
| 3-hydroxybutyric acid, µmol/L | 33.0 (5–821) | 23.4 (5–539) | <0.001 |
| Acetoacetic acid, µmol/L | 5.0 (5–140) | 5 (5–113) | 0.046 |
| Human chorionic gonadotropin, IU/L | 137,000 (4640–341,000) | 129,000 (2620–284,000) | 0.072 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Noshiro, K.; Umazume, T.; Hattori, R.; Kataoka, S.; Yamada, T.; Watari, H. Changes in Serum Levels of Ketone Bodies and Human Chorionic Gonadotropin during Pregnancy in Relation to the Neonatal Body Shape: A Retrospective Analysis. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1971. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091971
Noshiro K, Umazume T, Hattori R, Kataoka S, Yamada T, Watari H. Changes in Serum Levels of Ketone Bodies and Human Chorionic Gonadotropin during Pregnancy in Relation to the Neonatal Body Shape: A Retrospective Analysis. Nutrients. 2022; 14(9):1971. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091971
Chicago/Turabian StyleNoshiro, Kiwamu, Takeshi Umazume, Rifumi Hattori, Soromon Kataoka, Takashi Yamada, and Hidemichi Watari. 2022. "Changes in Serum Levels of Ketone Bodies and Human Chorionic Gonadotropin during Pregnancy in Relation to the Neonatal Body Shape: A Retrospective Analysis" Nutrients 14, no. 9: 1971. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091971
APA StyleNoshiro, K., Umazume, T., Hattori, R., Kataoka, S., Yamada, T., & Watari, H. (2022). Changes in Serum Levels of Ketone Bodies and Human Chorionic Gonadotropin during Pregnancy in Relation to the Neonatal Body Shape: A Retrospective Analysis. Nutrients, 14(9), 1971. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091971







