The Impact of a Very-Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet in the Gut Microbiota Composition in Obesity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
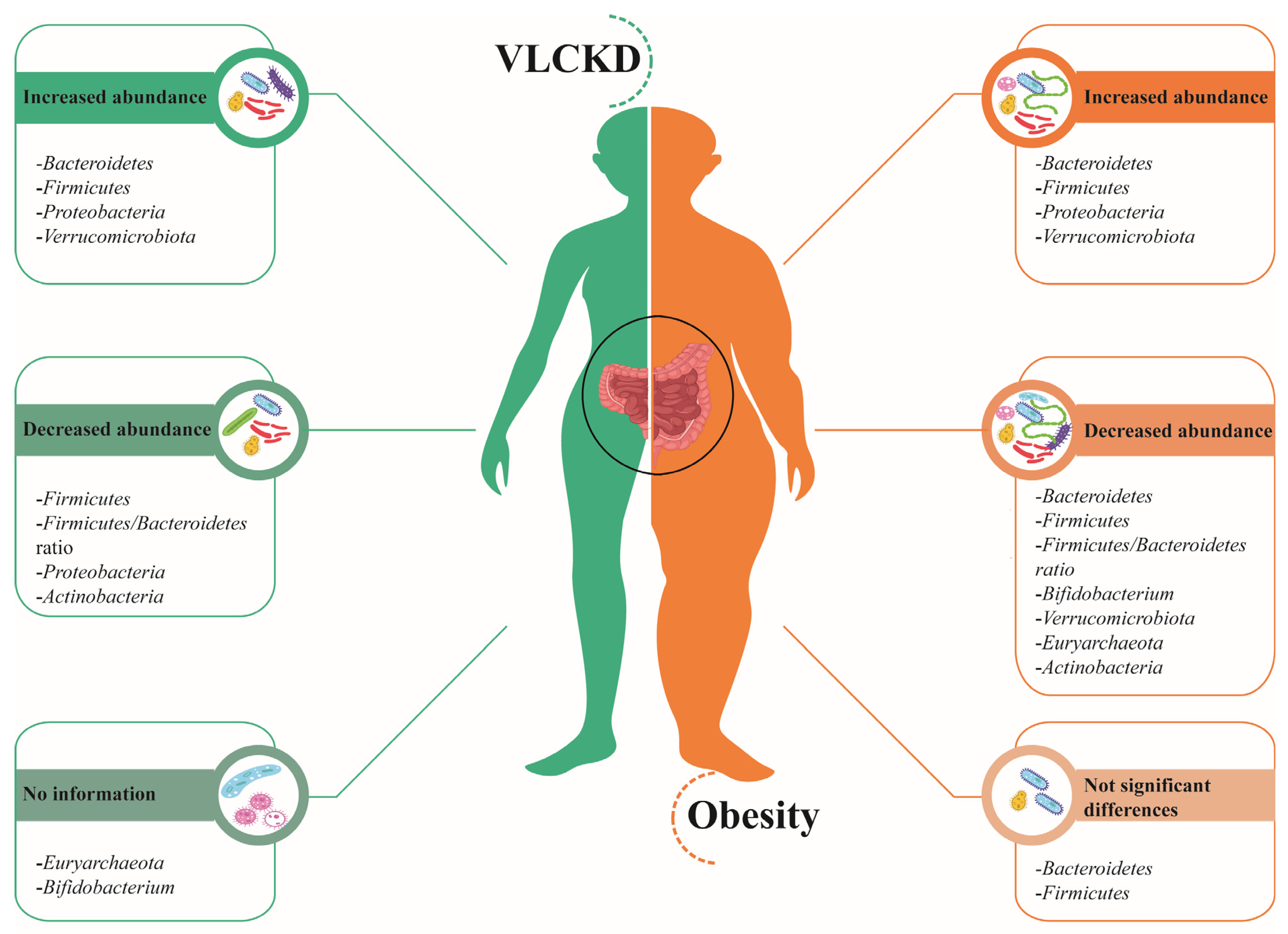
2. Gut Microbiota in Obesity
3. Impact of a Very-Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet (VLCKD) on the Microbiota of Subjects with Obesity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Future Directions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Very low-calorie ketogenic diet | VLCKD |
| Ketogenic diet | KD |
| Low-calorie ketogenic diet | LCKD |
| Acetoacetate | AcAc |
| 3-hydroxybutyrate | BHB |
| World Health Organization | WHO |
| Body mass index | BMI |
| Cardiovascular disease | CVD |
| Short-chain fatty acids | SCFA |
| Mediterranean diet | MD |
| Gamma amino butyric acid | GABA |
| Lipopolysaccharides | LPS |
| Very low-energy diet | VLED |
| Intermittent fasting | IF |
References
- Dhamija, R.; Eckert, S.; Wirrell, E. Ketogenic Diet. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 2022, 40, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guarnotta, V.; Emanuele, F.; Amodei, R.; Giordano, C. Very Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet: A Potential Application in the Treatment of Hypercortisolism Comorbidities. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dilliraj, L.N.; Schiuma, G.; Lara, D.; Strazzabosco, G.; Clement, J.; Giovannini, P.; Trapella, C.; Narducci, M.; Rizzo, R. The Evolution of Ketosis: Potential Impact on Clinical Conditions. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhillon, K.; Gupta, S. Biochemistry, Ketogenesis. In Biochemistry, Ketogenesis; StatPearls Publishing: Tampa, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Alharbi, A.; Al-Sowayan, N.S. The Effect of Ketogenic-Diet on Health. Food Nutr. Sci. 2020, 11, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rui, L. Energy Metabolism in the Liver. Compr. Physiol. 2014, 4, 177. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, A.; Li, Z.; Lyu, J.; Yu, L.; Wei, S.; Xue, L.; Wang, H.; Chen, G.-Q. On the nutritional and therapeutic effects of ketone body d-β-hydroxybutyrate. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 6229–6243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopaschuk, G.D.; Karwi, Q.G.; Ho, K.L.; Pherwani, S.; Ketema, E.B. Ketone metabolism in the failing heart. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2020, 1865, 158813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarnyai, Z.; Palmer, C.M. Ketogenic Therapy in Serious Mental Illness: Emerging Evidence. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2021, 23, 434–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storoni, M.; Plant, G.T.; Patti, F. The Therapeutic Potential of the Ketogenic Diet in Treating Progressive Multiple Sclerosis. Mult. Scler. Int. 2015, 2015, 681289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henderson, S.T. Ketone bodies as a therapeutic for Alzheimer’s disease. Neurotherapeutics 2008, 5, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grochowska, K.; Przeliorz, A. The Effect of the Ketogenic Diet on the Therapy of Neurodegenerative Diseases and Its Impact on Improving Cognitive Functions. Rev. Artic. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. Extra 2022, 12, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stubbs, B.J.; Koutnik, A.P.; Goldberg, E.L.; Upadhyay, V.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Verdin, E.; Newman, J.C. Investigating Ketone Bodies as Immunometabolic Countermeasures against Respiratory Viral Infections. Med 2020, 1, 43–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muscogiuri, G.; Barrea, L.; Laudisio, D.; Pugliese, G.; Salzano, C.; Savastano, S.; Colao, A. The management of very low-calorie ketogenic diet in obesity outpatient clinic: A practical guide. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Di Rosa, C.; Lattanzi, G.; Taylor, S.F.; Manfrini, S.; Khazrai, Y.M. Very low calorie ketogenic diets in overweight and obesity treatment: Effects on anthropometric parameters, body composition, satiety, lipid profile and microbiota. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2020, 14, 491–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrea, L.; Verde, L.; Vetrani, C.; Marino, F.; Aprano, S.; Savastano, S.; Colao, A.; Muscogiuri, G. VLCKD: A real time safety study in obesity. J. Transl. Med. 2022, 20, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrea, L.; de Alteriis, G.; Muscogiuri, G.; Vetrani, C.; Verde, L.; Camajani, E.; Aprano, S.; Colao, A.; Savastano, S. Impact of a Very Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet (VLCKD) on Changes in Handgrip Strength in Women with Obesity. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goossens, C.; Weckx, R.; Derde, S.; Perre, S.V.; Derese, I.; Van Veldhoven, P.P.; Ghesquière, B.; Berghe, G.V.D.; Langouche, L. Additional file 1 of Altered cholesterol homeostasis in critical illness-induced muscle weakness: Effect of exogenous 3-hydroxybutyrate. Crit. Care 2021, 25, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutnik, A.P.; Poff, A.M.; Ward, N.P.; DeBlasi, J.M.; Soliven, M.A.; Romero, M.A.; Roberson, P.A.; Fox, C.D.; Roberts, M.D.; D’Agostino, D.P. Ketone Bodies Attenuate Wasting in Models of Atrophy. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2020, 11, 973–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guevara-Ramírez, P.; Cadena-Ullauri, S.; Ruiz-Pozo, V.A.; Tamayo-Trujillo, R.; Paz-Cruz, E.; Simancas-Racines, D.; Zambrano, A.K. Genetics, genomics, and diet interactions in obesity in the Latin American environment. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1063286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Obesity and Overweight. In Springer Reference; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Haththotuwa, R.N.; Wijeyaratne, C.N.; Senarath, U. Worldwide epidemic of obesity. In Obesity and Obstetrics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ignatieva, E.V.; Afonnikov, D.A.; Saik, O.V.; Rogaev, E.I.; Kolchanov, N.A. A compendium of human genes regulating feeding behavior and body weight, its functional characterization and identification of GWAS genes involved in brain-specific PPI network. BMC Genet. 2016, 17 (Suppl. S3), 89–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cleveland Clinic. Triglycerides and Heart Health—How Triglycerides Impact Heart Health. 2022. Available online: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/17583-triglycerides--heart-health (accessed on 16 April 2023).
- Division of Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Obesity. National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion. Health Effects of Overweight and Obesity | Healthy Weight, Nutrition, and Physical Activity; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2022.
- Cepeda-Lopez, A.C.; Baye, K. Obesity, iron deficiency and anaemia: A complex relationship. Public Health Nutr. 2020, 23, 1703–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campión, J.; Milagro, F.; Martínez, J.A. Epigenetics and Obesity. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2010, 94, 291–347. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Seidell, J.C.; Halberstadt, J. The Global Burden of Obesity and the Challenges of Prevention. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2015, 66 (Suppl. S2), 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vetrani, C.; Di Nisio, A.; Paschou, S.A.; Barrea, L.; Muscogiuri, G.; Graziadio, C.; Savastano, S.; Colao, A.; on behalf of the Obesity Programs of Nutrition, Education, Research and Assessment (OPERA) Group. From Gut Microbiota through Low-Grade Inflammation to Obesity: Key Players and Potential Targets. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrea, L.; Verde, L.; Santangeli, P.; Lucà, S.; Docimo, A.; Savastano, S.; Colao, A.; Muscogiuri, G. Very low-calorie ketogenic diet (VLCKD): An antihypertensive nutritional approach. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoli, A. Ketogenic diet for obesity: Friend or foe? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 2092–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bezerra Bueno, N.; Vieira De Melo, I.S.; Lima De Oliveira, S.; Da, T.; Ataide, R. Systematic Review with Meta-analysis Very-low-carbohydrate ketogenic diet v. low-fat diet for long-term weight loss: A meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 110, 1178–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Attaye, I.; van Oppenraaij, S.; Warmbrunn, M.V.; Nieuwdorp, M. The Role of the Gut Microbiota on the Beneficial Effects of Ketogenic Diets. Nutrients 2022, 14, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamayo-Trujillo, R.; Guevara-Ramírez, P.; Cadena-Ullauri, S.; Paz-Cruz, E.; Ruiz-Pozo, V.A.; Zambrano, A.K. Human virome: Implications in cancer. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagliabue, A.; Ferraris, C.; Uggeri, F.; Trentani, C.; Bertoli, S.; de Giorgis, V.; Veggiotti, P.; Elli, M. Short-term impact of a classical ketogenic diet on gut microbiota in GLUT1 Deficiency Syndrome: A 3-month prospective observational study. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2017, 17, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoli, A.; Mancin, L.; Bianco, A.; Thomas, E.; Piccini, F. Ketogenic Diet and Microbiota: Friends or Enemies? Genes 2019, 10, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Hul, M.; Cani, P.D. The gut microbiota in obesity and weight management: Microbes as friends or foe? Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2023, 19, 258–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres-Fuentes, C.; Schellekens, H.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. The microbiota–gut–brain axis in obesity. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 2, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Backhed, F.; Fulton, L.; Gordon, J.I. Marked alterations in the distal gut microbiome linked to diet-induced obesity. Cell Host Microbe 2008, 3, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ley, R.E.; Mahowald, M.A.; Magrini, V.; Mardis, E.R.; Gordon, J.I. An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature 2006, 444, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huttenhower, C.; Gevers, D.; Knight, R.; Abubucker, S.; Badger, J.H.; Chinwalla, A.T.; Heather, H.; Creasy, H.H.; Earl, A.M.; Fulton, R.S.; et al. Structure, function and diversity of the healthy human microbiome. Nature 2012, 486, 207–214. [Google Scholar]
- Ley, R.E.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Klein, S.; Gordon, J.I. Human Gut Microbes Associated with Obesity. Nature 2006, 444, 1022–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldram, A.; Holmes, E.; Wang, Y.; Rantalainen, M.; Wilson, I.D.; Tuohy, K.M.; McCartney, A.L.; Gibson, G.R.; Nicholson, J.K. Top-Down Systems Biology Modeling of Host Metabotype−Microbiome Associations in Obese Rodents. J. Proteome Res. 2009, 8, 2361–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zou, R.; Guo, M.; Zheng, H. Characteristics of gut microbiota in people with obesity. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0255446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwiertz, A.; Taras, D.; Schäfer, K.; Beijer, S.; Bos, N.A.; Donus, C.; Hardt, P.D. Microbiota and SCFA in Lean and Overweight Healthy Subjects. Obesity 2010, 18, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koliada, A.; Syzenko, G.; Moseiko, V.; Budovska, L.; Puchkov, K.; Perederiy, V.; Gavalko, Y.; Dorofeyev, A.; Romanenko, M.; Sineok, L.; et al. Association between body mass index and Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio in an adult Ukrainian population. BMC Microbiol. 2017, 17, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; DiBaise, J.K.; Zuccolo, A.; Kudrna, D.; Braidotti, M.; Yu, Y.; Parameswaran, P.; Crowell, M.D.; Wing, R.; Rittmann, B.E.; et al. Human Gut Microbiota in Obesity and after Gastric Bypass. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 2365–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bervoets, L.; Van Hoorenbeeck, K.; Kortleven, I.; Van Noten, C.; Hens, N.; Vael, C.; Goossens, H.; Desager, K.N.; Vankerckhoven, V. Differences in gut microbiota composition between obese and lean children: A cross-sectional study. Gut Pathog. 2013, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Million, M.; Thuny, F.; Angelakis, E.; Casalta, J.-P.; Giorgi, R.; Habib, G.; Raoult, D. Lactobacillus reuteri and Escherichia coli in the human gut microbiota may predict weight gain associated with vancomycin treatment. Nutr. Diabetes 2013, 3, e87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karlsson, F.H.; Tremaroli, V.; Nookaew, I.; Bergström, G.; Behre, C.J.; Fagerberg, B.; Nielsen, J.; Bäckhed, F. Gut metagenome in European women with normal, impaired and diabetic glucose control. Nature 2013, 498, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armougom, F.; Henry, M.; Vialettes, B.; Raccah, D.; Raoult, D. Monitoring Bacterial Community of Human Gut Microbiota Reveals an Increase in Lactobacillus in Obese Patients and Methanogens in Anorexic Patients. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Z.; Jiang, W.; Huang, W.; Lin, Y.; Chan, F.K.; Ng, S.C. Gut microbiota in patients with obesity and metabolic disorders—A systematic review. Genes Nutr. 2022, 17, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Hu, Y.; Bruner, D.W. Composition of gut microbiota and its association with body mass index and lifestyle factors in a cohort of 7–18 years old children from the American Gut Project. Pediatr. Obes. 2019, 14, e12480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Navarrete, J.M.; Serino, M.; Blasco-Baque, V.; Azalbert, V.; Barton, R.H.; Cardellini, M.; Latorre, J.; Ortega, F.; Sabater-Masdeu, M.; Burcelin, R.; et al. Gut Microbiota Interacts with Markers of Adipose Tissue Browning, Insulin Action and Plasma Acetate in Morbid Obesity. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, 1700721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.-M.; Letchumanan, V.; Tan, L.T.-H.; Hong, K.-W.; Wong, S.-H.; Ab Mutalib, N.-S.; Lee, L.-H.; Law, J.W.-F. Ketogenic Diet: A Dietary Intervention via Gut Microbiome Modulation for the Treatment of Neurological and Nutritional Disorders (a Narrative Review). Nutrients 2022, 14, 3566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Repiso, C.; Hernández-García, C.; García-Almeida, J.M.; Bellido, D.; Martín-Núñez, G.M.; Sánchez-Alcoholado, L.; Alcaide-Torres, J.; Sajoux, I.; Tinahones, F.J.; Moreno-Indias, I. Effect of Synbiotic Supplementation in a Very-Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet on Weight Loss Achievement and Gut Microbiota: A Randomized Controlled Pilot Study. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 63, e1900167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konopiński, M.K. Shannon diversity index: A call to replace the original Shannon’s formula with unbiased estimator in the population genetics studies. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-R.; Zheng, H.-M.; Zhang, G.-X.; Chen, F.-L.; Chen, L.-D.; Yang, Z.-C. High Oscillospira abundance indicates constipation and low BMI in the Guangdong Gut Microbiome Project. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Wen, Z.; Liu, W.; Meng, L.; Huang, H. Oscillospira—A candidate for the next-generation probiotics. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1987783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, H.; Cao, M.; Guo, M.; He, J.; Zhang, B.; Xiao, C. Gut Microbiota Characteristics of People with Obesity by Meta-Analysis of Existing Datasets. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; An, J.; Kim, J.; Choi, D.; Song, Y.; Lee, C.-K.; Kong, H.; Kim, S.B.; Kim, K. A Novel Bacterium, Butyricimonas virosa, Preventing HFD-Induced Diabetes and Metabolic Disorders in Mice via GLP-1 Receptor. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 858192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashtanova, D.A.; Tkacheva, O.N.; Doudinskaya, E.N.; Strazhesko, I.D.; Kotovskaya, Y.V.; Popenko, A.S.; Tyakht, A.V.; Alexeev, D.G. Gut Microbiota in Patients with Different Metabolic Statuses: Moscow Study. Microorganisms 2018, 6, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.-L.; Li, M.; Sheng, Y.; Chen, L.; Cann, I.; Du, Z.-Y. Citrobacter Species Increase Energy Harvest by Modulating Intestinal Microbiota in Fish: Nondominant Species Play. mSystems 2020, 5, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Repiso, C.; Molina-Vega, M.; Bernal-López, M.R.; Garrido-Sánchez, L.; García-Almeida, J.M.; Sajoux, I.; Moreno-Indias, I.; Tinahones, F.J. Different Weight Loss Intervention Approaches Reveal a Lack of a Common Pattern of Gut Microbiota Changes. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmas, V.; Pisanu, S.; Madau, V.; Casula, E.; Deledda, A.; Cusano, R.; Uva, P.; Vascellari, S.; Loviselli, A.; Manzin, A.; et al. Gut microbiota markers associated with obesity and overweight in Italian adults. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crovesy, L.; Ostrowski, M.; Ferreira, D.M.T.P.; Rosado, E.L.; Soares, M. Effect of Lactobacillus on body weight and body fat in overweight subjects: A systematic review of randomized controlled clinical trials. Int. J. Obes. 2017, 41, 1607–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, B.; Hu, J.; Nie, S.; Xiong, T.; Xie, M. Intervention of five strains of Lactobacillus on obesity in mice induced by high-fat diet. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 72, 104078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Million, M.; Maraninchi, M.; Henry, M.; Armougom, F.; Richet, H.; Carrieri, P.; Valero, R.; Raccah, D.; Vialettes, B.; Raoult, D. Obesity-associated gut microbiota is enriched in Lactobacillus reuteri and depleted in Bifidobacterium animalis and Methanobrevibacter smithii. Int. J. Obes. 2011, 36, 817–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Basciani, S.; Camajani, E.; Contini, S.; Persichetti, A.; Risi, R.; Bertoldi, L.; Strigari, L.; Prossomariti, G.; Watanabe, M.; Mariani, S.; et al. Very-Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diets With Whey, Vegetable, or Animal Protein in Patients With Obesity: A Randomized Pilot Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, 2939–2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanov, S.; Berlec, A.; Štrukelj, B. The Influence of Probiotics on the Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes Ratio in the Treatment of Obesity and Inflammatory Bowel disease. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborti, C.K. New-found link between microbiota and obesity. World J. Gastrointest. Pathophysiol. 2015, 6, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Hamady, M.; Yatsunenko, T.; Cantarel, B.L.; Duncan, A.; Ley, R.E.; Sogin, M.L.; Jones, W.J.; Roe, B.A.; Affourtit, J.P.; et al. A core gut microbiome in obese and lean twins. Nature 2009, 457, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deledda, A.; Palmas, V.; Heidrich, V.; Fosci, M.; Lombardo, M.; Cambarau, G.; Lai, A.; Melis, M.; Loi, E.; Loviselli, A.; et al. Dynamics of Gut Microbiota and Clinical Variables after Ketogenic and Mediterranean Diets in Drug-Naïve Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Obesity. Metabolites 2022, 12, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Guo, P.; Mao, R.; Ren, Z.; Wen, J.; Yang, Q.; Yan, T.; Yu, J.; Zhang, T.; Liu, Y. Gut Microbiota Signature of Obese Adults Across Different Classifications. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. Targets Ther. 2022, 15, 3933–3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Depommier, C.; Everard, A.; Druart, C.; Plovier, H.; Van Hul, M.; Vieira-Silva, S.; Falony, G.; Raes, J.; Maiter, D.; Delzenne, N.M.; et al. Supplementation with Akkermansia muciniphila in overweight and obese human volunteers: A proof-of-concept exploratory study. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1096–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plovier, H.; Everard, A.; Druart, C.; Depommier, C.; Van Hul, M.; Geurts, L.; Chilloux, J.; Ottman, N.; Duparc, T.; Lichtenstein, L.; et al. A purified membrane protein from Akkermansia muciniphila or the pasteurized bacterium improves metabolism in obese and diabetic mice. Nat. Med. 2016, 23, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waters, J.L.; Ley, R.E. The human gut bacteria Christensenellaceae are widespread, heritable, and associated with health. BMC Biol. 2019, 17, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ley, R.E.; Hamady, M.; Lozupone, C.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ramey, R.R.; Bircher, J.S.; Schlegel, M.L.; Tucker, T.A.; Schrenzel, M.D.; Knight, R.; et al. Evolution of Mammals and Their Gut Microbes. Science 2008, 320, 1647–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Swidsinski, A.; Dörffel, Y.; Loening-Baucke, V.; Gille, C.; Göktas, Ö.; Reißhauer, A.; Neuhaus, J.; Weylandt, K.-H.; Guschin, A.; Bock, M. Reduced Mass and Diversity of the Colonic Microbiome in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis and Their Improvement with Ketogenic Diet. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gilbert, J.A.; Blaser, M.J.; Caporaso, J.G.; Jansson, J.K.; Lynch, S.V.; Knight, R. Current understanding of the human microbiome. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, J.; Li, R.; Raes, J.; Arumugam, M.; Burgdorf, K.S.; Manichanh, C.; Nielsen, T.; Pons, N.; Levenez, F.; Yamada, T.; et al. A human gut microbial gene catalogue established by metagenomic sequencing. Nature 2010, 464, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barrett, E.; Ross, R.P.; O’Toole, P.W.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Stanton, C. Gamma-Aminobutyric acid production by culturable bacteria from the human intestine. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 113, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bravo, J.A.; Forsythe, P.; Chew, M.V.; Escaravage, E.; Savignac, H.M.; Dinan, T.G.; Bienenstock, J.; Cryan, J.F. Ingestion of Lactobacillus strain regulates emotional behavior and central GABA receptor expression in a mouse via the vagus nerve. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 16050–16055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rondanelli, M.; Gasparri, C.; Peroni, G.; Faliva, M.A.; Naso, M.; Perna, S.; Bazire, P.; Sajoux, I.; Maugeri, R.; Rigon, C. The Potential Roles of Very Low Calorie, Very Low Calorie Ketogenic Diets and Very Low Carbohydrate Diets on the Gut Microbiota Composition. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 662591. [Google Scholar]
- Arumugam, M.; Raes, J.; Pelletier, E.; Paslier, D.L.; Yamada, T.; Mende, D.R.; Fernandes, G.R.; Tap, J.; Bruls, T.; Bertalan, M.; et al. Enterotypes of the human gut microbiome. Nature 2011, 473, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cuevas-Sierra, A.; Ramos-Lopez, O.; Riezu-Boj, J.I.; Milagro, F.I.; Martinez, J.A. Diet, Gut Microbiota, and Obesity: Links with Host Genetics and Epigenetics and Potential Applications. Adv. Nutr. 2019, 10, S17–S30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gohar, A.; Shakeel, M.; Atkinson, R.L.; Haleem, D.J. Potential mechanisms of improvement in body weight, metabolic profile, and liver metabolism by honey in rats on a high fat diet. PharmaNutrition 2020, 14, 100227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinninella, E.; Raoul, P.; Cintoni, M.; Franceschi, F.; Miggiano, G.A.D.; Gasbarrini, A.; Mele, M.C. What Is the Healthy Gut Microbiota Composition? A Changing Ecosystem across Age, Environment, Diet, and Diseases. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mamani-Ortiz, Y.; Sebastián, M.S.; Armaza, A.X.; Luizaga, J.M.; Illanes, D.E.; Ferrel, M.; Mosquera, P.A. Prevalence and determinants of cardiovascular disease risk factors using the WHO STEPS approach in Cochabamba, Bolivia. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Son, J.; Koekkoek, L.L.; La Fleur, S.E.; Serlie, M.J.; Nieuwdorp, M. The Role of the Gut Microbiota in the Gut–Brain Axis in Obesity: Mechanisms and Future Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijnikman, A.S.; Aydin, O.; Prodan, A.; Tremaroli, V.; Herrema, H.; Levin, E.; Acherman, Y.; Bruin, S.; Gerdes, V.; Backhed, F.; et al. Distinct differences in gut microbial composition and functional potential from lean to morbidly obese subjects. J. Intern. Med. 2020, 288, 699–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Mahony, S.M.; Clarke, G.; Borre, Y.E.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Serotonin, tryptophan metabolism and the brain-gut-microbiome axis. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 277, 32–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modasia, A.; Parker, A.; Jones, E.; Stentz, R.; Brion, A.; Goldson, A.; Defernez, M.; Wileman, T.; Blackshaw, L.A.; Carding, S.R. Regulation of Enteroendocrine Cell Networks by the Major Human Gut Symbiont Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 575595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, C.D.; Maukonen, J.; Scott, K.P.; Virtanen, K.A.; Pietiläinen, K.H.; Saarela, M. Impact of a very low-energy diet on the fecal microbiota of obese individuals. Eur. J. Nutr. 2014, 53, 1421–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Gao, H.; Ren, Q.; He, J. The abundance of bifidobacterium in relation to visceral obesity and serum uric acid. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remely, M.; Hippe, B.; Geretschlaeger, I.; Stegmayer, S.; Hoefinger, I.; Haslberger, A. Increased gut microbiota diversity and abundance of Faecalibacterium prausnitzii and Akkermansia after fasting: A pilot study. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2015, 127, 394–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maioli, T.U.; Borras-nogues, E.; Torres, L.; Barbosa, S.C. Possible Bene fits of Faecalibacterium prausnitzii for Obesity-Associated Gut Disorders. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 740636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, R.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, C.; Yuan, H.; Yang, Z.; Sun, L. Gut bacteria Akkermansia is associated with reduced risk of obesity: Evidence from the American Gut Project. Nutr. Metab. 2020, 17, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, Z.; Du, W.; Xiao, C.; Su, C.; Gou, W.; Shen, L.; Zhang, J.; Fu, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, Z.; et al. Gut microbiota signatures of long-term and short-term plant-based dietary pattern and cardiometabolic health: A prospective cohort study. BMC Med. 2022, 20, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losasso, C.; Eckert, E.M.; Mastrorilli, E.; Villiger, J.; Mancin, M.; Patuzzi, I.; Di Cesare, A.; Cibin, V.; Barrucci, F.; Pernthaler, J.; et al. Assessing the Influence of Vegan, Vegetarian and Omnivore Oriented Westernized Dietary Styles on Human Gut Microbiota: A Cross Sectional Study. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zambrano, A.K.; Cadena-Ullauri, S.; Guevara-Ramírez, P.; Frias-Toral, E.; Ruiz-Pozo, V.A.; Paz-Cruz, E.; Tamayo-Trujillo, R.; Chapela, S.; Montalván, M.; Sarno, G.; et al. The Impact of a Very-Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet in the Gut Microbiota Composition in Obesity. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2728. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15122728
Zambrano AK, Cadena-Ullauri S, Guevara-Ramírez P, Frias-Toral E, Ruiz-Pozo VA, Paz-Cruz E, Tamayo-Trujillo R, Chapela S, Montalván M, Sarno G, et al. The Impact of a Very-Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet in the Gut Microbiota Composition in Obesity. Nutrients. 2023; 15(12):2728. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15122728
Chicago/Turabian StyleZambrano, Ana Karina, Santiago Cadena-Ullauri, Patricia Guevara-Ramírez, Evelyn Frias-Toral, Viviana A. Ruiz-Pozo, Elius Paz-Cruz, Rafael Tamayo-Trujillo, Sebastián Chapela, Martha Montalván, Gerardo Sarno, and et al. 2023. "The Impact of a Very-Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet in the Gut Microbiota Composition in Obesity" Nutrients 15, no. 12: 2728. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15122728
APA StyleZambrano, A. K., Cadena-Ullauri, S., Guevara-Ramírez, P., Frias-Toral, E., Ruiz-Pozo, V. A., Paz-Cruz, E., Tamayo-Trujillo, R., Chapela, S., Montalván, M., Sarno, G., Guerra, C. V., & Simancas-Racines, D. (2023). The Impact of a Very-Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet in the Gut Microbiota Composition in Obesity. Nutrients, 15(12), 2728. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15122728